Rapid Detection Method for Rail Corrugation in Metro Lines Based on Data Fusion of Train-Borne Vibration and Noise
-
摘要:
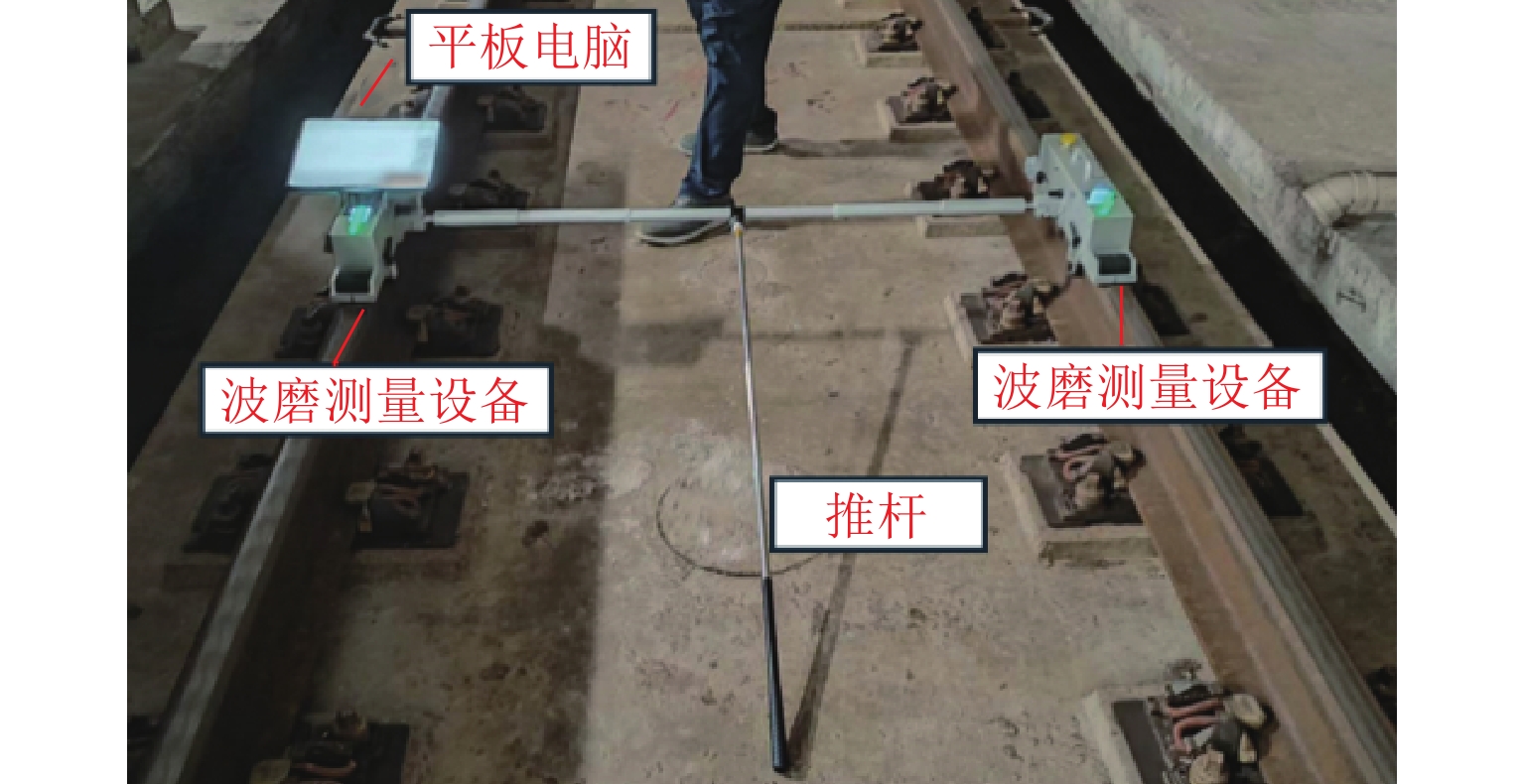
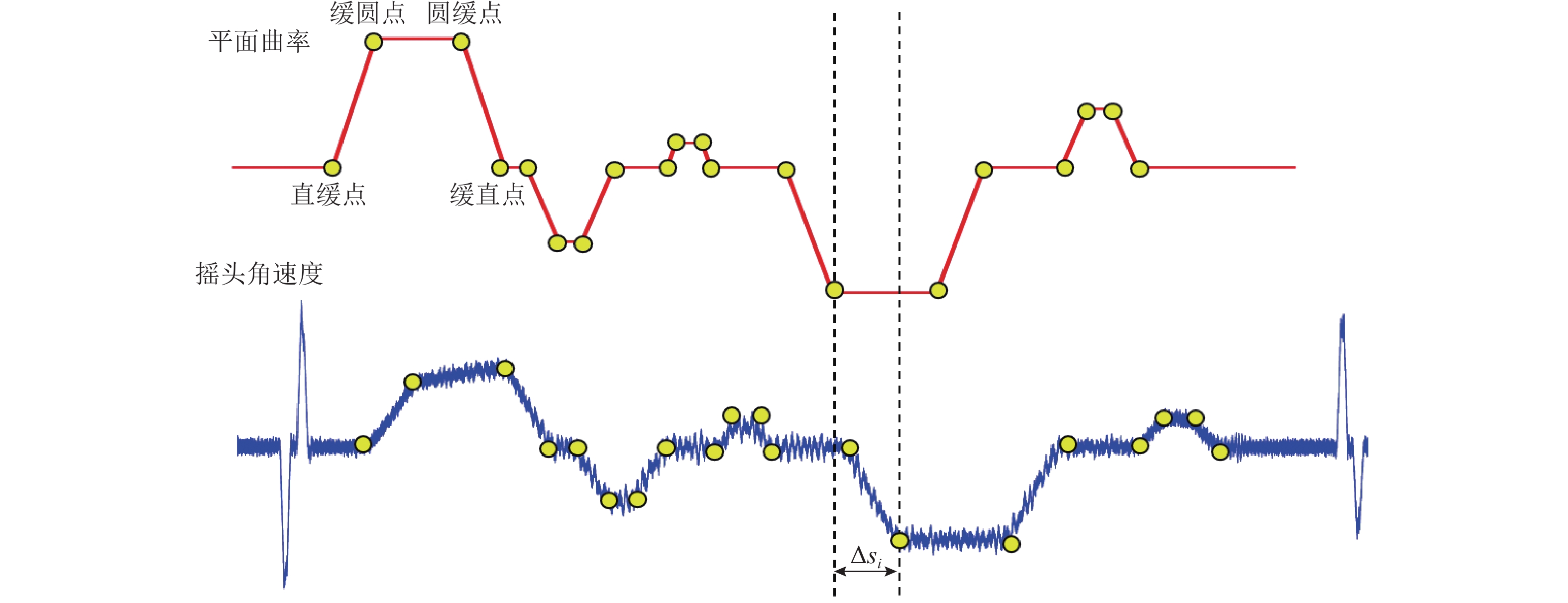
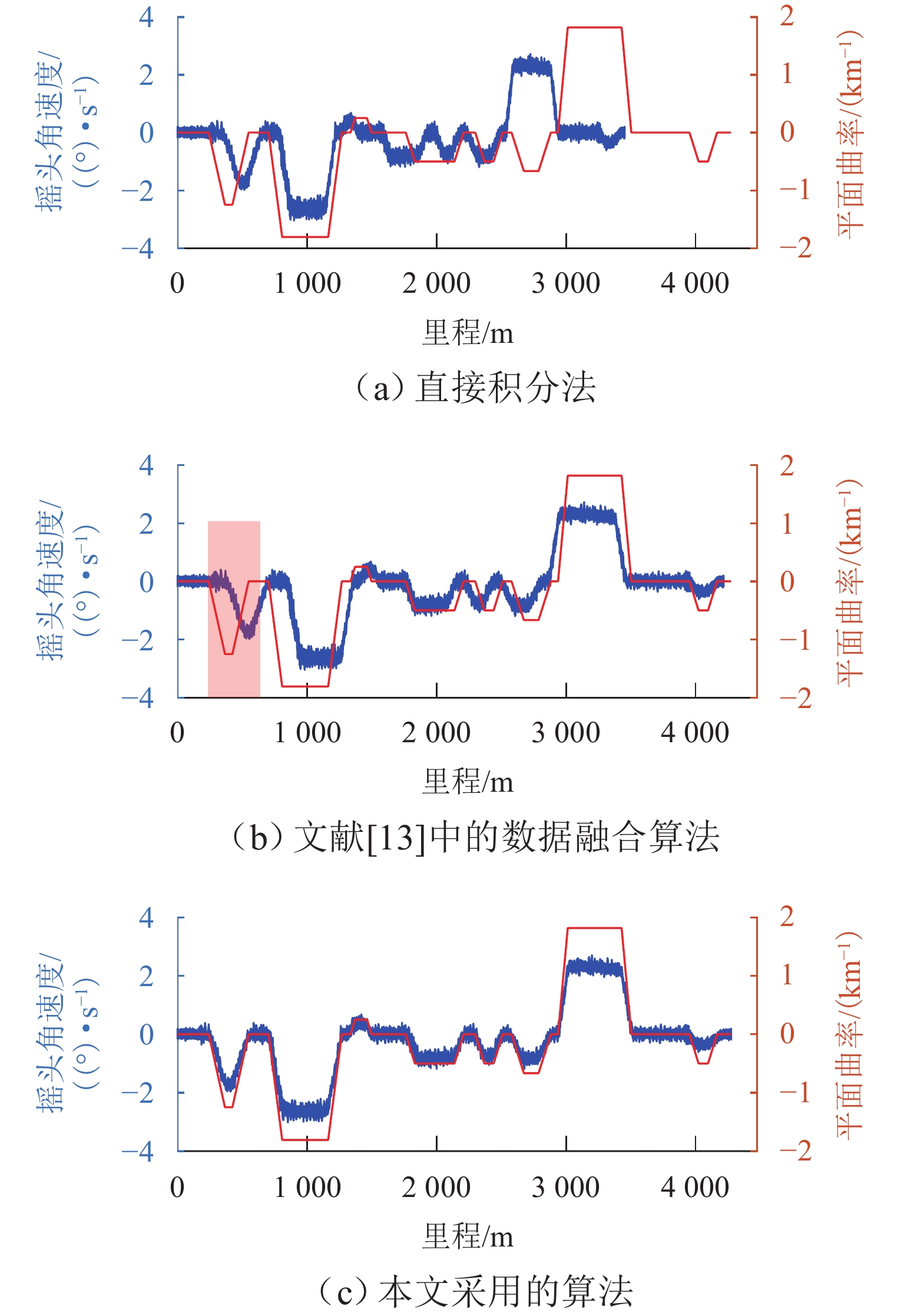
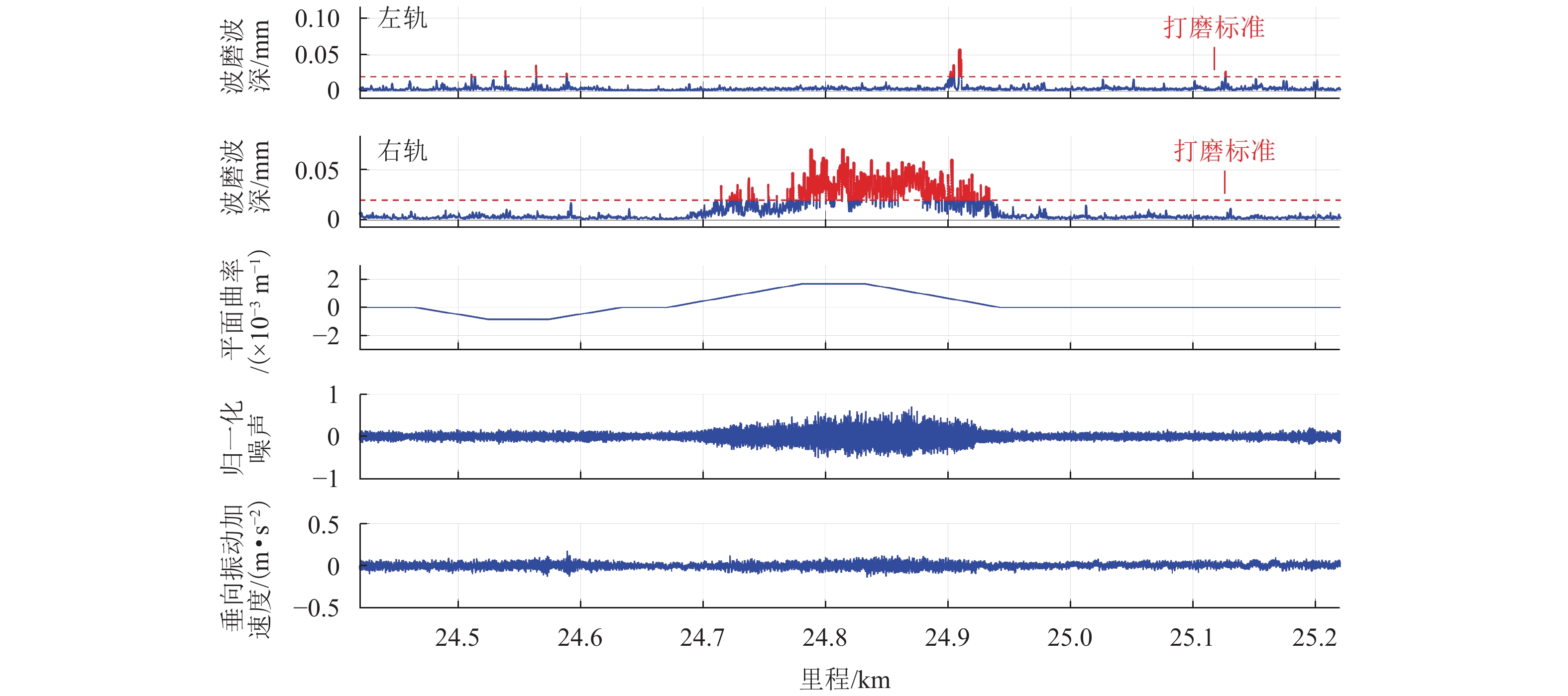
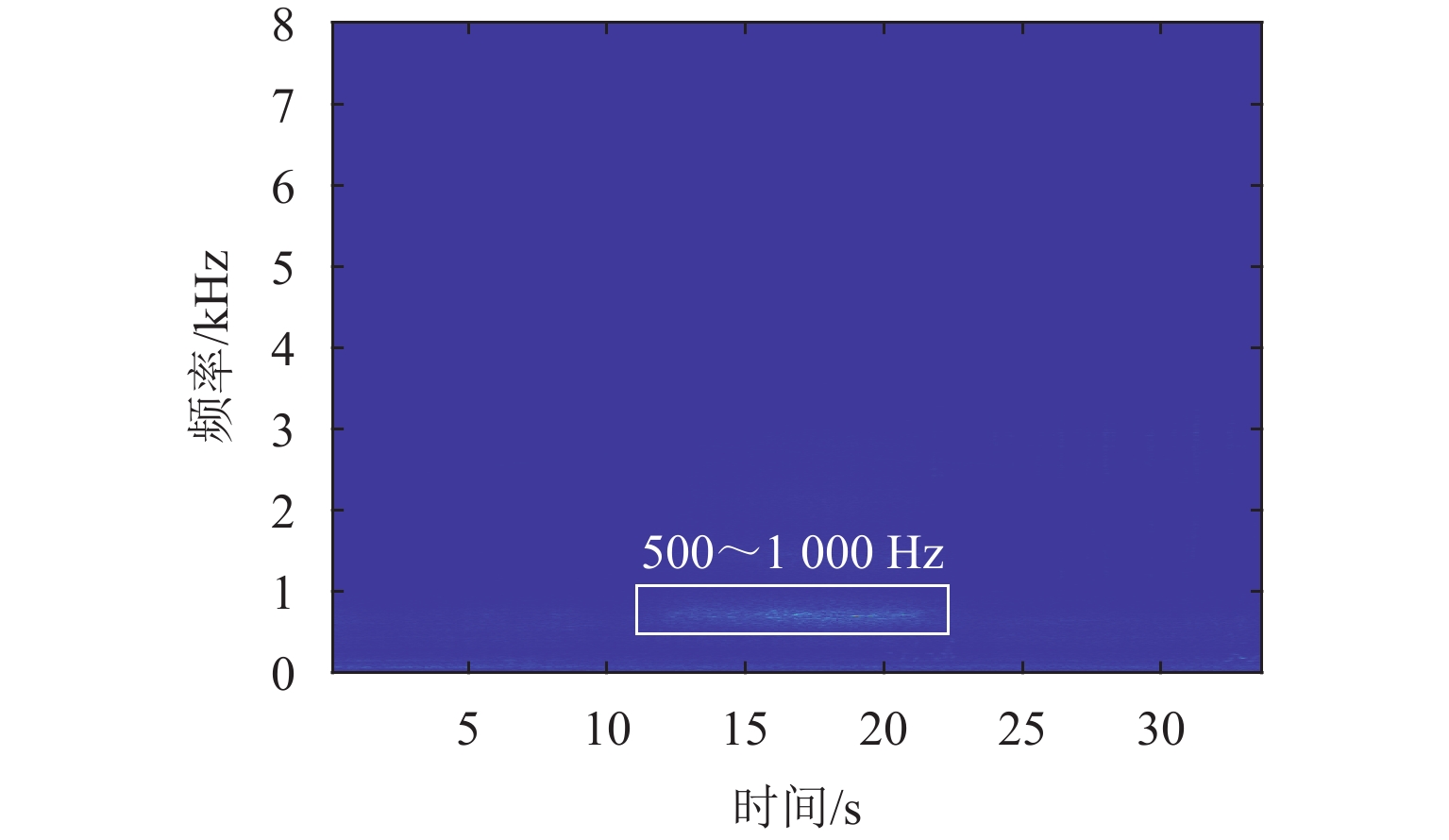
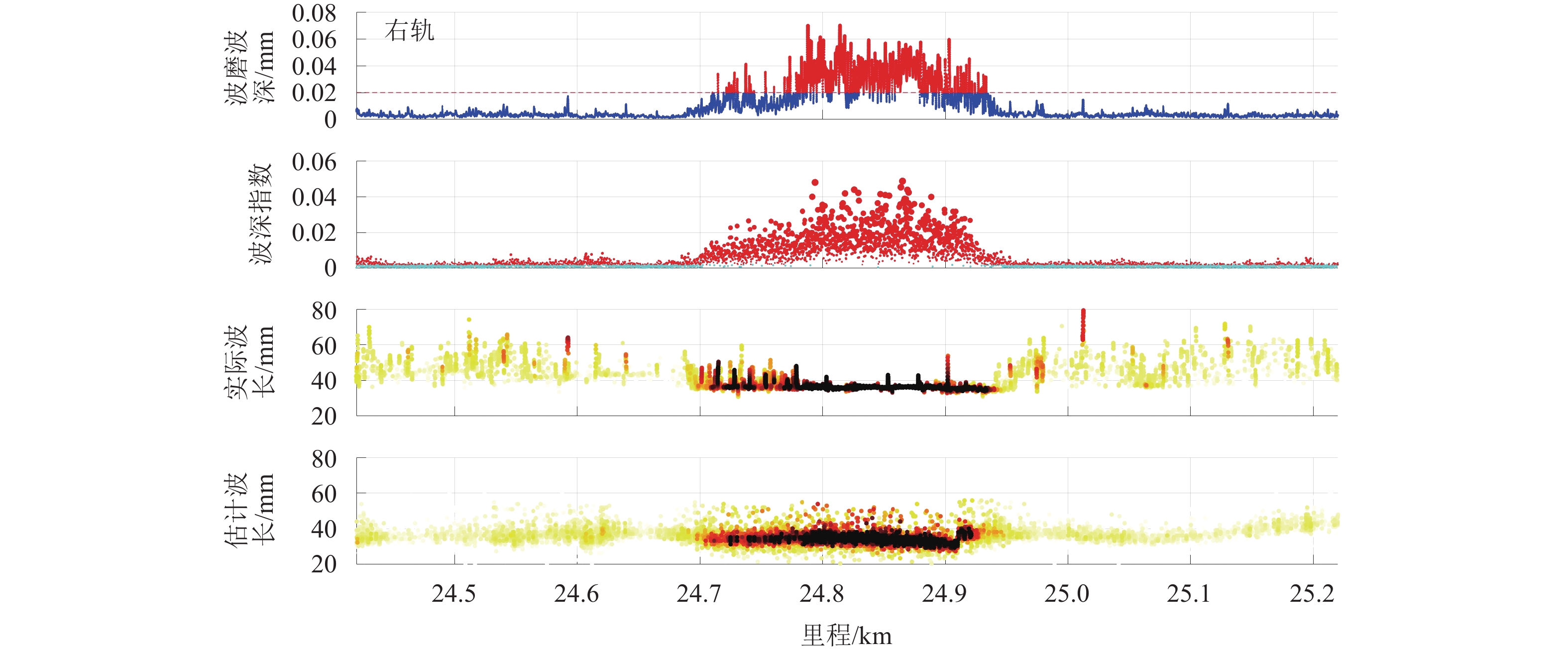
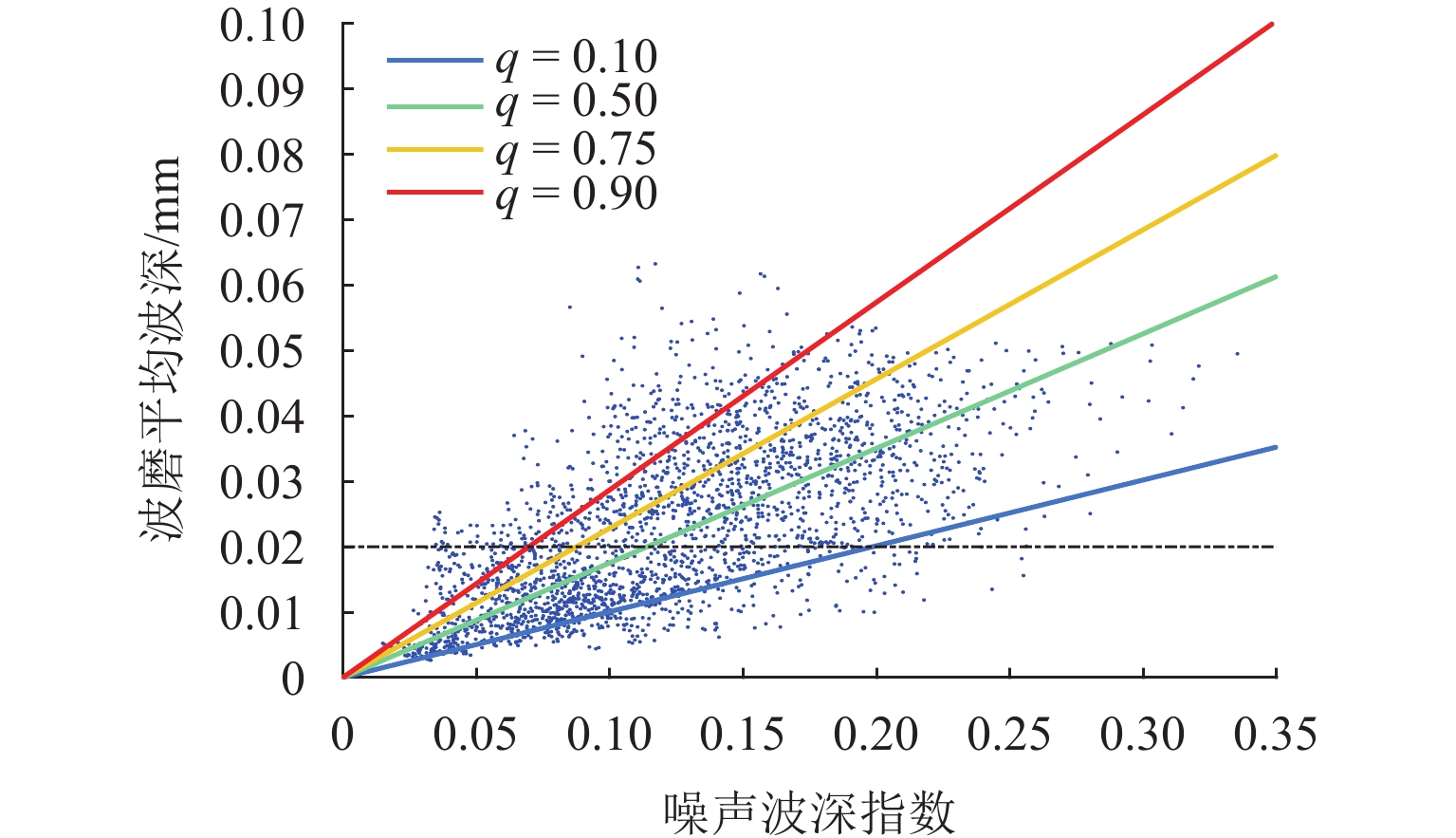
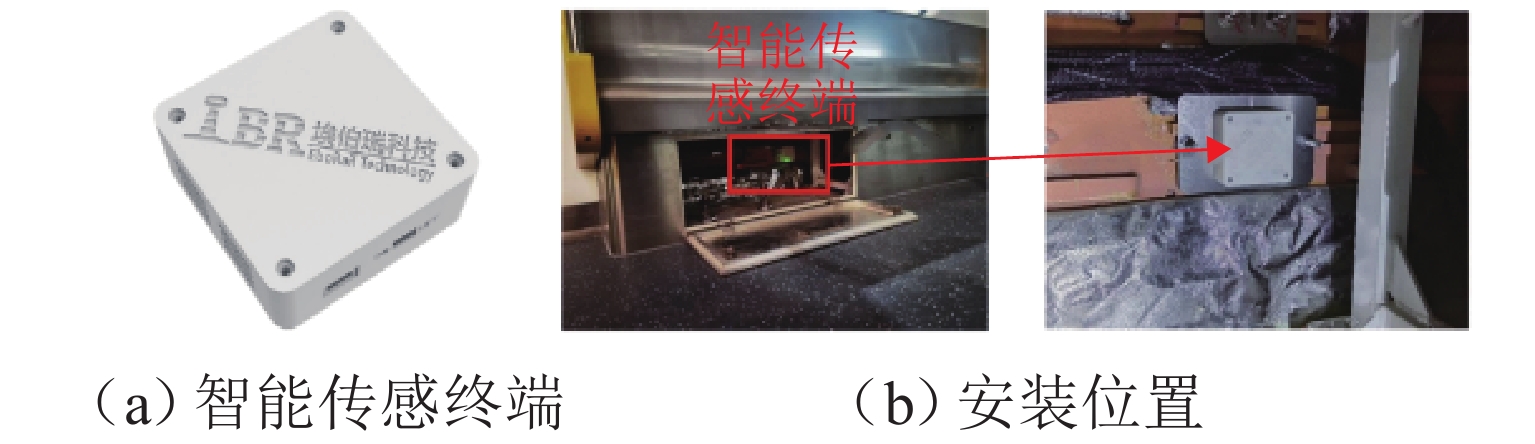
实现地铁钢轨波磨的快速辨识与精准定位,可以方便地铁运维部门制定合理的维修计划,对于节省地铁工务作业具有重要意义. 本研究利用低成本的便携式车载传感终端,快速检测地铁列车在全线的车体振动与噪声数据;在此基础之上,考虑到地下环境中难以获取稳定的GPS信号,采用基于纵向加速度二次积分、车体摇头角速度与线路平面曲率匹配的多源数据融合方法,实现对振噪检测数据的精准里程定位;进一步,结合现场波磨检测结果,提出了波深指数的振噪声纹特征,辨识钢轨波磨,并利用分位数回归建立起波深指数与波磨波深之间的关联关系. 研究结果表明:基于波深指数的波磨辨识和定位结果与现场结果一致,波磨主要波长集中在40 mm,并且随着噪声波深指数的增大,钢轨波磨的波深呈现出“扇形”式增长,符合分位数回归特征,可进一步估算在不同分位数下波噪管理标准.
Abstract:The rapid identification and accurate localization of rail corrugation in metro lines are of significant importance for the maintenance departments of metros to formulate reasonable maintenance plans, thereby saving considerable efforts in metro operational works. In this study, low-cost, portable, and vehicle-mounted sensing terminals were utilized to detect the vibration and noise of metro trains across the entire line. Given the difficulty in obtaining stable GPS signals in underground environments, a multi-source data fusion method based on the secondary integration of longitudinal acceleration, the yaw rate of the vehicle body, and the matching with the line’s planar curvature was adopted to achieve precise mileage localization of the detected vibration and noise data. Building upon this foundation and in conjunction with on-site corrugation detection results, a vibrational-noise feature of the wave depth index for identifying rail corrugation was proposed. Furthermore, by utilizing quantile regression, a correlation between the wave depth index and corrugation depth was established. The findings indicate that the corrugation identification and localization results based on the wave depth index are consistent with on-site observations, with the primary wavelength of corrugation concentrated around 40 mm. Additionally, as the wave depth index increases, the corrugation depth exhibits a “fan-shaped” growth pattern, consistent with the characteristics of quantile regression, enabling the estimation of corrugation noise management thresholds at different quantile levels.
-
-
[1] 金学松, 李霞, 李伟, 等. 铁路钢轨波浪形磨损研究进展[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2016, 51(2): 264-273. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2016.02.006JIN Xuesong, LI Xia, LI Wei, et al. Review of rail corrugation progress[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2016, 51(2): 264-273. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2016.02.006 [2] LI X M, HU Z H, ZOU C. Noise annoyance and vibration perception assessment on passengers during train operation in Guangzhou Metro[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2022, 29(3): 4246-4259. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-15896-x [3] 吴越, 韩健, 左齐宇, 等. 钢轨波磨对高速列车车轮多边形磨耗产生与发展的影响[J]. 机械工程学报, 2020, 56(17): 198-208. doi: 10.3901/JME.2020.17.198WU Yue, HAN Jian, ZUO Qiyu, et al. Effect of rail corrugation on initiation and development of polygonal wear on high-speed train wheels[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2020, 56(17): 198-208. doi: 10.3901/JME.2020.17.198 [4] 崔晓璐, 彭双千, 徐佳, 等. 钢轨波磨区段科隆蛋扣件弹条断裂机理[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2025, 60(1): 205-213.CUI Xiaolu, PENG Shuangqian, XU Jia, et al. Fracture Mechanism of Cologne-Egg Fastener Clips in Rail Corrugation Sections[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2025, 60(1): 205-213. [5] 祁亚运, 邹睿, 戴焕云, 等. 车轮凹磨耦合作用下高速线路钢轨波磨安全限值研究[J/OL]. 西南交通大学学报, 1-10[2025-06-14]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/51.1277.u.20250520.1421.002.html. [6] 王阳, 肖宏, 张智海, 等. 基于一维卷积神经网络的钢轨波磨迁移诊断方法[J]. 铁道学报, 2025, 47(4): 115-123.WANG Yang, XIAO Hong, ZHANG Zhihai, et al. Rail corrugation migration diagnosis method based on one-dimensional convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2025, 47(4): 115-123. [7] 崔晓璐, 葛亚存, 徐官宝, 等. 山地地铁小半径曲线有/无轨缝区钢轨波磨成因对比研究[J/OL]. 西南交通大学学报, 1-10[2025-06-14]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/51.1277.U.20250226.1438.010.html. [8] 程祺. 基于车内噪声与轴箱振动加速度响应的波磨检测方法研究[D]. 石家庄: 石家庄铁道大学, 2023. [9] 徐晓迪, 牛留斌, 孙善超, 等. 基于轴箱振动加速度的钢轨波磨评价方法及应用[J]. 中国铁道科学, 2021, 42(6): 18-26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4632.2021.06.03XU Xiaodi, NIU Liubin, SUN Shanchao, et al. Evaluation method and application of rail corrugation based on axle box vibration acceleration[J]. China Railway Science, 2021, 42(6): 18-26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4632.2021.06.03 [10] 牛留斌, 祖宏林, 徐晓迪, 等. 基于轴箱垂向振动加速度的波磨谷深值估算方法及应用[J]. 中国铁道科学, 2023, 44(1): 25-38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4632.2023.01.03NIU Liubin, ZU Honglin, XU Xiaodi, et al. Estimation method and application of depth of rail corrugation based on vertical vibration acceleration of axle box[J]. China Railway Science, 2023, 44(1): 25-38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4632.2023.01.03 [11] BOCCIOLONE M, CAPRIOLI A, CIGADA A, et al. A measurement system for quick rail inspection and effective track maintenance strategy[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2007, 21(3): 1242-1254. doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2006.02.007 [12] 韩立, 张毅超, 陈迎庆, 等. 基于声纹特征的地铁钢轨波磨实时诊断系统开发及应用[J]. 铁路节能环保与安全卫生, 2023, 13(4): 11-17, 23.HAN Li, ZHANG Yichao, CHEN Yingqing, et al. Development and application of real-time diagnosis system for rail corrugation of subway based on voiceprint features[J]. Railway Energy Saving & Environmental Protection & Occupational Safety and Health, 2023, 13(4): 11-17, 23. [13] 从建力, 王源, 徐舟, 等. 振噪融合的地铁钢轨波磨快速测量方法[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2023, 58(3): 677-684. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20220260CONG Jianli, WANG Yuan, XU Zhou, et al. Rapid measurement method of subway rail corrugation based on vibration and noise fusion[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2023, 58(3): 677-684. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20220260 [14] RODRÍGUEZ A, SAÑUDO R, MIRANDA M, et al. Smartphones and tablets applications in railways, ride comfort and track quality. transition zones analysis[J]. Measurement, 2021, 182: 109644. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2021.109644 [15] CONG J L, GAO M Y, WANG Y, et al. Subway rail transit monitoring by built-in sensor platform of smartphone[J]. Frontiers of Information Technology & Electronic Engineering, 2020, 21(8): 1226-1238. [16] 王阳, 肖宏, 张智海, 等. 基于车内振动噪声响应的钢轨波磨状态评估方法[J/OL]. 机械工程学报, 1-15[2025-04-17]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2187.th.20231129.1502.028.html. [17] 汤雪扬, 蔡小培, 王伟华, 等. 基于粒子概率神经网络算法的钢轨波磨识别[J]. 浙江大学学报(工学版), 2023, 57(9): 1766-1774. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-973X.2023.09.008TANG Xueyang, CAI Xiaopei, WANG Weihua, et al. Rail corrugation recognition based on particle probabilistic neural network algorithm[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science), 2023, 57(9): 1766-1774. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-973X.2023.09.008 [18] CAI X P, TANG X Y, CHANG W H, et al. Machine learning-based rail corrugation recognition: a metro vehicle response and noise perspective[J]. Philosophical Transactions Series A, Mathematical, Physical, and Engineering Sciences, 2023, 381(2254): 20220171. [19] WEI Z L, SUN X F, YANG F, et al. Carriage interior noise-based inspection for rail corrugation on high-speed railway track[J]. Applied Acoustics, 2022, 196: 108881. doi: 10.1016/j.apacoust.2022.108881 [20] 牛道安, 魏子龙, 孙宪夫, 等. 小半径曲线钢轨波磨激扰下列车车内振动噪声特性[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2023, 23(1): 143-155.NIU Daoan, WEI Zilong, SUN Xianfu, et al. Train interior vibration and noise characteristics induced by rail corrugation with small-radius curves[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2023, 23(1): 143-155. [21] 何庆, 汪健辉, 李晨钟, 等. 基于分位数回归的轨道质量指数阈值合理性数据分析[J]. 铁道学报, 2023, 45(7): 99-105. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2023.07.012HE Qing, WANG Jianhui, LI Chenzhong, et al. Data analysis of rationality of threshold of track quality index based on quantile regression[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2023, 45(7): 99-105. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2023.07.012 [22] BOGOYA J D, BOGOYA J M, PEÑUELA A J. Value-added in higher education: ordinary least squares and quantile regression for a Colombian case[J]. Ingeniería e Investigación, 2017, 37(3): 30-36. [23] British Standards Institution. Railway Applications-Track-Acceptance of Works-Part 3: Acceptance of Rail Grinding, Milling and Planning Work in Track: BS EN 13231-3: 2006[S]. London: British Standards Institution, 2006. [24] NG A K, MARTUA L. Analysis and prediction of rail corrugation growth and axle box acceleration signals for different railway track configurations[C]//2021 7th International Conference on Control, Automation and Robotics (ICCAR). Singapore: IEEE, 2021: 275-279. [25] TORSTENSSON P T, SCHILKE M. Rail corrugation growth on small radius curves—measurements and validation of a numerical prediction model[J]. Wear, 2013, 303(1/2): 381-396. -




 下载:
下载: