Fuzzy Comprehensive Evaluation and Improved Design of Levitation System for Medium and Low Speed Maglev Trains
-
摘要:
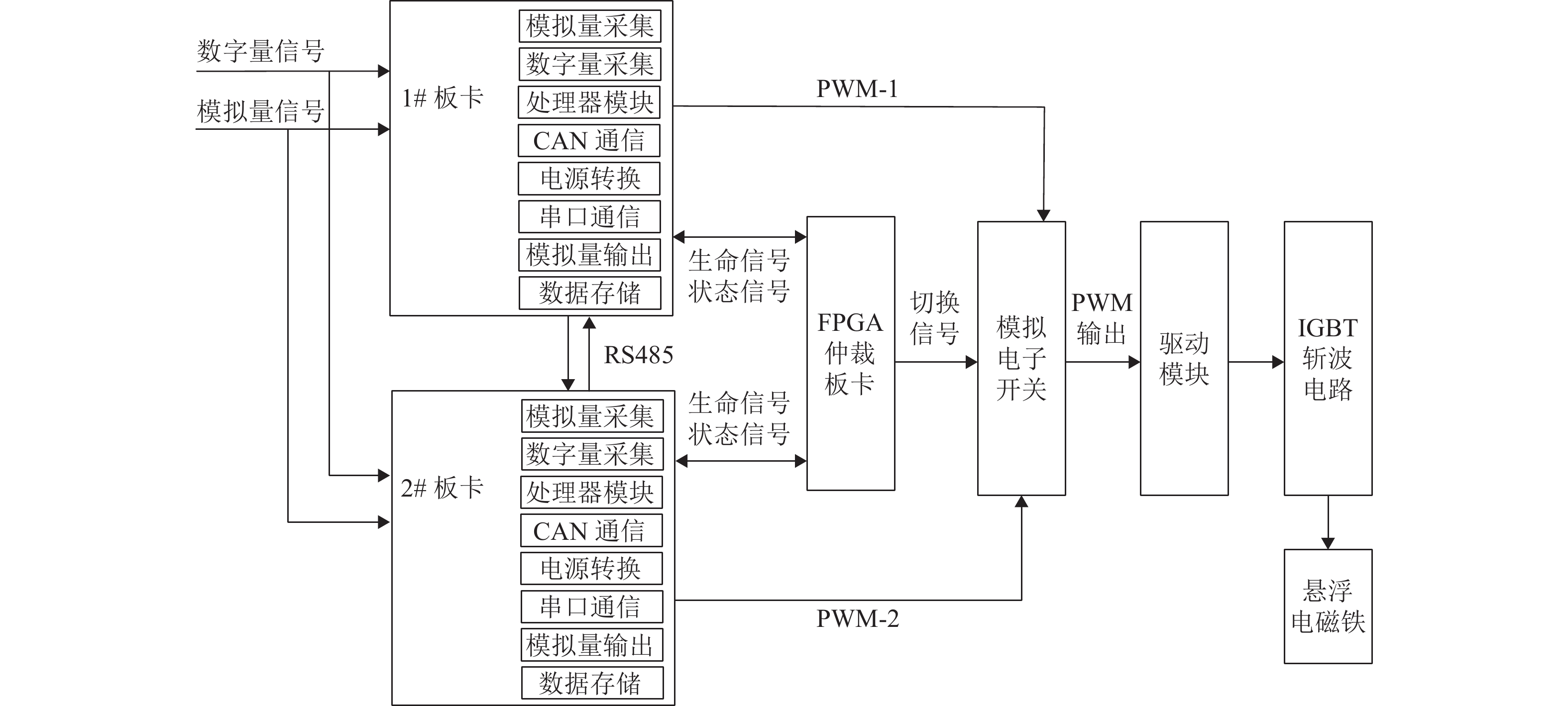
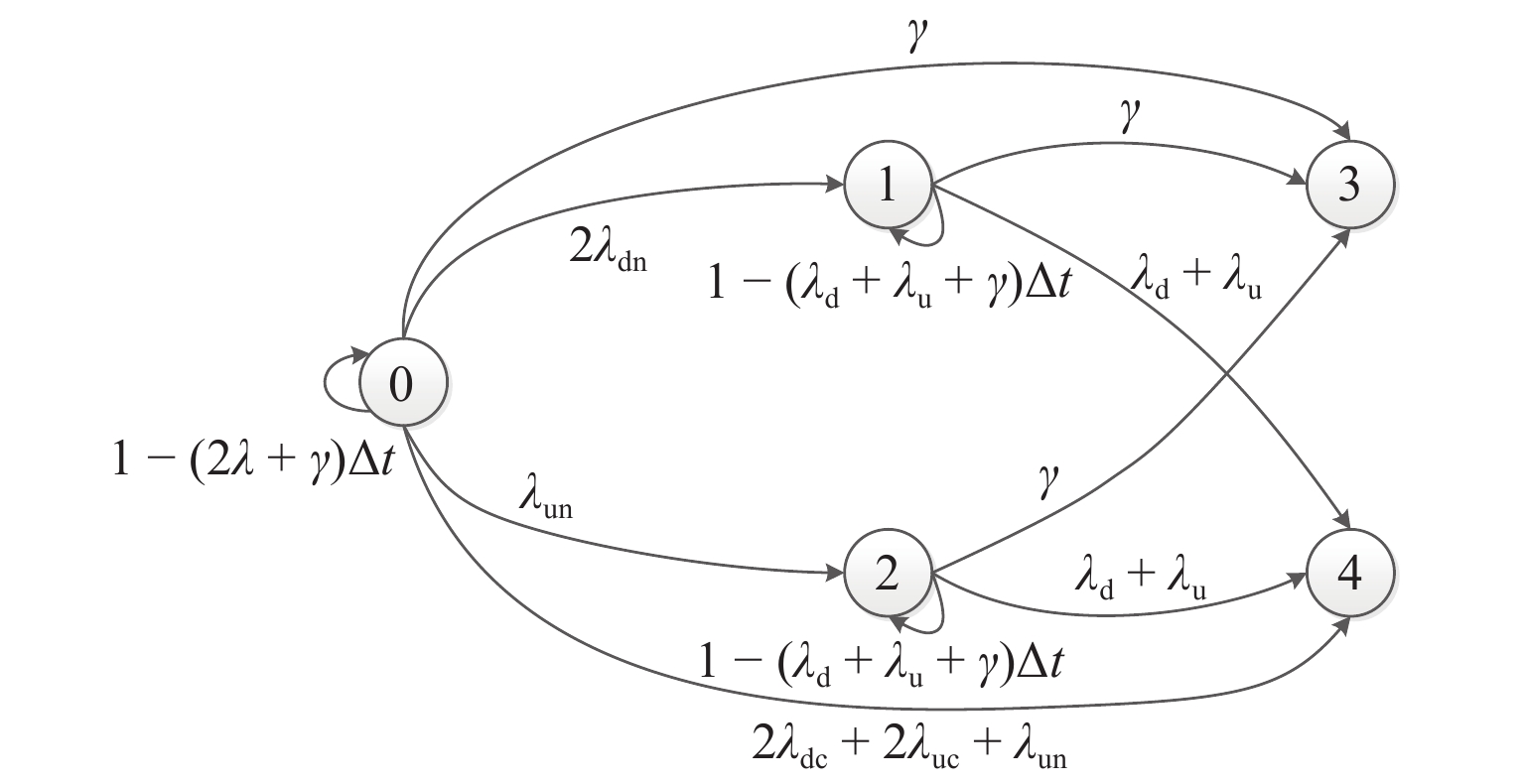
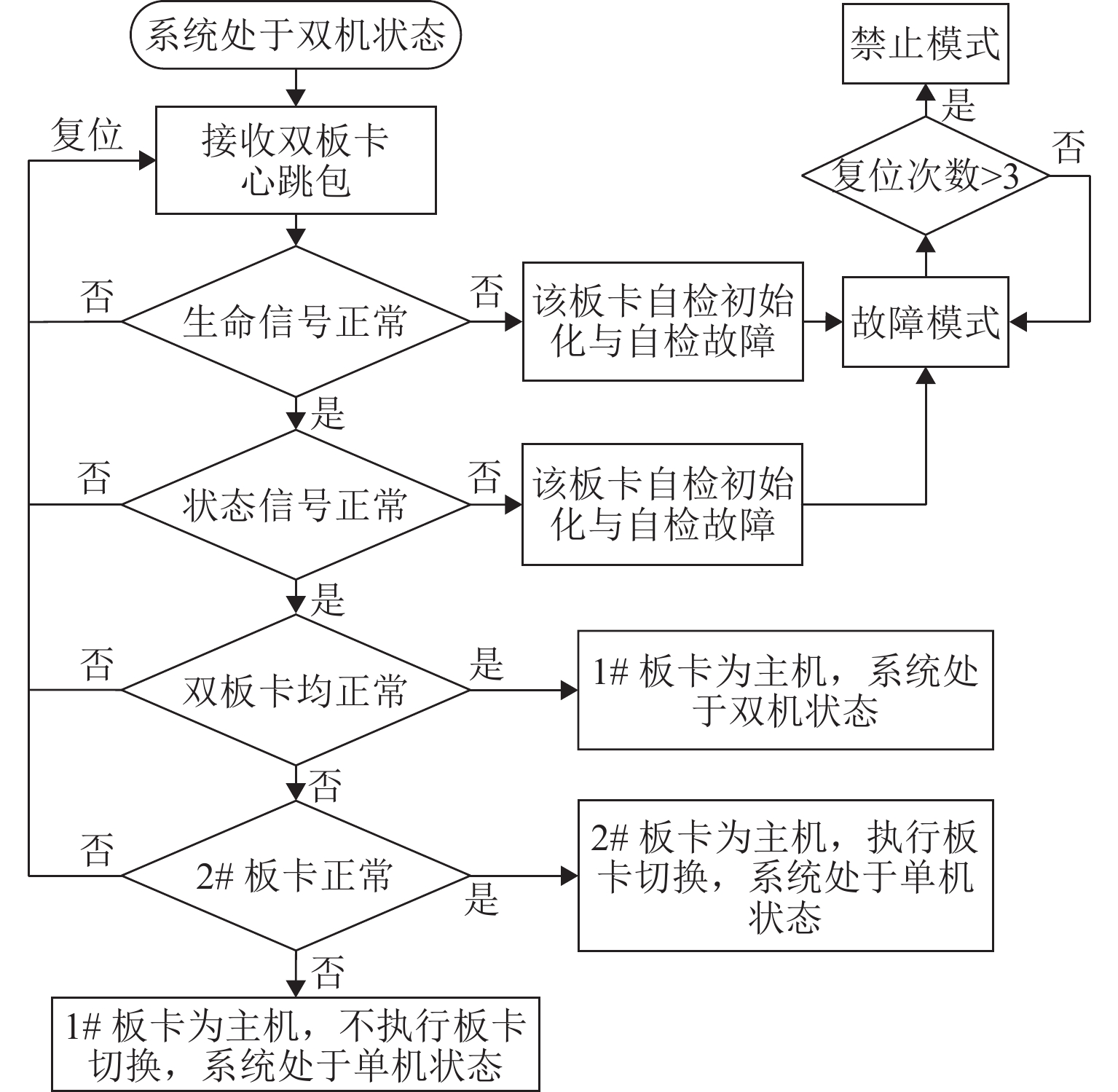
为提高某型中低速磁浮列车悬浮系统的容错能力,运用故障模式、影响及危害度分析(FMECA)方法对系统进行可靠性分析评估,识别出典型失效模式;通过专家模糊综合评价量化指标,以降低主观偏差,避免危害性取值重复的问题;利用层次分析法(AHP)对不同影响因素进行权值分配,使计算得到的各故障模式的综合危害性等级更符合实际工程需求;进一步,基于马尔可夫理论,针对综合危害性等级较高的故障模式提出改进措施;最后,研制样机并在单悬浮架试验台上开展悬浮试验与故障模拟试验. 研究结果表明:控制板、接口板和电源模块的综合危害等级最高,分别为
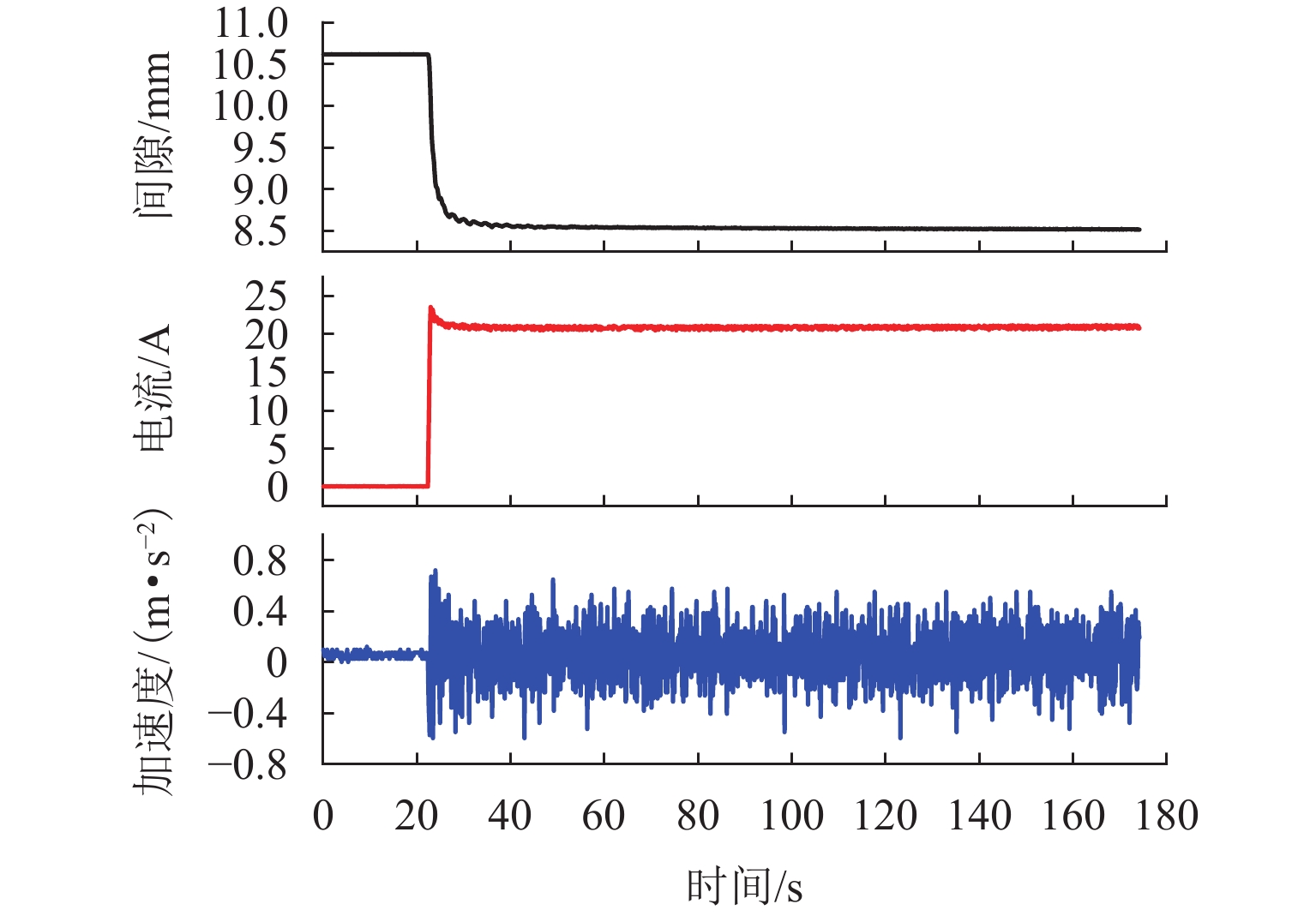
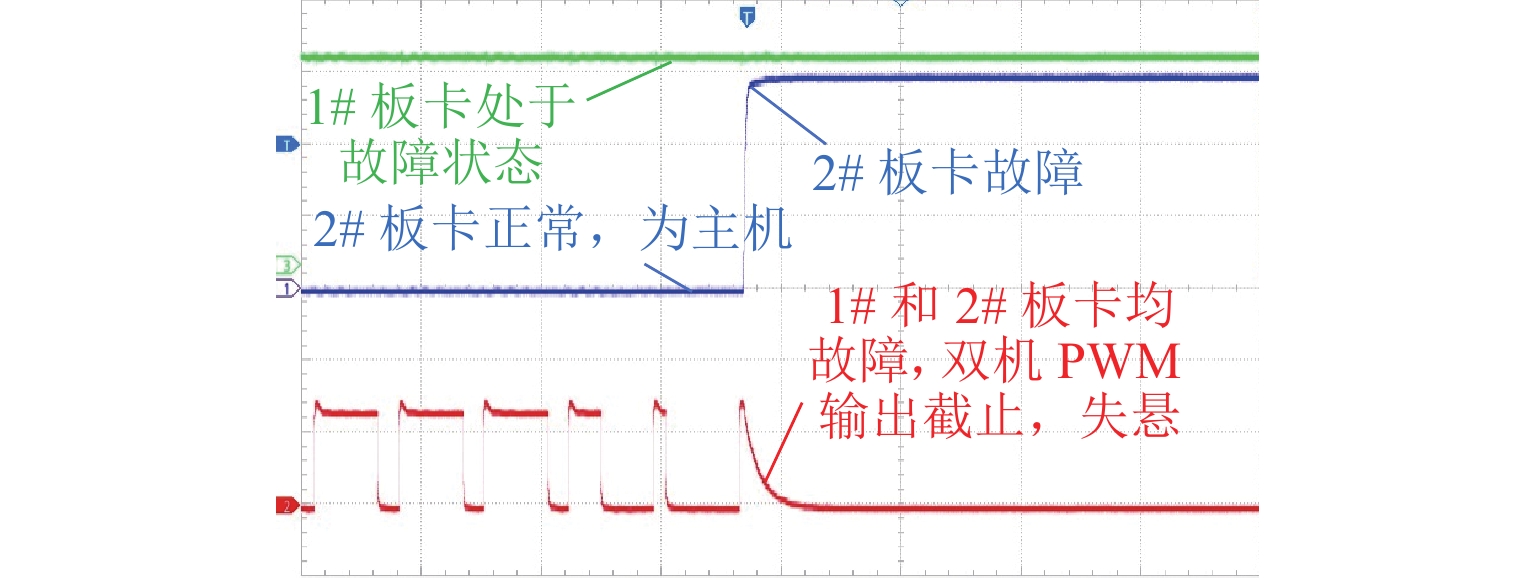
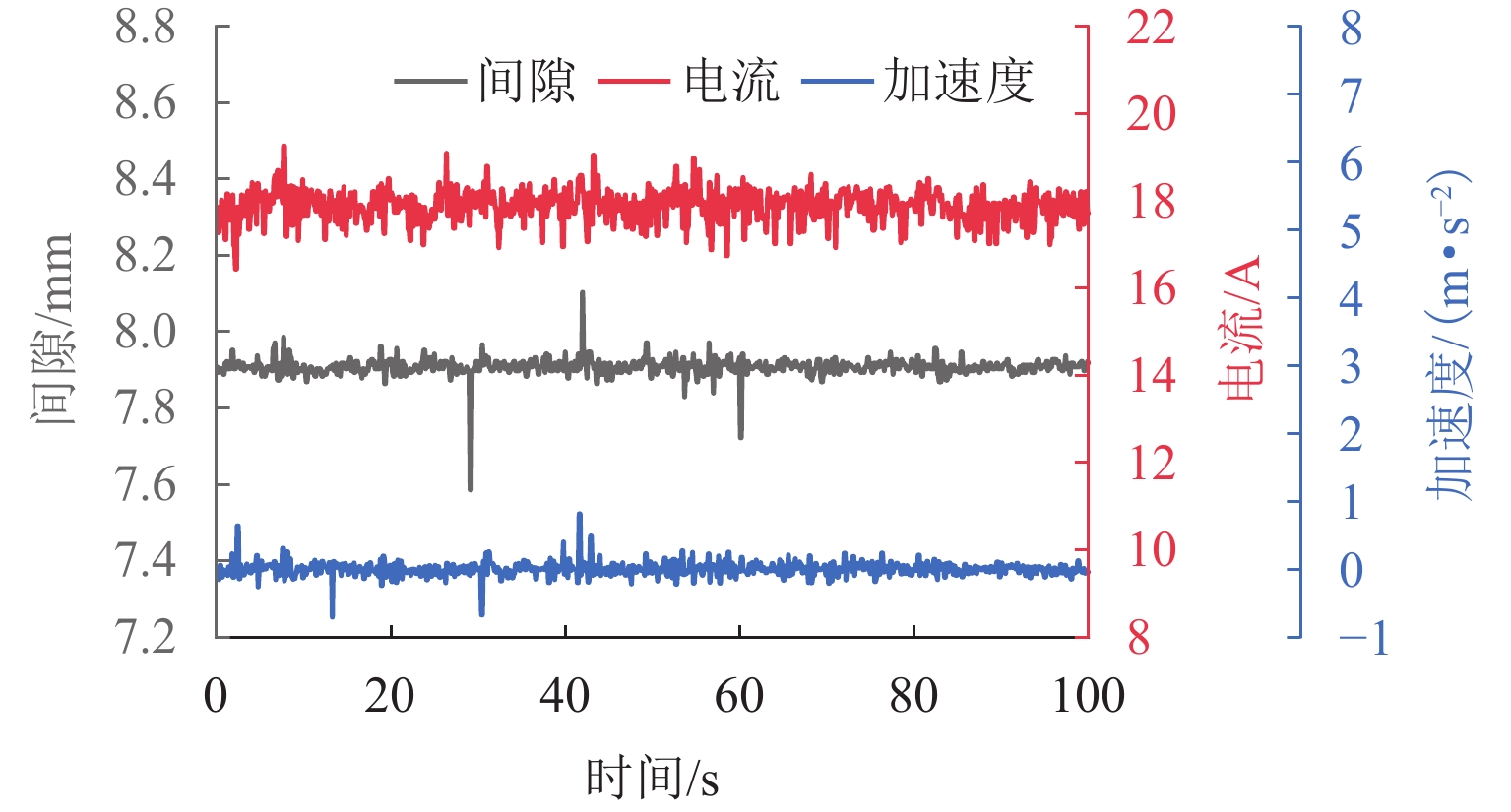
6.3147 、5.4841 和5.6534 ;故障发生后,主从机切换时间小于100 μs,悬浮间隙均方根误差小于0.1 mm,加速度波动在0.6 m/s2内.Abstract:To enhance the fault tolerance capability of the levitation system of a medium and low speed maglev train, a reliability analysis was conducted using Failure Mode, Effects, and Criticality Analysis (FMECA), identifying typical failure modes. A fuzzy comprehensive evaluation based on expert judgment was employed to quantify the indicators, reducing subjective bias, and avoiding duplication of hazard values. The analytic hierarchy process (AHP) was used to assign weights to different influencing factors, ensuring that the calculated comprehensive hazard levels of failure modes better reflect practical engineering needs. Furthermore, based on Markov theory, improvement measures were proposed for failure modes with high comprehensive hazard levels. A prototype was developed, and levitation and fault simulation tests were conducted on a single levitation test bench. The results indicate that the control board, interface board, and power module exhibit the highest comprehensive hazard levels, which are 6.314 7, 5.484 1, and 5.653 4, respectively. After a fault occurs, the master–slave switching time is less than 100 μs, with the levitation gap root-mean-square error remaining below 0.1 mm and acceleration fluctuations within 0.6 m/s2.
-
Key words:
- maglev train /
- levitation system /
- fault tolerance /
- fuzzy rule
-
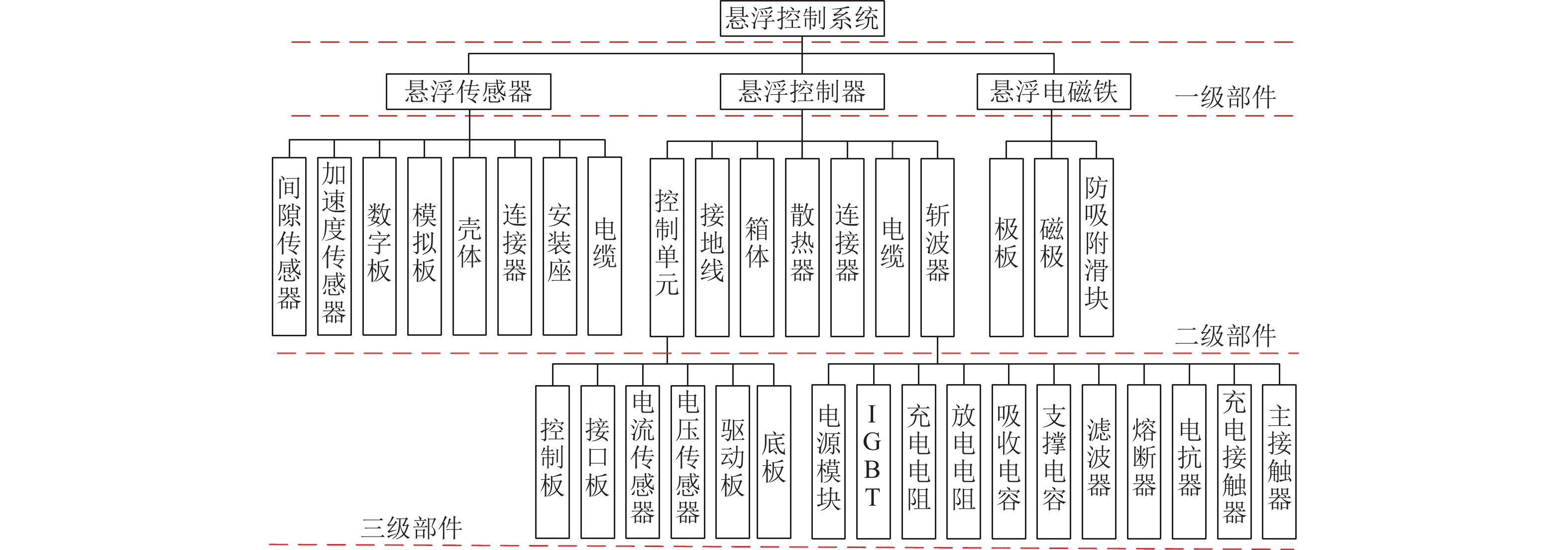
表 1 悬浮系统典型故障模式FMEA分析结果
Table 1. FMEA results of typical failure modes in levitation system
最低约定层次 故障模式 故障原因 系统影响 整车影响 控制板 无 PWM 输出/输出错误 源端电压不稳;过温虚焊,断路;抗振动冲击过大;内部短路;程序运行错误 驱动板无法接收到 PWM,单点无法悬浮 车辆单点失悬或掉点砸轨,双点故障进入救援模式 接口板 悬浮控制故障 过温虚焊,断路;抗振动冲击能力差;抗干扰能力差;内部短路;源端电压不稳 控制板无法接收悬浮传感器信号,无法悬浮;控制板接收错误电流信号,悬浮失稳 车辆单点失悬,双点故障进入救援模式;车辆单点连续打轨,车辆降速运营 110 V 转24 V 电源模块 DC 24 V 断路 耐压能不足;温度过高;抗干扰能力不足 悬浮传感器及悬浮控制电路无法得电,悬浮控制缺少输入 车辆单点失悬,双点故障进入救援模式 电流传感器 信号输出不稳定;无输出信号 过流;接触不良;温度过高 无法监测悬浮电流,实际电流与预期存在误差,悬浮失稳 车辆单点连续打轨,车辆降速运营 电压传感器 信号输出不稳定 过压;接触不良 主接触器无法闭合 车辆单点失悬,双点故障进入救援模式 驱动板 无法启动 IGBT 击穿导致的过流;抗振动冲击能力差;抗干扰能力差;高温虚焊 无法控制 IGBT 开断 车辆单点失悬,双点故障进入救援模式 IGBT 击穿 电磁铁短路;温度过高 无悬浮电流输出 车辆单点失悬,双点故障进入救援模式 支撑电容 损坏 老化;电容质量问题;温度过高 单支撑电容损坏无影响 击穿 过压 主电路短路,悬浮控制器停机 车辆单点失悬,双点故障进入救援模式 表 2 影响因素的评价等级划分
Table 2. Evaluation level classification for influencing factors
影响因素 等级 1 3 5 7 9 影响概率 几乎没有 极少 偶尔 可能 经常 严重程度 可忽略 轻微的 临界的 危急的 灾难的 综合检修难度 极低 较低 中等 较难 很难 表 3 因素重要度判断值
Table 3. Judgment values for factor importance
相对评价值 极重要 很重要 重要 略重要 同等 评分 9 7 5 3 1 注:8、6、4、2为评价值的中间值. 表 4 1~9阶判断矩阵${I_{\mathrm{R}}}$值
Table 4. Judgment matrices${I_{\mathrm{R}}}$for orders 1–9
阶数 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 ${I_{\mathrm{R}}}$ 0 0 0.58 0.90 1.12 1.24 1.32 1.41 1.45 表 5 各故障模式的综合危害等级
Table 5. Comprehensive hazard levels for each failure mode
部件 综合危害等级 部件 综合危害等级 控制板 6.3147 驱动板 3.8714 接口板 5.4841 充电电阻 3.7696 110 V/24 V
电源5.6534 吸收电容 2.9501 IGBT 4.5688 支撑电容 2.9932 电流传感器 4.1590 电压传感器 3.7798 主接触器 4.2963 熔断器 3.4600 -
[1] LEE H W, KIM K C, LEE J. Review of maglev train technologies[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2006, 42(7): 1917-1925. doi: 10.1109/TMAG.2006.875842 [2] 徐飞,罗世辉,邓自刚. 磁悬浮轨道交通关键技术及全速度域应用研究[J]. 铁道学报,2019,41(3): 40-49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2019.03.006XU Fei, LUO Shihui, DENG Zigang. Study on key technologies and whole speed range application of maglev rail transport[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2019, 41(3): 40-49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2019.03.006 [3] THORNTON R D. Efficient and affordable maglev opportunities in the United States[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2009, 97(11): 1901-1921. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2009.2030251 [4] 翟婉明,赵春发. 现代轨道交通工程科技前沿与挑战[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2016,51(2): 209-226. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2016.02.001ZHAI Wanming, ZHAO Chunfa. Frontiers and challenges of sciences and technologies in modern railway engineering[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2016, 51(2): 209-226. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2016.02.001 [5] 马卫华,胡俊雄,李铁,等. EMS型中低速磁浮列车悬浮架技术研究综述[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2023,58(4): 720-733. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20210971MA Weihua, HU Junxiong, LI Tie, et al. Technologies research review of electro-magnetic suspension medium-low-speed maglev train levitation frame[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2023, 58(4): 720-733. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20210971 [6] 马卫华,罗世辉,张敏,等. 中低速磁浮车辆研究综述[J]. 交通运输工程学报,2021,21(1): 199-216.MA Weihua, LUO Shihui, ZHANG Min, et al. Research review on medium and low speed maglev vehicle[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2021, 21(1): 199-216. [7] 陈文彬,李晓阳,童邦安,等. 谐波减速器的传动效率确信可靠性建模与分析[J]. 振动工程学报,2022,35(1): 237-245.CHEN Wenbin, LI Xiaoyang, TONG Bang’an, et al. Belief reliability modeling and analysis for transmission efficiency of harmonic gear[J]. Journal of Vibration Engineering, 2022, 35(1): 237-245. [8] CATELANI M, CIANI L, GALAR D, et al. FMECA assessment for railway safety-critical systems investigating a new risk threshold method[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 86243-86253. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3088948 [9] BEN BRAHIM I, ADDOUCHE S A, EL MHAMEDI A, et al. Build a Bayesian network from FMECA in the production of automotive parts: diagnosis and prediction[J]. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 2019, 52(13): 2572-2577. doi: 10.1016/j.ifacol.2019.11.594 [10] LIN S, JIA L M, WANG Y H. Safety assessment of complex electromechanical systems based on hesitant interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy theory[J]. International Journal of Fuzzy Systems, 2019, 21(8): 2405-2420. doi: 10.1007/s40815-019-00729-4 [11] CATELANI M, CIANI L, GALAR D, et al. Risk assessment of a wind turbine: a new FMECA-based tool with RPN threshold estimation[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 20181-20190. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2968812 [12] ASWIN K R, RENJITH V R, AKSHAY K R. FMECA using fuzzy logic and grey theory: a comparitve case study applied to ammonia storage facility[J]. International Journal of System Assurance Engineering and Management, 2022, 13(4): 2084-2103. [13] RENJITH V R, JOSE KALATHIL M, KUMAR P H, et al. Fuzzy FMECA (failure mode effect and criticality analysis) of LNG storage facility[J]. Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries, 2018, 56: 537-547. doi: 10.1016/j.jlp.2018.01.002 [14] GIARDINA M, MORALE M. Safety study of an LNG regasification plant using an FMECA and HAZOP integrated methodology[J]. Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries, 2015, 35: 35-45. doi: 10.1016/j.jlp.2015.03.013 [15] 于涵,张和生. 基于模糊综合评价的动车组牵引传动系统改进FMECA[J]. 铁道学报,2022,44(9): 33-41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.100-8360.2022.09.05YU Han, ZHANG Hesheng. Improved FMECA for traction transmission system of EMU based on fuzzy comprehensive evaluation[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2022, 44(9): 33-41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.100-8360.2022.09.05 [16] SUN Y G, LI F X, LIN G B, et al. Adaptive fault-tolerant control of high-speed maglev train suspension system with partial actuator failure: design and experiments[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University—Science A, 2023, 24(3): 272-283. doi: 10.1631/jzus.A2200189 [17] ZHAI M D, LONG Z Q, LI X L. Fault-tolerant control of magnetic levitation system based on state observer in high speed maglev train[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 31624-31633. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2898108 [18] 佘龙华,邹东升,李建泉,等. 磁悬浮控制器DSP的容错设计[J]. 机车电传动,2006(1): 33-35. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-128X.2006.01.010SHE Longhua, ZOU Dongsheng, LI Jianquan, et al. Design of error tolerance for maglev controller DSP[J]. Electric Drive for Locomotives, 2006(1): 33-35. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-128X.2006.01.010 [19] SUNG H K, KIM D, CHO H, et al. Fault tolerant control of electromagnetic levitation system[J]. Advances in Industrial Control, 2004, 57(10): 676-689. [20] KIM H J, KIM C K, KWON S. Design of a fault-tolerant levitation controller for magnetic levitation vehicle[C]//2007 International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS). Seoul: IEEE, 2007: 1977-1980. [21] ZHAI M D, LI X L, LONG Z Q. Research on redundancy and fault-tolerant control technology of levitation join-structure in high speed maglev train[M]//Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Electrical and Information Technologies for Rail Transportation (EITRT) 2017. Singapore: Springer, 2018: 671-678. [22] JANG K H, KOOK Y S, SHIN B C, et al. Redundancy performance of levitation controller for maglev vehicle EcoBee[C]//2018 21st International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS). Jeju: IEEE, 2018: 898-902. [23] LIANG S, ZENG J W, JIN L, et al. Computer design and test of suspension control based on two-machine hot standby for speed maglev train[C]//2020 39th Chinese Control Conference (CCC). Shenyang: IEEE, 2020: 4147-4152. [24] JIN L, LONG Z Q, ZENG J W. Research on fault-tolerant control problem for suspension system of medium speed maglev train[C]//2017 29th Chinese Control and Decision Conference (CCDC). Chongqing: IEEE, 2017: 2993-2998. [25] 徐俊起,佟来生,荣立军,等. 磁浮列车悬浮控制系统工程化应用中的关键技术[J]. 城市轨道交通研究,2018,21(12): 14-17.XU Junqi, TONG Laisheng, RONG Lijun, et al. Key technologies of levitation control system applied to maglev train in practical engineering[J]. Urban Mass Transit, 2018, 21(12): 14-17. -




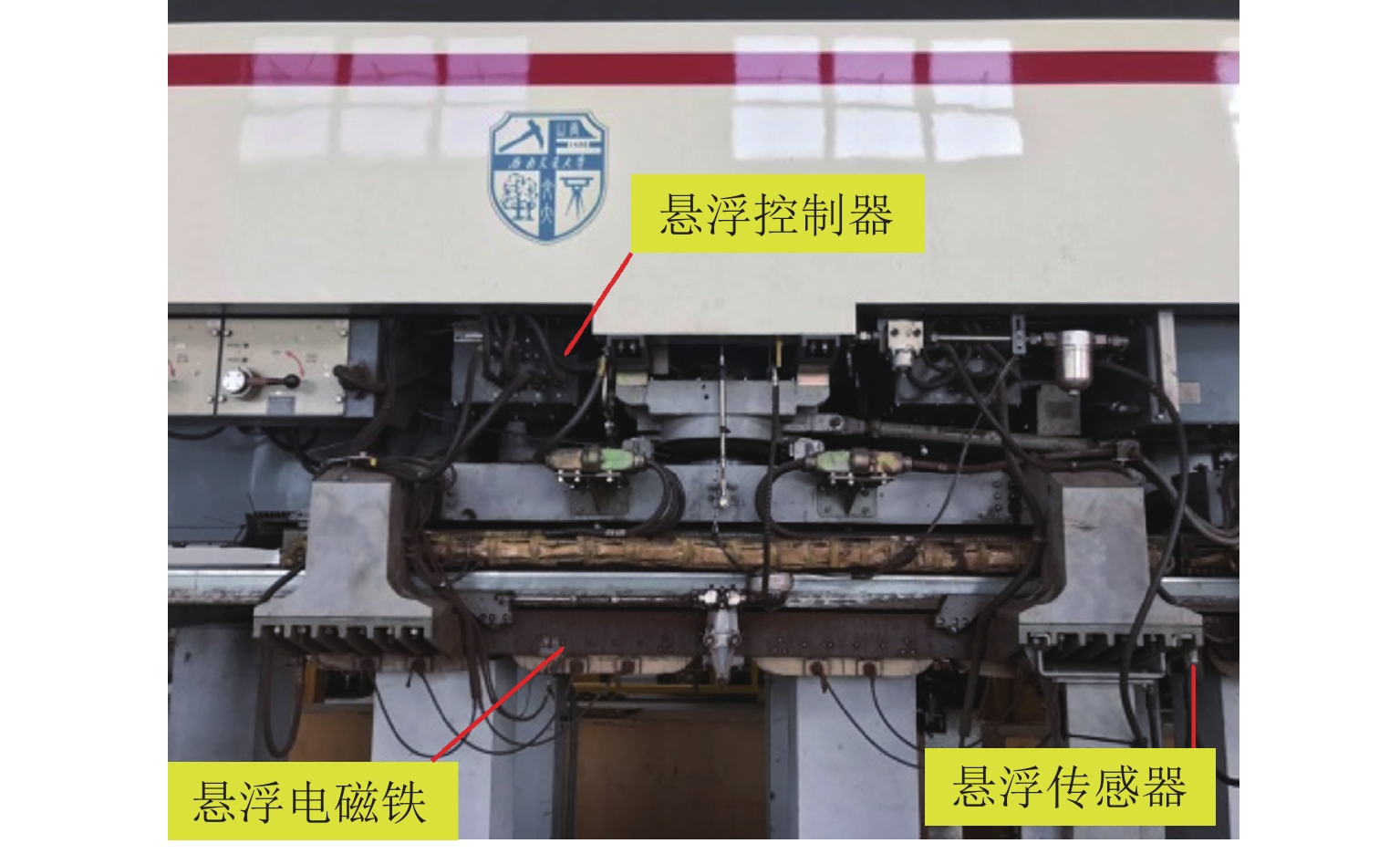
 下载:
下载: