Characteristics of Micro-Pressure Wave Noise at High-Speed Metro Tunnel Exits and Noise Reduction
-
摘要:
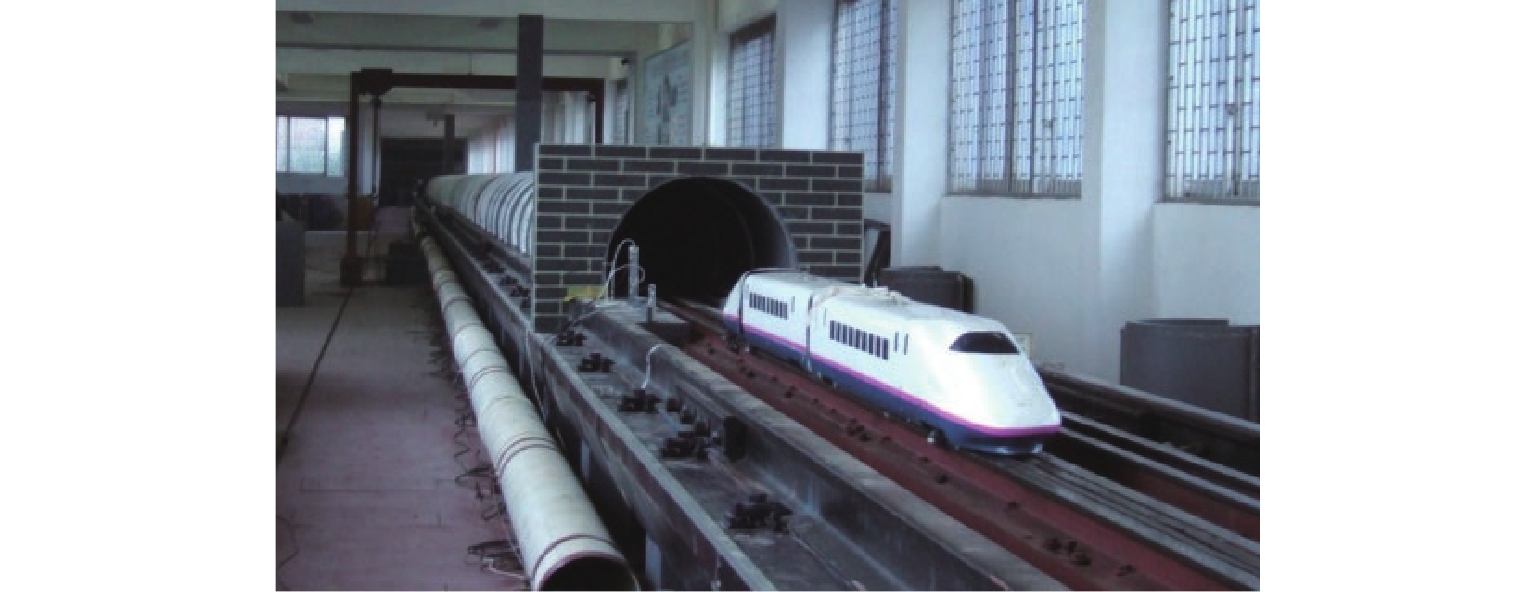
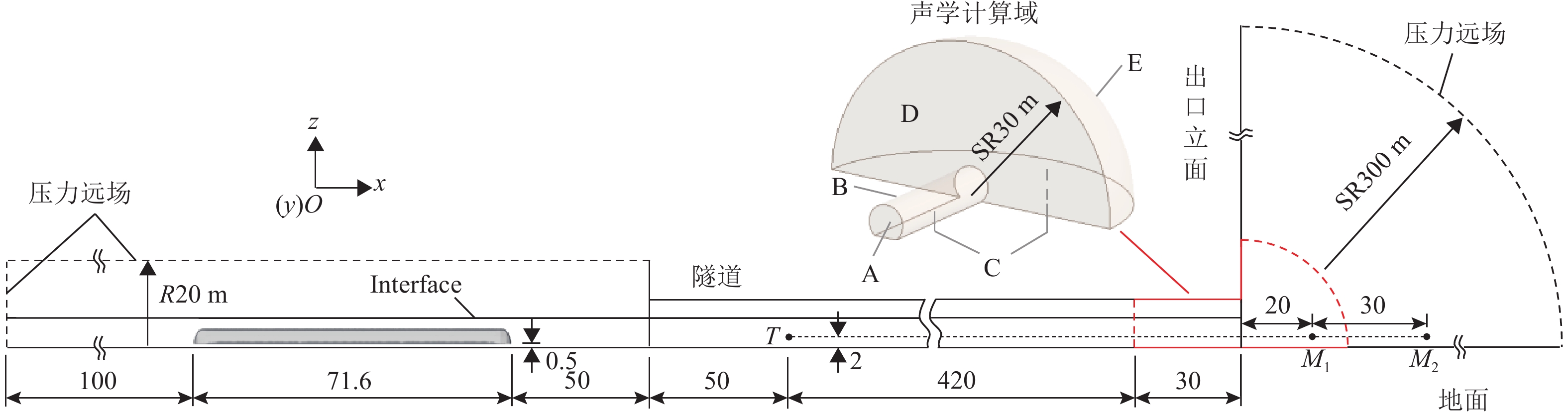
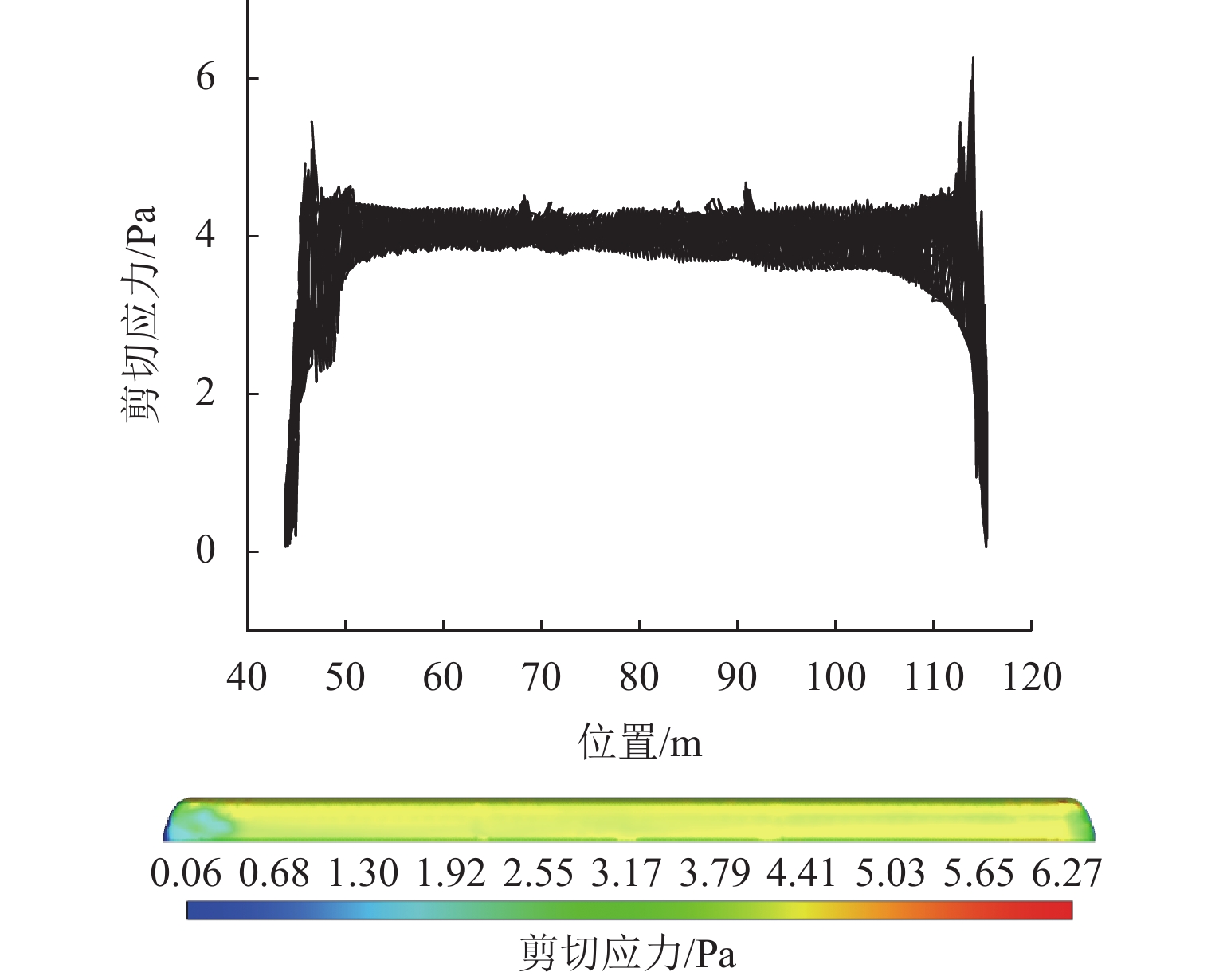
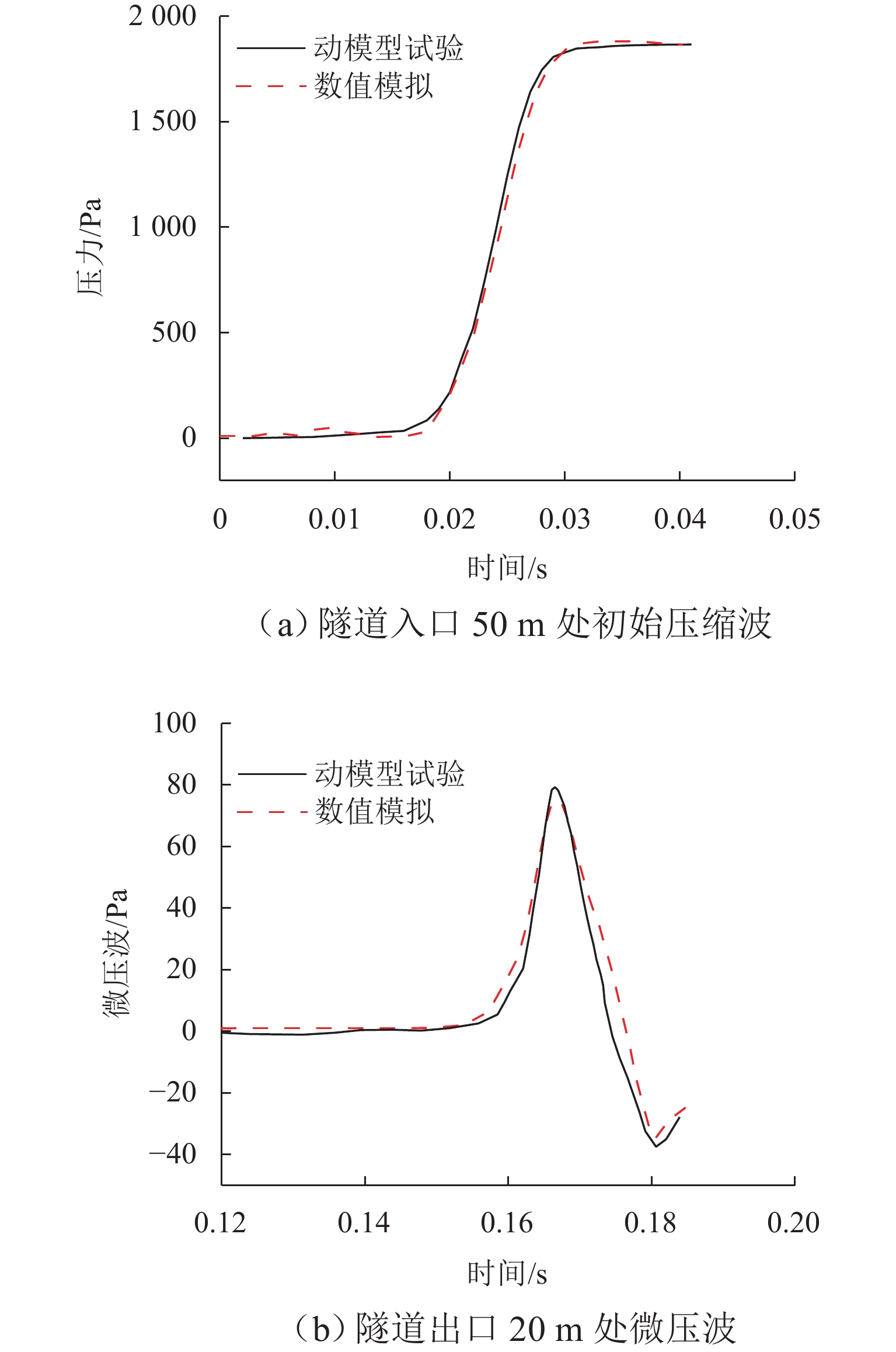
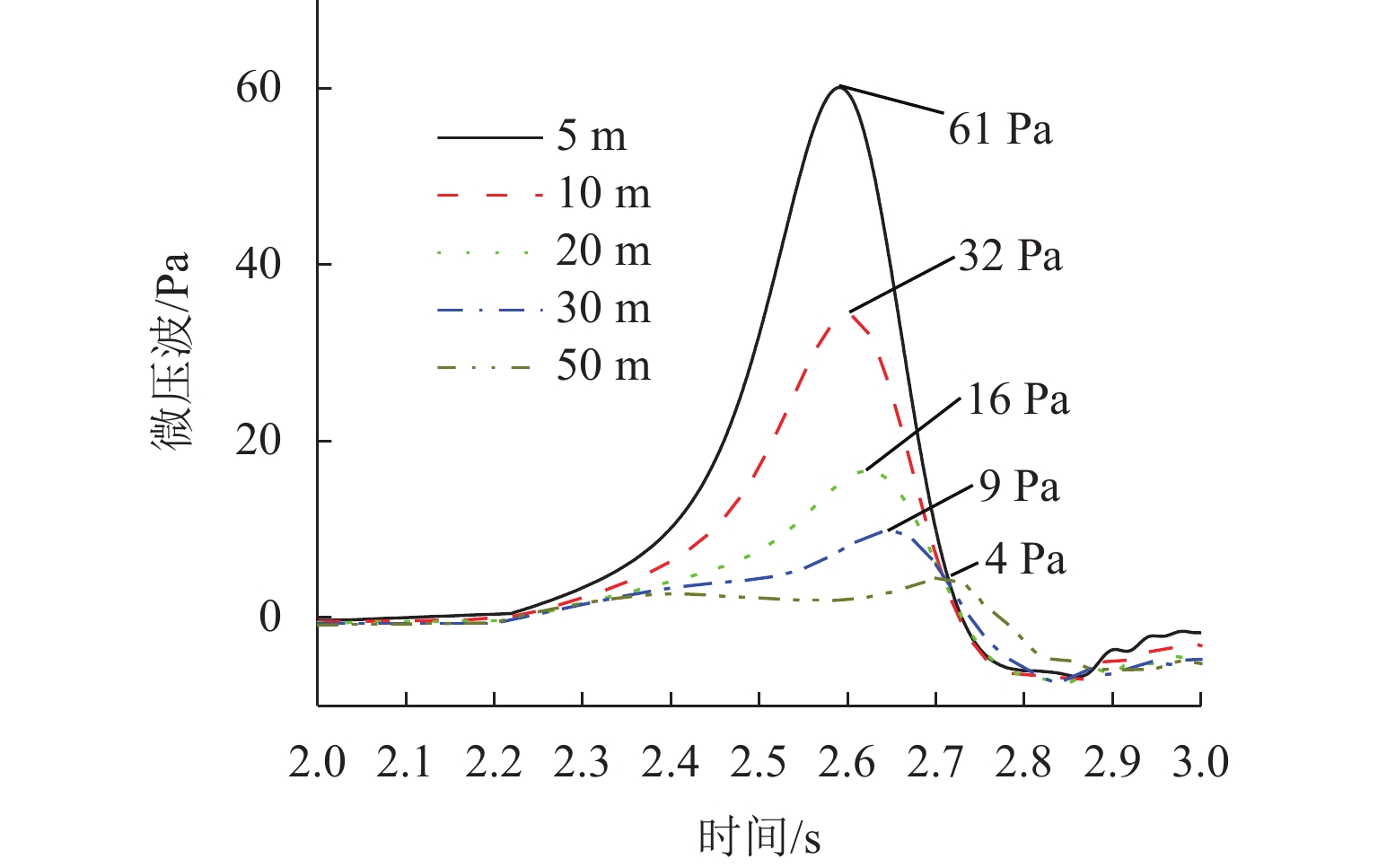
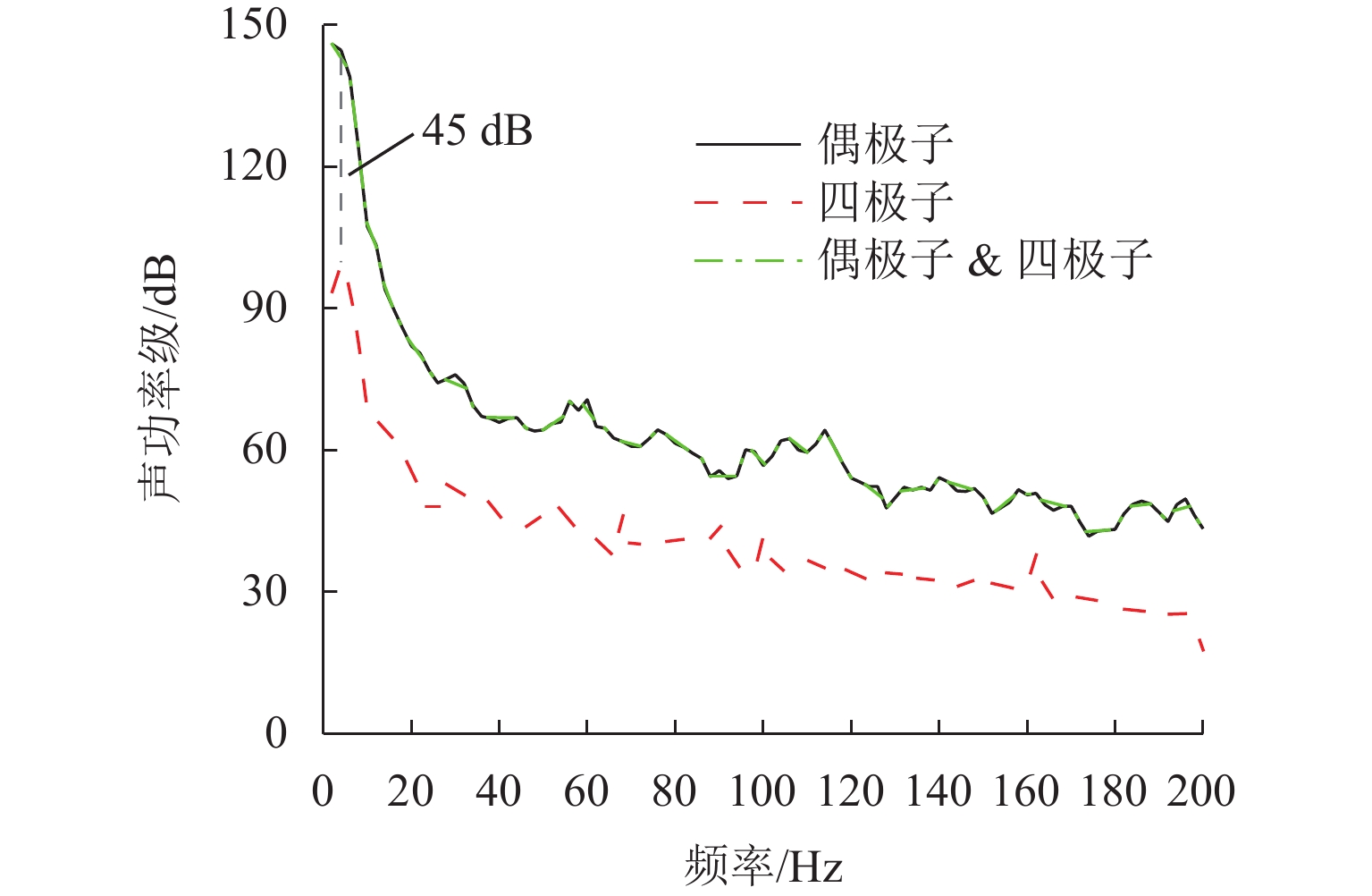
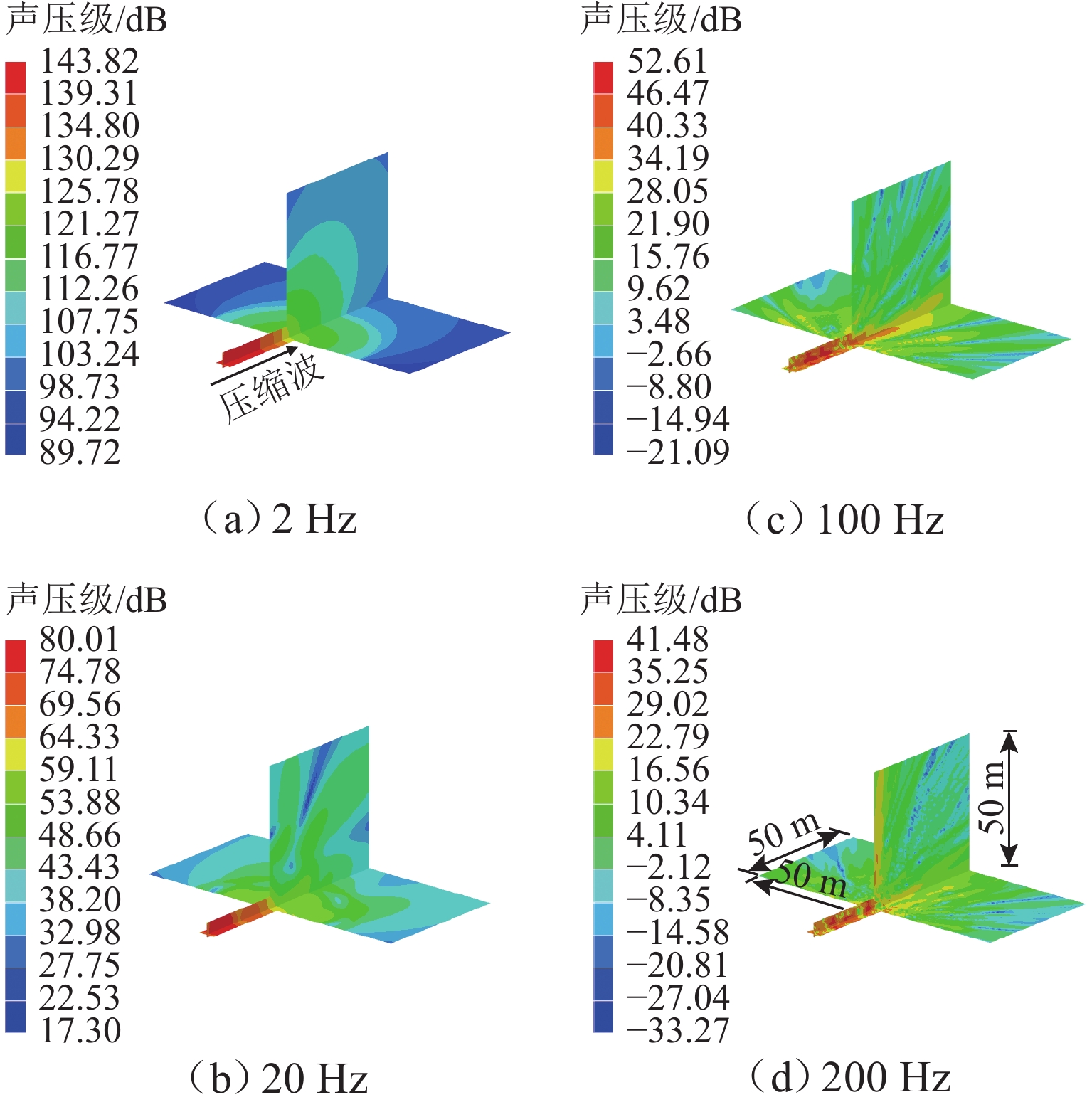
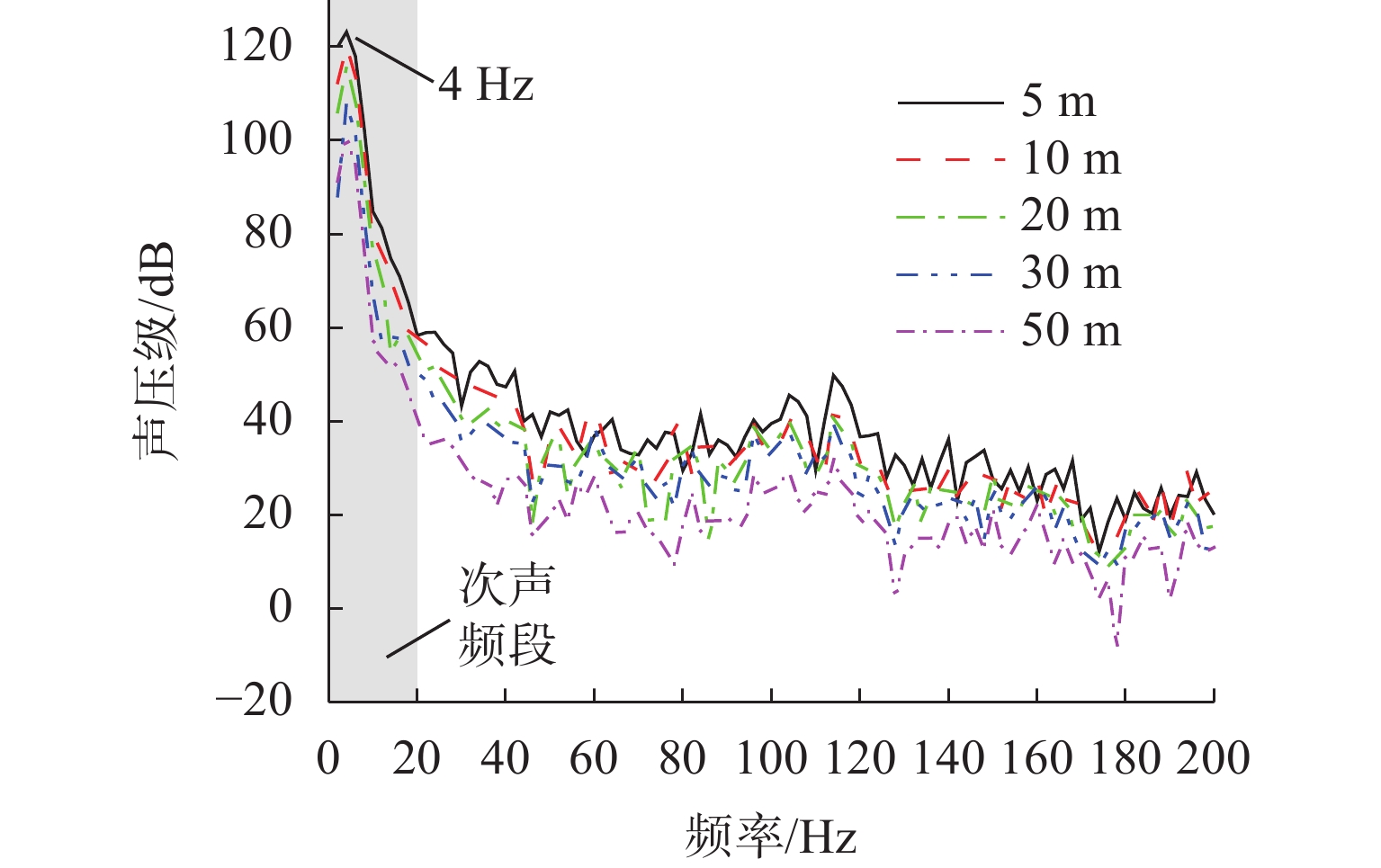
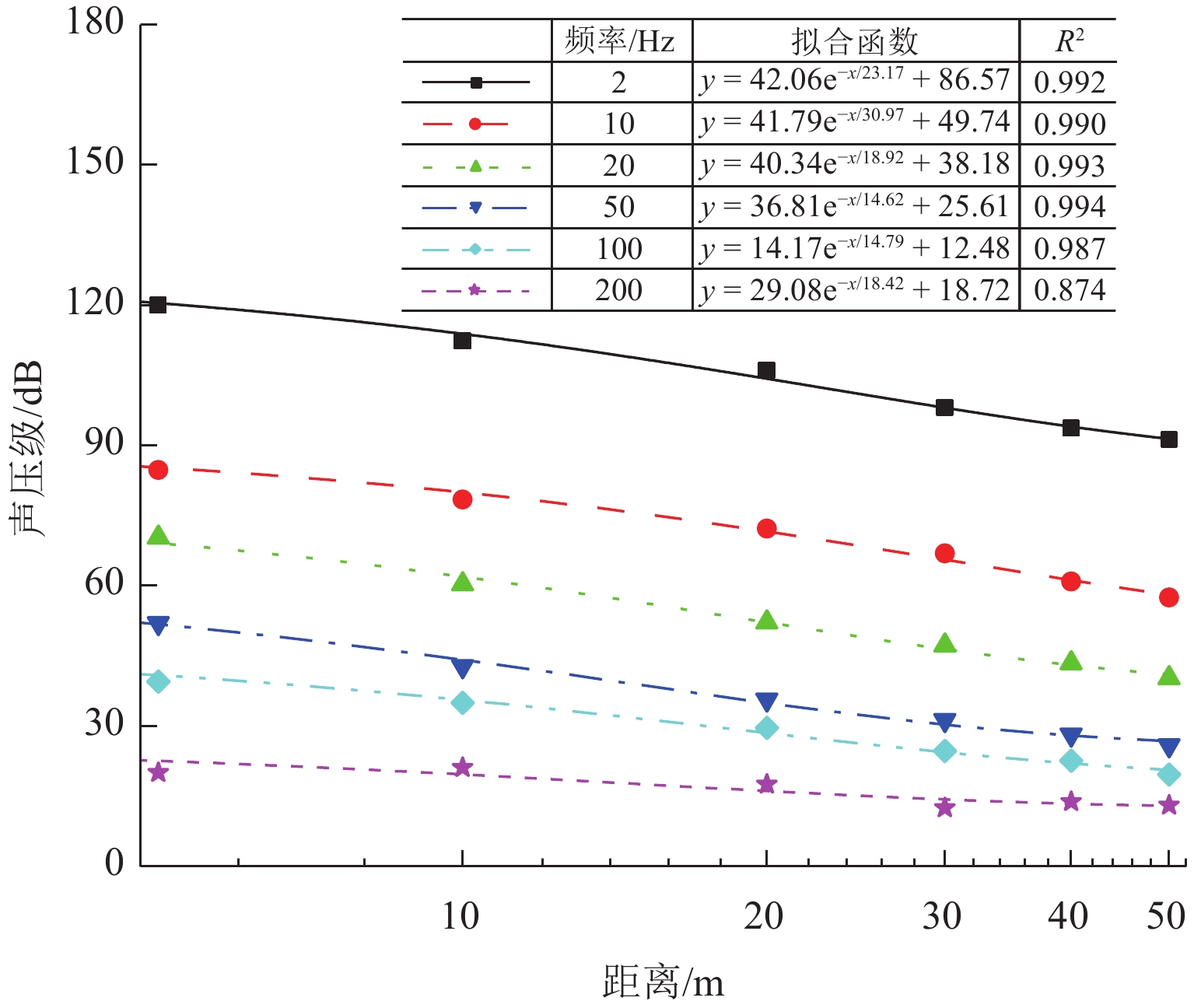
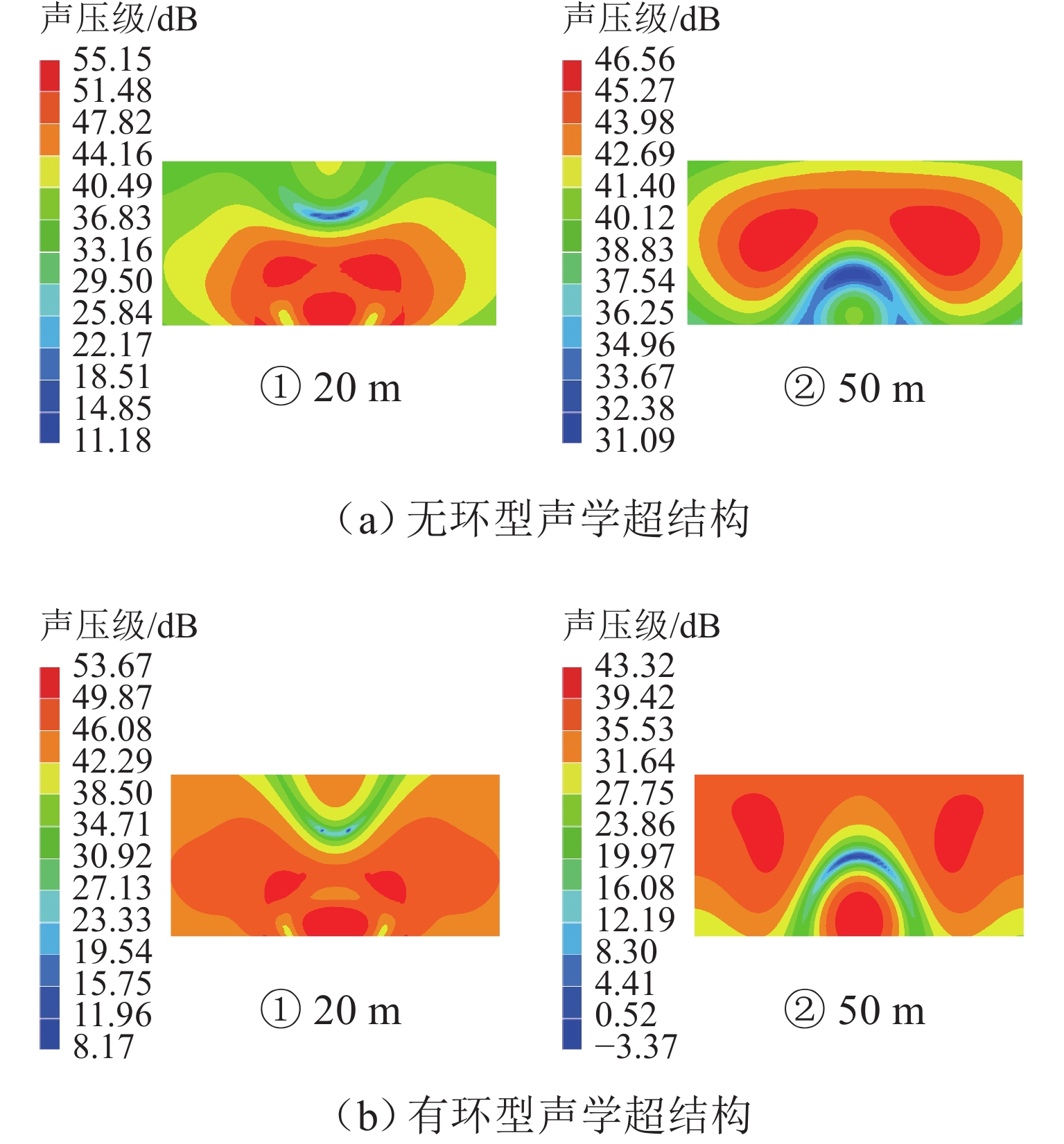
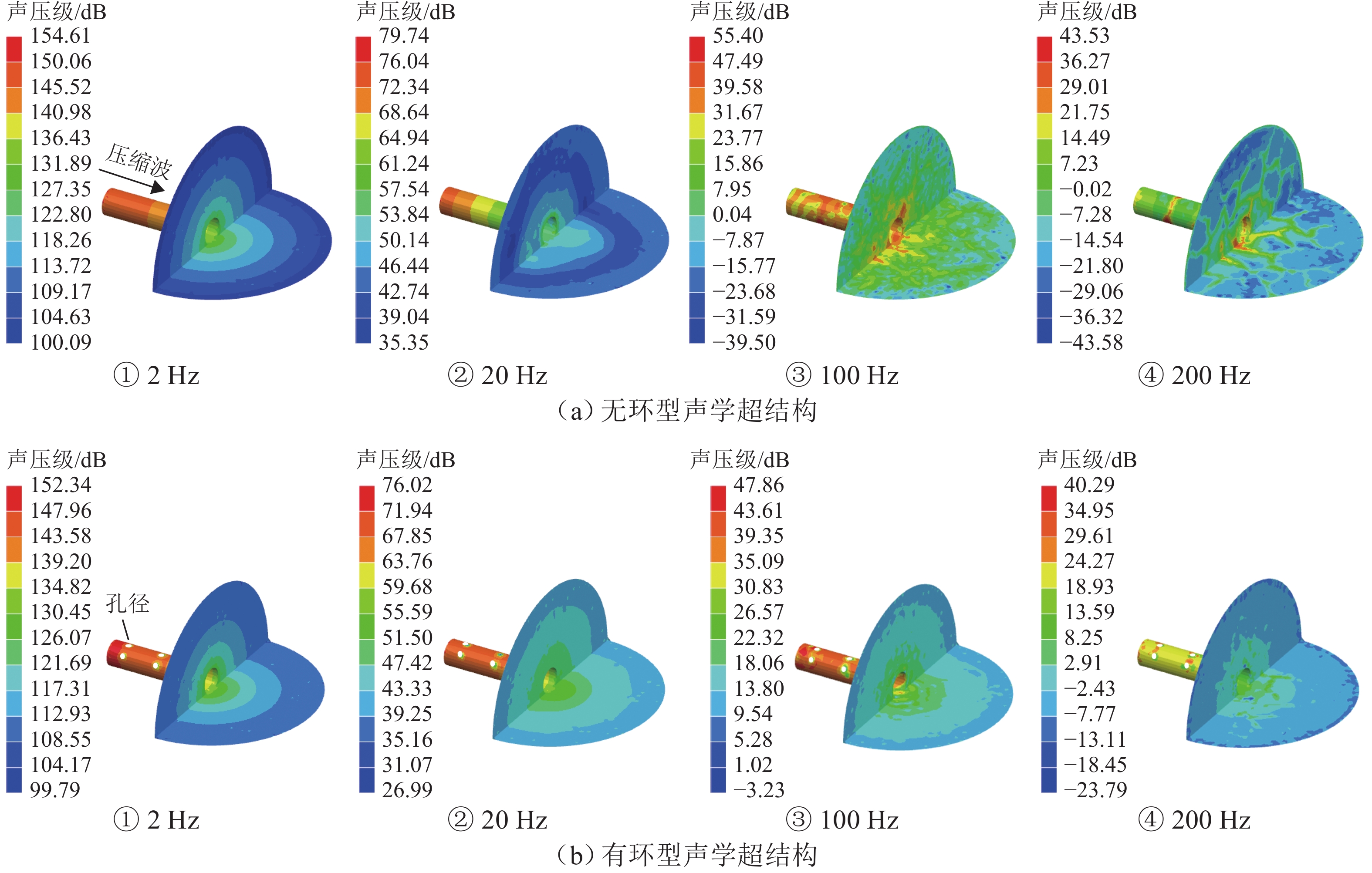
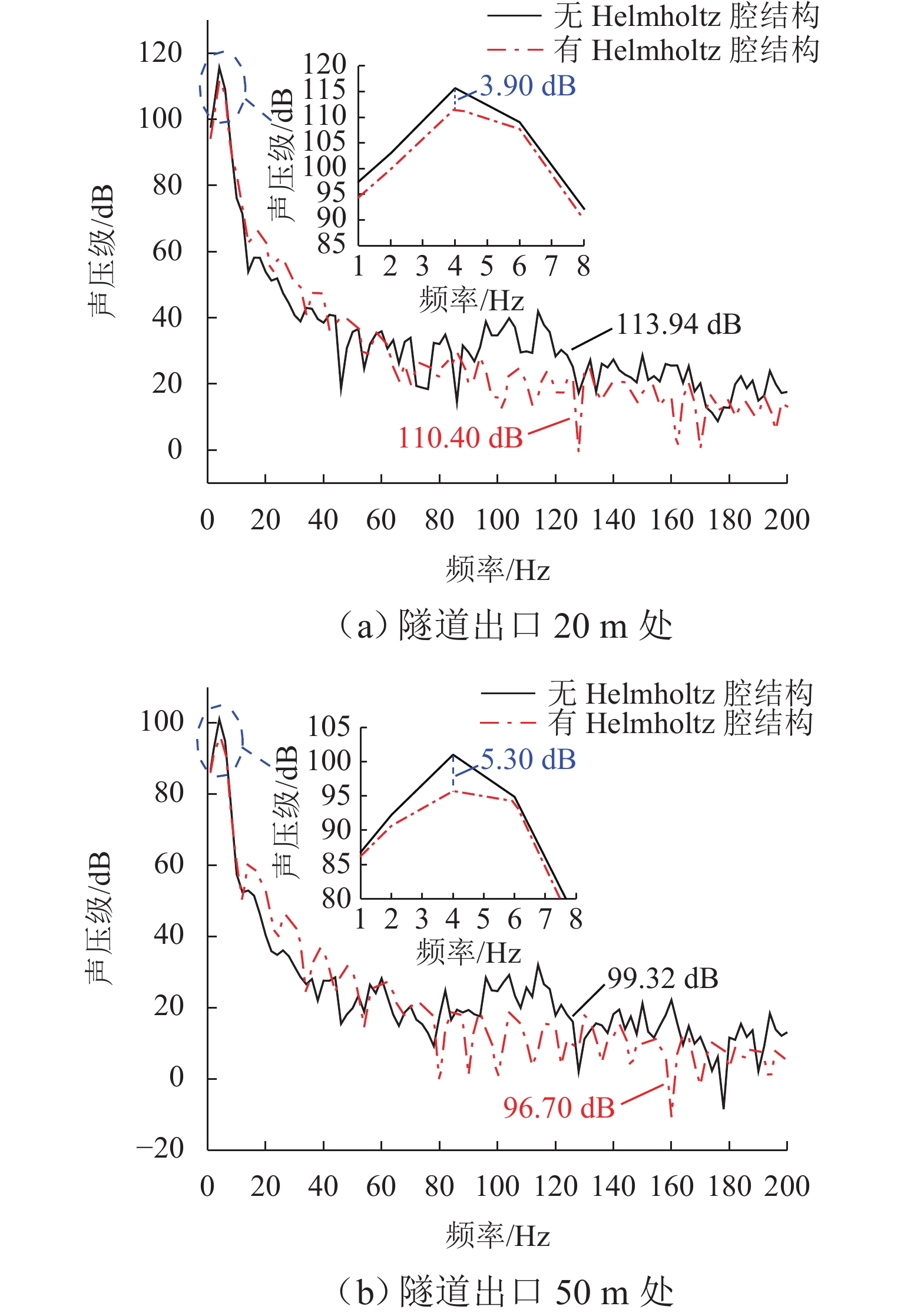
高速地铁进入隧道产生的初始压缩波传播到隧道出口时会产生微压波并引发噪声,某些情况下还会出现音爆现象,给当地居民带来严重的环境问题. 为有效控制隧道出口的微压波噪声,对微压波噪声的声学特性进行数值模拟研究,并提出一种针对低频微压波噪声的声学抑制结构. 首先,采用大涡模拟(LES)方法获取隧道出口的近场非定常流场数据,使用Ffowcs Williams-Hawkings (FW-H)声学类比来预测微压波噪声的声源类型;其次,基于非定常流场数据采用声学有限元法(AFEM)计算微压波噪声的远场辐射,并分析隧道洞口声学结构对微压波噪声的减缓效果;最后,通过动模型试验验证数值方法的准确性. 结果表明:当列车速度为160 km/h时,隧道出口微压波噪声中偶极子噪声占据主导地位;偶极子噪声以半椭球面的形式向外辐射,其能量主要集中在20 Hz频率以下,峰值频率为4 Hz;偶极子噪声沿隧道出口方向上的衰减满足指数衰减规律;隧道洞口增设声学结构后微压波噪声有明显降低,隧道洞口外不同纵向平面上的噪声声压级降低约3.00 dB,标准测点(20 m和50 m)处的声压级分别降低3.54 dB和2.62 dB.
Abstract:Micro-pressure waves are generated and noise is induced when the initial compression wave generated during the entry of a high-speed metro train into a tunnel propagates to the tunnel exit. In some cases, sonic booms may also occur, resulting in serious environmental problems for residents. To effectively control the micro-pressure wave noise at tunnel exits, numerical simulation studies on the acoustic characteristics of micro-pressure wave noise were conducted, and an acoustic suppression structure targeting low-frequency micro-pressure wave noise was proposed. Firstly, large eddy simulation (LES) was employed to obtain near-field unsteady flow field data at the tunnel exit, using the Ffowcs Williams-Hawkings (FW-H) acoustic analogy to predict the type of micro-pressure wave noise sources. Secondly, based on the unsteady flow field data, the acoustic finite element method (AFEM) was utilized to compute the far-field radiation of micro-pressure wave noise and analyze the mitigating effect of acoustic structures of the tunnel exit on micro-pressure wave noise. Finally, the accuracy of the numerical methods was validated through a moving model test. The results indicate that at a train speed of 160 km/h, dipole noise predominates in the micro-pressure wave noise at the tunnel exit. Dipole noise radiates outward in a semi-ellipsoidal shape, with its energy mainly concentrated below 20 Hz and a peak frequency being 4 Hz. The attenuation of dipole noise in the tunnel exit direction follows an exponential decay law. Adding acoustic structures at the tunnel exit significantly reduces micro-pressure wave noise. Specifically, the sound pressure levels (SPLs) outside the tunnel exit across various longitudinal planes decrease by approximately 3.00 dB. At the designated measurement points, located at 20 m and 50 m, the SPLs are reduced by 3.54 dB and 2.62 dB, respectively.
-
Key words:
- tunnel exit /
- micro-pressure wave noise /
- noise characteristics /
- acoustic structures /
- noise reduction
-
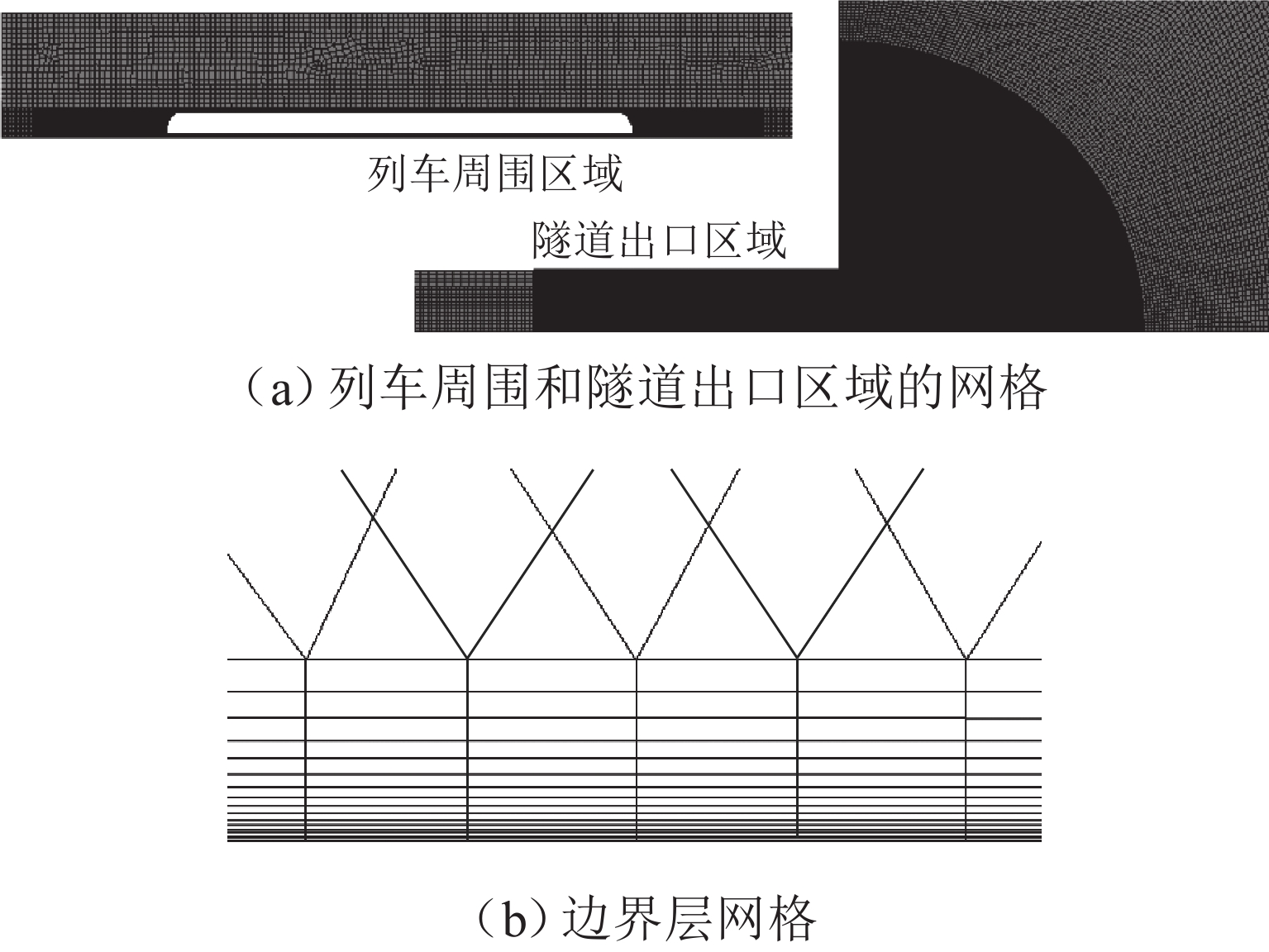
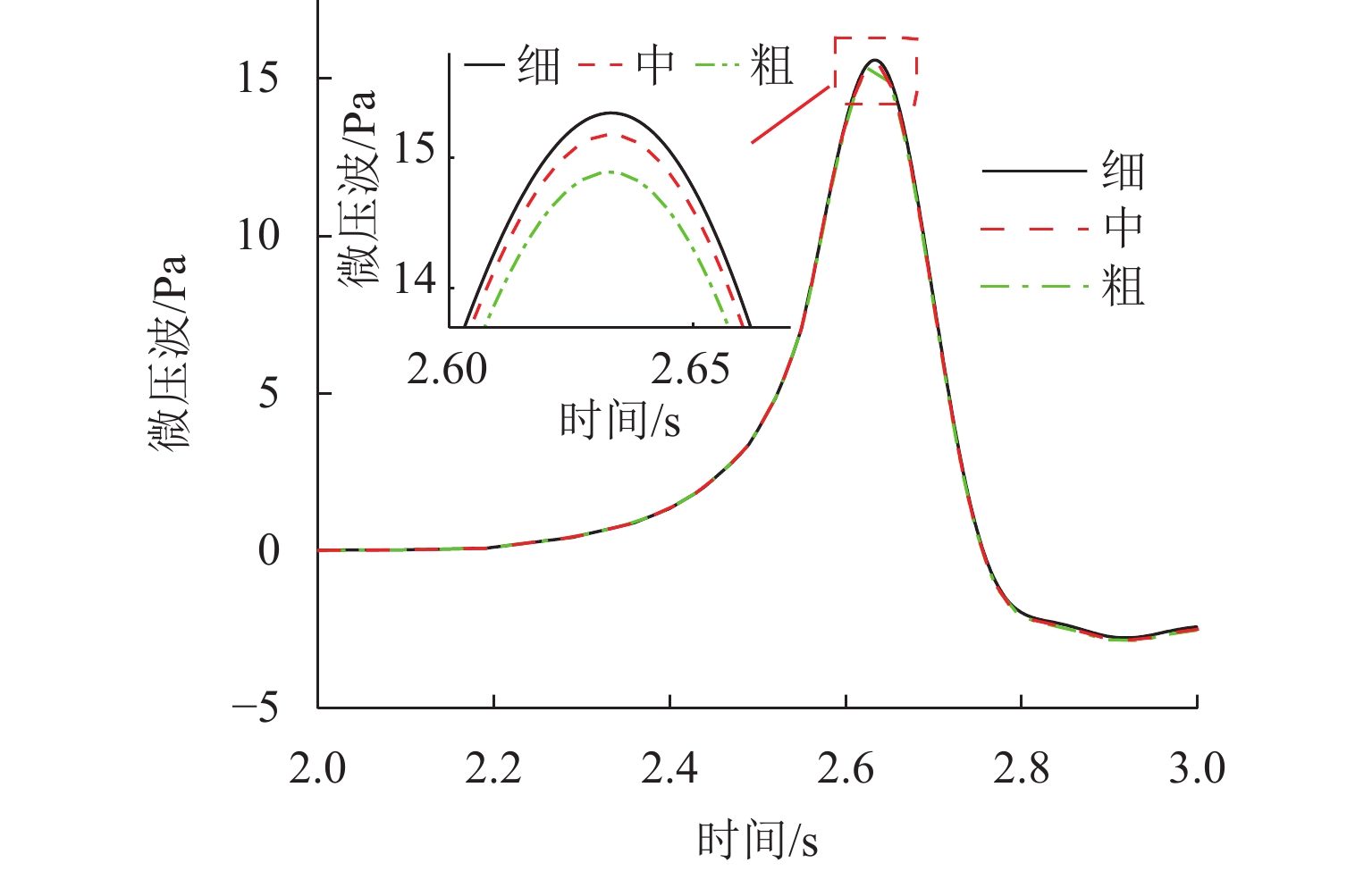
表 1 网格独立性检测
Table 1. Grid independence verification
网格 基础尺寸/m 边界层第一层高度/mm 网格总数/万个 压力幅值/Pa 偏差/% 微压波幅值/Pa 偏差/% 粗 0.6 0.01 1843 1143 14.8 中 0.4 0.01 2574 1158 1.31 15.4 4.05 细 0.2 0.01 3667 1165 0.60 15.6 1.30 表 2 数值模拟与动模型试验结果
Table 2. Numerical simulation and moving model test results
模式 压力幅值/Pa 微压波幅值/Pa 动模型试验 1864.1 79.2 数值模拟 1882.2 75.4 偏差/% 0.96 4.8 表 3 环型声学超结构的降噪效果
Table 3. Noise reduction effect of ring-type acoustic superstructures
dB 隧道出口形式 20 m 处声压级 50 m 处声压级 4 Hz 1~200 Hz 4 Hz 1~200 Hz 无环型声学超结构 115.70 113.94 101.02 99.32 有环型声学超结构 111.74 110.40 95.72 96.70 降噪损失 3.96 3.54 5.30 2.62 降噪百分比/% 3.42 3.11 5.25 2.64 -
[1] MIYACHI T. Non-linear acoustic analysis of the pressure rise of the compression wave generated by a train entering a tunnel[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2019, 458: 365-375. doi: 10.1016/j.jsv.2019.06.033 [2] WANG H L, VARDY A E, BI H Q. Characteristics of pressure waves radiated from tunnel portals in cuttings[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2022, 521: 116664. doi: 10.1016/j.jsv.2021.116664 [3] WANG H L, VARDY A E, BI H Q. Micro-pressure wave radiation from tunnel portals in deep cuttings[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part F: Journal of Rail and Rapid Transit, 2023, 237(2): 166-178. doi: 10.1177/09544097221099393 [4] 赵有明, 马伟斌, 程爱君, 等. 高速铁路隧道气动效应[M]. 北京: 中国铁道出版社, 2012. [5] AOKI T, MATSUO K, HIDAKA H, et al. Attenuation and distorsion of propagating compression waves in a high-speed railway model and in real tunnels[M]//Shock Waves @ Marseille Ⅲ. Berlin: Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 1995: 347-352. [6] YOON T S, S L, J H H, et al. Prediction and validation on the sonic boom by a high-speed train entering a tunnel[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2001, 247(2): 195-211. doi: 10.1006/jsvi.2000.3482 [7] RIVERO J M, GONZÁLEZ-MARTÍNEZ E, RODRÍGUEZ-FERNÁNDEZ M. A methodology for the prediction of the sonic boom in tunnels of high-speed trains[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2019, 446: 37-56. doi: 10.1016/j.jsv.2019.01.016 [8] 刘金通. 高铁隧道内压缩波传播规律及微气压波声学特性初步分析[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2018. [9] KIKUCHI, LIDA, TAKASAKI, et al. Field measurement of wayside low-frequency noise emitted from tunnel portals and trains of high-speed railway[J]. Noise Notes, 2006, 5(3): 5-18. doi: 10.1260/147547306781539550 [10] OZAWA S, MAEDA T. Tunnel entrance hoods for reduction of micro-pressure wave[J]. Quarterly Reports of Rtri, 1988, 29(3): 134-139. [11] 廖欣, 王东镇, 孙召进, 等. 高速列车进出隧道噪声问题及控制[C]//2010中国西部声学学术交流会论文集. 腾冲: [出版者不详], 2010: 58-61. [12] 杜麒麟. 遂渝铁路隧道洞口噪声特性分析[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2015. [13] THOMPSON D J, LATORRE IGLESIAS E, LIU X W, et al. Recent developments in the prediction and control of aerodynamic noise from high-speed trains[J]. International Journal of Rail Transportation, 2015, 3(3): 119-150. doi: 10.1080/23248378.2015.1052996 [14] ZHANG Y D, ZHANG J Y, LI T, et al. Investigation of the aeroacoustic behavior and aerodynamic noise of a high-speed train pantograph[J]. Science China Technological Sciences, 2017, 60(4): 561-575. doi: 10.1007/s11431-016-0649-6 [15] VASILYEV O V, LUND T S, MOIN P. A general class of commutative filters for LES in complex geometries[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 1998, 146(1): 82-104. doi: 10.1006/jcph.1998.6060 [16] DI MARE L, JONES W P. LES of turbulent flow past a swept fence[J]. International Journal of Heat and Fluid Flow, 2003, 24(4): 606-615. doi: 10.1016/S0142-727X(03)00054-7 [17] FFOWCS-WILLIAMS J E, HAWKINGS D L. Sound generation by turbulence and surfaces in arbitrary motion[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London Series A: Mathematical and Physical Sciences, 1969, 264(1151): 321-342. doi: 10.1098/rsta.1969.0031 [18] 陈羽, 柳壹明, 毛懋, 等. 高速列车底部结构参数对气动噪声影响规律[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2023, 58(5): 1171-1179.CHEN Yu, LIU Yiming, MAO Mao, et al. Influence of underbody parameters of high-speed trains on aerodynamic noise[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2023, 58(5): 1171-1179. [19] 刘加利, 于梦阁, 陈大伟, 等. 考虑四极子声源的高速磁浮列车气动噪声数值模拟方法[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2024, 59(1): 54-61.LIU Jiali, YU Mengge, CHEN Dawei, et al. Numerical simulation method of aerodynamic noise of high-speed maglev train considering quadrupole noise source[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2024, 59(1): 54-61. [20] 李增刚, 詹福良. Virtual. Lab Acoustics声学仿真计算高级应用实例[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2010. [21] BERENGER J P. A perfectly matched layer for the absorption of electromagnetic waves[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 1994, 114(2): 185-200. doi: 10.1006/jcph.1994.1159 [22] 李田, 秦登, 张继业, 等. 基于半模型的高速列车远场气动噪声计算方法[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2023, 58(2): 272-279, 286.LI Tian, QIN Deng, ZHANG Jiye, et al. Numerical approach for far-field aerodynamic noise of high-speed trains based on half model[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2023, 58(2): 272-279, 286. [23] ZHANG L, THUROW K, STOLL N, et al. Influence of the geometry of equal-transect oblique tunnel portal on compression wave and micro-pressure wave generated by high-speed trains entering tunnels[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2018, 178: 1-17. doi: 10.1016/j.jweia.2018.05.003 -




 下载:
下载: