Comparison of Causes of Rail Corrugation in Sections with and without Rail Gaps in Small Radius Curves of Mountainous Metro
-
摘要:
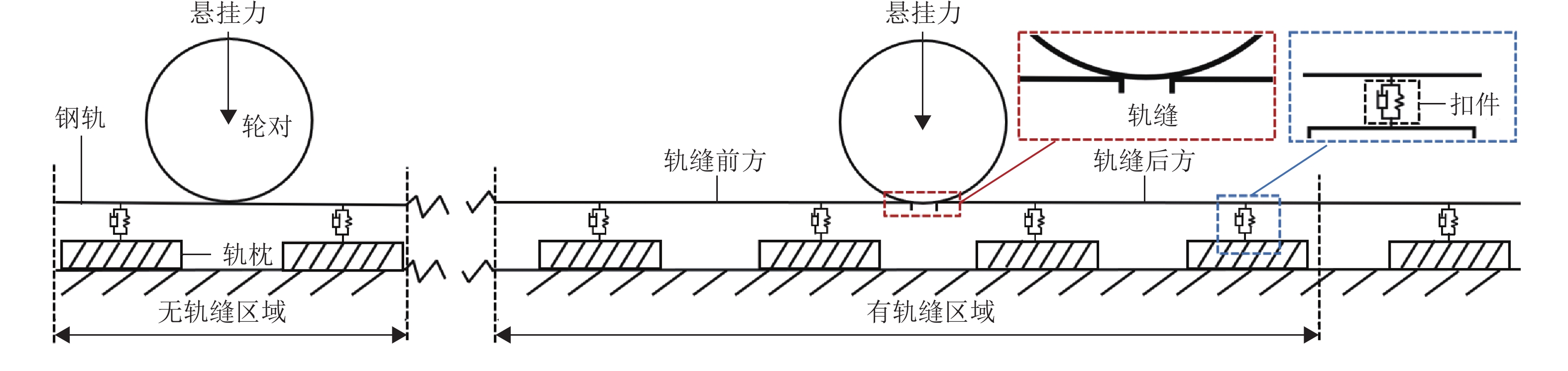
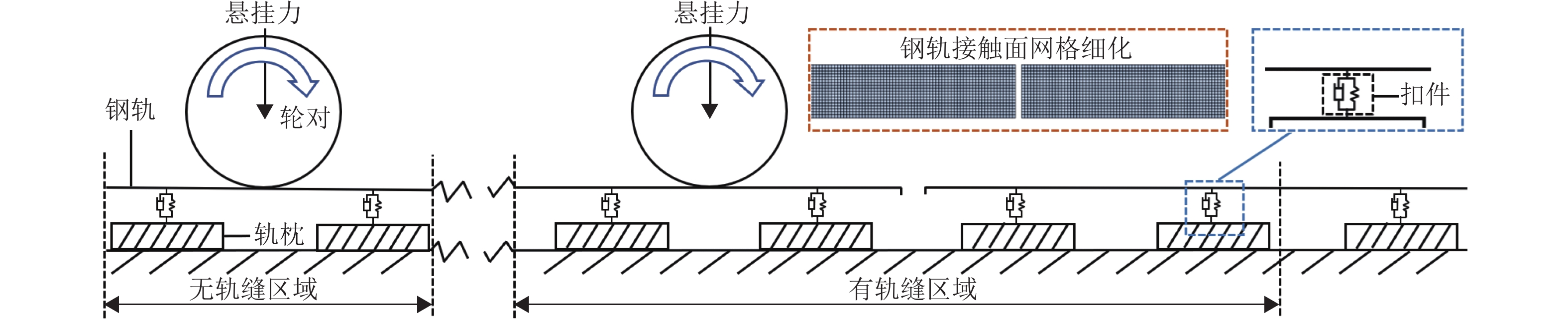
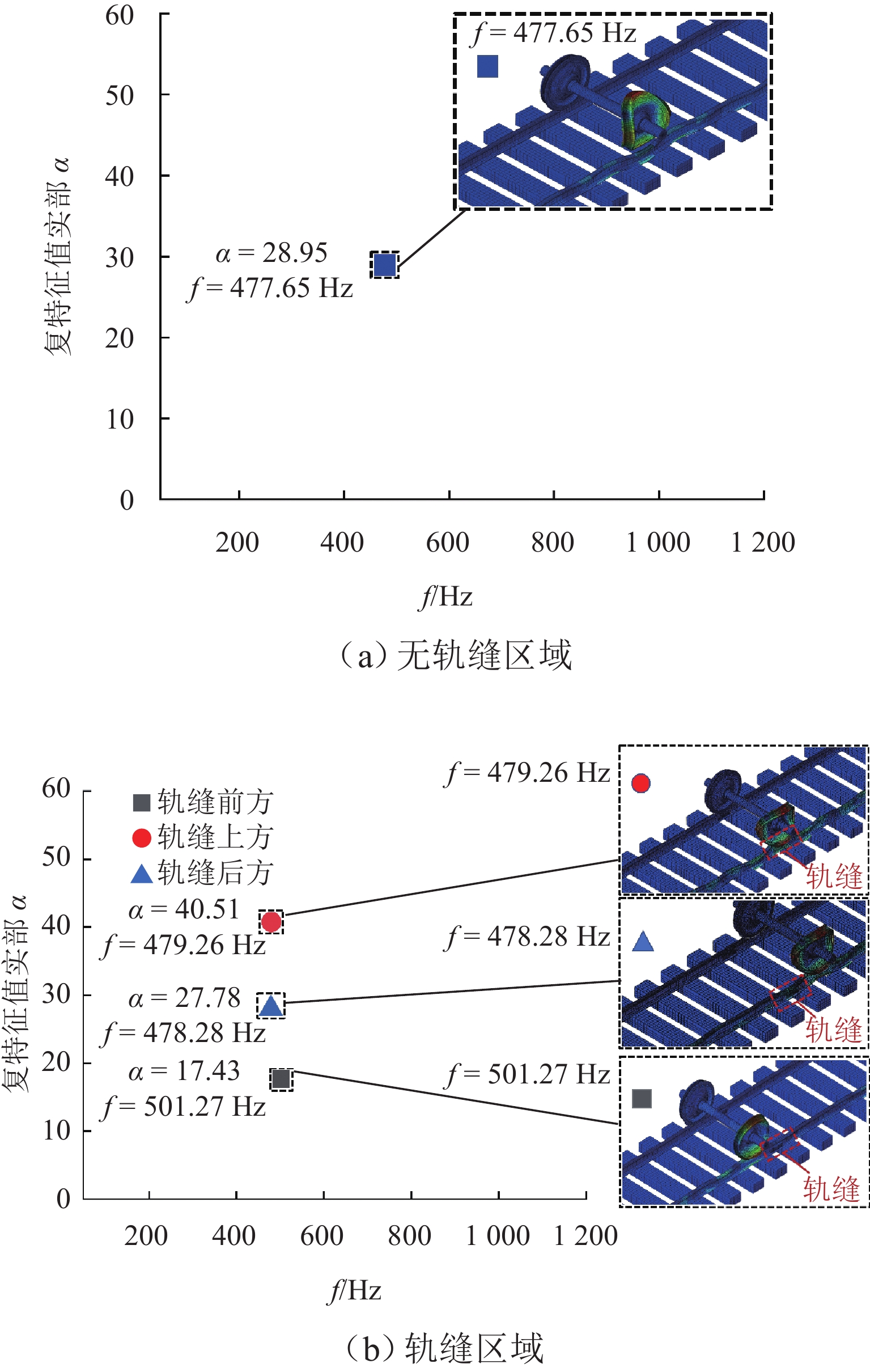
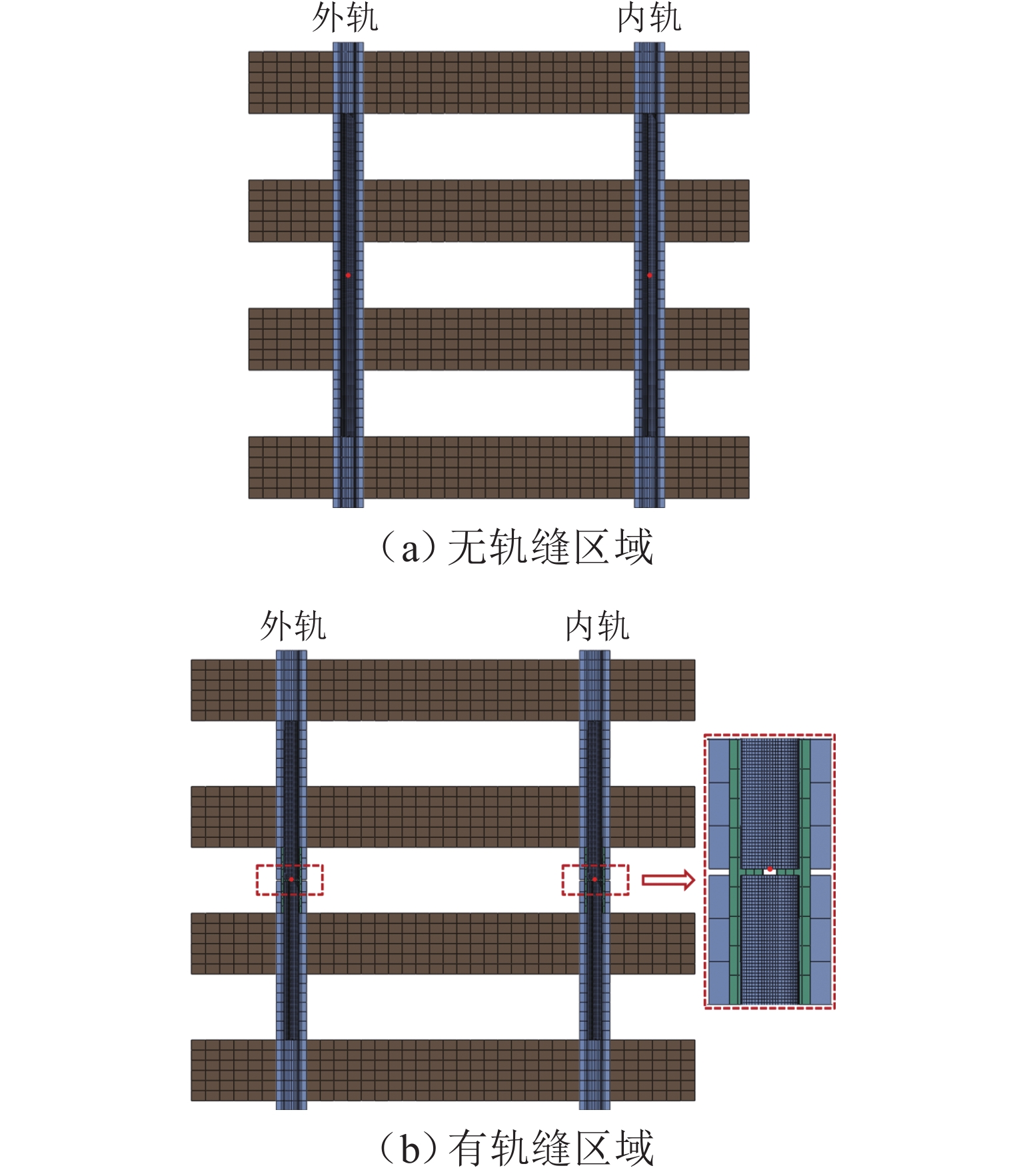
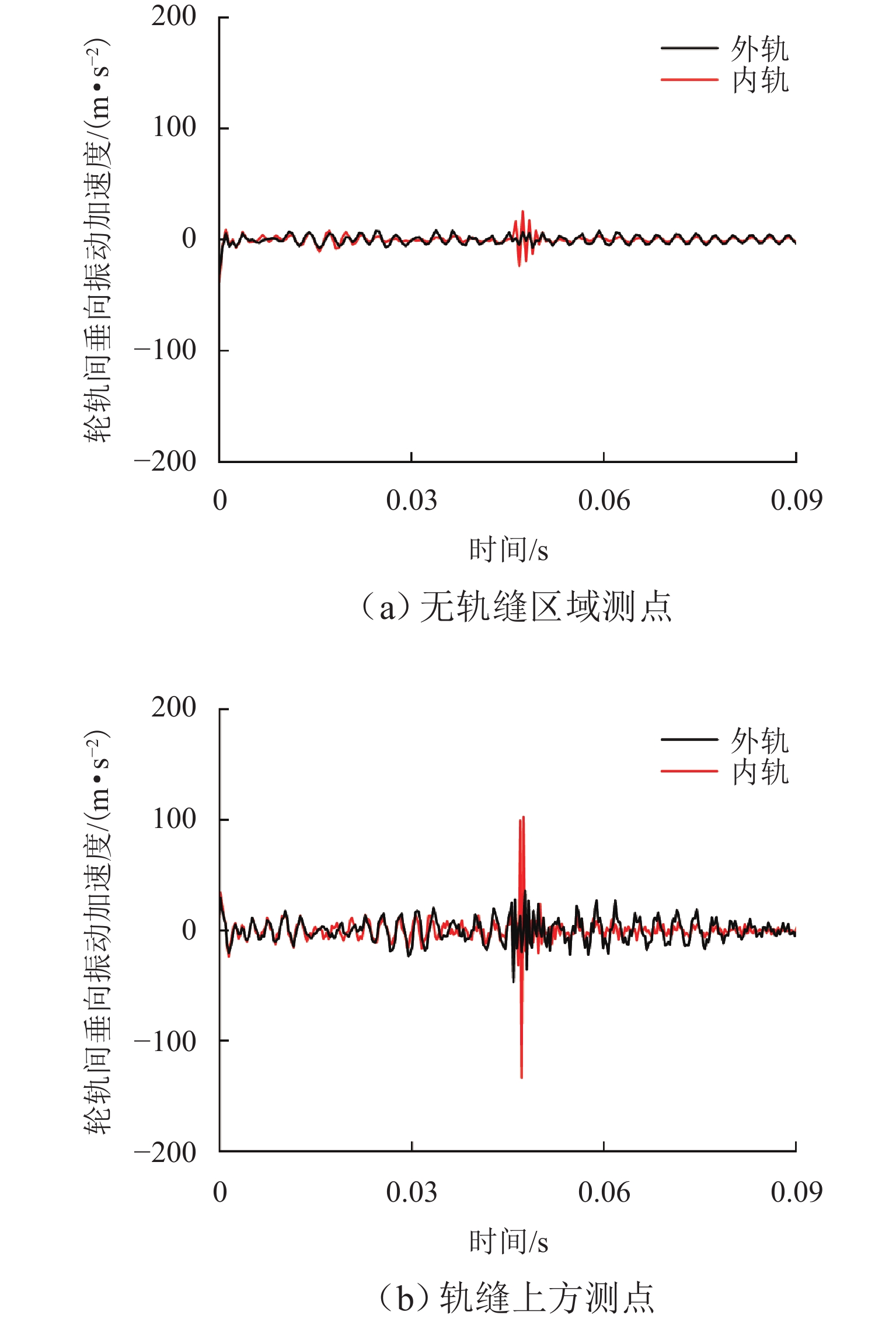
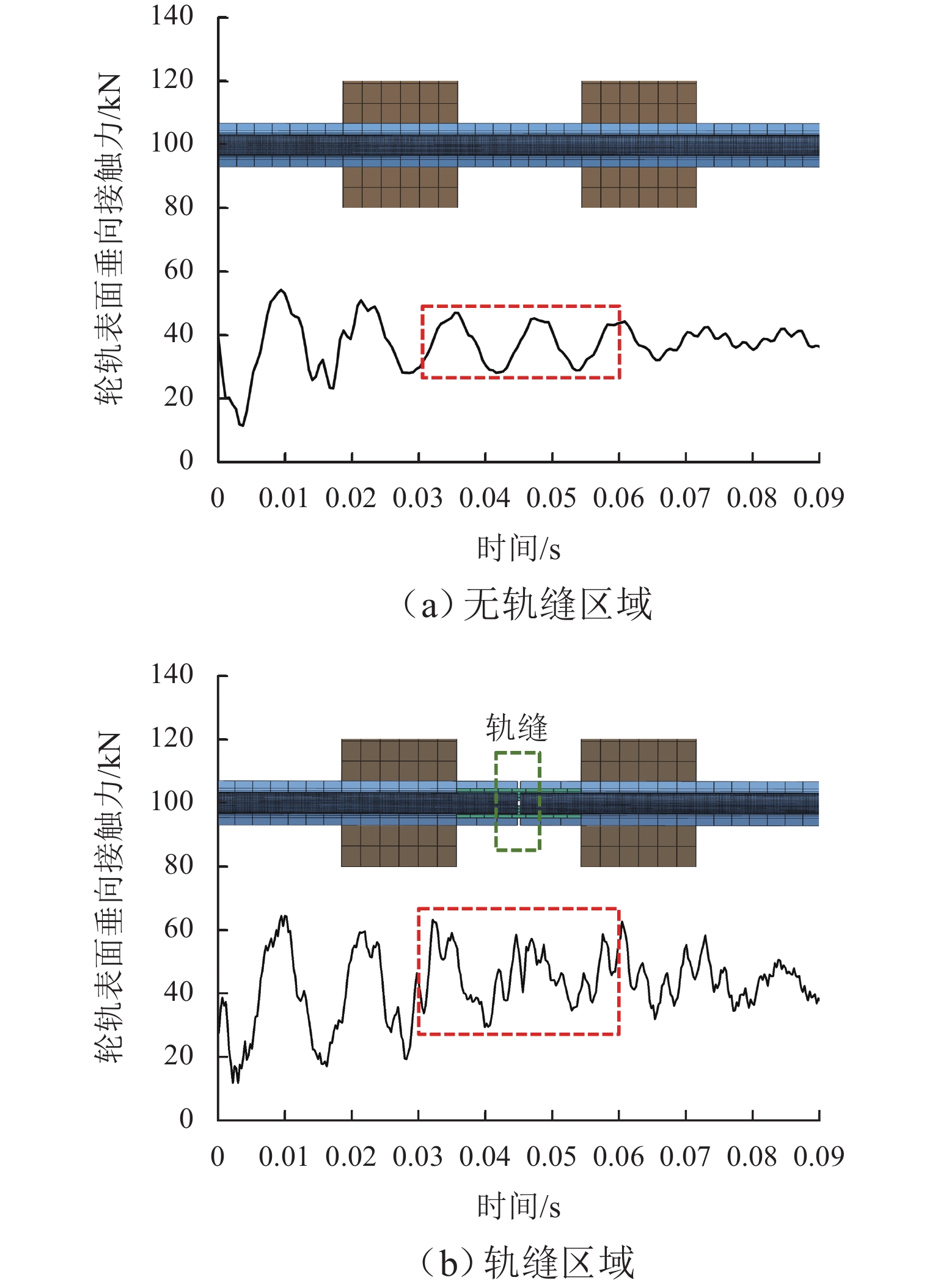
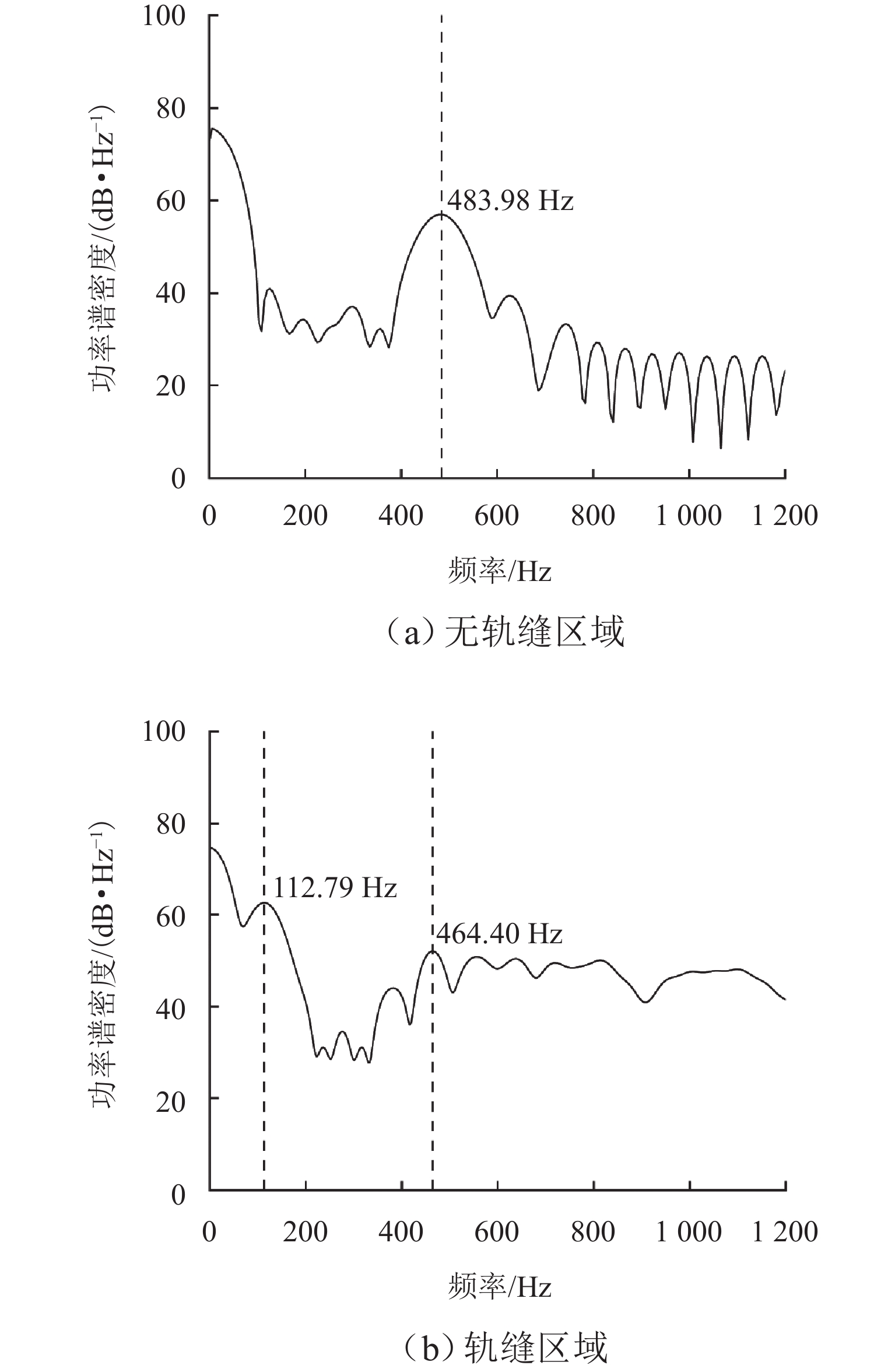
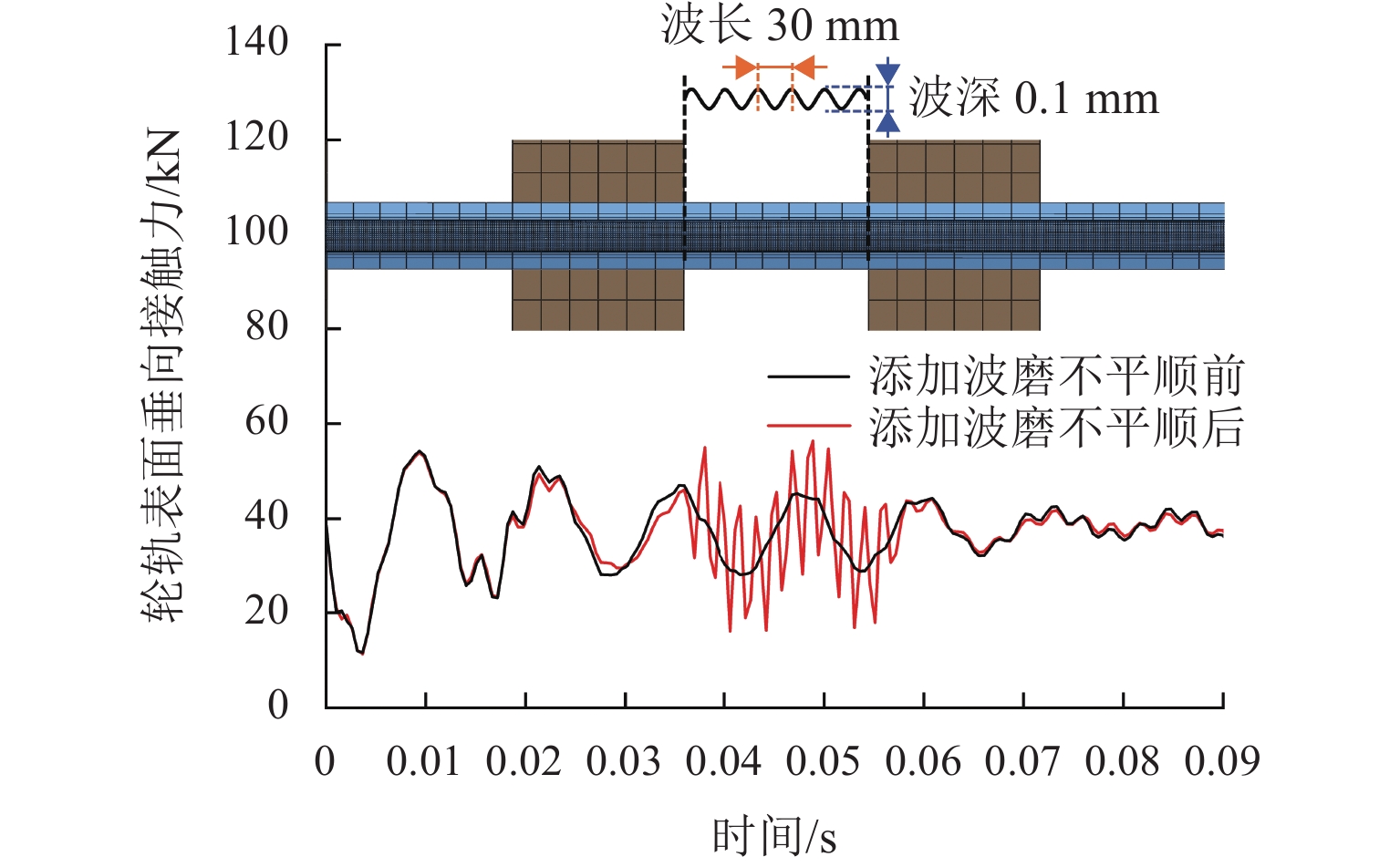
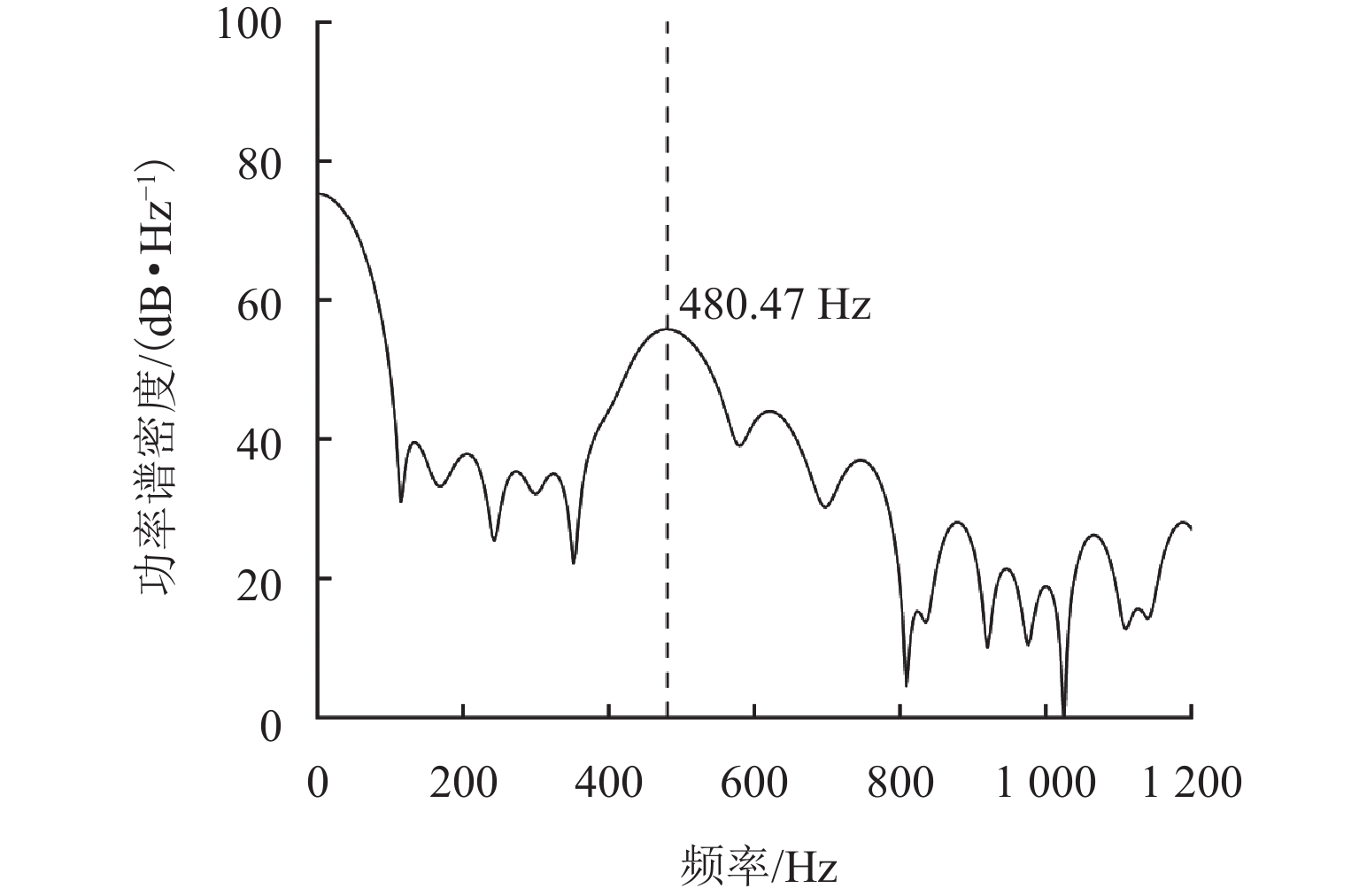
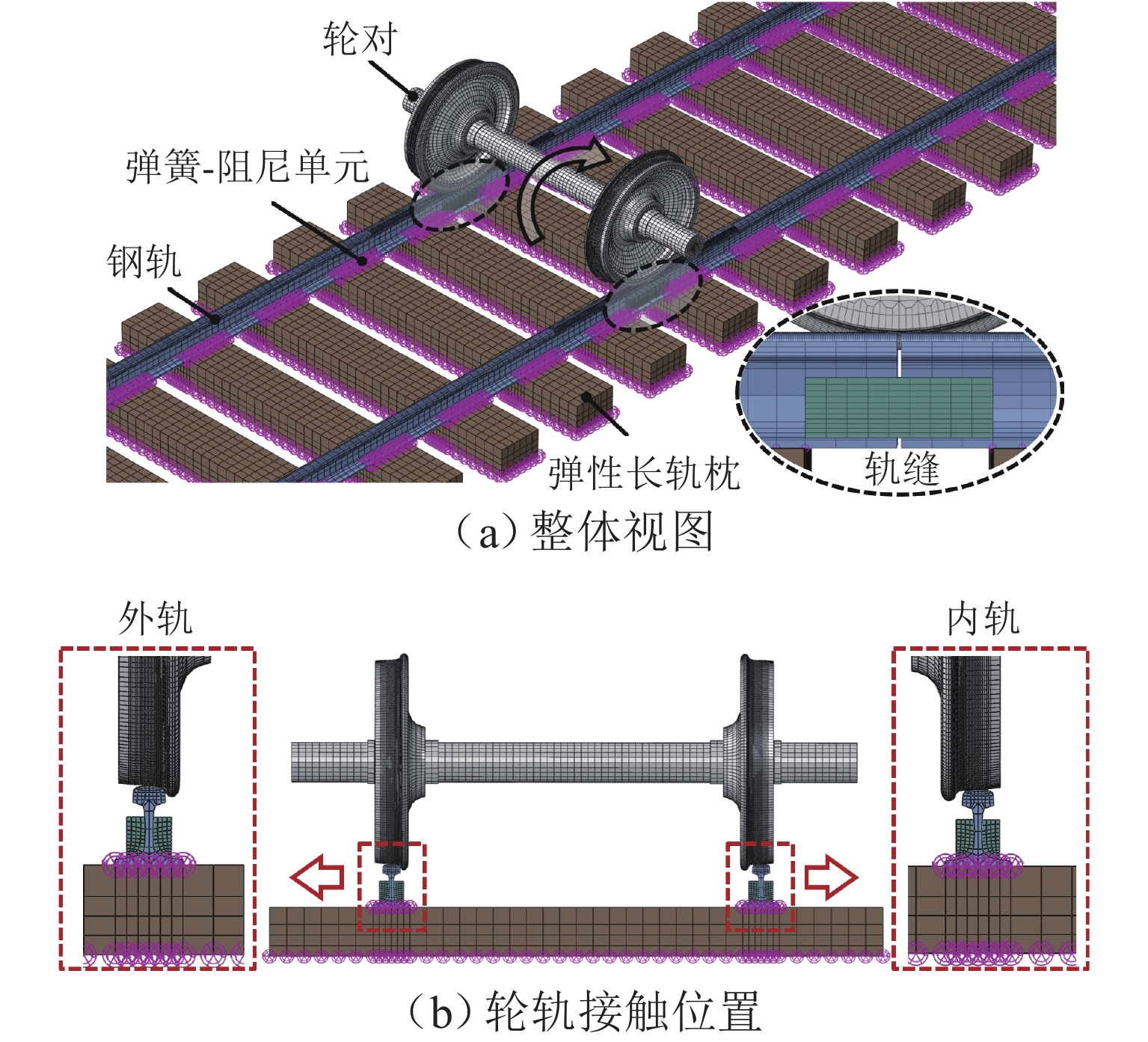
针对重庆地铁小半径曲线有/无轨缝区域存在的2种不同钢轨波磨现象(无轨缝区域的波磨为发生在内轨上的短波波磨,有轨缝区域的波磨为发生在内轨上的长短波波磨),本文基于摩擦耦合振动理论开展2种钢轨波磨现象成因的对比研究. 结合现场调研,针对小半径曲线有/无轨缝区域,建立轮轨系统有限元模型,采用复特征值分析法对比分析2种区域轮轨系统的稳定性;采用瞬时动态分析法探究轨缝不平顺和钢轨波磨不平顺影响下轮轨系统的动态响应. 结果表明:轮轨系统在小半径曲线有/无轨缝区域均存在摩擦自激振动,主要频率分别为 479.26 Hz 与 477.65 Hz,可诱导波长30~40 mm 的短波波磨;轨缝不平顺会增大轮轨系统动态响应,引发的反馈振动主要频率为112.79 Hz,进而诱导波长150~160 mm 的长波波磨;短波波磨不平顺的反馈振动仅起到加剧自身波磨深度的作用,并未诱导新波长波磨产生.
Abstract:To address the two types of rail corrugation in small radius curves of the Chongqing metro (short-wavelength corrugation on inner rails in the sections without rail gaps, and long and short-wavelength corrugation on inner rails in the sections with rail gaps), the comparative study on the causes of two types of rail corrugation was conducted based on the theory of wheel-rail frictional coupling vibration. The finite element models of the wheel-rail systems in the section with and without rail gaps in small radius curves were established, and their stabilities were investigated using the complex eigenvalue analysis method. Then, the dynamic response of the wheel-rail system under the effects of rail gap and rail corrugation irregularities was investigated using the transient dynamic analysis method. The results have shown that the wheel-rail system exhibits frictional self-excited vibration in both sections with and without rail gaps on small-radius curves, with main frequencies of 479.26 Hz and 477.65 Hz, respectively, which can induce short-wavelength corrugation from 30 to 40 mm. Rail surface irregularities increase the dynamic response of the wheel-rail system. The induced feedback vibration has a main frequency of 112.79 Hz, thus inducing long-wavelength corrugation from 150 to 160 mm. The feedback vibration induced by short-wavelength corrugation irregularities only serves to increase the depth of the short-wavelength corrugation itself and does not induce corrugation with a new wavelength.
-
表 1 DTVI 2扣件弹簧刚度及阻尼参数
Table 1. Spring stiffness and damping coefficient of DTVI 2 fasteners
方向 钢轨扣件 轨枕支撑 刚度/
(MN·m−1)阻尼/
(N·s·m−1)刚度/
(MN·m−1)阻尼/
(N·s·m−1)横向 8.79 1927.26 垂向 40.73 9898.70 170 31000 纵向 8.79 1927.96 -
[1] 宋启峰, 陈光雄, 董丙杰, 等. 地铁梯形轨枕轨道钢轨波磨成因研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2025, 60(3): 714-721.SONG Qifeng, CHEN Guangxiong, DONG Bingjie, et al. Cause of rail corrugation on ladder sleeper track[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2025, 60(3): 714-721. [2] 高天赐, 江乐鹏, 从建力, 等. 基于车载振噪多源数据融合的地铁波磨快速检测方法研究[J/OL]. 西南交通大学学报, 2024: 1-9. (2024-07-17). http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=XNJT2024070200C&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ. [3] 崔晓璐, 万久渝, 彭双千, 等. 双非减振扣件区段钢轨波磨诱导弹条断裂机理和控制方法[J/OL]. 西南交通大学学报, 2024: 1-9. (2024-09-14). http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=XNJT20240913009&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ. [4] 金学松, 李霞, 李伟, 等. 铁路钢轨波浪形磨损研究进展[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2016, 51(2): 264-273.JIN Xuesong, LI Xia, LI Wei, et al. Review of rail corrugation progress[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2016, 51(2): 264-273. [5] EL BESHBICHI O, WAN C, BRUNI S, et al. Complex eigenvalue analysis and parameters analysis to investigate the formation of railhead corrugation in sharp curves[J]. Wear, 2020, 450: 203150. [6] MATSUMOTO A, SATO Y, ONO H, et al. Formation mechanism and countermeasures of rail corrugation on curved track[J]. Wear, 2002, 253(1/2): 178-184. [7] XU J, CUI X L, DING H H, et al. Optimization of vibration absorbers for the suppression of rail corrugation in the sharp curved section with Cologne-egg fasteners[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2024, 62(2): 395-410. doi: 10.1080/00423114.2023.2170255 [8] KURZECK B. Combined friction induced oscillations of wheelset and track during the curving of metros and their influence on corrugation[J]. Wear, 2011, 271(1/2): 299-310. [9] ROBLES R, CORREA N, VADILLO E G, et al. Comprehensive efficient vertical and lateral track dynamic model to study the evolution of rail corrugation in sharp curves[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2023, 545: 117448. doi: 10.1016/j.jsv.2022.117448 [10] WANG Z, LEI Z, ZHU J. Study on the formation mechanism of rail corrugation in small radius curves of metro[J]. Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 2023, 37(9): 4521-4532. doi: 10.1007/s12206-023-0809-7 [11] LEI Z Y, ZHOU Y L, LI L. Influence of different track structures on the development of corrugation in small radius curve section of subway[J]. Journal of Vibroengineering, 2023, 25(3): 534-547. doi: 10.21595/jve.2022.22929 [12] TORSTENSSON P T, PIERINGER A, NIELSEN J C O. Simulation of rail roughness growth on small radius curves using a non-Hertzian and non-steady wheel–rail contact model[J]. Wear, 2014, 314(1/2): 241-253. [13] CHEN G X. Friction-induced vibration of a railway wheelset-track system and its effect on rail corrugation[J]. Lubricants, 2020, 8(2): 18. doi: 10.3390/lubricants8020018 [14] YIN X X, WEI X K, ZHENG H C. Applying system dynamics of discrete supported track to analyze the rail corrugation causation on curved urban railway tracks[J]. Discrete Dynamics in Nature and Society, 2021, 2021(1): 9958163. [15] KANG X, CHEN G X, CHEN X, et al. Analysis of the generation mechanism and evolution of the wheel high-order polygonal wear of subway trains[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2023, 151: 107375. doi: 10.1016/j.engfailanal.2023.107375 [16] 仇超, 杨耕, 谢铠泽. 专用铁路简支梁桥上铺设50 m长钢轨预留轨缝研究[J]. 石家庄铁道大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 33(3): 97-102.QIU Chao, YANG Geng, XIE Kaize. Research of reserved joint gap of 50 m rail on simply supported beam bridges for access railroad[J]. Journal of Shijiazhuang Tiedao University (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 33(3): 97-102. [17] CUI X L, CHEN G X, YANG H G, et al. Study on rail corrugation of a metro tangential track with Cologne-egg type fasteners[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2016, 54(3): 353-369. doi: 10.1080/00423114.2015.1137955 [18] KURZECK B. Combined friction induced oscillations of wheelset and track during the curving of metros and their influence on corrugation[J]. Wear, 2011, 271(1/2): 299-310. [19] 陈光雄, 钱韦吉, 莫继良, 等. 轮轨摩擦自激振动引起小半径曲线钢轨波磨的瞬态动力学[J]. 机械工程学报, 2014, 50(9): 71-76. doi: 10.3901/JME.2014.09.071CHEN Guangxiong, QIAN Weiji, MO Jiliang, et al. A transient dynamics study on wear-type rail corrugation on a tight curve due to the friction-induced self-excited vibration of a wheelset-track system[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2014, 50(9): 71-76. doi: 10.3901/JME.2014.09.071 [20] NOBARI A, OUYANG H J, BANNISTER P. Statistics of complex eigenvalues in friction-induced vibration[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2015, 338: 169-183. doi: 10.1016/j.jsv.2014.10.017 [21] HORY C, BOUILLAUT L, AKNIN P. Time–frequency characterization of rail corrugation under a combined auto-regressive and matched filter scheme[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2012, 29: 174-186. doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2011.12.015 [22] CHEN G X, ZHOU Z R, OUYANG H, et al. A finite element study on rail corrugation based on saturated creep force-induced self-excited vibration of a wheelset–track system[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2010, 329(22): 4643-4655. doi: 10.1016/j.jsv.2010.05.011 [23] QIAN W J, CHEN G X, OUYANG H, et al. A transient dynamic study of the self-excited vibration of a railway wheel set–track system induced by saturated creep forces[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2014, 52(9): 1115-1138. doi: 10.1080/00423114.2014.924629 [24] 钱韦吉, 黄志强. 摩擦因数对摩擦自激振动影响规律的数值分析[J]. 振动与冲击, 2018, 37(18): 224-230.QIAN Weiji, HUANG Zhiqiang. Numerical analysis on the effects of friction coefficient on the friction-induced self-excited vibration[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2018, 37(18): 224-230. [25] 李英. 小半径曲线内轨波磨外轨无波磨原因的研究[J]. 表面技术, 2017, 46(8): 134-139.LI Ying. Causes of low rail corrugation and little high rail corrugation in minor radius curve route[J]. Surface Technology, 2017, 46(8): 134-139. [26] CUI X L, HUANG B, DU Z X, et al. Study on the mechanism of the abnormal phenomenon of rail corrugation in the curve interval of a mountain city metro[J]. Tribology Transactions, 2020, 63(6): 996-1007. doi: 10.1080/10402004.2020.1782551 [27] GARDIE E, DUBALE H, TEFERA E, et al. Numerical analysis of rail joint in a vertical applied load and determining the possible location of joints[J]. Forces in Mechanics, 2022, 6: 100064. doi: 10.1016/j.finmec.2021.100064 [28] MANDAL N K, DHANASEKAR M, SUN Y Q. Impact forces at dipped rail joints[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part F: Journal of Rail and Rapid Transit, 2016, 230(1): 271-282. doi: 10.1177/0954409714537816 [29] 徐井芒, 王凯, 高原, 等. 高速铁路无缝钢轨断缝瞬态冲击行为分析[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2020, 55(6): 1348-1354.XU Jingmang, WANG Kai, GAO Yuan, et al. Transient impact behavior analysis of rail broken gap on high-speed continuous welded rail[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2020, 55(6): 1348-1354. [30] CUI X L, CHEN G X, ZHAO J W, et al. Field investigation and numerical study of the rail corrugation caused by frictional self-excited vibration[J]. Wear, 2017, 376: 1919-1929. [31] REN L, XIE G, IWNICKI S D. Properties of wheel/rail longitudinal creep force due to sinusoidal short pitch corrugation on railway rails[J]. Wear, 2012, 284: 73-81. [32] BROCKLEY C A, KO P L. An investigation of rail corrugation using friction-induced vibration theory[J]. Wear, 1988, 128(1): 99-106. doi: 10.1016/0043-1648(88)90256-6 -




 下载:
下载: