Complex Nonlinear Behavior of Parabolic Two-Hinged Arches Subjected to a Midspan Concentrated Force
-
摘要:
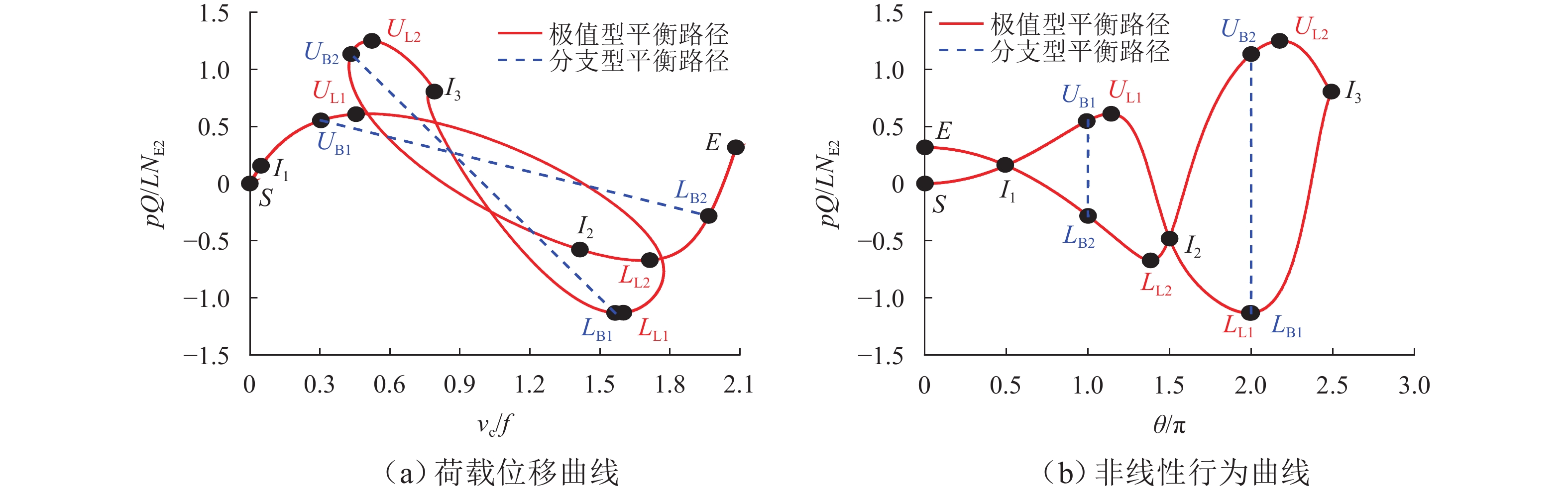
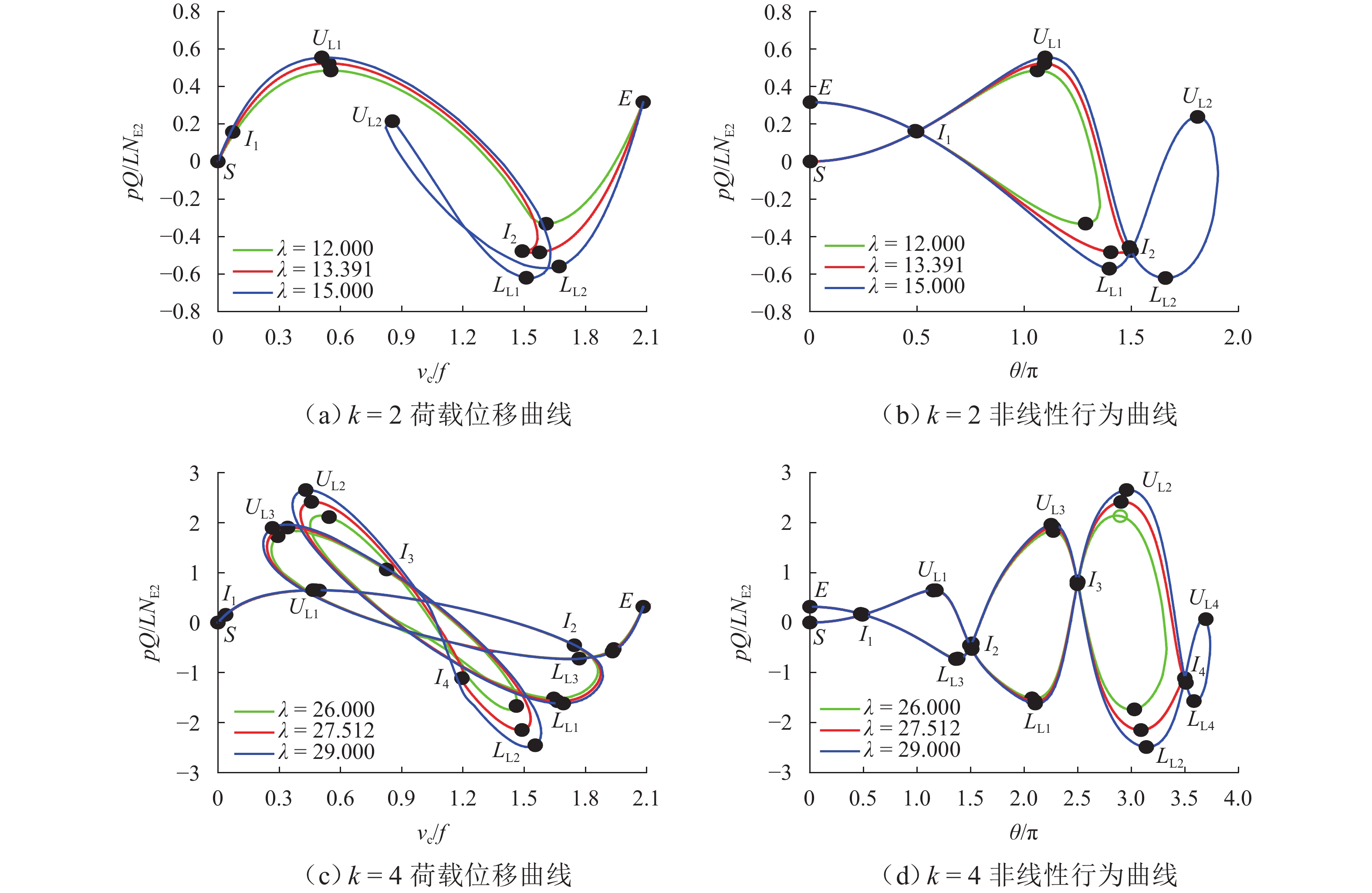
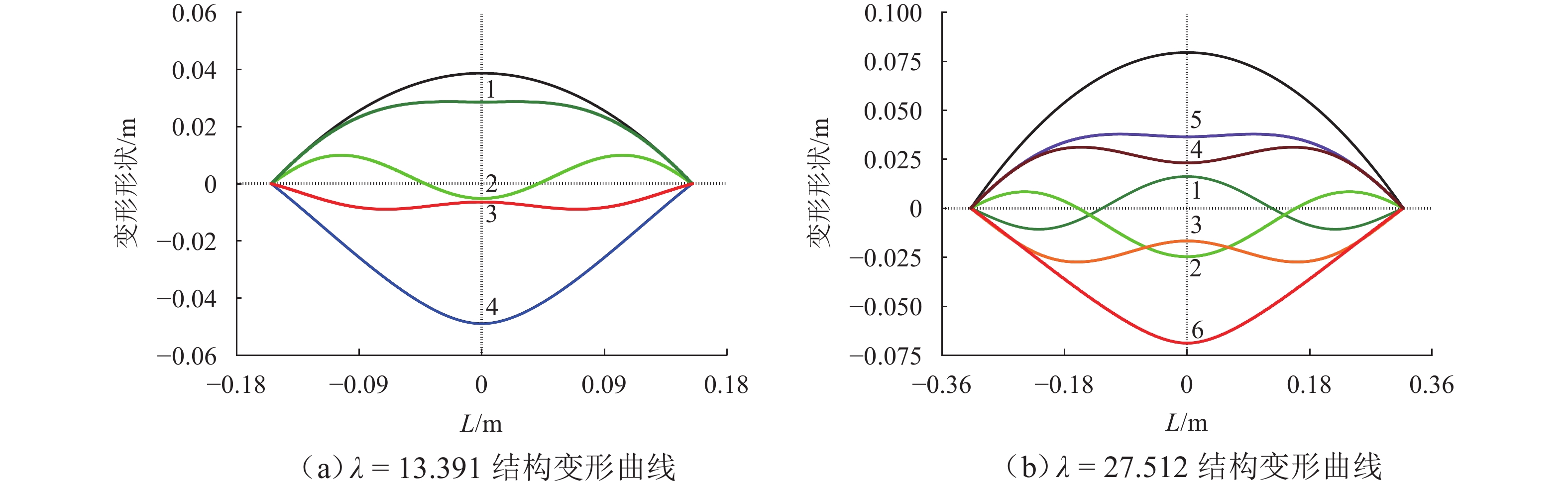
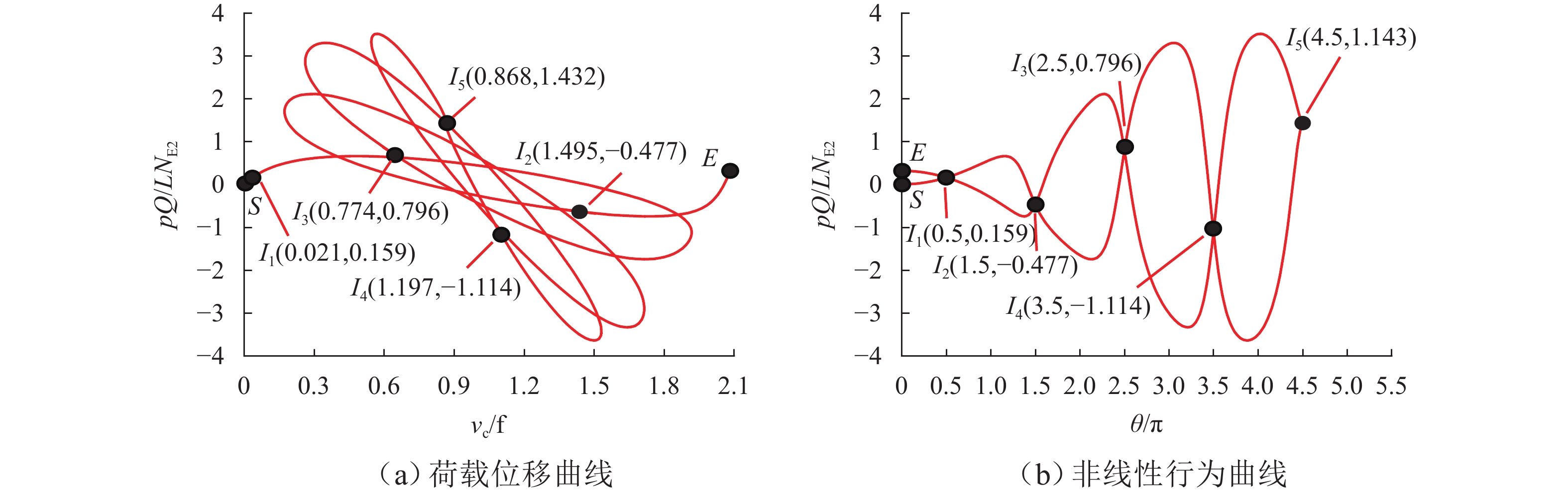
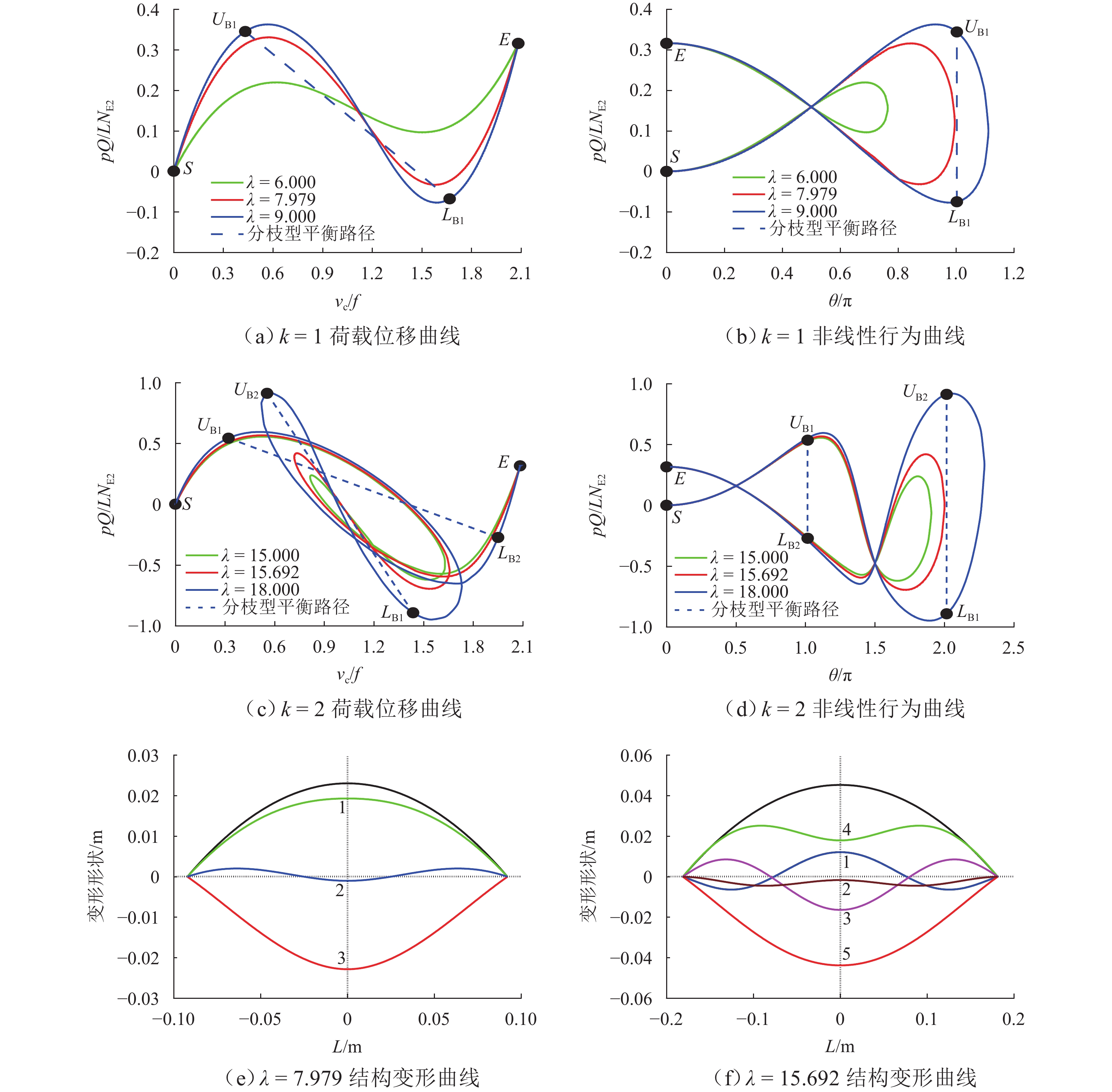
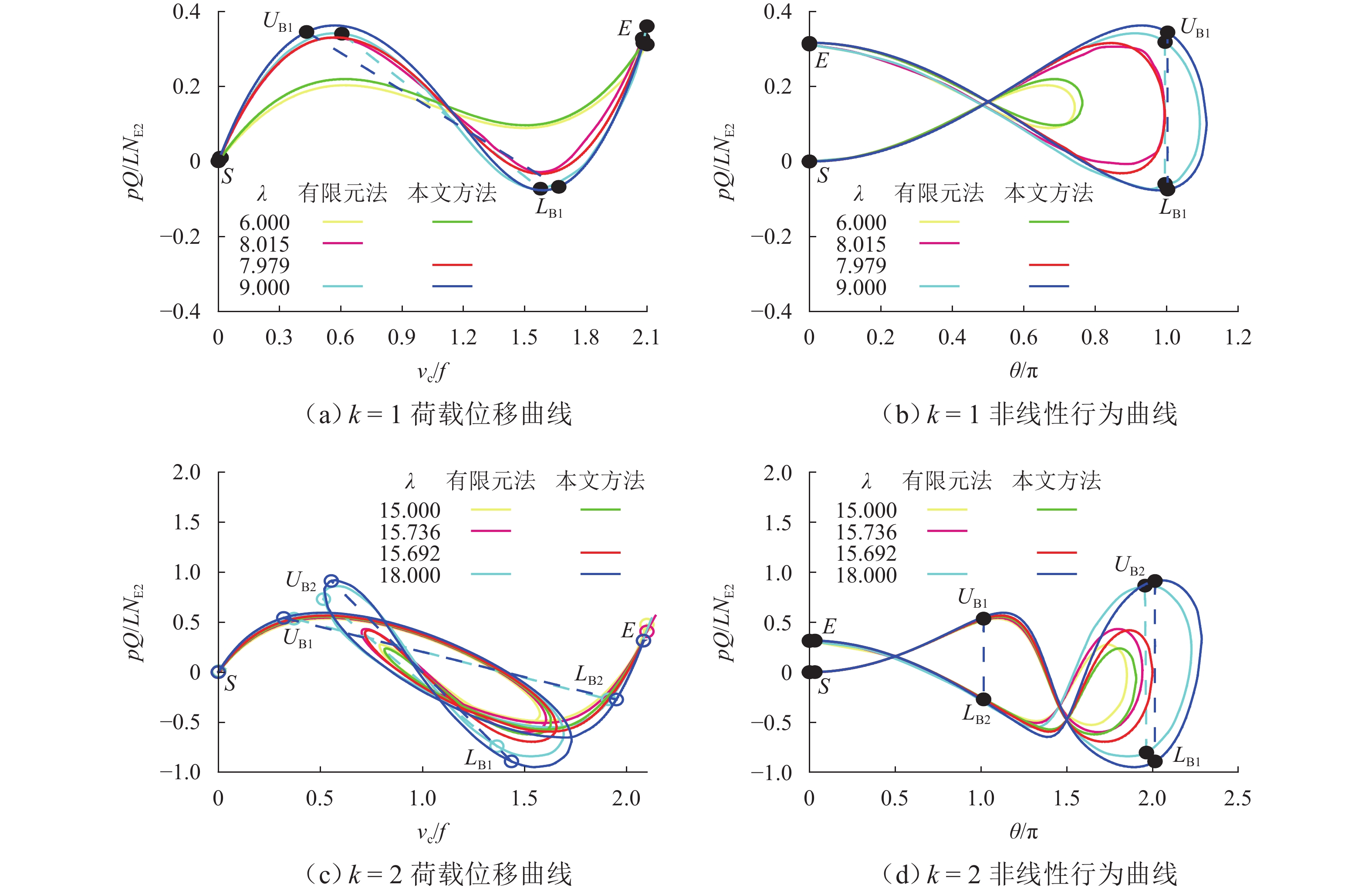
针对跨中集中力作用下抛物线两铰拱出现复杂非线性行为的现象,提出揭示其非线性行为规律的理论方法. 基于笛卡尔直角坐标系下拱结构非线性应变-位移关系,推演跨中集中力作用下抛物线两铰拱面内非线性平衡微分方程组及其高精度近似解析解;通过对该高精度近似解析在间断点处极限的分析,揭示跨中集中力作用下抛物线两铰拱复杂非线性现象的共性规律:1)当且仅当修正长细比大于等于极值型临界长细比时,跨中集中力作用下抛物线两铰拱发生极值型非线性行为,且极值型非线性平衡路径上出现多个极值点现象,极值点数量与参数
k 呈正相关;2)跨中集中力作用下抛物线两铰拱发生极值型非线性行为时,极值型非线性平衡路径经过特定点,特定点坐标固定且不随修正长细比变化而变化;3)当且仅当修正长细比大于等于分支型临界长细比时,跨中集中力作用下抛物线两铰拱发生分支型非线性行为,分支型非线性行为出现多条平衡路径现象. 通过与有限元结果对比表明:本文方法的跨中竖向集中力作用下抛物线两铰拱非线性平衡路径近似解析具有较高精度,揭示跨中集中力作用下抛物线两铰拱复杂非线性行为规律与有限元结果吻合较好,最大相对误差为9.05%,满足工程精度需要.Abstract:To investigate the complex nonlinear behavior of parabolic two-hinged arches subjected to a midspan concentrated force, a theoretical method was proposed to reveal its rule. Based on the nonlinear strain–displacement relationship of arches in the Cartesian right-angled coordinate system, nonlinear equilibrium differential equations of parabolic two-hinged arches subjected to a midspan concentrated force were derived, as well as the corresponding high-precision approximate analytical solutions of these nonlinear equations. The common rules of complex nonlinear behavior of parabolic two-hinged arches subjected to a midspan concentrated force were investigated by the limitation analysis of these high-precision approximate analytical solutions in discontinuous points: 1) If and only if the modified slenderness ratio is greater than or equal to the limit-pattern critical slenderness ratio, limit-pattern nonlinear behavior occurs in parabolic two-hinged arches subjected to a midspan concentrated force. Moreover, multiple extreme points appear on the limit-pattern nonlinear equilibrium path, and the number of extreme points is positively correlated with the parameter
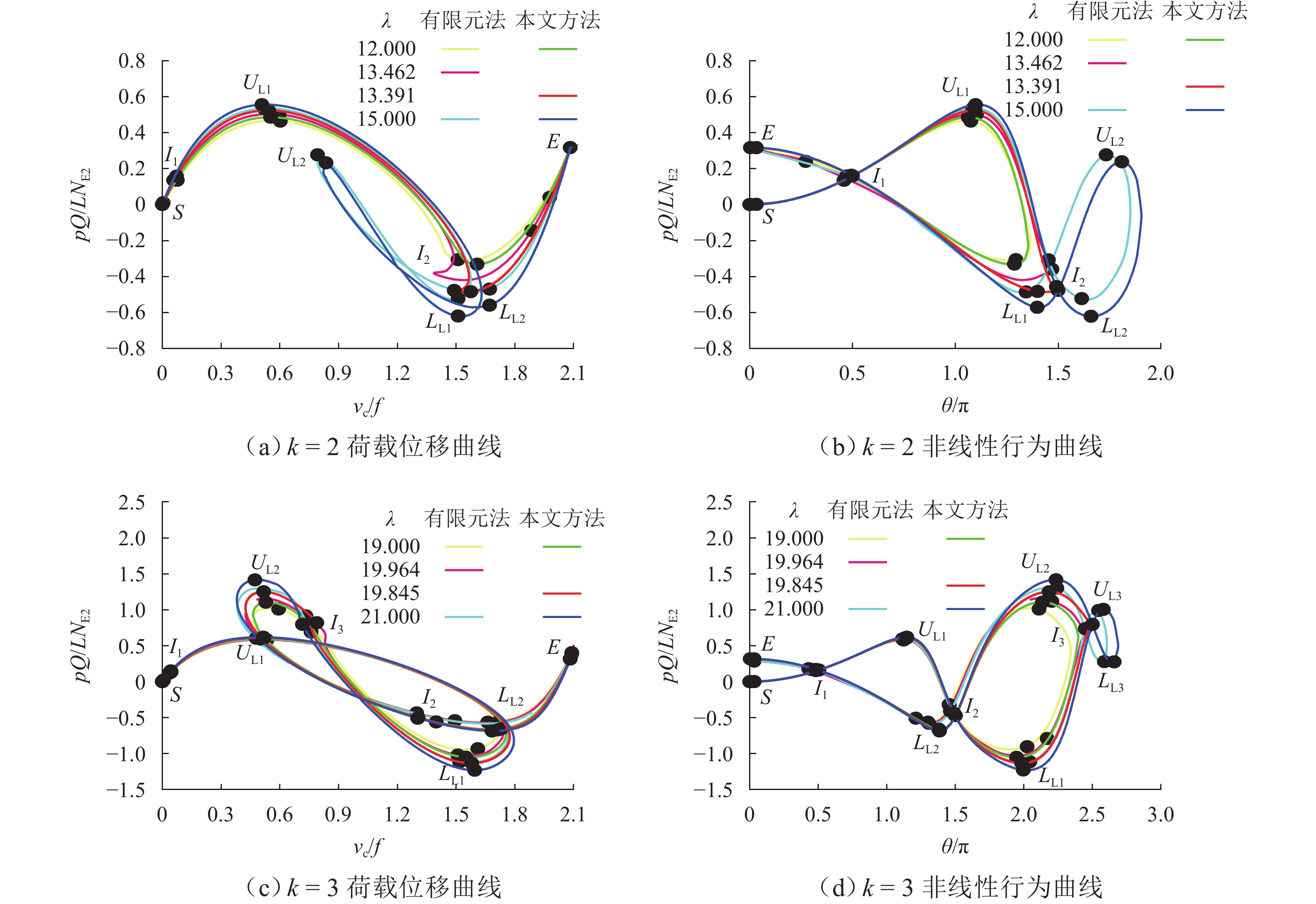
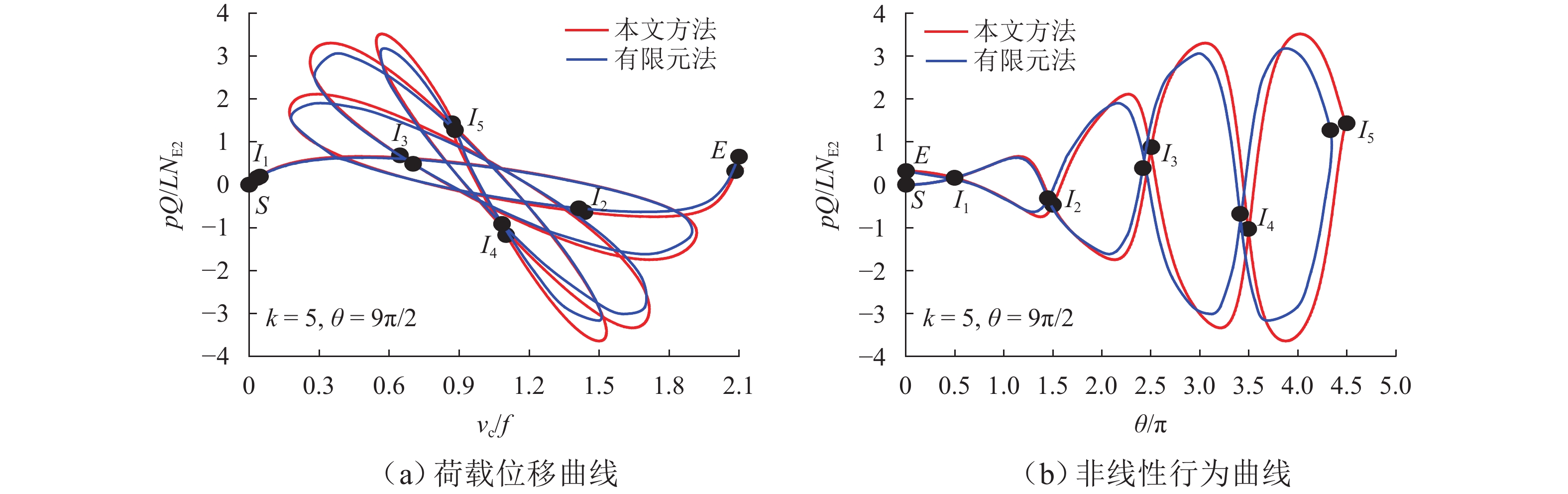
k . 2) When limit-pattern nonlinear behavior occurs in parabolic two-hinged arches subjected to a midspan concentrated force, the limit-pattern nonlinear equilibrium path passes through specific points. The coordinates of these points are fixed and do not change with variations in the modified slenderness ratio. 3) If and only if the modified slenderness ratio is greater than or equal to the bifurcation-pattern critical slenderness ratio, bifurcation-pattern nonlinear behavior occurs in parabolic two-hinged arches subjected to a midspan concentrated force. This bifurcation-pattern nonlinear behavior exhibits multiple equilibrium paths. Comparisons against nonlinear finite element results demonstrate that the proposed approximate analytical solutions of nonlinear equilibrium of parabolic two-hinged arches subjected to a vertical midspan concentrated force have sufficient accuracy, and the rules of complex nonlinear behavior of parabolic two-hinged arches subjected to a midspan concentrated force agree well with nonlinear finite element results. The maximum relative error is 9.05%, which meets the needs of engineering accuracy. -
表 1 抛物线两铰拱多极值点条件
Table 1. Multi-extreme point conditions of parabolic two-hinged arches
$k$ $ \theta $ $\lambda _{{\text{cr}}}^{{\text{sym}}}$ 上极值点数/个 下极值点数/个 1 ${{\text{π}} / 2}$ 3.905 1 1 2 ${{3{\text{π}} } / 2}$ 13.391 2 2 3 ${{5{\text{π}} } / 2}$ 19.845 3 3 4 ${{7{\text{π}} } / 2}$ 27.512 4 4 5 ${{9{\text{π}} } / 2}$ 34.987 5 5 表 2 抛物线两铰拱非线性行为曲线特定点
Table 2. Specific points of nonlinear behavior curve of parabolic two-hinged arches
$k$ $ \theta $ ${ {pQ} / ({L{N_{ {\text{E2} } } } }) }$ ${ { {v_{\text{c} } } } / f}$ 特定点 1 ${{\text{π}} /2}$ 0.159 0.021 I1 2 ${{3{\text{π}} } / 2}$ −0.477 1.495 I2 3 ${{5{\text{π}} } / 2}$ 0.796 0.774 I3 4 ${{7{\text{π}} } / 2}$ −1.114 1.197 I4 5 ${{9{\text{π}} }/ 2}$ 1.432 0.868 I5 表 3 分支型平衡路径临界修正长细比
Table 3. Critical modified slenderness ratio of bifurcation equilibrium path
$k$ $ \theta $ $\lambda _{{\text{cr}}}^{{\text{asy}}}$ 1 $\pi $ 7.979 2 $2{\text{π}} $ 15.692 3 $3{\text{π}} $ 23.271 4 $4{\text{π}} $ 30.928 5 $5{\text{π}} $ 38.591 表 4 抛物线两铰拱极值型平衡路径临界长细比验证
Table 4. Verification of critical slenderness ratio of limit-pattern equilibrium path of parabolic two-hinged arches
k 本文方法 有限元法 相对误差/% 1 3.905 3.906 0.26 2 13.391 13.462 0.53 3 19.845 19.964 0.55 4 27.512 27.724 0.76 5 34.987 35.269 0.80 表 5 抛物线两铰拱极值型非线性平衡路径特定点对比
Table 5. Comparison of specific points on limit-pattern nonlinear equilibrium path of parabolic two-hinged arches
参数 方法 I1 I2 I3 I4 I5 $ \dfrac{\theta }{{\text{π}} } $ 本文方法 0.500 1.500 2.500 3.500 4.500 有限元法 0.484 1.461 2.451 3.463 4.368 相对误差/% 3.20 2.60 1.96 1.06 2.93 $\dfrac{{pQ}}{{L{N_{{\text{E2}}}}}}$ 本文方法 0.159 −0.477 0.796 −1.114 1.432 有限元法 0.163 −0.458 0.724 −1.032 1.396 相对误差/% 2.45 3.98 9.05 7.36 2.51 $\dfrac{{{v_{\text{c}}}}}{f}$ 本文方法 0.021 1.495 0.774 1.197 0.868 有限元法 0.023 1.504 0.826 1.189 0.884 相对误差/% 8.70 0.60 6.30 0.67 1.81 表 6 抛物线两铰拱分支型临界长细比验证
Table 6. Comparison of critical slenderness ratio of bifurcation equilibrium path of parabolic two-hinged arches
k 本文方法 有限元法 相对误差 1 7.979 8.015 0.45% 2 15.692 15.736 0.28% 3 23.271 23.283 0.05% 4 30.928 31.045 0.38% 5 38.591 38.839 0.64% -
[1] 陈宝春, 张梦娇, 刘君平, 等. 我国混凝土拱桥应用现状与展望[J]. 福州大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 49(5): 716-726.CHEN Baochun, ZHANG Mengjiao, LIU Junping, et al. Application and prospects of concrete arch bridges in China[J]. Journal of Fuzhou University (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 49(5): 716-726. [2] ZHENG J L, WANG J J. Concrete-filled steel tube arch bridges in China[J]. Engineering, 2018, 4(1): 143-155. doi: 10.1016/j.eng.2017.12.003 [3] 张承文, 淳庆, 花全均, 等. 基于元遗传算法的石拱桥传感器优化布置及评价方法研究[J/OL]. 西南交通大学学报, 2024: 1-11. (2024-10-10). https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=XNJT20240913002&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ. [4] 彭仪普, 汤致远, 陈立, 等. 基于车-桥耦合的系杆拱桥吊杆疲劳损伤分析[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2025, 60(6): 1447-1454.PENG Yipu, TANG Zhiyuan, CHEN Li, et al. Fatigue damage of tied-arch bridge hangers based ontrain-bridge coupling[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2025, 60(6): 1447-1454. [5] 曾永平, 刘力维, 陶奇, 等. CFRP吊索中承式铁路拱桥缆索破断冲击效应数值研究[J/OL]. 西南交通大学学报, 2025: 1-10. (2025-04-07). https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=XNJT20250403005&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ. [6] BRADFORD M A, UY B, PI Y L. In-plane elastic stability of Arches under a central concentrated load[J]. Journal of Engineering Mechanics, 2002, 128(7): 710-719. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9399(2002)128:7(710) [7] KISS L P. Nonlinear stability analysis of FGM shallow Arches under an arbitrary concentrated radial force[J]. International Journal of Mechanics and Materials in Design, 2020, 16(1): 91-108. doi: 10.1007/s10999-019-09460-2 [8] PI Y L, BRADFORD M A, GUO Y L. Revisiting nonlinear in-plane elastic buckling and postbuckling analysis of shallow circular Arches under a central concentrated load[J]. Journal of Engineering Mechanics, 2016, 142(8): 04016046. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)EM.1943-7889.0001098 [9] PI Y L, BRADFORD M A, LIU A R. Nonlinear equilibrium and buckling of fixed shallow Arches subjected to an arbitrary radial concentrated load[J]. International Journal of Structural Stability and Dynamics, 2017, 17(8): 1750082. doi: 10.1142/S0219455417500821 [10] PI Y L. Non-linear in-plane multiple equilibria and buckling of pin-ended shallow circular Arches under an arbitrary radial point load[J]. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 2020, 77: 115-136. doi: 10.1016/j.apm.2019.07.021 [11] 张紫祥, 刘爱荣, 黄永辉, 等. 集中荷载作用下弹性扭转约束层合浅拱的非线性面内稳定[J]. 工程力学, 2020, 37(增1): 13-19, 31.ZHANG Zixiang, LIU Airong, HUANG Yonghui, et al. Nonlinear in-plane buckling of rotationally restrained shallow laminated Arches under a central concentrated load[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2020, 37(S1): 13-19, 31. [12] 张紫祥, 刘爱荣, 钟子林. 集中荷载作用下FRP圆弧拱的面内非线性弹性失稳研究[J]. 西安建筑科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 51(2): 230-234, 258.ZHANG Zixiang, LIU Airong, ZHONG Zilin. Nonlinear in-plane elastic buckling of FRP circular arch subjected to a central concentrated load[J]. Journal of Xi’an University of Architecture & Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2019, 51(2): 230-234, 258. [13] CAI J G, XU Y X, FENG J, et al. Effects of temperature variations on the in-plane stability of steel arch bridges[J]. Journal of Bridge Engineering, 2012, 17(2): 232-240. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)BE.1943-5592.0000208 [14] CAI J G, FENG J, CHEN Y, et al. In-plane elastic stability of fixed parabolic shallow Arches[J]. Science in China Series E: Technological Sciences, 2009, 52(3): 596-602. doi: 10.1007/s11431-009-0057-9 [15] BRADFORD M A, PI Y L, YANG G T, et al. Effects of approximations on non-linear in-plane elastic buckling and postbuckling analyses of shallow parabolic Arches[J]. Engineering Structures, 2015, 101: 58-67. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2015.07.008 [16] 刘璐璐, 刘爱荣, 卢汉文. T型截面拱在拱顶集中力作用下的平面外弯扭失稳[J]. 工程力学, 2020, 37(增1): 151-156.LIU Lulu, LIU Airong, LU Hanwen. Flexural-torsional buckling of pin-ended Arches with t-section under a central radial concentrated load[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2020, 37(S1): 151-156. [17] TSIATAS G C, BABOUSKOS N G. Linear and geometrically nonlinear analysis of non-uniform shallow arches under a central concentrated force[J]. International Journal of Non-Linear Mechanics, 2017, 92: 92-101. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnonlinmec.2017.03.019 [18] BATENI M, ESLAMI M R. Non-linear in-plane stability analysis of FGM circular shallow Arches under central concentrated force[J]. International Journal of Non-Linear Mechanics, 2014, 60: 58-69. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnonlinmec.2014.01.001 [19] KISS L P, JALALOVA P, MEHDIYEV Z. Deformations and internal forces in Arches under a concentrated force[J]. Journal of Mechanics of Materials and Structures, 2023, 18(4): 551-565. doi: 10.2140/jomms.2023.18.551 [20] 姜正荣, 邱俊明, 石开荣, 等. 考虑杆件初弯曲的弦支穹顶结构非线性屈曲分析[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2025, 60(3): 561-568.JIANG Zhengrong, QIU Junming, SHI Kairong, et al. Nonlinear buckling analysis of suspended domes considering initial curvature of members[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2025, 60(3): 561-568. [21] HU C F, PI Y L, GAO W, et al. In-plane non-linear elastic stability of parabolic Arches with different rise-to-span ratios[J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2018, 129: 74-84. doi: 10.1016/j.tws.2018.03.019 [22] HU C F, LI Z, LIU Z W, et al. In-plane non-linear elastic stability of arches subjected to multi-pattern distributed load[J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2020, 154: 106810. doi: 10.1016/j.tws.2020.106810 [23] BRADFORD M A, WANG T, PI Y L, et al. In-plane stability of parabolic arches with horizontal spring supports. I: theory[J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 2007, 133(8): 1130-1137. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9445(2007)133:8(1130) [24] 胡常福, 雷亮亮, 陈海龙, 等. 等截面抛物线拱桥内力实用解析解研究[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报, 2011, 8(5): 12-18.HU Changfu, LEI Liangliang, CHEN Hailong, et al. Research on practical analytic solution of parabolic arch bridges with uniform section[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2011, 8(5): 12-18. [25] HU C F, LI Z, HU Q S. On non-linear behavior and buckling of arch-beam structures[J]. Engineering Structures, 2021, 239: 112214. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2021.112214 -




 下载:
下载: