Management and Monitoring Suggestions for Beam-end Integration Device in Long-span High-speed Railway Bridge Based on Data Analysis and Physical Modeling
-
摘要:
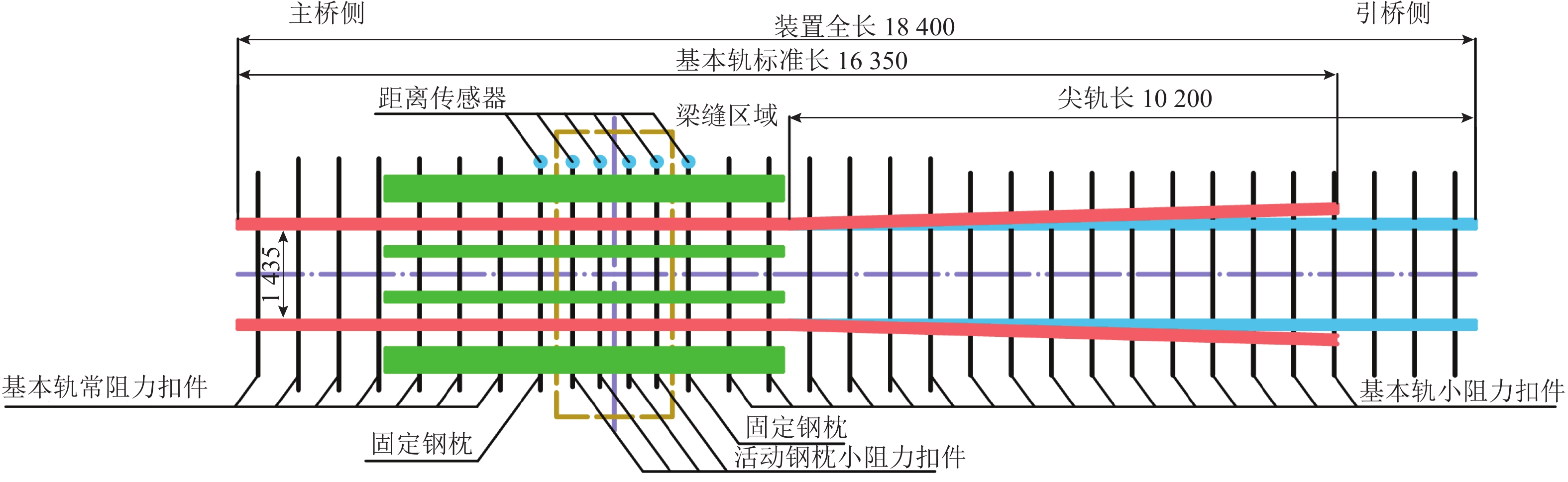
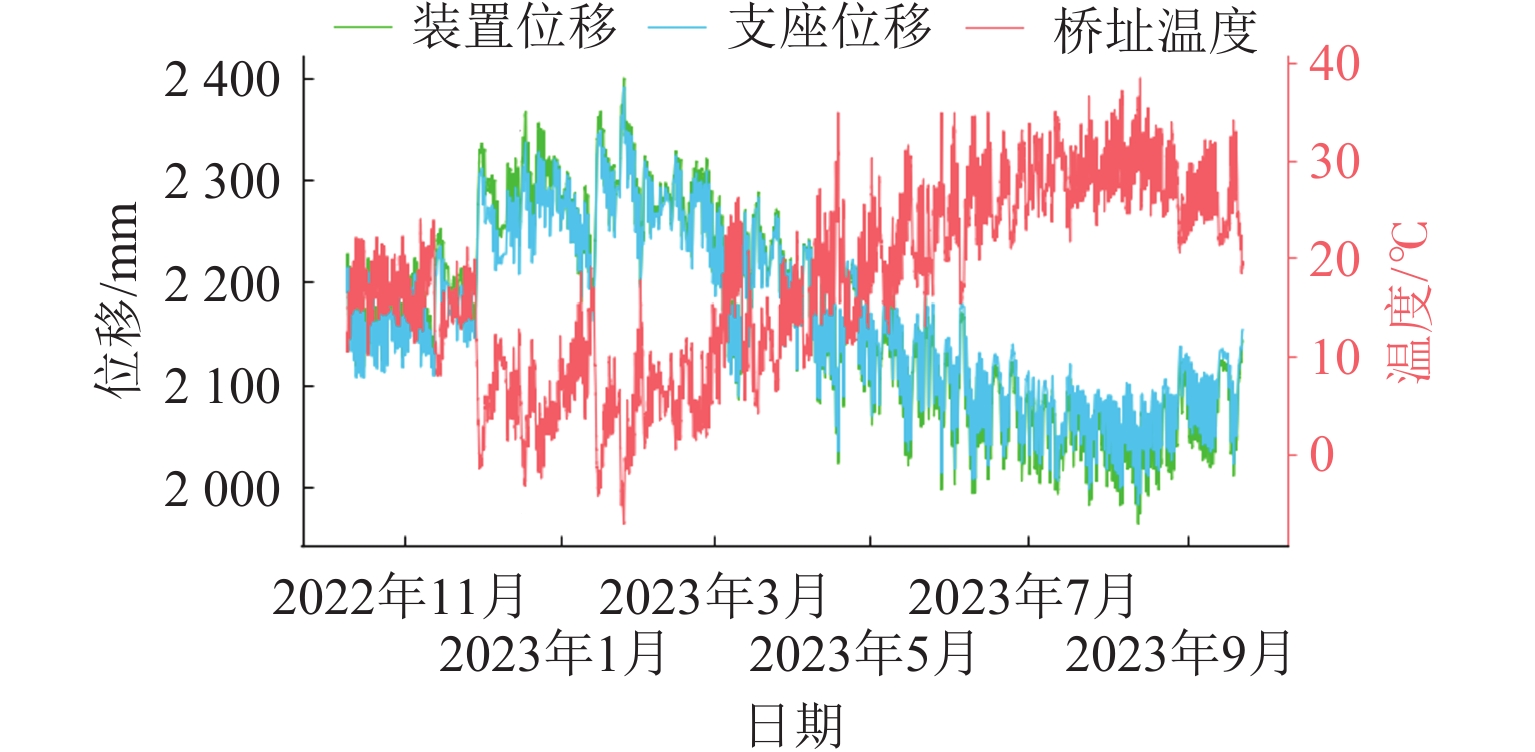
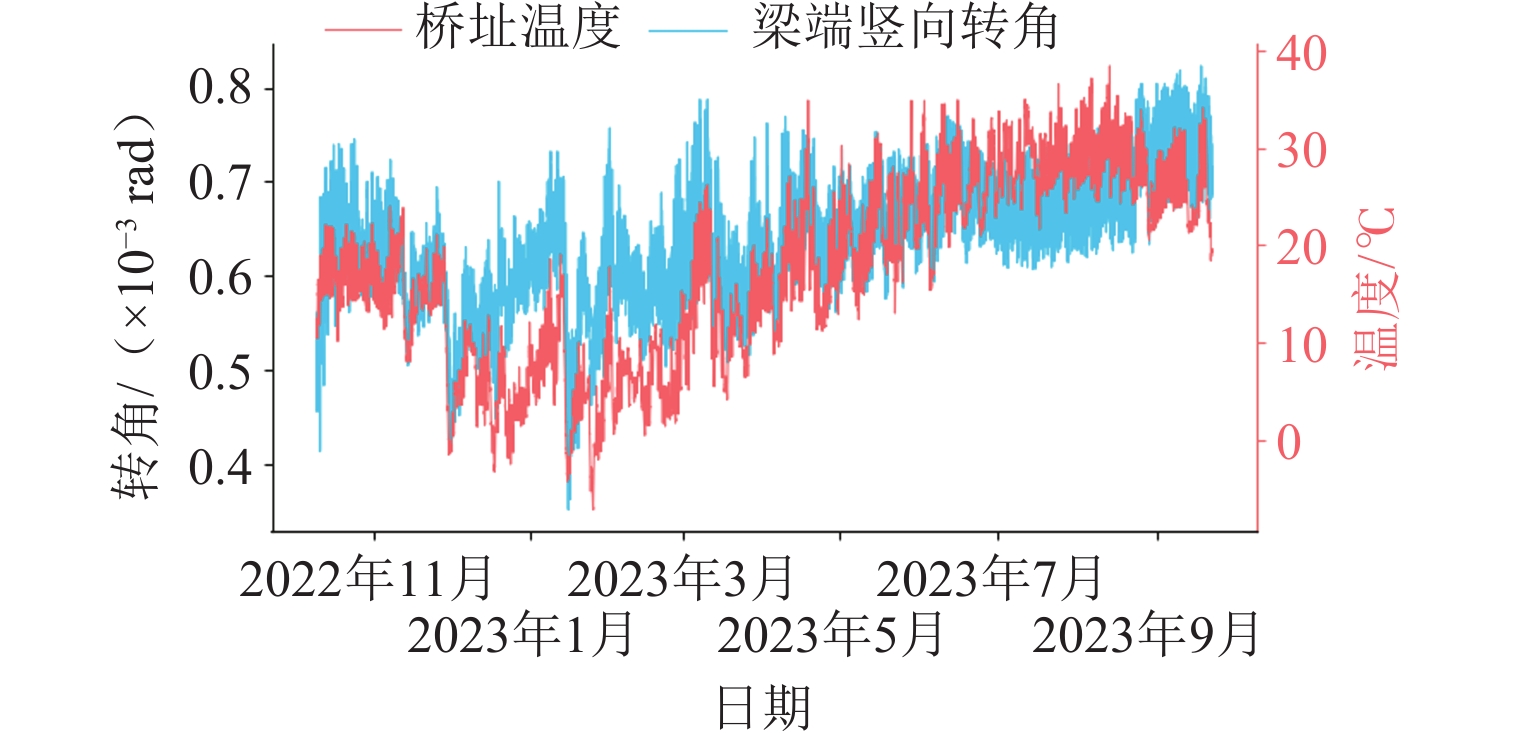
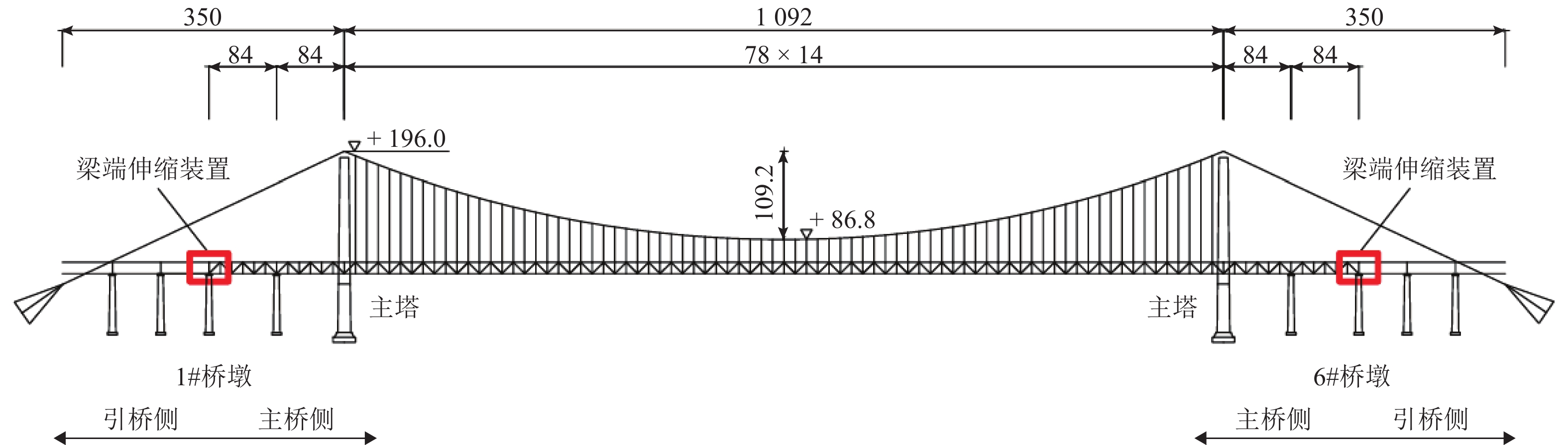
高速铁路大跨度桥梁梁端一体化装置结构复杂,易出现结构性轨道不平顺峰值,直接影响列车平稳运行,且目前缺乏针对性的相关管理标准. 为此,开展对梁端一体化装置监测管理值的研究,分析近年梁端监测数据,建立梁端一体化装置的有限元模型,并基于静态不平顺标准仿真得出梁端纵向伸缩、横向位移、下挠转角及固定钢枕抬升、钢轨空吊监测管理值建议,针对250 km/h行车速度,提出的Ⅰ级监测管理建议值分别为:梁端纵向压缩160 mm、横向位移7 mm、下挠转角3‰ rad,以及固定钢枕抬升3 mm、空吊2 mm. 结果表明:监测管理值能够判断装置是否出现异常,梁端纵向压缩对高低和轨距不平顺影响较大,横向位移对轨距影响较大,固定钢枕空吊和抬升会对轨道高低产生影响. 提出的梁端监测管理值可为高速铁路大跨度桥梁的运营维修提供参考依据.
Abstract:Beam-end integration devices in long-span high-speed railway bridges have complex structures and are prone to generating peak structural track irregularities, which directly affect train running stability. However, targeted monitoring and management criteria for such devices are currently lacking. In this study, monitoring management values for beam-end integration devices are investigated. Monitoring data collected in recent years are analyzed, and a finite element model of the beam-end integration device is established. Based on static irregularity standards, simulation analyses are conducted to propose monitoring management values for beam-end longitudinal displacement, lateral displacement, deflection angle, and fixed steel sleeper lifting and unsupported sleeper. For an operational speed of 250 km/h, the proposed Class Ⅰ monitoring management thresholds are as follows: beam-end longitudinal compression of 160 mm, lateral displacement of 7 mm, deflection angle of 3‰ rad, fixed steel sleeper lifting of 3 mm, and unsupported sleeper of 2 mm. The results show that the proposed monitoring management values can effectively identify abnormal conditions of the device. Longitudinal compression at the beam end significantly affects track profile and gauge irregularities; lateral displacement primarily influences gauge irregularity; both the fixed steel sleeper unsupported section and lifting impact track profile irregularity. The proposed monitoring management values provide a reference for the operation and maintenance of long-span high-speed railway bridges.
-
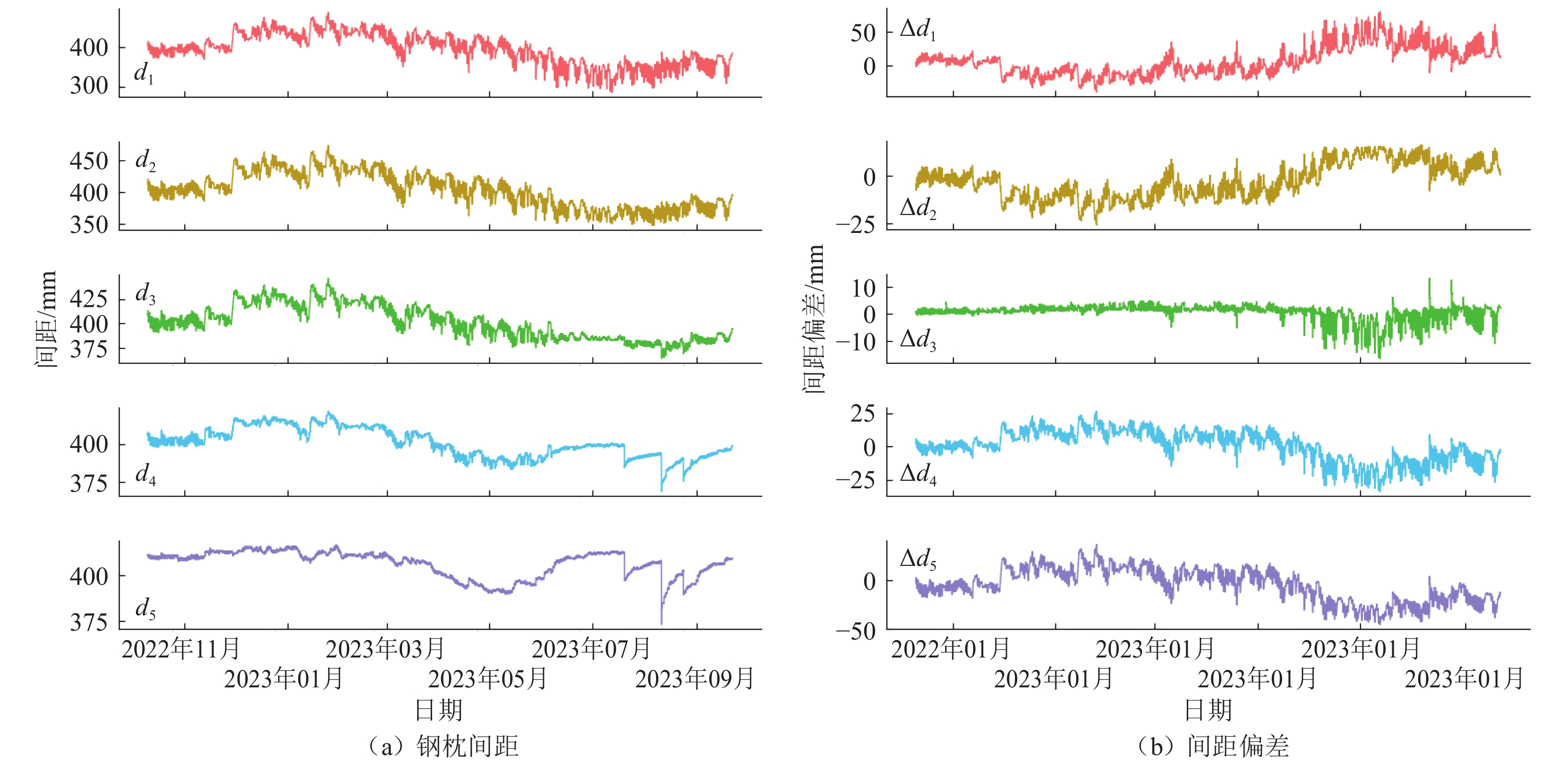
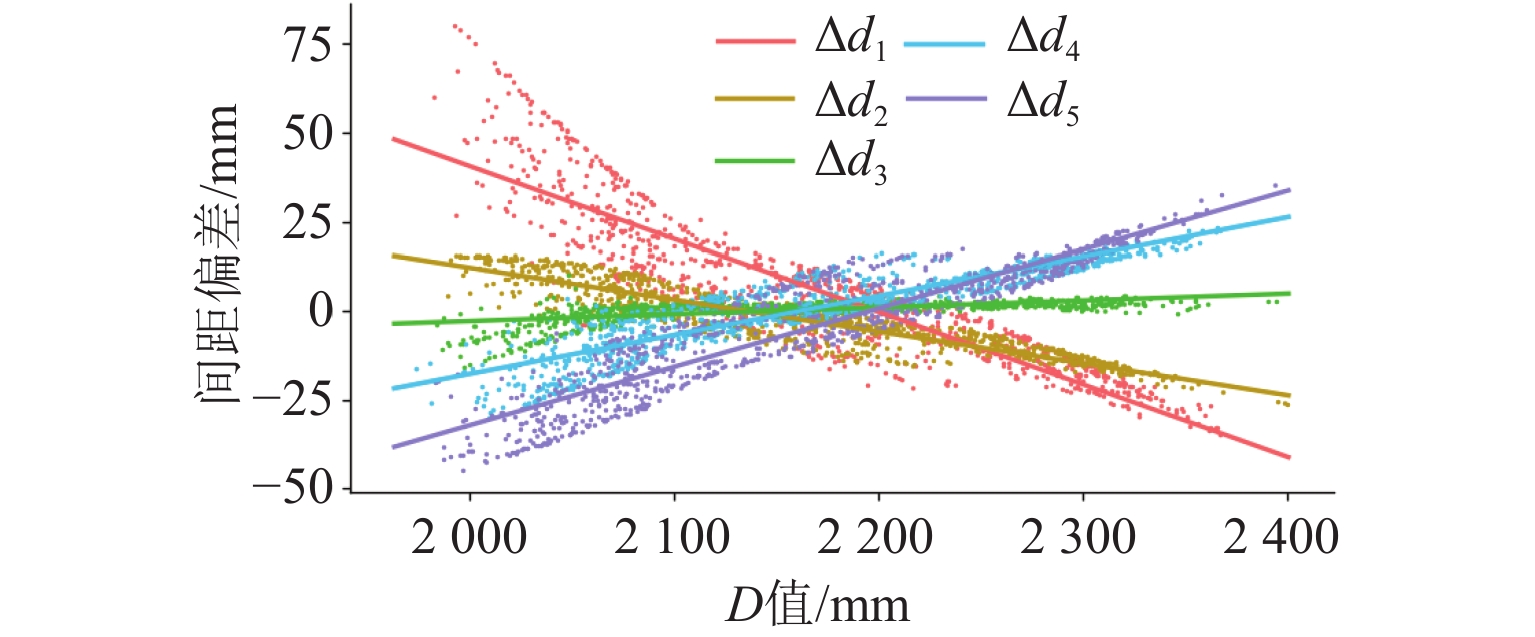
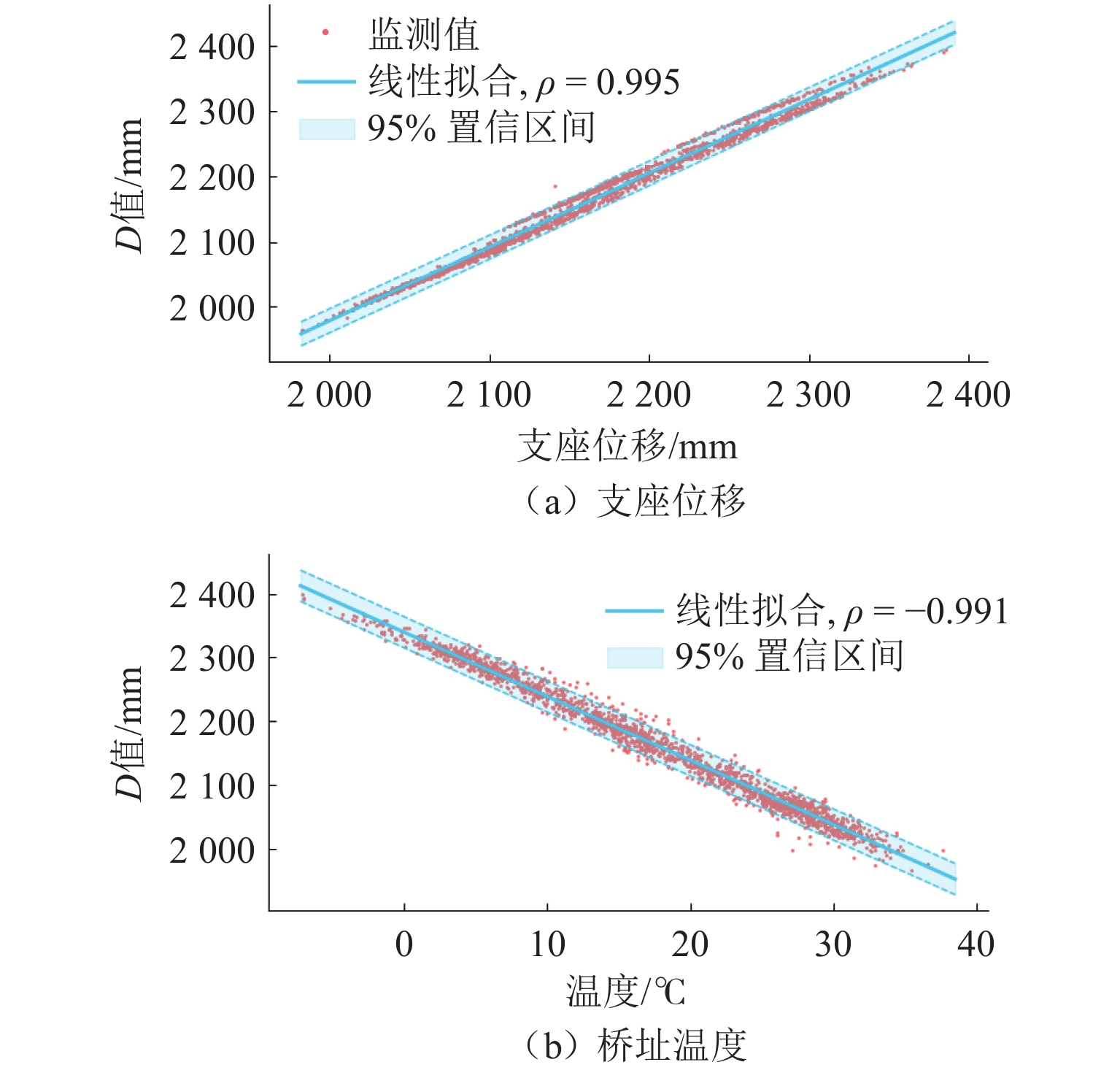
表 1 钢枕间距偏差与D值线性拟合结果
Table 1. Linear fitting results between steel sleeper spacing deviation with D-value
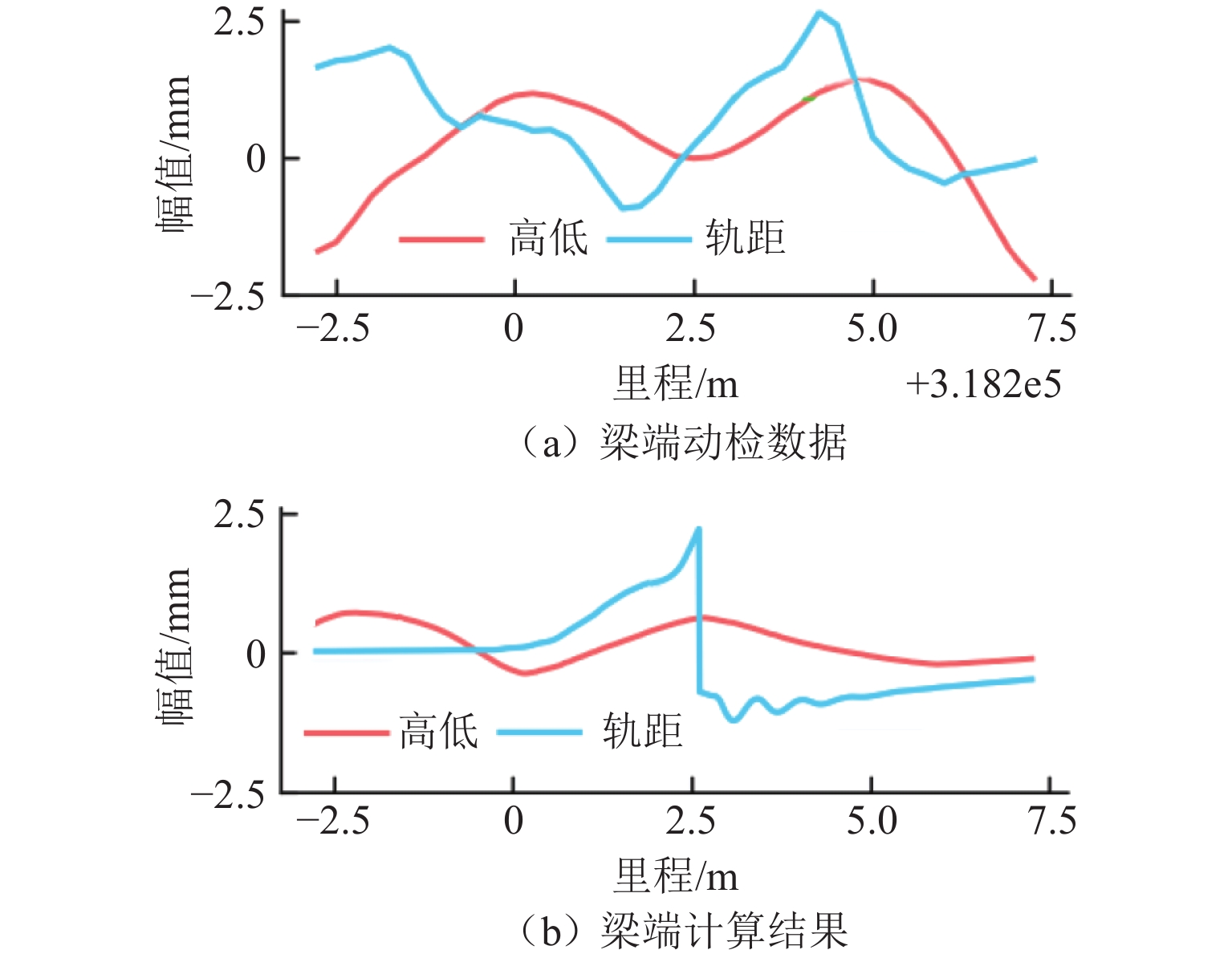
i $ {k}_{i} $ $ {b}_{i} $ ρ MSE R2 1 −0.20 448.94 −0.90 92.47 0.80 2 −0.09 191.31 −0.92 13.01 0.85 3 0.02 −41.44 0.62 5.36 0.39 4 0.11 −237.35 0.90 24.72 0.81 5 0.17 −361.46 0.93 40.94 0.86 表 2 动检和计算不平顺峰值对比
Table 2. Comparison of dynamic inspection and calculated irregularity peaks
mm 动检日期 实测高低 实测轨距 计算高低 计算轨距 高低误差 轨距误差 2022-11-06 1.41 2.64 0.78 2.40 0.03 0.24 2023-01-02 1.41 2.66 0.72 2.52 0.09 0.14 2023-03-06 1.53 2.53 0.80 2.40 0.13 0.13 2023-05-05 1.12 2.66 0.79 2.55 0.27 0.11 平均 0.13 0.16 表 3 不同速度等级5 m弦控制标准
Table 3. 5m chord control standards for different speed classes
mm 速度等级/(km•h−1) Ⅰ级 Ⅱ级 Ⅲ级 Ⅳ级 200~250 5 6 9 12 250(不含)~350 3 4 6 9 表 4 梁端附加不平顺分级评价指标(250 km/h)
Table 4. Grading evaluation indicators for beam-end additional irregularity (250 km/h)
mm 表 5 梁端变形分级管理值建议(250 km/h)
Table 5. Recommended graded management values for beam-end deformation (250 km/h)
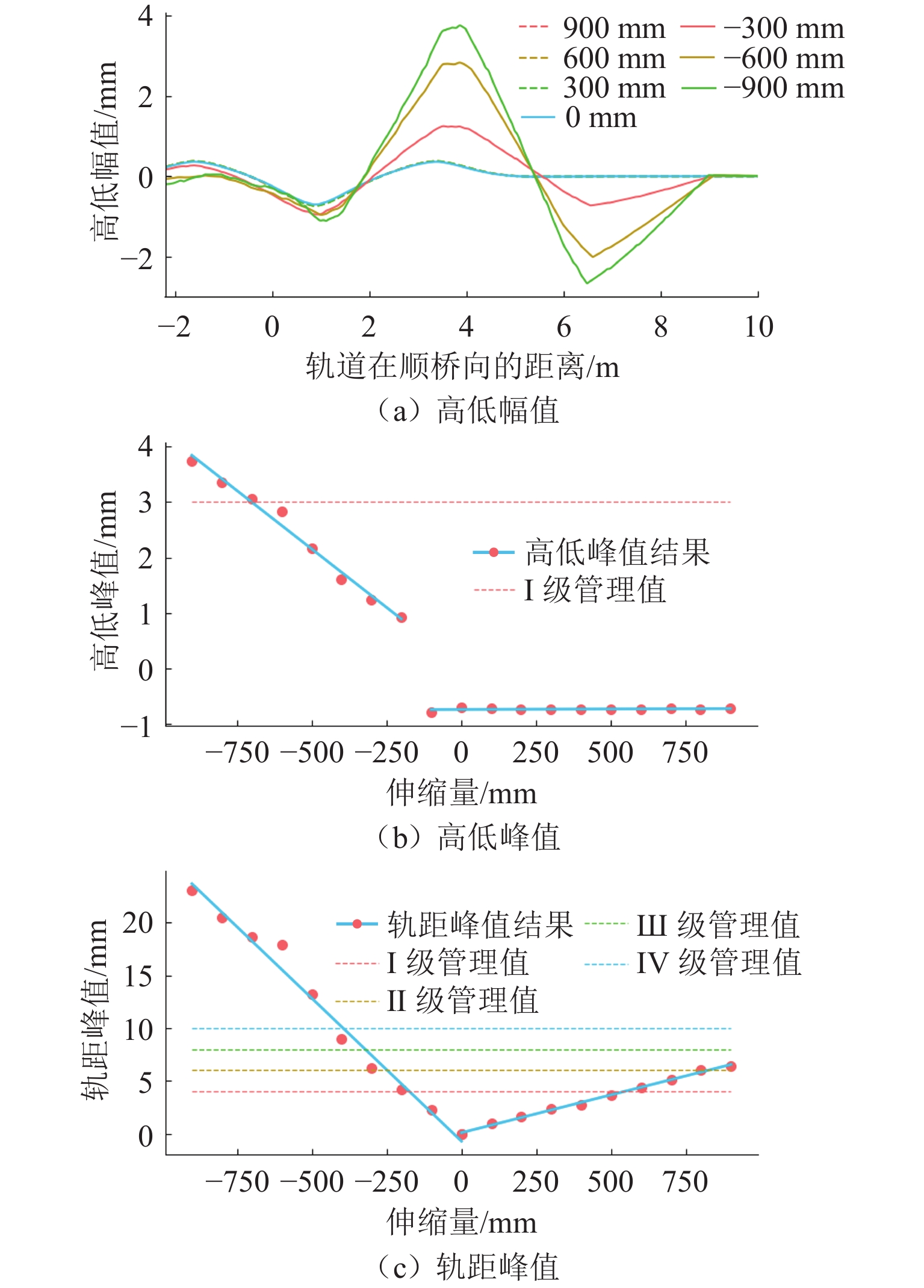
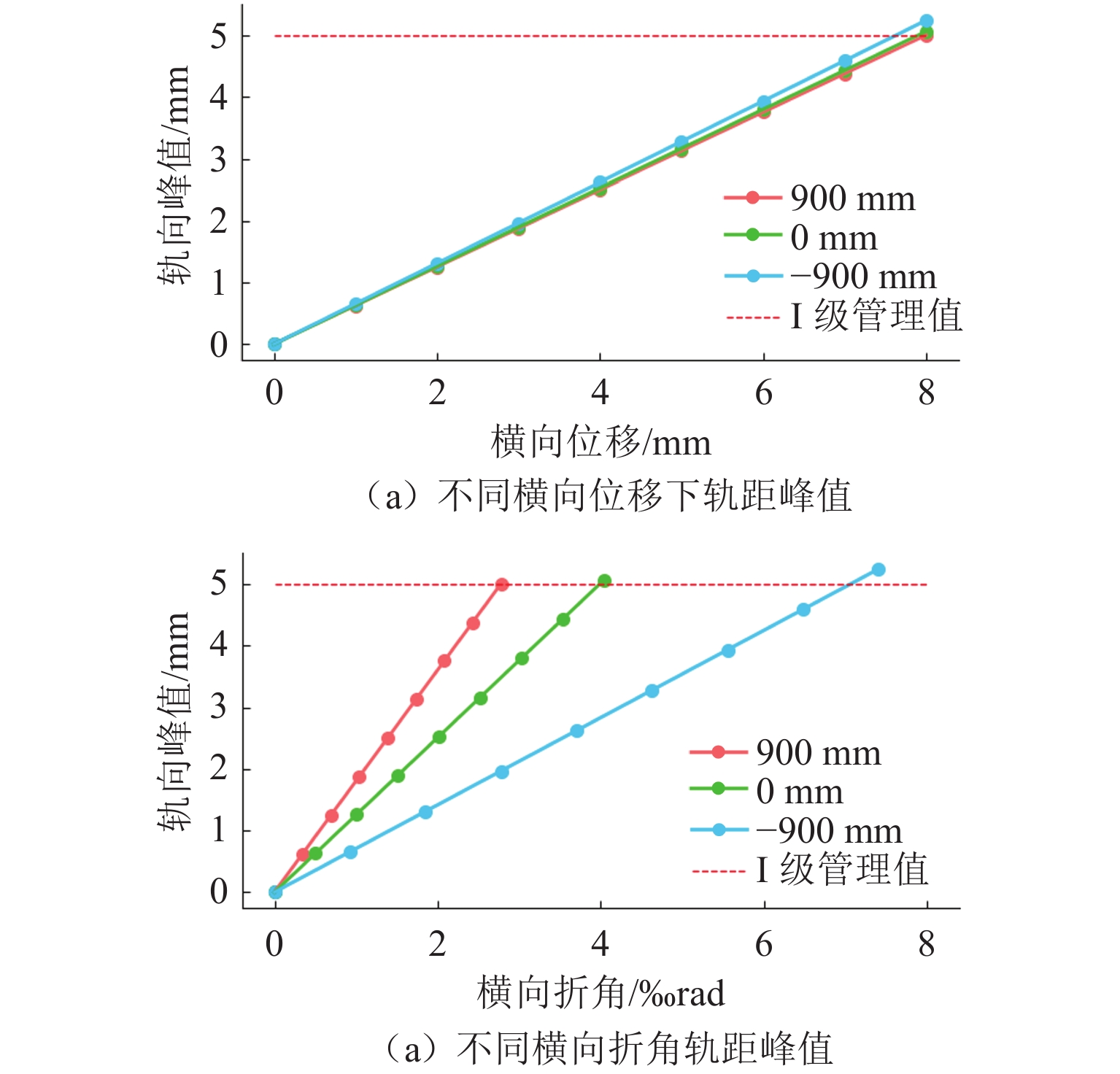
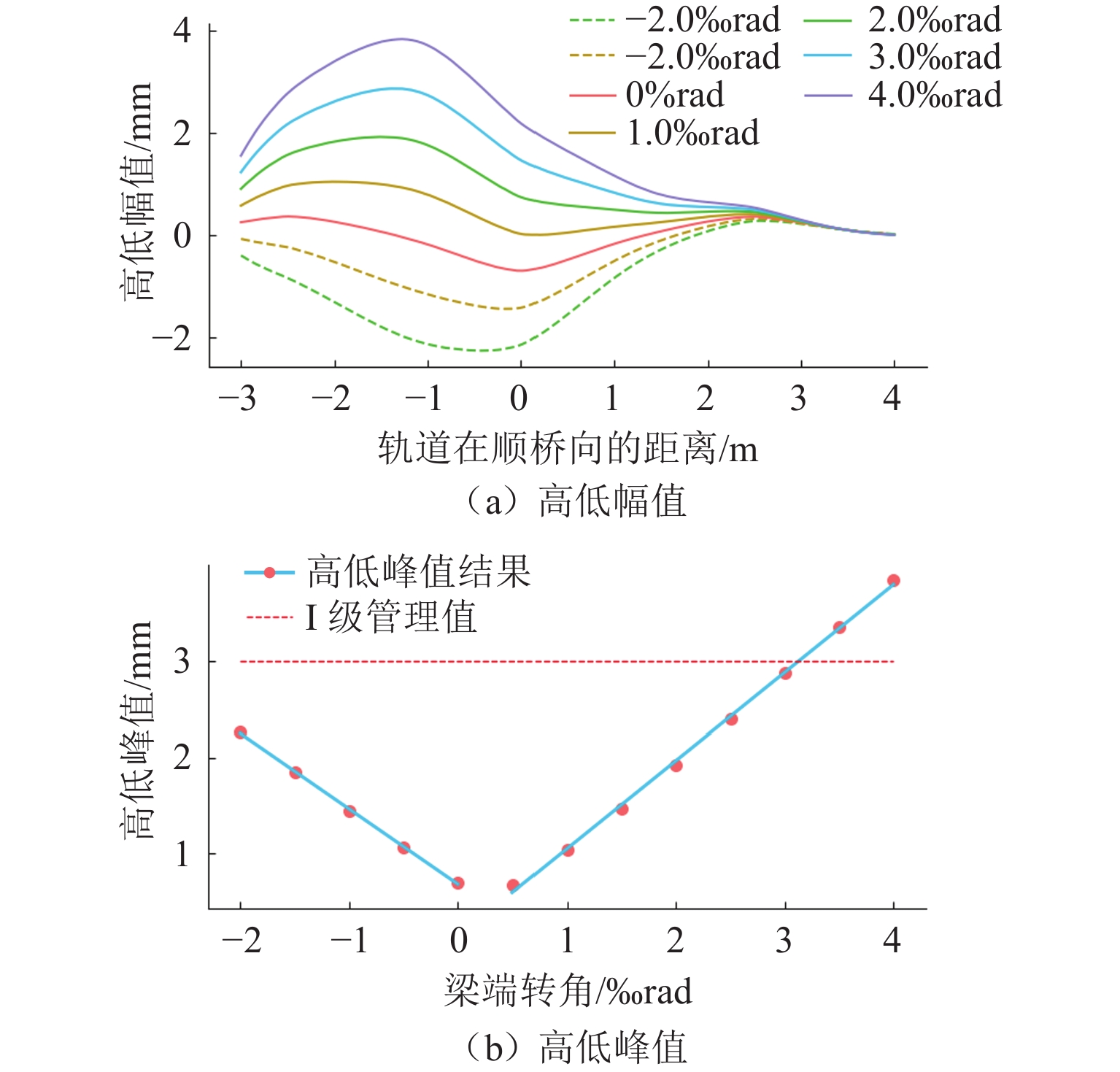
变形工况 Ⅰ级 Ⅱ级 Ⅲ级 Ⅳ级 纵向拉伸/mm 500* 800* 900 - 纵向压缩/mm 160* 240* 320 400 横向位移/mm 7* 11* 15 18 横向折角/‰ rad 3* 5* 7 9 下挠转角/‰ rad 3* 4* 8 11 注:Ⅰ级建议值取其与设计值的较小值,Ⅱ级取其与0.9倍设计值的较小值. 表 6 固定钢枕空吊和抬升分级管理值建议(250 km/h)
Table 6. Recommended graded management values for fixed steel sleeper unsupported section and lifting (250 km/h)
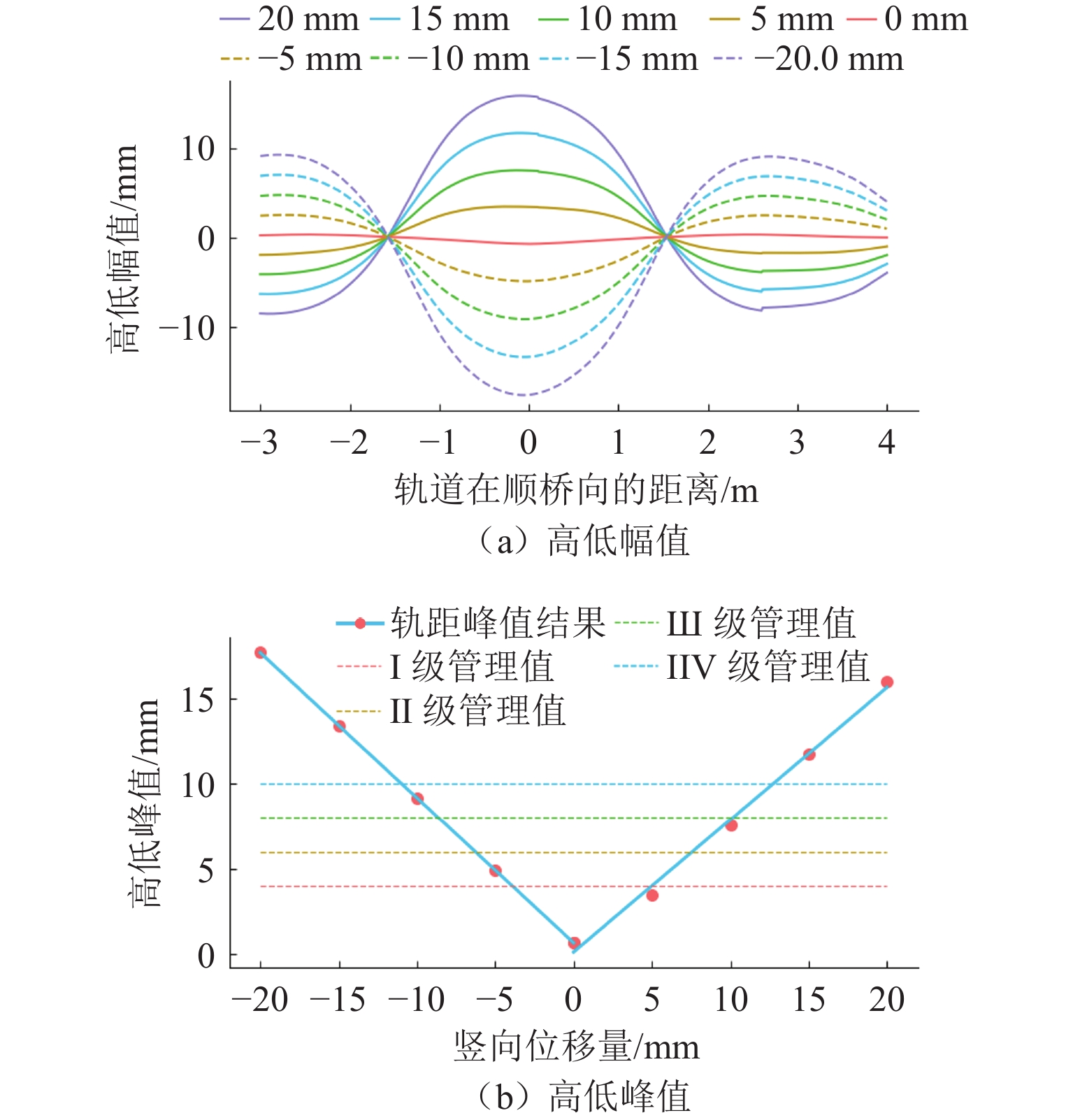
mm 类型 Ⅰ级 Ⅱ级 Ⅲ级 Ⅳ级 固定钢枕抬升 3 4 8 12 固定钢枕空吊 2 3 7 10 -
[1] QIN S Q, GAO Z Y. Developments and prospects of long-span high-speed railway bridge technologies in China[J]. Engineering, 2017, 3(6): 787-794. doi: 10.1016/j.eng.2017.11.001 [2] 杨静静, 高芒芒, 赵文博, 等. 大跨度铁路桥梁变形控制标准研究[J]. 铁道学报, 2023, 45(3): 137-143. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2023.03.016YANG Jingjing, GAO Mangmang, ZHAO Wenbo, et al. Research on deformation control standard of long-span railway bridge[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2023, 45(3): 137-143. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2023.03.016 [3] 李永乐, 向活跃, 万田保, 等. 大跨度铁路桥梁梁端伸缩装置对列车走行性影响的研究[J]. 铁道学报, 2012, 34(2): 94-99.LI Yongle, XIANG Huoyue, WAN Tianbao, et al. Performance of train running over expansion joints at beam ends of long-span railway bridge[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2012, 34(2): 94-99. [4] 郭辉, 蒋金洲, 高芒芒, 等. 高速铁路大跨度钢桥梁端伸缩装置设计研究[J]. 铁道建筑, 2020, 60(10): 1-7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003⁃1995.2020.10.01GUO Hui, JIANG Jinzhou, GAO Mangmang, et al. Research on bridge expansion joint of HSR long span steel bridges[J]. Railway Engineering, 2020, 60(10): 1-7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003⁃1995.2020.10.01 [5] 张晓明. 商合杭高铁芜湖长江公铁大桥钢轨伸缩调节器及梁端伸缩装置研究[J]. 中国铁路, 2020(6): 38-43.ZHANG Xiaoming. Research on rail expansion device and beam-end expansion device of Wuhu Yangtze River rail-cum-road bridge on Shangqiu-Hefei-Hangzhou high speed railway[J]. China Railway, 2020(6): 38-43. [6] LIAO T, SONG J, LAI J, et al. Experimental and numerical investigation of the expansion mechanism of beam-end expansion devices in large-span bridge[J]. Engineering Structures, 2024, 298: 117050.1-117050.16. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2023.117050 [7] 高芒芒, 臧晓秋, 熊建珍. 沪通长江大桥大位移梁端伸缩装置动力性能研究[J]. 桥梁建设, 2015, 45(6): 41-46.GAO Mangmang, ZANG Xiaoqiu, XIONG Jianzhen. Study of dynamic performance of large movement girder end expansion devices of hutong Changjiang River bridge[J]. Bridge Construction, 2015, 45(6): 41-46. [8] 王韫璐, 高芒芒, 杨静静, 等. 高速铁路大跨度桥梁端轨道动态不平顺特征分析[J]. 铁道建筑, 2023, 63(6): 7-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1995.2023.06.02WANG Yunlu, GAO Mangmang, YANG Jingjing, et al. Analysis of dynamic track irregularity characteristics at girder end of long span bridge in high speed railway[J]. Railway Engineering, 2023, 63(6): 7-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1995.2023.06.02 [9] 周智强, 邢书科, 王兆刚, 等. 高速铁路大跨度连续斜拉桥上梁端一体化装置性能研究[J]. 铁道标准设计, 2022, 68(4): 63-87.ZHOU Zhiqiang, XING Shuke, WANG Zhaogang, et al. Research on performance of upper beam end integration device of long span continuous cable-stayed bridge of high speed railways[J]. Railway Standard Design, 2022, 68(4): 63-87 [10] 胡晓依, 成棣, 孟凡迪, 等. 时速400公里高速铁路轮轨周期性短波不平顺的安全限值研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2025, 60(6): 1581-1592.HU Xiaoyi, CHENG Di, YAN Ziquan, et al. Safety limit for periodic short-wave irregularity of wheel and rail for high-speed railways at 400 km/h[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2025, 60(6): 1581-1592. [11] HU J H, WANG L H, SONG X P, et al. Field monitoring and response characteristics of longitudinal movements of expansion joints in long-span suspension bridges[J]. Measurement, 2020, 162: 107933.1-107933.13. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2020.107933 [12] 王森荣. 大跨度桥上钢轨伸缩调节器区轨道病害分析与监测研究[J]. 铁道标准设计, 2018, 62(1): 18-22. doi: 10.13238/j.issn.1004-2954.201701280002WANG Senrong. Defects analysis and monitoring research on track in rail expansion joint area on large span bridge[J]. Railway Standard Design, 2018, 62(1): 18-22. doi: 10.13238/j.issn.1004-2954.201701280002 [13] 凌烈鹏. 大跨度桥梁线桥一体化检测监测系统技术方案及应用[J]. 铁道建筑, 2023, 63(4): 33-37, 51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1995.2023.04.08LING Liepeng. Technical scheme and application of track-bridge integrated inspection and monitoring system for long-span bridges[J]. Railway Engineering, 2023, 63(4): 33-37,51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1995.2023.04.08 [14] 国家铁路局. 高速铁路设计规范: TB 10621—2014[S]. 北京: 中国铁道出版社, 2015. [15] 国家铁路局. 铁路桥涵设计规范: TB 10002—2017[S]. 北京: 中国铁道出版社, 2017LinkOut [16] 唐贺强, 徐恭义, 刘汉顺. 五峰山长江大桥主桥总体设计[J]. 桥梁建设, 2020, 50(6): 1-7.TANG Heqiang, XU Gongyi, LIU Hanshun. Overall design of main bridge of Wufengshan Changjiang River bridge[J]. Bridge Construction, 2020, 50(6): 1-7. [17] 苏朋飞. 大跨度铁路钢桥梁端伸缩装置设计与研究[D]. 北京: 中国铁道科学研究院, 2021. [18] 王韫璐. 大跨度桥梁端区域车-线-桥动力响应分析及轨道平顺性研究[D]. 北京: 中国铁道科学研究院, 2023. [19] 费维周. 铁路桥梁梁端伸缩装置的结构特点探讨[J]. 铁道标准设计, 2015, 59(7): 60-65. doi: 10.13238/j.issn.1004-2954.2015.07.014FEI Weizhou. Approach to structural features of telescopic devices at beam ends of railway bridge[J]. Railway Standard Design, 2015, 59(7): 60-65. doi: 10.13238/j.issn.1004-2954.2015.07.014 [20] 郭辉, 苏朋飞, 赵欣欣, 等. 设计荷载作用下大跨度铁路悬索桥的梁端变位特征[J]. 铁道建筑, 2019, 59(1): 14-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1995.2019.01.04GUO Hui, SU Pengfei, ZHAO Xinxin, et al. Displacement characteristics at girder end of long span railway suspension bridge under design loads[J]. Railway Engineering, 2019, 59(1): 14-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1995.2019.01.04 [21] 国家铁路局. 铁路无缝线路设计规范: TB10015—2012[S]. 北京: 中国铁道出版社, 2013. [22] 杨飞, 刘丙强, 谭社会, 等. 高速铁路轨道静态几何不平顺弦测评价标准体系研究[J]. 铁道建筑, 2021, 61(6): 107-111, 120. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1995.2021.06.24YANG Fei, LIU Bingqiang, TAN Shehui, et al. Research on evaluation standard system of chord measurement for track static geometric irregularity of high speed railway[J]. Railway Engineering, 2021, 61(6): 107-111,120. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1995.2021.06.24 [23] 国家铁路局. 高速铁路线路维修规则: TG/GW 115—2012[S]. 北京: 中国铁道出版社, 2023. [24] 田新宇, 高亮, 杨飞, 等. 基于动态短弦的无砟轨道板周期性不平顺管理标准[J]. 中国铁道科学, 2020, 41(6): 30-38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4632.2020.06.04TIAN Xinyu, GAO Liang, YANG Fei, et al. Management standard for cyclic irregularity of ballastless track slab based on dynamic short chord[J]. China Railway Science, 2020, 41(6): 30-38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4632.2020.06.04 -




 下载:
下载: