Smoothing Methods of Wheel Out-of-Roundness Signals and Their Effects on Polygonal Wear Prediction
-
摘要:
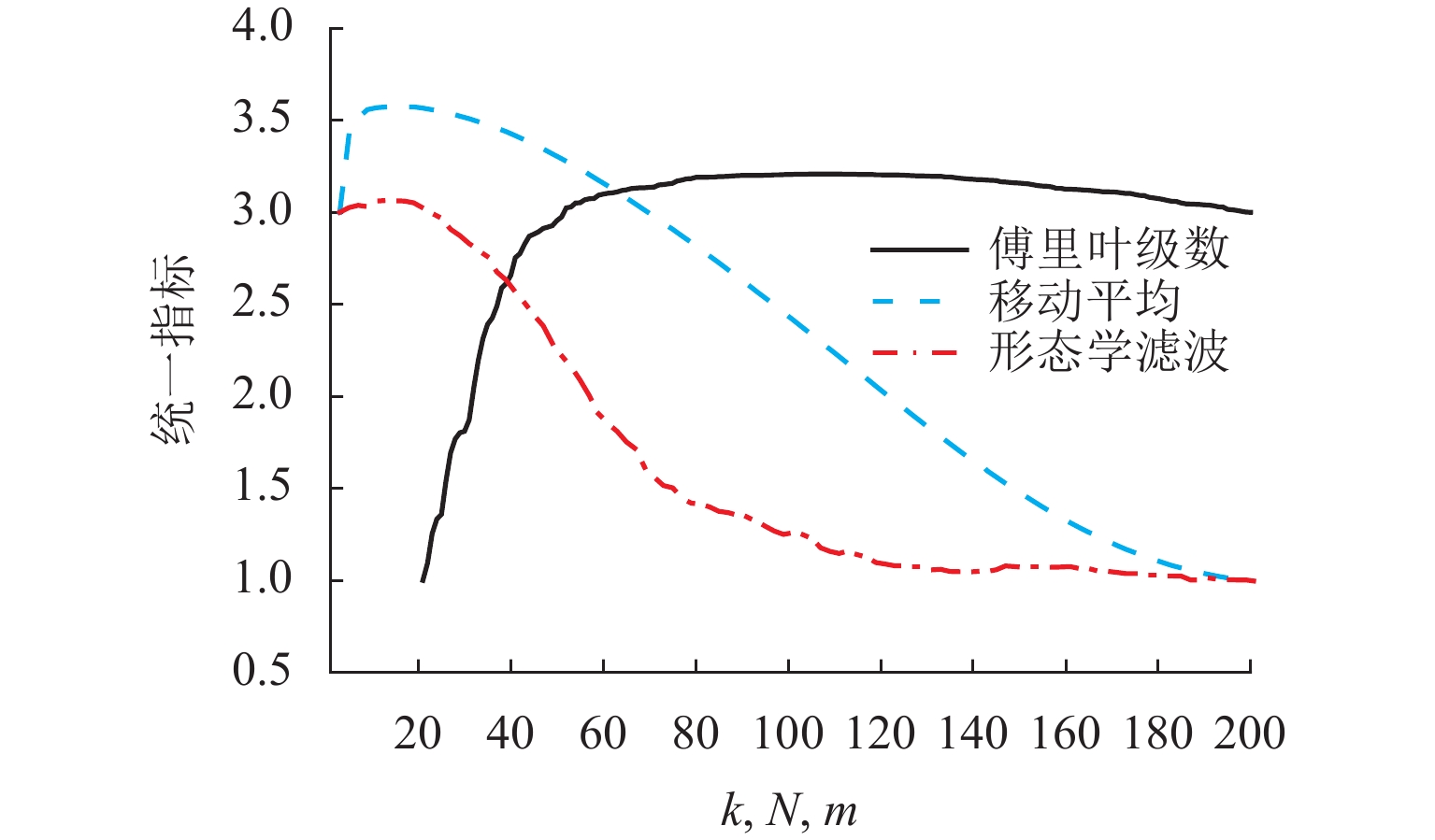
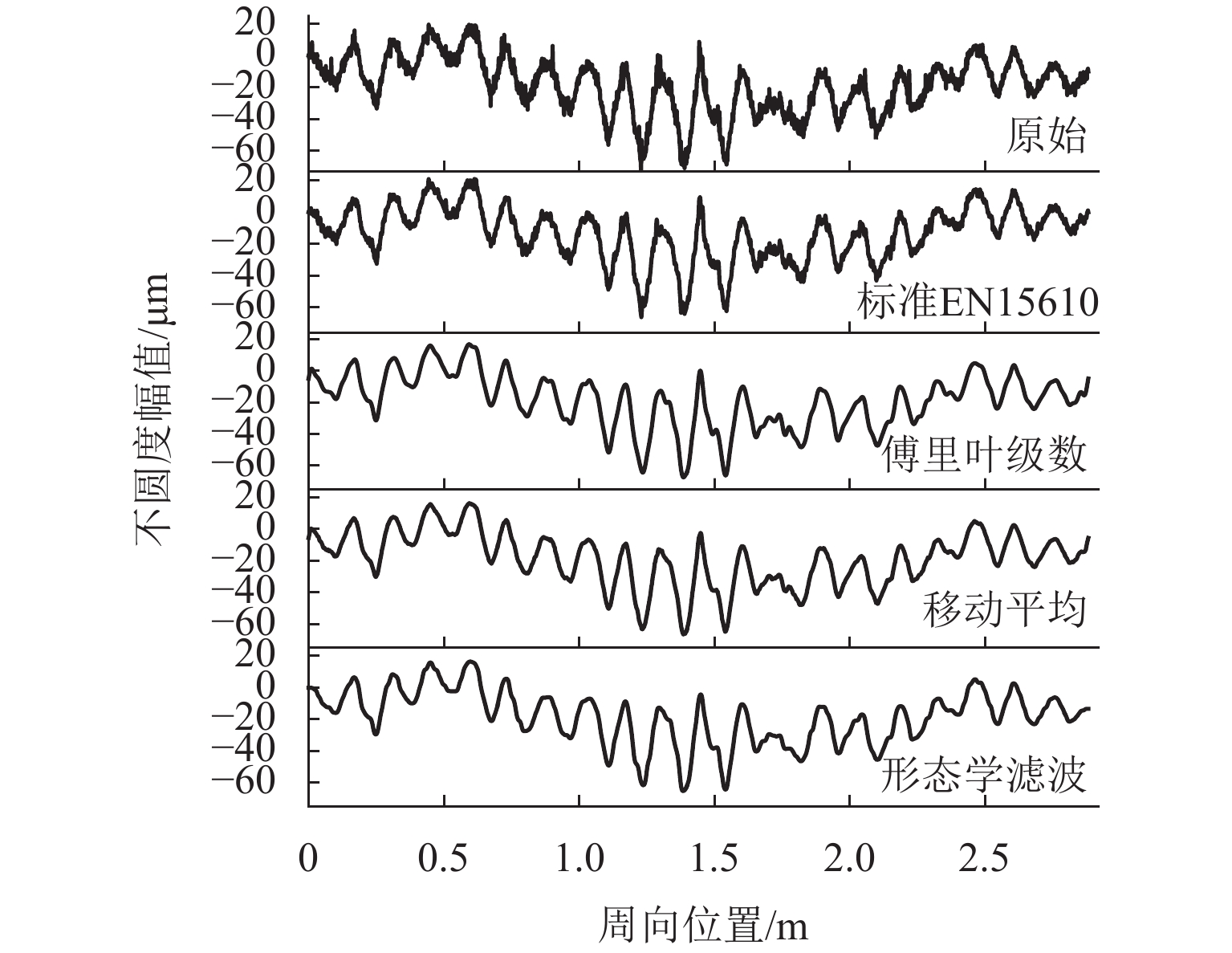
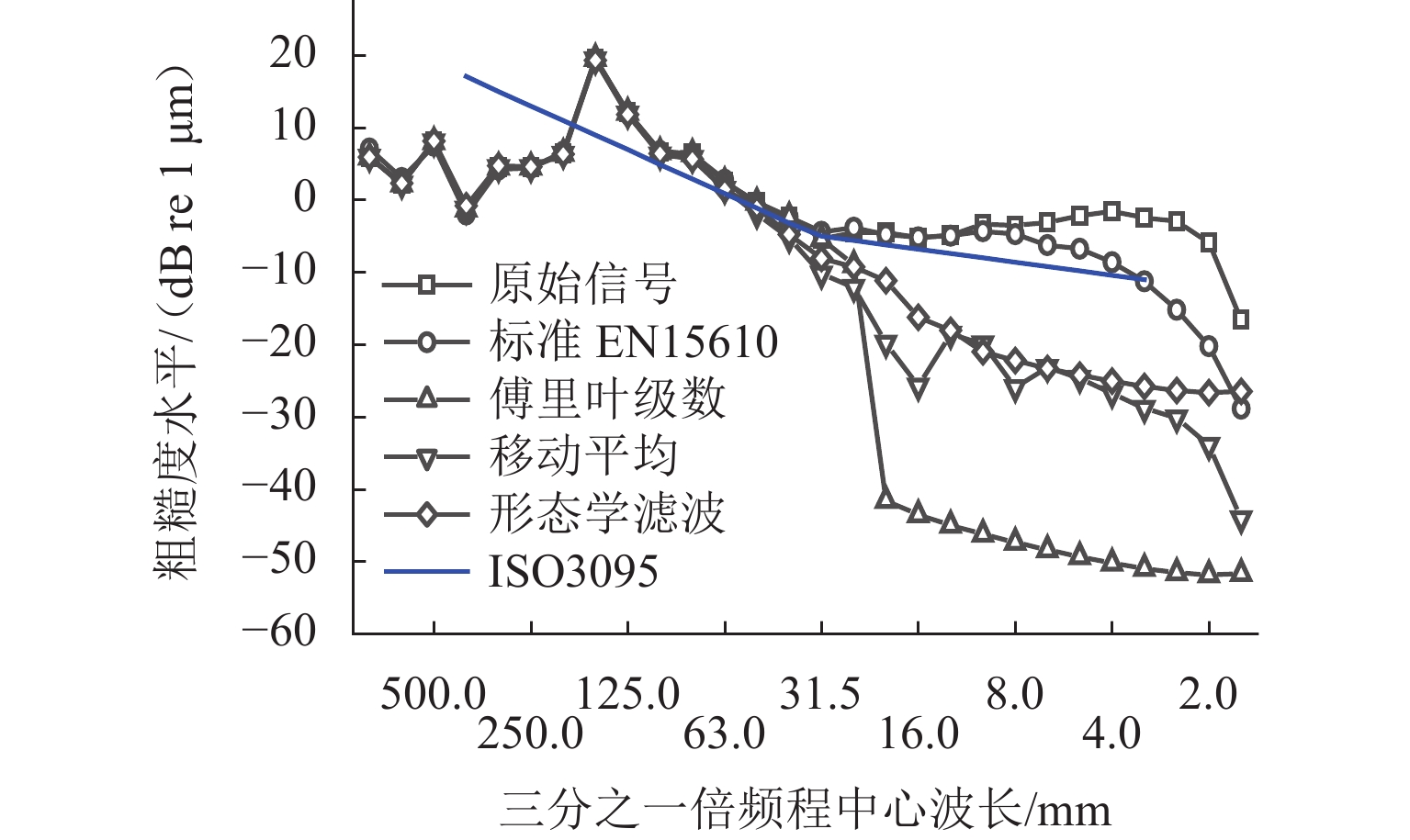
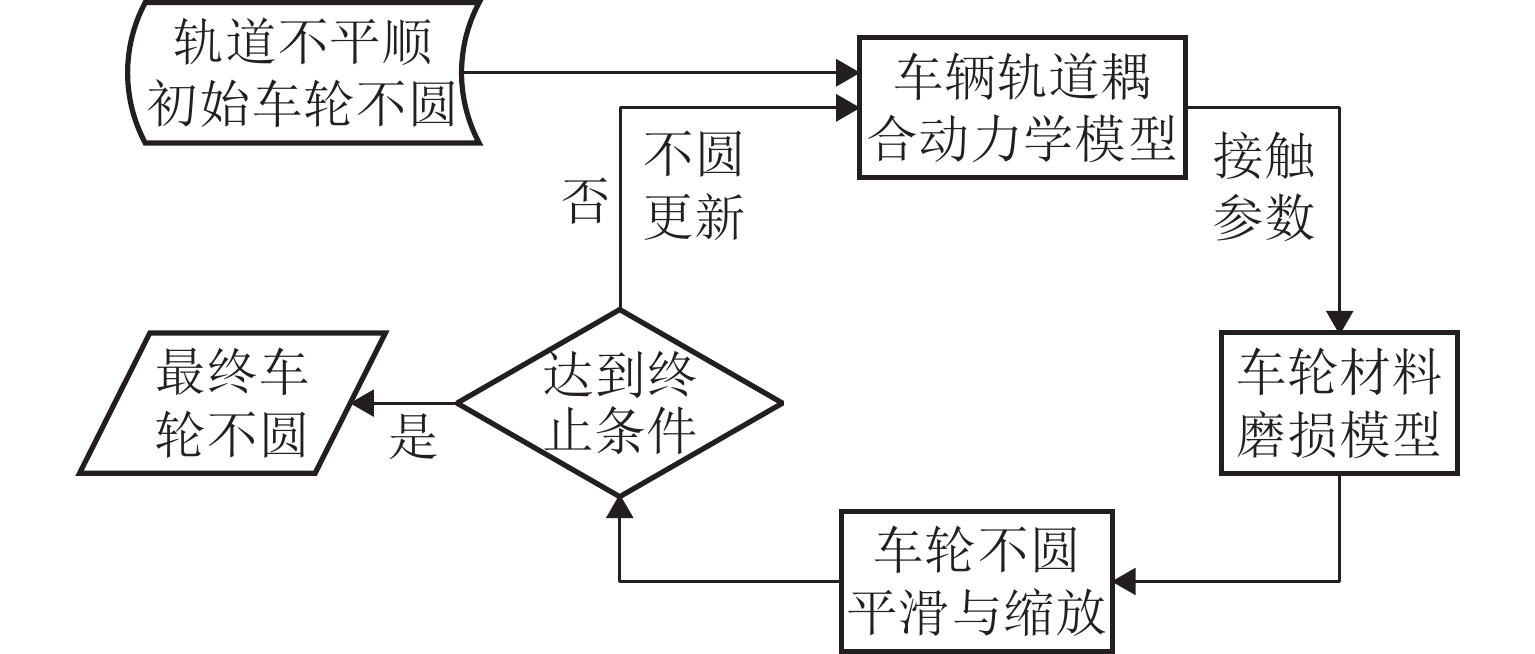
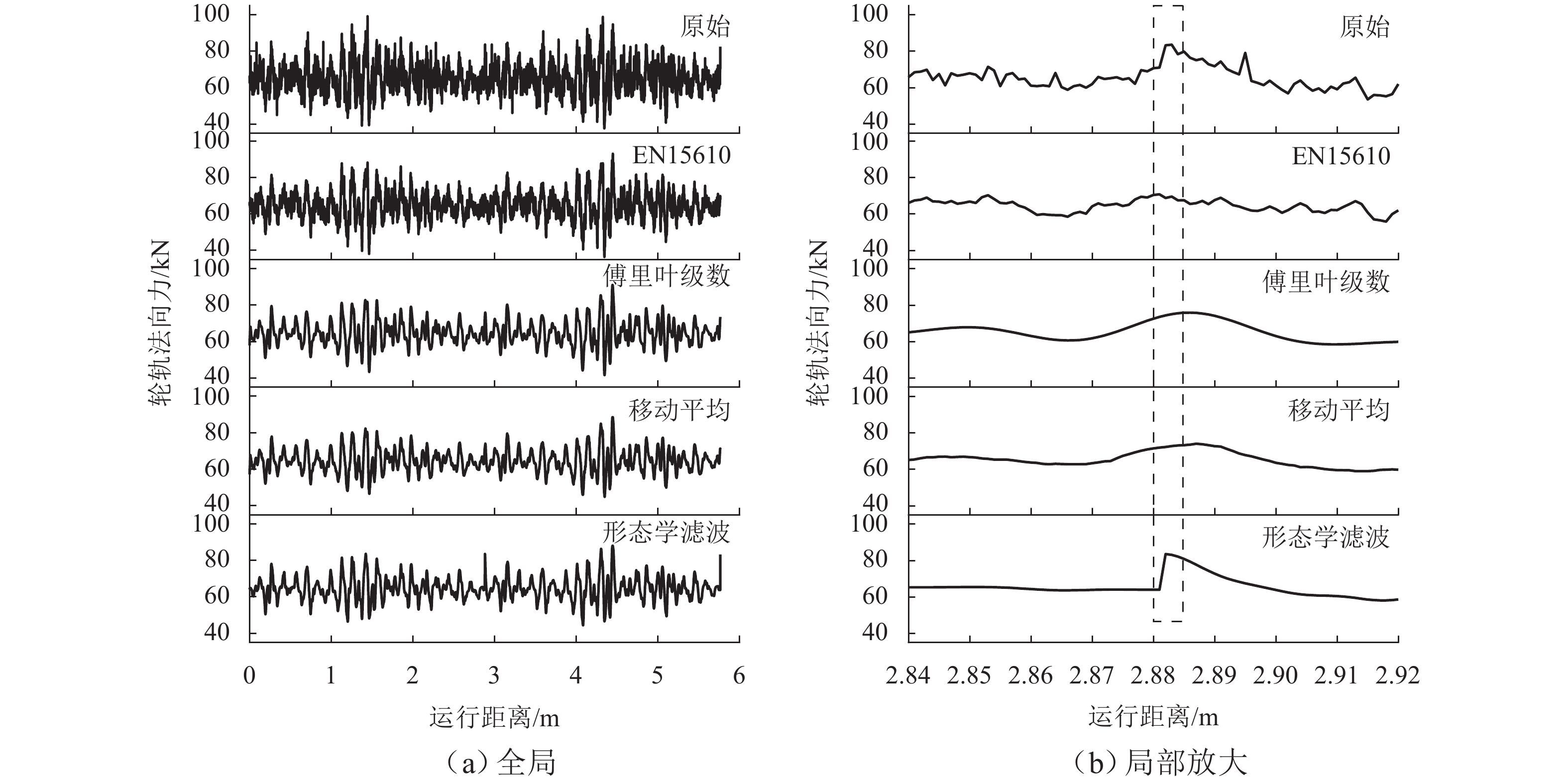
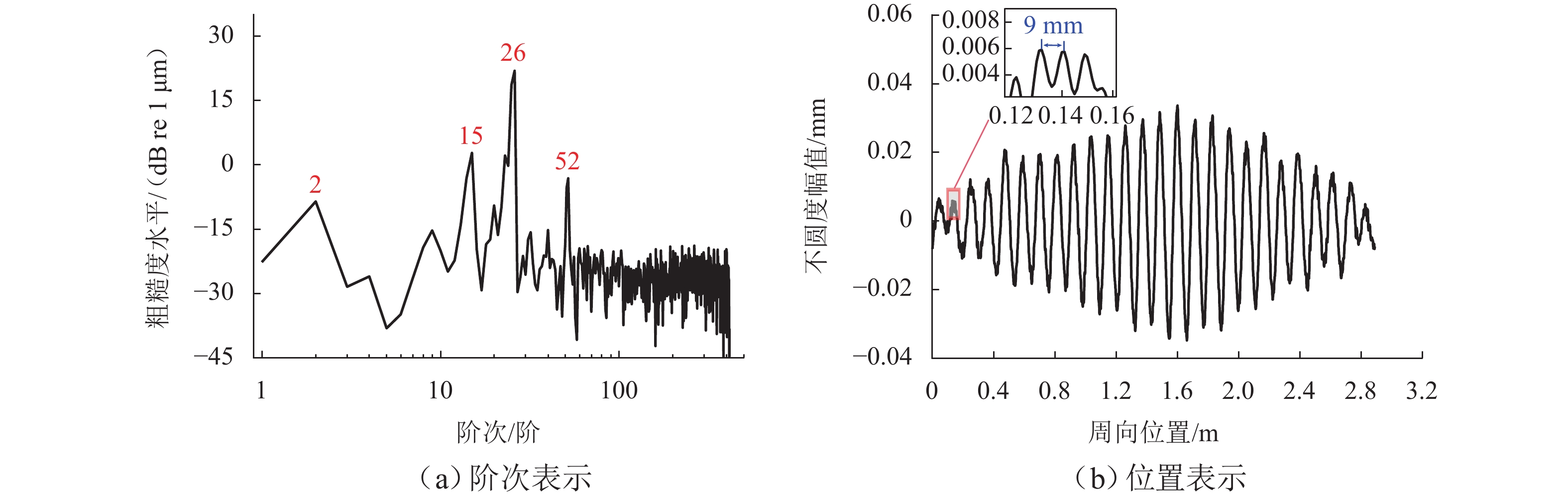
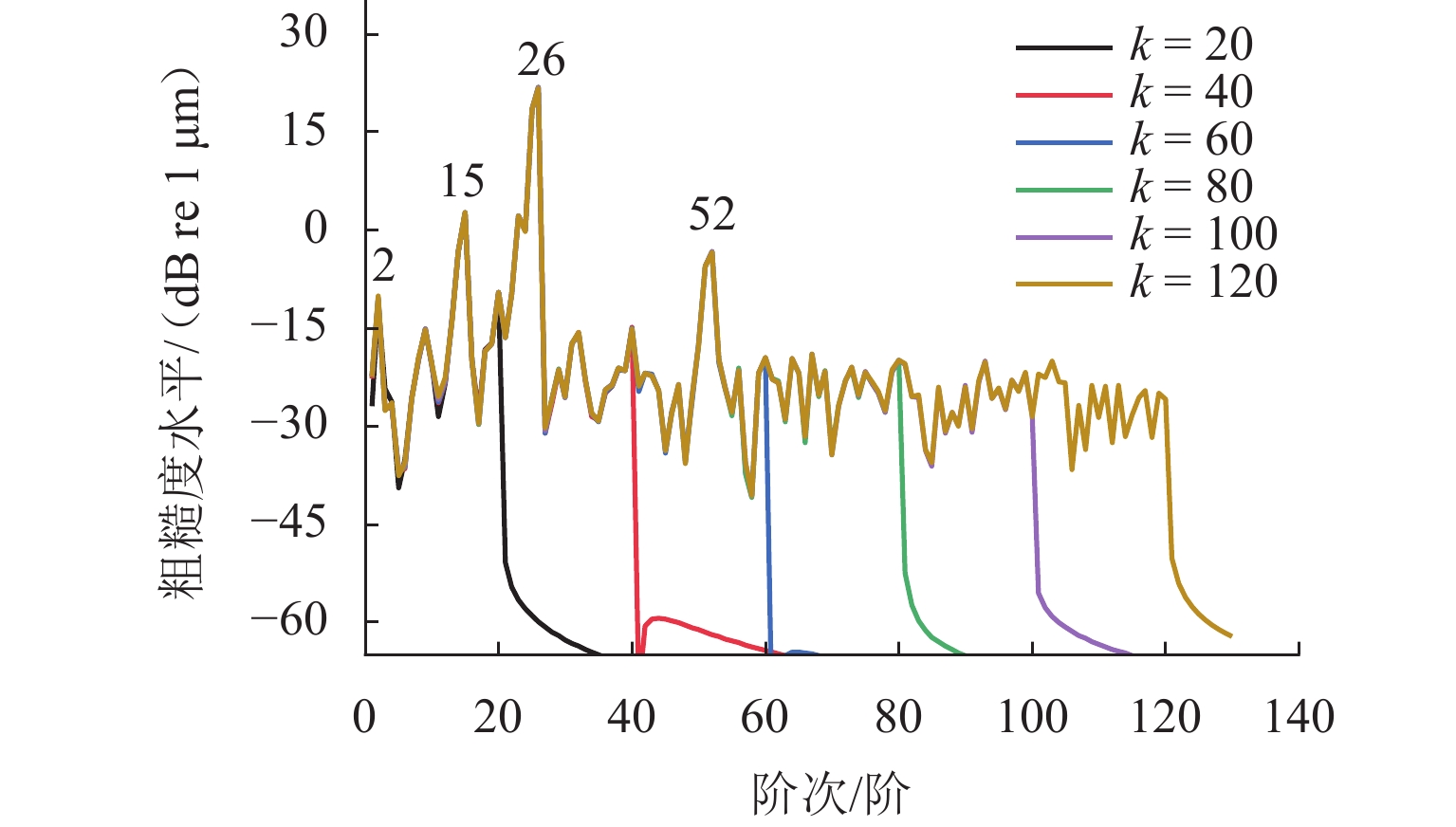
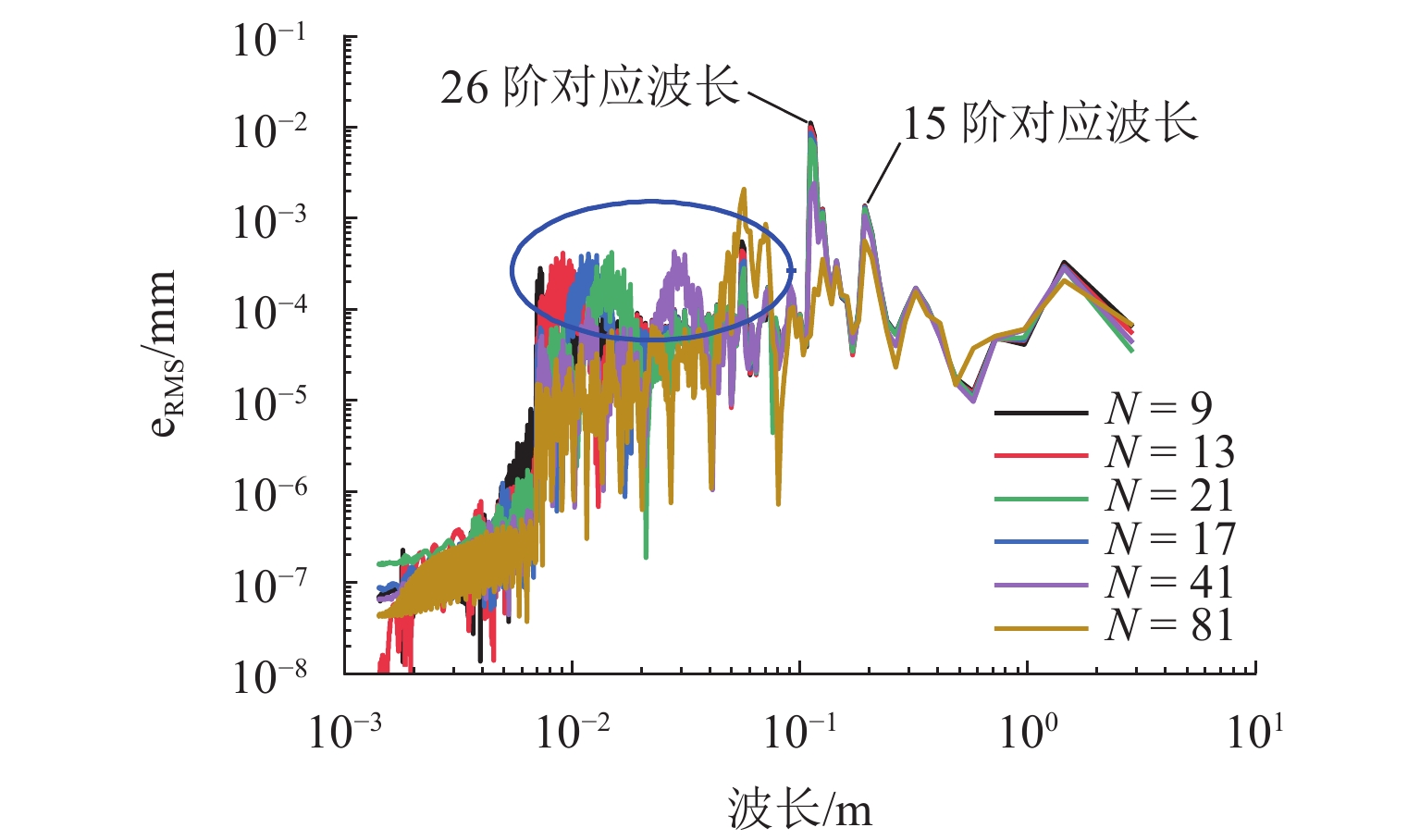
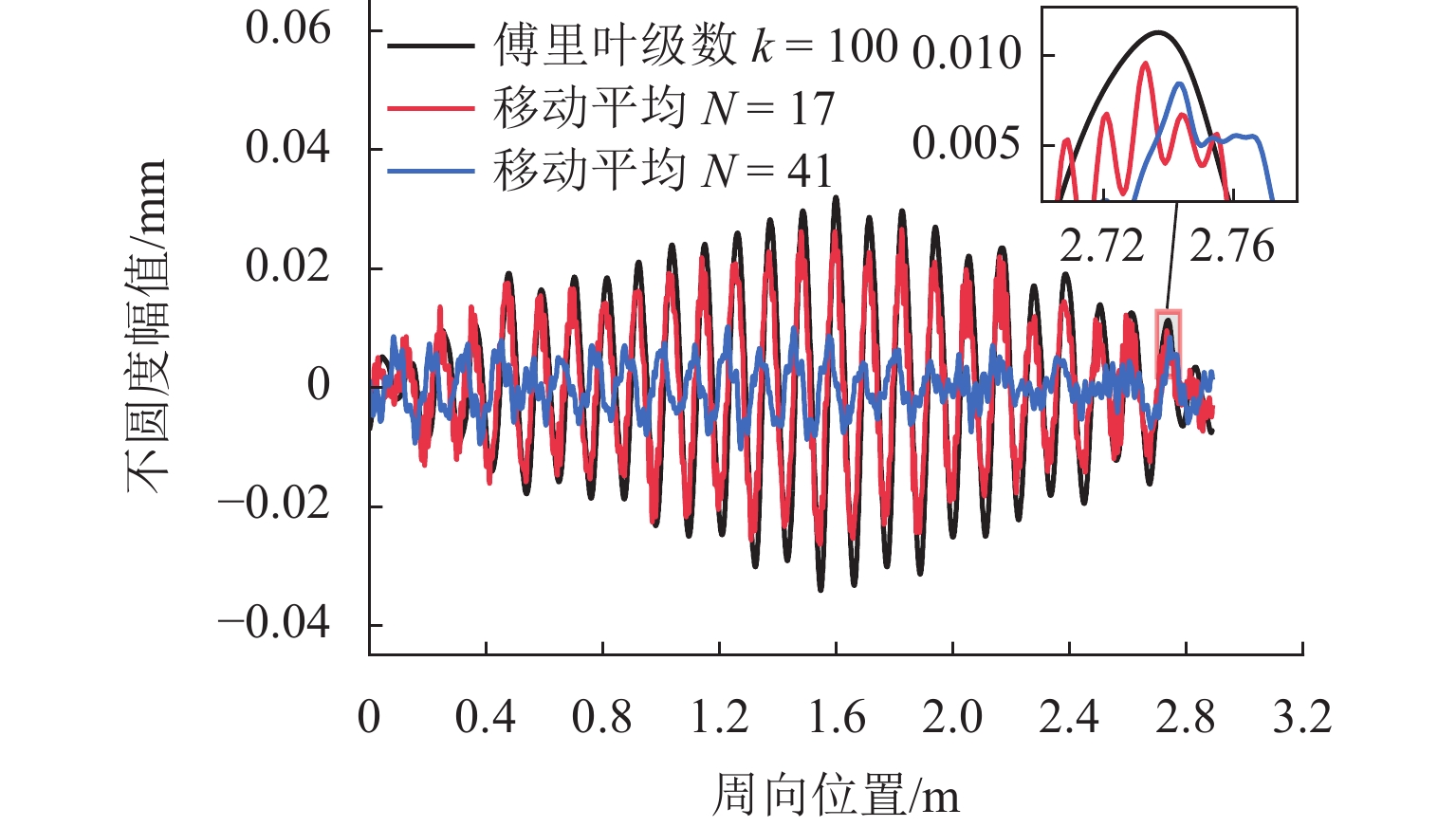
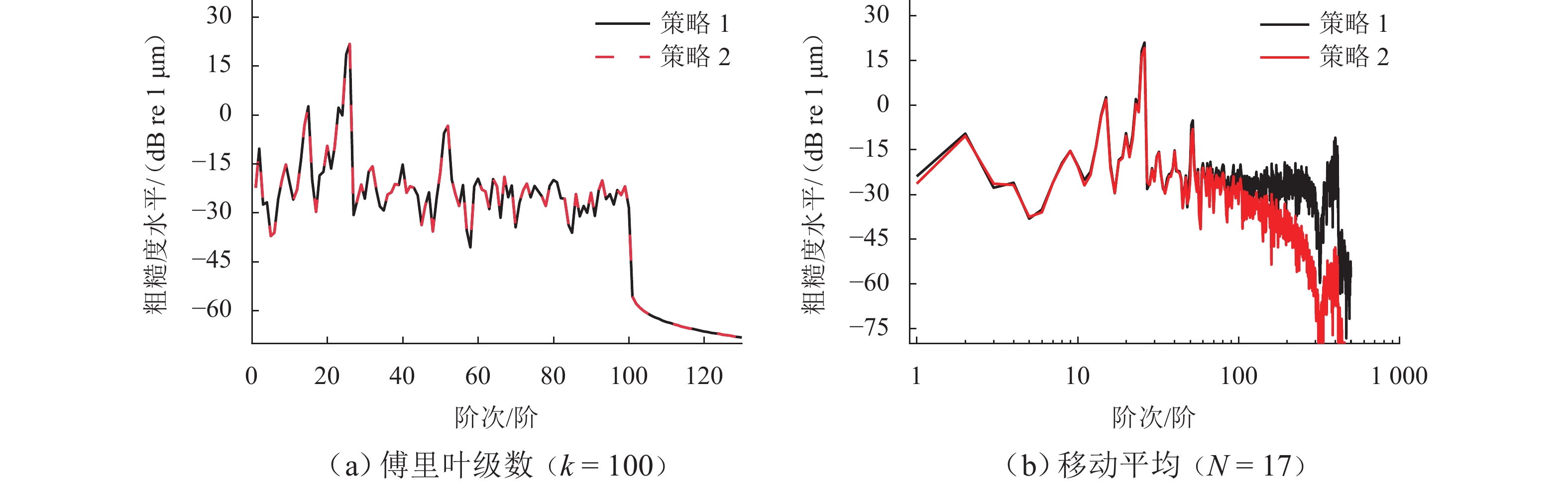
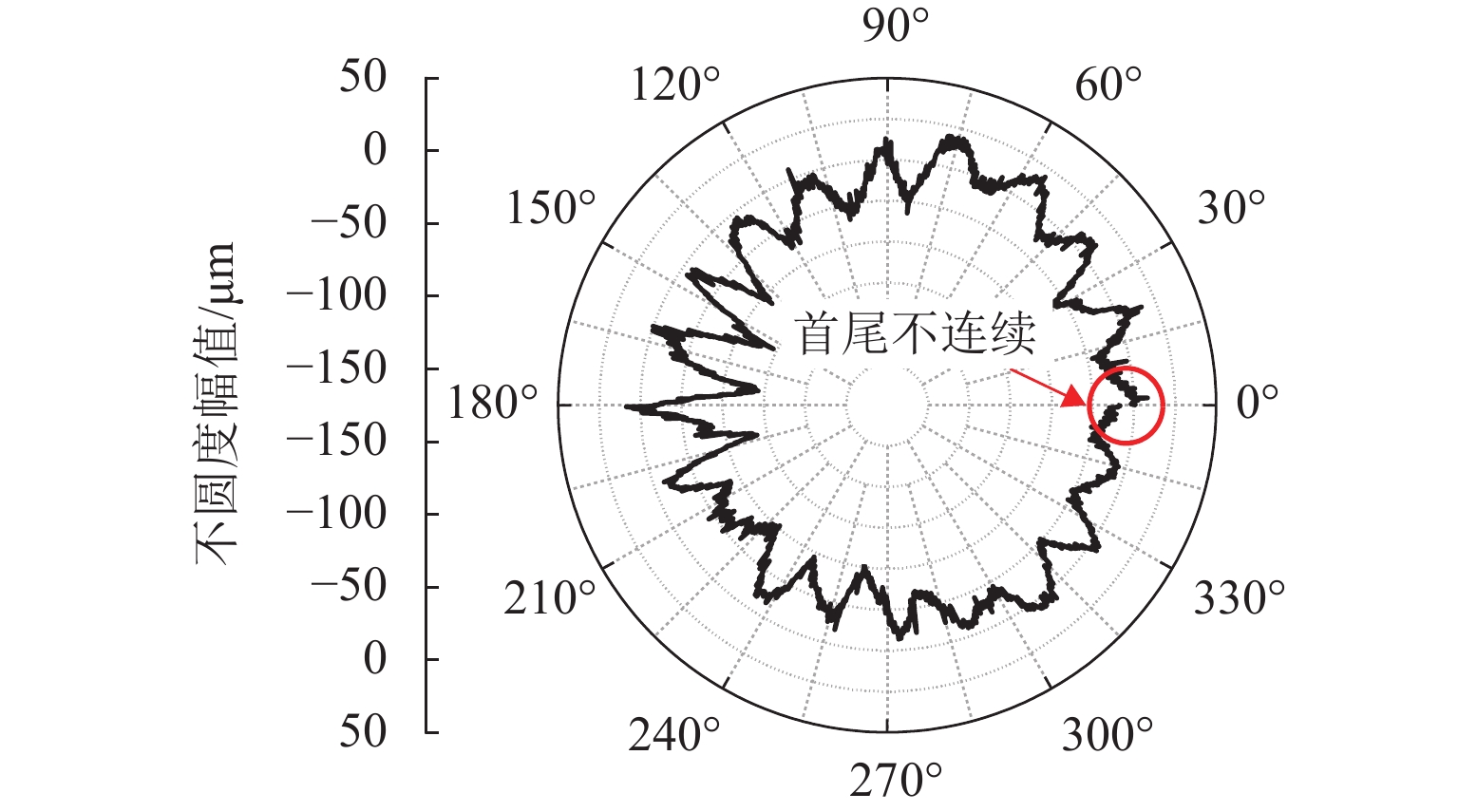
车轮踏面通常存在麻坑等缺陷,实测车轮非圆化信号往往包含高频噪声干扰,有时也会因为客观因素致使信号首尾端点不闭合. 车轮非圆化是车辆-轨道耦合动力学模型中重要的轮轨界面激扰,对轮轨动力相互作用仿真和车轮非圆化磨耗预测具有重要影响,选取合适的平滑方法是保证仿真结果准确性的关键. 本文对基于EN 15610标准、傅里叶级数、移动平均和形态学滤波等4种常用方法在实测车轮非圆化信号处理中的平滑效果展开研究,并讨论4种方法在车轮多边形磨耗预测中的适用性. 结果表明:在处理实测非圆化信号时,傅里叶级数和移动平均2种方法能够在保留原始信号的波形特征下达到良好的平滑去噪效果并保证车轮不圆数据首尾闭合;此外,2种方法也适合在多边形磨耗预测中使用,使用时建议傅里叶级数的阶数取值大于60,移动平均的平滑窗口长度取17 mm左右.
Abstract:As defects such as pitting usually occur on the wheel tread, the measured wheel out-of-roundness (OOR) signals often contain high-frequency noise interference, and sometimes the signals are discontinuous at the start and end points due to objective factors. Wheel OOR is an important wheel-rail interface excitation in the vehicle-track coupled dynamics model, exerting significant effects on the simulation of dynamic wheel-rail interaction and wheel OOR wear prediction. Selecting the suitable smoothing method is key to ensuring the accuracy of the simulation results. The smoothing effects of four commonly adopted methods based on the EN 15610 standard, Fourier series, moving average, and morphological filtering on processing wheel OOR signals were investigated, and the applicability of the four methods in predicting polygonal wear was discussed. The results indicate that the two methods of Fourier series and moving average can achieve sound smoothing and de-noising effect, preserve the waveform characteristics of original signals, and ensure continuity and differentiability at the start and end points of wheel OOR data when processing measured wheel OOR signals. Additionally, the two methods are also suitable for application in polygonal wear prediction. When the two methods are employed, the order of the Fourier series should be greater than 60 and the smoothing window length of moving average should be about 17 mm.
-
Key words:
- wheel /
- out-of-roundness /
- data smoothing /
- Fourier series /
- moving average /
- morphological filtering /
- polygonal wear prediction
-
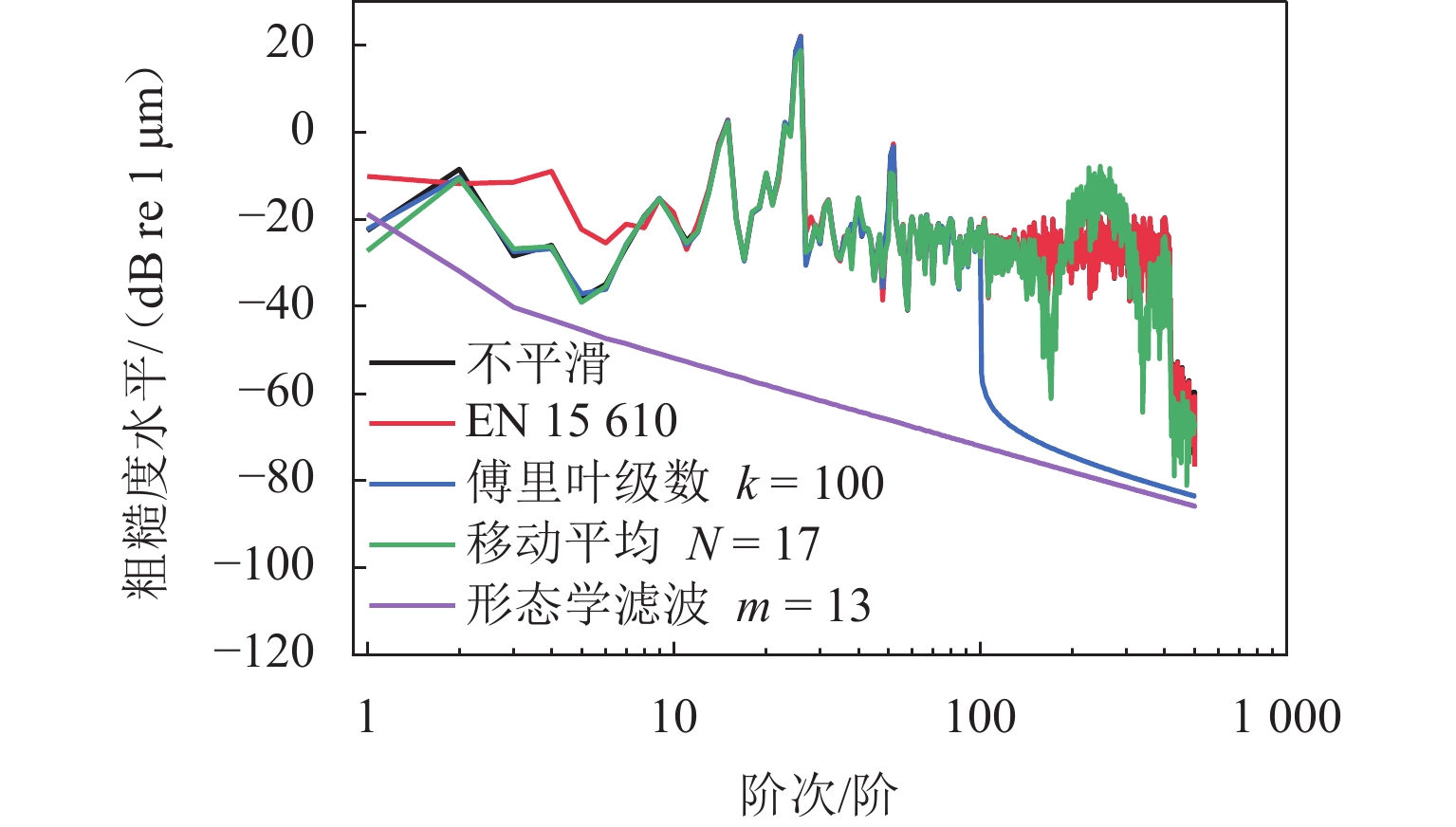
表 1 4种平滑方法处理结果的评价指标
Table 1. Evaluation indexes of processing results of four smoothing methods
方法 均方根误差 信噪比 平滑度 互相关系数 标准EN 15610 2.25 21.09 0.20 0.99 傅里叶级数 2.42 20.48 0.03 0.99 移动平均 2.48 20.25 0.03 0.99 形态学滤波 2.47 20.29 0.03 0.99 表 2 车辆−轨道耦合动力学模型主要参数
Table 2. Main parameters of vehicle-track coupled dynamics model
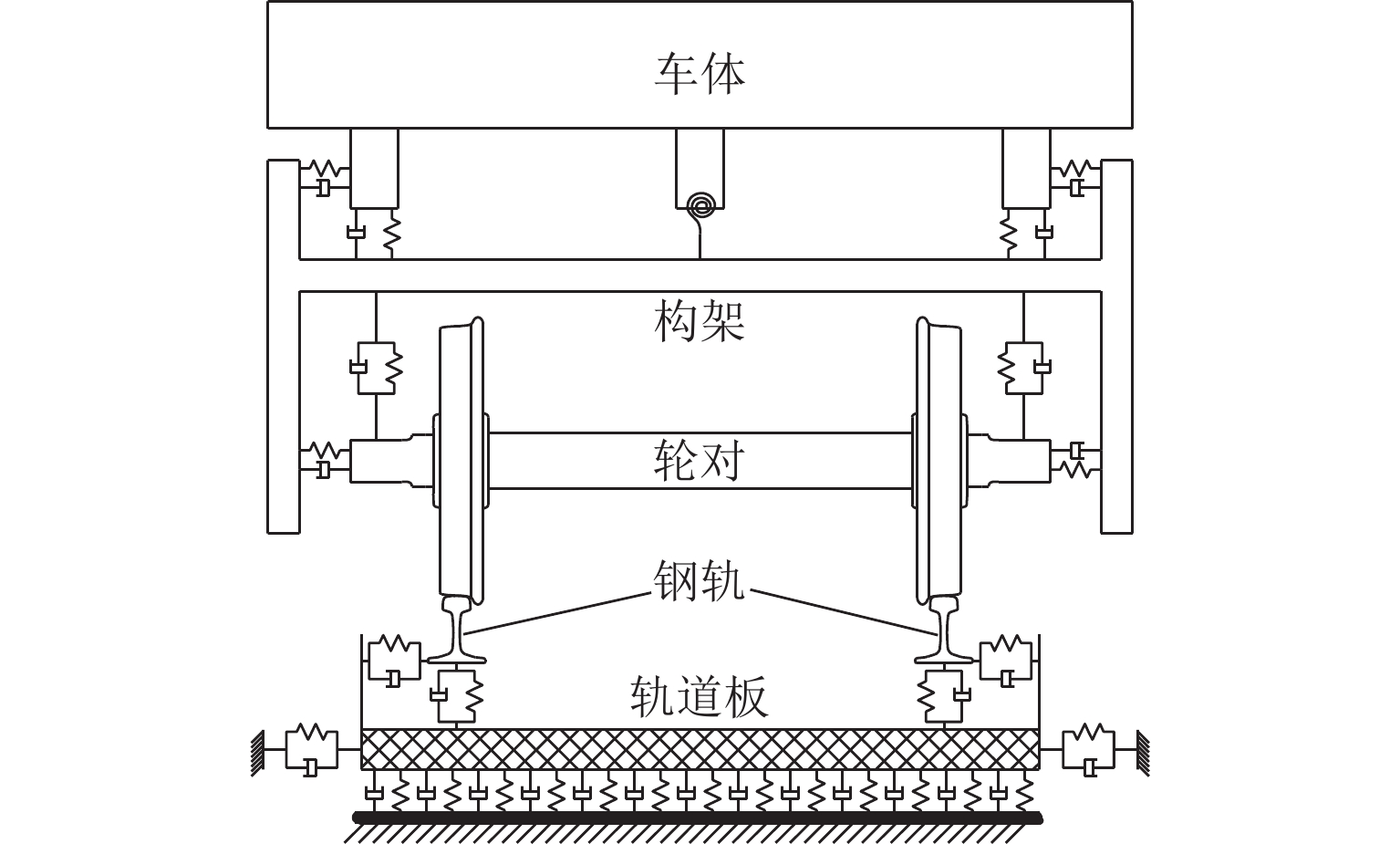
数值 参数 39.106 车体质量/t 2.495 构架质量/t 1.560 轮对质量/t 13.700 转臂节点纵向刚度/(MN•m−1) 1.182 一系钢簧垂向刚度/(MN•m−1) 0.240 二系悬挂垂向刚度/(MN•m−1) 0.46 车轮半径/m 8.9 车辆定距/m 2.5 轴距/m 40 扣件垂向刚度/MN•m−1 0.63 轨枕间距/m -
[1] TAO G Q, WEN Z F, JIN X S, et al. Polygonisation of railway wheels: a critical review[J]. Railway Engineering Science, 2020, 28(4): 317-345. doi: 10.1007/s40534-020-00222-x [2] TAO G Q, LIU M Q, XIE Q L, et al. Wheel–rail dynamic interaction caused by wheel out-of-roundness and its transmission between wheelsets[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part F: Journal of Rail and Rapid Transit, 2022, 236(3): 247-261. doi: 10.1177/09544097211016582 [3] 郭欣茹, 杨云帆, 王超, 等. 制动工况下多边形车轮对轮轨动态相互作用影响研究[J]. 机械工程学报, 2023, 59(8): 196-203. doi: 10.3901/JME.2023.08.196GUO Xinru, YANG Yunfan, WANG Chao, et al. Influence of wheel/rail dynamic interaction induced by polygonal wheels under braking condition[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2023, 59(8): 196-203. doi: 10.3901/JME.2023.08.196 [4] 吴越, 韩健, 刘佳, 等. 高速列车车轮多边形磨耗对轮轨力和转向架振动行为的影响[J]. 机械工程学报, 2018, 54(4): 37-46. doi: 10.3901/JME.2018.04.037WU Yue, HAN Jian, LIU Jia, et al. Effect of high-speed train polygonal wheels on wheel/rail contact force and bogie vibration[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2018, 54(4): 37-46. doi: 10.3901/JME.2018.04.037 [5] 韩光旭, 张捷, 肖新标, 等. 高速动车组车内异常振动噪声特性与车轮非圆化关系研究[J]. 机械工程学报, 2014, 50(22): 113-121. doi: 10.3901/JME.2014.22.113HAN Guangxu, ZHANG Jie, XIAO Xinbiao, et al. Study on high-speed train abnormal interior vibration and noise related to wheel roughness[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2014, 50(22): 113-121. doi: 10.3901/JME.2014.22.113 [6] XIE C X, TAO G Q, LIANG S L, et al. Understanding and treatment of brake pipe fracture of metro vehicle bogie[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2021, 128: 105614. doi: 10.1016/j.engfailanal.2021.105614 [7] ZHANG H J, YANG X X, XIE C X, et al. Experimental investigation of effect of wheel out-of-roundness on fracture of coil springs in metro vehicles[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2022, 142: 106811. doi: 10.1016/j.engfailanal.2022.106811 [8] 金学松, 吴越, 梁树林, 等. 车轮非圆化磨耗问题研究进展[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2018, 53(1): 1-14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2018.01.001JIN Xuesong, WU Yue, LIANG Shulin, et al. Mechanisms and countermeasures of out-of-roundness wear on railway vehicle wheels[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2018, 53(1): 1-14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2018.01.001 [9] 陶功权, 温泽峰, 金学松. 铁道车辆车轮非圆化磨耗形成机理及控制措施研究进展[J]. 机械工程学报, 2021, 57(6): 106-120. doi: 10.3901/JME.2021.06.106TAO Gongquan, WEN Zefeng, JIN Xuesong. Advances in formation mechanism and mitigation measures of out-of-round railway vehicle wheels[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2021, 57(6): 106-120. doi: 10.3901/JME.2021.06.106 [10] 施以旋, 戴焕云, 毛庆洲, 等. 基于车轨耦合的地铁车轮多边形形成机理研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2024, 59(6): 1357-1367, 1388.SHI Yixuan, DAI Huanyun, MAO Qingzhou, et al. Study on formation mechanism of metro wheel polygonal based on vehicle-track coupling[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2024, 59(6): 1357-1367, 1388. [11] 胡晓依, 成棣, 孟凡迪, 等. 时速400公里高速铁路轮轨周期性短波不平顺的安全限值研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2025, 60(6): 1581-1592.HU Xiaoyi, CHENG Di, MENG Fandi, et al. Safety limit for periodic short-wave irregularity of wheel and rail for high-speed railways at 400 km/h[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2025, 60(6): 1581-1592. [12] 吴越, 韩健, 左齐宇, 等. 钢轨波磨对高速列车车轮多边形磨耗产生与发展的影响[J]. 机械工程学报, 2020, 56(17): 198-208. doi: 10.3901/JME.2020.17.198WU Yue, HAN Jian, ZUO Qiyu, et al. Effect of rail corrugation on initiation and development of polygonal wear on high-speed train wheels[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2020, 56(17): 198-208. doi: 10.3901/JME.2020.17.198 [13] European Committee for Standardization. Railway applications-acoustics-rail and wheel roughness measurement related to noise generation: EN 15610: 2019[S]. Brussels: CEN-CENELEC Management Centre, 2019. [14] 陶功权, 谢清林, 刘晓龙, 等. 形态学滤波方法在车轮非圆化信号降噪中的应用[J]. 机械工程学报, 2020, 56(18): 116-122. doi: 10.3901/JME.2020.18.116TAO Gongquan, XIE Qinglin, LIU Xiaolong, et al. Application of morphology filtering method in the de-nosing of wheel out-of-roundness signals[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2020, 56(18): 116-122. doi: 10.3901/JME.2020.18.116 [15] FU B, BRUNI S, LUO S H. Study on wheel polygonization of a metro vehicle based on polygonal wear simulation[J]. Wear, 2019, 438: 203071. [16] YE Y G, SHI D C, KRAUSE P, et al. Wheel flat can cause or exacerbate wheel polygonization[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2020, 58(10): 1575-1604. doi: 10.1080/00423114.2019.1636098 [17] YANG X X, TAO G Q, LI W, et al. On the formation mechanism of high-order polygonal wear of metro train wheels: experiment and simulation[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2021, 127: 105512. doi: 10.1016/j.engfailanal.2021.105512 [18] LI Y F, LIANG X H, LIU W W, et al. Development of a morphological convolution operator for bearing fault detection[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2018, 421: 220-233. doi: 10.1016/j.jsv.2018.02.014 [19] 陶珂, 朱建军. 小波去噪质量评价方法的对比研究[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 2012, 32(2): 128-133. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-5942.2012.02.029TAO Ke, ZHU Jianjun. A comparative study on validity assessment of wavelet de-noising[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 2012, 32(2): 128-133. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-5942.2012.02.029 [20] 谢清林, 陶功权, 刘孟奇, 等. 数学形态学滤波在钢轨波磨波长识别中的应用[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 52(5): 1724-1732.XIE Qinglin, TAO Gongquan, LIU Mengqi, et al. Application of mathematical morphology filter in recognition of rail corrugation wavelength[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2021, 52(5): 1724-1732. [21] 翟婉明. 车辆−轨道耦合动力学(下册)[M]. 4版. 北京: 科学出版社, 2015. [22] KALKER J J. A fast algorithm for the simplified theory of rolling contact[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 1982, 11(1): 1-13. doi: 10.1080/00423118208968684 [23] BRAGHIN F, LEWIS R, DWYER-JOYCE R S, et al. A mathematical model to predict railway wheel profile evolution due to wear[J]. Wear, 2006, 261(11/12): 1253-1264. [24] CAI W B, CHI M R, WU X W, et al. Experimental and numerical analysis of the polygonal wear of high-speed trains[J]. Wear, 2019, 440: 203079. [25] 王鹏, 陶功权, 杨晓璇, 等. 中国高速列车车轮多边形磨耗特征分析[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2023, 58(6): 1357-1365. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20210777WANG Peng, TAO Gongquan, YANG Xiaoxuan, et al. Analysis of polygonal wear characteristics of Chinese high-speed train wheels[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2023, 58(6): 1357-1365. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20210777 -




 下载:
下载: