Prediction of Fretting Damage and Fatigue of Spline Pair Between Cylinder and Shaft of Piston Pump
-
摘要:
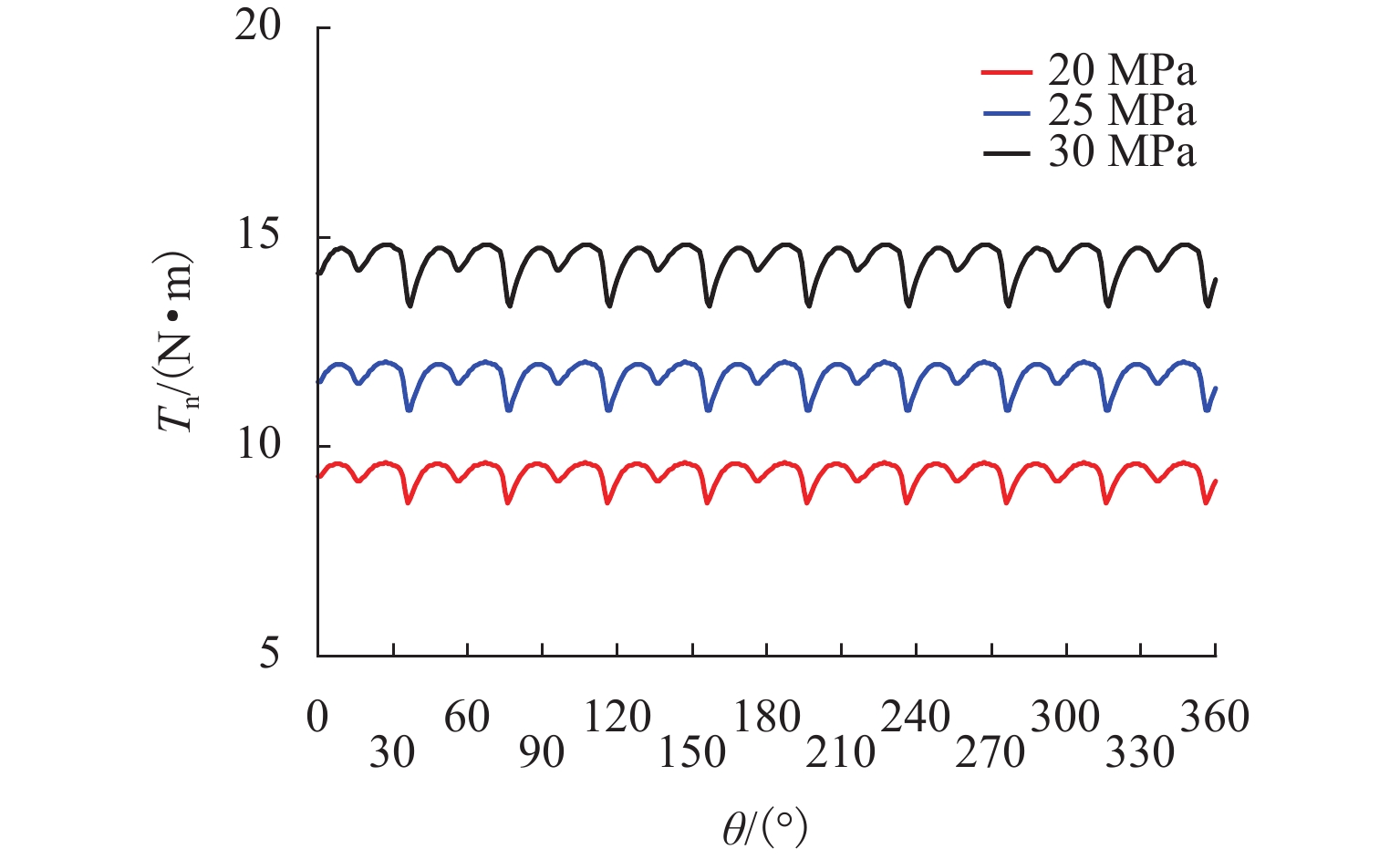
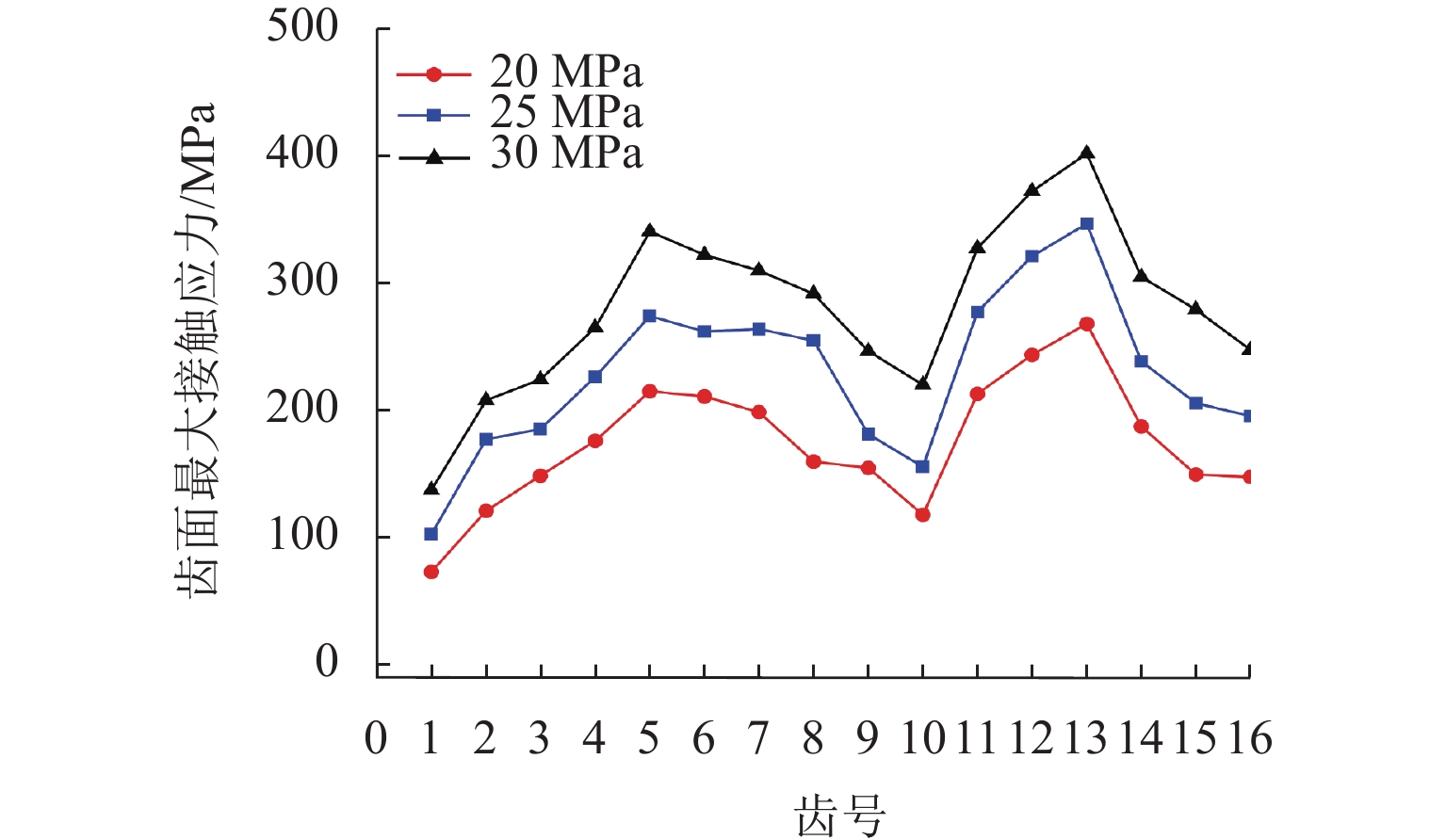
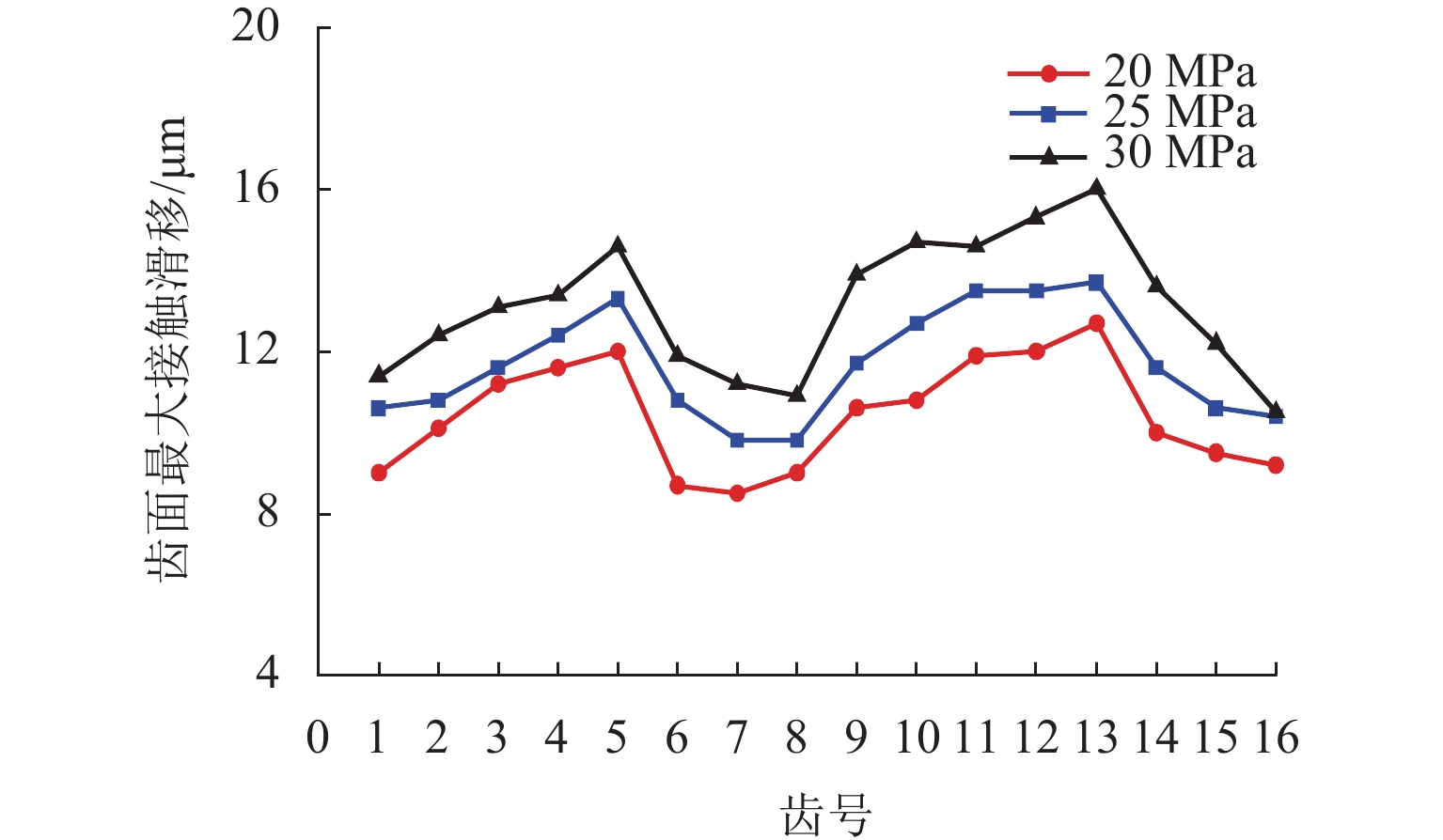
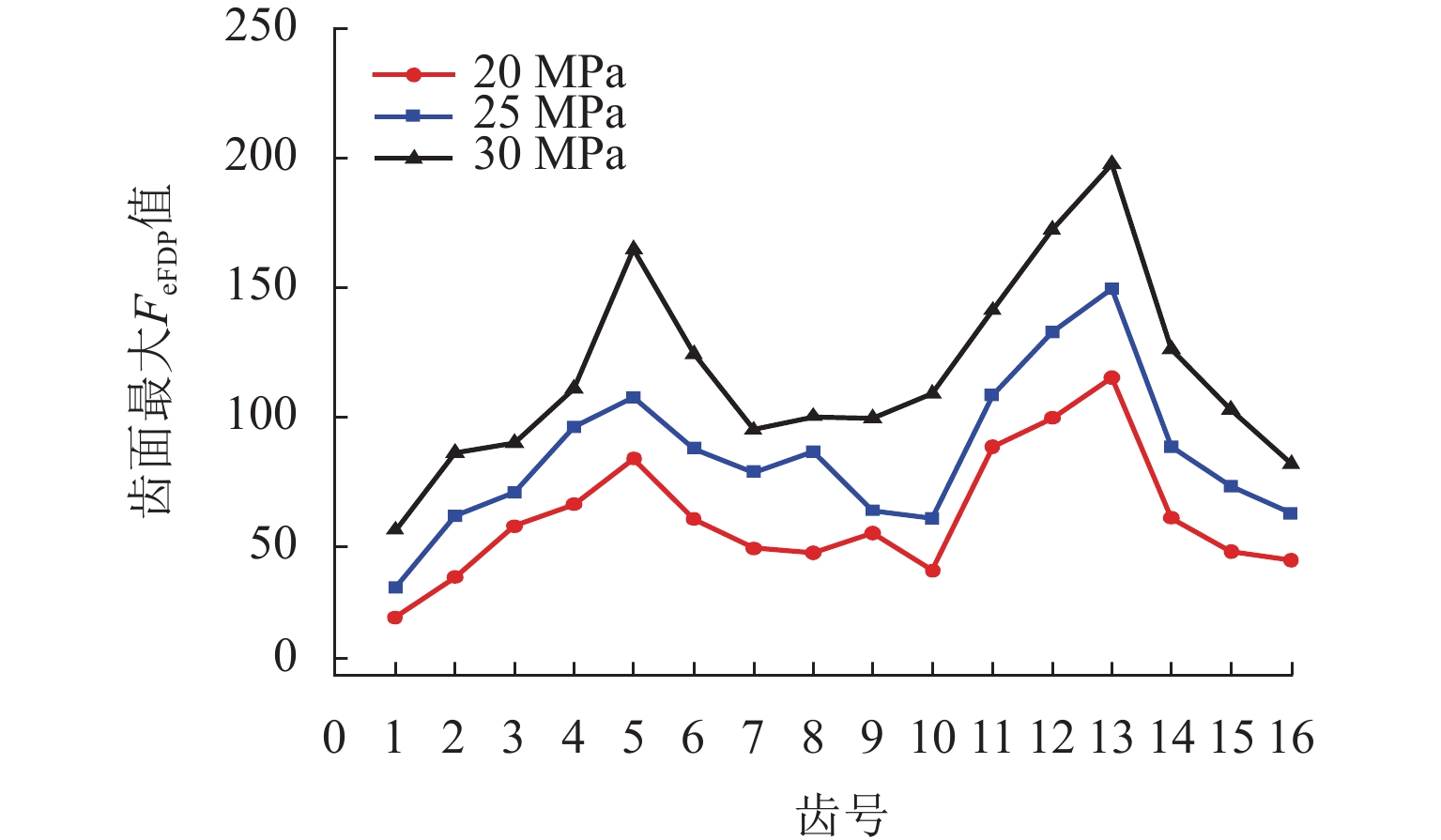
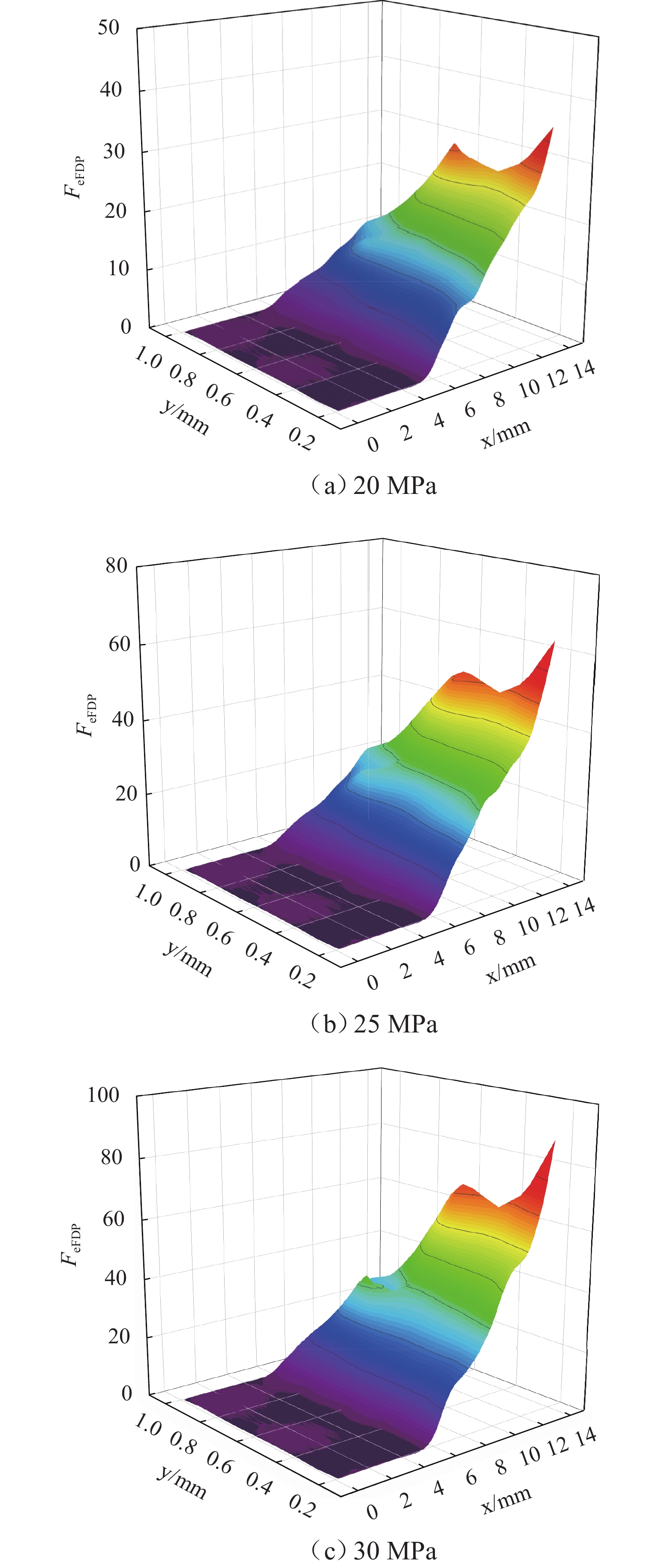
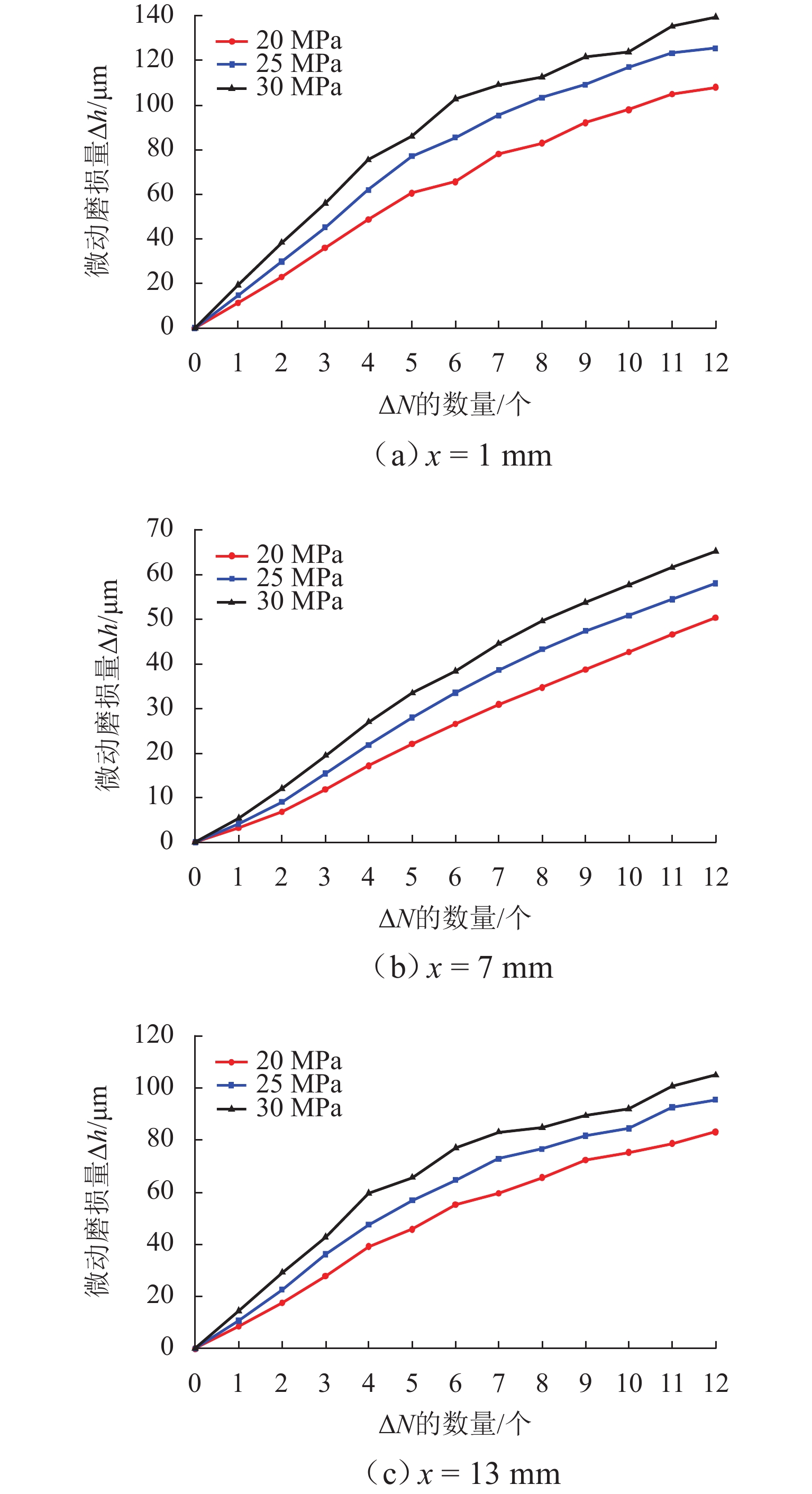
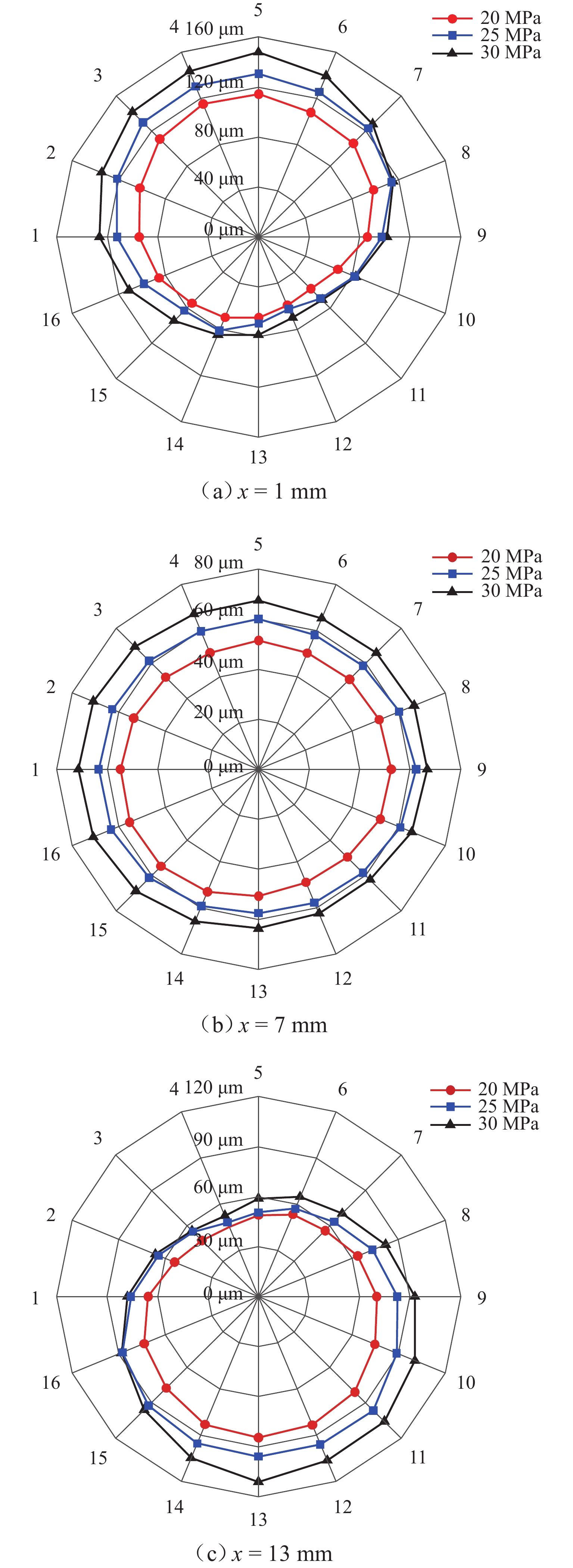
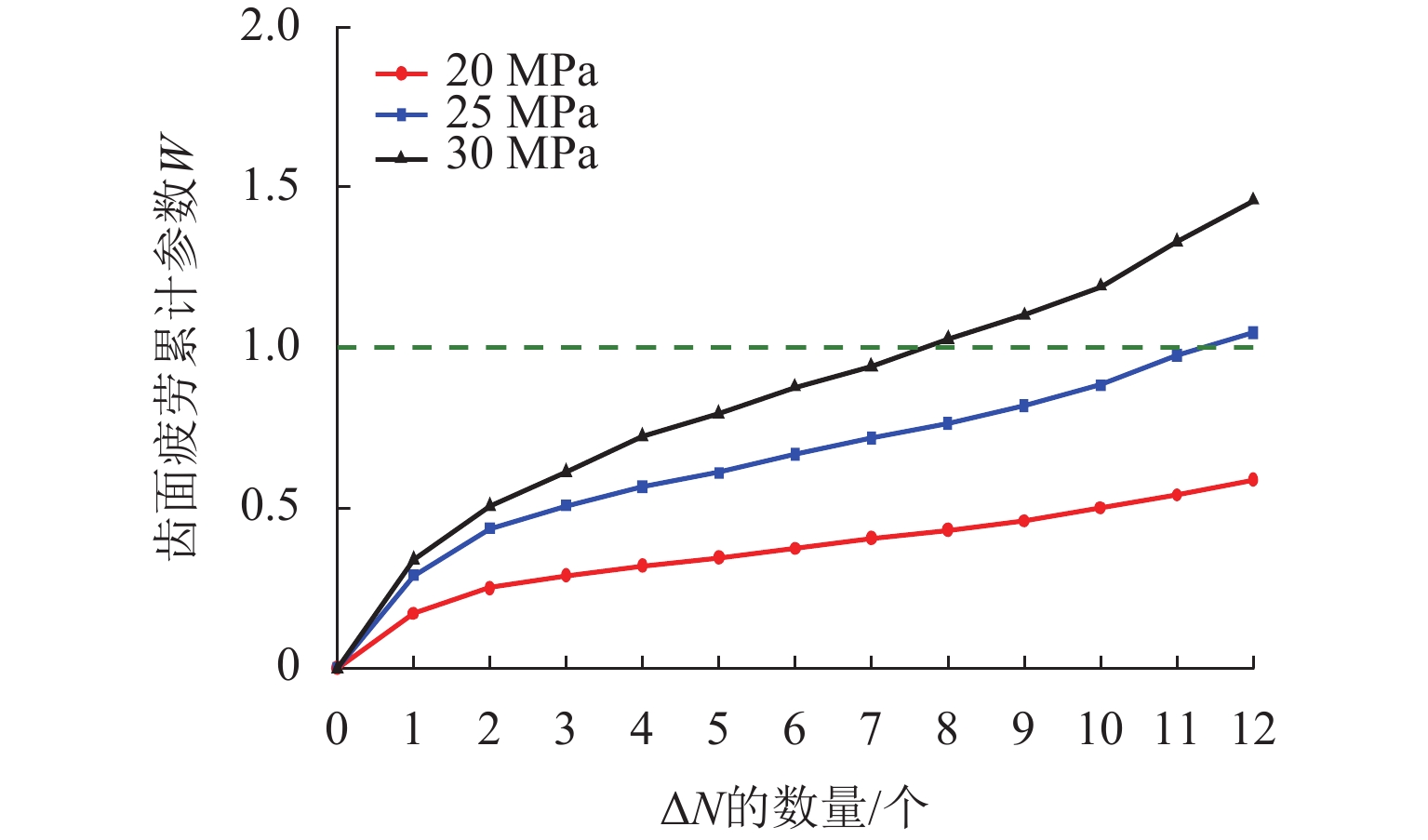
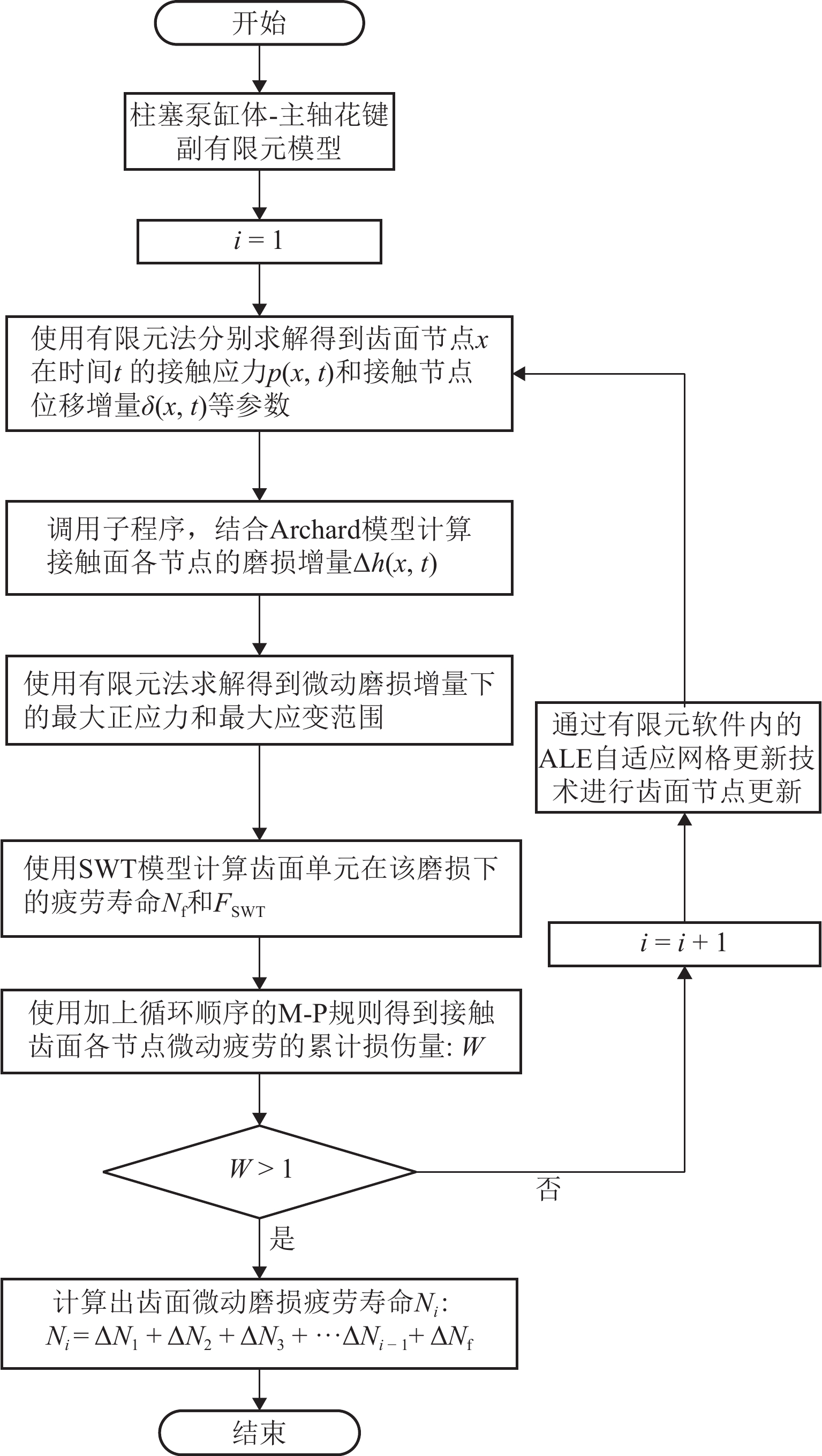
柱塞泵在运行过程中,其缸体和主轴花键副的碰撞行为会加剧花键的齿面磨损,降低其运行可靠性. 为预知主轴花键的使用寿命,本文结合Archard模型和SWT (smith Watson topper)模型,对柱塞泵不同出口压力下花键副的微动损伤和疲劳寿命进行分析. 首先,通过有限元法建立轴向柱塞泵缸体-主轴花键副微动损伤有限元模型;其次,基于建立的有限元模型,对不同出口压力工况下的柱塞泵齿面Ruiz微动损伤参数的分布进行分析,并预估其花键齿面的微动磨损增量;最后,结合M-P (palmgren miner)规则,加上循环疲劳载荷的响应,得到预测的轴向柱塞泵的齿面疲劳寿命. 研究结果表明:柱塞泵花键齿面最大Ruiz损伤参数主要集中在花键齿面端部;柱塞泵花键两端的损伤较为严重,中部的损伤较轻,花键前端和后端的磨损量比中部的磨损量分别高出114%和62%;柱塞泵出口压力的变大会加剧齿面磨损,大大减少花键副使用寿命,出口压力为30 MPa时的寿命相较于20 MPa时的寿命降低60%. 研究结果对柱塞泵花键运行的可靠性和后续的优化分析具有一定指导意义.
Abstract:During the operation of a piston pump, the contact behavior of the spline pair between the cylinder and the shaft aggravates the tooth surface wear of the spline and reduces its operational reliability. To predict the service life of the shaft spline, the Archard model and the SWT model were combined to analyze the fretting damage and fatigue life of the spline pair under different outlet pressures of the piston pump. First, a finite element model for fretting damage of the spline pair between the cylinder and the shaft of an axial piston pump was established using the finite element method. Second, based on the established finite element model, the distribution of Ruiz fretting damage parameters on the tooth surfaces of the piston pump under different outlet pressure conditions was analyzed, and the fretting wear increments of the spline tooth surfaces were predicted. Finally, combined with the Miner-Palmgren (M-P) rule and the response under cyclic fatigue loading, the predicted tooth surface fatigue life of the axial piston pump was obtained. The results show that the maximum Ruiz damage parameter of the piston pump spline tooth surface is mainly concentrated at the ends of the spline tooth surface. The damage at both ends of the spline is more severe, while the damage in the middle region is relatively slight, and the wear at the front and rear ends of the spline is 114% and 62% higher than that in the middle region, respectively. An increase in the outlet pressure of the piston pump intensifies tooth surface wear and significantly reduces the service life of the spline pair, and the fatigue life at an outlet pressure of 30 MPa is reduced by 60% compared with that at 20 MPa. The results provide guidance for the operational reliability and subsequent optimization analysis of piston pump splines.
-
Key words:
- axial piston pump /
- finite element method /
- Ruiz damage distribution /
- fretting wear /
- fatigue life
-
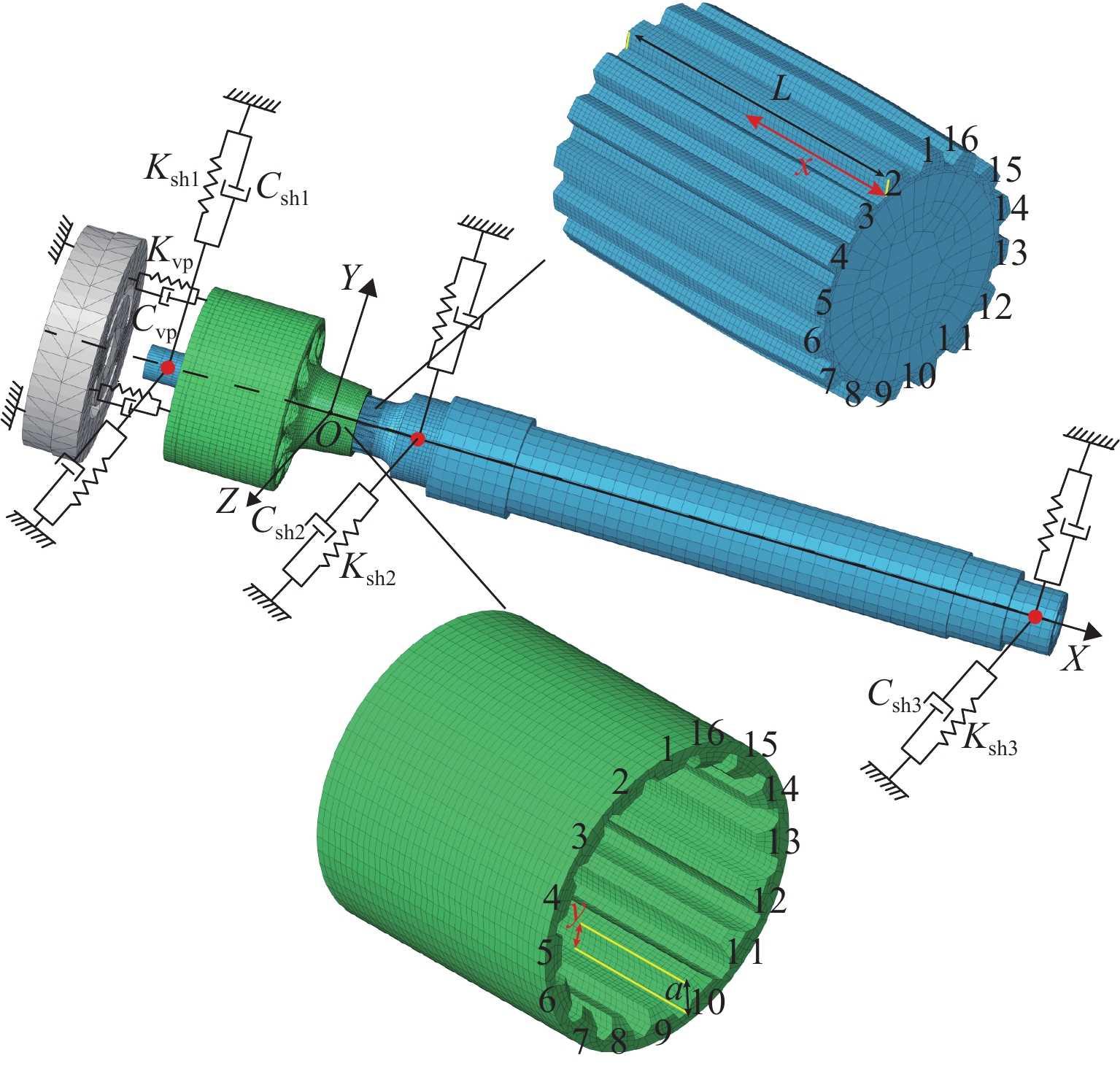
表 1 缸体-主轴花键副参数
Table 1. Parameters of cylinder and shaft spline pair
参数 齿数 压力角/(°) 齿顶圆直径/mm 齿厚/mm 泊松比 模数/mm 齿槽宽/mm 齿根圆直径/mm 弹性模量E/MPa 外花键 16 30 12.75 1.31 0.28 0.75 1.12 1.12 211000 内花键 16 30 11.36 1.29 0.28 0.75 1.04 13.13 211000 表 2 刚度阻尼设置参数
Table 2. Parameters of stiffness and damping
参数名称 参数值 轴承1沿Y向的刚度Ksh1y/(N•m−1) 2.8 × 107 轴承1沿Z向的刚度Ksh1z/(N•m−1) 2.8 × 107 轴承1沿Y向的阻尼Csh1y/(N•s•m−1) 2.0 × 103 轴承1沿Z向的阻尼Csh1z/(N•s•m−1) 2.0 × 103 轴承2沿Y向的刚度Ksh2y/(N•m−1) 3.2 × 107 轴承2沿Z向的刚度Ksh2z/(N•m−1) 3.2 × 107 轴承2沿Y向的阻尼Csh2y/(N•s•m−1) 1.0 × 103 轴承2沿Z向的阻尼Csh2z/(N•s•m−1) 1.0 × 103 轴承3沿Y向的刚度Ksh3y/(N•m−1) 2.0 × 107 轴承3沿Z向的刚度Ksh3z/(N•m−1) 2.0 × 107 轴承3沿Y向的阻尼Csh3y/(N•s•m−1) 2.0 × 103 轴承3沿Z向的阻尼Csh3z/(N•s•m−1) 2.0 × 103 缸体与配流盘间的刚度Kvp/(N•m−1) 8.5 × 108 缸体与配流盘间的阻尼Cvp/(N•s•m−1) 1.0 × 103 表 3 柱塞泵花键疲劳寿命预测
Table 3. Prediction of fatigue life of spline pair of the piston pump
出口压力值/MPa 预测寿命/万次 预测寿命/h 20 1954 81.4 25 1166 48.5 30 772 32.1 -
[1] Shaogan Ye, Junhui Zhang, Bing Xu, et al. Theoretical investigation of the contributions of the excitation forces to the vibration of an axial piston pump, Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2019, 129: 201-217. [2] Manring, N. D. The Torque on the Input Shaft of an Axial-Piston Swash-Plate Type Hydrostatic Pump[J]. Journal of Dynamic Systems, Measurement, and Control, 1998, 120(01): 57-62. doi: 10.1115/1.2801322 [3] Manring N D, Dong Z. The impact of using a secondary swash-plate angle within an axial piston pump[J]. Journal of Dynamic Systems, Measurement, and Control, 2004, 126(1): 65-74. doi: 10.1115/1.1648313 [4] 王海涛, 崔永红, 董雪莲. 渐开线花键联接磨损特性研究[J]. 科技创新与应用, 2016(15): 5-6. doi: 10.19981/j.cn23-1581/g3.2016.15.003WANG Haitao, CUI Yonghong, DONG Xuelian. Study on Wear Characteristics of Involute Spline Connection[J]. Technology Innovation and Application, 2016(15): 5-6. doi: 10.19981/j.cn23-1581/g3.2016.15.003 [5] Jeung H, Kwon J, Lee Y C. Crack initiation and propagation under fretting fatigue of inconel 600 alloy[J]. Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 2015, 29(12): 5241-5244. doi: 10.1007/s12206-015-1124-8 [6] Cuffaro V, Curà F, Mura A, Test Rig for Spline Cou-plings Working in Misaligned Conditions[J]. Journal of Tribology, 2014, 136(1): 1-7. [7] Curà F, Mura A, Adamo F, Fatigue damage in spline couplings: numerical simulations and experimental vali-dation[J]. Procedia Structural Integrity. 2017, 5: 1326-1333. [8] J. Ding, W. S. Sum, R. Sabesan, et al. Fretting fatigue predictions in a complex coupling[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2007, 29(7) : 1229–1244. [9] Duan L, Ning K, Wang L, et al. Damage mechanisms of spline teeth of friction plates under non-uniform impact[J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2024, 296: 109859. doi: 10.1016/j.engfracmech.2024.109859 [10] Xue X, Huo Q, Hong L. Fretting Wear-Fatigue Life Prediction for Aero-Engine’s Involute Spline Couplings Based on Abaqus[J]. Journal of Aerospace Engineering, 2019, 32(6): 04019081-04019081. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)AS.1943-5525.0001058 [11] Xue X, Jia J, Huo Q, et al. Experimental investigation and prediction method of fretting wear in rack-plane spline couplings[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers Part J Journal of Engineering Tribology, 2020, 235(5): 1025-1037. doi: 10.1177/1350650120939838 [12] Xiangzhen X, Yifan L, Liqi S, et al. Mechanism and prediction method of fretting damage in involute spline couplings of aero-engine[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2023, 148. [13] 肖立, 徐颖强, 陈智勇, 等. 直升机浮动渐开线花键微动磨损影响因素分析[J]. 航空动力学报, 2021, 36(4): 751-766. doi: 10.13224/j.cnki.jasp.2021.04.008Xiao Li, Xu Yingqiang, Chen Zhiyong, et al. Analysis of influencing factors of fretting wear with helicopter floating involute spline[J]. Journal of Aerospace Power, 2021, 36(4): 751-766. doi: 10.13224/j.cnki.jasp.2021.04.008 [14] 肖立, 徐颖强, 陈智勇, 等. 浮动渐开线花键微动损伤及磨损疲劳预测[J]. 西北工业大学学报, 2022, 40(3): 549-559. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2758.2022.03.010Xiao Li, Xu Yingqiang, Chen Zhiyong, et al. Prediction of fretting damage and wear fatigue of floating involute spline couplings[J]. Northwestern polytechnical university., 2022, 40(3): 549-559. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2758.2022.03.010 [15] 陈壮, 董庆兵, 罗振涛, 等. 花键微动磨损和损伤累积的耦合机制及寿命预测[J]. 机械工程学报, 2023, 59(3): 133-143.Chen Zhuang, Dong Qingbing, Luo Zhentao, et al. Coupling Mechanism of Fretting Wear and Damage Accumulation of Spline Couplings and Service Life Prediction[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2023, 59(3): 133-143. [16] 袁周致远, 吉伯海, 傅慧, 等. 疲劳裂纹气动冲击的维修机理及效果[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2024, 59(2): 307-314.YUANZHOU Zhiyuan, JI Bohai, FU Hui, et al. Fatigue Crack Repair Mechanism and Effect by Pneumatic Impact Treatment[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2024, 59(2): 307-314. [17] 喻天翔, 赵庆岩, 尚柏林, 等. 考虑间隙不确定性的花键概率疲劳寿命预测方法[J]. 机械工程学报, 2022, 58(16): 391-402.Yu Tianxiang, Zhao Qingyan, Shang Bolin, et al. Probabilistic Fatigue Life Prediction Method of Spline Considering Clearance Uncertainty[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2022, 58(16): 391-402. [18] 董丙杰, 陈光雄, 冯晓航, 等. 钢轨波磨激励下的e型弹条振动疲劳断裂机理[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2025, 60(5): 1287-1295.DONG Bingjie, CHEN Guangxiong, FENG Xiaohang, et al. Vibration Fatigue Fracture Mechanism of e-Type Clip Under Rail Corrugation Excitation[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2025, 60(5): 1287-1295. [19] Ruiz C, Wang Z P, Webb P H. Techniques for the characterization of fretting fatigue damage[J]. ASTM SPECIAL TECHNICAL PUBLICATION, 1992, 1159: 170. doi: 10.1520/stp25829s [20] Vidner J, Leidich E. Enhanced Ruiz criterion for the evaluation of crack initiation in contact subjected to fretting fatigue[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2007, 29(9-11): 2040-2049. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2007.02.010 [21] Madge J, Leen S, Shipway P. The critical role of fretting wear in the analysis of fretting fatigue[J]. Wear, 2006, 263(1): 542-551. doi: 10.1016/j.wear.2006.11.021 [22] 薛向珍. 航空渐开线花键副微动磨损机理及磨损量预估方法研究[D]. 西北工业大学, 2017.Xue Xiangzhen. Investigation on maechanism and prediction method of fretting wear in aero-engine involute spline coupling[D]. Northwestern polytechnical university, 2017. [23] J. Ding, S. B. Leen, E. J. Williams, et al. Finite element simulation of fretting wear-fatigue interaction in spline couplings[J], Tribology-Materials, Surfaces & Interfaces, 2008, 2: 1, 10-24. [24] Smith K N, Topper T H, Watson P. A stress–strain function for the fatigue of metals[J]. Journal of Materials, 1970, 5: 767-778. [25] Madge J, Leen S, McColl I, et al. Contact-evolution based prediction of fretting fatigue life: Effect of slip amplitude[J]. Wear, 2006, 262(9): 1159-1170. doi: 10.1016/j.wear.2006.11.004 -




 下载:
下载: