Hopf Bifurcation Characteristic Analysis of Straddle-Type Monorail Vehicle Bogie Based on Spatial Perturbations
-
摘要:
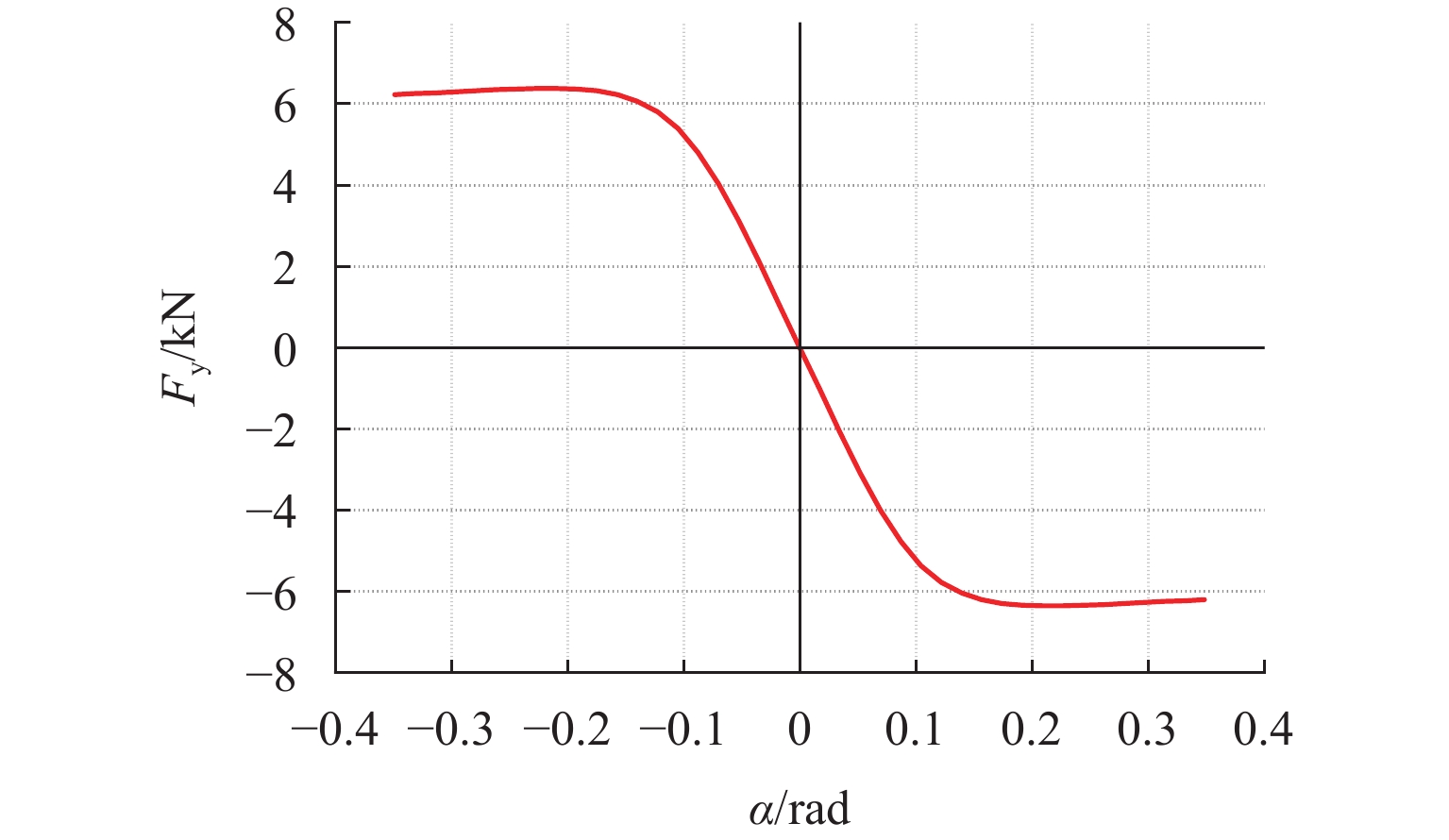
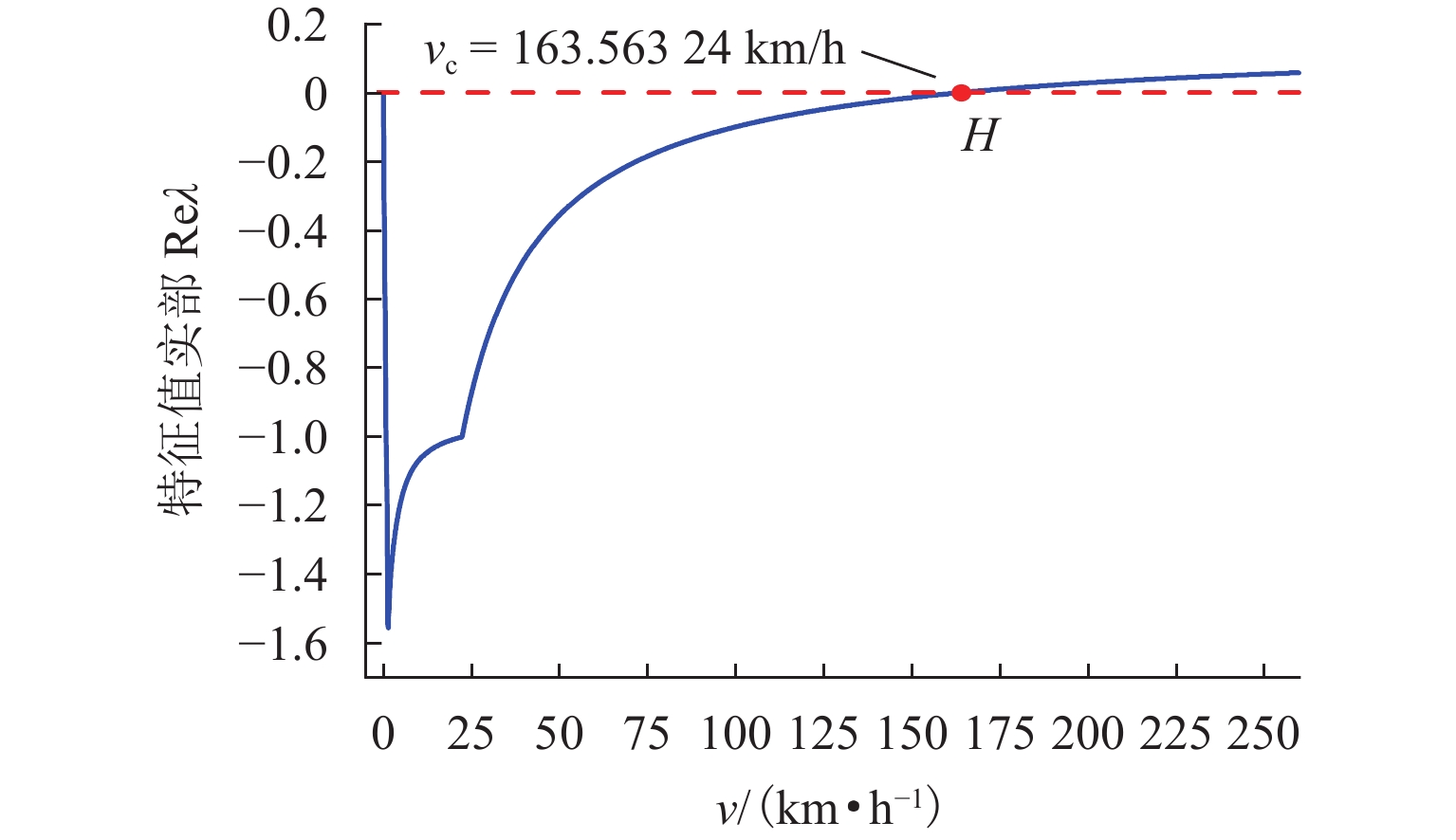
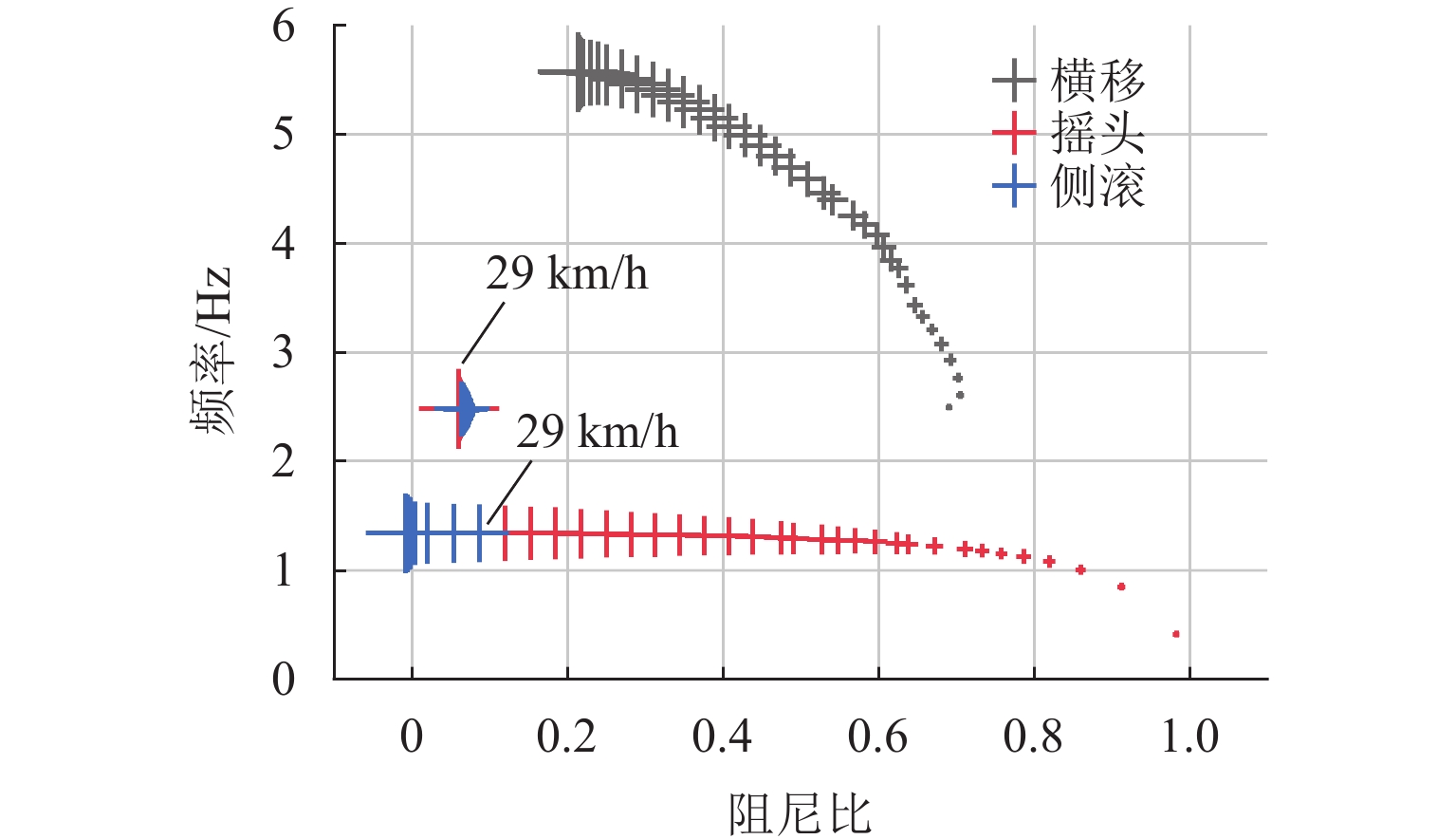
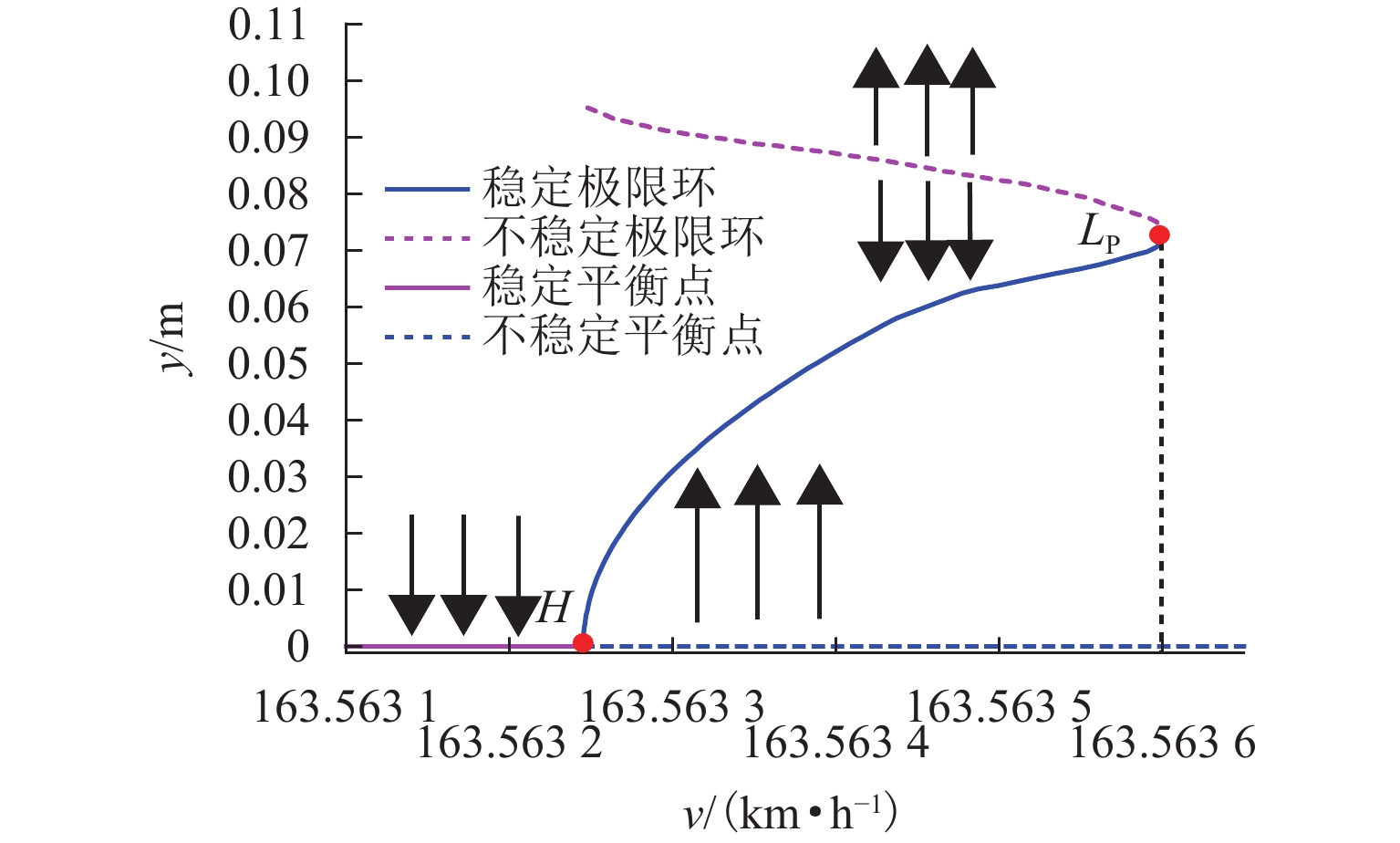
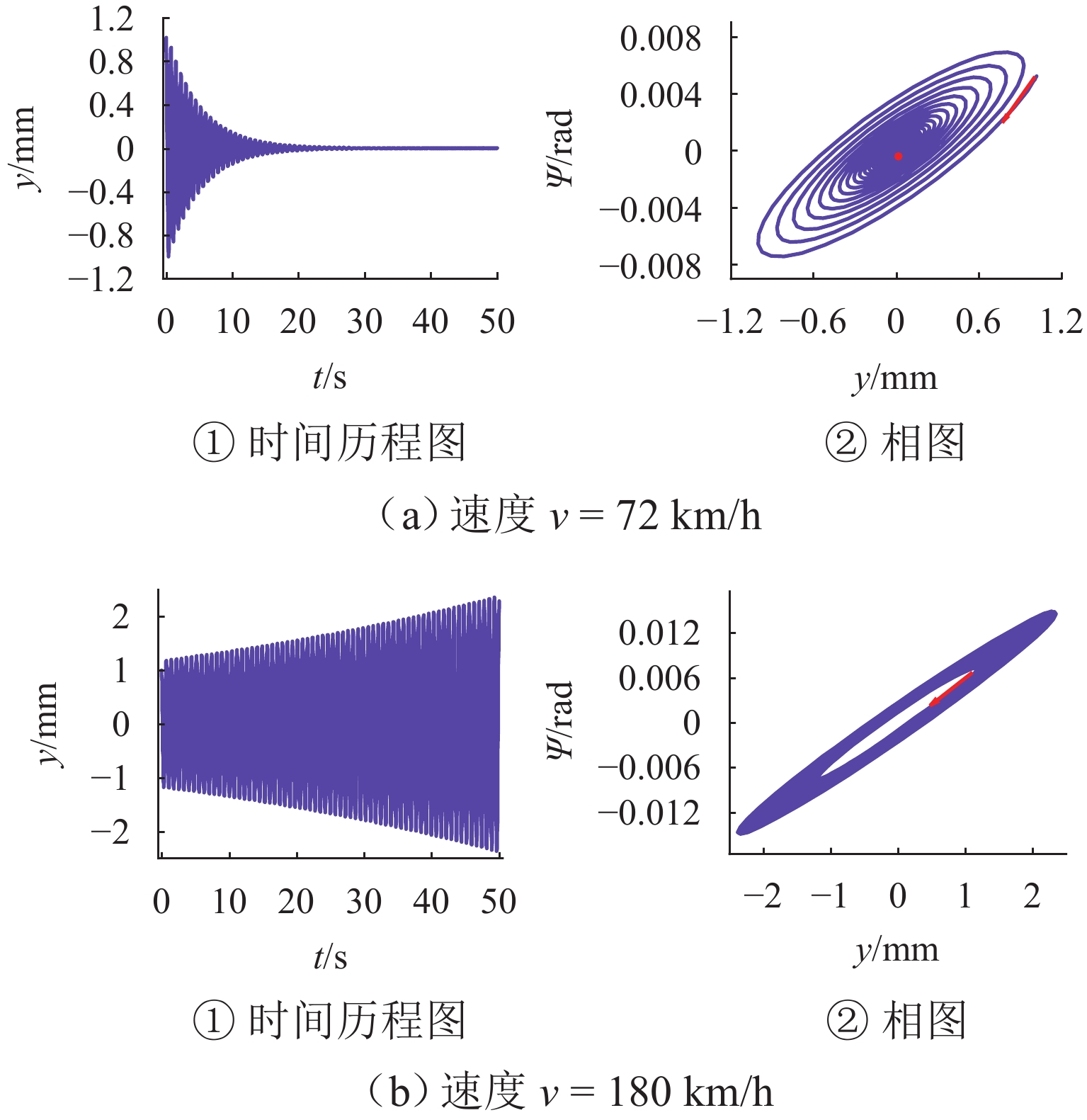
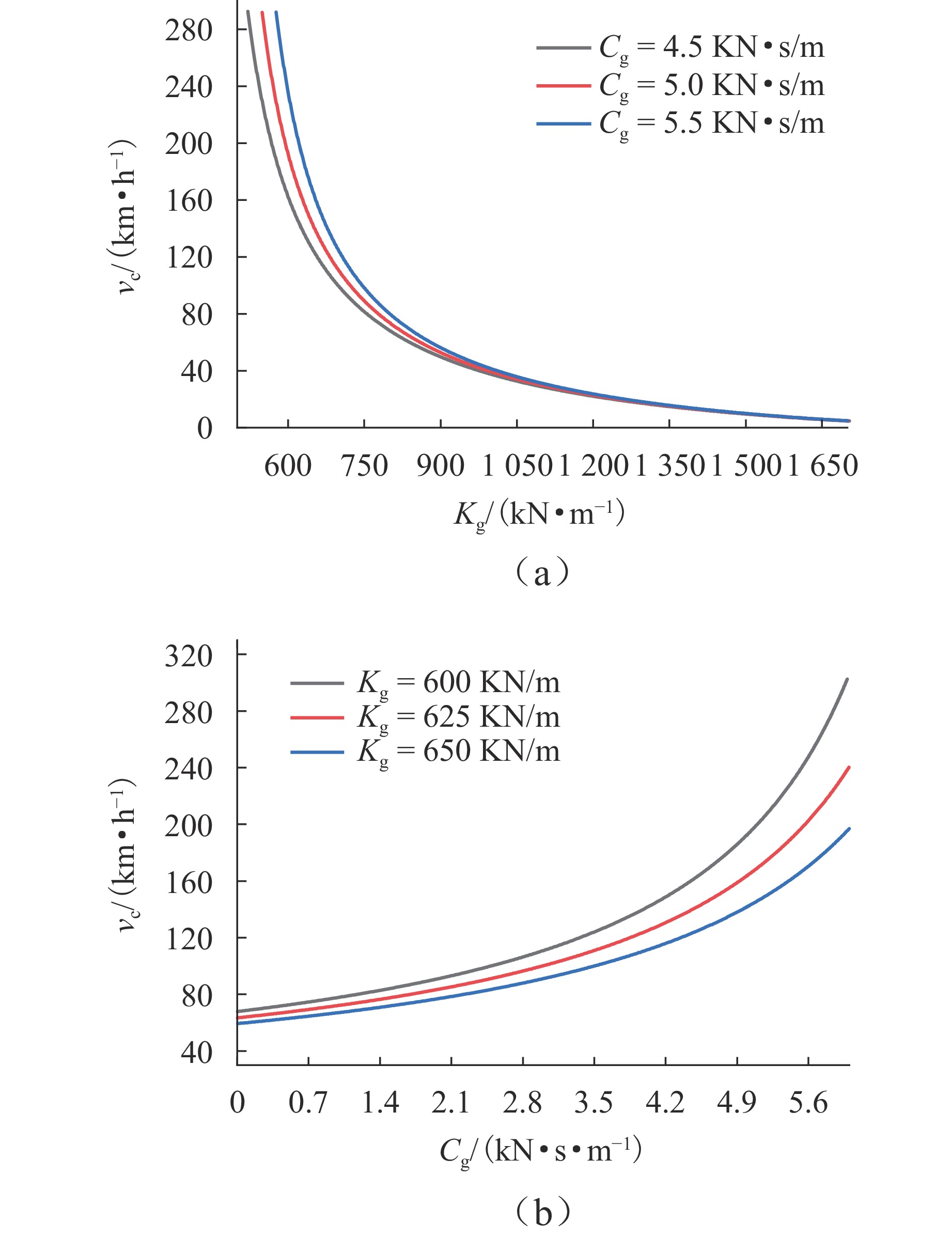
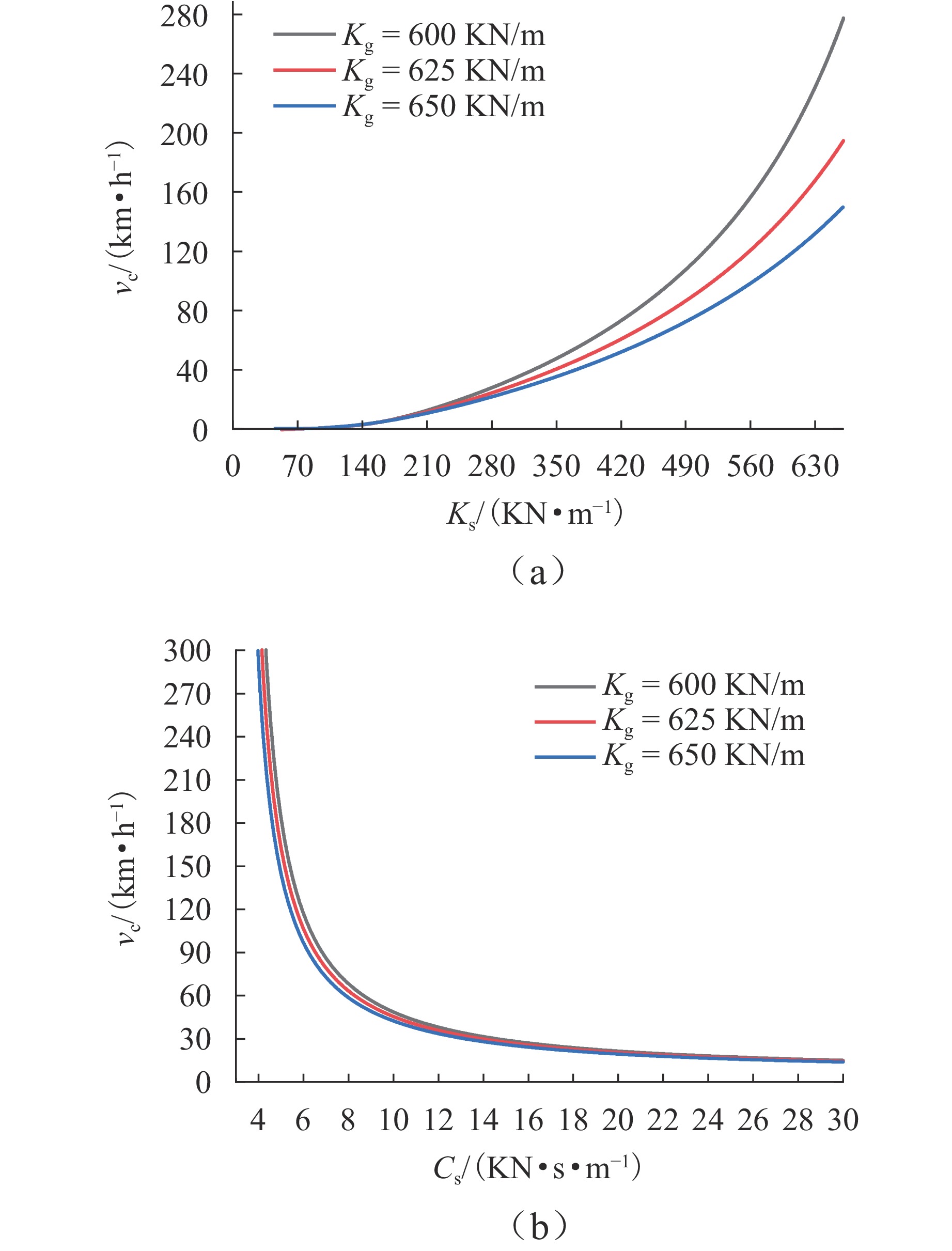
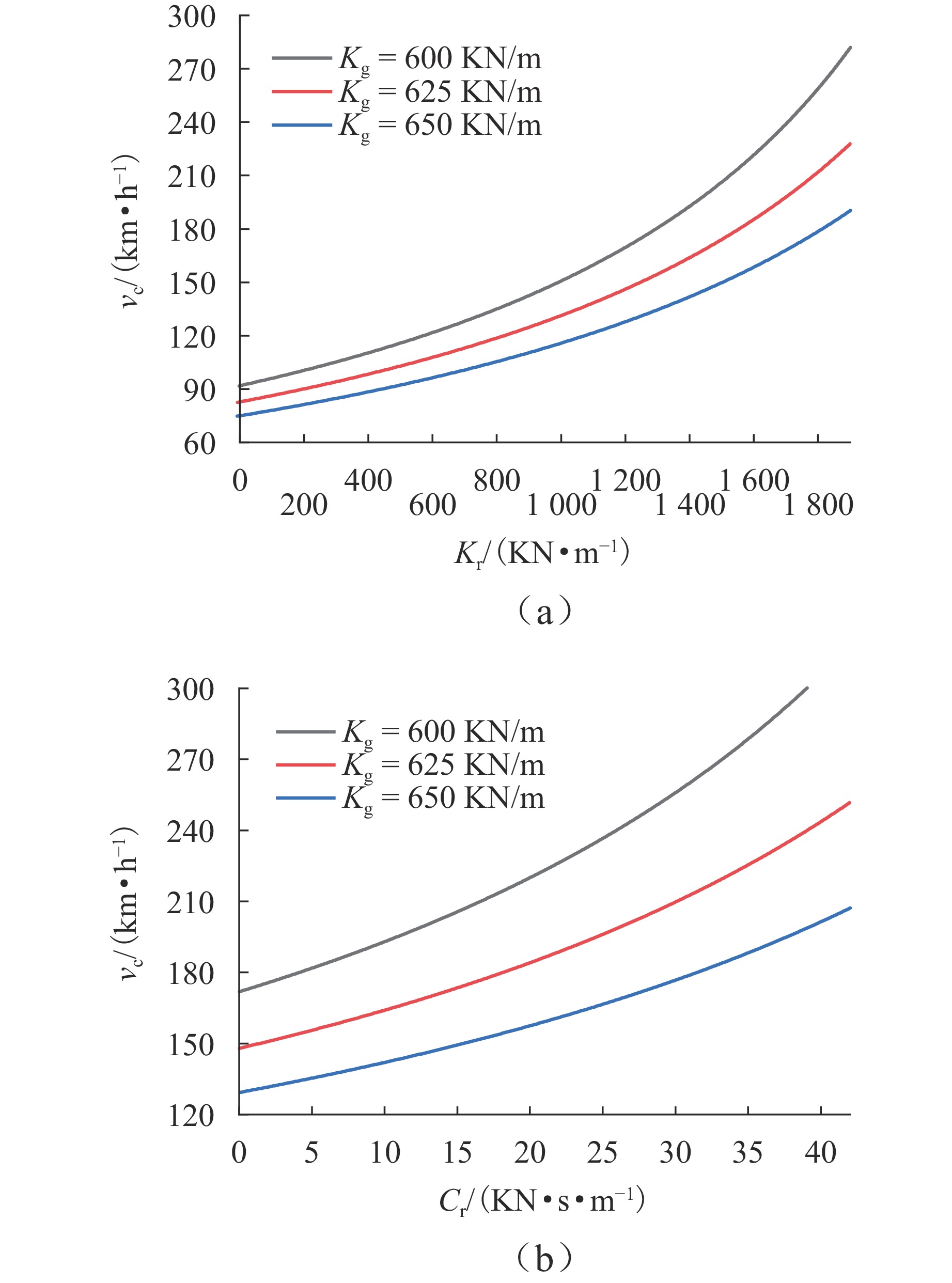
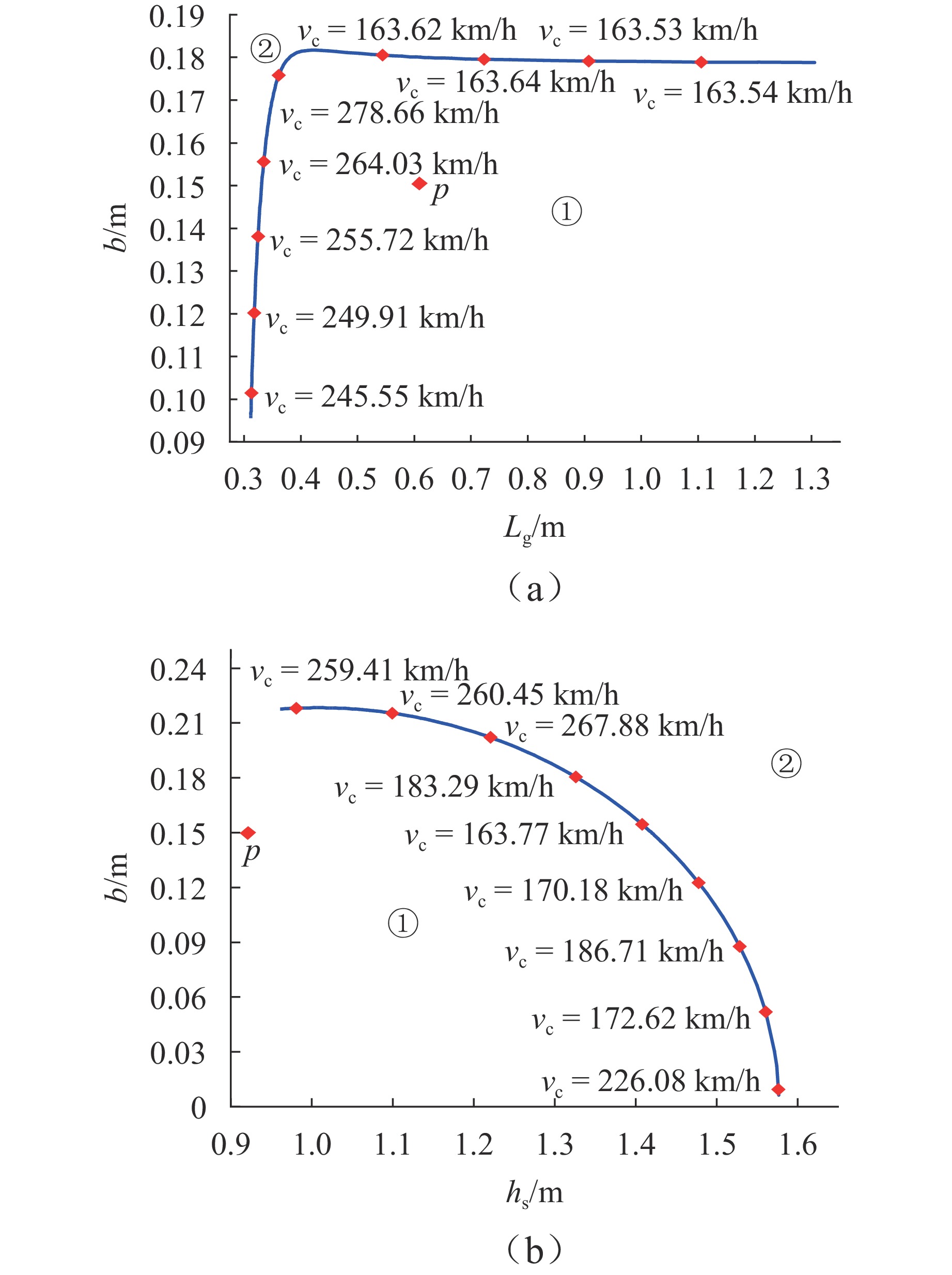
为探究跨座式单轨车辆转向架的稳定性问题,基于轮轨接触关系下轮胎力学特性的空间激扰,对跨座式单轨车辆转向架系统进行Hopf分岔特性分析. 首先,建立考虑空间激扰的三自由度车辆转向架非线性动力学模型;其次,采用Hurwitz稳定性判据求解转向架系统的临界速度,引入中心流形稳定性指标判断系统的Hopf分岔类型,并利用MATCONT工具包对理论分析结果进行数值验证;最后,探讨不同空间激扰条件对转向架系统稳定性的影响. 研究结果表明:在低速运动状态下转向架以2.4 Hz的侧滚运动为主,中高速运动状态下主要表现为摇头和侧滚的耦合运动为主,频率在1.3 Hz~2.4 Hz;当速度达到163.563 24 km/h时,系统发生超临界Hopf分岔,出现稳定极限环,且在速度为163.563 6 km/h时发生鞍结分岔,系统又出现不稳定极限环;空间激扰作用下,转向架的临界速度随导向轮径向刚度和稳定轮径向阻尼的增大而减小,随导向轮径向阻尼、稳定轮径向刚度以及走行轮径向刚度和阻尼的增加而提高;此外,转向架结构参数的改变可引发系统超临界与亚临界Hopf分岔之间的迁移,为避免亚临界Hopf分岔导致系统运动状态突变,应合理设计转向架的结构参数.
Abstract:To investigate the stability of the bogie in a straddle-type monorail vehicle, the Hopf bifurcation characteristics of the straddle-type monorail vehicle bogie system were analyzed based on the spatial perturbations of the mechanical properties under the wheel-rail contact relationship. Firstly, a three-degree-of-freedom nonlinear dynamic model of the vehicle bogie, incorporating spatial perturbations, was established. Secondly, the Hurwitz stability criterion was employed to solve for the critical speed of the bogie system, and the type of Hopf bifurcation was identified via the center manifold stability index. The theoretical results were further validated numerically using the MATCONT toolbox. Finally, the influence of different spatial perturbation conditions on the stability of the bogie system was discussed. The research results show that at a motion state of low speeds, the bogie primarily exhibits rolling motion with a frequency of 2.4 Hz; at a motion state of medium and high speeds, the motion is dominated by coupled yawing and rolling, with frequencies ranging from 1.3 Hz to 2.4 Hz. When the speed reaches 163.563 24 km/h, the system undergoes a supercritical Hopf bifurcation, resulting in the emergence of a stable limit cycle; at a speed of 163.563 6 km/h, a saddle-node bifurcation occurs, leading to an unstable limit cycle. Under spatial perturbations, the critical speed of the bogie decreases with increasing radial stiffness of the guiding wheel and radial damping of the stabilizing wheel but increases with greater radial damping of the guiding wheel, radial stiffness of the stabilizing wheel, as well as the radial stiffness and damping of the running wheel. Moreover, changes in the structural parameters of the bogie can induce transitions between supercritical and subcritical Hopf bifurcations. To avoid subcritical Hopf bifurcations that may cause abrupt changes in the system’s motion state, the structural parameters of the bogie should be carefully designed.
-
Key words:
- straddle-type monorail vehicle /
- stability /
- Hopf bifurcation /
- spatial perturbation /
- critical speed
-
表 1 转向架系统模型参数
Table 1. Model parameters of bogie system
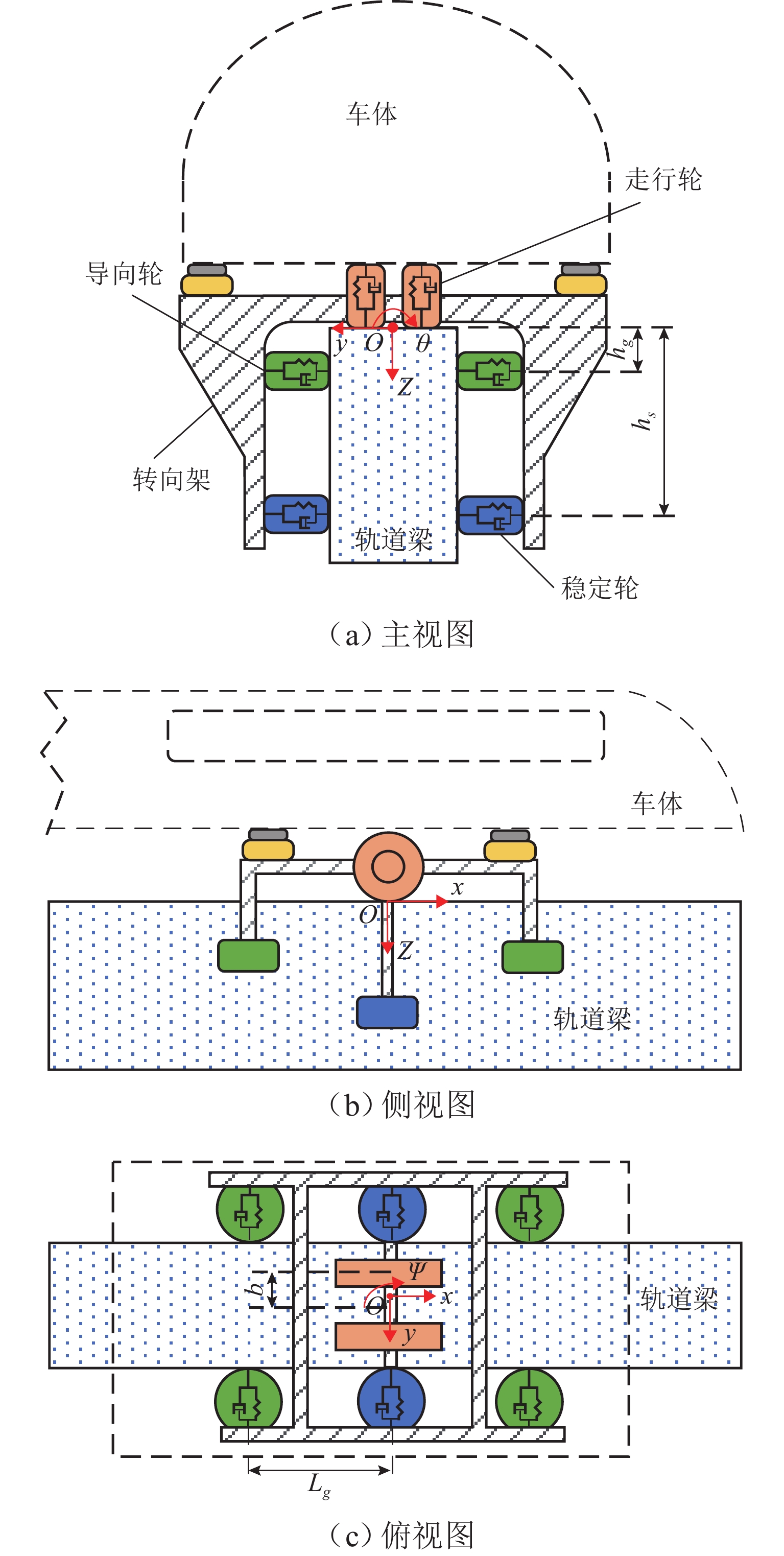
参数 定义 数值 m/kg 转向架质量 2400 Jz/(kg·m2) 转向架z向转动惯量 3898 Jx/(kg·m2) 转向架x向转动惯量 980 v/(km·h−1) 转向架运行速度 — $ K_{\alpha }^{\prime} $/(KN·m·rad−1) 走行轮的回正刚度 10.75 Kτ/(KN·rad−1) 走行轮的切向刚度 33.333 Kr/(KN·m−1) 走行轮的径向刚度 1400 Cr/(KN·s·m−1) 走行轮的径向阻尼 9.8 Kg/Ks/(KN·m−1) 导向轮/稳定轮的径向刚度 625 Cg/Cs/(KN·s·m−1) 导向轮/稳定轮的径向阻尼 5 Lg/m 导向轮纵向跨距的1/2 0.6085 b/m 两走行轮轴距的1/2 0.15 hs/m 稳定轮到转向架质心的垂向距离 0.92 hg/m 导向轮到转向架质心的垂向距离 0.14 ht/m 走行轮中心到转向架质心的高度 0.5 表 2 轮胎模型参数拟合结果相关性检验
Table 2. Correlation test of tire model parameter fitting results
决定系数 调整决定系数 误差平方和 均方根误差 0.9997 0.9997 1.5972 × 10589.3745 表 3 系统的特征值
Table 3. Eigenvalues of system
特征值 临界速度 1 8.403i 2 −8.403i 3 −7.793 + 34.946i 4 −7.793 - 34.946i 5 −0.955 + 15.570i 6 −0.955 - 15.570i -
[1] 郭风琪, 陈柯源, 顾发根, 等. 我国跨座式单轨旅游交通系统的现状与发展[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 52(12): 4540-4551. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2021.12.034GUO Fengqi, CHEN Keyuan, GU Fagen, et al. Reviews on current situation and development of straddle-type monorail tour transit system in China[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2021, 52(12): 4540-4551. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2021.12.034 [2] 仇成群, 李沛润, 陈钊, 等. 跨座式单轨列车走行轮轮胎的不均匀磨损[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2022, 57(1): 112-119. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20210291QIU Chengqun, LI Peirun, CHEN Zhao, et al. Uneven wear of running wheel tires of straddle monorail train[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2022, 57(1): 112-119. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20210291 [3] 李韵文, 杨阳, 魏德豪, 等. 跨座式单轨交通列车技术特点及发展展望[J]. 轨道交通装备与技术, 2024(4): 7-11. doi: 10.13711/j.cnki.cn32-1836/u.2024.04.002LI Yunwen, YANG Yang, WEI Dehao, et al. Technical characteristics and prospects of straddle monorail trains[J]. Rail Transportation Equipment and Technology, 2024(4): 7-11. doi: 10.13711/j.cnki.cn32-1836/u.2024.04.002 [4] 任利惠, 李稳, 冷涵, 等. 轮胎式轨道交通车辆动力学研究现状与挑战[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2021, 21(6): 8-30. doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2021.06.002REN Lihui, LI Wen, LENG Han, et al. Research on dynamics of rail transit vehicle with tire running gears: state-of-arts and challenges[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2021, 21(6): 8-30. doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2021.06.002 [5] 杜子学, 文孝霞, 杨震, 等. 跨座式单轨车辆走行轮偏磨损因子模型研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2019, 54(2): 373-380. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20170349DU Zixue, WEN Xiaoxia, YANG Zhen, et al. Study on partial-wear-factor model monorail vehicle running wheel[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2019, 54(2): 373-380. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20170349 [6] WANG Z W, YIN Z H, ALLEN P, et al. Dynamic analysis of enhanced gear transmissions in the vehicle-track coupled dynamic system of a high-speed train[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2022, 60(8): 2716-2738. doi: 10.1080/00423114.2021.1928246 [7] 杜子学, 何超, 杨震, 等. 基于刚柔耦合的跨坐式单轨车辆受电弓疲劳分析[J]. 城市轨道交通研究, 2021, 24(1): 16-21. doi: 10.16037/j.1007-869x.2021.01.004DU Zixue, HE Chao, YANG Zhen, et al. Fatigue analysis of pantograph for straddle monorail vehicle based on rigid-flexible coupling[J]. Urban Mass Transit, 2021, 24(1): 16-21. doi: 10.16037/j.1007-869x.2021.01.004 [8] LEE C H, KAWATANI M, KIM C W, et al. Dynamic response of a monorail steel bridge under a moving train[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2006, 294(3): 562-579. doi: 10.1016/j.jsv.2005.12.028 [9] LEE C H, KIM C W, KAWATANI M, et al. Dynamic response analysis of monorail bridges under moving trains and riding comfort of trains[J]. Engineering Structures, 2005, 27(14): 1999-2013. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2005.06.014 [10] 任利惠, 周劲松, 沈钢. 跨坐式独轨车辆动力学模型及仿真[J]. 中国铁道科学, 2004, 25(5): 26-32. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-4632.2004.05.005REN Lihui, ZHOU Jinsong, SHEN Gang. Dynamics model and simulation study of a straddle type monorail car[J]. China Railway Science, 2004, 25(5): 26-32. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-4632.2004.05.005 [11] LENG H, REN L H, JI Y J, et al. Radial adjustment mechanism of a newly designed coupled-bogie for the straddle-type monorail vehicle[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2020, 58(9): 1407-1427. doi: 10.1080/00423114.2019.1632464 [12] JI Y J, REN L H, HUANG Y P. Passive radial mechanism of a bogie with the auxiliary steering device for the straddle monorail vehicle[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2021, 59(9): 1418-1442. doi: 10.1080/00423114.2020.1755046 [13] ZHOU J C, LIU Y H, GAO J J, et al. Shimmy analysis of straddle-type monorail vehicle with single-axle bogies based on factor model[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2024, 62(5): 1063-1084. doi: 10.1080/00423114.2023.2211694 [14] 魏恒, 卢剑伟, 叶盛勇, 等. 基于中心流形理论的多维耦合摆振系统稳定性分析[J]. 机械工程学报, 2023, 59(4): 155-162.WEI Heng, LU Jianwei, YE Shengyong, et al. Stability analysis of multi-dimensional coupled shimmy system based on center manifold theory[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2023, 59(4): 155-162. [15] WANG Y, XU B B, MENG H D. Enhanced vehicle shimmy performance using inerter-based suppression mechanism[J]. Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation, 2024, 130: 107800. doi: 10.1016/j.cnsns.2023.107800 [16] GUO J Y, SHI H L, LUO R, et al. Bifurcation analysis of a railway wheelset with nonlinear wheel–rail contact[J]. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2021, 104(2): 989-1005. doi: 10.1007/s11071-021-06373-8 [17] ZHANG X, LIU Y Q, YANG S P, et al. Bifurcation analysis of the bogie system with time delay and the influence of parameters on the system[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2024, 62(7): 1739-1755. doi: 10.1080/00423114.2023.2252536 [18] RAN S H, BESSELINK I J M, NIJMEIJER H. Energy analysis of the Von Schlippe tyre model with application to shimmy[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2015, 53(12): 1795-1810. doi: 10.1080/00423114.2015.1093151 [19] 吕国敏, 杨百岭, 杜子学, 等. 新一代单轴跨座式单轨车辆的曲线通过性能[J]. 城市轨道交通研究, 2024, 27(1): 87-93, 99. doi: 10.16037/j.1007-869x.2024.01.016LYU Guomin, YANG Bailing, DU Zixue, et al. Curve-passing performance of new generation single-axle straddle monorail vehicle[J]. Urban Mass Transit, 2024, 27(1): 87-93,99. doi: 10.16037/j.1007-869x.2024.01.016 [20] ZHOU J C. Research of normal contact stiffness of straddle-type monorail tyres based on fractal theory[J]. Mechanics, 2019, 25(3): 248-254. doi: 10.5755/j01.mech.25.3.22265 [21] ZHOU J C, DU Z X, YANG Z, et al. Dynamics study of straddle-type monorail vehicle with single-axle bogies-based full-scale rigid-flexible coupling dynamic model[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 110249-110257. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2933991 [22] DU Z X, WEN X X, ZHAO D Y, et al. Numerical analysis of partial abrasion of the straddle-type monorail vehicle running tyre[J]. Transactions of FAMENA, 2017, 41(1): 99-112. doi: 10.21278/TOF.41109 [23] JIANG Y Z, WU P B, ZENG J, et al. Comparison of the curve negotiation properties of two different articulated monorail vehicles[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part F: Journal of Rail and Rapid Transit, 2019, 233(8): 831-843. doi: 10.1177/0954409718810946 [24] PACEJKA H B, BAKKER E. The magic formula tyre model[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 1992, 21(S1): 1-18. [25] JIANG Y Z, WU P B, ZENG J, et al. Multi-parameter and multi-objective optimisation of articulated monorail vehicle system dynamics using genetic algorithm[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2020, 58(1): 74-91. doi: 10.1080/00423114.2019.1566557 [26] MIAO P C, LI D H, YUE Y, et al. Stability and Bautin bifurcation of four-wheel-steering vehicle system with driver steering control[J]. Chaos, 2023, 33(8): 083122. doi: 10.1063/5.0158869 [27] 武世江, 张继业, 隋皓, 等. 轮对系统的Hopf分岔研究[J]. 力学学报, 2021, 53(9): 2569-2581. doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-21-321WU Shijiang, ZHANG Jiye, SUI Hao, et al. Hopf bifurcation study of wheelset system[J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2021, 53(9): 2569-2581. doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-21-321 [28] 王美琪, 曾思恒, 李源, 等. 二自由度磁浮列车悬浮系统时滞控制研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2024, 59(4): 812-822.WANG Meiqi, ZENG Siheng, LI Yuan, et al. Research on time lag control of levitation system of two-degree-of-freedom magnetic levitation train[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2024, 59(4): 812-822. [29] DING W J. Self-excited vibration: theory, paradigms, and research methods[J]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2011. [30] DHOOGE, GOVAERTS, KUZNETSOV, et al. New features of the software MatCont for bifurcation analysis of dynamical systems[J]. Mathematical and Computer Modelling of Dynamical Systems, 2008, 14(2): 147-175. [31] 张宁, 李田, 马健, 等. 拖车系统车身摆振的非线性动力学分析[J]. 机械工程学报, 2019, 55(24): 127-136.ZHANG Ning, LI Tian, MA Jian, et al. Nonlinear dynamics analysis of the body sway of car-trailer combinations[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2019, 55(24): 127-136. [32] 丁旺才, 刘涛, 吴少培, 等. 碰撞与黏滑振动驱动系统的周期运动转迁与驱动特性[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2025, 60(6): 1623-1634.DING Wangcai, LIU Tao, WU Shaopei, et al. Periodic motion transition and driving characteristics of collision and stick-slipvibration-driven system[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2025, 60(6): 1623-1634. [33] 肖乾, 李子珺, 周新建. 胎压变化对跨座式单轨车桥耦合系统振动影响[J]. 噪声与振动控制, 2020, 40(6): 20-28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1355.2020.06.004XIAO Qian, LI Zijun, ZHOU Xinjian. Impacts of tire pressure on the vibration of straddle monorail vehicle-bridge coupling systems[J]. Noise and Vibration Control, 2020, 40(6): 20-28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1355.2020.06.004 [34] 李自康, 戴春辉, 黄翠翠, 等. 基于多种群遗传算法的磁浮列车自抗扰速度控制[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2025, 60(4): 912-920. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20240113LI Zikang, DAI Chunhui, HUANG Cuicui, et al. Active disturbance rejection speed control for maglev trains based on multiple population genetic algorithm[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2025, 60(4): 912-920. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20240113 -




 下载:
下载: