Online Identification of Ship Motion in Different Maneuvering Conditions
-
摘要:
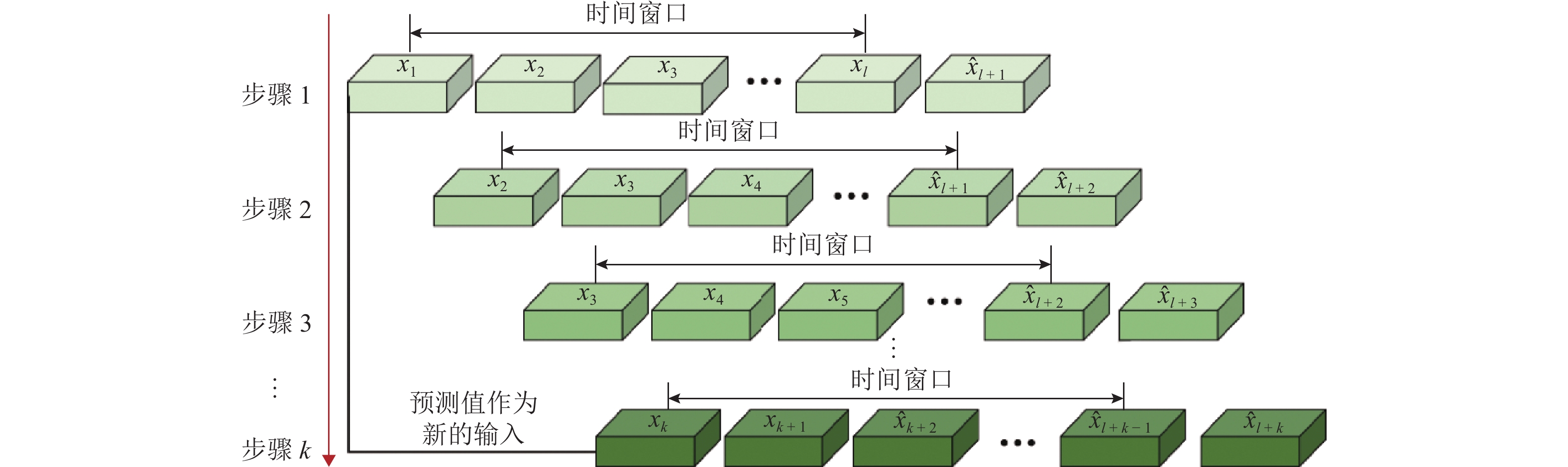
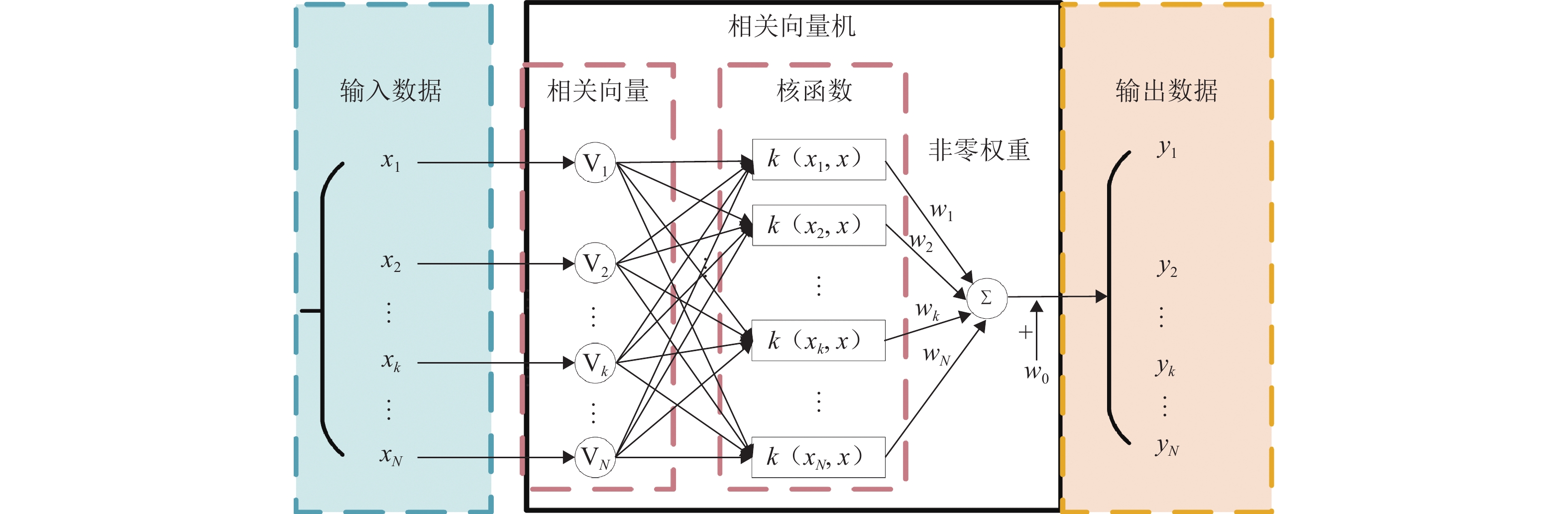
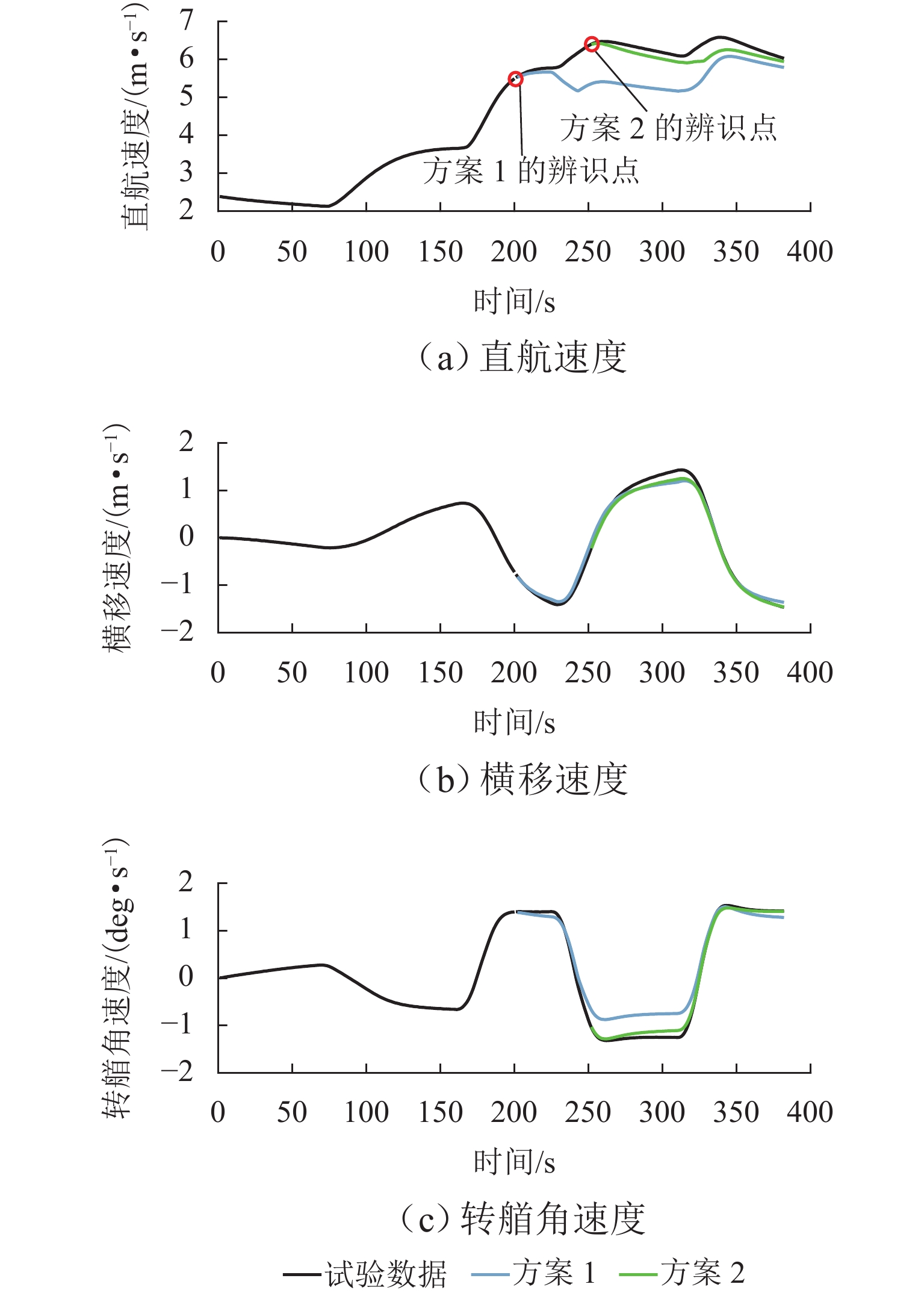
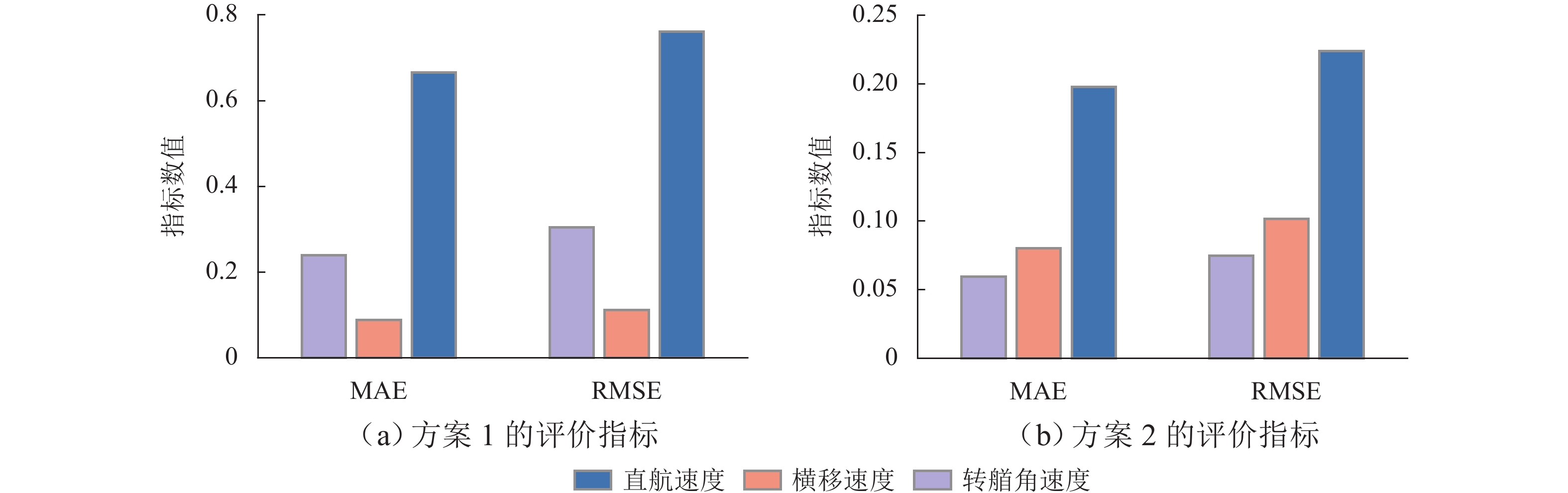
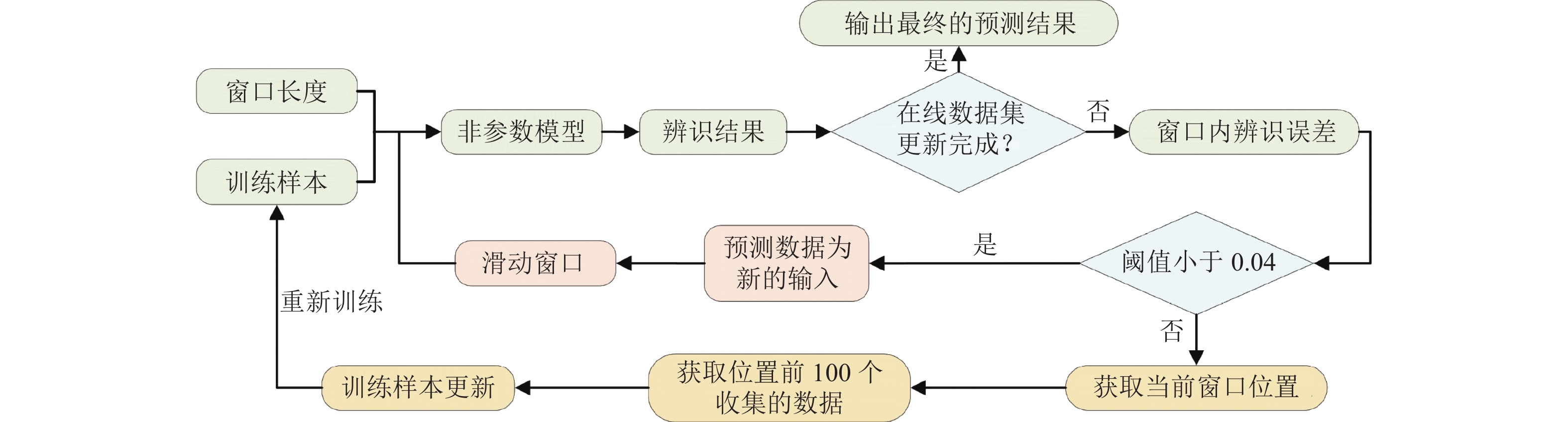
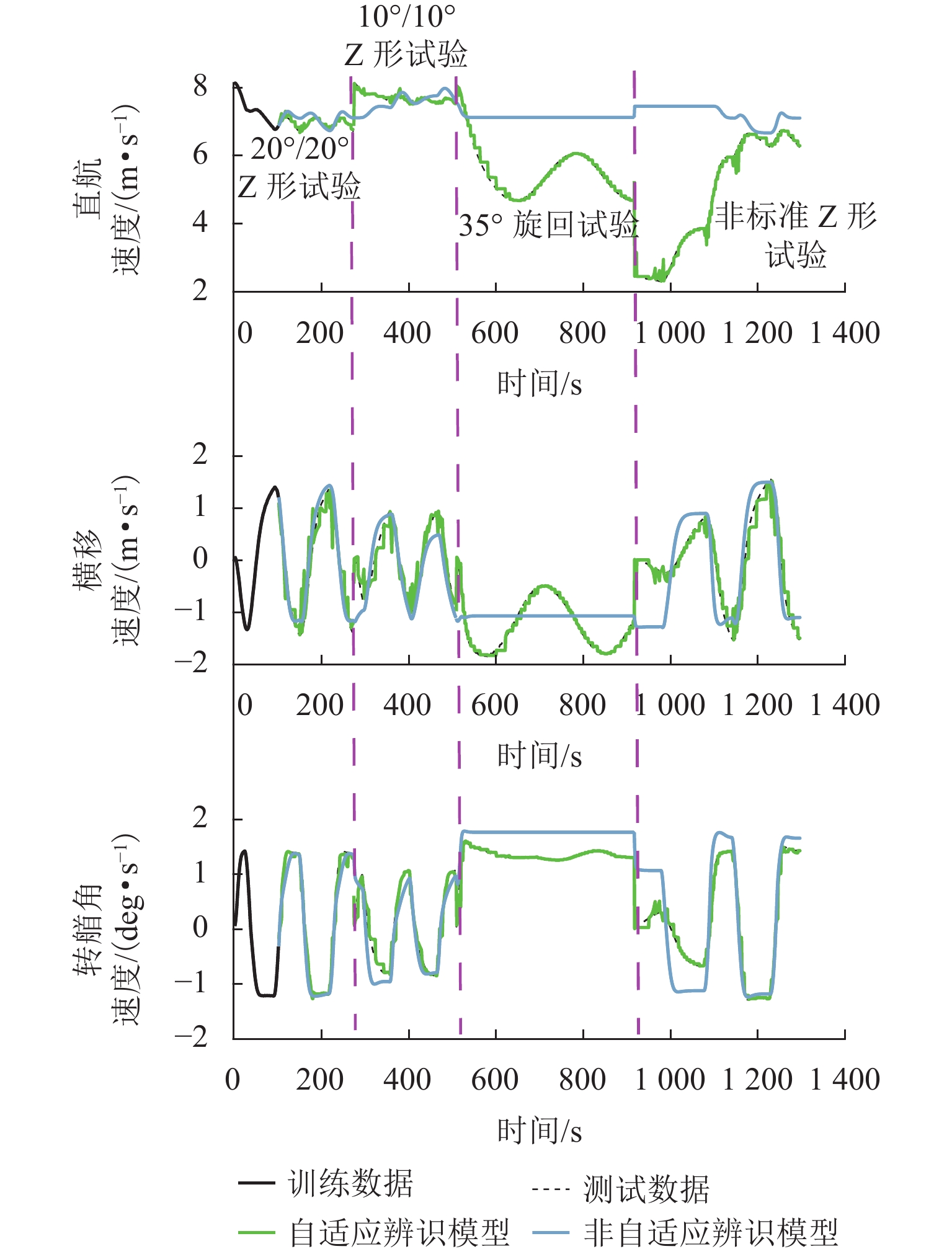
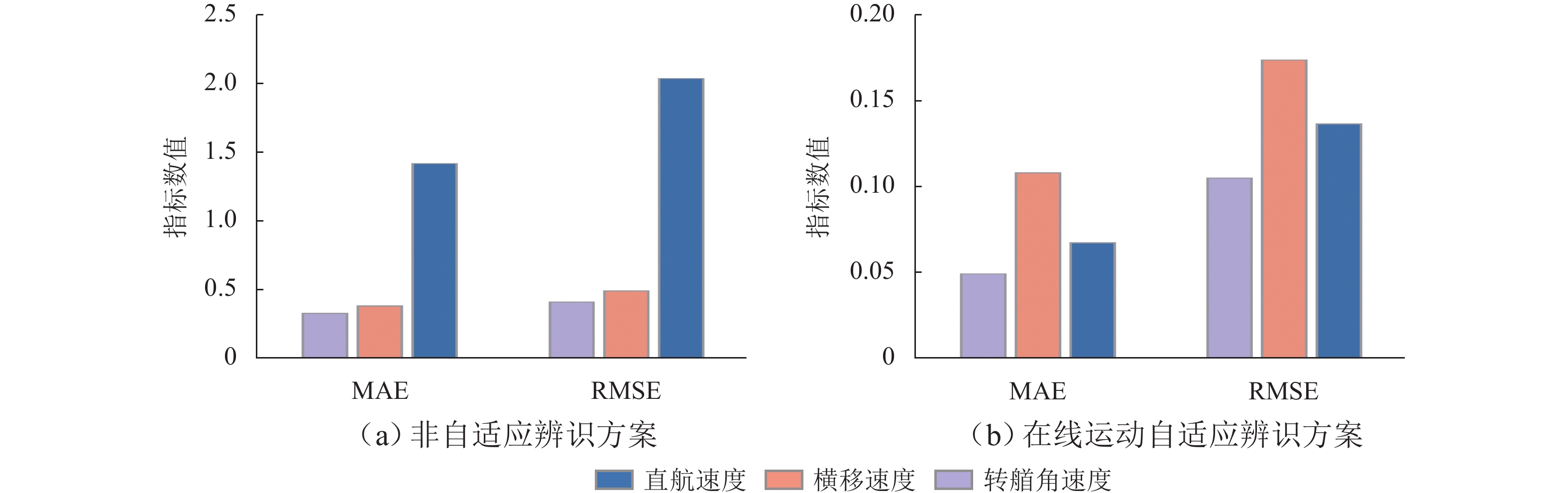
为提高船舶运动辨识建模的准确性和船舶在航行过程中的自主性和安全性,建立了适用于不同操纵工况下的船舶运动在线非参数模型. 首先,鉴于不同操纵条件下船舶航行特征的复杂性和在线非参数辨识的挑战,结合滑动时间窗和相关向量机,提出一种自适应更新的船舶运动非参数辨识方法;其次,通过2种不同的训练样本选择方案,验证基于相关向量机的离线非参数辨识模型的有效性,并强调训练样本质量的重要性;最后,基于所提辨识方法以及自适应非参数模型更新准则,实现3自由度船舶运动状态、航向角以及运动轨迹的在线非参数辨识,并将所提方案的辨识结果与非自适应辨识方案得到的结果进行对比. 试验结果表明:所提方案能够根据操纵工况的变化自适应更新非参数模型,其辨识结果的平均绝对误差和均方根误差分别小于0.11和0.18,而非自适应辨识结果的2种评价指标分别小于1.43和2.10,充分验证了所提方案在泛化性方面的显著优势,展现出更高的辨识精度,并进一步证明其在多种不同操纵工况下的适用性.
-
关键词:
- 船舶运动建模 /
- 船舶运动非参数辨识 /
- 在线自适应非参数模型 /
- 滑动时间窗 /
- 相关向量机
Abstract:An online non-parametric model for ship motion applicable to various maneuvering conditions was developed to enhance the accuracy of ship motion identification modeling and the autonomy and safety of ships during navigation. Firstly, given the complexity of ship navigation characteristics in different maneuvering conditions and challenges of online non-parametric identification, an adaptively updated ship motion non-parametric identification method was proposed by combining the sliding time window and relevance vector machine (RVM). Secondly, the effectiveness of offline non-parametric identification models based on RVM was validated via two different training sample selection schemes, with the importance of training sample quality emphasized. Finally, based on the proposed identification method and adaptive non-parametric model updating rule, online non-parametric identification for the three-degree-of-freedom ship motion states, course, and motion trajectory was conducted, and the identification results of the proposed scheme were compared with those of the non-adaptive identification scheme. The experimental results show that the proposed scheme can adaptively update the non-parametric model according to maneuvering condition changes. The mean absolute error (MAE) and root mean square error (RMSE) of the proposed scheme’s identification results are less than 0.11 and 0.18 respectively, while the MAE and RMSE of the non-adaptive method’s identification results are below 1.43 and 2.10 respectively. This fully validates the proposed scheme’s significant advantages in generalization, demonstrating higher identification accuracy and further confirming its applicability in various maneuvering conditions.
-
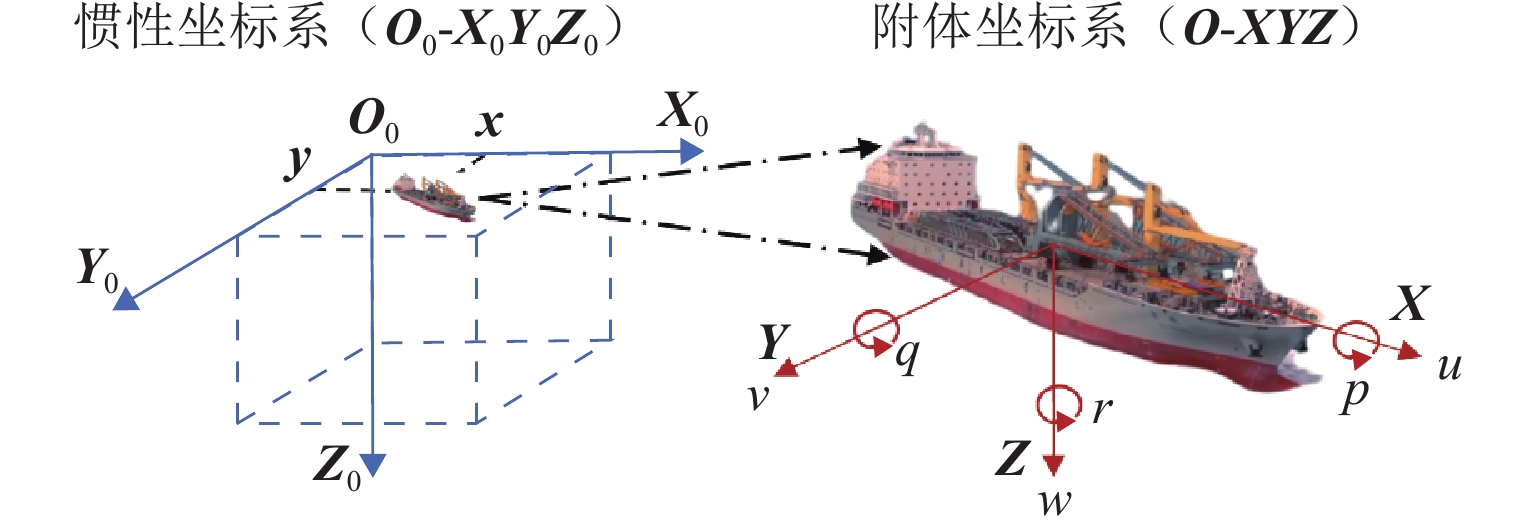
表 1 所用船舶主尺度参数
Table 1. Main particulars of the employed ship
主尺度 两柱间长L/m 船宽/m 平均吃水/m 方形系数 排水体积/m3 数值 130 19 4.5 0.4053 450 5 表 2 在线船舶运动数据集
Table 2. Online ship motion dataset
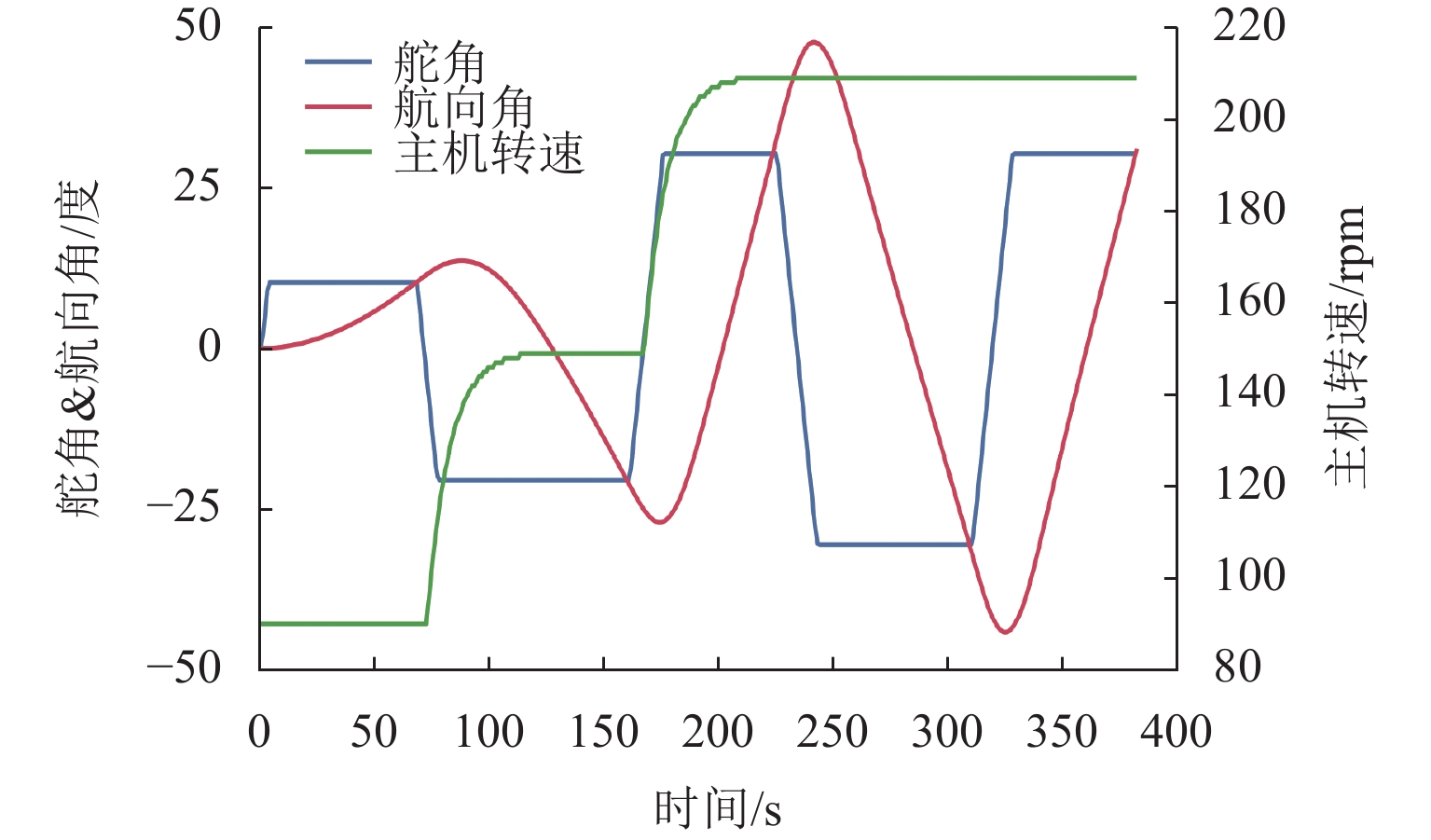
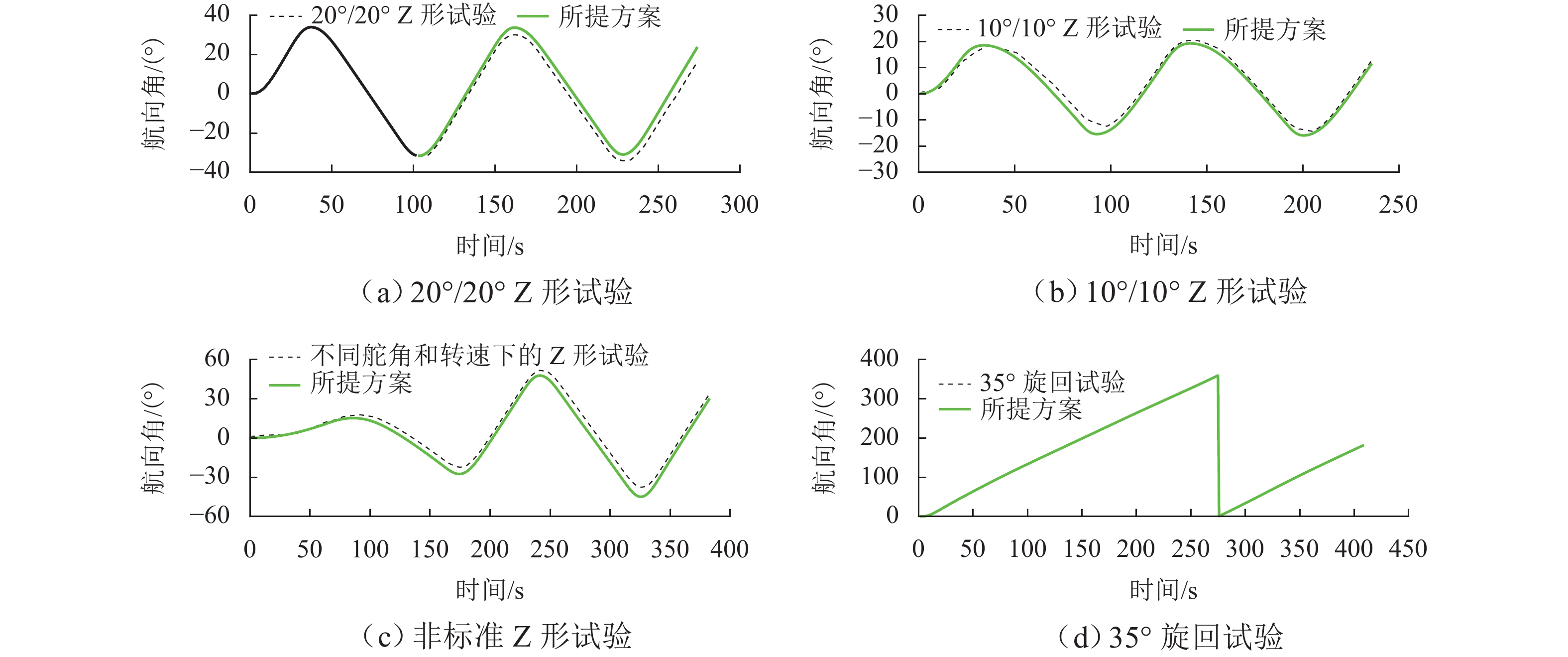
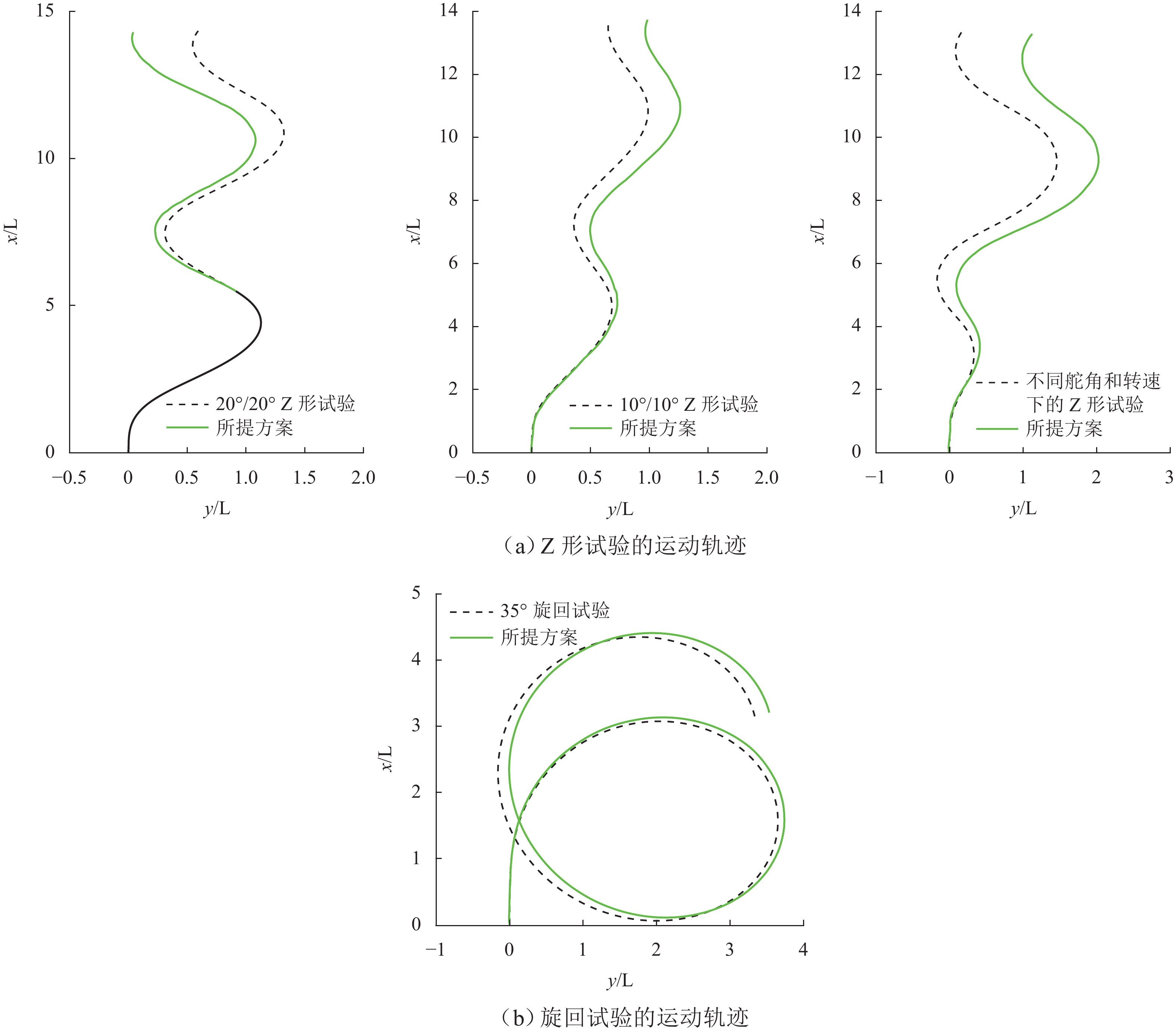
试验类型 10°/10° Z形试验 20°/20° Z形试验 非标准 Z形试验 35° 旋回试验 样本数量/个 235 273 384 408 -
[1] 梅瀚雨, 廖海黎, 王昌将. 基于自编码器的非线性气动力辨识及非线性颤振分析[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2025, 60(3): 599-607. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20230261MEI Hanyu, LIAO Haili, WANG Changjiang. Nonlinear aerodynamic force identification and nonlinear flutter analysis based on autoencoder[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2025, 60(3): 599-607. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20230261 [2] 丰富, 胡海林, 钟德鸣, 等. 基于改进互联型全阶观测器的直线感应电机在线参数辨识[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2024, 59(4): 776-785. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20230507FENG Fu, HU Hailin, ZHONG Deming, et al. Online parameter identification of linear induction motors based on improved interconnected full-order observer[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2024, 59(4): 776-785. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20230507 [3] 张显库, 祝慧颖. 基于正弦函数处理新息的船舶模型参数辨识新算法[J]. 中国舰船研究, 2021, 16(5): 158-162. doi: 10.19693/j.issn.1673-3185.02122ZHANG Xianku, ZHU Huiying. New identification algorithm for ship model parameters based on sinusoidal function processing innovation[J]. Chinese Journal of Ship Research, 2021, 16(5): 158-162. doi: 10.19693/j.issn.1673-3185.02122 [4] 朱曼, 文元桥, 孙吴强, 等. 一种基于扩展状态观测器的智能船舶Nomoto模型参数辨识方法[J]. 中国舰船研究, 2023, 18(3): 75-85. doi: 10.19693/j.issn.1673-3185.02552ZHU Man, WEN Yuanqiao, SUN Wuqiang, et al. Extended state observer-based parameter identification of Nomoto model for autonomous vessels[J]. Chinese Journal of Ship Research, 2023, 18(3): 75-85. doi: 10.19693/j.issn.1673-3185.02552 [5] SONG C Y, ZHANG X K, ZHANG G Q. Nonlinear identification for 4-DOF ship maneuvering modeling via full-scale trial data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2021, 69(2): 1829-1835. doi: 10.1109/tie.2021.3062255 [6] 谢朔, 陈德山, 初秀民, 等. 改进多新息卡尔曼滤波法辨识船舶响应模型[J]. 哈尔滨工程大学学报, 2018, 39(2): 282-289. doi: 10.11990/jheu.201610070XIE Shuo, CHEN Deshan, CHU Xiumin, et al. Identification of ship response model based on improved multi-innovation extended Kalman filter[J]. Journal of Harbin Engineering University, 2018, 39(2): 282-289. doi: 10.11990/jheu.201610070 [7] ZHU M, SUN W Q, HAHN A, et al. Adaptive modeling of maritime autonomous surface ships with uncertainty using a weighted LS-SVR robust to outliers[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2020, 200: 107053. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2020.107053 [8] CHEN L J, YANG P Y, LI S W, et al. Grey-box identification modeling of ship maneuvering motion based on LS-SVM[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2022, 266: 112957. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2022.112957 [9] LUO W L, ZHANG Z C. Modeling of ship maneuvering motion using neural networks[J]. Journal of Marine Science and Application, 2016, 15(4): 426-432. doi: 10.1007/s11804-016-1380-8 [10] 王惠琴, 郭瑞丽, 何永强, 等. 基于NGO优化的CNN-BiLSTM-AM滑坡位移预测模型[J/OL]. 西南交通大学学报, 2025: 1-12. (2025-02-26). https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=XNJT2025022500A&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ. [11] 令晓明, 张真, 刘燕山, 等. 多尺度相关的iAFF-Res2Net声纹识别模型[J/OL]. 西南交通大学学报, 2024: 1-9. (2024-10-31). https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=XNJT20241030007&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ. [12] ZHANG Y Y, WANG Z H, ZOU Z J. Black-box modeling of ship maneuvering motion based on multi-output nu-support vector regression with random excitation signal[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2022, 257: 111279. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2022.111279 [13] NIE Z H, SHEN F, XU D J, et al. An EMD-SVR model for short-term prediction of ship motion using mirror symmetry and SVR algorithms to eliminate EMD boundary effect[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2020, 217: 107927. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2020.107927 [14] JIANG L C, SHANG X B, JIN B, et al. Black-box modeling of ship maneuvering motion using multi-output least-squares support vector regression based on optimal mixed kernel function[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2024, 293: 116663. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2023.116663 [15] ZHANG X F, MENG Y, LIU Z C, et al. Modified grey wolf optimizer-based support vector regression for ship maneuvering identification with full-scale trial[J]. Journal of Marine Science and Technology, 2022, 27(1): 576-588. doi: 10.1007/s00773-021-00858-2 [16] 裴天琪, 于曹阳, 钟一鸣, 等. 基于改进加权最小二乘支持向量机的X舵潜水器操纵运动模型辨识[J]. 中国造船, 2023, 64(2): 1-12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4882.2023.02.001PEI Tianqi, YU Caoyang, ZHONG Yiming, et al. Parameter identification for maneuvering model of underwater vehicle with X-rudder based on improved WLSSVM[J]. Shipbuilding of China, 2023, 64(2): 1-12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4882.2023.02.001 [17] ZHANG T, ZHENG X Q, LIU M X. Multiscale attention-based LSTM for ship motion prediction[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2021, 230: 109066. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2021.109066 [18] 董磊, 马翔, 封佳祥, 等. 基于改进LSTM的船舶操纵运动在线预报方法研究[J]. 中国造船, 2023, 64(2): 184-198. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4882.2023.02.017DONG Lei, MA Xiang, FENG Jiaxiang, et al. Online prediction method of ship maneuvering motion based on improved long-short term memory neural network[J]. Shipbuilding of China, 2023, 64(2): 184-198. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4882.2023.02.017 [19] JIANG Y, HOU X R, WANG X G, et al. Identification modeling and prediction of ship maneuvering motion based on LSTM deep neural network[J]. Journal of Marine Science and Technology, 2022, 27(1): 125-137. doi: 10.1007/s00773-021-00819-9 [20] 王小敏, 熊旭洲, 杨勇, 等. 基于轨出电压暂态特征的轨道电路分路不良识别[J/OL]. 西南交通大学学报, 2025: 1-9. (2025-01-02). https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=XNJT2024123000C&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ. [21] XUE Y F, CHEN G, LI Z T, et al. Online identification of a ship maneuvering model using a fast noisy input Gaussian process[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2022, 250: 110704. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2022.110704 [22] OUYANG Z L, LIU S Y, ZOU Z J. Nonparametric modeling of ship maneuvering motion in waves based on Gaussian process regression[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2022, 264: 112100. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2022.112100 [23] 白伟伟, 任俊生, 李铁山, 等. 基于局部最优LWL的船舶操纵运动辨识建模[J]. 哈尔滨工程大学学报, 2017, 38(5): 676-683. doi: 10.11990/jheu.201512082BAI Weiwei, REN Junsheng, LI Tieshan, et al. Locally optimal-based LWL identification modeling for ship manoeuvring motion[J]. Journal of Harbin Engineering University, 2017, 38(5): 676-683. doi: 10.11990/jheu.201512082 [24] ZHANG Z, REN J S, BAI W W. MIMO non-parametric modeling of ship maneuvering motion for marine simulator using adaptive moment estimation locally weighted learning[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2022, 261: 112103. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2022.112103 [25] MENG Y, ZHANG X K, ZHANG X F, et al. Weighted multi-kernel relevance vector machine for 3 DOF ship manoeuvring modeling with full-scale trial data[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2023, 273: 113969. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2023.113969 [26] CHEN Z W, ZHANG S Y, SHI N, et al. Online state-of-health estimation of lithium-ion battery based on relevance vector machine with dynamic integration[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2022, 129: 109615. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2022.109615 [27] MENG Y, ZHANG X K, ZHANG G Q, et al. Sparse Bayesian relevance vector machine identification modeling and its application to ship maneuvering motion prediction[J]. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 2023, 11(8): 1572. doi: 10.3390/jmse11081572 -




 下载:
下载: