Resilient Positioning Navigation and Timing System and Key Technologies for Rail Transit
-
摘要:
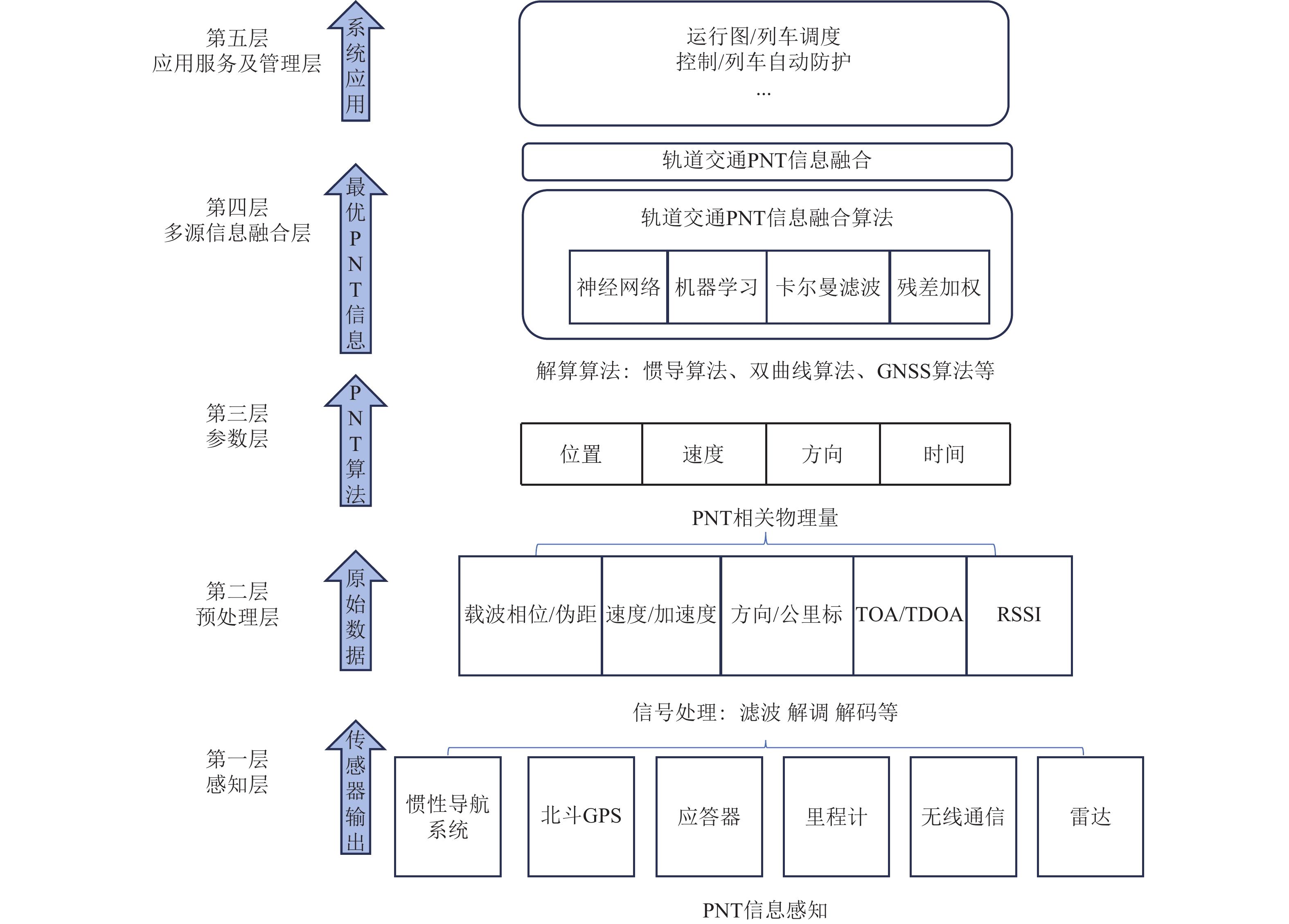
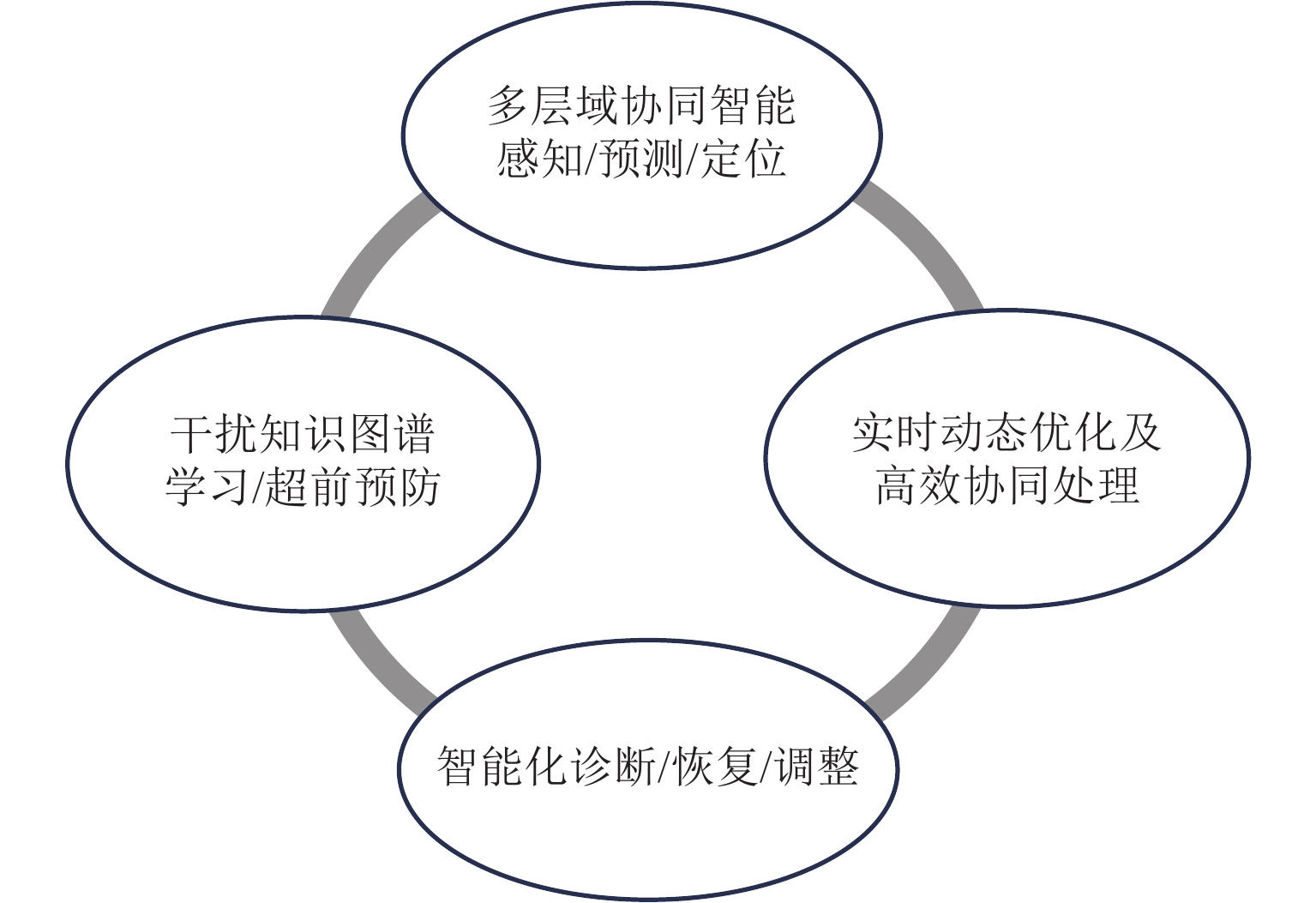
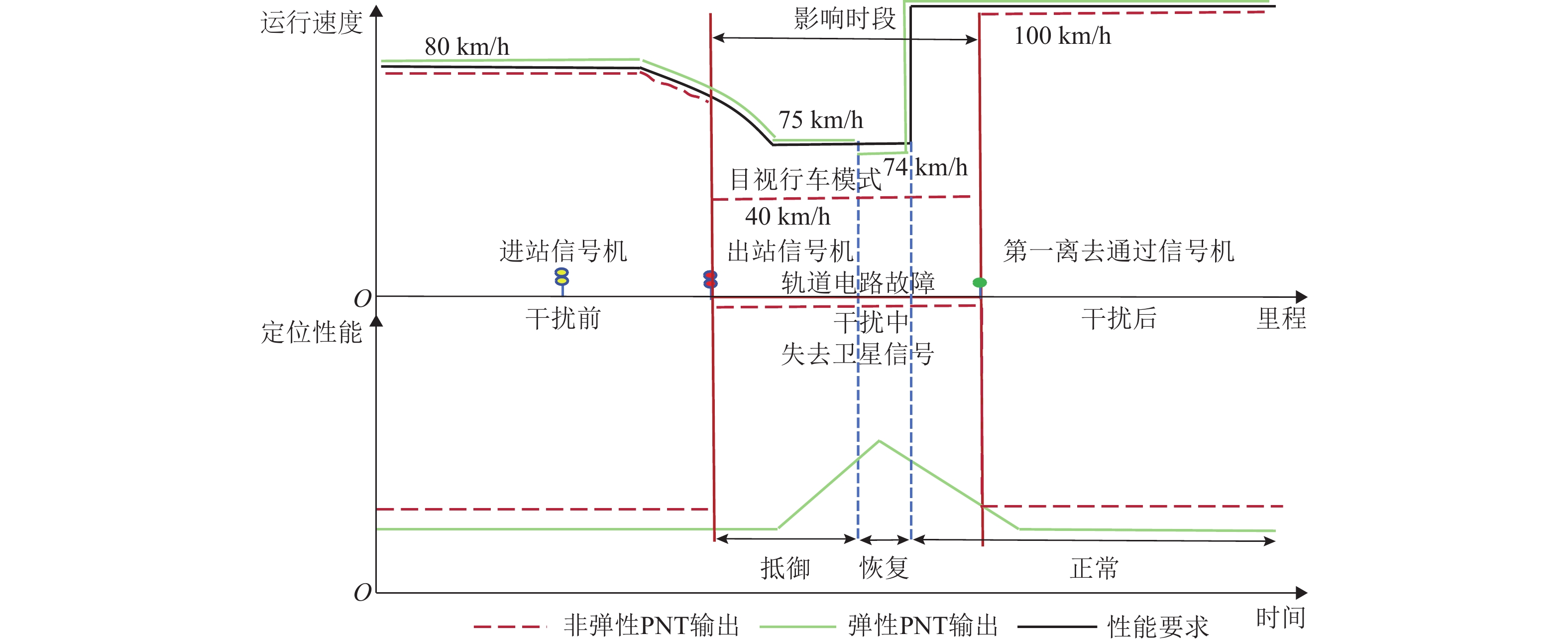
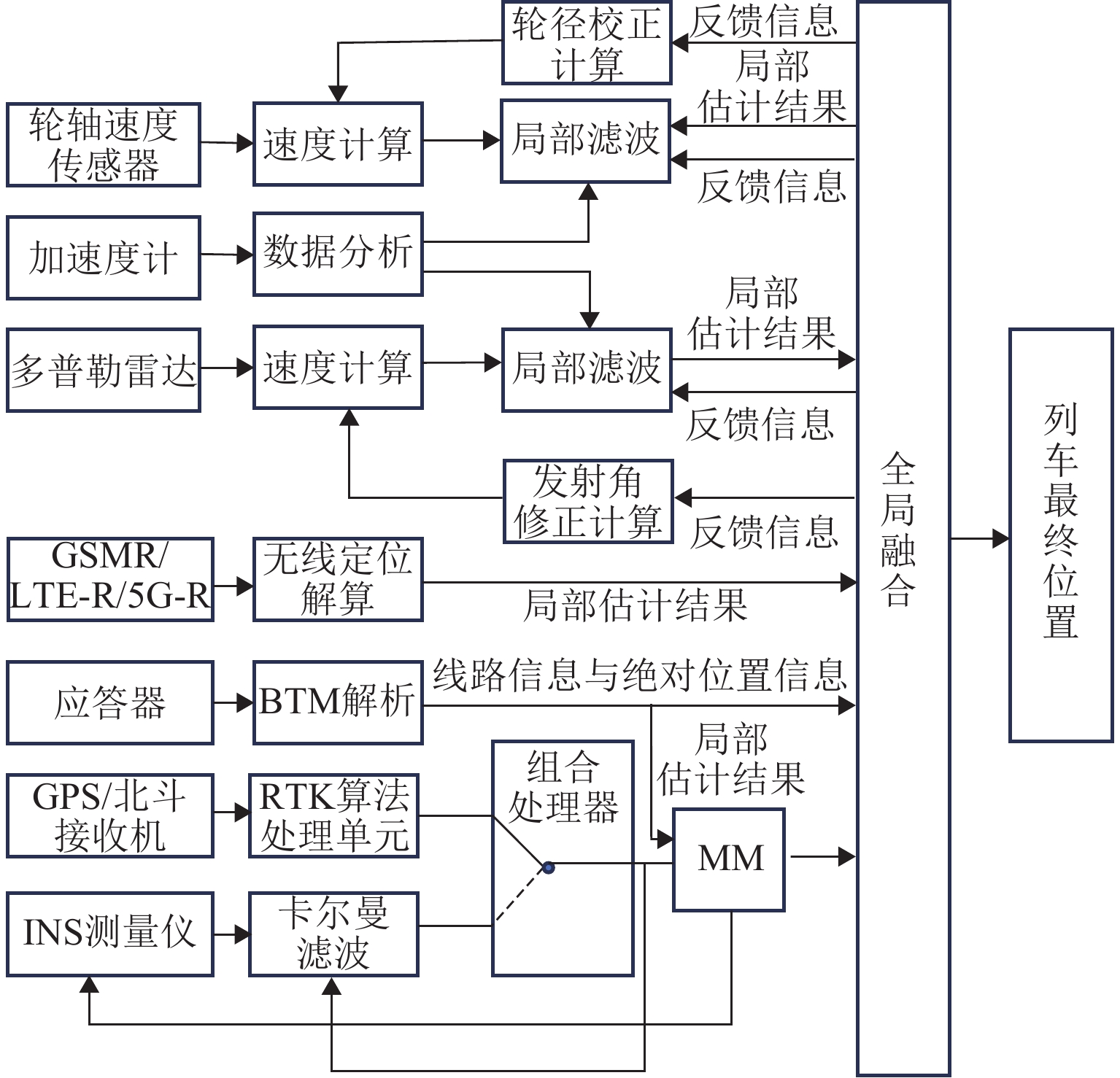
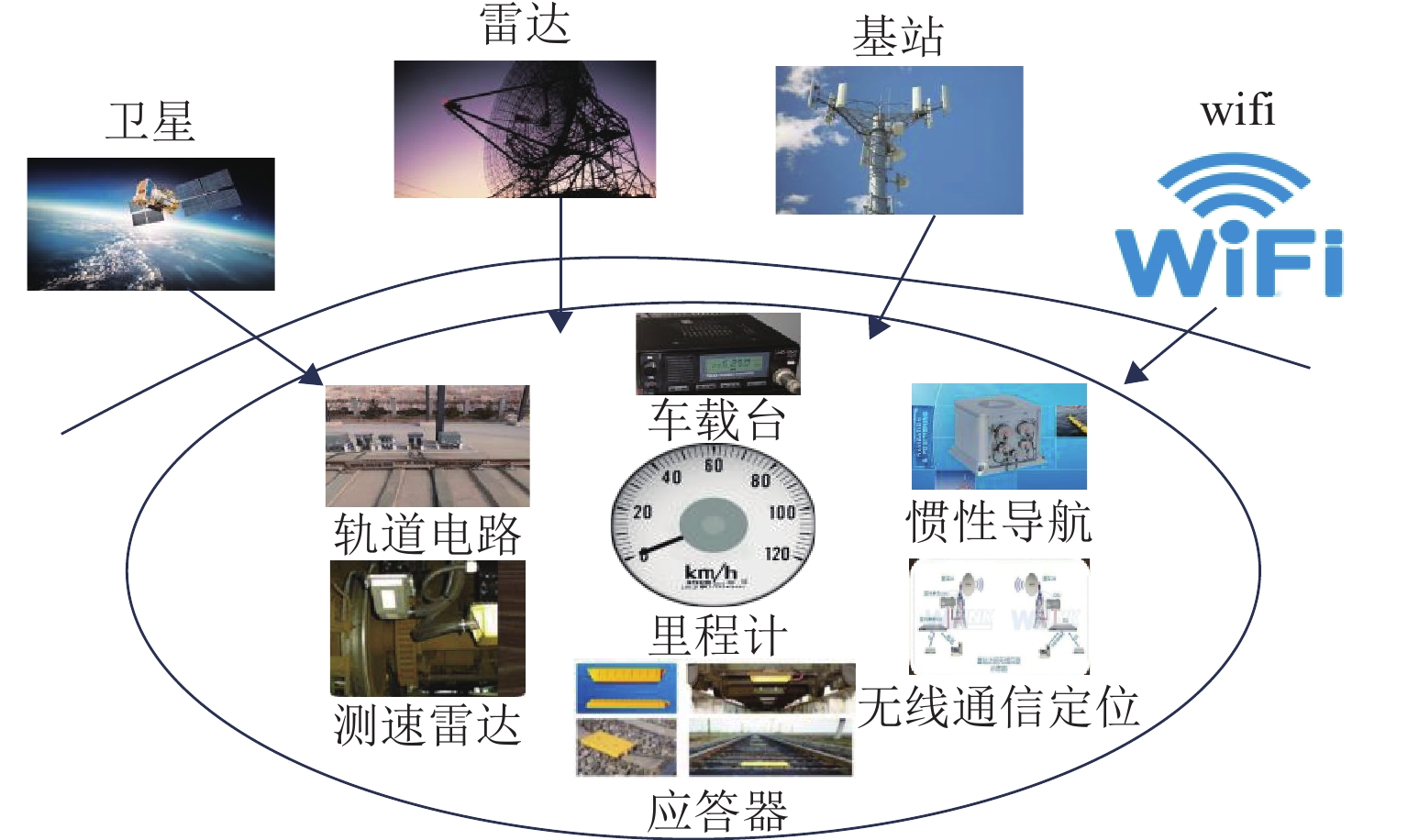
精确、连续的位置信息是保障轨道交通列车安全、高效运营的关键. 然而,在隧道、高架、城市峡谷及郊区等构成的复杂运营环境中,实现无缝的精确定位仍是当前列车定位系统面临的严峻挑战. 弹性导航、定位与授时(Positioning Navigation and Timing,PNT)通过融合多种PNT信息源,能够生成连续可用、可靠、稳健的位置信息,具备抵御危害、适应风险和干扰的能力,为解决上述难题提供了可行路径,并已在军事国防、航空航天等领域展现出巨大潜力. 为促进该技术在轨道交通领域的应用与发展,本文在分析轨道交通行业用户对导航、定位与授时需求的基础上,结合当前轨道交通既有系统的导航定位能力,提出适用于轨道交通的弹性PNT体系概念与架构. 并从轨道交通PNT特殊性出发,归纳轨道交通弹性PNT系统的基本特征与评价指标,阐述弹性与精确性、完好性、连续性、可用性等指标的关系. 最后,以轨道交通多源PNT传感器为基础,包含GNSS (global navigation satellite system)、应答器、5G-R (5G-railway)等,重点探讨轨道交通弹性PNT技术体系及信息融合等关键技术,并指出多源信息深度融合与弹性融合架构是未来轨道交通实现连续无缝定位的重要研究方向.
Abstract:Accurate and uninterrupted position information is crucial for ensuring the safe and efficient operation of rail transit trains. However, realizing seamless and precise positioning still poses a significant challenge for current train positioning systems operating in complex environments such as tunnels, elevated tracks, urban canyons, and suburban areas. A resilient positioning, navigation, and timing (PNT) system can produce continuous, reliable, and robust position information by integrating diverse PNT information sources. It can withstand hazards, adapt to risks, and counteract interference, offering a viable solution to the aforementioned challenges and demonstrating significant potential in fields such as military defense and aerospace. To promote the application and development of this technology in the rail transit sector, the navigation, positioning, and timing requirements of users of the rail transit industry were analyzed. According to the existing navigation and positioning capabilities of rail transit systems, the concept and framework of a resilient PNT system tailored for rail transit was proposed. Given the unique characteristics of rail transit PNT, the fundamental characteristics and evaluation metrics of the resilient PNT system of rail transit were summarized, and the relationship between resilience and accuracy, integrity, continuity, availability, and other indicators was elaborated. On the basis of multi-source PNT sensors, including global navigation satellite system (GNSS), responders, and 5G-railway (5G-R), the key technologies of the resilient PNT technology system and information fusion for rail transit were discussed. In conclusion, deep fusion of multi-source information and resilient fusion architecture are important research directions for achieving continuous seamless positioning in future rail transit.
-
Key words:
- rail transit /
- resilience /
- positioning, navigation, and timing
-
表 1 轨道交通弹性PNT应用场景及潜在性能要求
Table 1. Application scenarios of resilient PNT for rail transit and potential performance requirements
应用案例 服务目标/对象 使用
环境定位精度 可靠性/% 定位更新速率/s TTFF
(time to
first fix)/s定位服务延迟 其他指标 弹性等级 列车控制 列车定位,速度监督曲线计算,虚拟闭塞,列车追踪间隔预警,列车超速预警 站外/
室外绝对位置精度:水平10~30 m (概率99%),速度精度:水平5 m/s (概率9%) $\geqslant $99 0.1 <10
<30 ms连续性要求高,可用性(概率 95%),可维修性和安全性要求高 4 级 可穿戴设备 旅客服务,工作人员
管理站内/
车内2 m 水平 99 1~30 10 1 s 低功耗 1 级 1~3 m 竖直 紧急通话 列车工作人员 站外/
室外50 m 水平 95 30 60 s 可信度 3 级 3 m 竖直 列车位置获取/辅助驾驶 列车管理与调度 站内/
站外1~3 m 水平 99 0.1 10 30 ms 连续跟踪/抗干扰 4 级 2.5 m 竖直 防撞/虚拟耦合列车 列车管理与调度 站内/
站外1~3 m 水平 99 0.1 10 低延迟 自组网/抗干扰 4 级 2.5 m 竖直 设备巡检自动驾驶 轨道巡检服务 站外 0.1 m 水平 99 10 低功耗/抗干扰/信息安全 3 级 0.1 m 竖直 基础设施形变监测 桥梁、边坡等 沿线 0.002 m 水平
0.005 m 竖直95 -
[1] 朱爱红, 李博, 杨亮. 高速列车定位技术与组合定位系统研究[J]. 中国铁路, 2013(5): 59-63. doi: 10.19549/j.issn.1001-683x.2013.05.017 [2] 杨元喜. 弹性PNT基本框架[J]. 测绘学报, 2018, 47(7): 893-898. doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2018.20180149YANG Yuanxi. Resilient PNT concept frame[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2018, 47(7): 893-898. doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2018.20180149 [3] 杨元喜, 任夏, 贾小林, 等. 以北斗系统为核心的国家安全PNT体系发展趋势[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2023, 53(5): 917-927. [4] 杨元喜. 综合PNT体系及其关键技术[J]. 测绘学报, 2016, 45(5): 505-510.YANG Yuanxi. Concepts of comprehensive PNT and related key technologies[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2016, 45(5): 505-510. [5] 卞鸿巍, 许江宁, 何泓洋, 等. 水下PNT体系信息架构及关键问题[J]. 导航定位与授时, 2022, 9(3): 31-39. doi: 10.19306/j.cnki.2095-8110.2022.03.004BIAN Hongwei, XU Jiangning, HE Hongyang, et al. Information architecture and key issues of underwater PNT system[J]. Navigation Positioning and Timing, 2022, 9(3): 31-39. doi: 10.19306/j.cnki.2095-8110.2022.03.004 [6] 王小宁, 张锐, 角淑媛, 浅析PNT体系的弹性[C]//第十二届中国卫星导航年会. 武汉: 华中师范大学, 2018. [7] 明锋, 杨元喜, 曾安敏, 等. 弹性PNT概念内涵、特征及其辨析[J]. 测绘通报, 2023(4): 79-86, 176.MING Feng, YANG Yuanxi, ZENG Anmin, et al. The conceptual connotation, characteristics and discrimination of resilient PNT[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, 2023(4): 79-86, 176. [8] 曾海涛. 通信导航定位系统的精度评估方法及其对比[J]. 通信电源技术, 2023(13): 209-211, 215. [9] 帅玮祎, 董绪荣, 王军, 等. 列车定位中GNSS的RAMS研究与评估[J]. 铁道学报, 2020, 42(6): 70-78.SHUAI Weiyi, DONG Xurong, WANG Jun, et al. RAMS research and evaluation of GNSS for train positioning[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2020, 42(6): 70-78. [10] 刘勇, 罗德林, 石翠, 等. 基于T-S模糊故障树的多态导航系统性能可靠性[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2021, 47(2): 240-246.LIU Yong, LUO Delin, SHI Cui, et al. Performance reliability of multi-state navigation system based on T-S fuzzy fault tree[J]Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2021, 47(2): 240-246. [11] 明锋, 曾安敏. 弹性PNT最新进展及相关问题研究[J]. 导航定位学报, 2022, 10(4): 1-10, 48.MING Feng, ZENG Anmin. Recent advancement and research on related issues for resilient PNT[J]. Journal of Navigation and Positioning, 2022, 10(4): 1-10, 48. [12] 刘经南, 罗亚荣, 郭迟, 等. PNT智能与智能PNT[J]. 测绘学报, 2022, 51(6): 811-828.LIU Jingnan, LUO Yarong, GUO Chi, et al. PNT intelligence and intelligent PNT[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2022, 51(6): 811-828. [13] 倪秀琳. 基于LoRa的应答器辅助定位系统[J]. 电子测量技术, 2023, 46(18): 179-185. doi: 10.19651/j.cnki.emt.2313883NI Xiulin. Balise auxiliary positioning system based on LoRa[J]. Electronic Measurement Technology, 2023, 46(18): 179-185. doi: 10.19651/j.cnki.emt.2313883 [14] 王思琦, 刘江, 蔡伯根, 等. 基于局域定位场景聚类的虚拟应答器布局优化方法研究[J]. 铁道学报, 2023, 45(8): 77-86. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2023.08.009WANG Siqi, LIU Jiang, CAI Baigen, et al. Research on optimized virtual balise placement method based on local positioning scenario clustering[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2023, 45(8): 77-86. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2023.08.009 [15] 王剑, 王思琦, 蔡伯根, 等. 基于列车运行状态组合预测的虚拟应答器捕获方法[J]. 中国铁道科学, 2023, 44(1): 202-213.WANG Jian, WANG Siqi, CAI Baigen, et al. Virtual balise capture method based on combination prediction of train operation state[J]. China Railway Science, 2023, 44(1): 202-213. [16] GAN Q P, LI K C, YUAN L, et al. Filtering approach to online estimate the position of high-speed train[C]//2016 IEEE 19th International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC). Rio de Janeiro: IEEE, 2016: 1168-1173. [17] 王剑, 凌浩, 姜维, 等. 基于多星座卫星定位与惯性导航全状态融合的列车组合导航系统[J]. 铁道学报, 2022, 44(11): 45-52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2022.11.006WANG Jian, LING Hao, JIANG Wei, et al. Integrated train navigation system based on full state fusion of multi-constellation satellite positioning and inertial navigation[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2022, 44(11): 45-52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2022.11.006 [18] ZHENG W, MA S J, HUA Z X, et al. Train integrated positioning method based on GPS/INS/RFID[C]//2016 35th Chinese Control Conference (CCC). Chengdu: IEEE, 2016: 5858-5862. [19] WEI P S, CHEN Y G. Combined GNSS/INS positioning scheme with the introduction of virtual transponders[C]//2023 4th International Conference on Mechatronics Technology and Intelligent Manufacturing (ICMTIM). Nanjing: IEEE, 2023: 309-312. [20] LIU J, ZHAO X L, CAI B G, et al. Pseudolite constellation optimization for seamless train positioning in GNSS-challenged railway stations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2022, 23(8): 13636-13654. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2021.3126167 [21] TIAN R, DONG X R. An improved divergence-free hatch filter algorithm toward sub-meter train positioning with GNSS single-frequency observations only[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 112027-112040. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3002781 [22] MENG Y, FENG J X, WANG W. An enhanced INS/GNSS integrated system with ODO for train positioning[C]//2021 IEEE 4th Advanced Information Management, Communicates, Electronic and Automation Control Conference (IMCEC). Chongqing: IEEE, 2021: 1315-1318. [23] 欧阳籽勃, 史天运, 王萌. 基于克里金法的列车定位方法研究[J]. 铁道标准设计, 2022, 66(5): 172-177. doi: 10.13238/j.issn.1004-2954.202102200004OUYANG Zibo, SHI Tianyun, WANG Meng. Research of train positioning method based on the Kriging method[J]. Railway Standard Design, 2022, 66(5): 172-177. doi: 10.13238/j.issn.1004-2954.202102200004 [24] XU Y L, ZHANG Y P. A novel method of train positioning based on visible light communication[C]//2020 IEEE 2nd International Conference on Civil Aviation Safety and Information Technology (ICCASIT. Weihai: IEEE, 2020: 670-674. [25] TALVITIE J, LEVANEN T, KOIVISTO M, et al. Positioning and location-aware communications for modern railways with 5G new radio[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2019, 57(9): 24-30. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.001.1800954 [26] 庄凌凡, 刘留, 张嘉驰, 等. 基于5G蜂窝网络的城市列车高精度定位探讨[J]. 导航定位学报, 2020, 8(5): 1-10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4999.2020.05.001ZHUANG Lingfan, LIU Liu, ZHANG Jiachi, et al. High precision positioning of urban train based on 5G cellular network[J]. Journal of Navigation and Positioning, 2020, 8(5): 1-10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4999.2020.05.001 [27] 蔚保国, 鲍亚川, 杨梦焕, 等. 通导一体化概念框架与关键技术研究进展[J]. 导航定位与授时, 2022, 9(2): 1-14. doi: 10.19306/j.cnki.2095-8110.2022.02.001YU Baoguo, BAO Yachuan, YANG Menghuan, et al. Conceptual framework and research progress on communication and navigation integration[J]. Navigation Positioning and Timing, 2022, 9(2): 1-14. doi: 10.19306/j.cnki.2095-8110.2022.02.001 [28] 王小敏, 雷筱, 张亚东. 基于改进自适应IMM算法的高速列车组合定位[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2024, 46(3): 817-825. doi: 10.11999/JEIT230251WANG Xiaomin, LEI Xiao, ZHANG Yadong. Combined positioning of high-speed train based on improved adaptive IMM algorithm[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2024, 46(3): 817-825. doi: 10.11999/JEIT230251 [29] 莫志松, 安鸿飞. 新型列控系统列车综合自主定位技术研究[J]. 铁道学报, 2022, 44(1): 56-64.MO Zhisong, AN Hongfei. Research on comprehensive autonomous positioning technology of new train control system[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2022, 44(1): 56-64. [30] WANG X Y, XU H G, DONG D C, et al. Train velocity measurement and positioning system based on spatial filter[C]//2021 IEEE 94th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC2021-Fall). Norman: IEEE, 2021: 1-4. [31] HEIRICH O, SIEBLER B, SAND S, et al. Measurement methods for train localization with onboard sensors[C]//2020 European Navigation Conference (ENC). Dresden: IEEE, 2020: 1-10. [32] LÖFFLER W, BENGTSSON M. Using probabilistic geometrical map information for train localization[C]//2022 25th International Conference on Information Fusion (FUSION). Linköping: IEEE, 2022: 1-8. [33] LIU Y M, LU D B, CAI B G, et al. Comprehensive probability map-matching method for digital track map validation[C]//2021 International Conference on Electromagnetics in Advanced Applications (ICEAA). Honolulu: IEEE, 2021: 305-310. [34] 张昕, 翟凌露, 王舰深, 等. 基于加权融合的常导高速磁浮列车UKF定位算法[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2024, 59(4): 832-838. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20230501ZHANG Xin, ZHAI Linglu, WANG Jianshen, et al. Weighted fusion-based unscented Kalman filter positioning algorithm for normal-conducting high-speed maglev trains[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2024, 59(4): 832-838. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20230501 [35] 王运明, 程相, 李卫东, 等. 基于因子图的BDS/IMU列车定位信息融合模型[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报, 2023, 20(3): 1077-1084. doi: 10.19713/j.cnki.43-1423/u.t20220672WANG Yunming, CHENG Xiang, LI Weidong, et al. Information fusion model of BDS/IMU train positioning based on factor graph[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2023, 20(3): 1077-1084. doi: 10.19713/j.cnki.43-1423/u.t20220672 [36] 李鹏, 闫光辉, 陈光武. 改进的联邦EKF在列车组合定位中的应用[J]. 铁道学报, 2022, 44(9): 65-70.LI Peng, YAN Guanghui, CHEN Guangwu, Application of improved federated EKF in integrated train positioning[J], Journal of the China Railway Society, 2022, 44(9): 65-70. [37] 罗淼, 党建武, 郝占军, 等. 基于卷积神经网络的列车位置指纹定位算法研究[J]. 铁道学报, 2023, 45(1): 42-50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2023.01.006LUO Miao, DANG Jianwu, HAO Zhanjun, et al. Study of train location fingerprint positioning algorithm based on convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2023, 45(1): 42-50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2023.01.006 [38] 陈永刚, 王妍, 白邓宇, 等. 基于LSTM网络辅助无迹粒子滤波的列车定位方法研究[J]. 云南大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 43(3): 477-485. doi: 10.7540/j.ynu.20200388CHEN Yonggang, WANG Yan, BAI Dengyu, et al. Research on train positioning method based on LSTM network aided unscented particle filter[J]. Journal of Yunnan University (Natural Sciences Edition), 2021, 43(3): 477-485. doi: 10.7540/j.ynu.20200388 [39] CHENG R J, SONG Y D, CHEN D W, et al. Intelligent positioning approach for high speed trains based on ant colony optimization and machine learning algorithms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2019, 20(10): 3737-3746. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2018.2878442 -




 下载:
下载: