Infrared Small Target Detection Based on Temporal Local Spatial Entropy and Spatial Multi-Scale Feature
-
摘要:
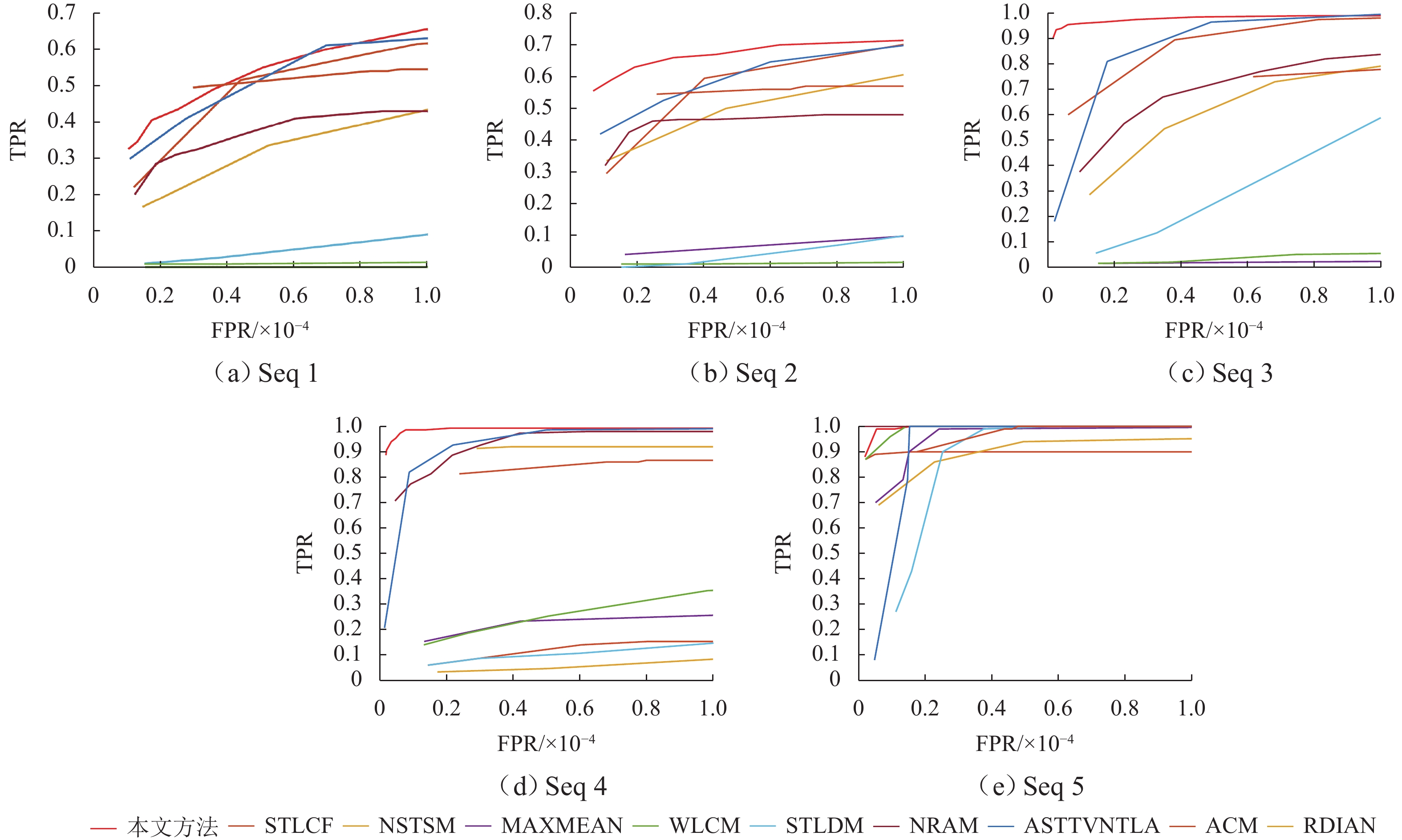
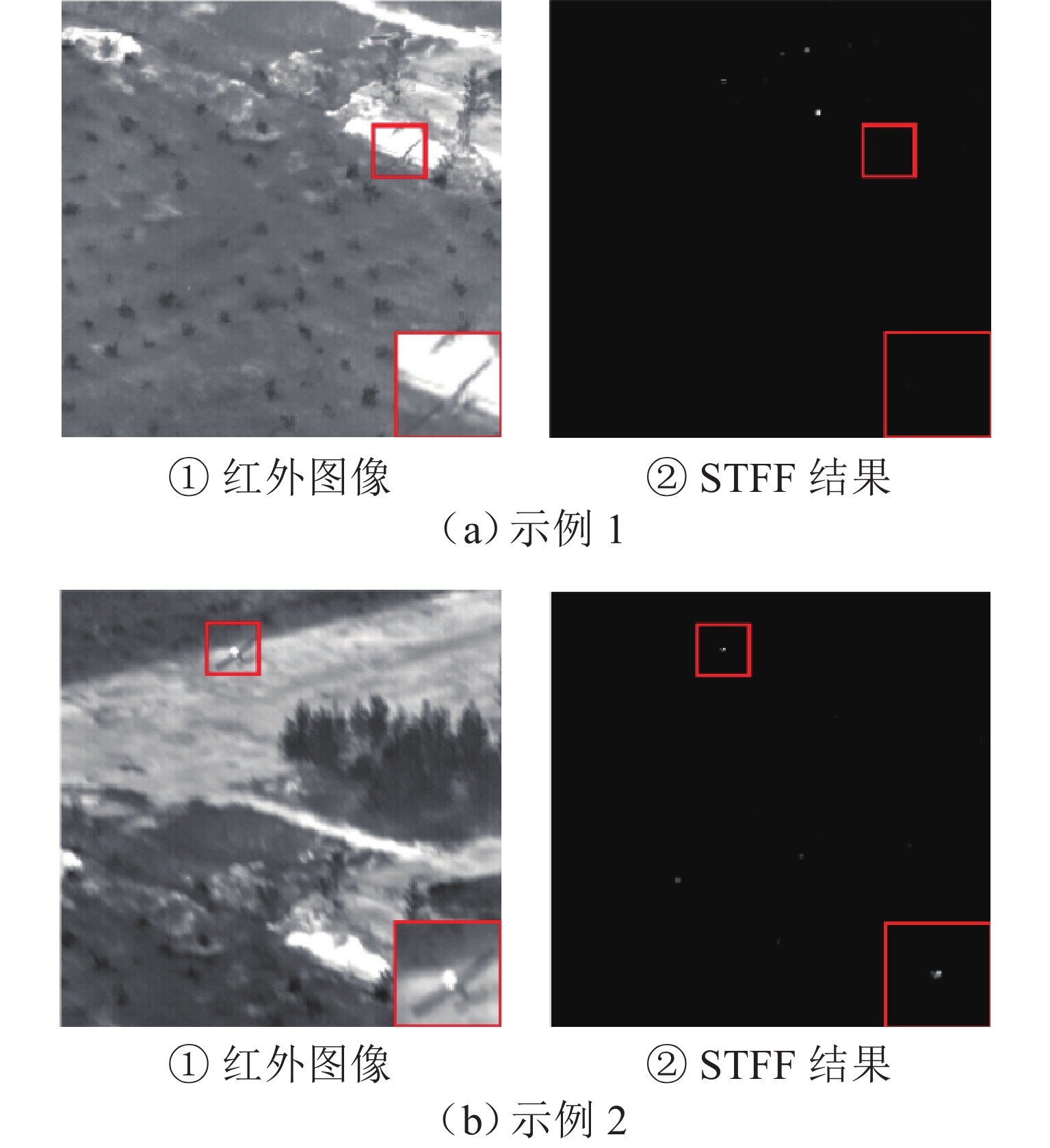
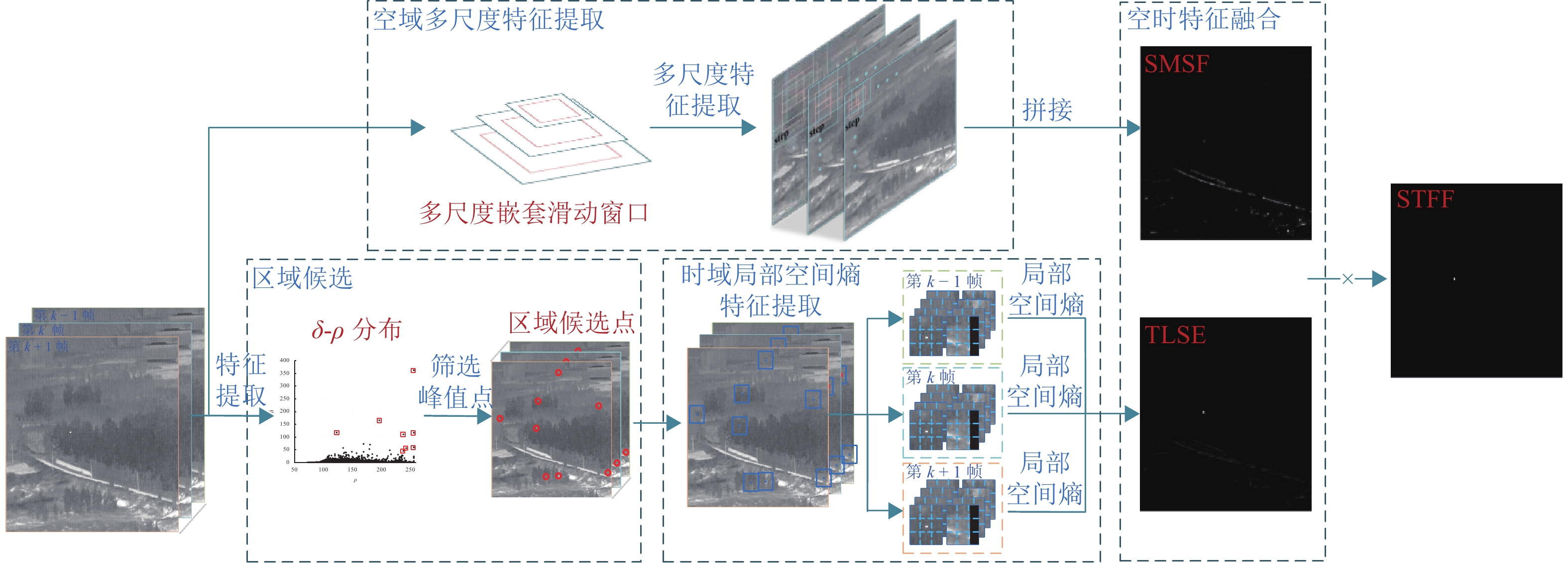
红外成像技术广泛应用于军事和民用领域,其中红外小目标检测作为应用中不可或缺的环节,具有重要的实际价值. 针对现有方法无法有效区分类目标稀疏结构与真实目标的问题,本文提出一种融合时域局部空间熵与空域多尺度特征的红外小目标检测算法. 在时域分支上首先设计基于图像块相似性度量的密度峰值聚类算法,定位红外小目标候选区域,减少对背景的冗余计算. 进一步地,提出一种基于帧间局部差异的时域局部空间熵,充分挖掘目标与背景熵值在局部区域的不同变化特性,解决类目标稀疏结构引起的虚警问题. 此外,引入空域多尺度特征提取分支,构建时空融合特征,降低候选区域定位中的漏检率,提高对不同尺度小目标的检测能力. 在5组不同场景的序列上与9种算法进行对比,本文所提出方法的BSF (background suppression factor)均优于其他方法的,在表现最好的序列5上其BSF值是次优方法的2.02倍,且在ROC (receiver operating characteristic curve)曲线中4组序列上表现为最优. 综上所述,相比于其他方法,所提出方法能够在类目标稀疏结构干扰下精准检出小目标.
Abstract:Infrared imaging technology is widely used in military and civilian fields. As an indispensable part of the application, infrared small target detection has important practical significance. However, the existing methods hardly distinguish the real target from the target-like sparse structure. Therefore, an infrared small target detection algorithm was proposed by fusing the temporal local spatial entropy and the spatial multi-scale feature. In the temporal branch, a density peak clustering algorithm based on the similarity measurement of patches was designed to locate the candidate region of infrared small targets and reduce redundant calculation of backgrounds. Moreover, temporal local spatial entropy based on the local difference between frames was proposed to explore the variations in target and background entropy values in local regions and solve the false alarm caused by the target-like sparse structure. In addition, the spatial multi-scale feature branch was introduced to construct the spatio-temporal fusion feature, reducing the missed detection rate in the location of candidate regions and improving the detection ability of small targets at different scales. Compared with that of nine algorithms on five sets of sequences, the background suppression factor (BSF) of the proposed method is superior. The BSF is 2.02 times better than that of the suboptimal method on the best-performing sequence 5, and it is optimal on four sets of sequences in the receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC). In summary, compared with other methods, the proposed method can detect small targets accurately under the target-like sparse structure.
-
表 1 各序列详细信息
Table 1. Description for each sequence
序列 帧 分辨率/
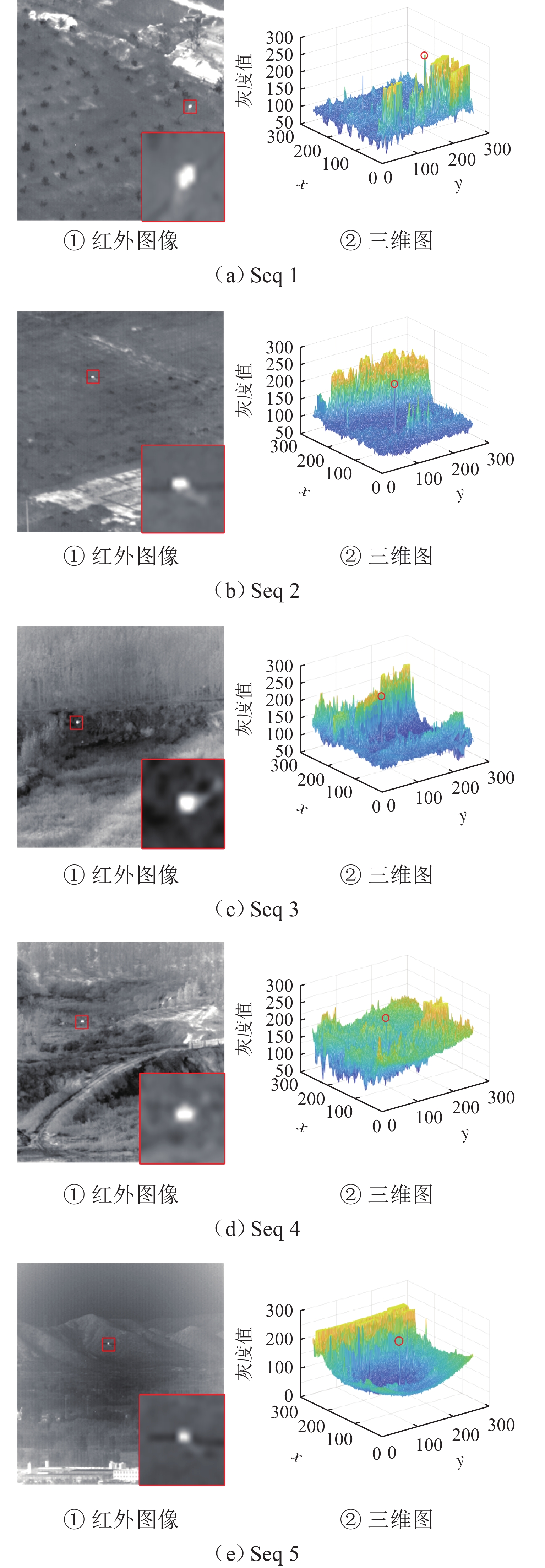
像素背景描述 目标特征 Seq 1 200 256 × 256 近距离、高亮块状背景 部分帧目标
淹没Seq 2 200 256 × 256 高亮块状背景、低对比度地面背景 目标由近及远 Seq 3 200 256 × 256 高亮度光纹、地空背景 扩展目标、目标机动 Seq 4 150 256 × 256 植被、地空背景 目标形状变化 Seq 5 100 256 × 256 高亮度建筑物、噪点干扰 高斯形状 表 2 不同算法在5组序列上的定性对比结果
Table 2. Qualitative comparison results of different algorithms on five sets of sequences

表 3 在5个序列上10种方法的BSF、SCRG结果
Table 3. BSF and SCRG results of 10 methods on five sequences
指标 方法 Seq 1 Seq 2 Seq 3 Seq 4 Seq 5 SCRG MAXMEAN 0.1675 0.2504 0.2258 0.5809 18.9805 WLCM 0.7712 0.8673 0.9183 1.2899 23.5724 NRAM 17.0208 25.7585 28.6412 51.2311 133.5389 STLCF 3.4151 3.4846 5.4057 0.5579 16.3252 STLDM 3.4364 4.1492 11.4342 2.3862 111.5879 ASTTV-NTLA 22.5991 29.4344 3.5312 2.9850 0.1765 NSTSM 10.6381 17.2334 15.4689 1.0603 163.8064 ACM 11.1839 6.9492 26.7686 33.8603 194.6835 RDIAN 17.8196 17.0500 26.9992 44.4159 46.3680 STFF 18.3526 28.2757 40.8815 68.7667 449.2500 BSF MAXMEAN 1115.5920 916.1936 625.3778 442.7659 711.9334 WLCM 715.7735 579.3265 556.9580 389.5317 506.5658 NRAM 5492.4800 5730.4223 4212.5532 5112.0712 2721.1857 STLCF 535.9361 493.4616 627.2045 364.0858 371.9604 STLDM 2264.2647 2115.5049 3018.7691 1916.0918 1908.8198 ASTTV-NTLA 5152.2584 5750.8548 333.0346 178.7372 77.6619 NSTSM 1778.6651 2271.0224 2063.3393 1204.0717 2249.0059 ACM 2113.3549 5966.8174 1967.2721 2062.1592 1860.3962 RDIAN 2873.5632 2041.9871 2224.4897 3180.8297 866.3432 STFF 7093.3875 7575.9045 6363.5806 7055.7701 5484.5020 表 4 实时性能表现对比
Table 4. Real-time performance comparison
s 序列 MAXMEAN WLCM NRAM STLCF STLDM ASTTV-NTLA NSTSM ACM RDIAN STFF Seq 1 0.0113 1.6204 0.3306 23.3607 10.7320 1.8871 0.2020 0.0334 0.1110 1.6258 Seq 2 0.0033 1.5935 0.3132 23.7134 10.5746 1.8757 0.1904 0.0323 0.1119 1.6127 Seq 3 0.0164 1.6091 0.2755 22.5361 10.2368 1.7116 0.1770 0.0320 0.1064 1.6838 Seq 4 0.0163 1.5866 0.3026 21.5019 10.1293 1.8103 0.1821 0.0394 0.1101 1.6064 Seq 5 0.0159 1.6025 0.3615 21.9445 10.2612 1.7122 0.1767 0.0536 0.1246 1.5978 表 5 消融实验结果
Table 5. Experimental results of ablation
模块 SCRG BSF TLSE 2.6330 1995.5313 TLSE+DPC4RP 5.4320 4051.9170 TLSE+SMSF 13.2874 4301.1759 TLSE+DPC4RP+SMSF 18.3526 7093.3875 -
[1] 鞠宏浩, 程楷钧, 邓彩连, 等. 无人机空地网络研究综述[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2024, 59(4): 877-889.JU Honghao, CHENG Kaijun, DENG Cailian, et al. A survey on air-ground networks of unmanned aerial vehicles[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2024, 59(4): 877-889. [2] 赵鹏鹏, 李庶中, 李迅, 等. 融合视觉显著性和局部熵的红外弱小目标检测[J]. 中国光学, 2022, 15(2): 267-275. doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0170ZHAO Pengpeng, LI Shuzhong, LI Xun, et al. Infrared dim small target detection based on visual saliency and local entropy[J]. Chinese Optics, 2022, 15(2): 267-275. doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0170 [3] KOU R K, WANG C P, PENG Z M, et al. Infrared small target segmentation networks: a survey[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2023, 143: 109788. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2023.109788 [4] DESHPANDE S D, ER M H, VENKATESWARLU R, et al. Max-mean and max-median filters for detection of small targets[C]//Signal and Data Processing of Small Targets 1999. Denver: SPIE, 1999: 74-83. [5] 楼晨风, 张湧, 尹佳琪. 基于Robinson-Guard滤波器和像素聚拢度的小目标检测方法[J]. 光学学报, 2020, 40(15): 19-28.LOU Chenfeng, ZHANG Yong, YIN Jiaqi. Small target detection method based on Robinson-guard filter and pixel convergence[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2020, 40(15): 19-28. [6] 吴文怡, 吴一全. 基于Contourlet变换的红外弱小目标检测方法[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2008, 37(1): 136-138.WU Wenyi, WU Yiquan. Method of infrared dim targets detection based on Contourlet transform[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2008, 37(1): 136-138. [7] SUN Y Q, TIAN J W, LIU J. Background suppression based-on wavelet transformation to detect infrared target[C]//2005 International Conference on Machine Learning and Cybernetics. Guangzhou: IEEE, 2005: 4611-4615. [8] TANG W, ZHENG Y B, LU R T, et al. A novel infrared dim small target detection algorithm based on frequency domain saliency[C]//2016 IEEE Advanced Information Management, Communicates, Electronic and Automation Control Conference (IMCEC). Xi’an: IEEE, 2016: 1053-1057. [9] 李俊宏, 张萍, 王晓玮, 等. 红外弱小目标检测算法综述[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2020, 25(9): 1739-1753. doi: 10.11834/jig.190574LI Junhong, ZHANG Ping, WANG Xiaowei, et al. Infrared small-target detection algorithms: a survey[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2020, 25(9): 1739-1753. doi: 10.11834/jig.190574 [10] DAI Y M, WU Y Q. Reweighted infrared patch-tensor model with both nonlocal and local priors for single-frame small target detection[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2017, 10(8): 3752-3767. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2017.2700023 [11] ZHANG L D, PENG Z M. Infrared small target detection based on partial sum of the tensor nuclear norm[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(4): 382-415. doi: 10.3390/rs11040382 [12] LIU T, YANG J G, LI B Y, et al. Nonconvex tensor low-rank approximation for infrared small target detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 60: 5614718. [13] PHILIP CHEN C L, LI H, WEI Y T, et al. A local contrast method for small infrared target detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(1): 574-581. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2242477 [14] ZHANG X Y, RU J Y, WU C D. Infrared small target detection based on gradient correlation filtering and contrast measurement[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5603012. [15] DENG L Z, ZHU H, TAO C, et al. Infrared moving point target detection based on spatial–temporal local contrast filter[J]. Infrared Physics & Technology, 2016, 76: 168-173. [16] PANG D D, SHAN T, MA P G, et al. A novel spatiotemporal saliency method for low-altitude slow small infrared target detection[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2021, 19: 7000705. [17] DAI Y M, WU Y Q, ZHOU F, et al. Asymmetric contextual modulation for infrared small target detection[C]//2021 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV). Waikoloa: IEEE, 2021: 949-958. [18] LI B Y, XIAO C, WANG L G, et al. Dense nested attention network for infrared small target detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2023, 32: 1745-1758. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2022.3199107 [19] YAN P T, HOU R Z, DUAN X G, et al. STDMANet: spatio-temporal differential multiscale attention network for small moving infrared target detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5602516. [20] KOU R K, WANG C P, FU Q, et al. Infrared small target detection based on the improved density peak global search and human visual local contrast mechanism[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2022, 15: 6144-6157. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2022.3193884 [21] 李泽琛, 李恒超, 胡文帅, 等. 多尺度注意力学习的Faster R-CNN口罩人脸检测模型[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2021, 56(5): 1002-1010.LI Zechen, LI Hengchao, HU Wenshuai, et al. Masked face detection model based on multi-scale attention-driven faster R-CNN[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2021, 56(5): 1002-1010. [22] 回丙伟, 宋志勇, 范红旗, 等. 地/空背景下红外图像弱小飞机目标检测跟踪数据集[J]. 中国科学数据, 2020, 5(3): 291-302.HUI Bingwei, SONG Zhiyong, FAN Hongqi, et al. A dataset for infrared detection and tracking of dim-small aircraft targets under ground/air background[J]. China Scientific Data, 2020, 5(3): 291-302. [23] LIU J, HE Z Q, CHEN Z L, et al. Tiny and dim infrared target detection based on weighted local contrast[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2018, 15(11): 1780-1784. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2018.2856762 [24] ZHANG L D, PENG L B, ZHANG T F, et al. Infrared small target detection via non-convex rank approximation minimization joint l2, 1 norm[J]. Remote Sensing, 2018, 10(11): 1821-1846. doi: 10.3390/rs10111821 [25] DU P, HAMDULLA A. Infrared moving small-target detection using spatial–temporal local difference measure[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2019, 17(10): 1817-1821. [26] SUN H, BAI J X, YANG F, et al. Receptive-field and direction induced attention network for infrared dim small target detection with a large-scale dataset IRDST[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5000513. -




 下载:
下载: