Miniaturized Dual-Band Trackside Antenna Design and Its Electromagnetic Compatibility Study
-
摘要:
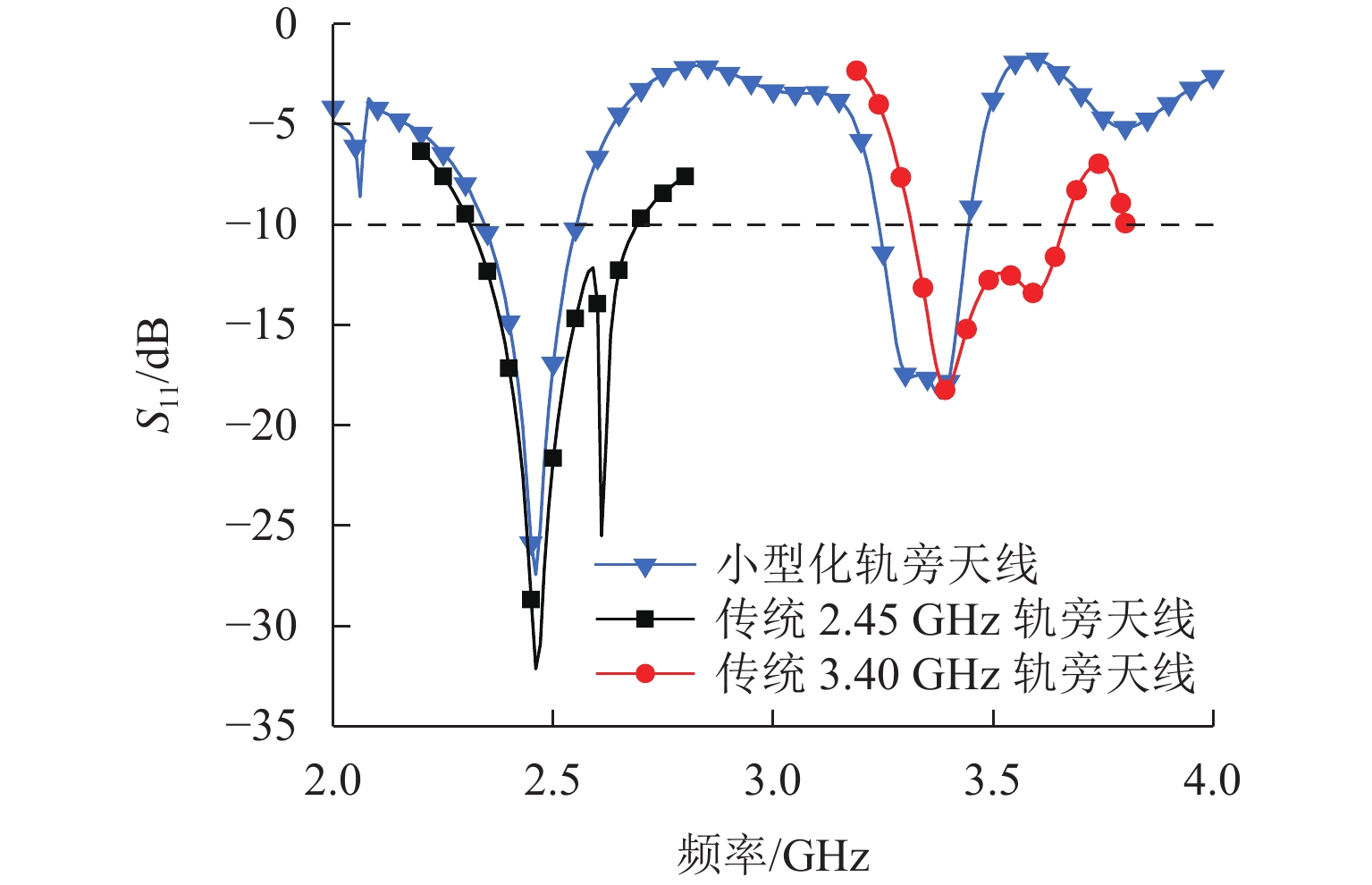
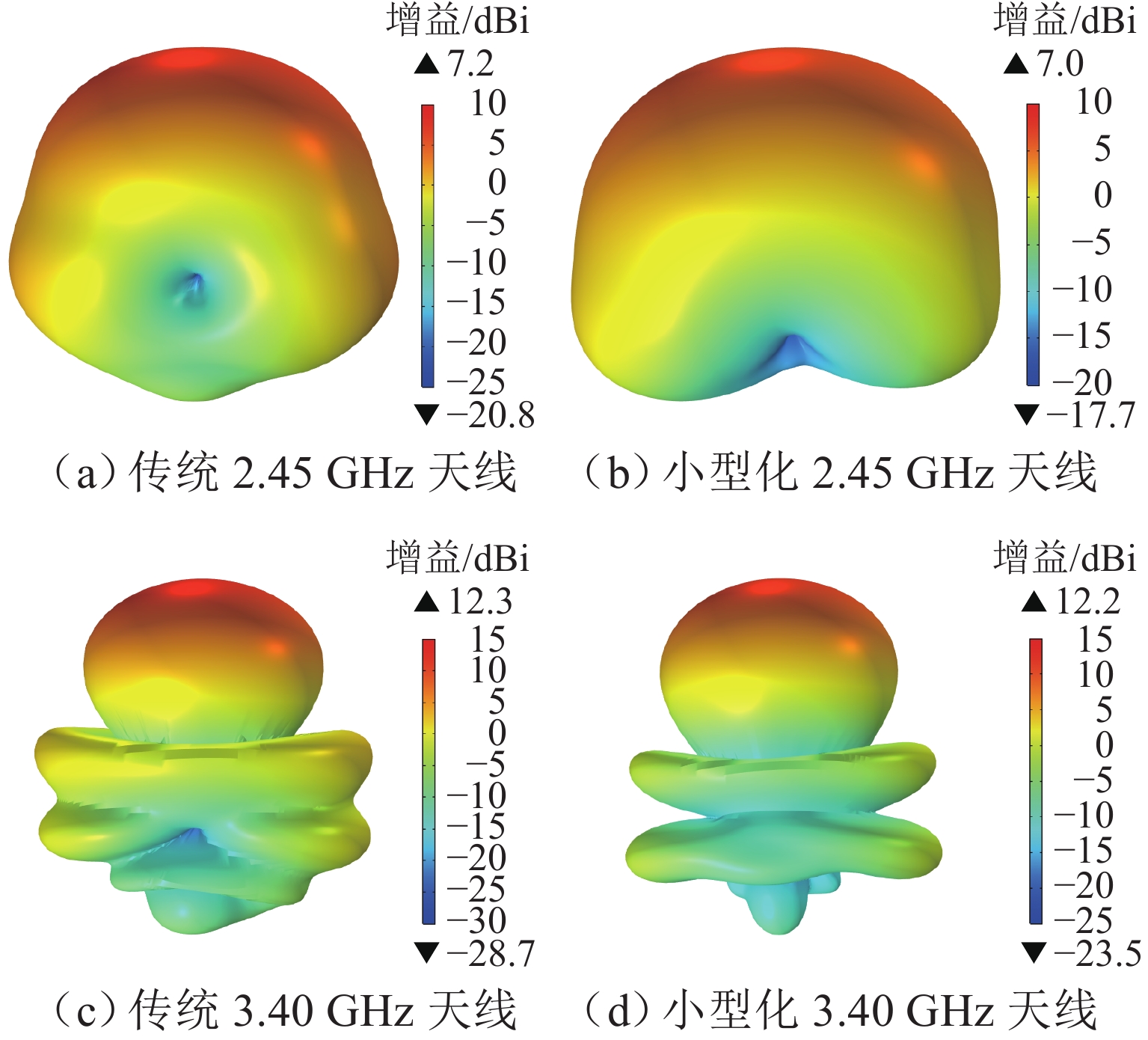
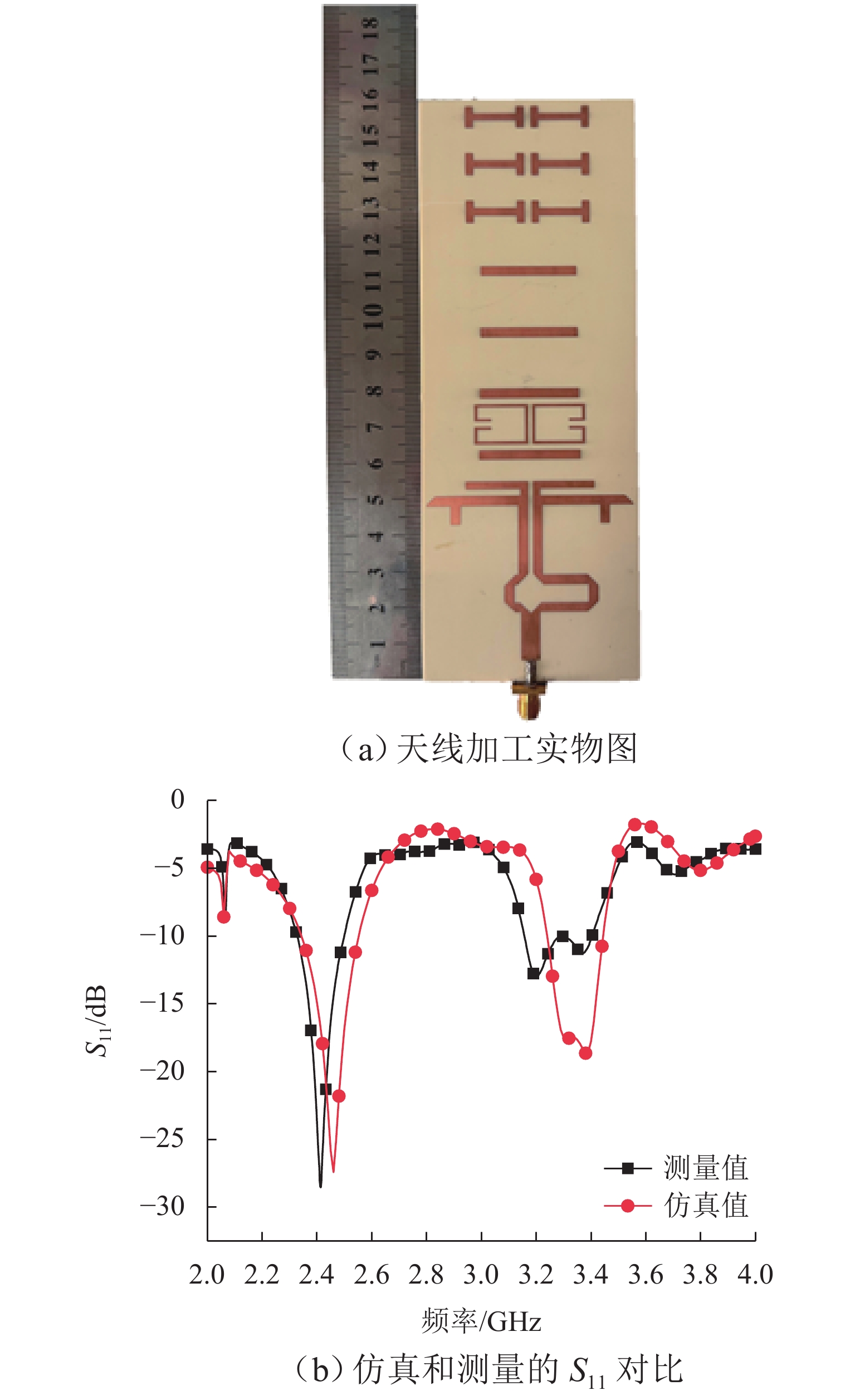
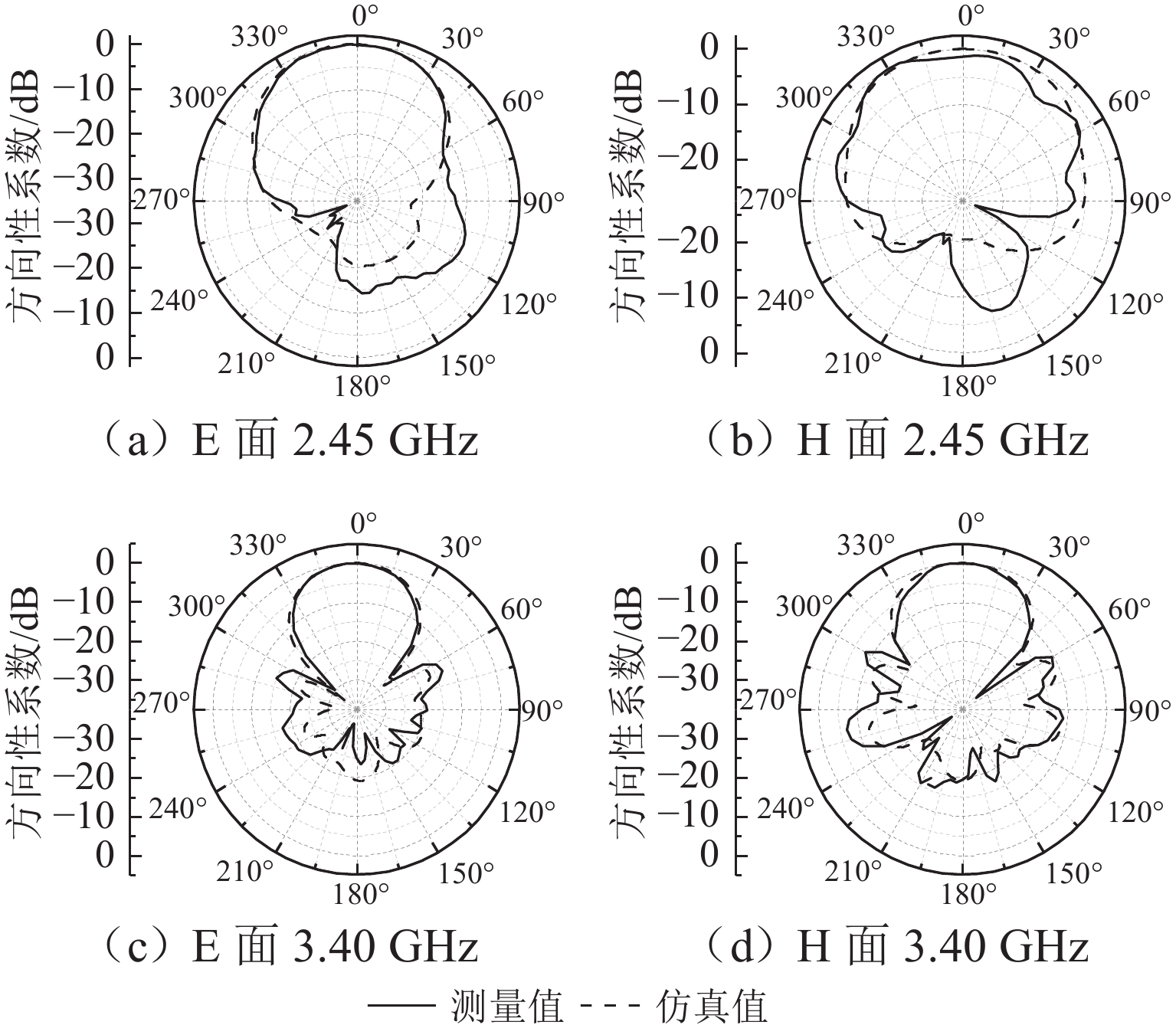
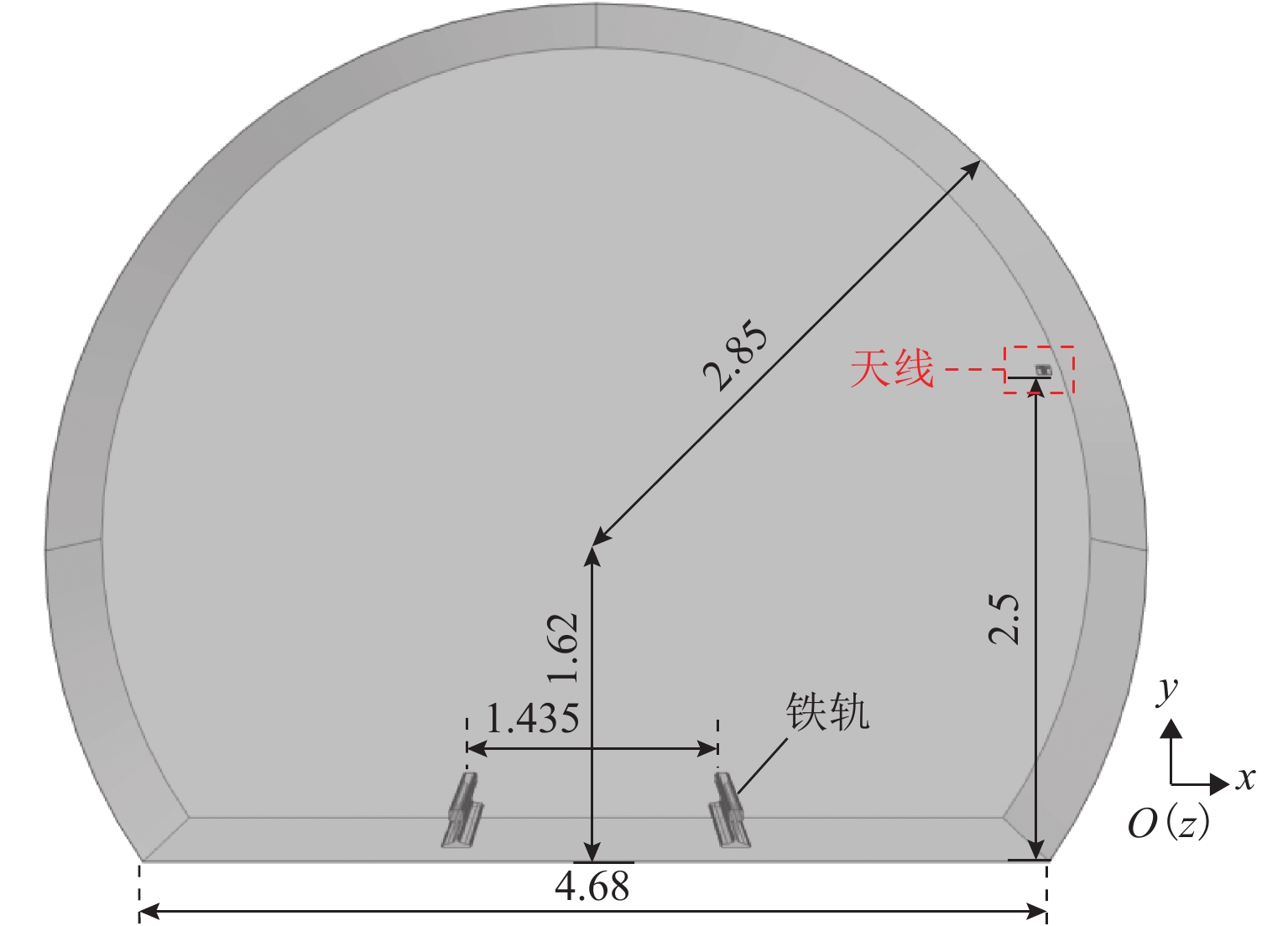
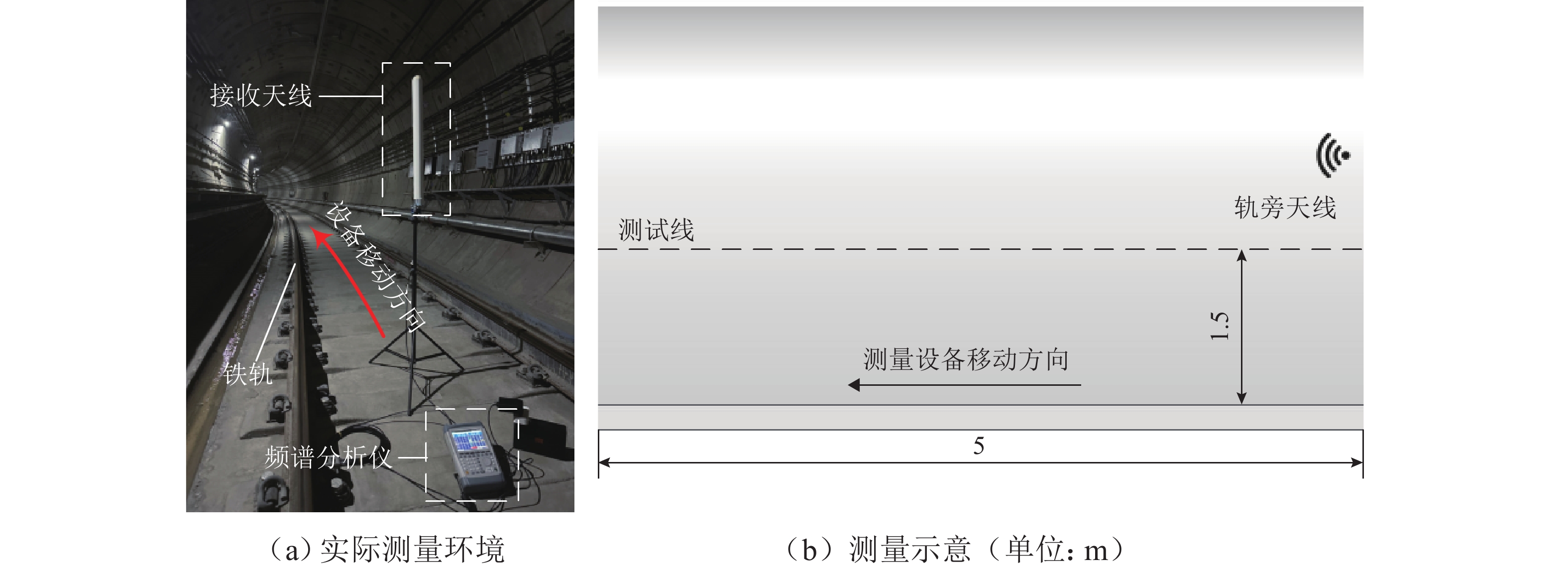
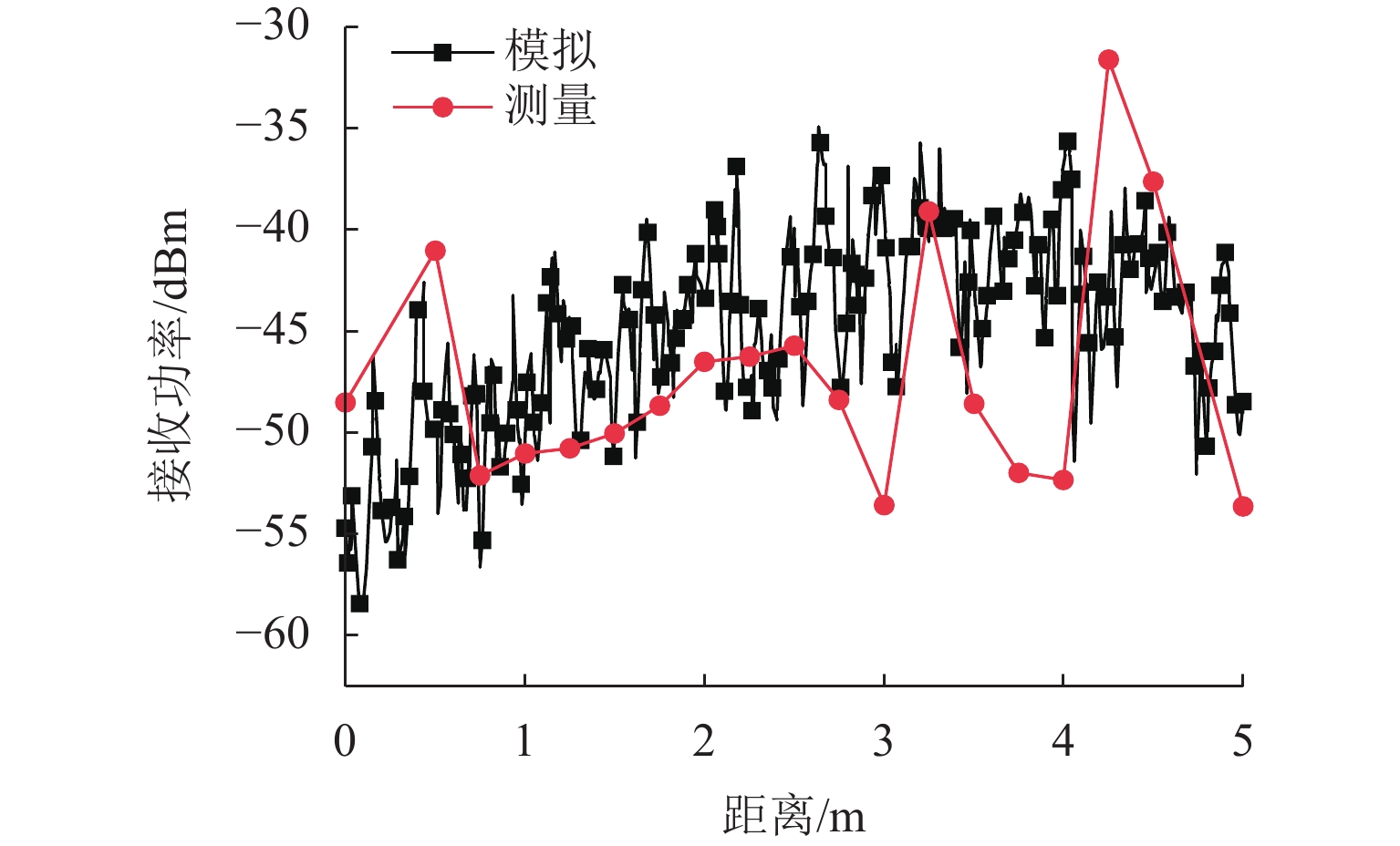
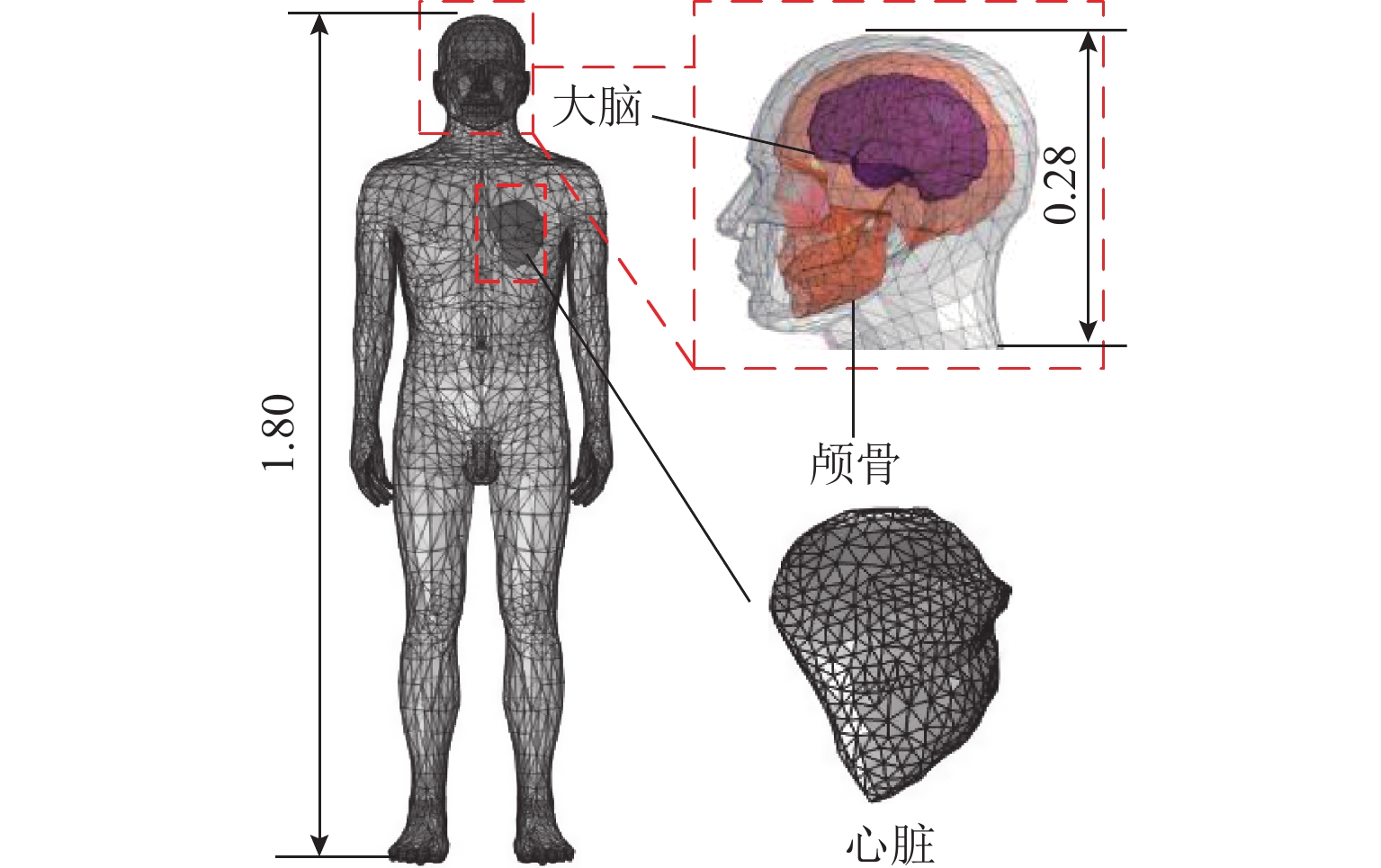
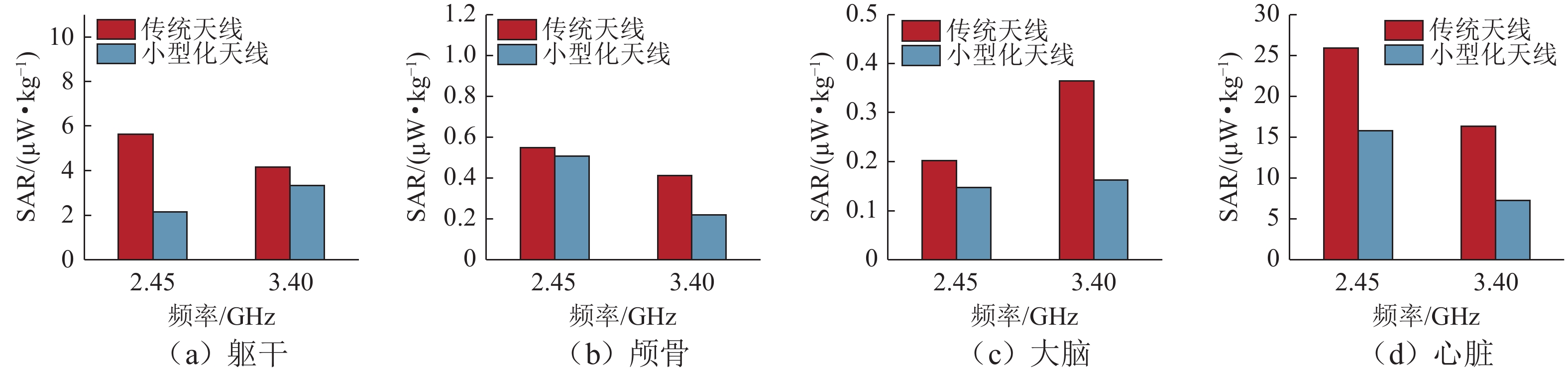
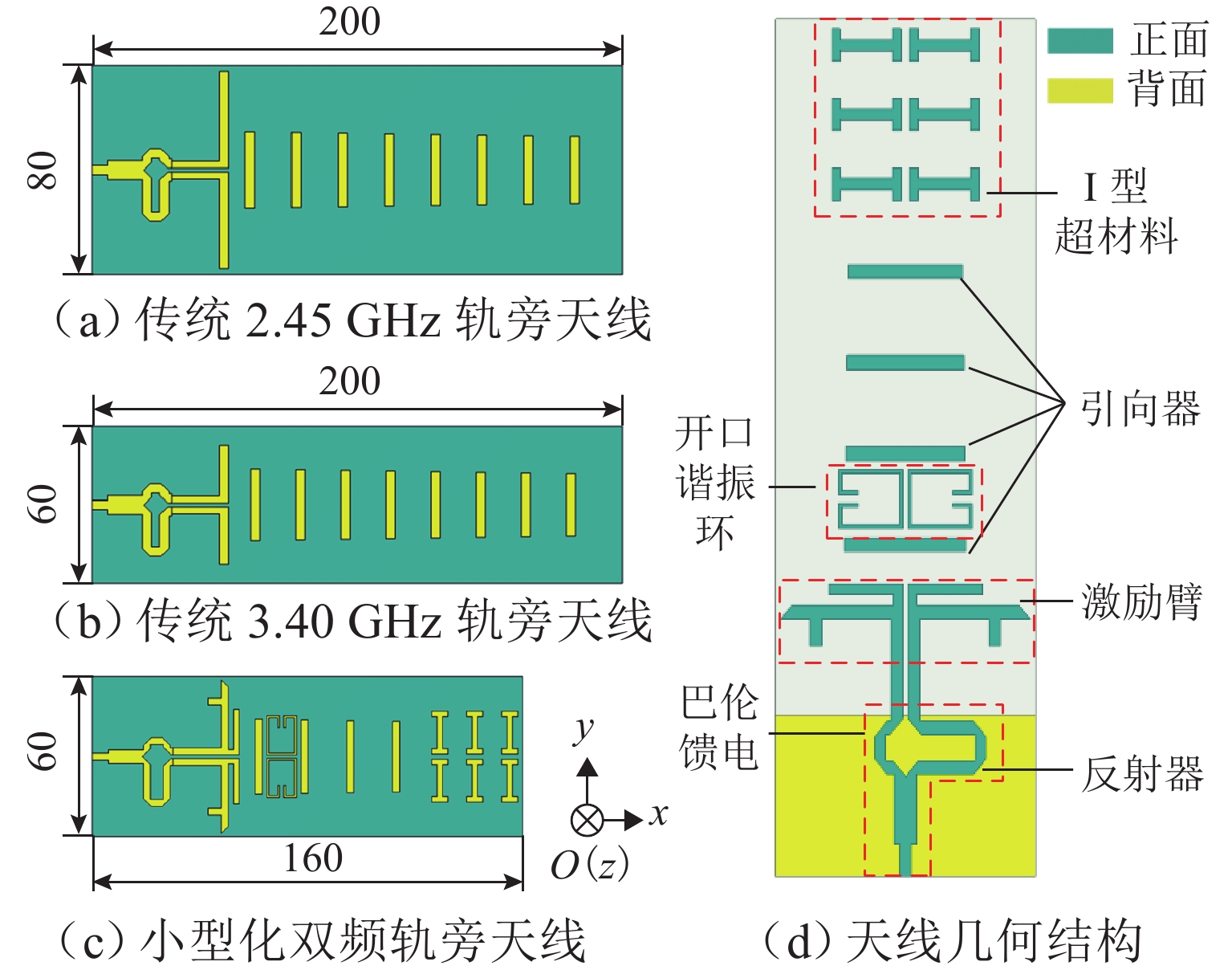
为满足隧道内5G通信需求并提高轨旁天线利用率,提出一种基于超材料的双频轨旁天线,该天线具有同时支持列车自动控制系统和民用5G无线通信的能力. 首先,根据5G通信部署方案设计小型化双频轨旁天线,并使用有限元法模拟其在小型化前后的电磁特性,评估对隧道内电磁环境及其他辐射源的影响;其次,构建包含躯干、颅骨、大脑、心脏等重要组织的轻量化人体模型,以对比仿真传统单频轨旁天线和小型化双频轨旁天线的辐射对人体组织比吸收率(specific absorption rate, SAR)的影响. 研究结果表明:与传统单频轨旁天线相对,小型化双频轨旁天线工作在2.45 GHz和3.40 GHz频段的体积分别减小40%和20%,其周围隧道空间电场分别降低2.09%和6.57%以上,漏泄同轴电缆上的感应电场强度分别减小19.67%和32.41%,天线小型化后降低了对周围辐射源的影响,提高隧道内轨旁天线的电磁兼容性;小型化双频天线使人体躯干、颅骨、大脑、心脏的SAR值分别降低19.76%、46.60%、55.62%、55.28%以上,显著减小了天线对轨旁工作人员的辐射影响.
Abstract:To meet the demand for 5G communication in tunnels and increase the utilization rate of trackside antennas, a dual-band trackside antenna based on metamaterials was proposed, which could support both automatic train control systems and civil 5G wireless communication. First, a miniaturized dual-band trackside antenna was designed based on the 5G communication deployment scheme, and the finite element method was used to simulate the electromagnetic properties of the antenna before and after miniaturization. The impact on the electromagnetic environment and other radiation sources in the tunnel was evaluated. Second, a lightweight human body model containing important tissue such as the trunk, skull, brain, and heart was constructed, so as to compare the effects of radiation on the specific absorption rate (SAR) of human tissue between the simulated traditional single-band trackside antenna and the miniaturized dual-band trackside antenna. The results show that the miniaturized dual-band trackside antenna is 40% and 20% smaller than the traditional single-band trackside antenna when the antenna operates at 2.45 GHz and 3.40 GHz, respectively, and the electric field strength in the surrounding tunnel space is reduced by over 2.09% and 6.57%. The induced electric field strength on the leaky coaxial cable is reduced by 19.67% and 32.41%, respectively. The miniaturization of the antenna effectively reduces the impact on surrounding radiation sources and improves the electromagnetic compatibility of the trackside antenna inside the tunnel. The miniaturized dual-band trackside antenna makes the SAR values absorbed by the trunk, skull, brain, and heart of the human body drop by 19.76%, 46.60%, 55.62%, and 55.28%, respectively, which significantly decreases the radiation impact of the trackside antenna on occupational groups.
-
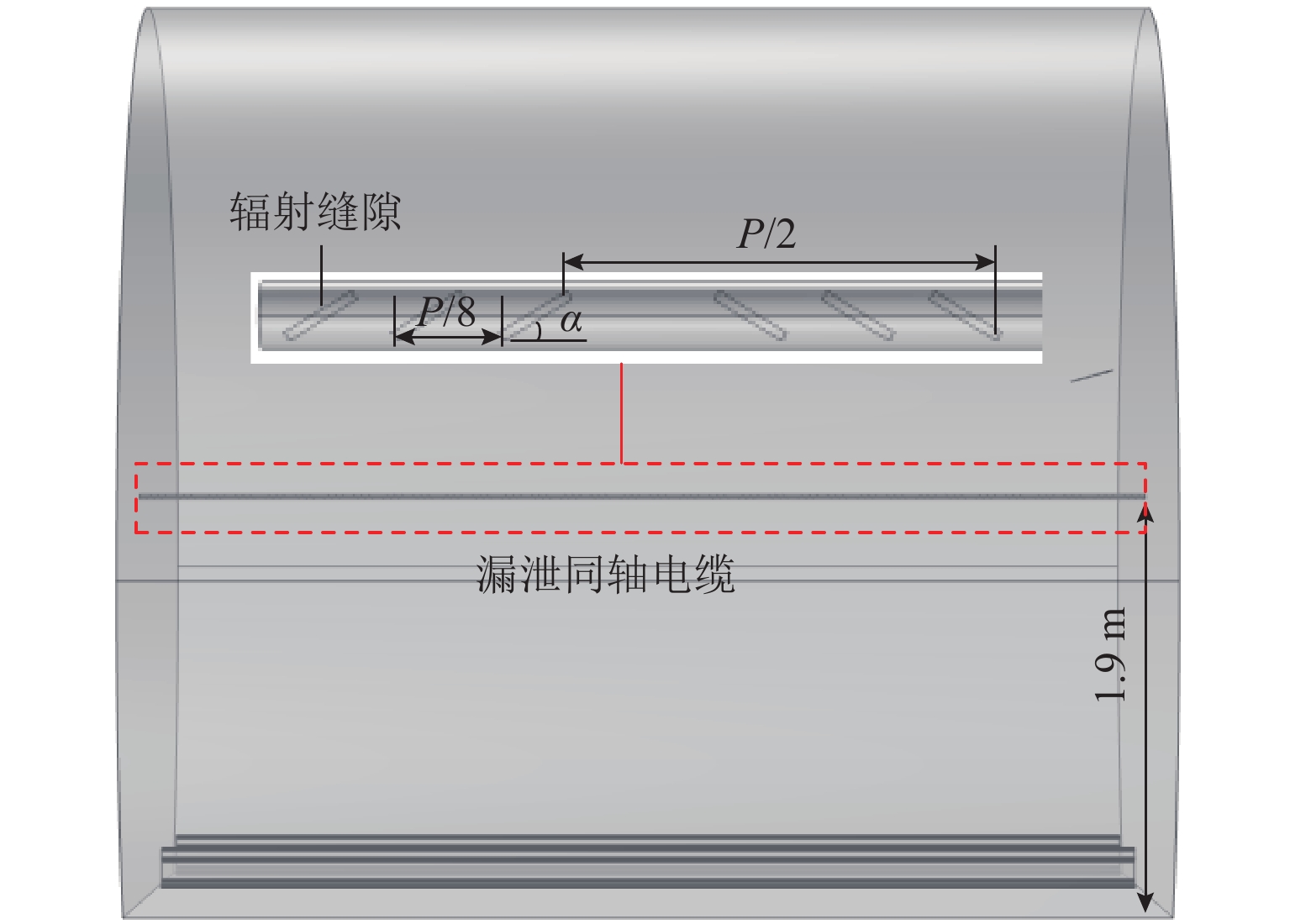
表 1 不同天线辐射下漏缆上的感应电场强度
Table 1. Induced electric field strength on leaky cables under different antenna radiations
频率/
GHz传统天线/
(V•m−1)小型化天线/
(V•m−1)减小比例% 2.45 1.22 0.98 19.67 3.40 3.24 2.19 32.41 表 2 人体组织介电参数和组织密度
Table 2. Dielectric parameters and density of human tissue
组织 2.45 GHz 3.40 GHz ρ/(kg•m−3) εr σ/(S•m−1) εr σ/(S•m−1) 躯干 41.31 1.57 40.18 2.19 1297 颅骨 18.55 0.81 17.53 1.16 1990 大脑 42.54 1.51 41.28 2.15 1038 心脏 54.81 2.26 53.01 3.11 1050 表 3 躯干电场强度最大仿真值与ICNIRP限值对比
Table 3. Comparison of simulated electric field strength maxima of trunk with ICNIRP limits
V/m 频率/GHz 仿真值 ICNIRP 限值 2.45 0.07 61 3.40 0.09 61 表 4 躯干SAR最大仿真值与ICNIRP限值对比
Table 4. Comparison of simulated SAR maxima of trunk with ICNIRP limits
W/kg 频率/GHz 仿真值 ICNIRP 限值 2.45 2.15 × 10−6 2 3.40 3.33 × 10−6 2 -
[1] 中国城市轨道交通协会. 中国城市轨道交通智慧城轨发展纲要[J]. 城市轨道交通,2020,4:8-23. [2] 中国城市轨道交通协会. 2023年上半年中国内地城市轨道交通线路汇总分析[J]. 现代城市轨道交通,2023,7:117-118. [3] 周文颖. 地铁列车司机室高频电磁暴露安全评估研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州交通大学,2018. [4] BRISO-RODRIGUEZ C, CRUZ J M, ALONSO J I. Measurements and modeling of distributed antenna systems in railway tunnels[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2007, 56(5): 2870-2879. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2007.900500 [5] 人民邮电报. 中国工程院院士姚富强:电磁环境应纳入可持续发展战略[R/OL]. (2023-09-19) [2024-10-15]. https://www.cnii.com.cn/rmydb/202309/t20230919_505081.html. [6] WANG T H, LI B, ZHAO K F, et al. Evaluation of electromagnetic exposure of the human with a coronary stent implant from an electric vehicle wireless power transfer device[J]. Electronics, 2023, 12(20): 4231.1-4231.16. [7] 田瑞,逯迈. 高速铁路25 kV接触线工频电磁暴露剂量学仿真研究[J]. 高电压技术,2017,43(8): 2505-2512.TIAN Rui, LU Mai. Dosimetry simulation research on power frequency electromagetic exposure of 25 kV contact line over the high-speed railway[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2017, 43(8): 2505-2512. [8] 牛大鹏,朱峰,邱日强,等. 高铁离线电弧射频和车内低频电磁暴露的特性研究[J]. 高电压技术,2016,42(8): 2587-2595.NIU Dapeng, ZHU Feng, QIU Riqiang, et al. Study on the characteristics of off-line arc’s radio-frequency and low-frequency electromagnetic exposure inside the high speed rail train[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2016, 42(8): 2587-2595. [9] ZHOU W Y, LU M. Miniaturization of quasi-Yagi antenna array with high gain using split-ring resonators[J]. International Journal of Antennas and Propagation, 2020, 2020: 4915848.1-4915848.12. [10] AHDI REZAEIEH S, ANTONIADES M A, ABBOSH A M. Miniaturization of planar yagi antennas using mu-negative metamaterial-loaded reflector[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2017, 65(12): 6827-6837. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2017.2758174 [11] MUKHERJEE S, ROY A, MAITY S, et al. Electromagnetic band gap coupled tri-notched miniaturized ultra-wideband antenna loaded with slot and parasitic strip[J]. International Journal of Communication Systems, 2023, 36(15): e5565.1-e5565.22. [12] LOW J H, CHEE P S, LIM E H. Liquid EBG-backed stretchable slot antenna for human body[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2022, 70(10): 9120-9129. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2022.3184456 [13] ZHANG Y M, LAN T Y, ZHANG S, et al. Harmonic-suppressed dual-resonance decoupling network with near-zero insertion loss for patch antenna arrays[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2023, 71(8): 6959-6964. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2023.3276579 [14] LI M, WANG M, JIANG L J, et al. Decoupling of antennas with adjacent frequency bands using cascaded decoupling network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2021, 69(2): 1173-1178. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2020.3010956 [15] 陶莹,牛刚,张祖威,等. 高铁电磁辐射对女乘务员卵巢功能的影响[J]. 中山大学学报(医学科学版),2014,35(2): 274-277.TAO Ying, NIU Gang, ZHANG Zuwei, et al. Effects of electromagnetic radiation in high-speed train on ovarian function of stewardess[J]. Journal of Sun Yat-Sen University (Medical Sciences), 2014, 35(2): 274-277. [16] ZHANG C, LI C S, YANG L, et al. Assessment of twin fetal exposure to environmental magnetic and electromagnetic fields[J]. Bioelectromagnetics, 2022, 43(3): 160-173. doi: 10.1002/bem.22397 [17] 李光烈,逯迈,李锦屏,等. 超导磁悬浮轨道磁场对乘客电磁暴露安全评估[J]. 现代电子技术,2022,45(6): 112-118.LI Guanglie, LU Mai, LI Jinping, et al. Safety assessment of passengers in electromagnetic exposure to magnetic field on superconducting magnetic levitation track[J]. Modern Electronics Technique, 2022, 45(6): 112-118. [18] LI J, LU M. Safety assessment of occupational electromagnetic exposure for subway attendant by leaky coaxial cable[J]. Journal of Electrical Engineering & Technology, 2024, 19(3): 1701-1713. [19] SUGUMARAN B, BALASUBRAMANIAN R, PALANISWAMY S K. Reduced specific absorption rate compact flexible monopole antenna system for smart wearable wireless communications[J]. Engineering Science and Technology, an International Journal, 2021, 24(3): 682-693. doi: 10.1016/j.jestch.2020.12.012 [20] 朱峰,高晨轩,唐毓涛. 弓网电弧对机场终端全向信标台电磁骚扰的影响[J]. 中国铁道科学,2018,39(1): 116-121. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4632.2018.01.16ZHU Feng, GAO Chenxuan, TANG Yutao. Influence of pantograph-catenary arc on electromagnetic disturbance of airport terminal omnidirectional beacon[J]. China Railway Science, 2018, 39(1): 116-121. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4632.2018.01.16 [21] GUAN K, ZHONG Z D, ALONSO J I, et al. Measurement of distributed antenna systems at 2.4 GHz in a realistic subway tunnel environment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2012, 61(2): 834-837. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2011.2178623 [22] 何金良. 电磁兼容概论[M]. 北京: 科学出版社,2010. [23] GOSSELIN M C, NEUFELD E, MOSER H, et al. Development of a new generation of high-resolution anatomical models for medical device evaluation: the virtual population 3.0[J]. Physics in Medicine and Biology, 2014, 59(18): 5287-5303. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/59/18/5287 [24] GABRIEL C, GABRIEL S, CORTHOUT E. The dielectric properties of biological tissuesⅠ: literature survey[J]. Physics in Medicine and Biology, 1996, 41(11): 2231-2249. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/41/11/001 [25] MARTELLOSIO A, PASIAN M, BOZZI M, et al. Dielectric properties characterization from 0.5 to 50 GHz of breast cancer tissues[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2017, 65(3): 998-1011. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2016.2631162 [26] International Commission on Non-Ionizing Radiation Protection (ICNIRP). Guidelines for limiting exposure to electromagnetic fields (100 kHz to 300 GHz)[J]. Health Physics, 2020, 118(5): 483-524. doi: 10.1097/HP.0000000000001210 -




 下载:
下载: