Elastic Wave Control of Rail Structure Based on Inertial Amplification Mechanism
-
摘要:
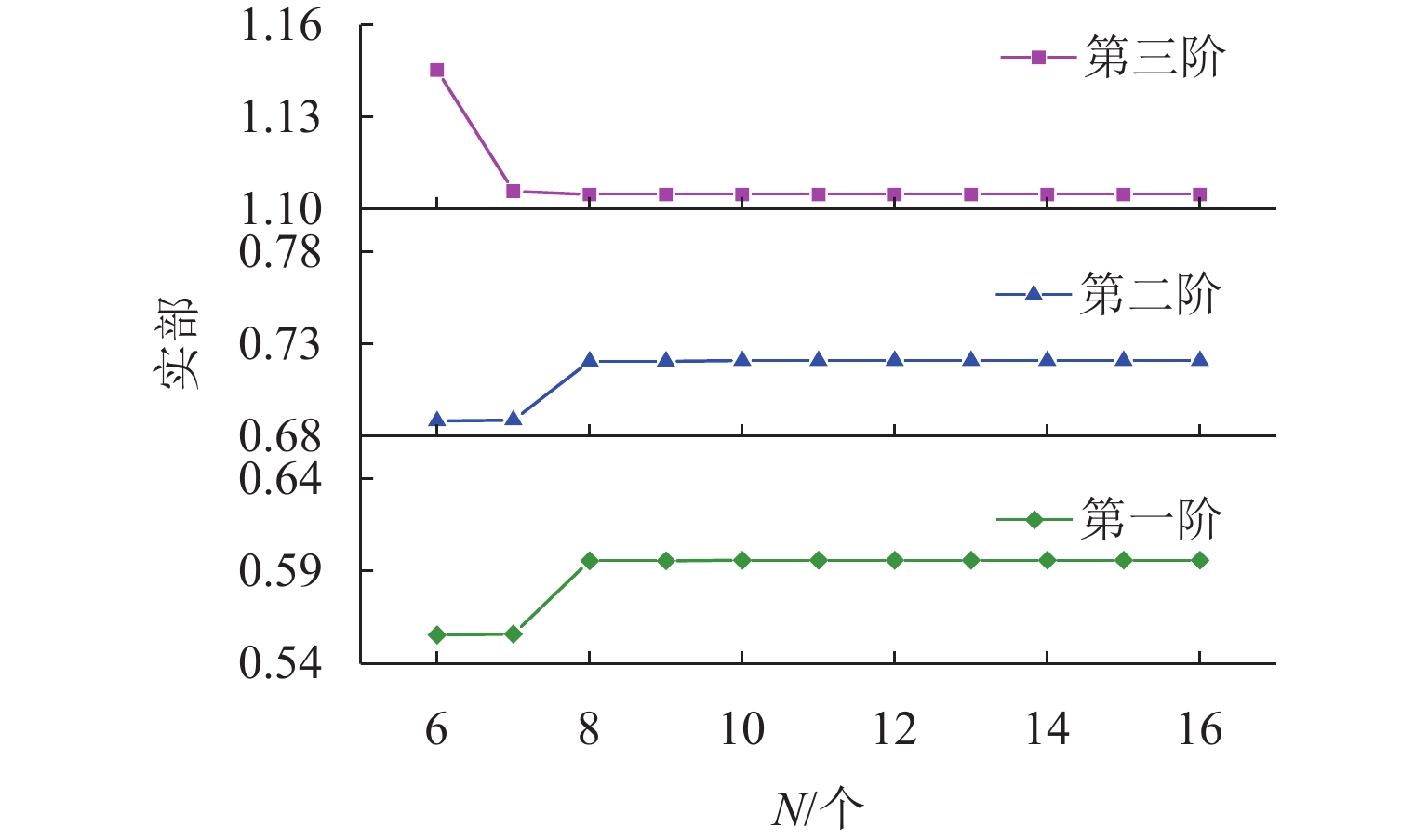
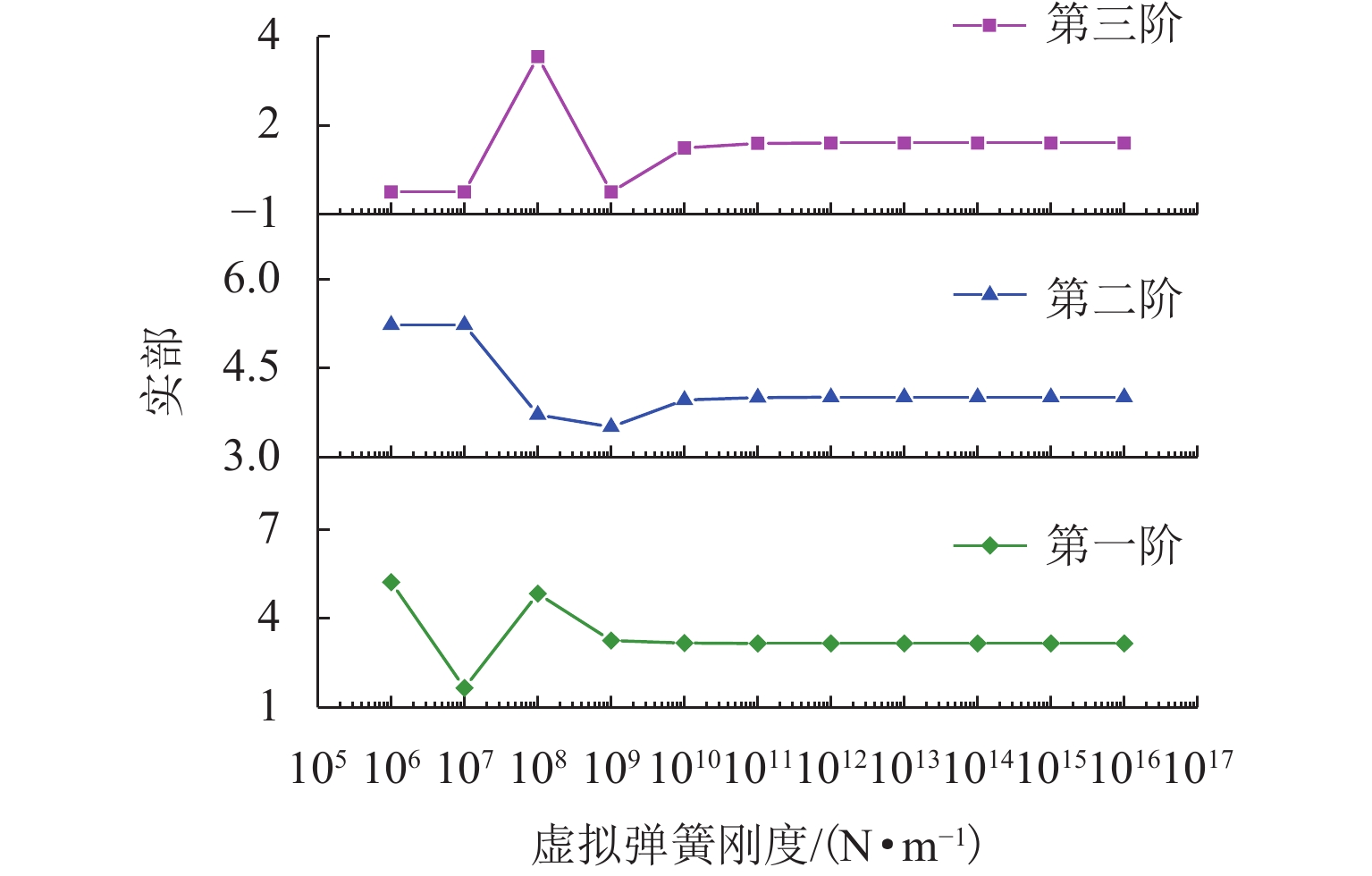
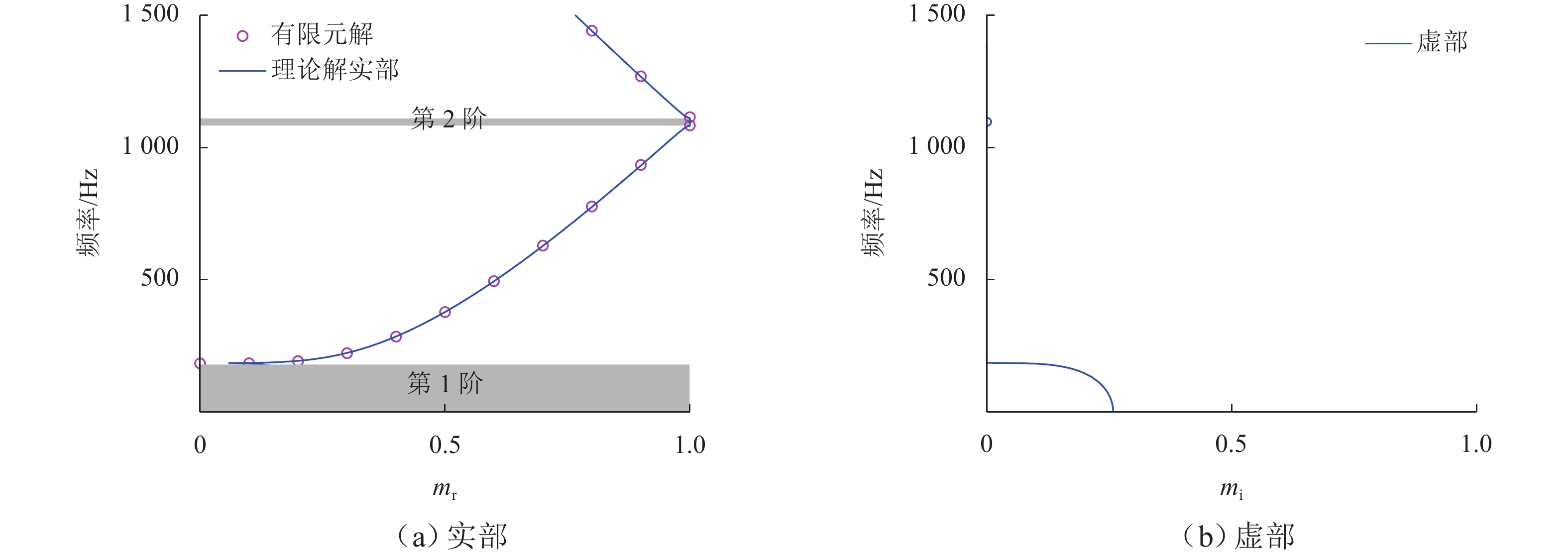
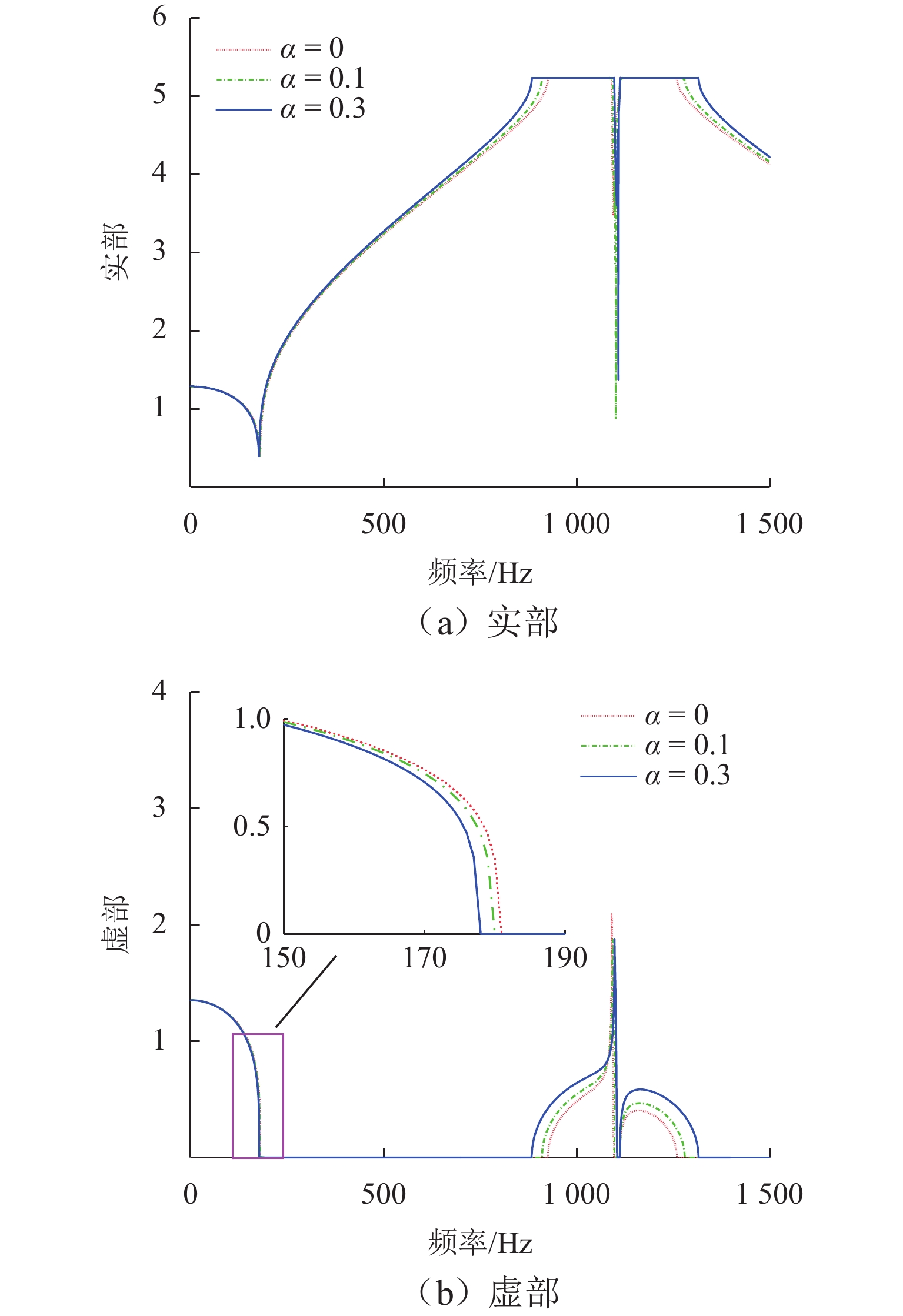
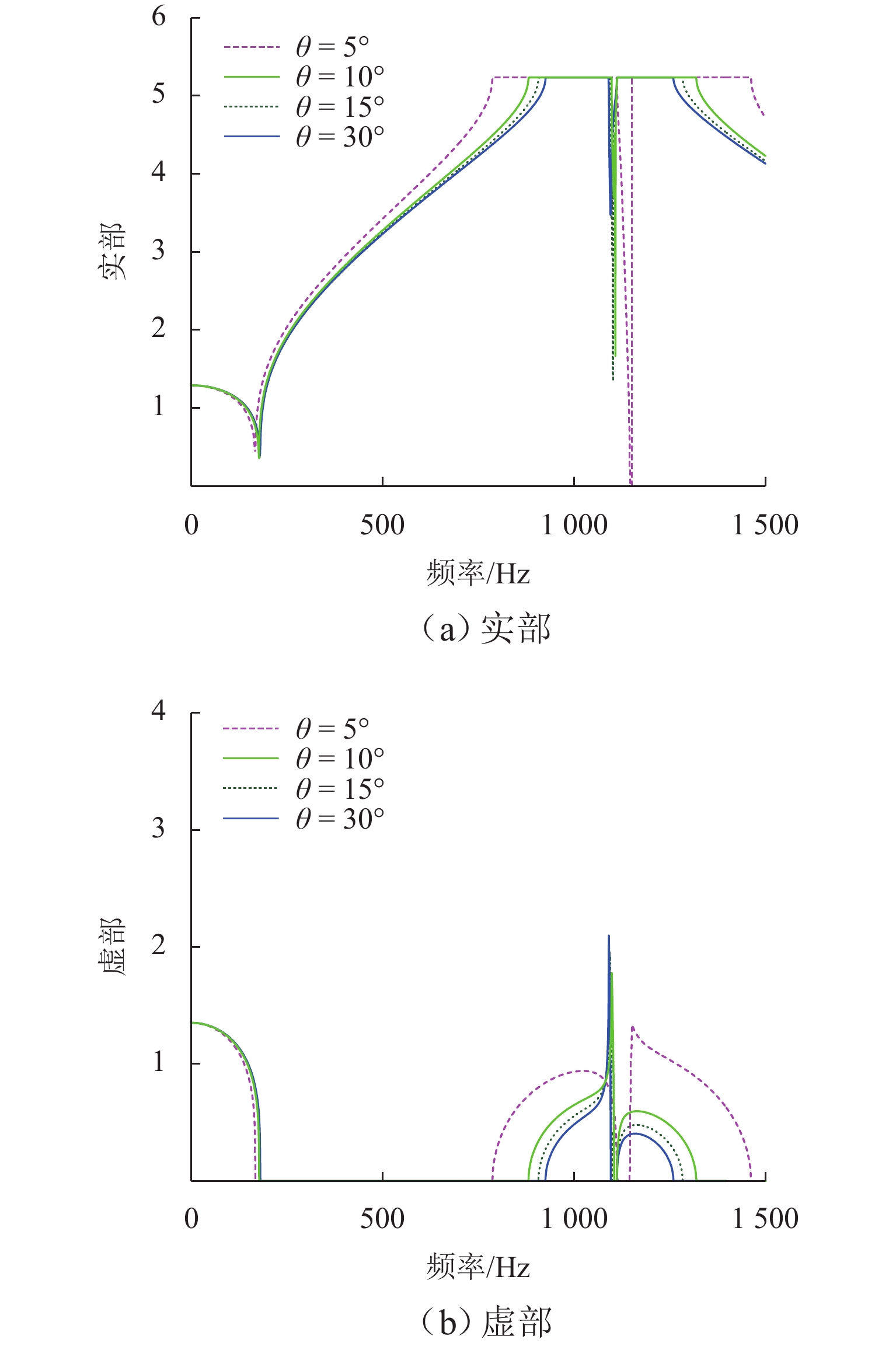
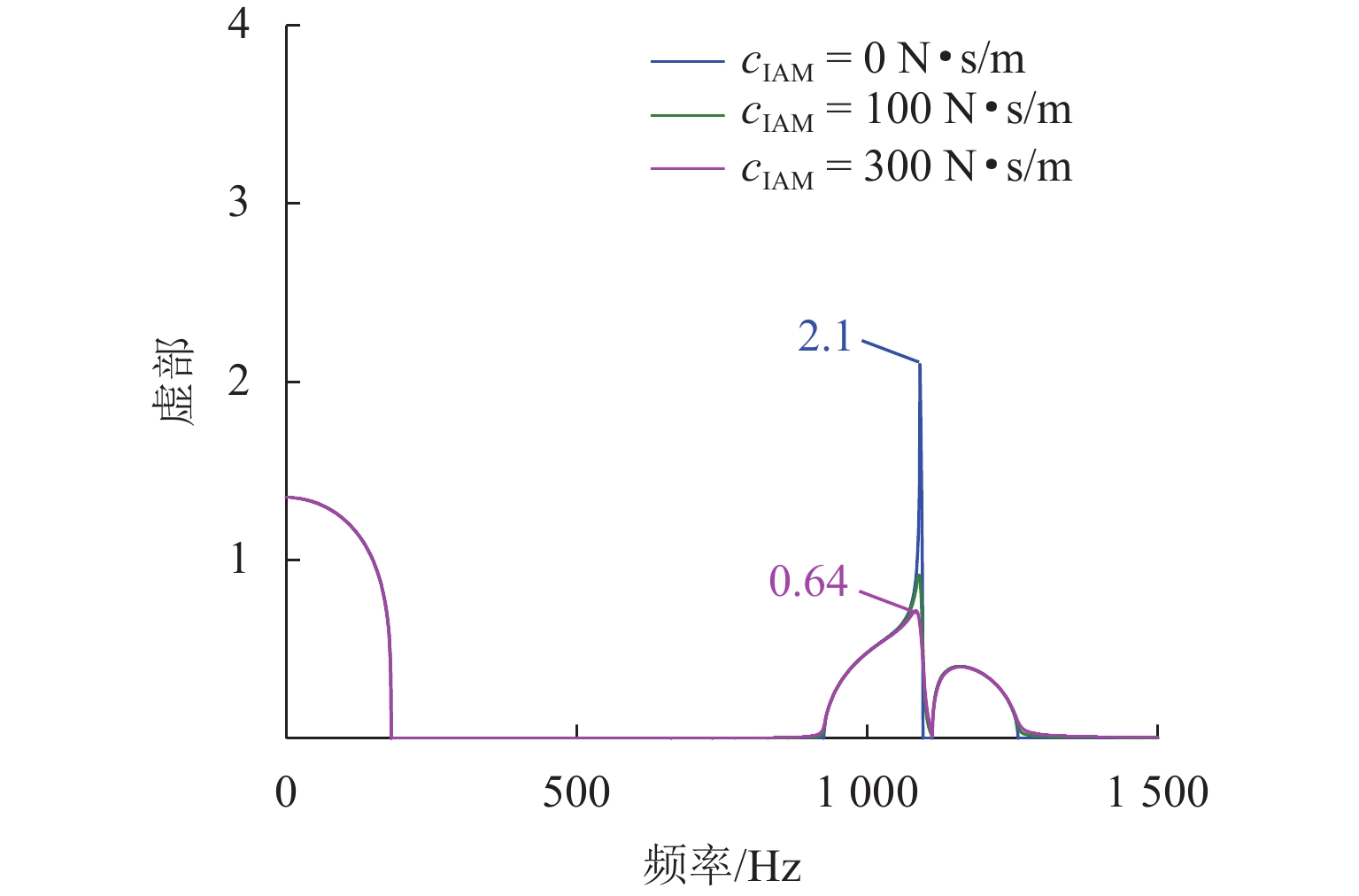
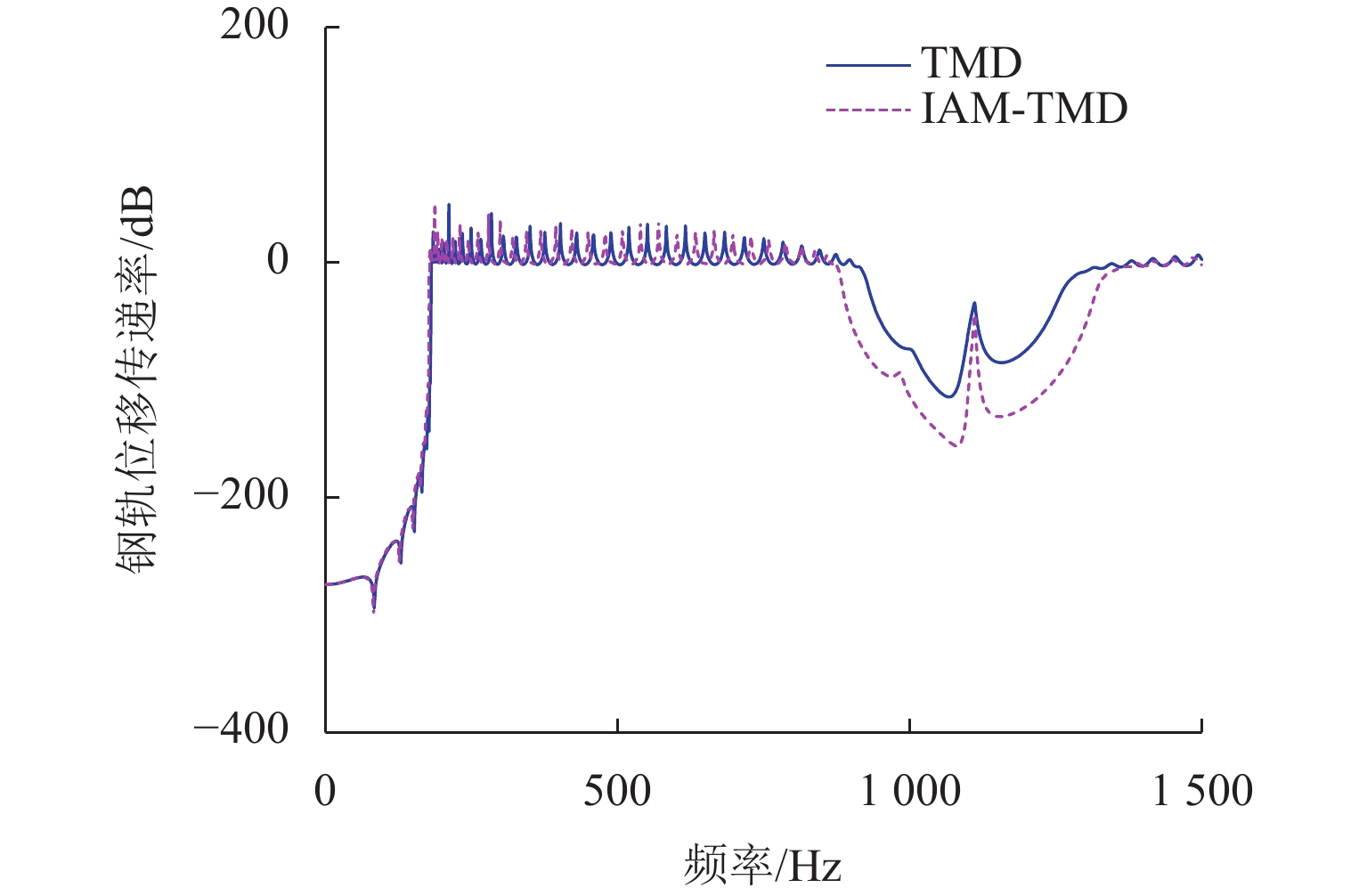
列车运行引起的振动噪声问题日益突出,传统调谐质量阻尼器(TMD)难以实现针对钢轨的轻质宽频减振,鉴于此,引入惯性放大机制(IAM),利用惯容实现TMD的更大有效工作质量,从而增强对轨道结构振动的抑制;利用能量法与虚拟弹簧法提出一种新的复能带特性求解方法,基于该方法建立配置有IAM-TMD的钢轨结构的复能带分析模型,并利用有限元求解结果验证模型的准确性;在此基础上,以复能带特性作为评价指标,探究IAM对传统钢轨TMD减振效果的影响机制,分析IAM质量比、杠杆角度、阻尼系数对钢轨结构内振动波传播的调控作用. 结果表明:复能带虚部能够详细地描述带隙内部波传播的衰减过程;应用
α =0.05,θ =10° 的IAM后,原TMD作用下的Bragg带隙由925~1260 Hz拓宽为881~1320 Hz,复能带虚部增大,衰减能力增强;IAM-TMD的减振效果与质量比、阻尼系数成正比,与杠杆角度成反比. 利用复能带特性对IAM进行了分析研究,其研究成果可为钢轨减振提供一种新的思路.Abstract:The problem of vibration and noise caused by train operation is increasingly prominent, and it is difficult for traditional tuned mass damper (TMD) to achieve lightweight and broadband vibration reduction for rail. In view of this, inertial amplification mechanism (IAM) was introduced to achieve greater effective working quality of TMD by using inerter, so as to enhance the suppression of rail structure vibration. A new method for solving the complex band characteristics was proposed by using the energy method and the virtual spring method, based on which the complex band analysis model of the rail structure configured with IAM-TMD was established, and the accuracy of the model was verified with the solving results of the finite element method (FEM). On this basis, the influence mechanism of IAM on the vibration reduction effect of traditional rail TMD was investigated by taking the complex band characteristics as the evaluation index, and the modulation effects of IAM mass ratio, lever angle, and damping coefficient on the propagation of vibration wave in the rail structure were analyzed. The results show that the imaginary part of the complex band can describe the attenuation process of wave propagation inside the bandgap well. After the application of the IAM with
α = 0.05 andθ = 10°, the original Bragg bandgap under TMD is widened from 925—1260 Hz to 881—1320 Hz, and the imaginary part of the complex band is increased, which implies that the attenuation capability of TMD is enhanced. The vibration reduction effect of IAM-TMD is proportional to the mass ratio and damping coefficient, and inversely proportional to the lever angle. The complex band characteristics are utilized to analyze the IAM, and the research results can provide a new idea for rail vibration reduction. -
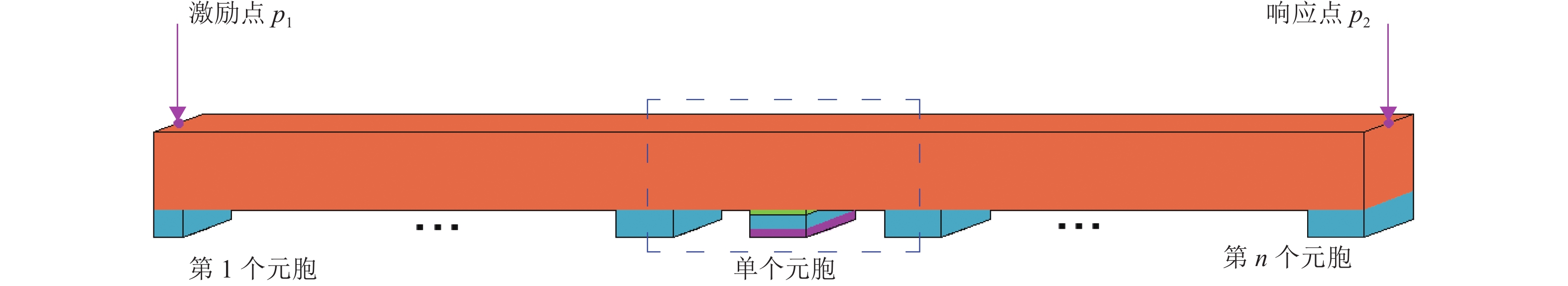
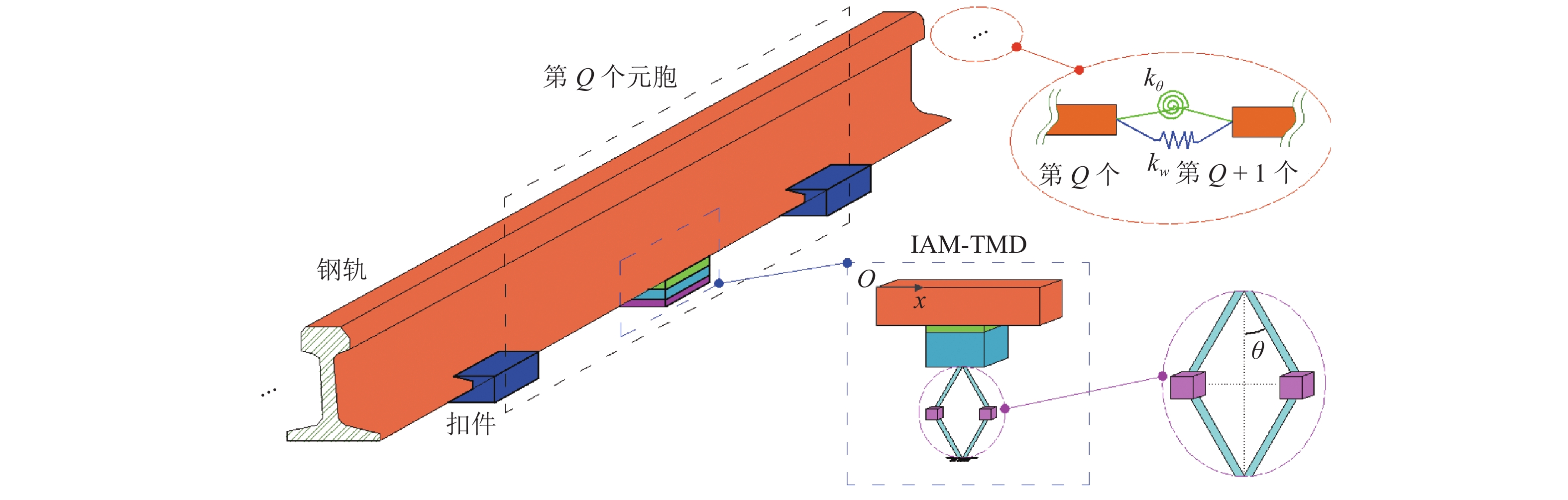
表 1 周期性IAM-TMD钢轨结构模型计算参数表
Table 1. Table of calculated parameters for the periodic IAM-TMD rail structure model
部件 参数 取值 钢轨 密度 /(kg•m−3) 7850 横截面积 /m2 7.745 × 10−3 弹性模量 /GPa 210 截面惯性矩 /m4 3.217 × 10−5 剪切修正因子 0.4 泊松比 0.3 TMD/IAM-TMD 主质量比 0.05 侧质量比 0.05 -
[1] 李伟, 周志军, 温泽峰. 地铁弹性短轨枕轨道的钢轨波磨萌生原因[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2021, 56(3): 619-626. doi: 10.35741/issn.0258-2724.56.3.50LI Wei, ZHOU Zhijun, WEN Zefeng. Initiation cause of subway rail corrugation on track with rubber-booted short sleepers[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2021, 56(3): 619-626. doi: 10.35741/issn.0258-2724.56.3.50 [2] HERMANN F. Device for damping vibrations of bodies: US0989958[P]. 1911-04-18. [3] LIU Z, ZHANG X, MAO Y, et al. Locally resonant sonic materials[J]. Science, 2000, 289(5485): 1734-1736. doi: 10.1126/science.289.5485.1734 [4] 肖祥, 薛宗颜. 基于TMD的大跨度斜拉桥风致随机振动控制研究[J/OL]. 武汉理工大学学报(交通科学与工程), 1-9. [2024-05-30]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/42.1824.U.20230704.1104.018.html. [5] 李晓露, 樊永欣, 尹绪超, 等. 精准调频钢轨阻尼器设计及试验研究[J]. 噪声与振动控制, 2023, 43(6): 263-269.LI Xiaolu, FAN Yongxin, YIN Xuchao, et al. Design and experimental study on accurate tuned rail dampers[J]. Noise and Vibration Control, 2023, 43(6): 263-269. [6] 许孝堂, 蒲黔辉, 尹学军, 等. 宽频式钢轨动力吸振器对波磨的影响分析[J]. 地震工程与工程振动, 2024, 44(2): 147-159.XU Xiaotang, PU Qianhui, YIN Xuejun et al. Study on the influence of wide-frequency tuned mass damper on rail corrugation[J]. Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Dynamics, 2024, 44(2): 147-159. [7] SMITH M C. Synthesis of mechanical networks: the inerter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2002, 47(10): 1648-1662. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2002.803532 [8] LAZAR I F, NEILD S A, WAGG D J. Vibration suppression of cables using tuned inerter dampers[J]. Engineering Structures, 2016, 122: 62-71. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2016.04.017 [9] MARIAN L, GIARALIS A. Optimal design of a novel tuned mass-damper–inerter (TMDI) passive vibration control configuration for stochastically support-excited structural systems[J]. Probabilistic Engineering Mechanics, 2014, 38: 156-164. doi: 10.1016/j.probengmech.2014.03.007 [10] 王振洲, 安子凡, 曹黎媛, 等. 多自由度结构-串并联调谐质量阻尼器减震性能[J]. 振动工程学报, 2024, 37(2): 318-325.WANG Zhenzhou, AN Zifan, CAO Liyuan, et al. Seismic performance of tuned tandem mass dampers for MDOF structures[J]. Journal of Vibration Engineering, 2024, 37(2): 318-325. [11] 刘欣鹏, 杨映雯, 孙毅, 等. 基于惯容系统位置的调谐质量阻尼器的振动控制研究[J]. 振动与冲击, 2023, 42(1): 215-223.LIU Xinpeng, YANG Yingwen, SUN Yi, et al. Vibration control of TMD based on position of inertial system[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2023, 42(1): 215-223. [12] CHENG Z B, PALERMO A, SHI Z F, et al. Enhanced tuned mass damper using an inertial amplification mechanism[J]. Journal of Sound Vibration, 2020, 475: 115267. doi: 10.1016/j.jsv.2020.115267 [13] 张群, 程志宝, 石志飞. 惯性增强动力吸振器-浮置板轨道低频减振性能研究[J/OL]. 铁道学报, 1-9. [2024-05-30]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2104.u.20240507.1737.002.html. [14] MEAD D J. Free wave propagation in periodically supported, infinite beams[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 1970, 11(2): 181-197. doi: 10.1016/S0022-460X(70)80062-1 [15] 农兴中, 李祥, 刘堂辉, 等. 浮置板下声子晶体隔振器带隙特性研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2019, 54(6): 1203-1209, 1276.NONG Xingzhong, LI Xiang, LIU Tanghui, et al. Band gap characteristics of vibration isolators of phononic crystals under floating slab[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2019, 54(6): 1203-1209, 1276. [16] 陈圣兵, 张浩, 宋玉宝. 声子晶体板复能带计算方法[J]. 振动工程学报, 2019, 32(3): 415-420.CHEN Shengbing, ZHANG Hao, SONG Yubao. Calculation method of complex band structure of phononic plates[J]. Journal of Vibration Engineering, 2019, 32(3): 415-420. [17] XIAO X, HE Z C, LI E, et al. A lightweight adaptive hybrid laminate metamaterial with higher design freedom for wave attenuation[J]. Composite Structures, 2020, 243: 112230. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2020.112230 [18] 付强, 姚飞, 张红艳. 局域共振夹芯超结构梁带隙特性及实验研究[J]. 人工晶体学报, 2024, 53(1): 65-72.FU Qiang, YAO Fei, ZHANG Hongyan. Band gap characteristics and experimental study of local resonance sandwich metastructure beam[J]. Journal of Synthetic Crystals, 2024, 53(1): 65-72. [19] 张书燕, 王艳锋. 反平面波在一维液体饱和多孔声子晶体中的传播特性[J]. 振动与冲击, 2022, 41(9): 283-289.ZHANG Shuyan, WANG Yanfeng. Propagation characteristics of anti-plane wave in one-dimensional fluid saturated porous phononic crystals[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2022, 41(9): 283-289. [20] LAUDE V, ACHAOUI Y, BENCHABANE S, et al. Evanescent Bloch waves and the complex band structure of phononic crystals[J]. Physical Review B, 2009, 80(9): 092301. [21] ZHU X Y, ZHONG S, ZHAO H D. Band gap structures for viscoelastic phononic crystals based on numerical and experimental investigation[J]. Applied Acoustics, 2016, 106: 93-104. doi: 10.1016/j.apacoust.2016.01.007 [22] GUO W J, YANG Z, FENG Q S, et al. A new method for band gap analysis of periodic structures using virtual spring model and energy functional variational principle[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2022, 168: 108634. doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2021.108634 [23] 冯青松, 戴承欣, 郭文杰, 等. 周期性钢弹簧浮置板轨道垂向振动带隙特性研究[J]. 中国铁道科学, 2022, 43(1): 17-28.FENG Qingsong, DAI Chengxin, GUO Wenjie, et al. Study on vertical vibration band gap properties of periodic steel spring floating slab track[J]. China Railway Science, 2022, 43(1): 17-28. [24] WU T X, LIU H P. Reducing the rail component of rolling noise by vibration absorber: theoretical prediction[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part F: Journal of Rail and Rapid Transit, 2009, 223(5): 473-483. doi: 10.1243/09544097JRRT263 [25] XIAO X B, LI Y G, ZHONG T S, et al. Theoretical investigation into the effect of rail vibration dampers on the dynamical behaviour of a high-speed railway track[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University: Science A, 2017, 18(8): 631-647. doi: 10.1631/jzus.A1600697 -




 下载:
下载: