Impact of Interconnected Power Supply for Electrified Railways on Power Grids and Its Solutions
-
摘要:
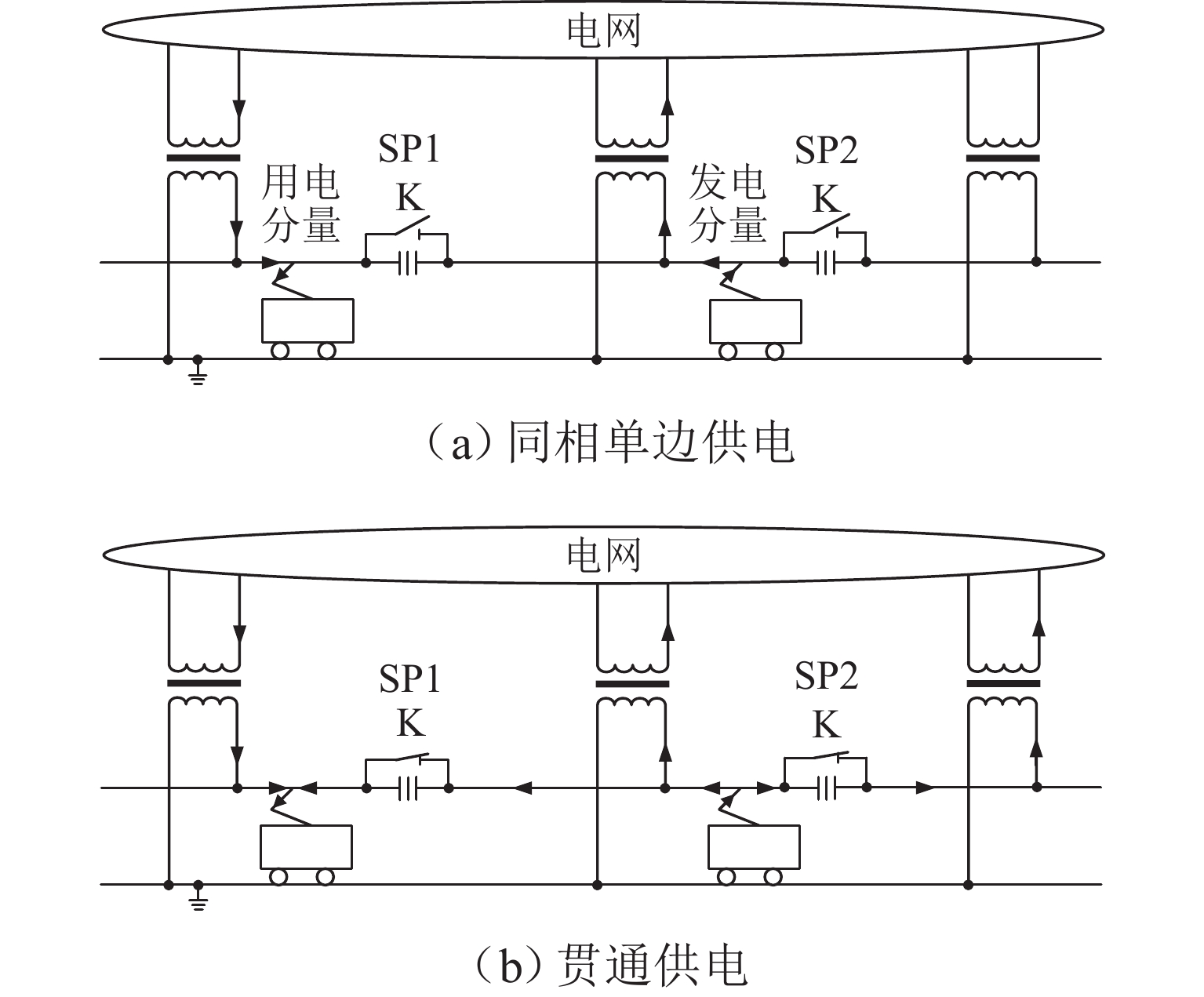
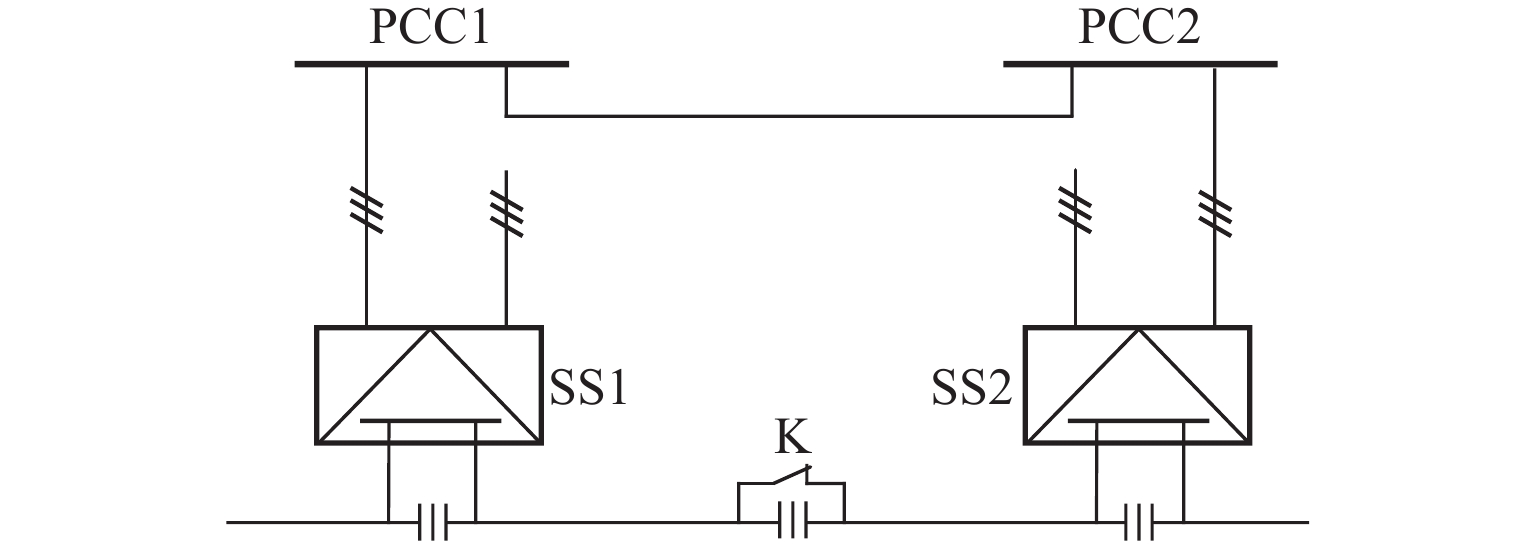
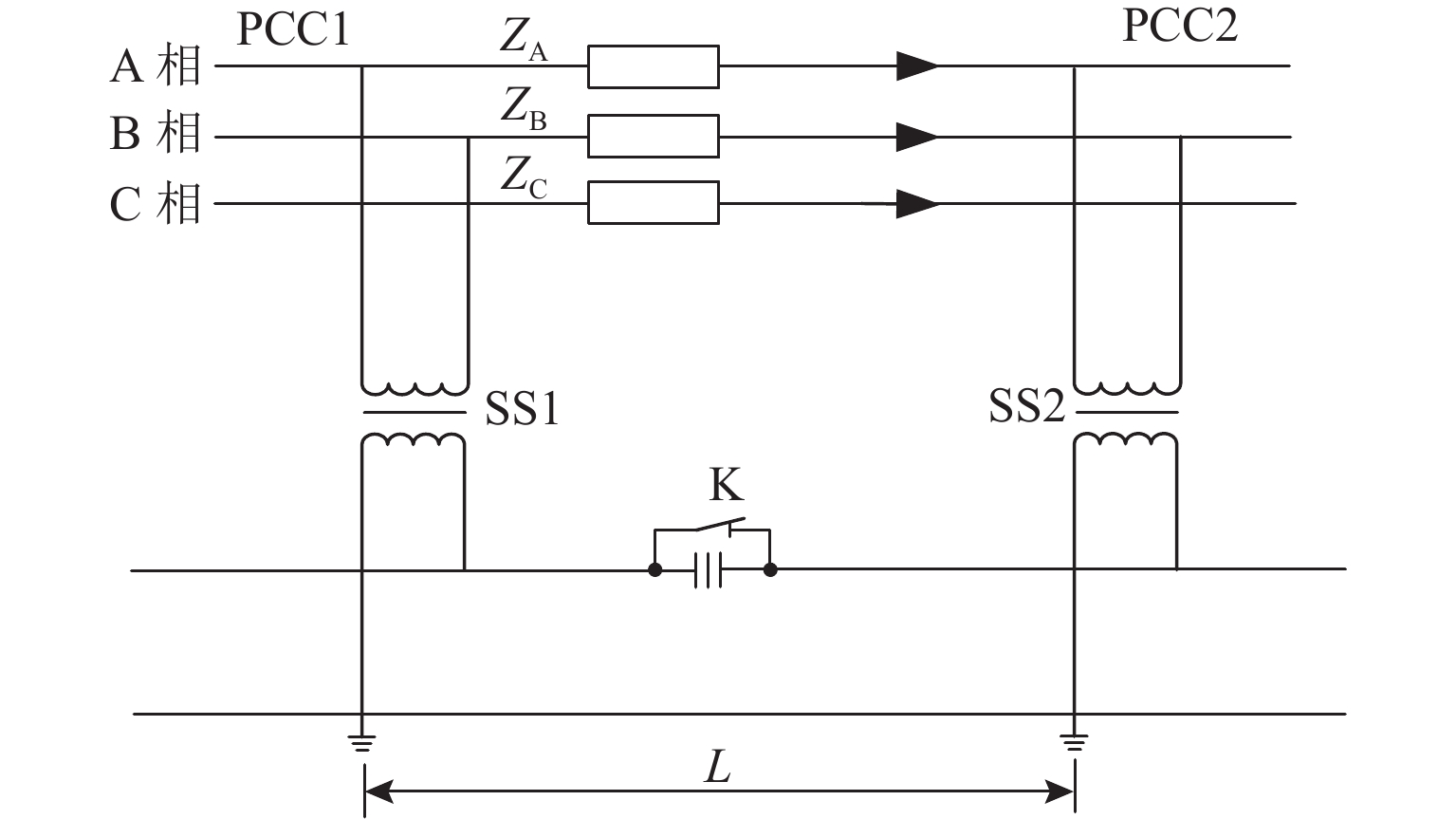
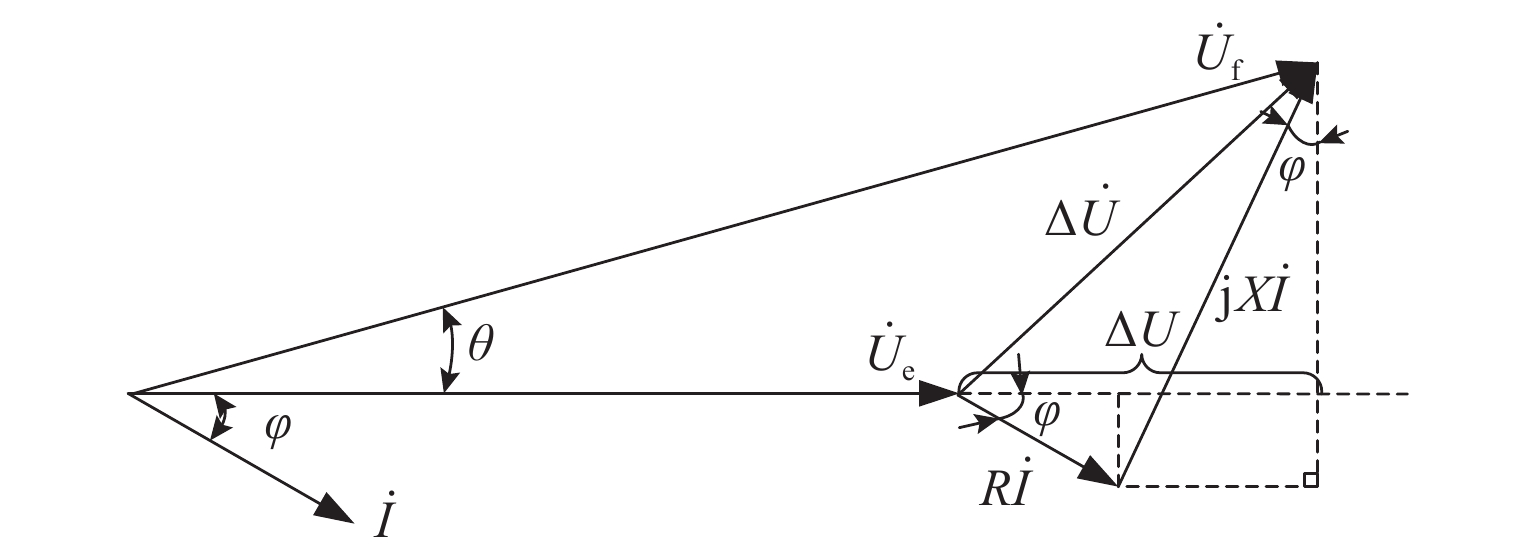
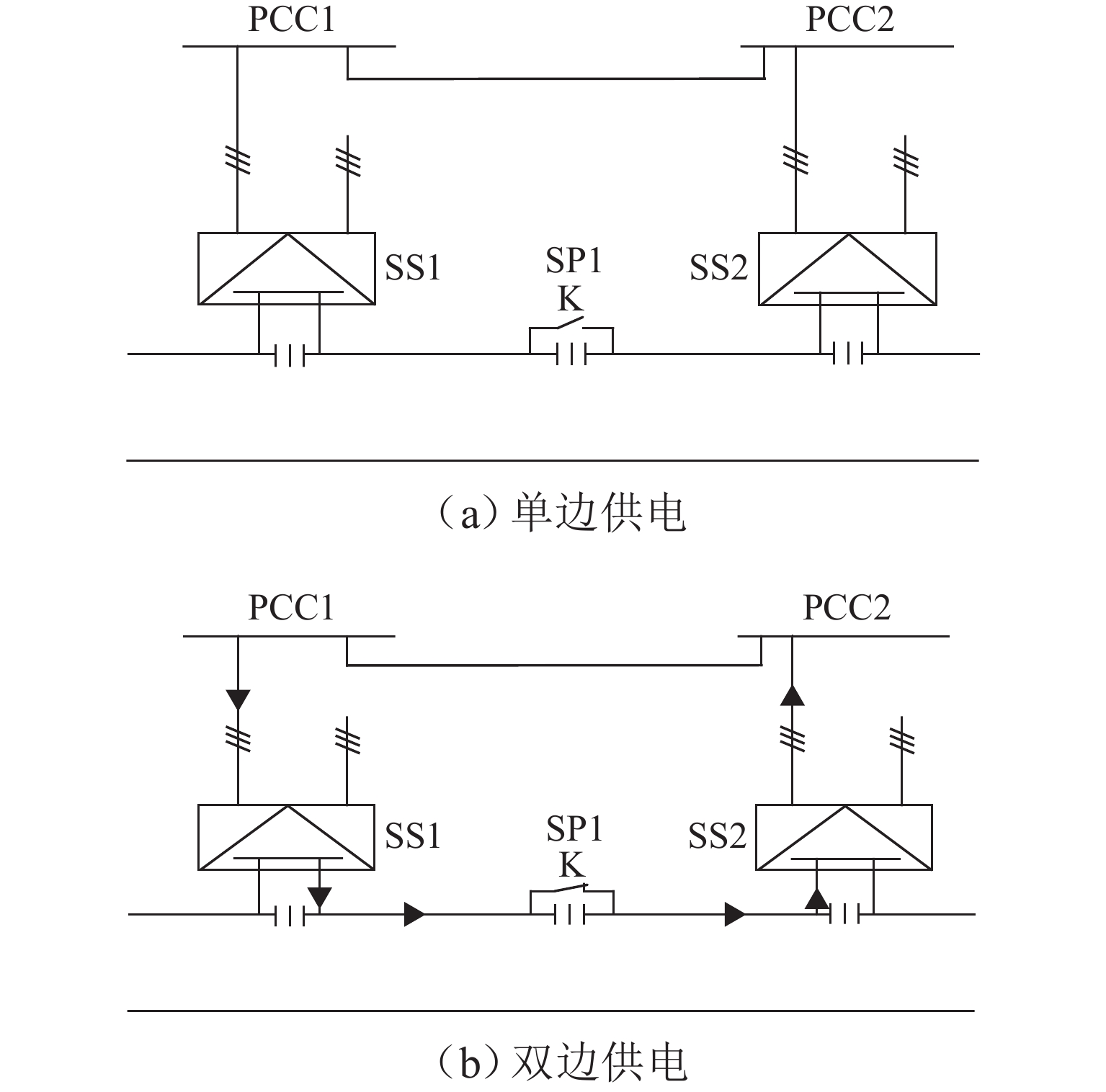
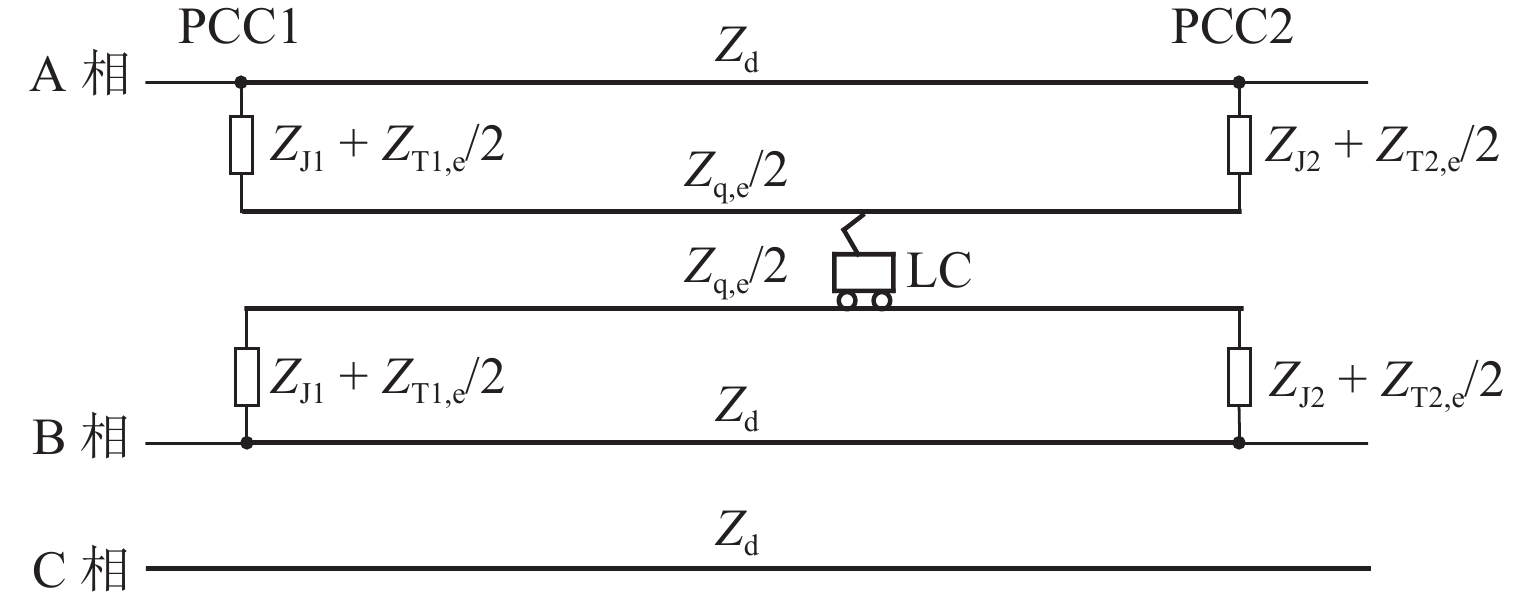
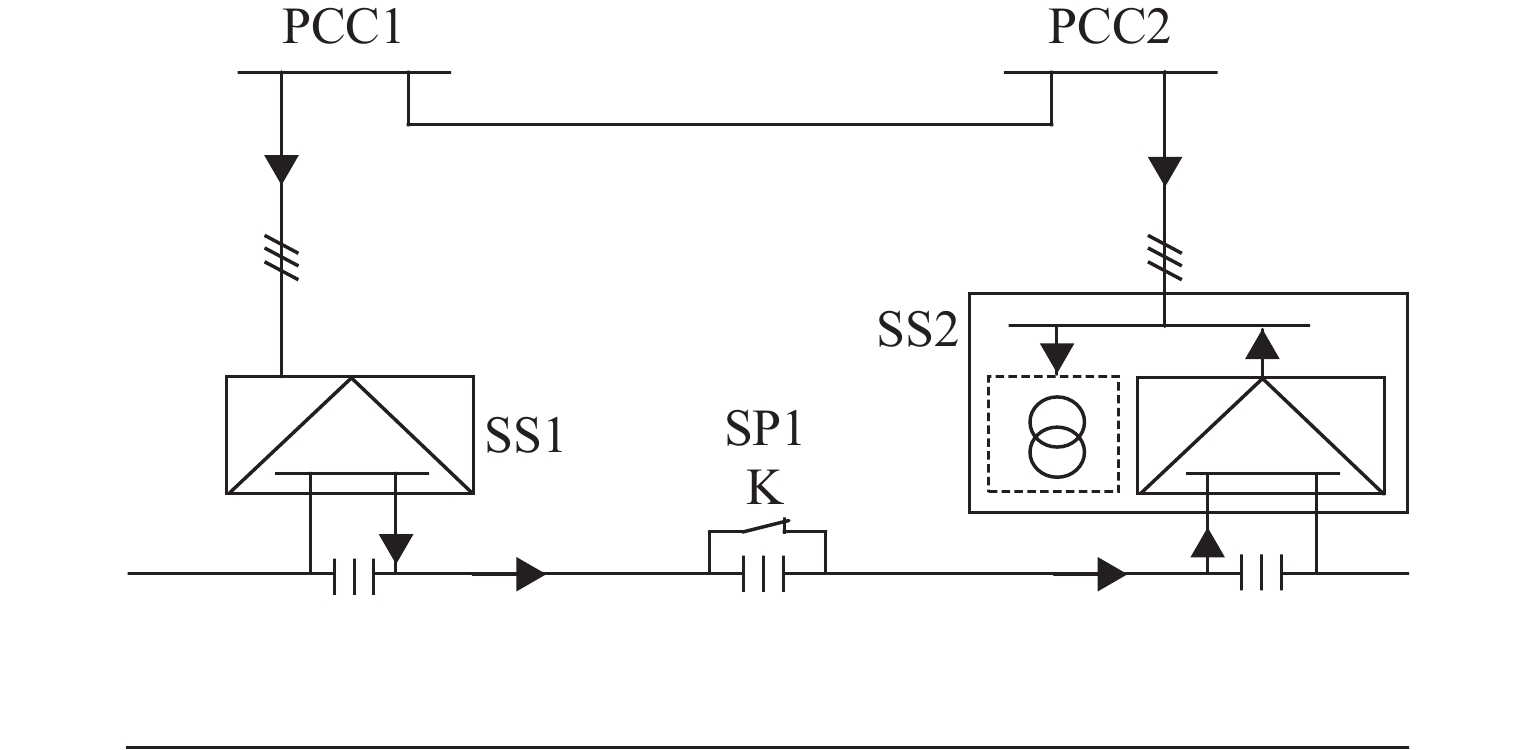
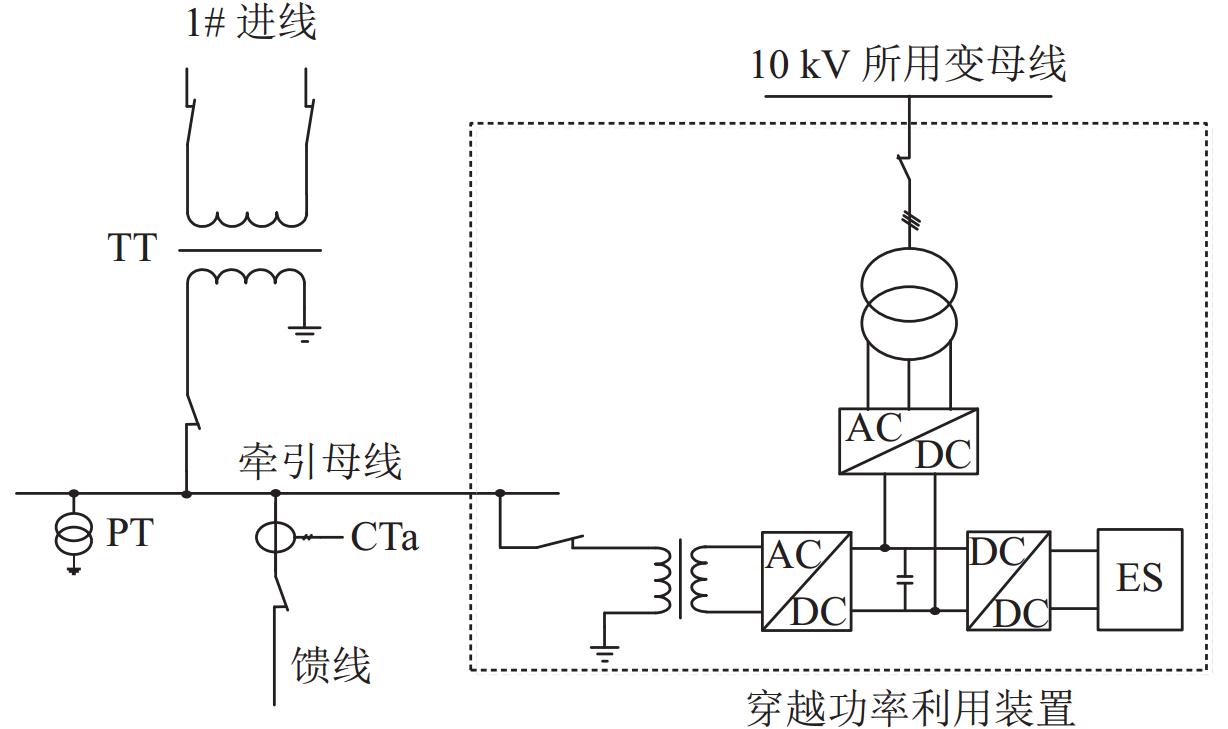
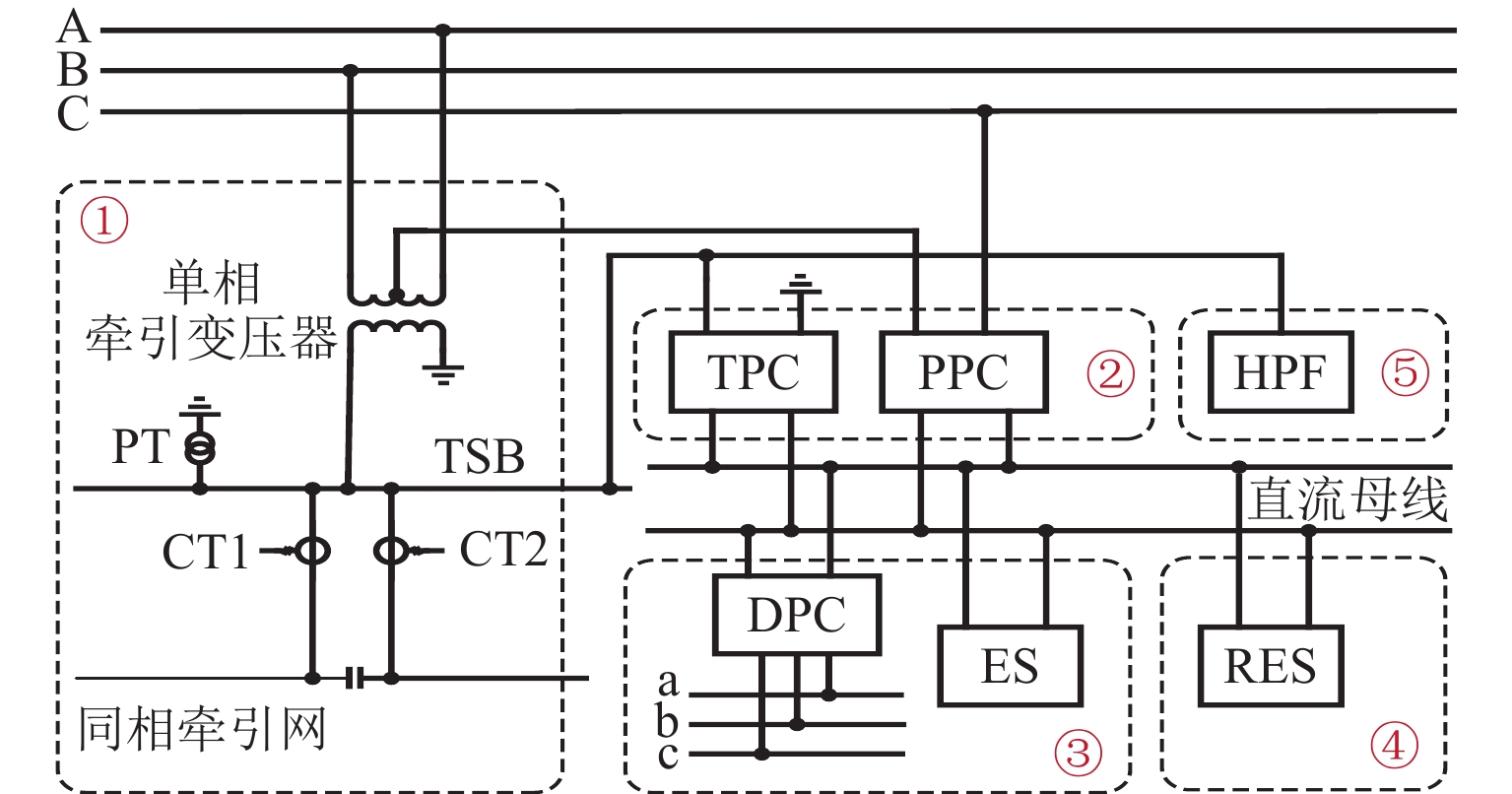
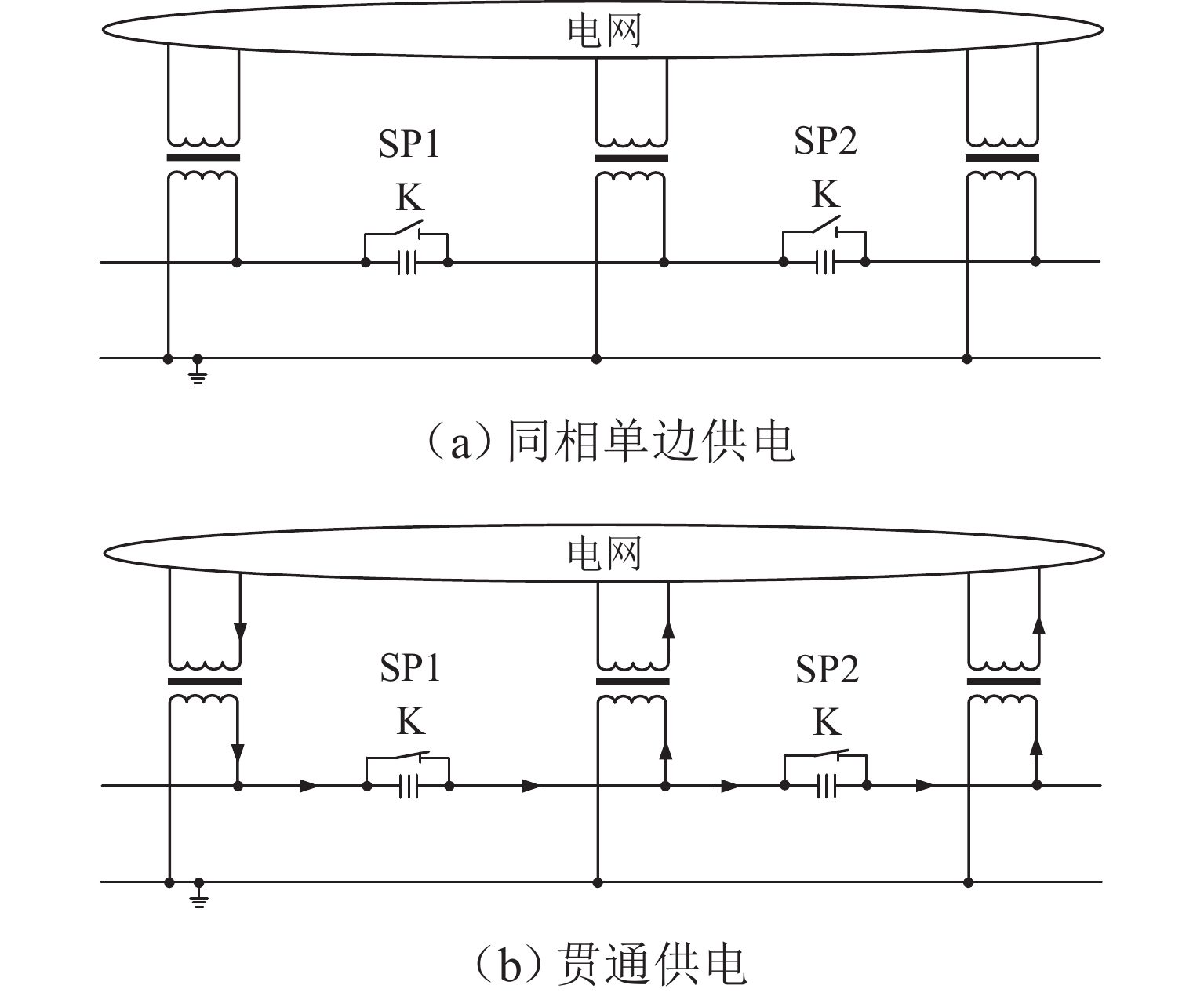
实现电气化铁路贯通供电,不仅需要解决铁路内部2个或者多个牵引变电所之间牵引网的双边供电,更重要的是解决铁路贯通供电给电网带来的影响. 本文研究对比单边供电系统与贯通供电系统对电网影响及其区别,结合电网合环规程,探讨双边供电的可实施性;构建贯通供电穿越功率计算模型,提出穿越功率监测方法以及树形供电、合建所和穿越功率利用3类穿越功率解决方案;在此基础上,综合负序治理和再生发电功率利用,提出多功能的智能牵引变电所方案,以消除对电网的不利影响,推动铁路更大范围实现贯通供电,取消电分相、消除无电区. 研究表明:在电网专用线供电情况下,若牵引变电所间距不超过80 km,双边供电时分区所的合环电压差不大于16.00%,相角差不大于12.00°,低于合环规程的规定值,符合要求,可以合环;与同相单边供电相比,贯通供电对电网产生的穿越功率问题可以得到很好解决,并且再生发电功率也能得到更好利用,技术指标优于单边供电.
Abstract:To realize the interconnected power supply for electrified railways, it is essential not only to address the bilateral power supply between two or more traction substations within the railway network but also to solve the impacts of interconnected power supply for railways on power grids. In this paper, the influence of single-end and interconnected power supply systems on the grid, as well as their differences, was compared, and the feasibility of bilateral power supply according to the grid loop closing regulation was discussed. A calculation model of through power for the interconnected power supply was developed, and a method for monitoring the through power was proposed. Three types of solutions for through power were introduced: tree-structured power supply, co-built substation, and through power utilization. A multi-functional intelligent traction substation was then proposed, integrating negative sequence control and regenerative power utilization to mitigate the adverse effects on the power grid. This can facilitate broader implementation of interconnected power supply in railways, eliminate phase separation, and address areas without power. The finding indicates that when power is supplied by dedicated lines from the grid and the distance between traction substations does not exceed 80 km, the voltage difference in the closed loop remains below 16.00% for a bilateral power supply, and the phase angle difference is within 12.00°, both of which are within the specified limits for loop closing regulation. Compared to the co-phase single-end power supply, interconnected power supply shows better performance in solving the issue of through power in power grids. Additionally, it enhances the utilization of regenerative power, offering better technical performance.
-
表 1 功率因数为0.95(滞后)时的电压差和相角差
Table 1. Voltage difference and phase angle difference at the power factor of 0.95 (lagging)
L/km 传输功率 200 MV•A 传输功率 300 MV•A 传输功率 500 MV•A ΔU/kV δU/% θ/(o) ΔU/kV δU/% θ/(o) ΔU/kV δU/% θ/(o) 50 3.49 2.74 3.23 5.38 4.23 4.78 9.44 7.43 7.74 60 4.23 3.33 3.85 6.56 5.16 5.69 11.60 9.13 9.16 70 4.99 3.93 4.47 7.77 6.12 6.58 13.85 10.90 10.53 80 5.77 4.54 5.08 9.02 7.10 7.45 16.17 12.73 11.85 表 2 功率因数为0.90(滞后)时的电压差和相角差
Table 2. Voltage difference and phase angle difference at the power factor of 0.90 (lagging)
L/km 传输功率 200 MV•A 传输功率 300 MV•A 传输功率 500 MV•A ΔU/kV δU/% θ/(o) ΔU/kV δU/% θ/(o) ΔU/kV δU/% θ/(o) 50 4.41 3.47 2.99 6.74 5.30 4.41 11.63 9.16 7.10 60 5.33 4.20 3.56 8.17 6.44 5.23 14.19 11.17 8.37 70 6.26 4.93 4.13 9.64 7.59 6.04 16.81 13.24 9.60 80 7.21 5.68 4.68 11.13 8.76 6.84 19.50 15.35 10.78 -
[1] 曹建猷. 电气化铁道供电系统[M]. 北京:中国铁道出版社,1983. [2] 苏)康•古•马克瓦尔特. 电气化铁路供电[M]. 袁则富,何其光,译. 峨眉山:西南交通大学出版社,1989. [3] 韩祯祥. 电力系统分析[M]. 5版. 杭州:浙江大学出版社,2013. [4] 李群湛,贺建闽,解绍锋. 电气化铁路电能质量分析与控制[M]. 成都:西南交通大学出版社,2011. [5] 于万聚. 高速电气化铁路接触网[M]. 成都:西南交通大学出版社,2003. [6] 邓志翔. 市域轨道交通供电系统设置电分相对于相关专业的影响分析[J]. 城市轨道交通研究,2019,22(12): 89-91,95.DENG Zhixiang. Impact of phase separation in suburban rail transit AC power supply system on the related specialties[J]. Urban Mass Transit, 2019, 22(12): 89-91,95. [7] 宫衍圣. 电力机车过关节式电分相过电压研究[J]. 铁道学报,2008,30(4): 103-107. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8360.2008.04.020GONG Yansheng. Research of over-voltages of electric locomotive passing the articulated phase insulator[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2008, 30(4): 103-107. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8360.2008.04.020 [8] 黄足平. 轨道交通采用25 kV交流制的电分相影响分析及处理对策[J]. 铁道标准设计,2016,60(11): 119-121.HUANG Zuping. The influence of 25 kV AC neutral section of urban rail transit and treatment measures[J]. Railway Standard Design, 2016, 60(11): 119-121. [9] 王希元,张光源. 高速铁路引入枢纽(地区)电分相缓坡设置方案研究[J]. 高速铁路技术,2024,15(3): 81-86.WANG Xiyuan, ZHANG Guangyuan. Study on setting scheme of phase break gentle slope for leading high-speed railway into terminal (area)[J]. High Speed Railway Technology, 2024, 15(3): 81-86. [10] 徐平,李东阳. 货运铁路接触网分相掉车问题浅析[J]. 电气化铁道,2021,32(6): 87-90.XU Ping, LI Dongyang. Discussion on issues of train halting within OCS phase break on freight track[J]. Electric Railway, 2021, 32(6): 87-90. [11] 李群湛. 牵引供电系统并联补偿方法的研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报,1986,21(2): 85-98.LI Qunzhan. A study of parallel compensation method in railway traction power supply systems[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 1986, 21(2): 85-98. [12] 李群湛. 同相供电系统的对称补偿[J]. 铁道学报,1991(增1): 35-43.LI Qunzhan. Symmetrical compensation in the traction feeding system without phase exchange[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 1991(S1): 35-43. [13] 李群湛. 电气化铁道并联综合补偿及其应用[M]. 北京:中国铁道出版社,1993. [14] 李群湛,贺建闽. 电气化铁路的同相供电系统与对称补偿技术[J]. 电力系统自动化,1996,20(4): 9-11,28.LI Qunzhan, HE Jianmin. Electrified railway feeding system without phase exchange and symmetrical compensation technology[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 1996, 20(4): 9-11,28. [15] 贺建闽,李群湛. 用于同相供电系统的对称补偿技术[J]. 铁道学报,1998,20(6): 47-51. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8360.1998.06.008HE Jianmin, LI Qunzhan. Symmetrical compensation technology used in feeding system without phase exchange[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 1998, 20(6): 47-51. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8360.1998.06.008 [16] 李群湛. 牵引变电所供电分析及综合补偿技术[M]. 北京:中国铁道出版社,2006. [17] 李群湛. 我国高速铁路牵引供电发展的若干关键技术问题[J]. 铁道学报,2010,32(4): 119-124. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2010.04.022LI Qunzhan. On some technical key problems in the development of traction power supply system for high-speed railway in China[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2010, 32(4): 119-124. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2010.04.022 [18] 李群湛. 论新一代牵引供电系统及其关键技术[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2014,49(4): 559-568. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2014.04.001LI Qunzhan. On new generation traction power supply system and its key technologies for electrification railway[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2014, 49(4): 559-568. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2014.04.001 [19] 李群湛,王辉,黄文勋,等. 电气化铁路牵引变电所群贯通供电系统及其关键技术[J]. 电工技术学报,2021,36(5): 1064-1074.LI Qunzhan, WANG Hui, HUANG Wenxun, et al. Interconnected power supply system of traction substation group and its key technologies for the electrified railway[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2021, 36(5): 1064-1074. [20] 国家质量监督检验检疫总局,中国国家标准化管理委员会. 电能质量:三相电压不平衡:GB/T 15543—2008[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社,2009. [21] 王辉. 电气化铁路新型贯通式同相供电方案及其供电能力研究[D]. 成都:西南交通大学,2022. [22] 李群湛,彭友,黄小红,等. 电气化铁路贯通供电系统穿越功率的治理措施[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2024,59(6): 1245-1255. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20220887LI Qunzhan, PENG You, HUANG Xiaohong, et al. Crossing power governance approach of continuous power supply system in electrified railway[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2024, 59(6): 1245-1255. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20220887 [23] 王帅. 电气化铁路贯通式同相供电牵引网保护与测距技术研究[D]. 成都:西南交通大学,2024. [24] 李群湛,王帅,易东,等. 电气化铁路贯通同相供电AT牵引网故障辨识与自愈技术研究[J]. 铁道学报,2022,44(7): 46-54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2022.07.006LI Qunzhan, WANG Shuai, YI Dong, et al. Research on fault identification and self-healing technology of AT traction network with co-phase power supply for electrified railway[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2022, 44(7): 46-54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2022.07.006 [25] 青海省电力公司. 青海省电力系统调度规程:Q/GDW 25-001-2012-10402[S]. 西宁:[出版者不详],2012. [26] 中国南方电网有限责任公司. 中国南方电网电力调度管理规程:Q/CSG 212045—2017[S]. 北京:中国电力出版社,2017 [27] 李群湛,贺建闽. 牵引供电系统分析[M]. 成都:西南交通大学出版社,2007. [28] 周志成. 基于树形双边供电的重载铁路贯通同相供电方案[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报,2020,17(3): 722-731.ZHOU Zhicheng. Cophase connected power supply scheme of heavy haul railway based on tree bilateral power supply[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2020, 17(3): 722-731. -




 下载:
下载: