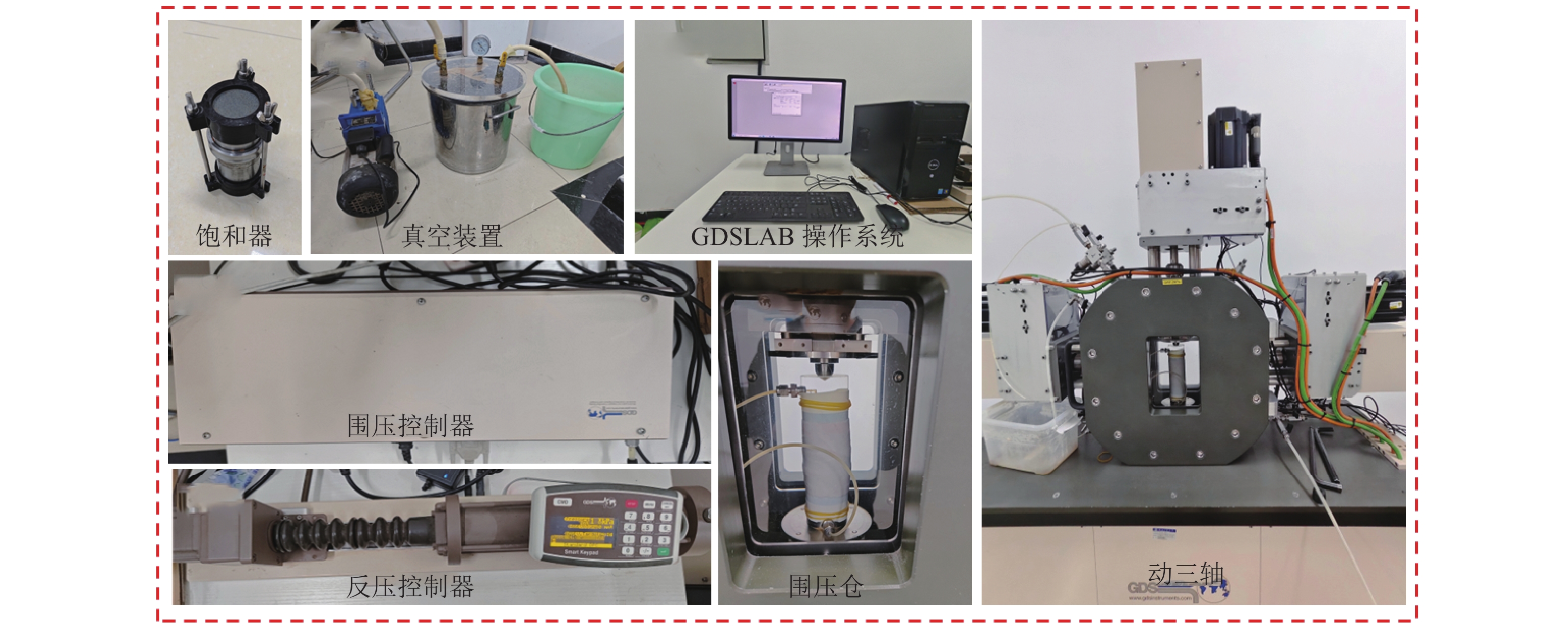
Experimental Study on Dynamic Strength of Subgrade Loess under Continuous and Intermittent Loads
-
摘要:
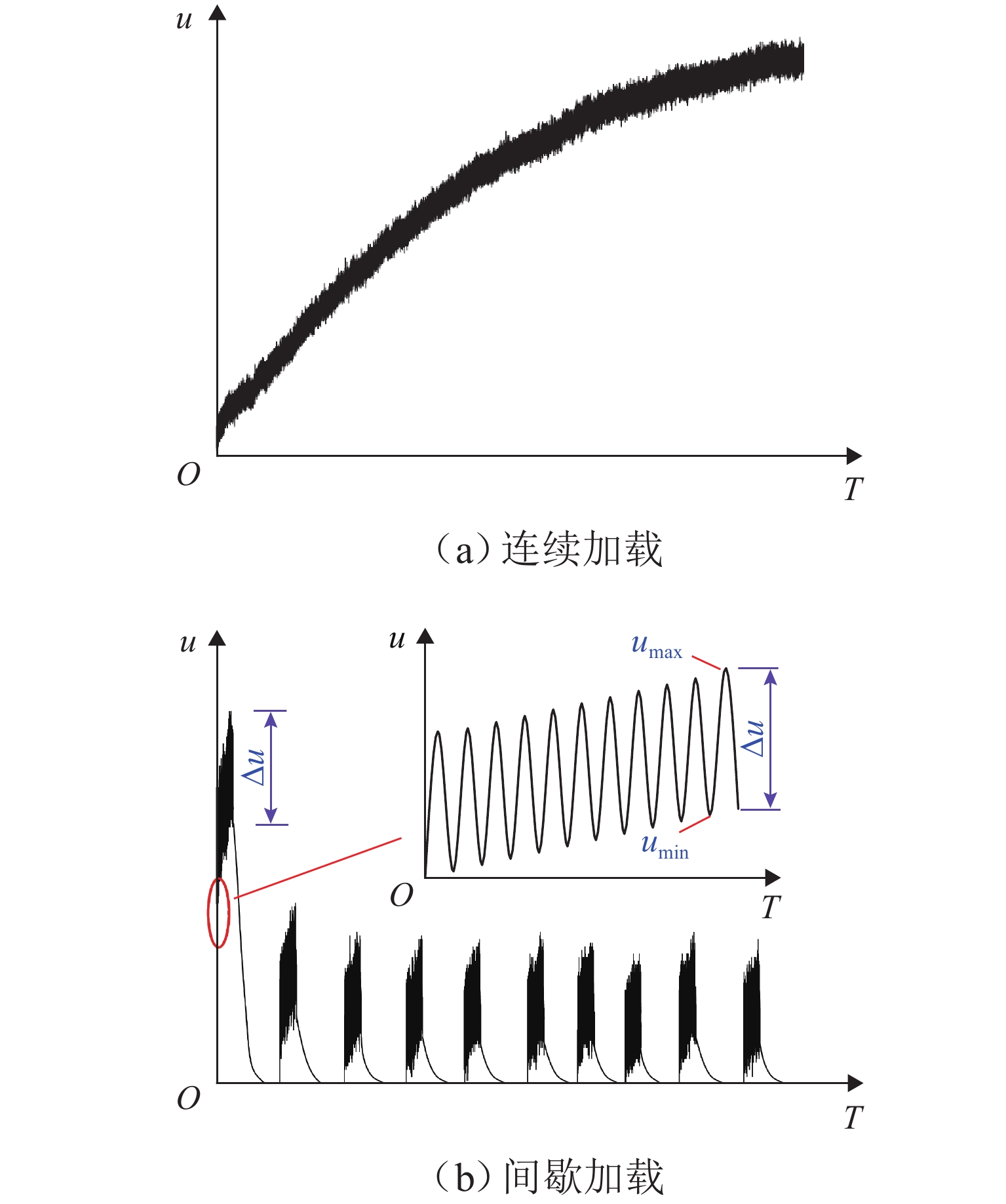
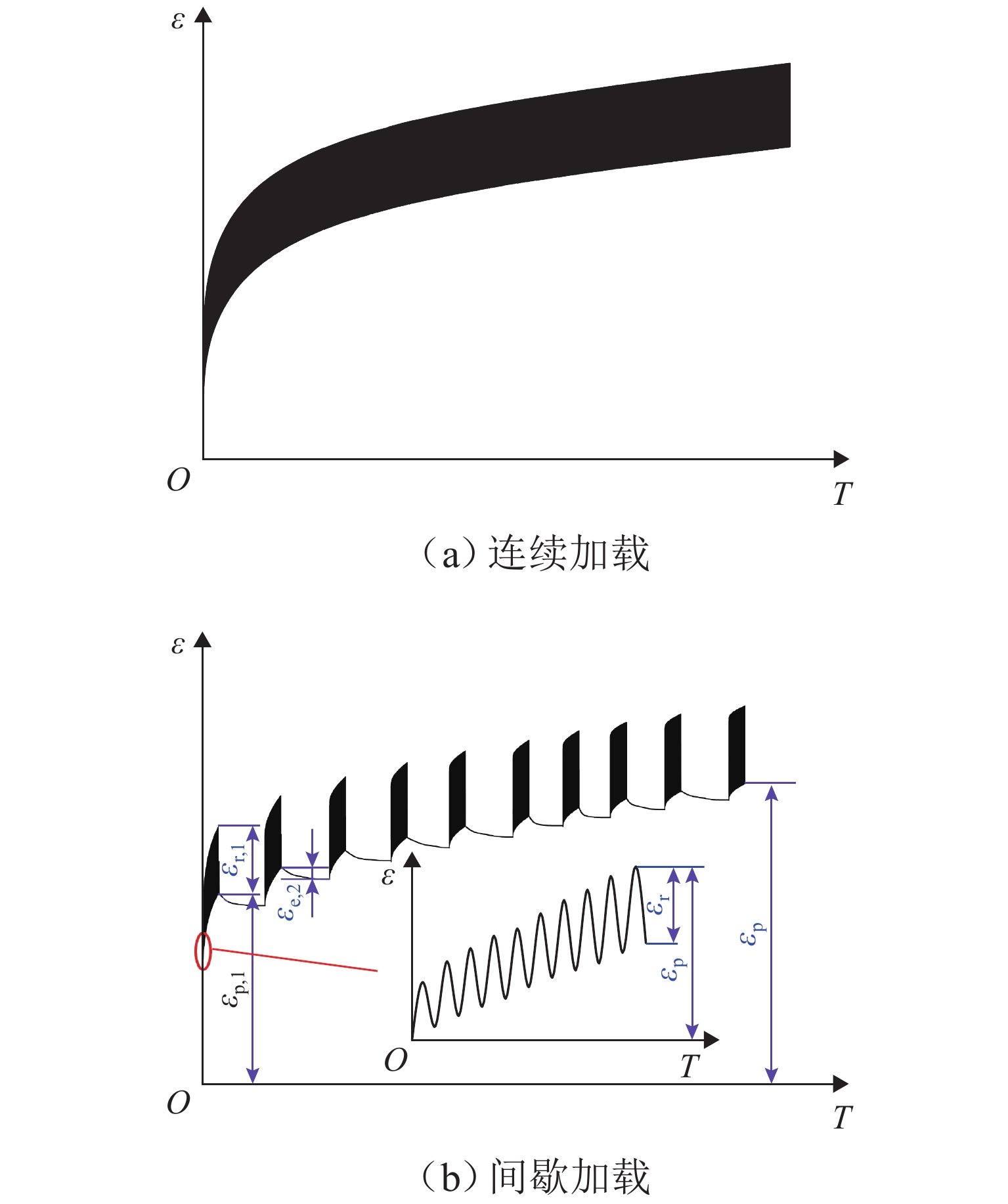
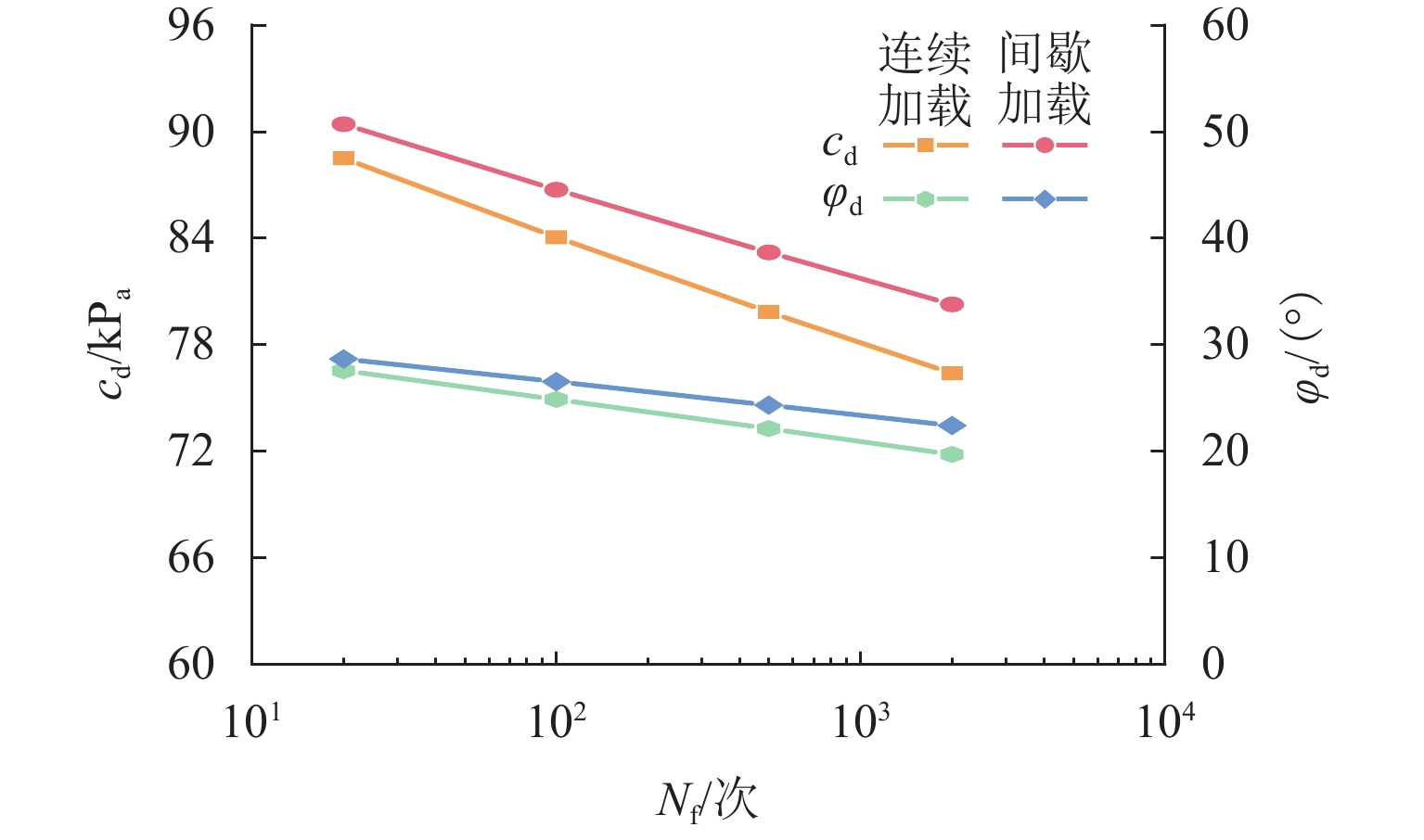
列车在运行过程中产生的周期性动应力对路基填料的动强度构成了显著挑战,现有研究多采用连续加载方式模拟列车荷载,未能充分反映列车荷载的间歇性,为探究连续、间歇加载下黄土路基的动强度差异性,采用GDS 动三轴仪设计一系列连续和间歇加载的固结不排水试验,探讨围压和动应力幅值对土体动强度的影响,并对比分析不同加载方式对路基黄土动强度及其强度参数的作用效果. 试验结果表明:黄土路基的动强度随着围压的增大而增大,但增长幅度却逐渐减小;动黏聚力(
c d)和动摩擦角($ {\varphi _{\text{d}}} $)随破坏次数(lgN f)的增大而减小,整体呈线性关系;相对于连续加载,间歇加载作用下土体的c d和$ {\varphi _{\text{d}}} $有明显提升,c d提高了2.18%~5.09%,$ {\varphi _{\text{d}}} $提高了4.03%~13.78%;通过引入静三轴抗剪强度对动强度进行归一化处理,提出以静强度为变量的黄土路基动强度经验公式,为评估路基在动力作用下的稳定性提供了重要依据.Abstract:The cyclic dynamic stress generated during train operation presents a significant challenge to the dynamic strength of subgrade fill materials. Existing research has mostly simulated train loads using continuous loading methods, which fails to fully reflect the intermittency of these loads. To investigate the differences in dynamic strength of loess subgrade under continuous and intermittent loading, a series of consolidated undrained tests under continuous and intermittent loading conditions were conducted using a GDS dynamic triaxial apparatus. The influences of confining pressure and dynamic stress amplitude on the dynamic strength of the soil were examined. The effects of different loading methods on the dynamic strength and strength parameters of the subgrade loess were compared. The experimental results indicate that the dynamic strength of the loess subgrade increases with higher confining pressure, but the growth rate diminishes gradually. Both dynamic cohesion (
c d) and dynamic friction angle ($ {\varphi _{\text{d}}} $) decrease with the increase in the failure cycles (lgN f), showing an overall linear relationship. Under intermittent loading, the soil exhibits a marked increase inc d and$ {\varphi _{\text{d}}} $compared to continuous loading, withc d increasing by 2.18%–5.09% and $ {\varphi _{\text{d}}} $ by 4.03%–13.78%. By normalizing the dynamic strength using the static triaxial shear strength, an empirical formula for the dynamic strength of the loess subgrade based on static strength is proposed, which provides a critical basis for assessing the stability of the subgrade under dynamic loads.-
Key words:
- subgrade loess /
- continuous loading /
- intermittent loading /
- dynamic strength /
- static strength
-
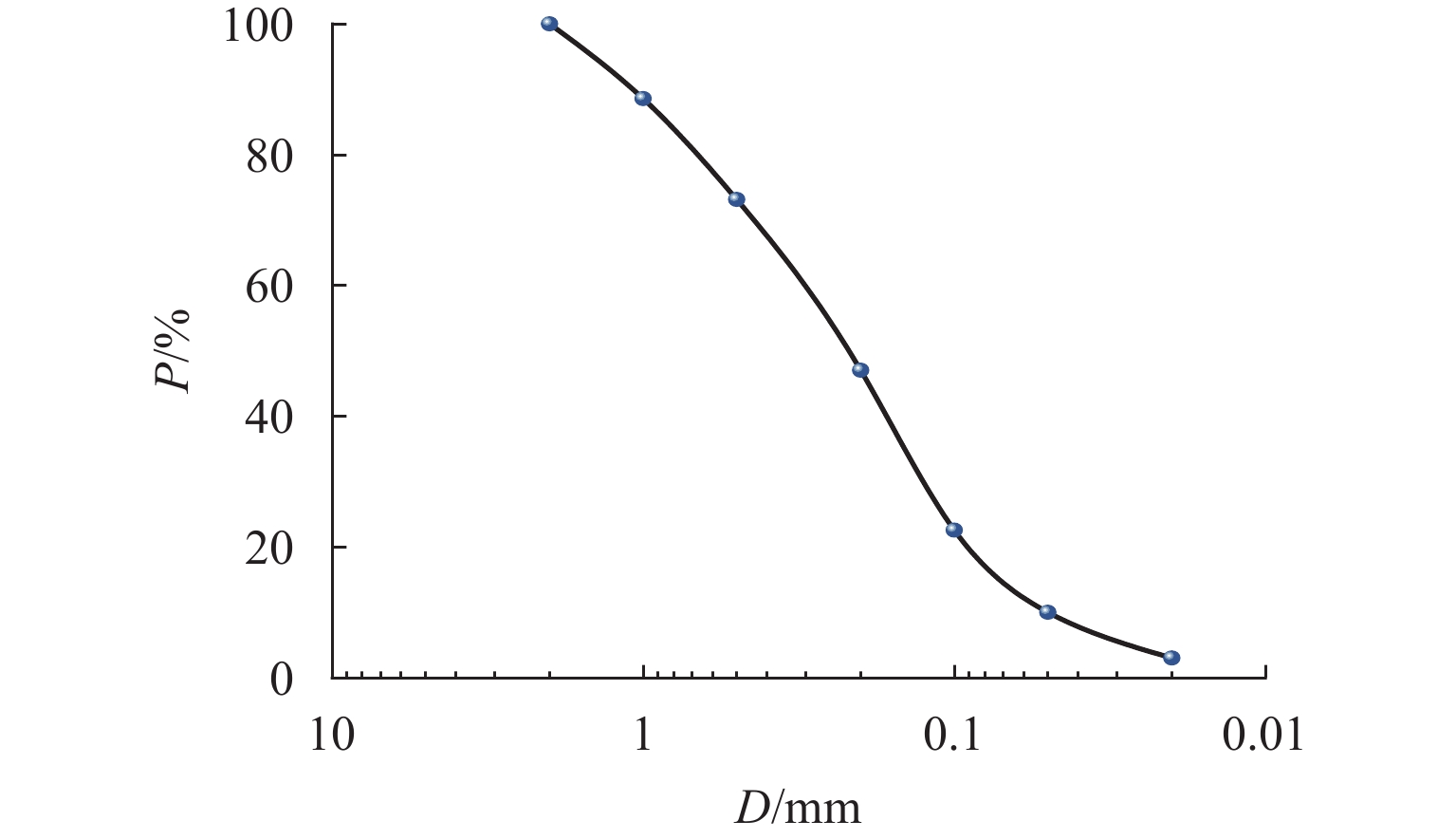
表 1 土的物理参数指标
Table 1. Indicators of physical parameters of soil
名称 Gs wopt/% ${\rho _{{\mathrm{dmax}} }}$/(g•cm−3) WL/% WP/% IP 取值 2.72 19.1 1.85 37.4 21.2 16.2 表 2 试验方案
Table 2. Experimental program
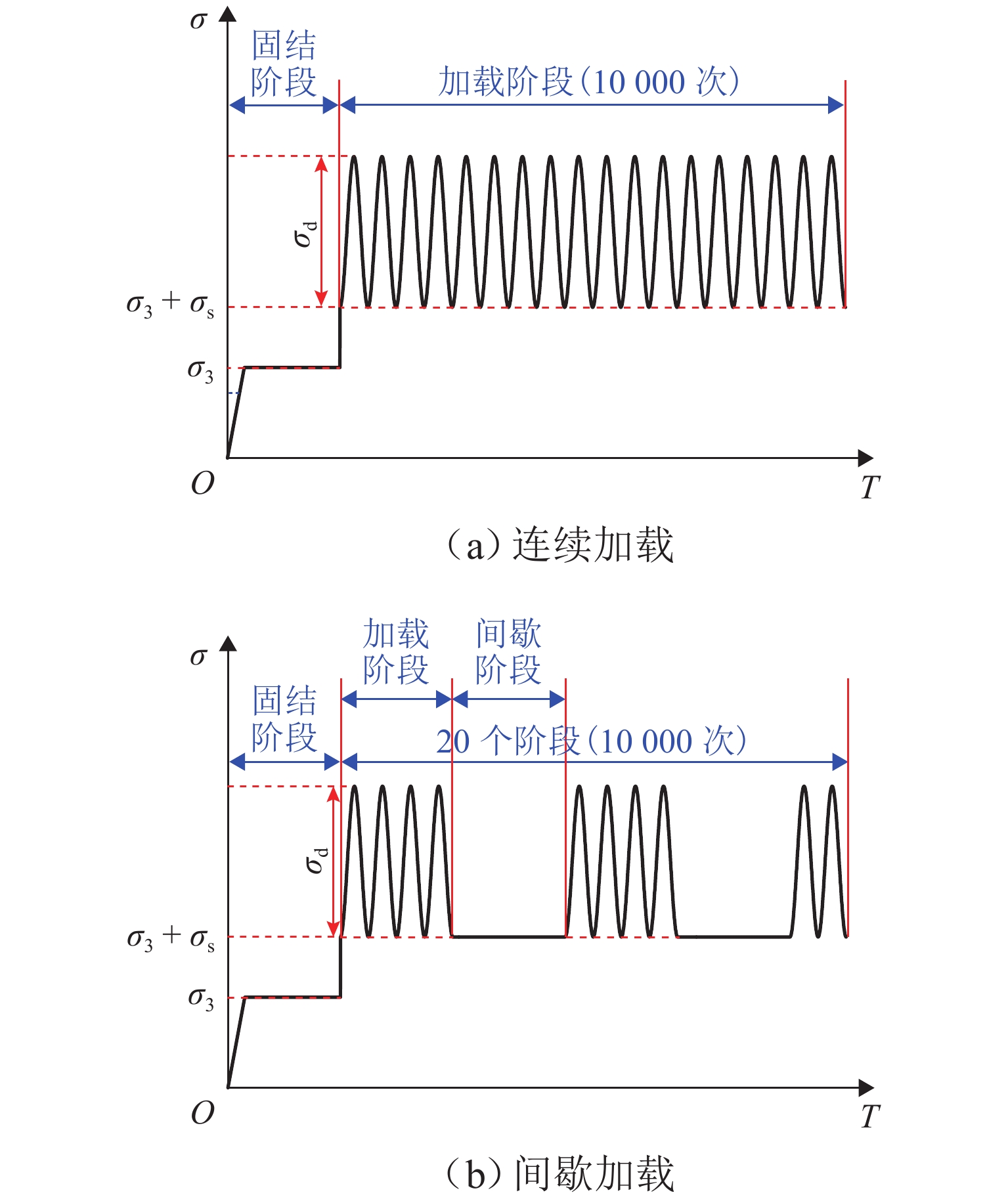
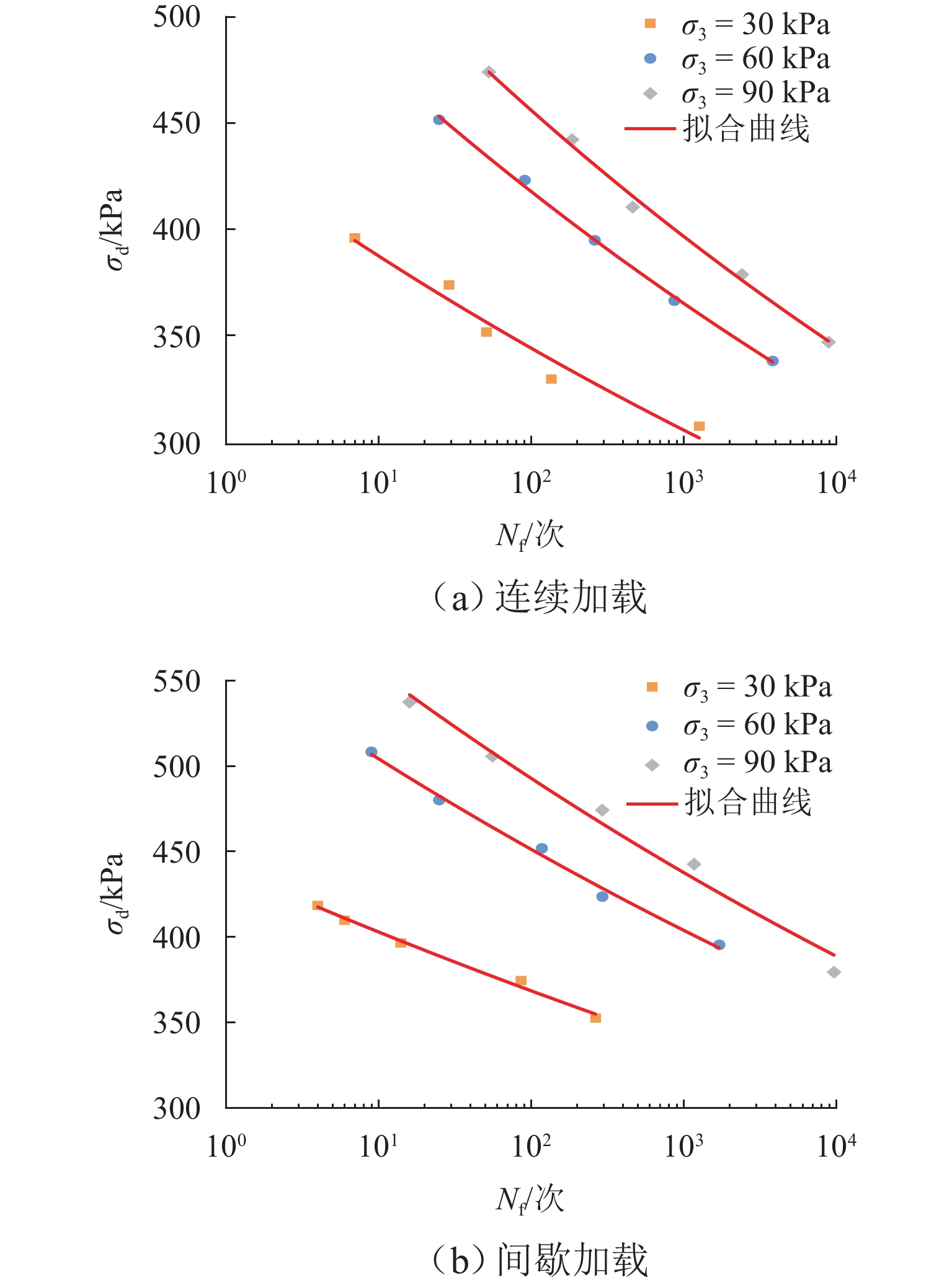
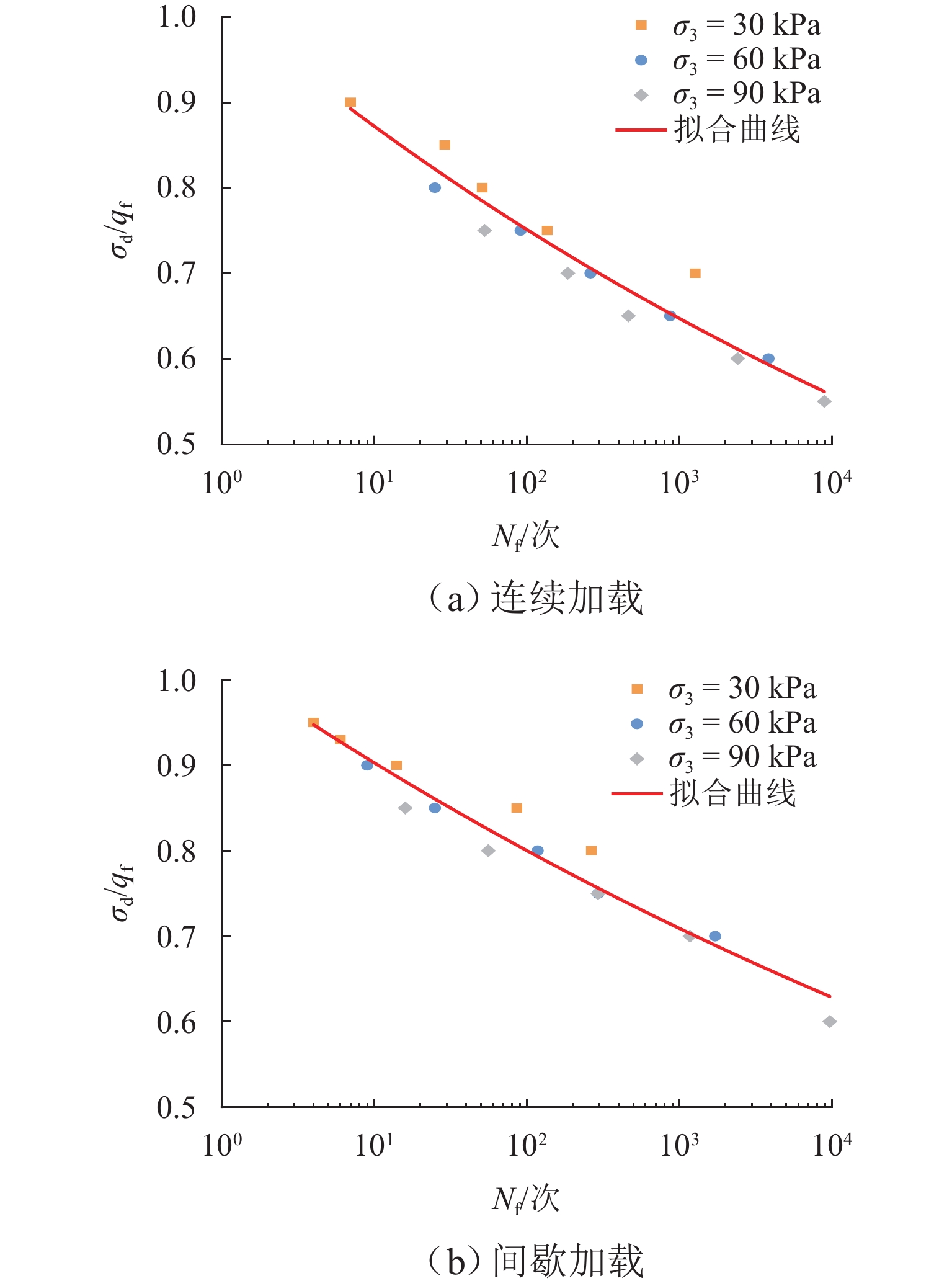
${\sigma _3}$/kPa ${q_{\text{f}}}$/kPa CCSR ${\sigma _{\text{d}}}$/kPa 加载方式 30 440.51 0.70、0.75、0.80、0.85、0.90 308.350、330.380、352.400、374.430、396.459 连续加载(加载到 10000 次或应变达到 10% 时结束)60 564.73 0.60、0.65、0.70、0.75、0.80 338.830、367.070、395.310、423.540、451.780 90 632.16 0.55、0.60、0.65、0.70、0.75、 347.680、379.290、410.900、442.510、474.120 30 440.51 0.80、0.85、0.90、0.93、0.95 352.400、374.430、396.450、409.670、418.480 间歇加载(每一阶段振动 200 次,停振 600 s,加载到 10000 次或应变达到 10% 时结束)60 564.73 0.70、0.75、0.80、0.85、0.90 395.310、423.540、451.780、480.020、508.250 90 632.16 0.60、0.70、0.75、0.80、0.85 379.290、442.510、474.120、505.720、537.330 表 3 动强度值及拟合参数表
Table 3. Dynamic strength values and fitting parameters
加载方式 ${\sigma _3}$/kPa ${\sigma _{{\text{d,}} 100}}$/kPa A d R2 连续加载 30 344.49 436.6573 0.035 0.9795 60 418.08 546.5850 0.048 0.9825 90 456.29 602.2356 0.047 0.9897 间歇加载 30 368.28 440.5294 0.0512 0.9888 60 451.42 563.4870 0.0581 0.9981 90 493.03 624.9116 0.0602 0.9671 表 4 不同破坏次数对应的抗剪强度指标
Table 4. Shear strength indexes corresponding to different numbers of damage
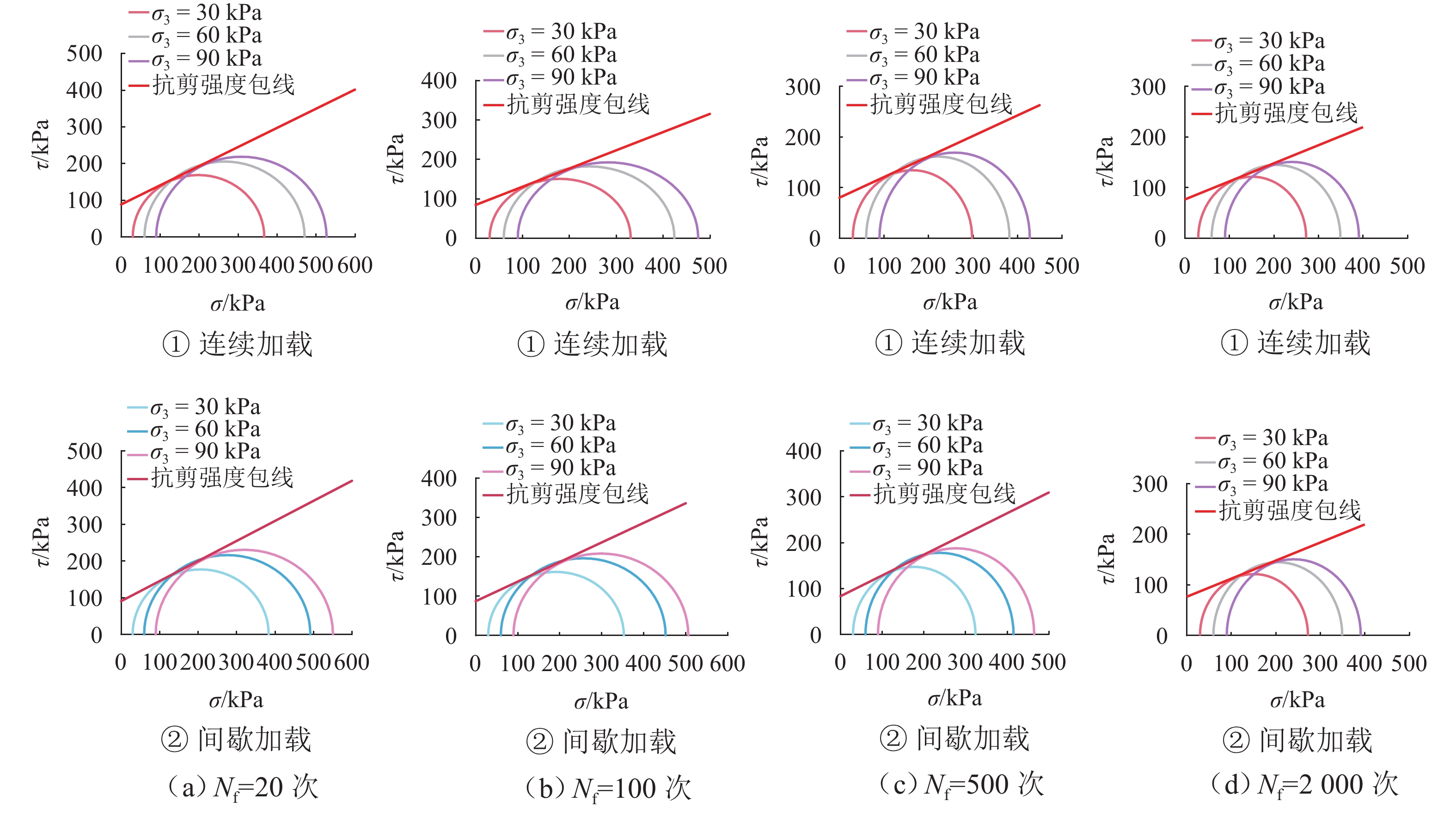
加载方式 Nf/次 $ {c_{\text{d}}} $/kPa $ {\varphi _{\text{d}}} $/(°) 连续加载 20 88.48 27.53 100 84.04 24.83 500 79.82 22.08 2000 76.36 19.66 间歇加载 20 90.41 28.64 100 86.72 26.48 500 83.18 24.29 2000 80.25 22.37 -
[1] WANG J H, LING X Z, LI Q L, et al. Accumulated permanent strain and critical dynamic stress of frozen silty clay under cyclic loading[J]. Cold Regions Science and Technology, 2018, 153: 130-143. doi: 10.1016/j.coldregions.2018.05.007 [2] YANG D, ZHUANG X S, TAO G L, et al. Cumulative plastic strain and shakedown analysis in loess subgrades under intermittent loads[J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 2025, 190: 109224.1-109224.12. [3] XIAO Z H, LIAO H J, WEN Y, et al. Accumulative deformation behaviour of loess under cyclic loading[J]. Materials Research Innovations, 2011, 15(S1): s539-s542. [4] 崔凯, 林维康. 非饱和混合土动剪切模量与阻尼比试验研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2016, 51(5): 1033-1040. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2016.05.028CUI Kai, LIN Weikang. Experimental study on dynamic shear modulus and damping ratio for unsaturated mixed soil[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2016, 51(5): 1033-1040. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2016.05.028 [5] WANG H J, SUN P, LIU E L, et al. Dynamic properties of Tianshui saturated remolded loess: a laboratory study[J]. Engineering Geology, 2020, 272: 105570.1-105570.13. [6] 王铁行, 郝延周, 汪朝, 等. 干湿循环作用下压实黄土动强度性质试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2020, 39(6): 1242-1251.WANG Tiehang, HAO Yanzhou, WANG Zhao, et al. Experimental study on dynamic strength properties of compacted loess under wetting-drying cycles[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2020, 39(6): 1242-1251. [7] LIU X, QIN Z H, YANG J. Undrained cyclic behaviour of loess with initial shear stress: a focus on failure mode[J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 2023, 171: 107971.1-107971.11. [8] 田堪良, 张慧莉, 张伯平, 等. 动扭剪荷载作用下非饱和黄土动力特性试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2004, 23(24): 4151-4155. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2004.24.010TIAN Kanliang, ZHANG Huili, ZHANG Boping, et al. Experimental study on dynamic characteristics of unsaturated loess under dynamic torsional shear load[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2004, 23(24): 4151-4155. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2004.24.010 [9] 杨庆, 王猛, 栾茂田, 等. 非饱和粉土静、动强度对比试验研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2010, 31(1): 71-75, 80. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2010.01.013YANG Qing, WANG Meng, LUAN Maotian, et al. Experimental research of correlation on static and dynamic strength of unsaturated silty clay[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2010, 31(1): 71-75, 80. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2010.01.013 [10] 郑刚, 霍海峰, 雷华阳. 循环荷载后原状与重塑饱和粉质黏土不排水强度性状研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2012, 34(3): 400-408.ZHENG Gang, HUO Haifeng, LEI Huayang. Undrained strength characteristics of saturated undisturbed and remolded silty clay after cyclic loading[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2012, 34(3): 400-408. [11] 庄心善, 赵汉文, 陶高梁, 等. 循环荷载下弱膨胀土累积变形与动强度特性试验研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2020, 41(10): 3192-3200.ZHUANG Xinshan, ZHAO Hanwen, TAO Gaoliang, et al. Accumulated deformation and dynamic strength properties of weak expansive soil under cyclic loading[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2020, 41(10): 3192-3200. [12] LI Y F, NIE R S, LENG W M, et al. Cumulative permanent strain and critical dynamic stress of silty filler for subgrade subjected to intermittent cyclic loading of trains[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 2021, 80(4): 3079-3096. doi: 10.1007/s10064-021-02125-5 [13] WANG Y P, ZHANG S J, ZHAO S P, et al. Plastic strain characteristics on frozen silty clay subjected to intermittent vehicle loads[J]. Transportation Geotechnics, 2023, 43: 101147.1-101147.11. [14] LIU J S, REN Y, ZHU K X, et al. Dynamic characteristics of freezing–thawing aeolian soil under intermittent cyclic loading[J]. International Journal of Geomechanics, 2023, 23(10): 04023171.1-04023171.12. [15] 庄心善, 杨端, 张博文, 等. 间歇荷载下路基黄土累积塑性变形及刚度软化研究[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报, 2025, 22(4): 1576-1588.ZHUANG Xinshan, YANG Duan, ZHANG Bowen, et al. Investigation of subgrade loess’s cumulative plastic deformation and stiffness softening under intermittent loads[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2025, 22(4): 1576-1588. [16] 聂如松, 董俊利, 梅慧浩, 等. 考虑时间间歇效应的粉土动力特性[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2021, 56(5): 1125-1134.NIE Rusong, DONG Junli, MEI Huihao, et al. Dynamic characteristics of silt considering time intermittent effect[J]. Journal of southwest jiaotong university, 2021, 56(5): 1125-1134. [17] 国家市场监督管理总局. 土工试验方法标准: GB/T 50123—2019[S]. 北京: 中国计划出版社出版, 2019. [18] 王寒, 黄雪峰, 邱明明, 等. 压实黄土高压力下湿陷变形特性试验研究[J]. 自然灾害学报, 2023, 32(1): 122-130.WANG Han, HUANG Xuefeng, QIU Mingming, et al. Experimental study on the deformation characteristics of compacted loess under high pressure[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 2023, 32(1): 122-130. [19] YANG J J, ZHU S Y, XU L, et al. A 3D train-track-tunnel-soil coupled dynamics model based on semi-analytical cylindrical layer element[J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2025, 179: 106966.1-106966.120. [20] LI Y F, NIE R S, YUE Z R, et al. Dynamic behaviors of fine-grained subgrade soil under single-stage and multi-stage intermittent cyclic loading: Permanent deformation and its prediction model[J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 2021, 142: 106548.1-106548.12. [21] NIE R S, LI Y F, LENG W M, et al. Plastic deformation and critical dynamic stress of fine-grained soils under intermittent loading of trains[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2021, 40(4): 828-841. [22] 吴遥杰, 周浩东, 宫全美. 间歇循环荷载下粉土路基动力特性及累积变形研究[J]. 华东交通大学学报, 2022, 39(4): 1-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0523.2022.4.hdjtdxxb202204001WU Yaojie, ZHOU Haodong, GONG Quanmei. Study on dynamic characteristics and accumulative deformation of silty subgrade soil under intermittent cyclic loading[J]. Journal of East China Jiaotong University, 2022, 39(4): 1-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0523.2022.4.hdjtdxxb202204001 [23] YANG D, ZHUANG X, LI X, et al. Effects of lignin on the dynamic characteristics and mechanisms of silty soil[J]. International Journal of Geomechanics, 2025, 25(6): 04025099. doi: 10.1061/IJGNAI.GMENG-10988 [24] ANDERSEN K H, LAURITZSEN R. Bearing capacity for foundations with cyclic loads[J]. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 1988, 114(5): 540-555. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9410(1988)114:5(540) [25] 中国机械工业联合会. 地基动力特性测试规范: GB/T 50269—2015[S]. 北京: 中国计划出版社, 2015. [26] 王兰民. 黄土动力学[M]. 北京: 地震出版社, 2003. [27] 陈存礼, 杨鹏, 何军芳. 饱和击实黄土的动力特性研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2007, 28(8): 1551-1556. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2007.08.005CHEN Cunli, YANG Peng, HE Junfang. Research on dynamic characteristics of saturated compacted loess[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2007, 28(8): 1551-1556. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2007.08.005 [28] AI X H, LUO F, MA W, et al. The study on the dynamic deformation characteristics of loess reinforced by nano-silica based on shakedown theory[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2025, 458: 139546.1-139546.17. [29] SOBCZYK K, CHMIELEWSKI R, KRUSZKA L, et al. Strength Characterization of Soils’ Properties at High Strain Rates Using the Hopkinson Technique—A Review of Experimental Testing[J]. Materials, 2021, 15(1): 274. doi: 10.3390/ma15010274 [30] WANG B, DONG J, LUO C X, et al. Study of soil strength variation patterns under temperature changes using piezoelectric testing technology[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 2024, 83(12): 513.1-513.18. [31] DENG L S, ZHANG C, FAN W, et al. Three-dimensional microstructure evolution of loess liquefaction based on the μm-CT quantitative observations[J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 2024, 178: 108442.1-108442.12. -




 下载:
下载: