Evolutionary Characteristics of Jet Vortex Structure in Grid Flocculation Tank
-
摘要:
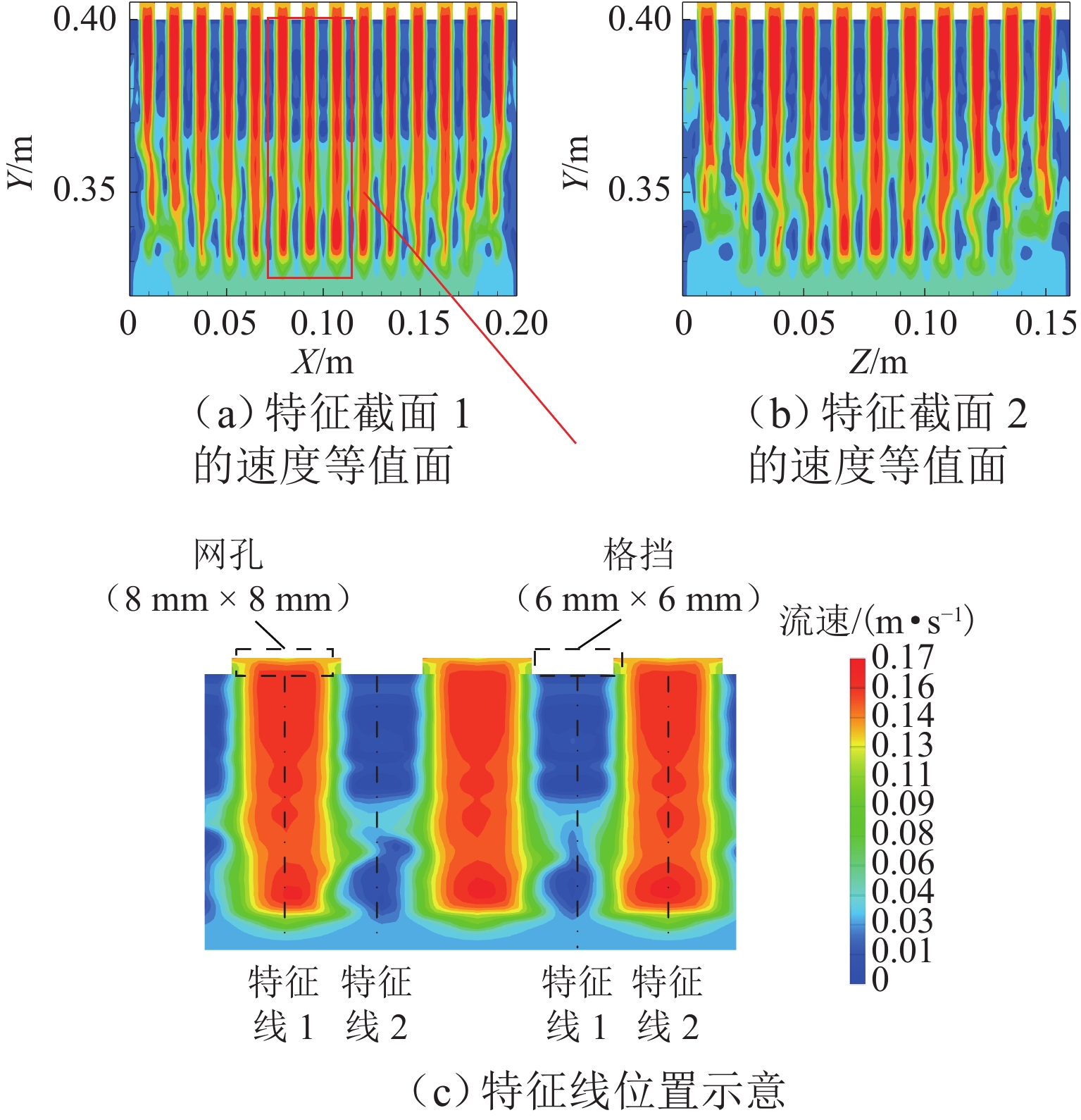
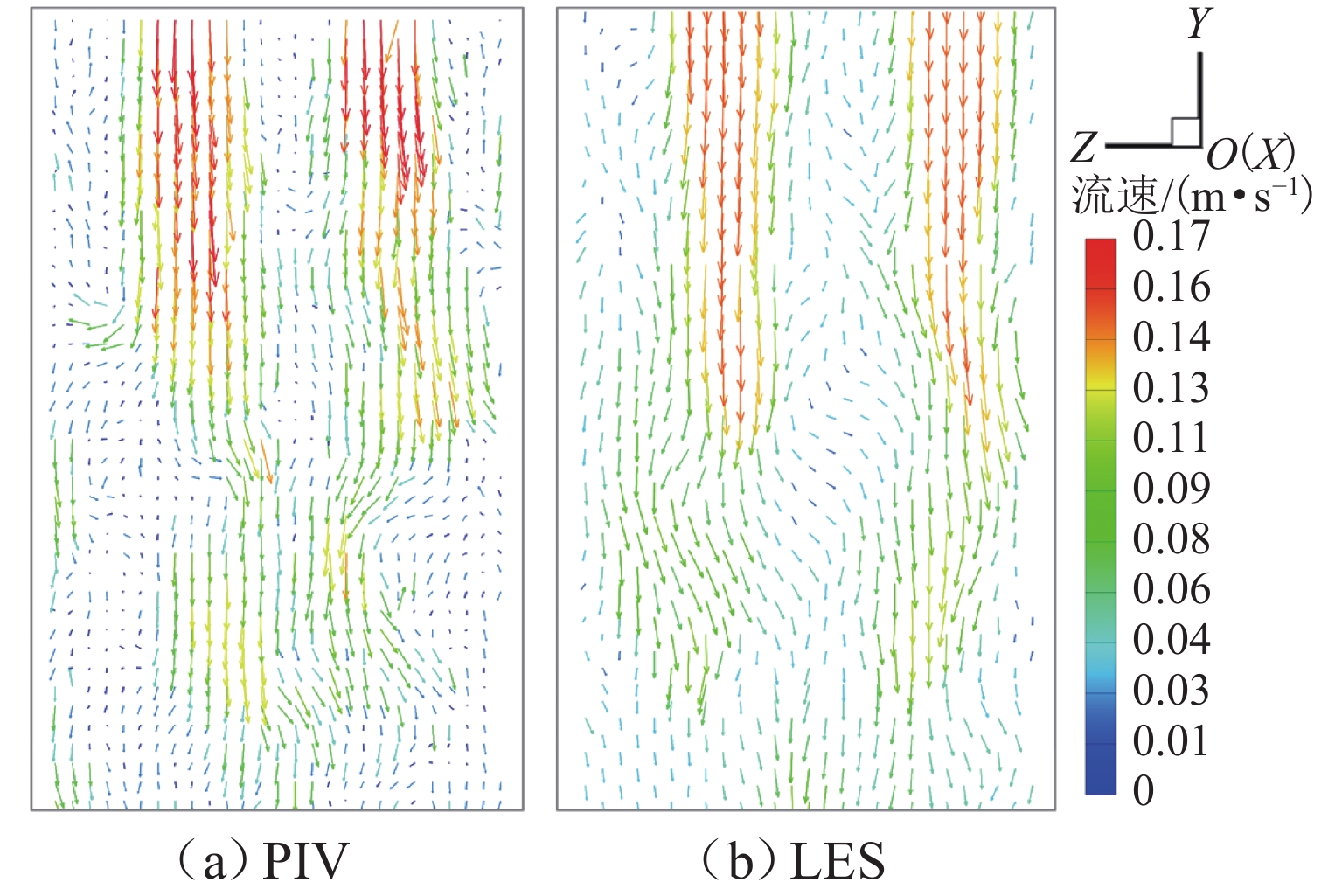
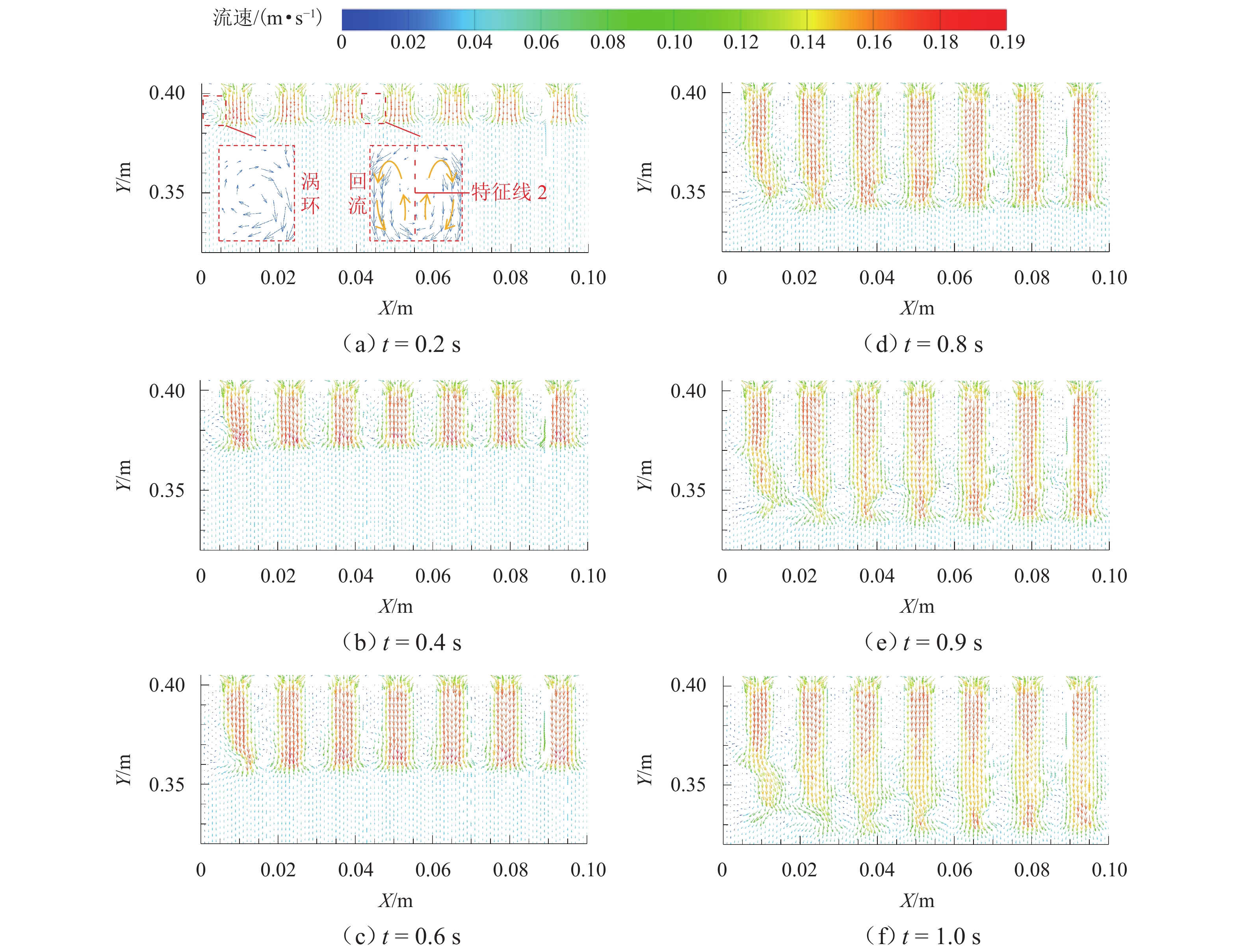
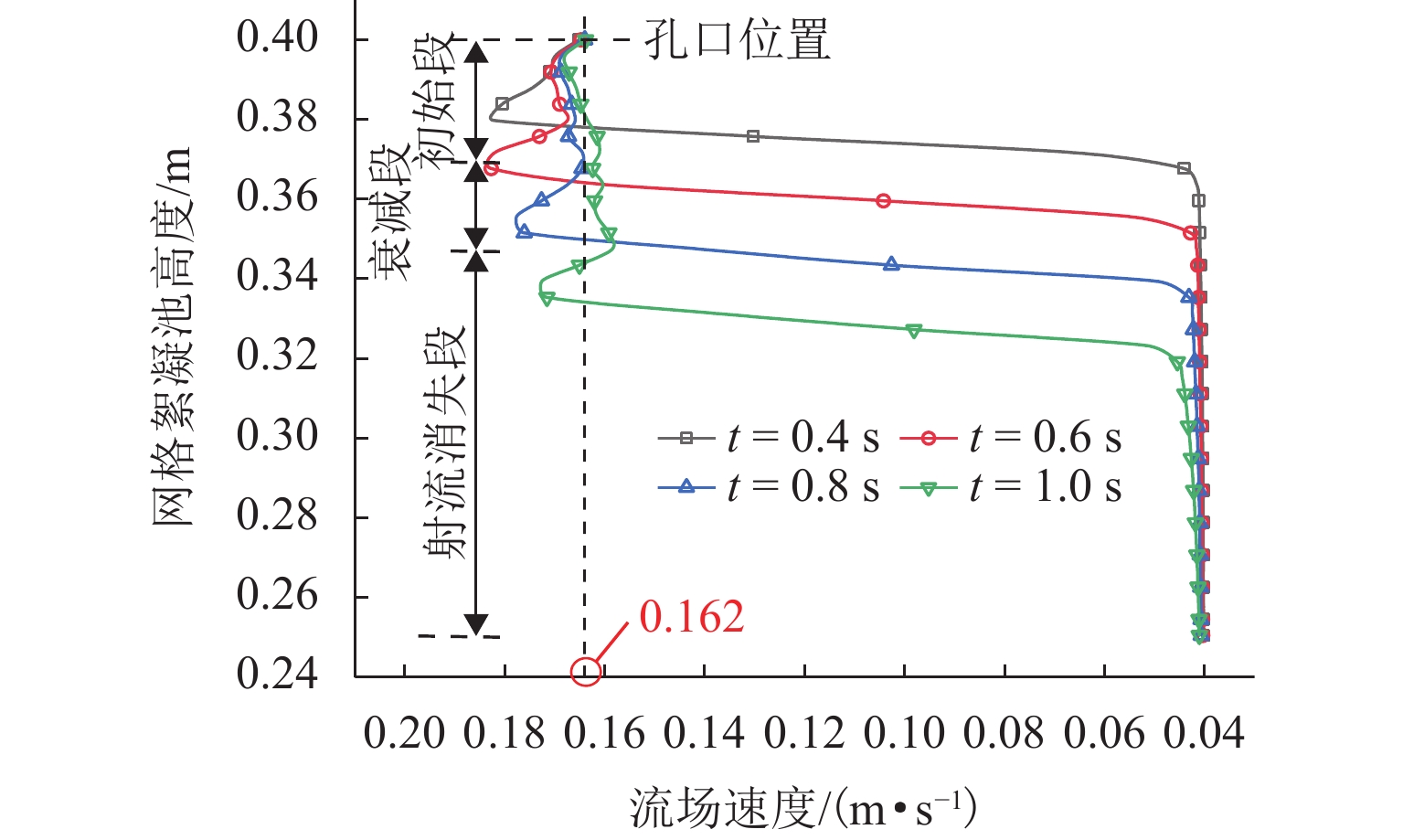
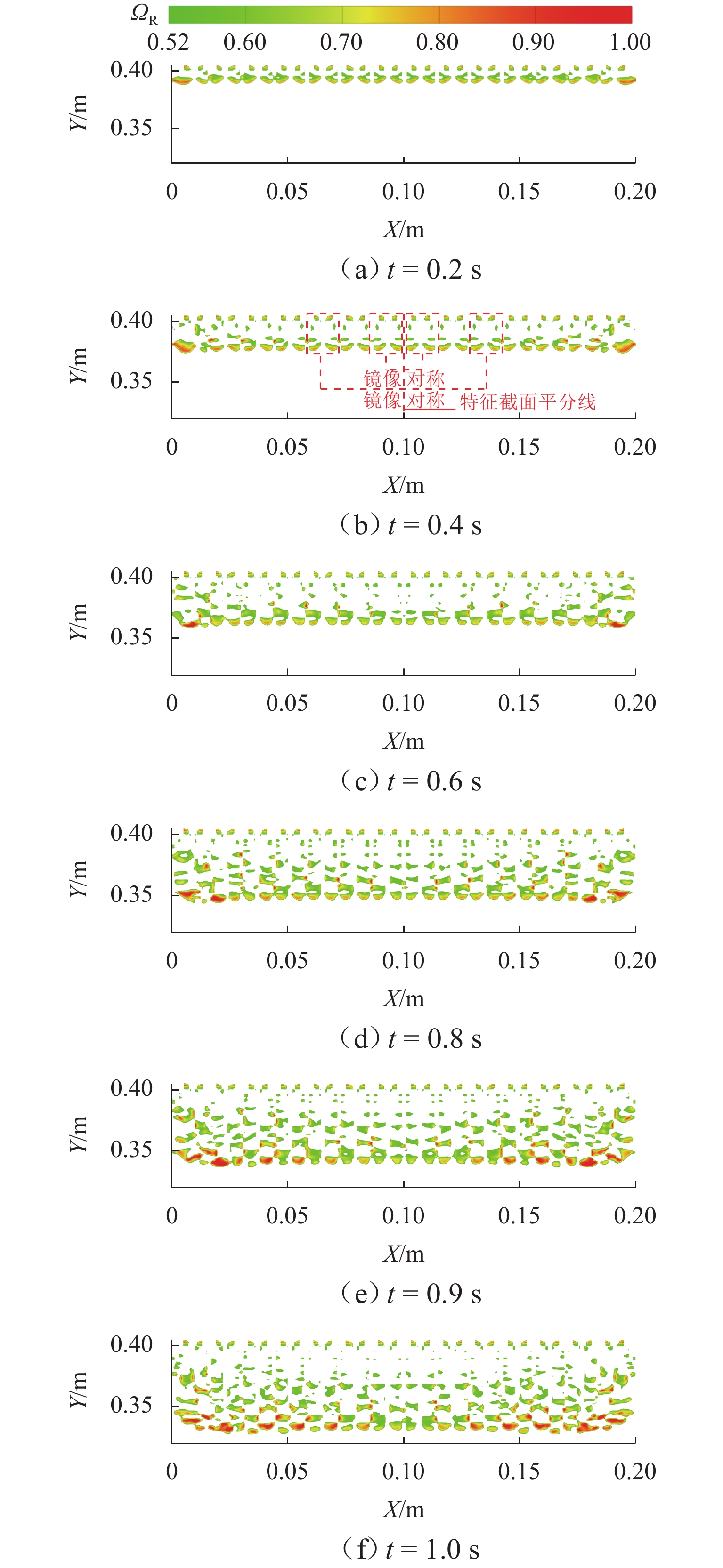
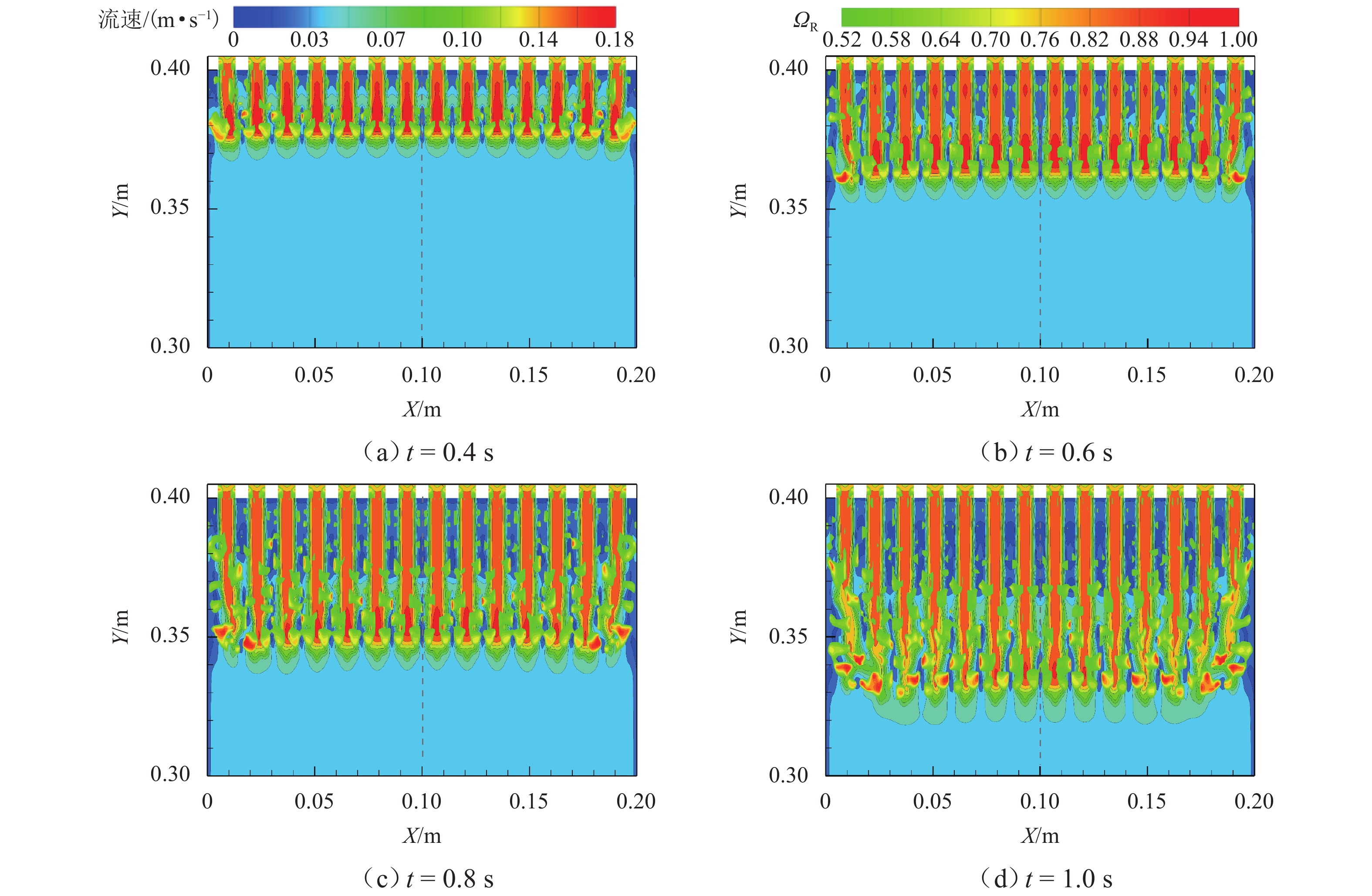
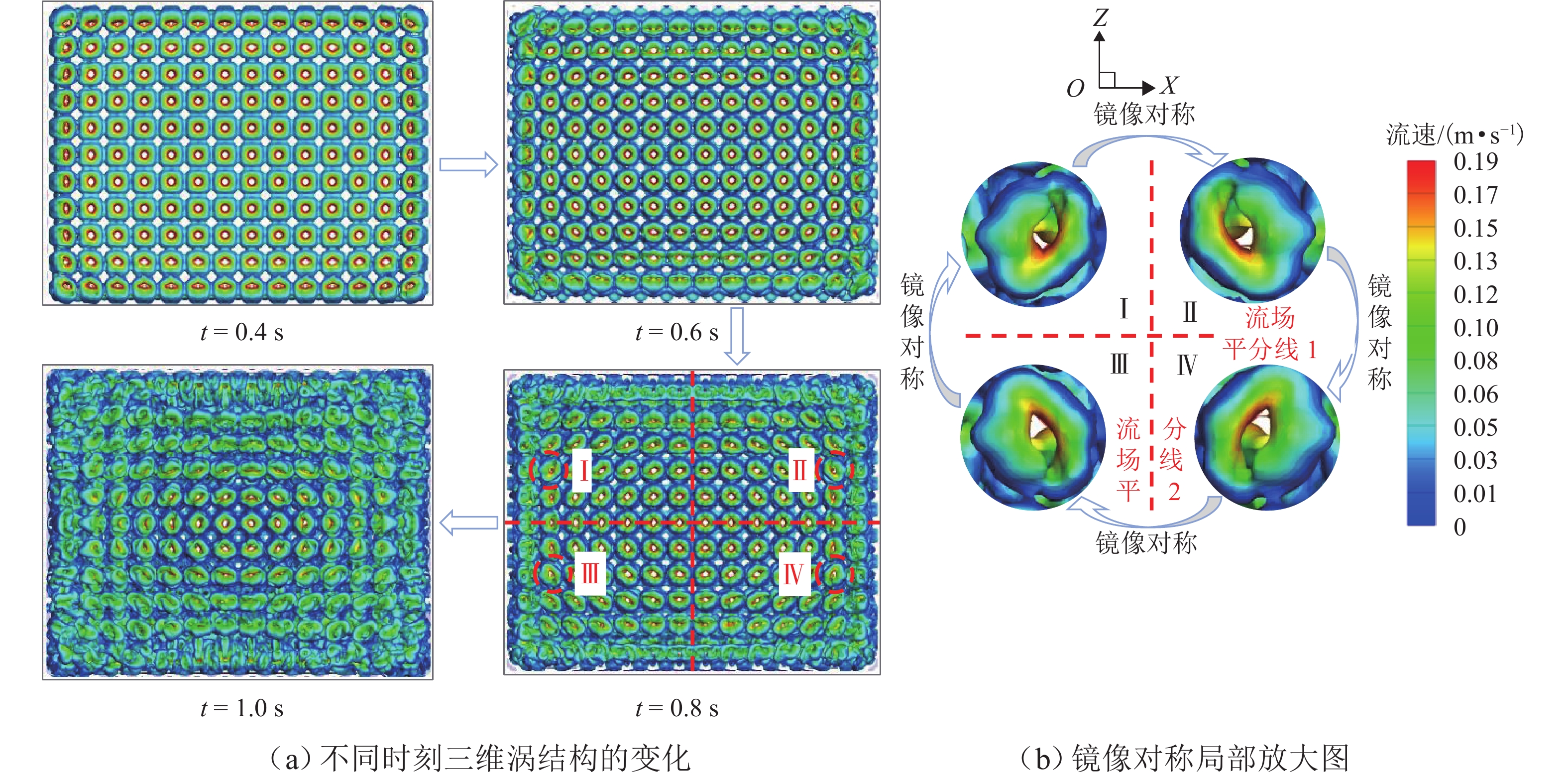
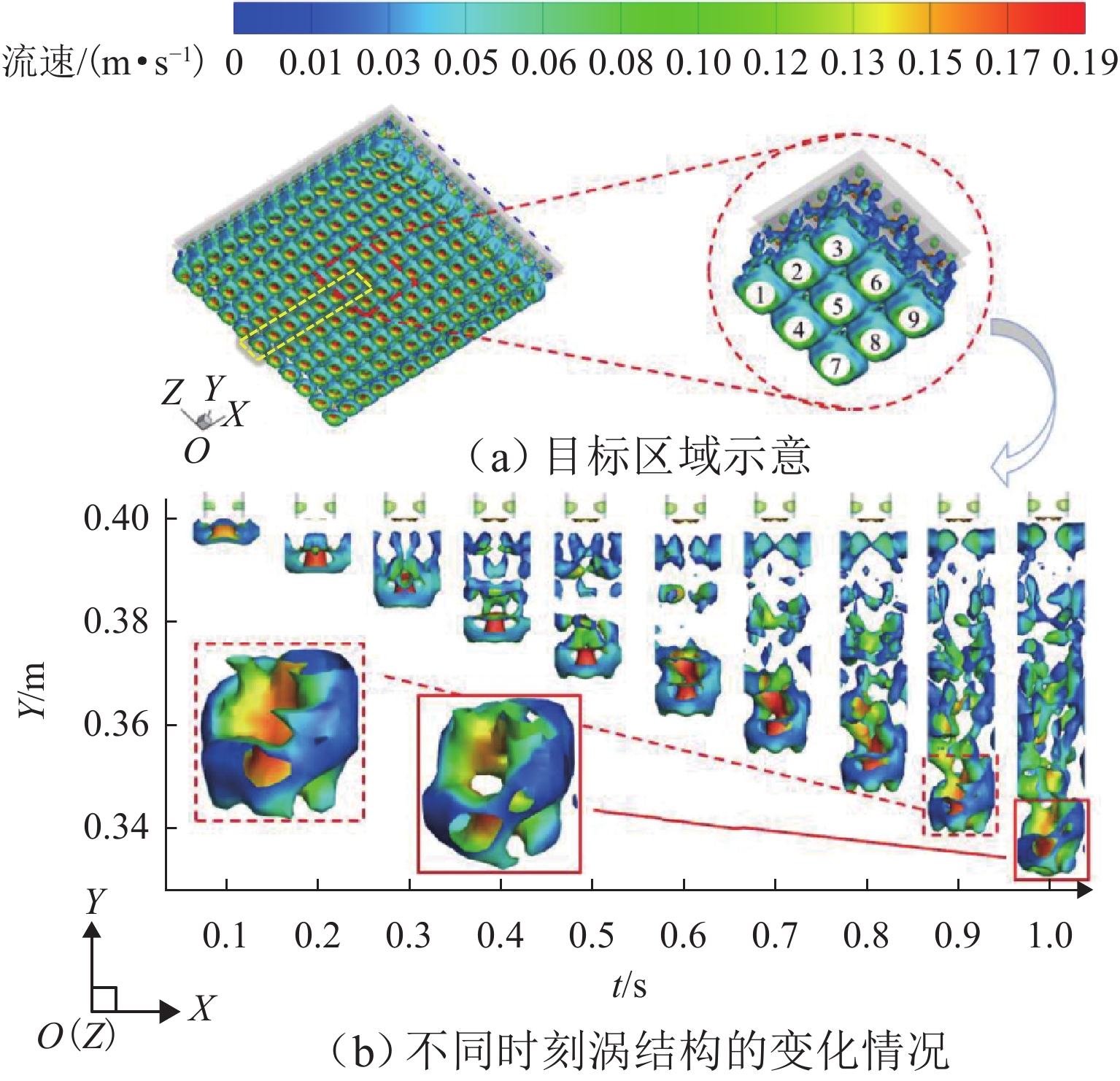
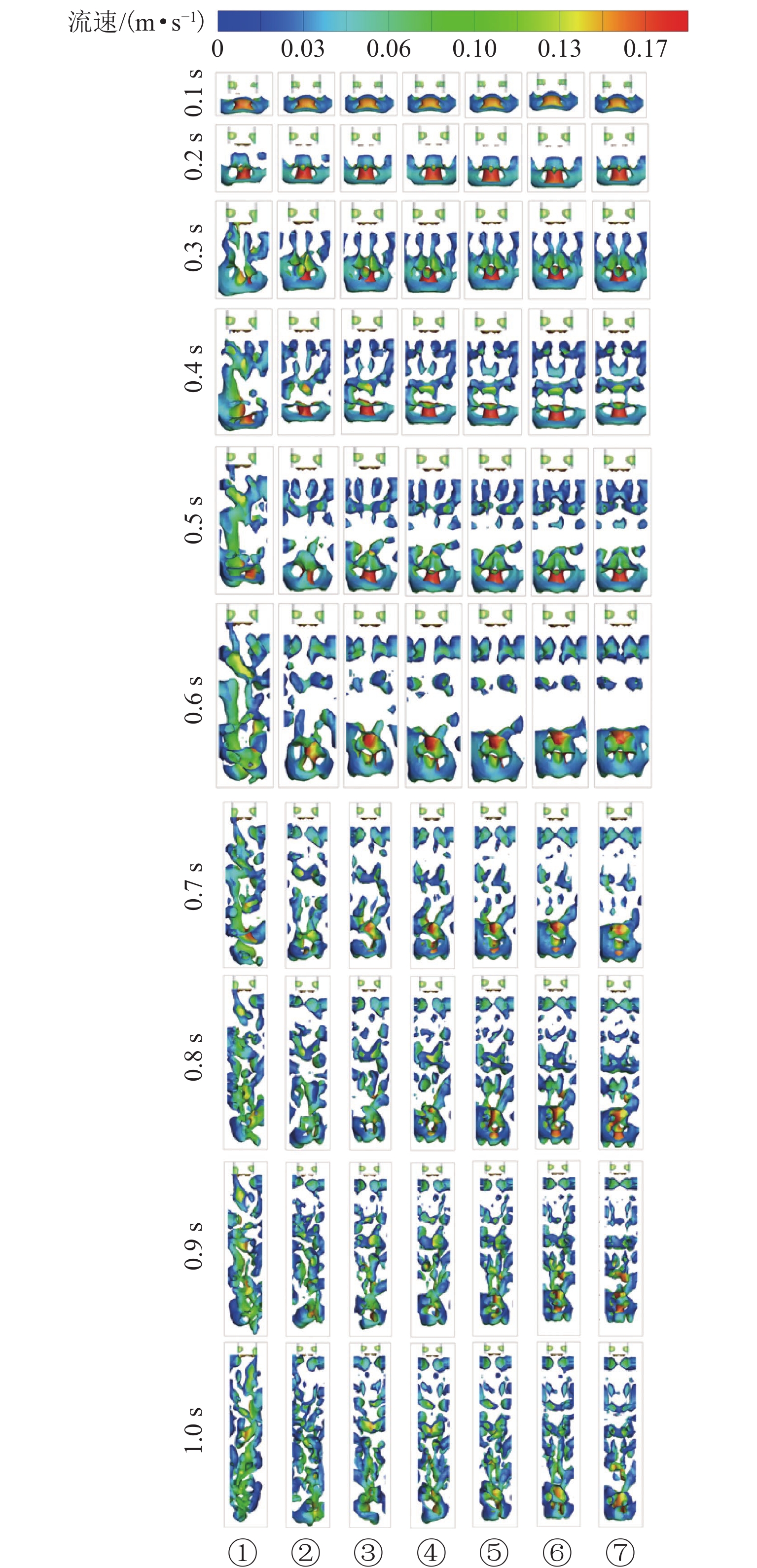
为探究网格絮凝池涡流中场射流涡结构的演化特征,采用大涡模拟(LES)对网格絮凝池涡流场进行瞬态模拟,从二维和三维的角度对网格涡流场进行研究. 结果表明:水流经过网格板后,立即在网孔后形成射流涡流场;在射流与背景流体间的剪切、卷吸和掺混作用下,格挡后方区域形成回流涡旋区,边壁处生成不断发展的涡环结构;这些涡环结构导致射流前端发生不同程度的变形与偏移,并抑其向前推进;涡旋主要分布在射流的边界层,其中射流前沿的涡结构聚集变化最快,其面积和强度最大,而靠近边壁处的涡结构强度变化最为显著,每一股射流的涡结构均关于射流轴心线呈镜像对称;此外,三维涡结构的前端形似一冠状结构,随射流向前发展,冠状结构会不断延伸、膨胀、变大,并最终离散和脱落;各时刻的涡结构分布与变化均表现出关于流场平分线的镜像对称性,且流场形态变化过程呈现出从边壁向流场中心发展的趋势.
Abstract:The large eddy simulation (LES) was employed to make a transient simulation of the flow field within the grid flocculation tank to investigate the evolutionary characteristics of the jet vortex flow structure of flow field within the grid flocculation tank. The grid flow field was analyzed from both two-dimensional and three-dimensional perspectives. The results indicate that a jet vortex flow field is formed immediately behind mesh holes as fluid flows through a grid plate. Due to shear, entrainment, and mixing between jet and background fluid, a backflow vortex zone is formed in the region behind the grid, accompanied by a continuously developing vortex ring structure along the side wall. The vortex ring structure causes varying degrees of deformation and displacement at the front of the jet, while also suppressing its forward movement. The vortices are mainly located within the boundary layer of the jet, with rapid changes occurring in their structure at its forefront. This area exhibits both maximum size and intensity. The most significant variations in vortex structure intensity are observed near the side wall, where the vortex structures of each jet display mirror symmetry about its axis. Additionally, the front of the three-dimensional vortex structure resembles a coronal formation. As the jet develops forward, the coronal structure will extend and swell to become larger and then will eventually discrete and detach. The distribution of vortex structure at each moment exhibits mirror symmetry with respect to the bisector of the flow field, while the variation process of the flow field morphology demonstrates a trend from the side wall towards the center of the flow field.
-
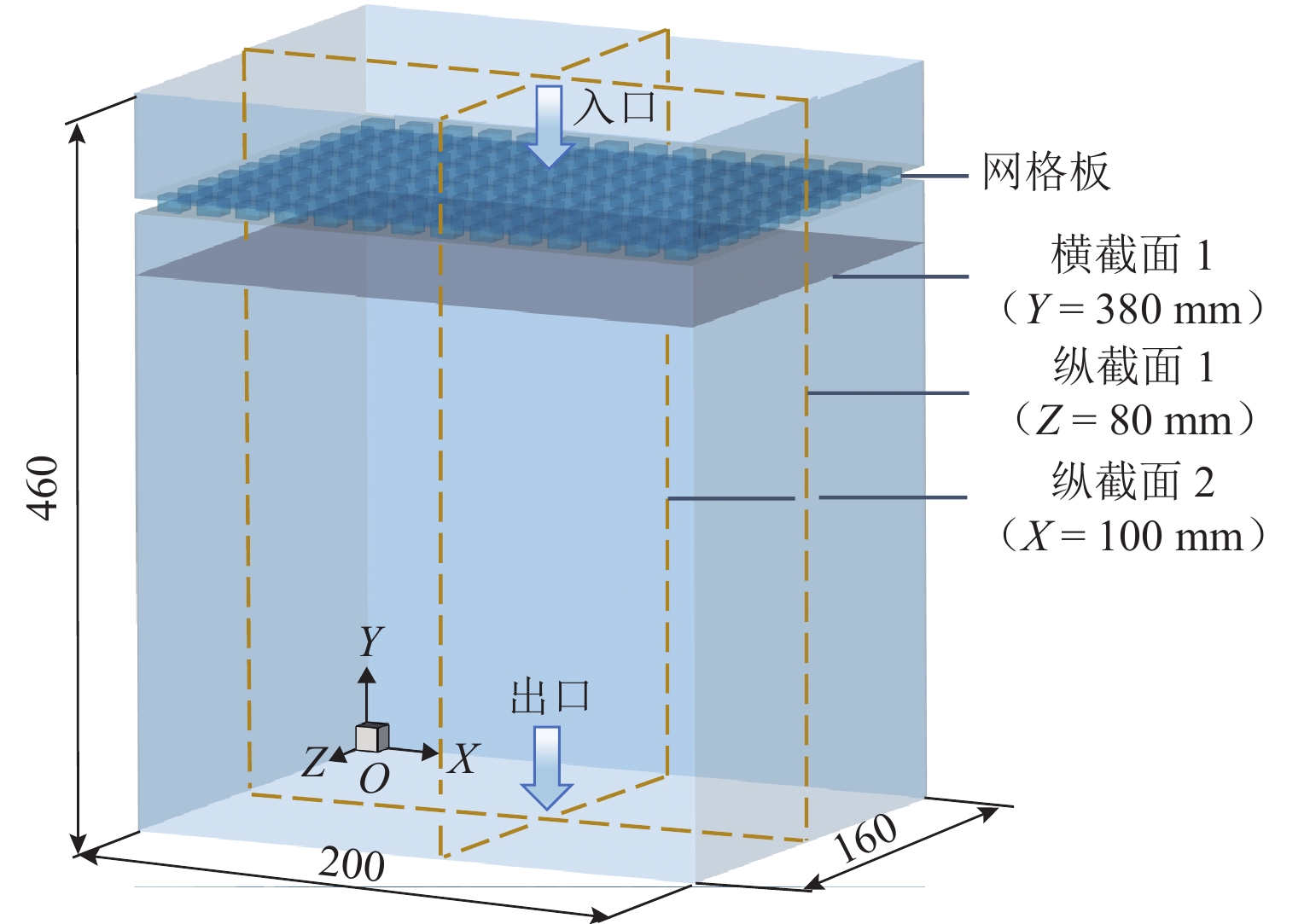
表 1 网格板尺寸参数
Table 1. Size parameters of
mm 编号 网格板的长、宽 网孔边长 格挡宽度 网格板厚度 1 200,160 8 4 5 2 200,160 8 6 5 3 200,160 8 8 5 4 200×160 8 10 5 5 200×160 8 12 5 -
[1] 常青. 絮凝动力学的现状与研究方法进展[J]. 环境科学学报, 2015, 35(10): 3042-3049.CHANG Qing. Current state of flocculation dynamics and methodology progress[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2015, 35(10): 3042-3049. [2] 毛玉红, 陈超, 王敏. Taylor-Couette波状涡的周期性特征研究[J]. 华中科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 52(4): 113-120.MAO Yuhong, CHEN Chao, WANG Min. Study on periodic characteristics of wavy vortex flow in Taylor-Couette[J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(4): 113-120. [3] 毛玉红, 陈超, 李亚蓉, 等. Taylor-Couette波状涡流场环隙波动的变化特征[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2025, 60(2): 425-433.MAO Yuhong, CHEN Chao, LI Yarong, et al. Fluctuation characteristics of wavy vortex field within annular gap in Taylor-Couette[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2025, 60(2): 425-433. [4] WU P J, WU A X, RUAN Z E, et al. Revealing the influence of additional structure on the flow field characteristics and flocculation performance in thickener feedwell through PIV experiments[J]. Powder Technology, 2024, 439: 119748. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2024.119748 [5] XIANG P, WAN Y H, WANG X, et al. Numerical simulation and experimental study of electrocoagulation grid flocculation tank[J]. Water Science and Technology, 2018, 78(3/4): 786-794. [6] BRAKNI O, KERKOUB Y, AMROUCHE F, et al. CFD investigation of the effect of flow field channel design based on constriction and enlargement configurations on PEMFC performance[J]. Fuel, 2024, 357: 129920. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2023.129920 [7] HUANG L, YUAN J L, PAN M, et al. CFD simulation and parameter optimization of the internal flow field of a disturbed air cyclone centrifugal classifier[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2023, 307: 122760. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2022.122760 [8] 伏雨, 龙云, 肖波, 等. 栅条絮凝池内部流场及颗粒运动状态模拟分析[J]. 环境工程, 2021, 39(4): 25-29, 85.FU Yu, LONG Yun, XIAO Bo, et al. Numerical simulation and analysis of flow field and particle motion in grid flocculation tank[J]. Environmental Engineering, 2021, 39(4): 25-29,85. [9] 刘存, 王庆涛, 陈翔宇, 等. 网格絮凝池结构参数对流场影响的数值模拟[J]. 水资源与水工程学报, 2018, 29(4): 162-167.LIU Cun, WANG Qingtao, CHEN Xiangyu, et al. Numerical simulation of the effect of the structure parameters on the flow field in grid flocculation tank[J]. Journal of Water Resources and Water Engineering, 2018, 29(4): 162-167. [10] FUREBY C. Towards the use of large eddy simulation in engineering[J]. Progress in Aerospace Sciences, 2008, 44(6): 381-396. doi: 10.1016/j.paerosci.2008.07.003 [11] 康啊真, 殷瑞涛, 祝兵, 等. 基于LES的跨海桥梁施工期围堰波流力数值模拟[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2020, 55(3): 537-544, 589.KANG Azhen, YIN Ruitao, ZHU Bing, et al. Numerical simulation of wave-current forces acting on cofferdam for sea-crossing bridge based on large eddy simulation[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2020, 55(3): 537-544,589. [12] 蒋媛, 刘锦阳, 回忆, 等. 水平肋板对高层建筑气动特性的影响研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2025, 60(5): 1-9.JIANG Yuan, LIU Jinyang, HUI Yi, et al. Study on the impact of horizontal ribs on the aerodynamic characteristics of high-rise building[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2025, 60(5): 1-9. [13] KANG M, JEON Y, YOU D. Neural-network-based mixed subgrid-scale model for turbulent flow[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2023, 962: A38. doi: 10.1017/jfm.2023.260 [14] 俞建阳, 王若玉, 陈浮, 等. 不同亚格子模型的对比分析及其运用[J]. 工程热物理学报, 2016, 37(11): 2311-2318.YU Jianyang, WANG Ruoyu, CHEN Fu, et al. A comparison of the different subgrid-scale models and its application[J]. Journal of Engineering Thermophysics, 2016, 37(11): 2311-2318. [15] MOSER R D, HAERING S W, YALLA G R. Statistical properties of subgrid-scale turbulence models[J]. Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics, 2021, 53: 255-286. doi: 10.1146/annurev-fluid-060420-023735 [16] WANG Y P, YUAN Z L, WANG J C. Ensemble data assimilation-based mixed subgrid-scale model for large-eddy simulations[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2023, 35(8): 085107. doi: 10.1063/5.0160482 [17] KIM M, PARK J, CHOI H. Large eddy simulation of flow over a circular cylinder with a neural-network-based subgrid-scale model[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2024, 984: A6. doi: 10.1017/jfm.2024.154 [18] 刘超群. Liutex-涡定义和第三代涡识别方法[J]. 空气动力学学报, 2020, 38(3): 413-431, 478.LIU Chaoqun. Liutex-third generation of vortex definition and identification methods[J]. Acta Aerodynamica Sinica, 2020, 38(3): 413-431, 478. [19] YU Y F, SHRESTHA P, ALVAREZ O, et al. Investigation of correlation between vorticity, Q, λci, λ2, Δ and liutex[J]. Computers & Fluids, 2021, 225: 104977. [20] 王义乾, 桂南. 第三代涡识别方法及其应用综述[J]. 水动力学研究与进展(A辑), 2019, 34(4): 413-429.WANG Yiqian, GUI Nan. A review of the third-generation vortex identification method and its applications[J]. Chinese Journal of Hydrodynamics, 2019, 34(4): 413-429. [21] LIU C Q, YU Y F. Mathematical foundation of liutex theory[J]. Journal of Hydrodynamics, 2022, 34(6): 981-993. doi: 10.1007/s42241-023-0091-2 [22] WANG D D, WANG Z H, FAN Y W, et al. Characterization of vortex structures with self-excited oscillations based on Liutex-Omega vortex identification method[J]. Journal of Hydrodynamics, 2023, 35(1): 95-111. doi: 10.1007/s42241-023-0011-5 [23] 王颖, 张巧玲, 杨振东. 多孔口紊动浮射流[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2021. [24] 曹建明. 射流的不稳定性理论[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2022. [25] HUANG G Y, LV X, CHEN W G, et al. Generation of nearly homogeneous isotropic turbulence using a novel oscillating grid system[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2024, 36(3): 035129. doi: 10.1063/5.0194089 -




 下载:
下载: