Research and Application of Electrical Twin with Acoustic Metastructures for Vehicle NVH
-
摘要:
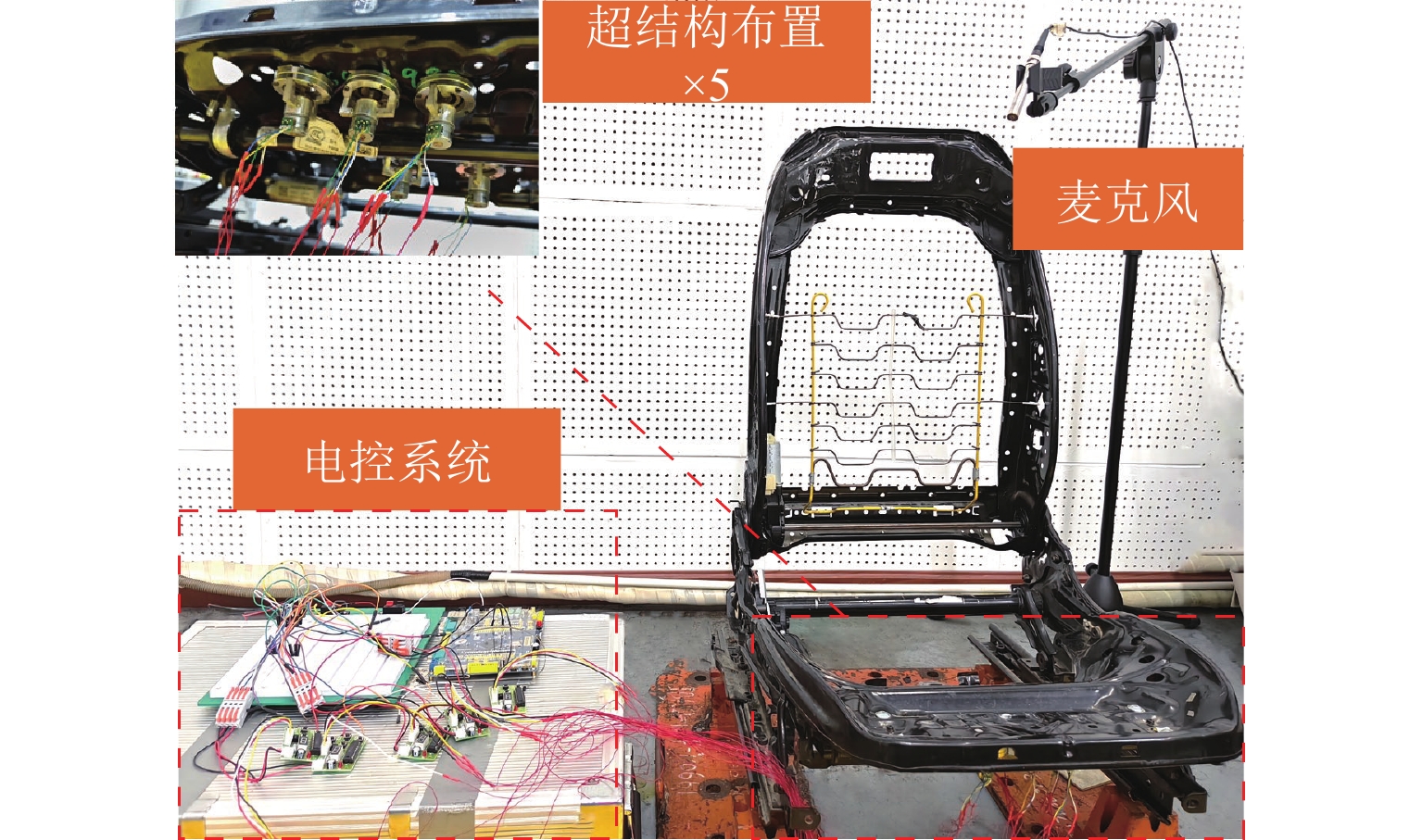
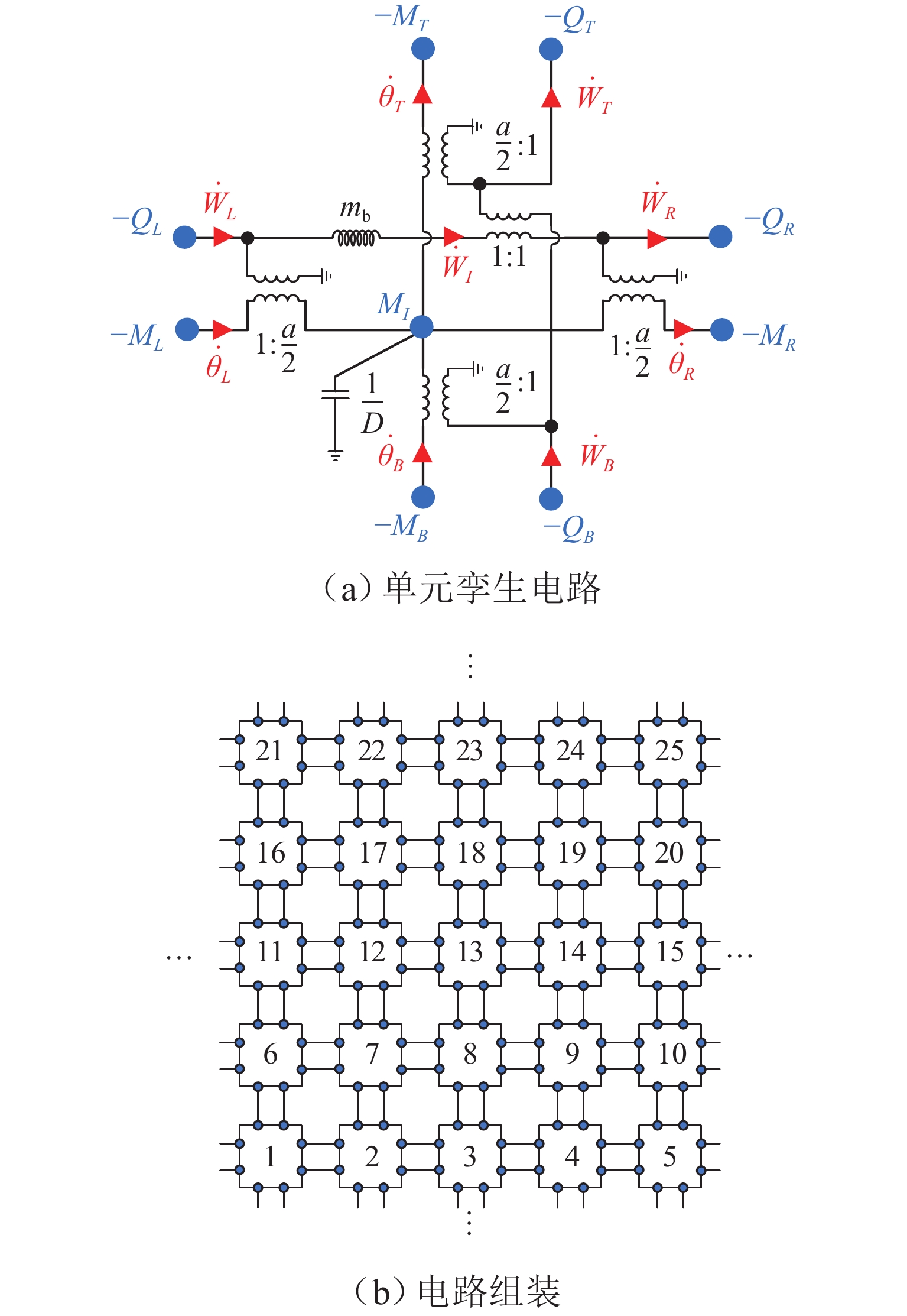
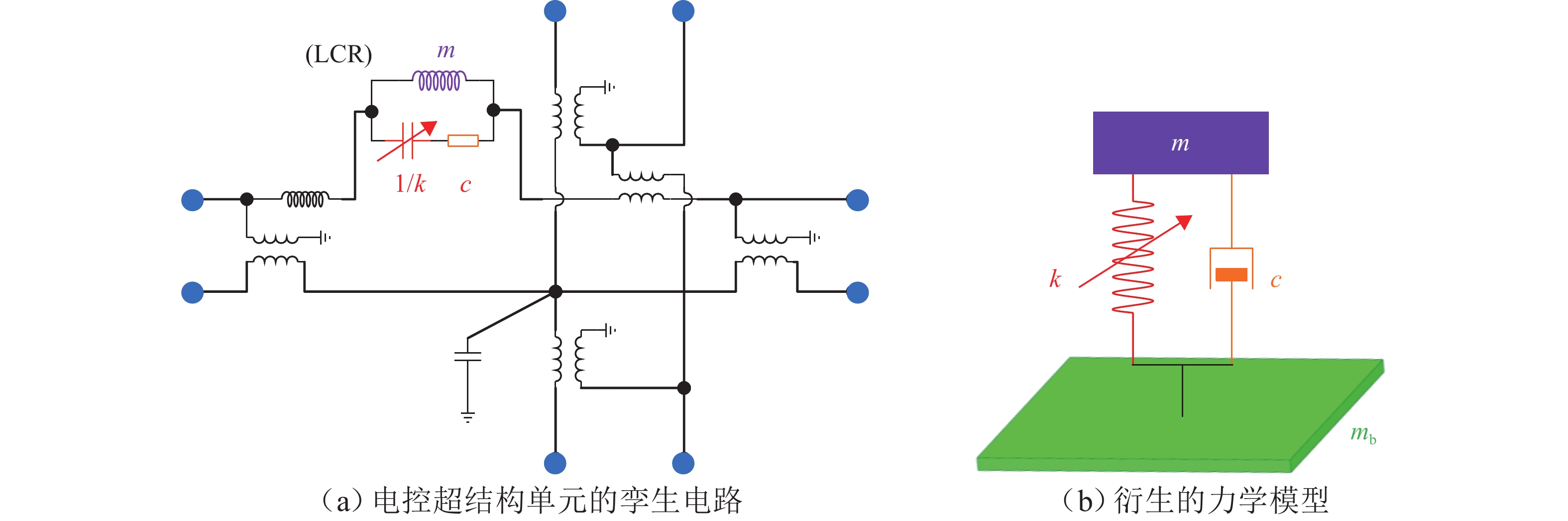
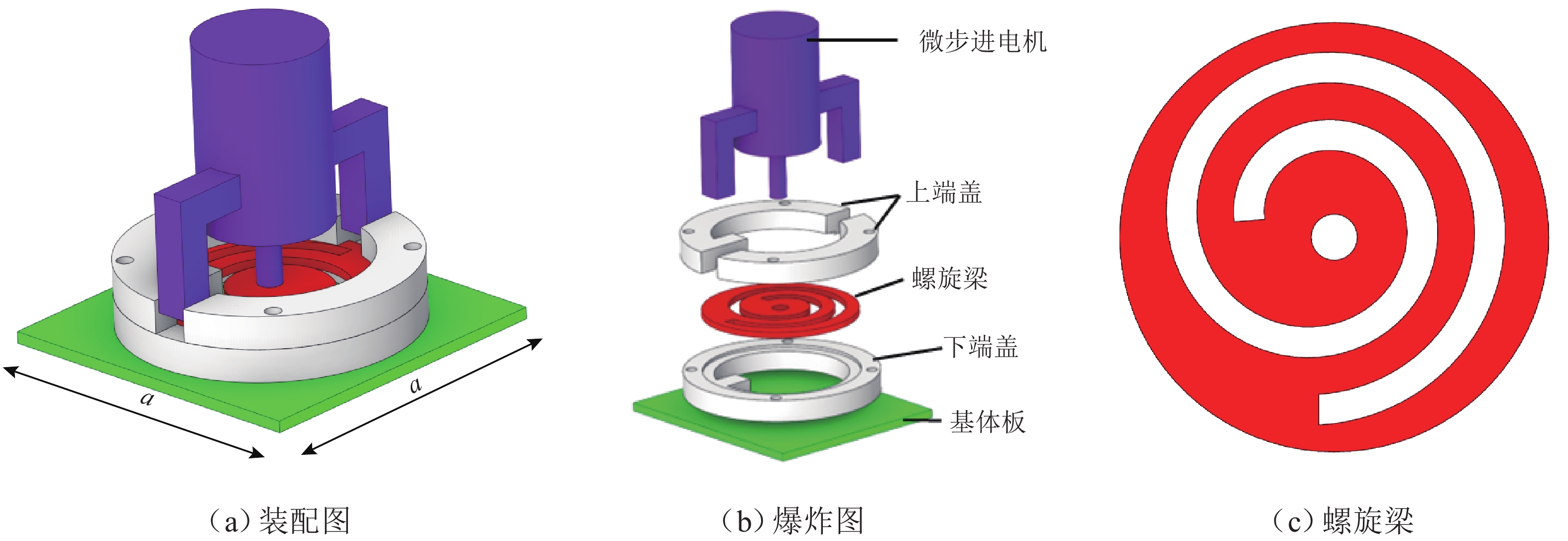
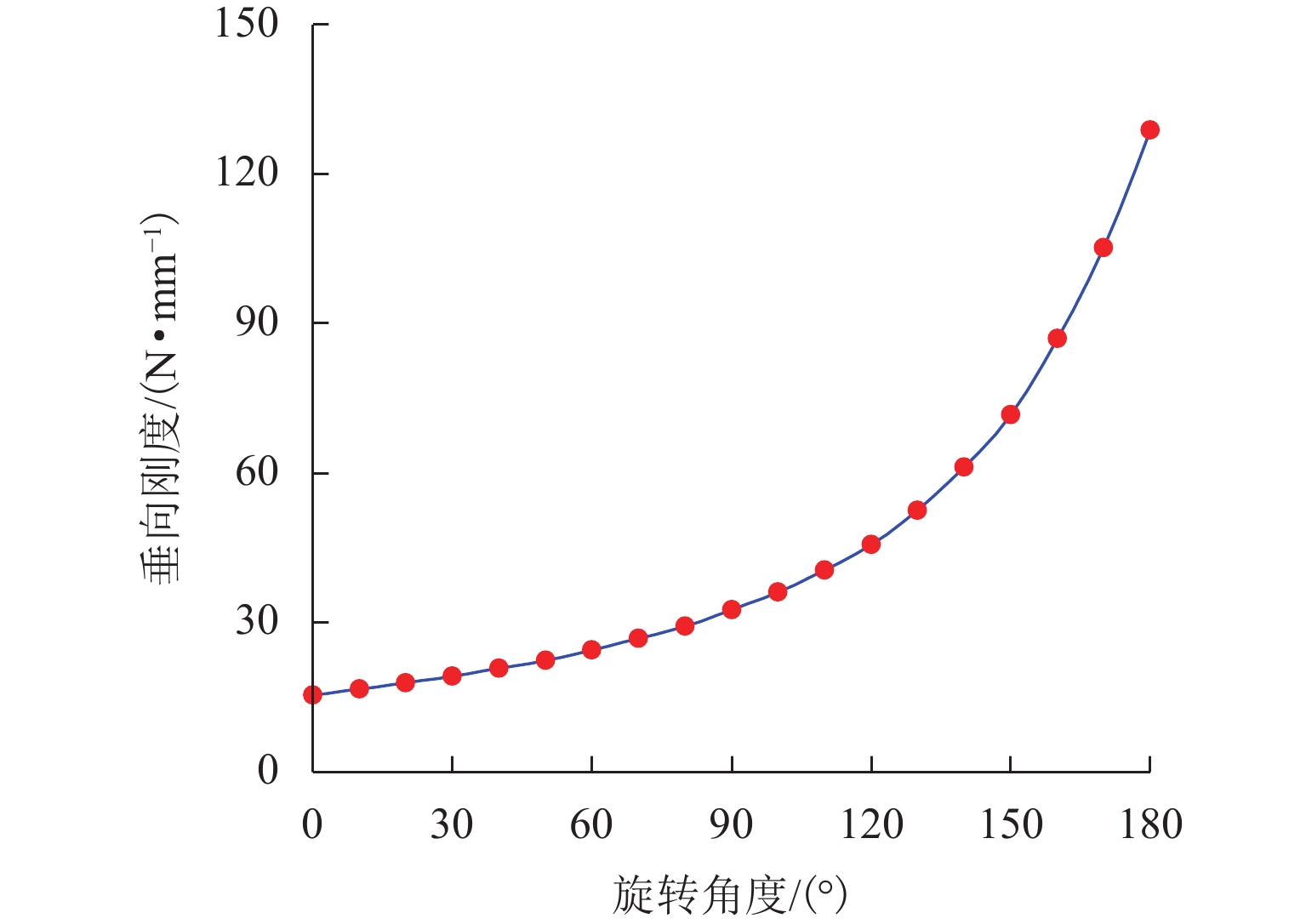
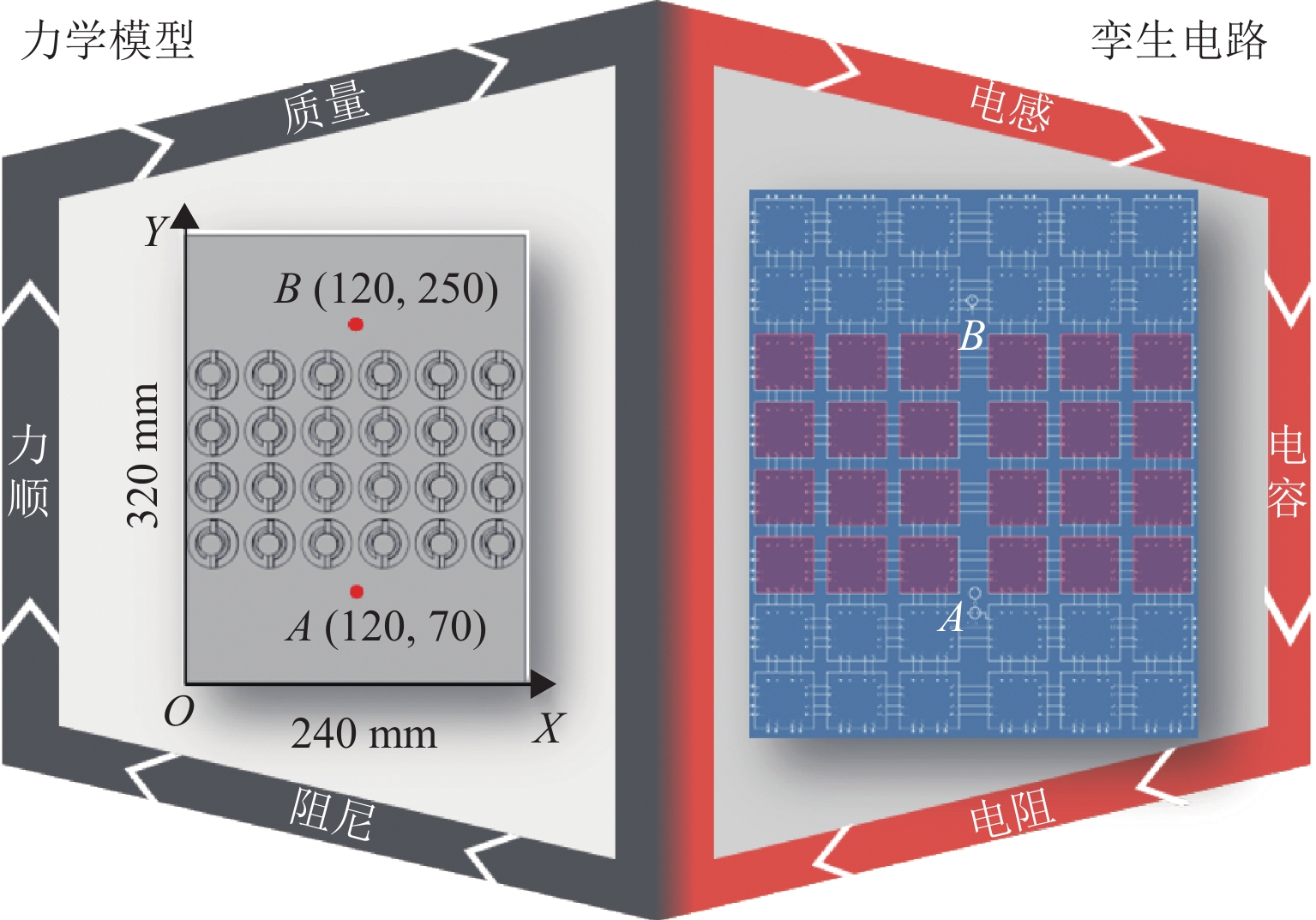
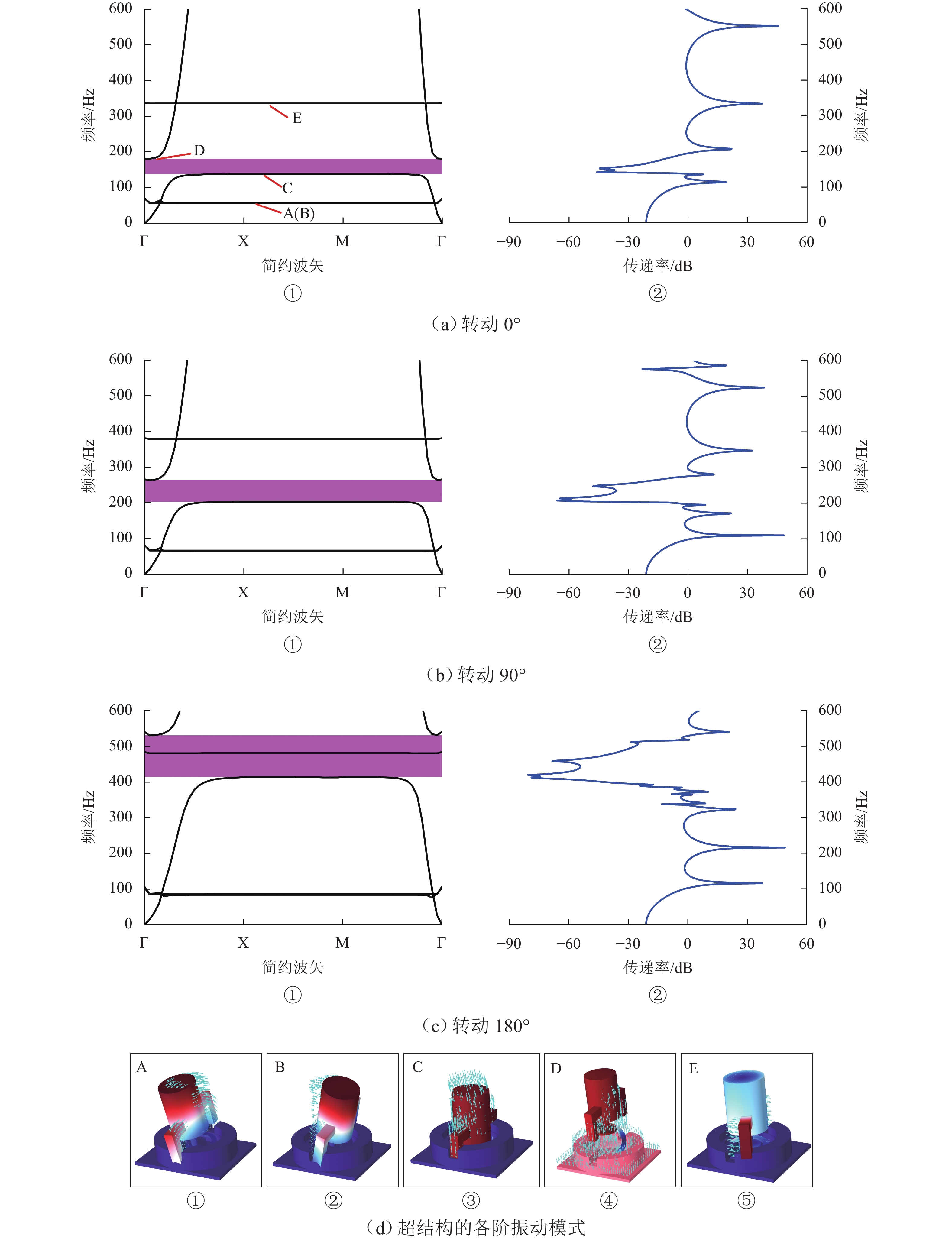
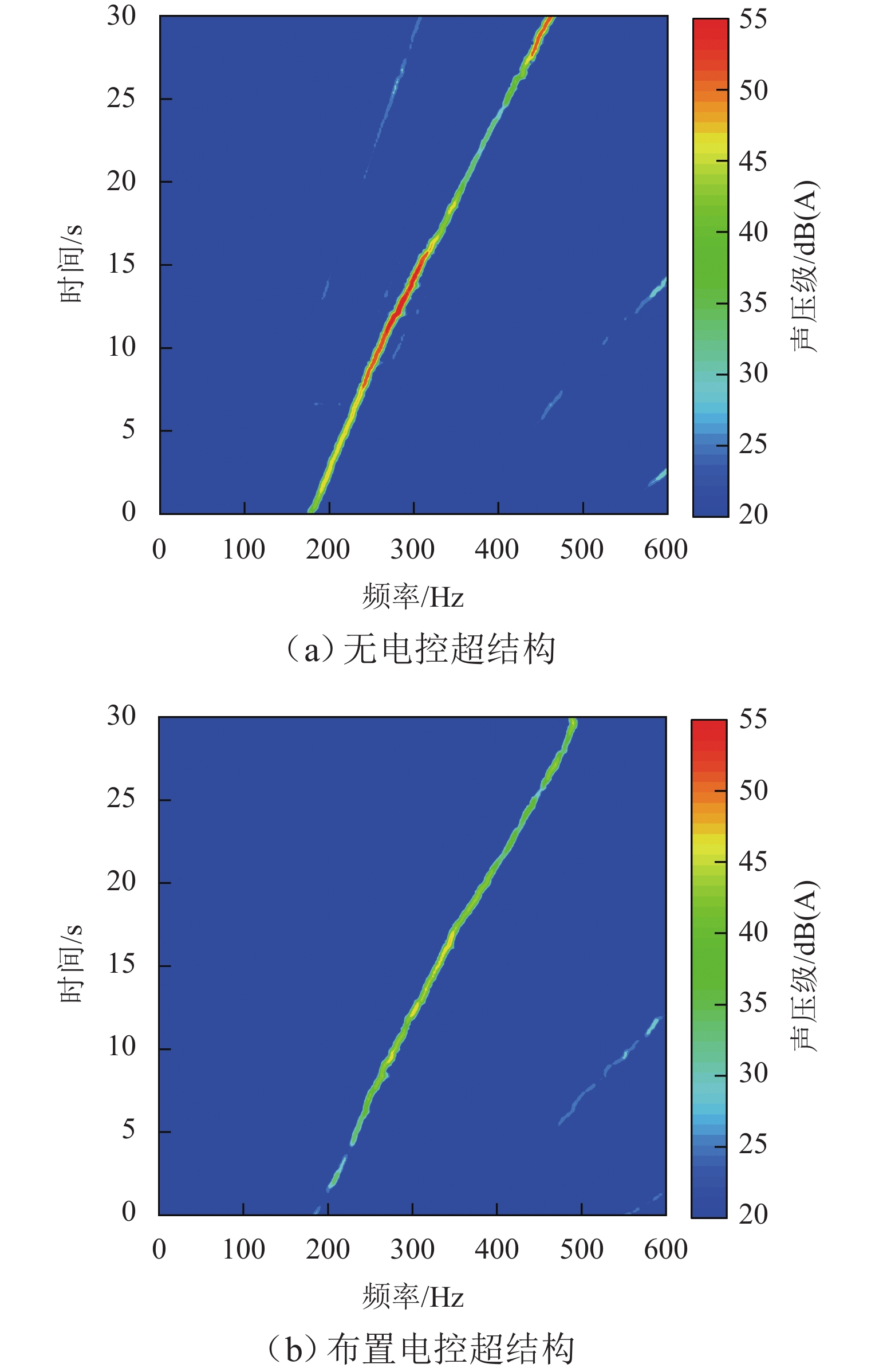
声学超结构因其独特的波操纵特性在车辆噪声、振动和声振舒适性(NVH)领域备受关注,但被动式声学超结构的低频带隙带宽窄且不可调,限制了其进一步的发展和应用. 为克服此难题,提出电控型声学超结构以灵活调谐带隙,并建立相应的电学孪生理论. 从经典的机电类比理论出发,基于有限差分法对Kirchhoff-love薄板建立了二维孪生电路;在此基础上,串联LCR谐振回路以形成超结构单元的孪生电路,引入可调电容以实现对电学带隙的调谐;从孪生电路中衍生出一种具体形态为螺旋型的电控超结构,并进行了仿真验证和应用实验. 结果表明:孪生电路可视为超结构在电学域中的精确映射,通过电控方式可有效调节超结构等效刚度,进而实现带隙调谐,其调谐规律可通过孪生电路进行高效预测与分析;所设计的螺旋型电控超结构对电动座椅的阶次跟踪降噪效果显著,在200~460 Hz的宽频范围内声压级平均下降约7.4 dB(A). 所提出的孪生电路有助于电控超结构的机电一体化设计,同时也为不同形态的电控超结构研究提供了理论范式.
Abstract:Due to their exceptional wave manipulation characteristics, acoustic metastructures have attracted substantial attention in vehicle noise, vibration, and harshness (NVH). However, the further development and application of passive acoustic metastructures are limited by the narrow and non-tunable low-frequency bandgaps and bandwidth. To address this challenge, an electrically controlled acoustic metastructure was proposed to enable flexible bandgap tuning, and the corresponding electrical twin theory was established. According to the classical electromechanical analogy, a two-dimensional electrical twin circuit for a Kirchhoff-Love thin plate was established by the finite difference method. Then, an inductance-capacitance-resistance (LCR) resonant circuit was connected in series to form the twin circuit of a metastructure unit, with a tunable capacitor introduced to achieve electrical bandgap tuning. Finally, a spiral-shaped electrically controlled metastructure was derived from the twin circuit and verified through simulations and experiments. The results confirm that the twin circuit constitutes an exact electrical-domain mapping of the metastructure. The equivalent stiffness of the metastructure can be adjusted by the electrical control, thereby facilitating bandgap tuning. The resulting tuning law can be efficiently predicted and analyzed by the twin circuit. The designed spiral-shaped electrically controlled metastructure exhibits a significant order-tracking noise reduction effect for electric seats, with an average sound pressure level reduction of approximately 7.4 dB(A) in the wide frequency range of 200–460 Hz. The proposed twin circuit contributes to the electromechanical integrated design of electrically controlled metastructures, and it provides a theoretical paradigm for the study of different types of electrically controlled metastructures.
-
Key words:
- vehicle NVH /
- vibration control /
- acoustic metastructure /
- electrical twin /
- bandgap
-
-
[1] HAZRA S, REDDY J K. A review paper on recent research of noise and vibration in ElectricVehicle powertrain mounting system[J]. SAE International Journal of Vehicle Dynamics, Stability, and NVH, 2021, 6(1): 3-22. doi: 10.4271/10-06-01-0001 [2] 黄思怡, 康健强. 电动汽车振动特性及NVH性能控制研究进展[J]. 汽车实用技术, 2023, 48(17): 200-205.HUANG Siyi, KANG Jianqiang. Research progress of vibration characteristics and NVH performance controlling of electric vehicles[J]. Automobile Applied Technology, 2023, 48(17): 200-205. [3] 《中国公路学报》编辑部. 中国汽车工程学术研究综述•2023[J]. 中国公路学报, 2023, 36(11): 1-192.Editorial Department of China Journal of Highway and Transport. Review on China’s automotive engineering research progress: 2023[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2023, 36(11): 1-192. [4] LIAO Y, HUANG H B, CHANG G B, et al. Research on low-frequency noise control of automobiles based on acoustic metamaterial[J]. Materials, 2022, 15(9): 3261. doi: 10.3390/ma15093261 [5] 农兴中, 李祥, 刘堂辉, 等. 浮置板下声子晶体隔振器带隙特性研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2019, 54(6): 1203-1209, 1276.NONG Xingzhong, LI Xiang, LIU Tanghui, et al. Band gap characteristics of vibration isolators of phononic crystals under floating slab[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2019, 54(6): 1203-1209, 1276. [6] OUDICH M, GERARD N J, DENG Y C, et al. Tailoring structure-borne sound through bandgap engineering in phononic crystals and metamaterials: a comprehensive review[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2023, 33(2): 2206309. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202206309 [7] VALIPOUR A, KARGOZARFARD M H, RAKHSHI M, et al. Metamaterials and their applications: an overview[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part L: Journal of Materials: Design and Applications, 2022, 236(11): 2171-2210. doi: 10.1177/1464420721995858 [8] JI G S, HUBER J. Recent progress in acoustic metamaterials and active piezoelectric acoustic metamaterials-A review[J]. Applied Materials Today, 2022, 26: 101260. doi: 10.1016/j.apmt.2021.101260 [9] SONG H, DING X D, CUI Z X, et al. Research progress and development trends of acoustic metamaterials[J]. Molecules, 2021, 26(13): 4018. doi: 10.3390/molecules26134018 [10] WANG X Z, ZHANG C, RUI S T, et al. Multi-scale material/structure integrated elastic metamaterial for broadband vibration absorbing[J]. Materials & Design, 2024, 238: 112705. [11] ZHANG C, ZHANG D, YIN F J, et al. “Borrow-force-attack-force” by multi-scale elastic metamaterial with nonlinear damping[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2025, 288: 111884. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2024.111884 [12] HAN D Y, PENG Y Y, LIU G S, et al. Tunable pipe-type acoustic metamaterials based on piezoelectric composite side-branches[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2021, 129(8): 084505. doi: 10.1063/5.0039751 [13] HU G B, AUSTIN A C M, SOROKIN V, et al. Metamaterial beam with graded local resonators for broadband vibration suppression[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2021, 146: 106982. doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2020.106982 [14] REN T, LIU C C, LI F M, et al. Active tunability of band gaps for a novel elastic metamaterial plate[J]. Acta Mechanica, 2020, 231(10): 4035-4053. doi: 10.1007/s00707-020-02728-1 [15] 张明, 谢延松, 李洪涛, 等. 一种高静-低动刚度磁弹簧的建模与特性分析[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2023, 58(4): 933-939, 946.ZHANG Ming, XIE Yansong, LI Hongtao, et al. Modeling and characteristic analysis of a magnetic spring with high static stiffness and low dynamic stiffness[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2023, 58(4): 933-939, 946. [16] 董小闵, 王凯翔, 李坪洋. 基于磁流变复合材料的磁流变阻尼器设计[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2023, 58(4): 896-902.DONG Xiaomin, WANG Kaixiang, LI Pingyang. Design of magnetorheological damper based on magnetorheological composite materials[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2023, 58(4): 896-902. [17] 张明, 李洪涛, 崔浩东, 等. 一种电磁式高静-低动刚度隔振系统建模与特性分析[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2024, 59(4): 858-866.ZHANG Ming, LI Hongtao, CUI Haodong, et al. Modeling and characteristic analysis of an electromagnetic isolation system with high static stiffness and low dynamic stiffness[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2024, 59(4): 858-866. [18] WANG K, ZHOU J X, OUYANG H J, et al. A semi-active metamaterial beam with electromagnetic quasi-zero-stiffness resonators for ultralow-frequency band gap tuning[J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2020, 176: 105548. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2020.105548 [19] XIA B Z, CHEN N, XIE L X, et al. Temperature-controlled tunable acoustic metamaterial with active band gap and negative bulk modulus[J]. Applied Acoustics, 2016, 112: 1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.apacoust.2016.05.005 [20] NING S W, YAN Z M, CHU D Y, et al. Ultralow-frequency tunable acoustic metamaterials through tuning gauge pressure and gas temperature[J]. Extreme Mechanics Letters, 2021, 44: 101218. doi: 10.1016/j.eml.2021.101218 [21] SHRESTHA M, LAU G K, CHIN Y W, et al. A tunable acoustic absorber using reconfigurable dielectric elastomer actuated petals[J]. Communications Engineering, 2024, 3: 11. doi: 10.1038/s44172-023-00159-z [22] WANG X Z, RUI S T, YANG S K, et al. A low-frequency pure metal metamaterial absorber with continuously tunable stiffness[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2024, 45(7): 1209-1224. doi: 10.1007/s10483-024-3158-7 [23] 张敏, 温晓东, 孙小伟, 等. 复合柱局域共振声子晶体的超宽带隙与可调性研究[J]. 噪声与振动控制, 2024, 44(4): 96-102.ZHANG Min, WEN Xiaodong, SUN Xiaowei, et al. Study on characteristics and tunability of ultra-wide band gaps for composite column locally resonant phononic crystals[J]. Noise and Vibration Control, 2024, 44(4): 96-102. [24] CHU J M, ZHOU G J, LIANG X, et al. A metamaterial for low-frequency vibration damping[J]. Materials Today Communications, 2023, 36: 106464. doi: 10.1016/j.mtcomm.2023.106464 [25] YAO J Y, XU K, YAO D H, et al. A metamaterial cylindrical shell with multiple graded resonators for broadband longitudinal wave attenuation[J]. Frontiers in Physics, 2023, 11: 1133586. doi: 10.3389/fphy.2023.1133586 [26] MIAO X J, ZHOU Z T, ZHANG Y Y, et al. A new-type lightweight helical elastic metamaterial with ultra-low-frequency bandgaps[J]. Physica Status Solidi (b), 2023, 260(1): 2200355. doi: 10.1002/pssb.202200355 [27] YAN G W, YAO S, LI Y L. Propagation of elastic waves in metamaterial plates with various lattices for low-frequency vibration attenuation[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2022, 536: 117140. doi: 10.1016/j.jsv.2022.117140 [28] DENG S Q, HE Y Y, WU Y D, et al. A locally resonant metamaterial beam with tunable electromagnetic stiffness based on the electromechanical analogy network[J]. Smart Materials and Structures, 2024, 33(5): 055052. doi: 10.1088/1361-665X/ad3ecc [29] LOSSOUARN B, DEÜ J F, AUCEJO M, et al. Multimodal vibration damping of a plate by piezoelectric coupling to its analogous electrical network[J]. Smart Materials and Structures, 2016, 25(11): 115042. doi: 10.1088/0964-1726/25/11/115042 [30] 吴九汇, 张思文, 沈礼. 螺旋局域共振单元声子晶体板结构的低频振动带隙特性研究[J]. 机械工程学报, 2013, 49(10): 62-69. doi: 10.3901/JME.2013.10.062WU Jiuhui, ZHANG Siwen, SHEN Li. Low-frequency vibration characteristics of periodic spiral resonators in phononic crystal plates[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2013, 49(10): 62-69. doi: 10.3901/JME.2013.10.062 -




 下载:
下载: