Numerical Simulation of Geyser Process Caused by High-Pressure Entrapped Air Release in Baffle-Drop Shafts
-
摘要:
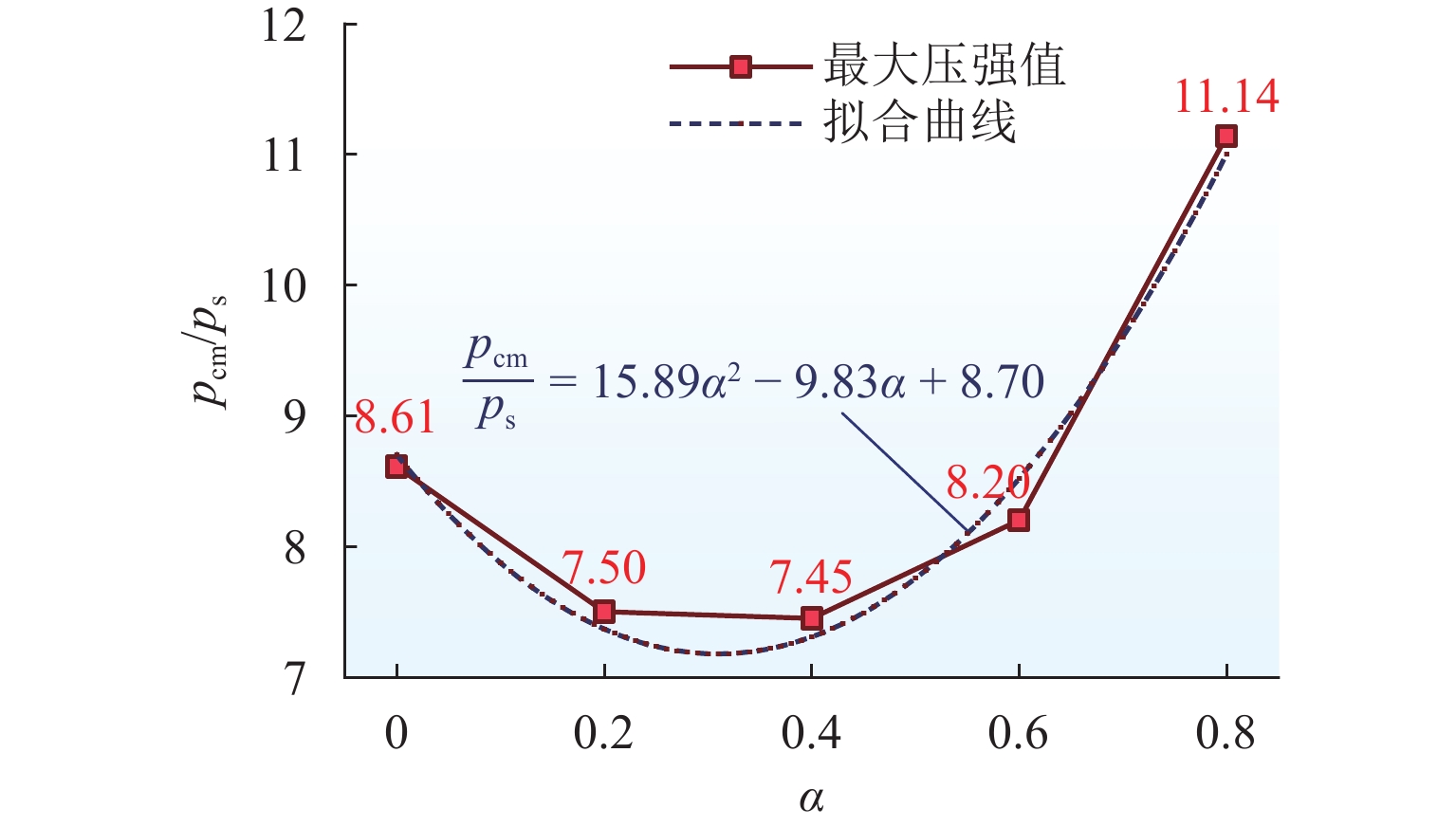
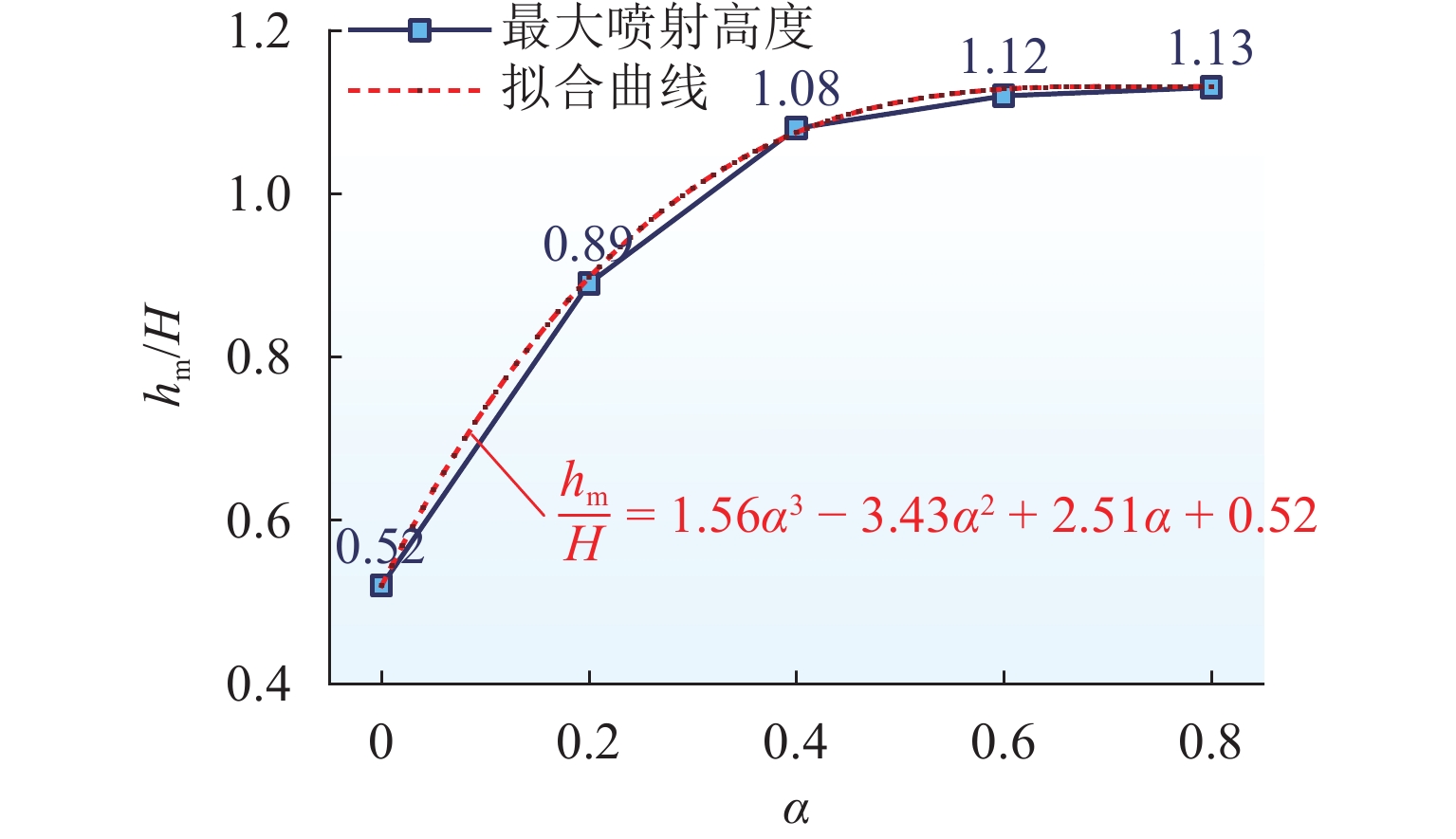
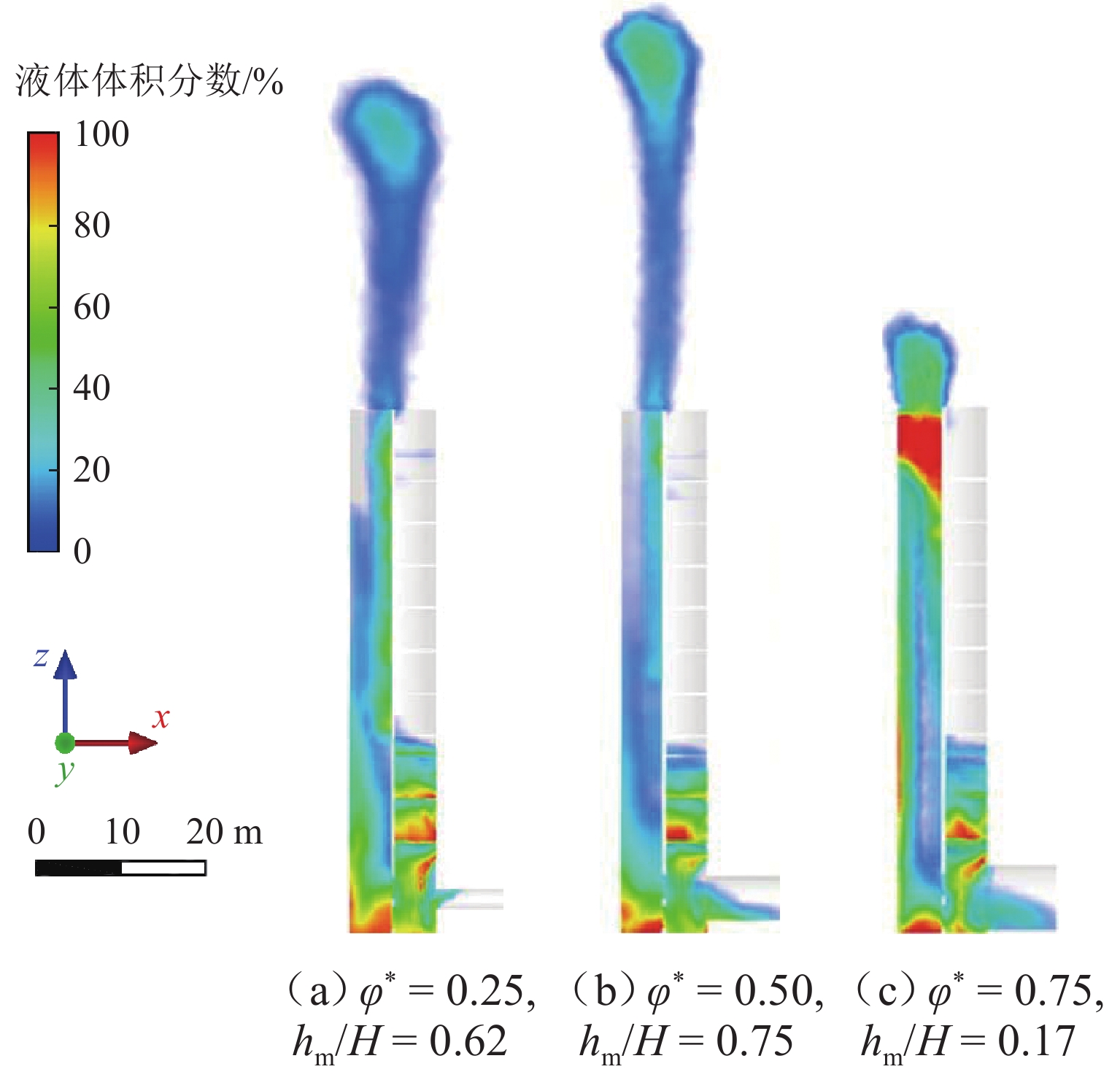
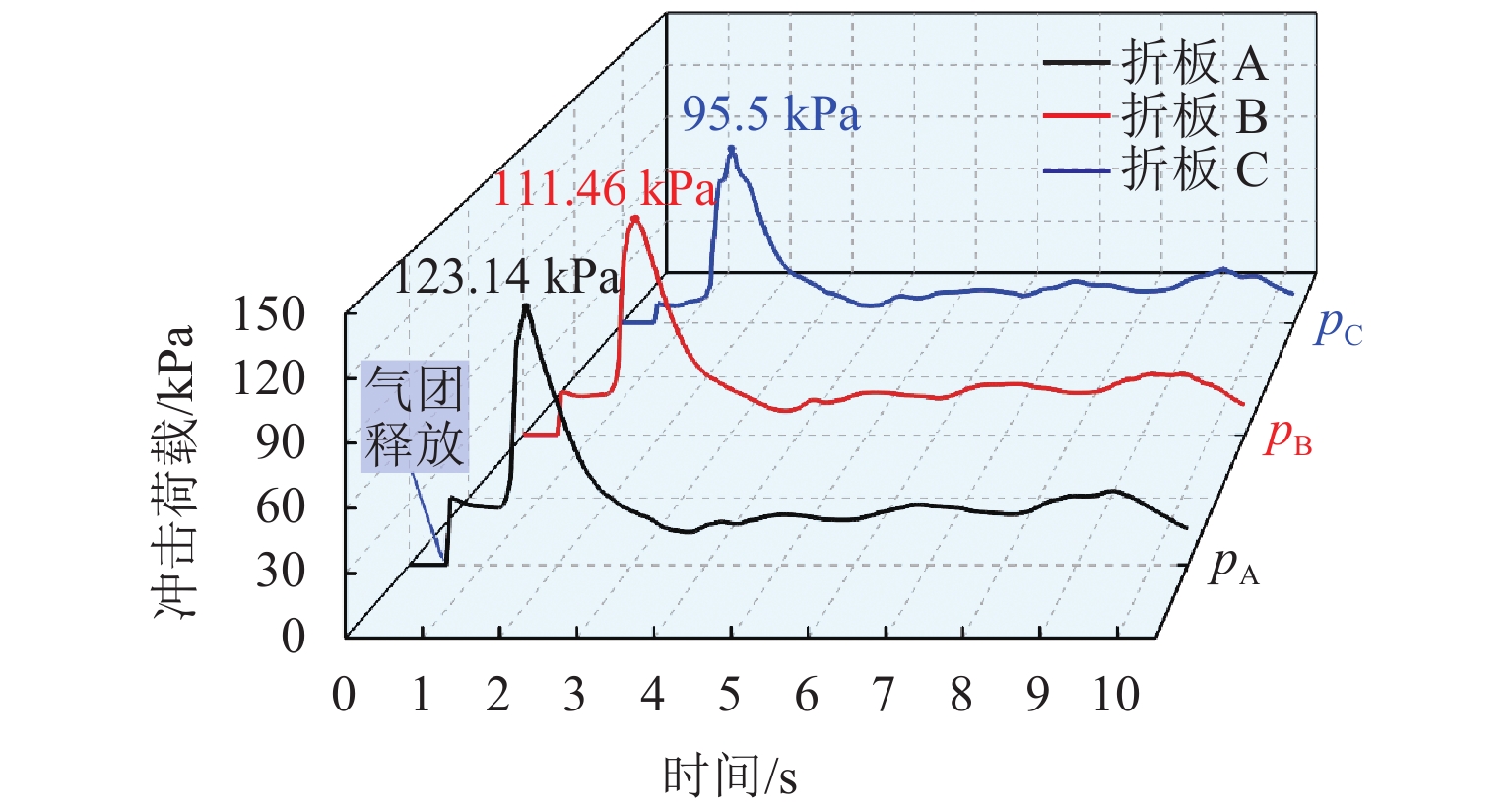
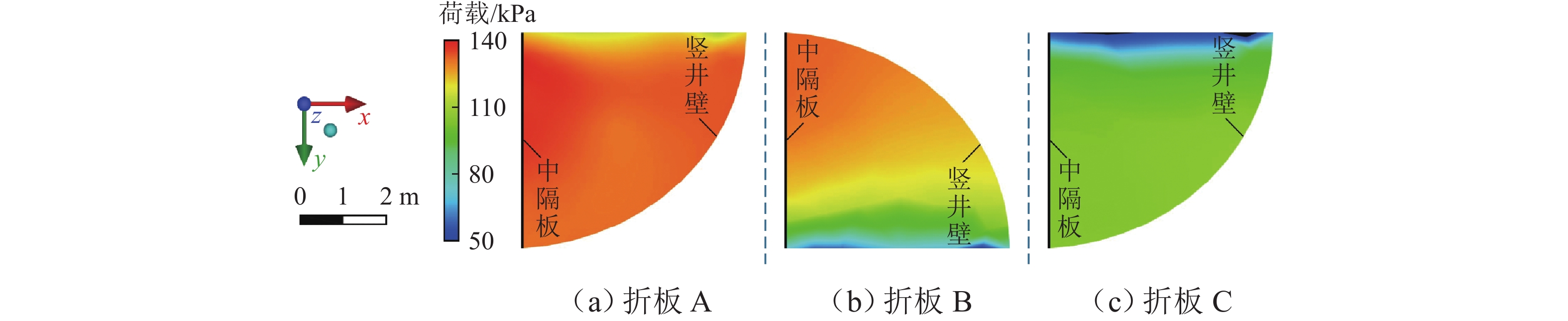
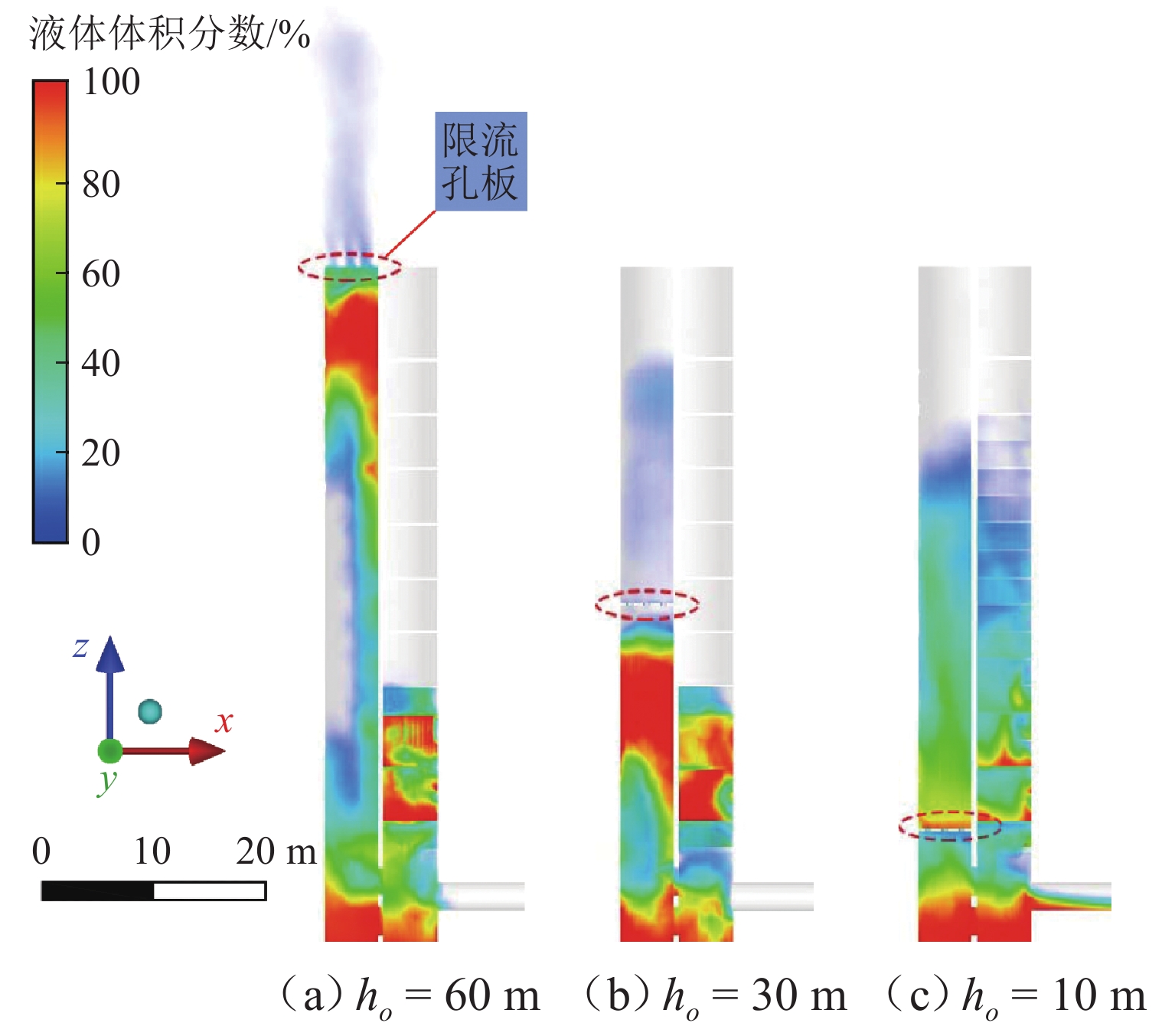
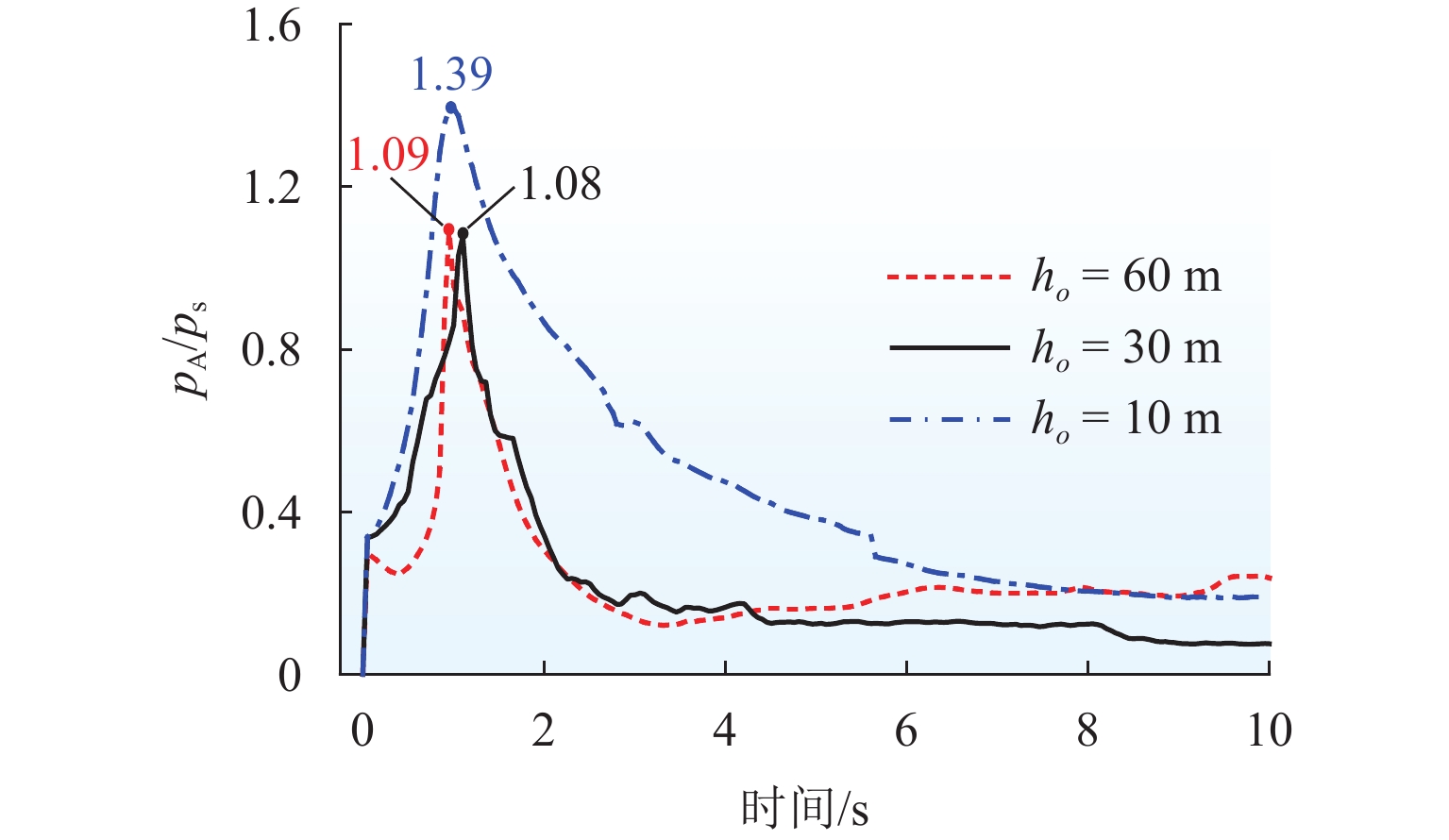
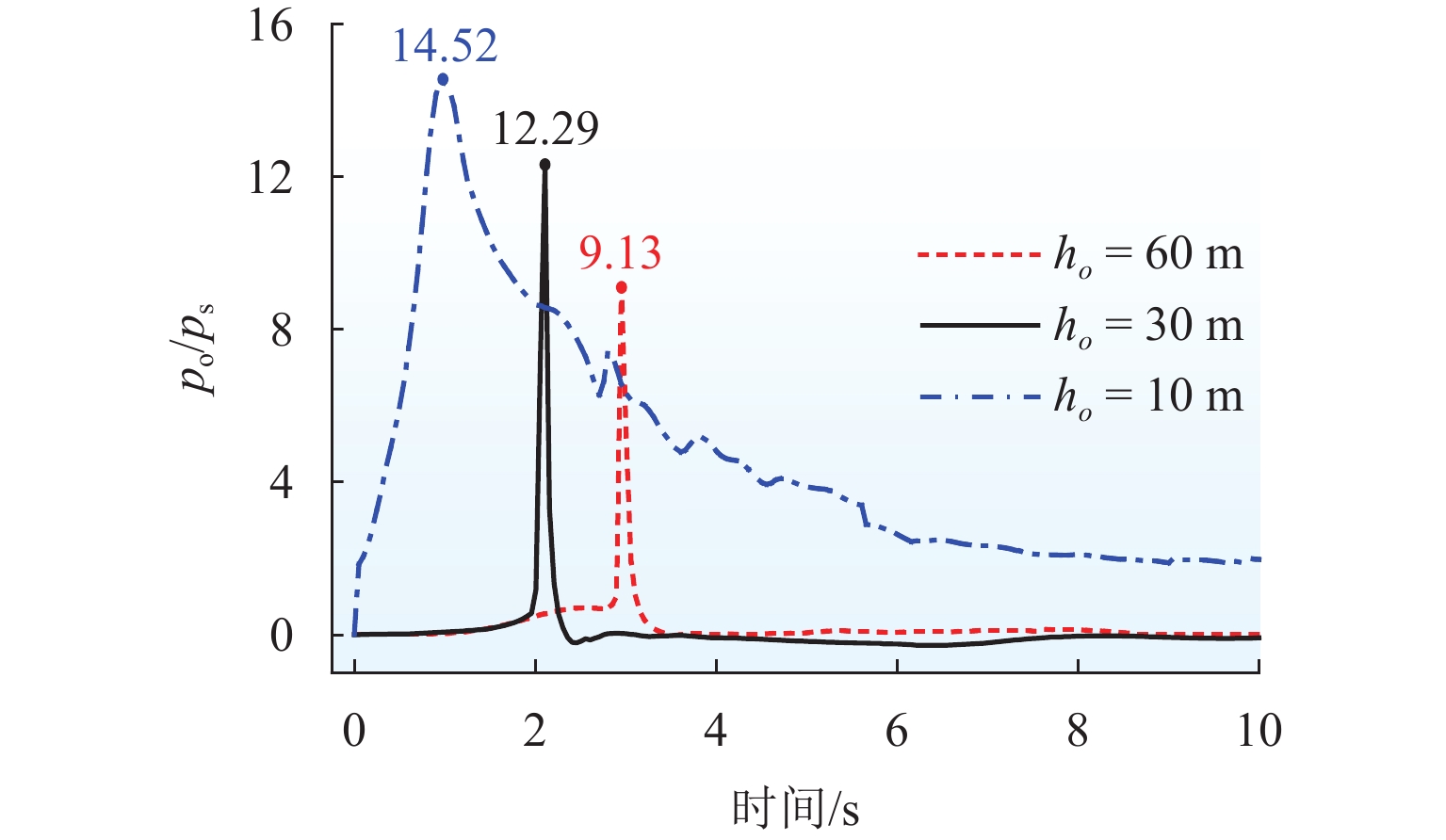
为解决折板型竖井在气爆过程中产生高速气水混合物而导致的结构及地面安全风险,采用数值模拟方法系统研究竖井内水体空泡份额和联络管直径对竖井压强和气爆强度的影响程度,分析竖井底部折板冲击荷载变化规律,提出在竖井中部设置限流孔板以控制气爆喷射强度. 研究结果表明:联络管压强随着空泡份额的提升先减小后增大,并在0.2~0.4内出现最小值;3种不同管径比中,联络管与竖井的直径比为1/2时,气爆喷射强度最为强烈;折板冲击荷载自下而上不断递减,同一折板上靠近中隔板和竖井壁一侧的冲击荷载均大于折板边缘上荷载;在竖井中部设置限流孔板能有效控制气爆强度,同时,限流孔板受到的冲击荷载为竖井底部折板荷载的10倍;研究成果为城市深隧排水系统安全运行提供参考.
Abstract:To reduce the structural and ground safety risks caused by the high-speed air–water mixture during geyser events in baffle-drop shafts, a numerical simulation was conducted to investigate the influence of void fraction and connecting pipe diameter on shaft pressure and geyser intensity. The variation patterns of impact loads on the baffles at the shaft bottom were analyzed, proposing the installation of a throttling orifice at the shaft midpoint to control the geyser intensity. The results show that the pressure in the connecting pipe first reduces and then increases with rising void fraction, reaching a minimum within the range of 0.2–0.4. Among the three diameter ratios considered, the geyser intensity reaches its maximum when the diameter of the connecting pipe is half that of the shaft. The impact load on the baffles decreases continuously from bottom to top, and for any given baffle, the impact load near the partition wall and shaft wall is greater than that at the baffle’s edge. Installing a throttling orifice at the shaft midpoint can effectively control the geyser intensity, and the impact load on the throttling orifice is 10 times greater than that on the bottom baffle. These findings provide a reference for the safe operation of urban deep tunnel drainage systems.
-
Key words:
- baffle-drop shaft /
- high-pressure entrapped air /
- geyser /
- pressure /
- impact load /
- numerical simulation
-
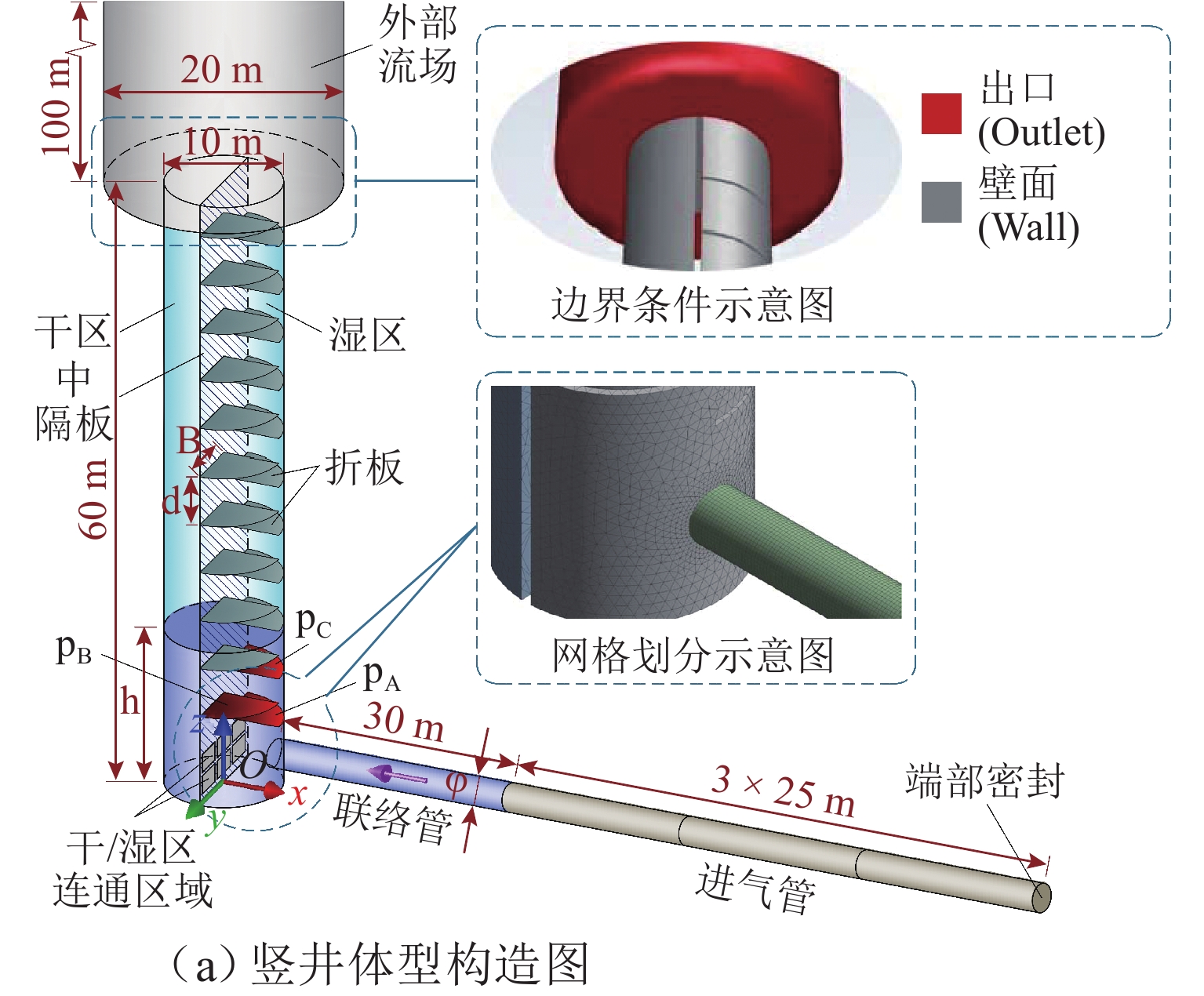
表 1 数值模型参数取值
Table 1. Parameters value of numerical model
h* p* V* S* 联络管
接入方式α φ* 0.167 0.5,1.0,1.5,2.0,2.5,3.0,3.5,4.0 0.026,0.052,0.078 0.478 竖井
湿区0,0.20,
0.40,0.60
0.800.25,0.50,0.75 0.250 0.333 0.417 -
[1] 刘家宏, 夏霖, 梅超, 等. 深隧排水系统在城市内涝防治中的作用分析[J]. 应用基础与工程科学学报, 2019, 27(2): 252-263. doi: 10.16058/j.issn.1005-0930.2019.02.002LIU Jiahong, XIA Lin, MEI Chao, et al. Effects of deep tunnel drainage system in urban waterlogging prevention[J]. Journal of Basic Science and Engineering, 2019, 27(2): 252-263. doi: 10.16058/j.issn.1005-0930.2019.02.002 [2] ZHOU F, HICKS F E, STEFFLER P M. Transient flow in a rapidly filling horizontal pipe containing trapped air[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2002, 128(6): 625-634. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(2002)128:6(625) [3] POZOS-ESTRADA O, POTHOF I, FUENTES-MARILES O A, et al. Failure of a drainage tunnel caused by an entrapped air pocket[J]. Urban Water Journal, 2015, 12(6): 446-454. doi: 10.1080/1573062X.2015.1041990 [4] WRIGHT S J, LEWIS J W, VASCONCELOS J G. Physical processes resulting in geysers in rapidly filling storm-water tunnels[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage Engineering, 2011, 137(3): 199-202. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)IR.1943-4774.0000176 [5] LEWIS J W. A physical investigation of air/water interactions leading to geyser events in rapid filling pipelines (PhD thesis)[D]. Michigan: University of Michigan, 2011. [6] CHOSIE C. Investigation on the kinematics of entrapped air pockets in stormwater storage tunnels (master thesis)[D]. Alabama: Auburn University, 2013. [7] MARTIN C S. Entrapped air in pipelines[C]// Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Pressure Surges. Bedford: British Hydromechanics Research Association, 1976: 15-27. [8] ZHOU F, HICKS F E, STEFFLER P M. Transient flow in a rapidly filling horizontal pipe containing trapped air[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2002, 128(6): 625-634. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(2002)128:6(625) [9] WRIGHT S J, VASCONCELOS J, et al. Surges associated with filling of stormwater storage tunnels[J]. Journal of Water Management Modeling, 2003, 115(8): 75-84. [10] VASCONCELOS J G. Dynamic approach to the description of flow regime transition in stormwater systems (PhD thesis)[D]. Michigan: University of Michigan, 2005. [11] VASCONCELOS J G, WRIGHT S J. Mechanisms for air pocket entrapment in stormwater storage tunnels[C]//World Environmental and Water Resource Congress 2006. Omaha: American Society of Civil Engineers, 2006: 1-10. [12] 安瑞冬, 游景皓, 廖磊, 等. 深层隧道排水系统中井隧水力学特性研究[J]. 水利学报, 2021, 52(12): 1498-1507. doi: 10.13243/j.cnki.slxb.20210090AN Ruidong, YOU Jinghao, LIAO Lei, et al. Study on the hydraulic characteristics of dropshaft and tunnel in the deep tunnel drainage system[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2021, 52(12): 1498-1507. doi: 10.13243/j.cnki.slxb.20210090 [13] 蒯重列, 王晓升, 孙振海, 等. 竖井形式对调蓄隧道系统井喷的抑制效果分析[J]. 水利水电科技进展, 2023, 43(3): 77-82.KUAI Zhonglie, WANG Xiaosheng, SUN Zhenhai, et al. Suppression effect on the geyser in storage tunnel system with different shaft forms[J]. Advances in Science and Technology of Water Resources, 2023, 43(3): 77-82. [14] VASCONCELOS J G, WRIGHT, S J. Laboratory investigation of surges formed during rapid filling of stormwater storage tunnels[C]//Proceedings of the 30th IAHR Congress. Thessaloniki: International Association for Hydro-Environment Engineering and Research, 2003: 1-8. [15] VASCONCELOS J G, WRIGHT S J. Surge associated with air expulsion in near-horizontal pipelines[C]// ASME/JSME 2003 4th Joint Fluids Summer Engineering Conference. Honolulu: [s.n.], 2009: 2897-2905. [16] VASCONCELOS J G, WRIGHT S J. Experimental investigation of surges in a stormwater storage tunnel[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2005, 131(10): 853-861. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(2005)131:10(853) [17] VASCONCELOS J G, LEITE G M. Pressure surges following sudden air pocket entrapment in storm-water tunnels[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2012, 138(12): 1081-1089. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)HY.1943-7900.0000616 [18] WRIGHT S J, DETERMAN K V, VARGAS S M. Pressure transients due to compression of trapped air in rapidly filling combined sewer overflow storage tunnels[C]//World Environmental and Water Resources Congress 2011. Palm Springs: American Society of Civil Engineers, 2011: 3550-3559. [19] AIMABLE R, ZECH Y. Experimental results on transient and intermittent flows in a sewer pipe model [C]// International Association of Hydraulic Engineering and Research Congress Theme B: Urban and Rural Water Systems for Sustainable Development. Louvain-la-Neuve: International Association of Hydraulic Engineering and Research , 2003: 377-384. [20] LI J, MCCORQUODALE A. Modeling mixed flow in storm sewers[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 1999, 125(11): 1170-1180. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(1999)125:11(1170) [21] LINGIREDDY S, WOOD D J, ZLOCZOWER N. Pressure surges in pipeline systems resulting from air releases[J]. Journal AWWA, 2004, 96(7): 88-94. doi: 10.1002/j.1551-8833.2004.tb10652.x [22] PERRON A, KISS L I, PONCSÁK S. An experimental investigation of the motion of single bubbles under a slightly inclined surface[J]. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 2006, 32(5): 606-622. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmultiphaseflow.2006.02.001 [23] 王晓升. 地下调蓄隧道系统滞留气团释放过程的井喷特性研究[D]. 上海: 上海大学, 2020. [24] 杨乾, 杨庆华, 郑立宁, 等. 深隧排水折板型竖井泄流消能的试验研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2020, 55(6): 1247-1256.YANG Qian, YANG Qinghua, ZHENG Lining, et al. Experimental study on discharge and energy dissipation of baffle-drop shaft in deep tunnel drainage system[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2020, 55(6): 1247-1256. [25] 杨乾, 杨庆华. 折板型竖井湍流耗散及消能机理分析[J]. 东南大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 50(3): 471-481. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0505.2020.03.009YANG Qian, YANG Qinghua. Analysis on turbulent dissipation and energy dissipation mechanism of baffle-drop shaft[J]. Journal of Southeast University (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 50(3): 471-481. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0505.2020.03.009 [26] 焦凤, 邓先和. 矩形自支撑缩放管换热器强化传热的结构优化[J]. 化工学报, 2013, 64(7): 2376-2385. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0438-1157.2013.07.010JIAO Feng, DENG Xianhe. Structural optimization of converging-diverging tube based on heat transfer enhancement for self-support rectangle heat exchanger[J]. CIESC Journal, 2013, 64(7): 2376-2385. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0438-1157.2013.07.010 [27] 杨乾, 杨庆华, 陈峰, 等. 气爆过程中折板型竖井水力特性试验研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2023, 58(5): 1026-1036. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20220163YANG Qian, YANG Qinghua, CHEN Feng, et al. Experimental study on hydraulic characteristics in baffle-drop shaft during gas explosion[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2023, 58(5): 1026-1036. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20220163 [28] LEON A S, ELAYEB I S, TANG Y. An experimental study on violent geysers in vertical pipes[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Research, 2019, 57(3): 283-294. doi: 10.1080/00221686.2018.1494052 -




 下载:
下载: