Injection Quantity Prediction of High-Pressure Common Rail Systems under Multiple Injections Based on Gaussian Process Regression
-
摘要:
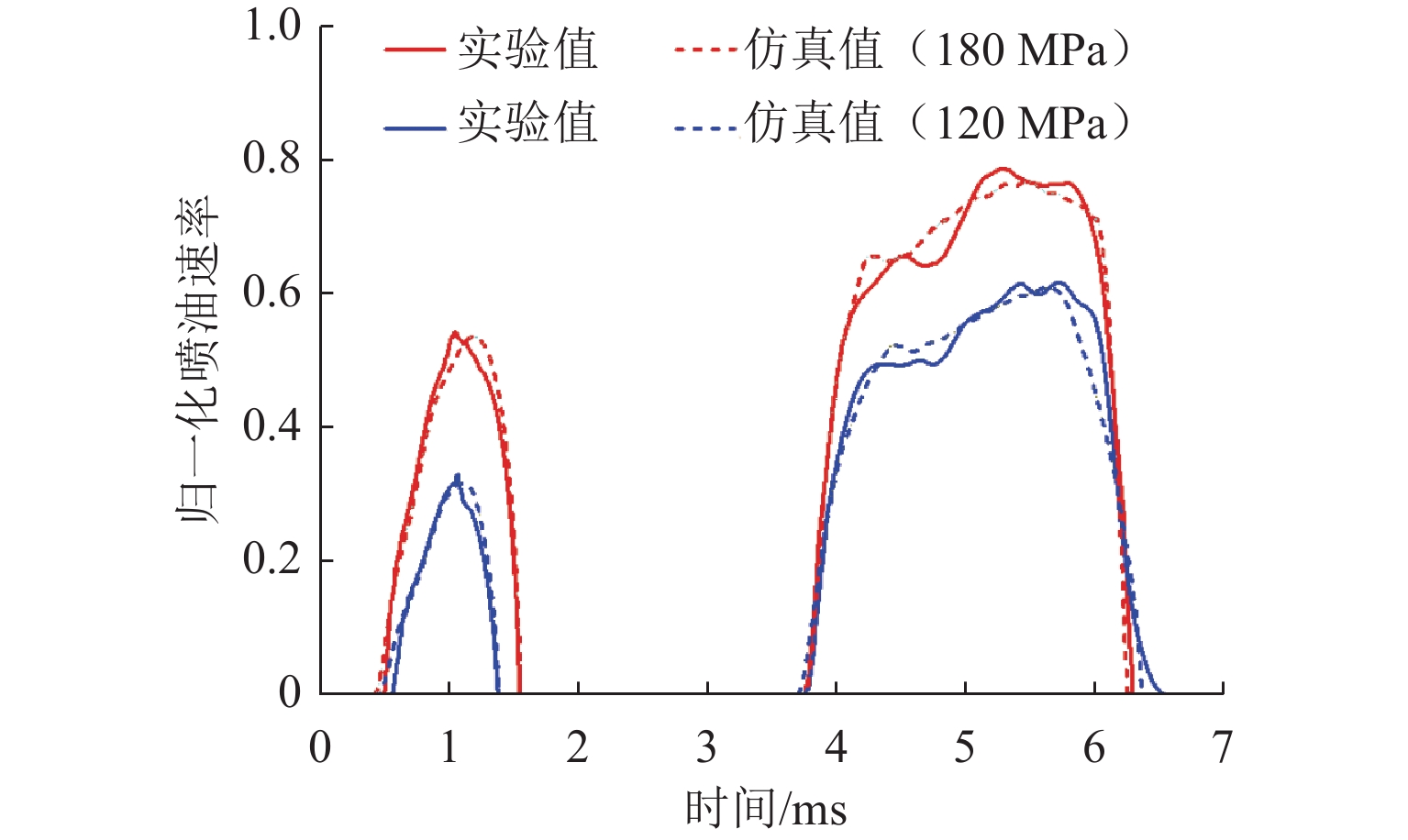
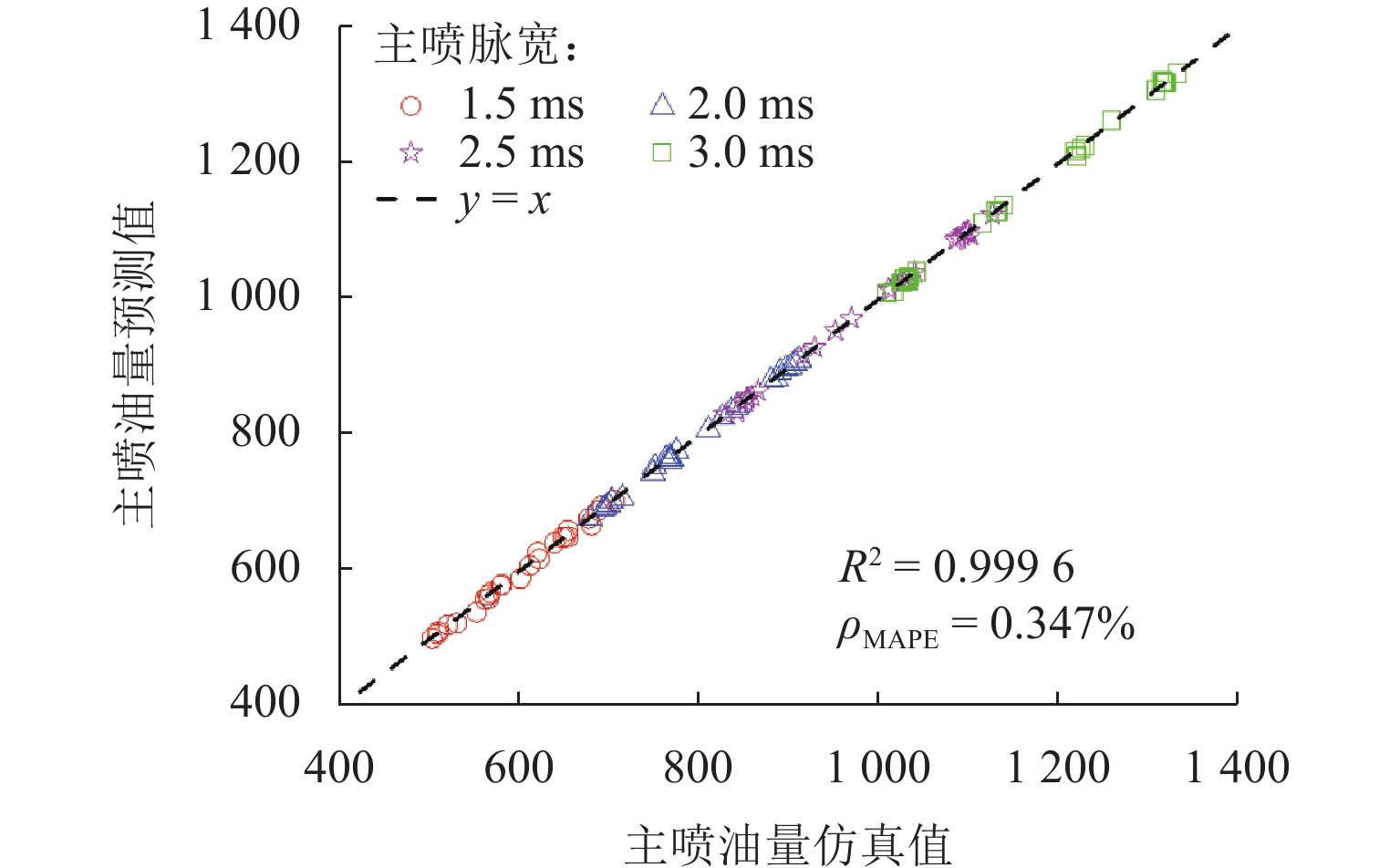
高压共轨系统多次喷射下,预喷引发的压力波使得主喷油量产生波动,导致缸内燃烧效率降低、排放污染物增加. 为实现多次喷射下喷油量的精确控制,本文提出一种基于高斯过程回归(Gaussian process regression,GPR)的多次喷射主喷油量数据驱动预测模型. 首先,采用D最优设计和二阶响应面方法,以轨压、预喷脉宽、预-主喷间隔和主喷脉宽为因素建立主喷油量响应面模型,通过方差分析揭示4个工况参数均属于极显著影响因素;然后,基于自主开发的多物理场耦合数字仿真平台,建立涵盖528组工况的主喷油量样本集并训练模型;最后,系统对比零均值、常数、线性和二次多项式等不同均值函数以及Seiso、Rqard和Matérn等不同核函数的组合形式,确定线性均值函数与二次有理核函数为最优配置. 结果表明:在测试工况下,GPR模型所预测主喷油量的平均绝对百分比误差为0.347%,决定系数
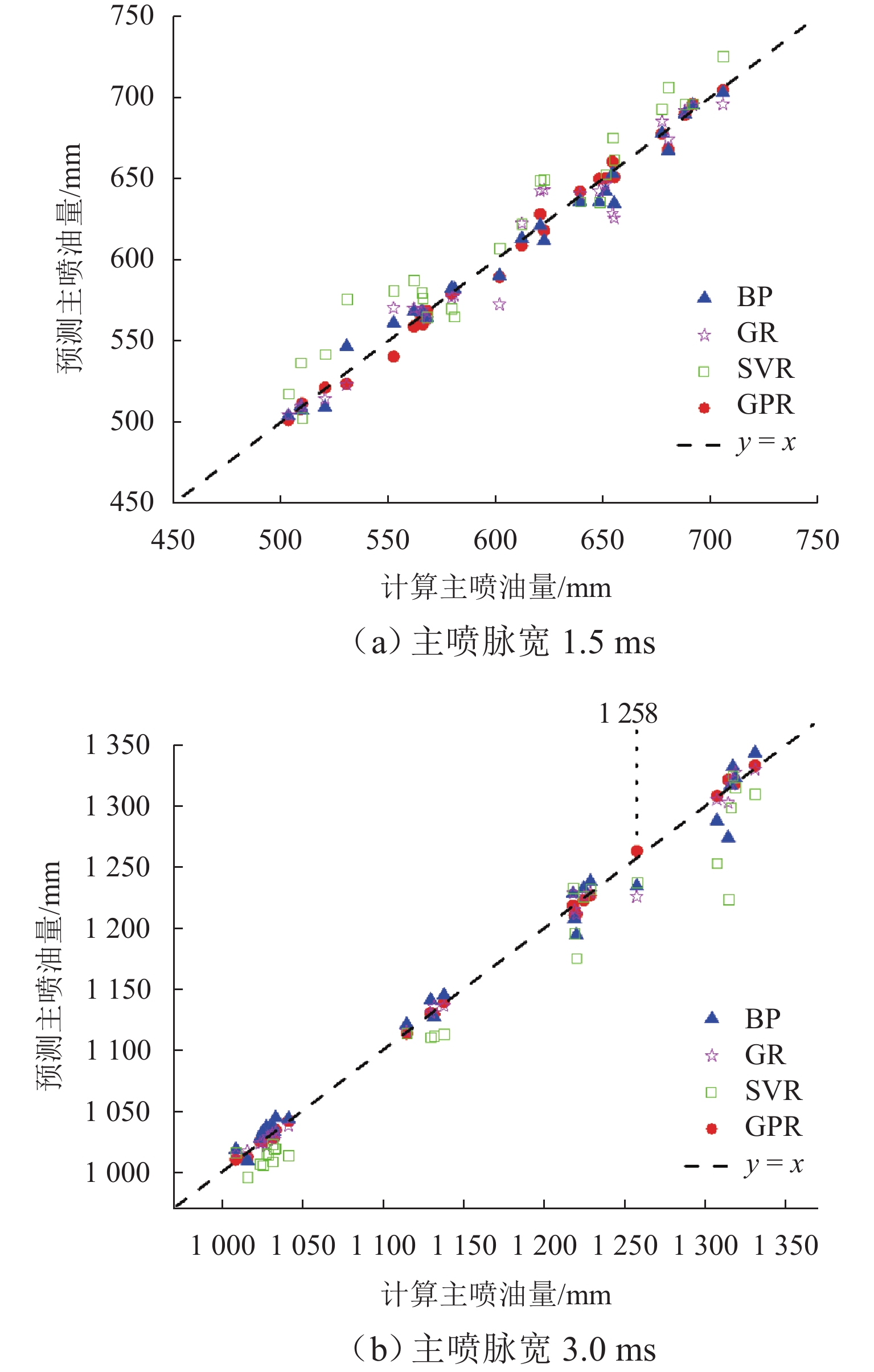
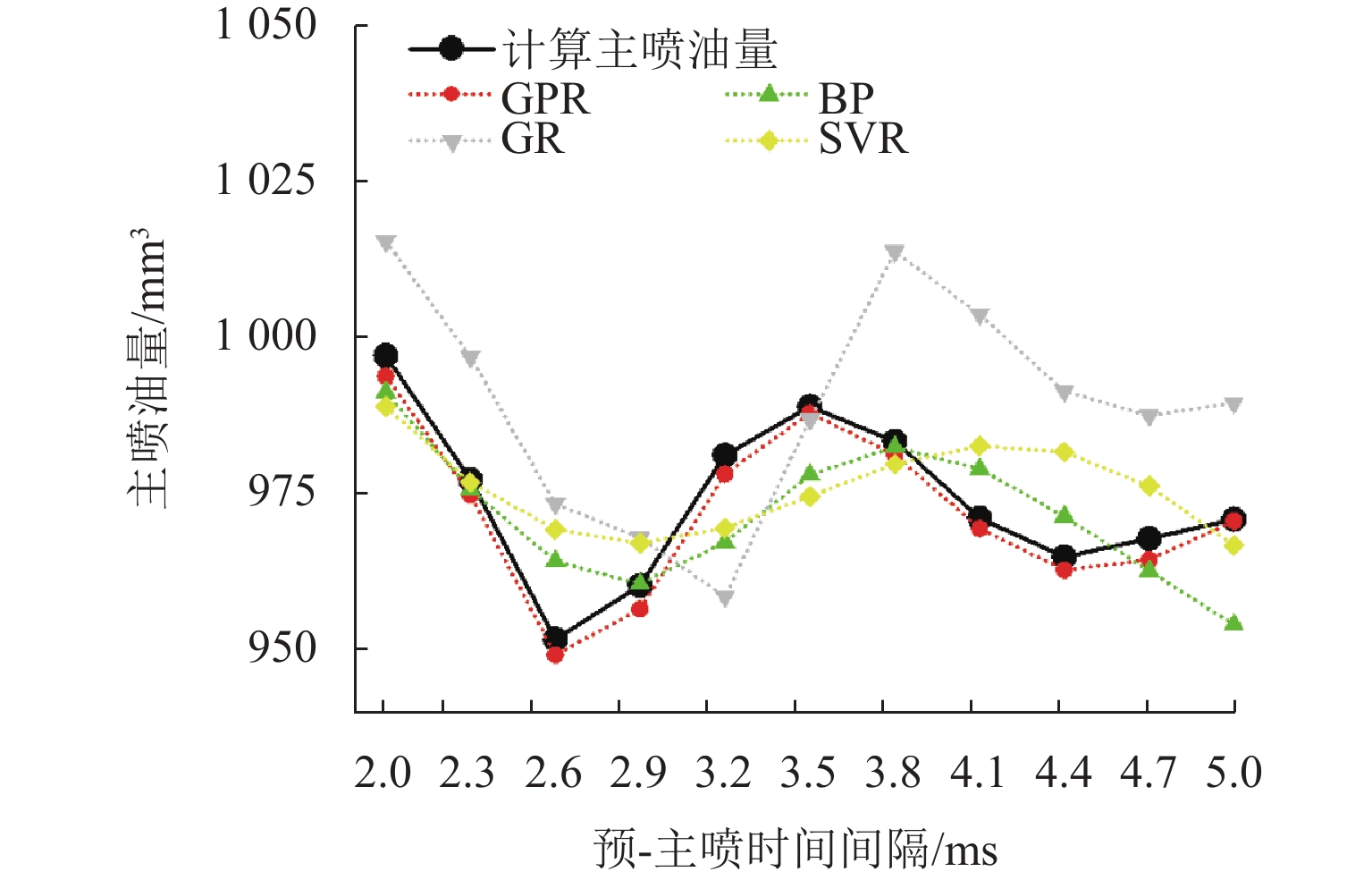
R 2为0.999 6,不同主喷脉宽和预-主喷间隔下的预测结果均紧密分布于回归线附近;在非测试工况下,该模型仍能准确再现主喷油量随预-主喷间隔变化的波动规律,与前馈式神经网络(BP)、广义回归神经网络(GR)和支持向量机回归(SVR)模型相比具有更低的误差与更高的一致性. 研究证明基于GPR的多次喷射主喷油量数据驱动模型兼具较高预测精度与良好泛化能力,可为高压共轨系统多次喷射下的精确控制提供模型支撑.Abstract:In high-pressure common rail systems under multiple injections, the pressure waves induced by the pilot injection cause fluctuations in the main injection quantity, thereby reducing in-cylinder combustion efficiency and increasing pollutant emissions. A data-driven prediction model for the main injection quantity based on Gaussian process regression (GPR) was proposed to achieve the accurate control of injection quantity under multiple injections. First, D-optimal design and a second-order response surface method were employed to build a response surface model for the main injection quantity by utilizing rail pressure, pilot-injection pulse width, pilot-main injection interval, and main-injection pulse width as factors. Analysis of variance indicates that the four operating parameters all have extremely significant effects on the main injection quantity. Then, based on a self-developed multi-physics coupled digital simulation platform, a dataset containing 528 operating conditions was constructed, and the model was trained. On this basis, several combinations of mean functions (zero, constant, linear, and quadratic polynomials) and different kernel functions (Seiso, Rqard, and Matérn) were systematically compared, and the linear mean function combined with the rational quadratic kernel function was identified as the optimal configuration. Results show that in test conditions, the mean absolute percentage error (MAPE) of main injection quantity predicted by the GPR-based model is 0.347% and the coefficient of determination
R 2 is0.9996 , with predictions at different main-pulse widths and pilot-main intervals clustered closely around the regression line. In non-test conditions, the model can still accurately reproduce the fluctuation law of the main injection quantity with varying pilot-main intervals, and features lower error and higher consistency than BP, GR, and SVR models. The proposed GPR-based data-driven model under multiple injections is proved to have both high prediction accuracy and sound generalization capability, providing model support for the precise control of high-pressure common rail systems under multiple injections. -
表 1 工况参数的变化范围
Table 1. Variation range of operating parameters
符号 参数 基准值 变化范围 X1 轨压/MPa 160 140~180 X2 预喷脉宽/ms 0.85 0.8~0.9 X3 时间间隔/ms 2.3 2.0~2.6 X4 主喷脉宽/ms 2.5 2~3 表 2 主喷油量响应面模型的评价指标
Table 2. Evaluation indexes of response surface model for main injection quantity
组成项 X1 X2 X3 X4 P值 < 0.0001 < 0.0001 < 0.0001 < 0.0001 表 3 样本数据集的工况参数
Table 3. Operating parameters of sample dataset
工况参数 数值 轨压/MPa 120, 140, 160, 180 预喷脉宽/ms 0.80, 0.85, 0.90 预-主喷间隔/ ms 2.0~5.0 主喷脉宽/ ms 1.5, 2.0, 2.5, 3.0 表 4 不同均值函数下的预测结果评价指标
Table 4. Evaluation indexes of prediction results for different mean functions
函数 ρRMSE ρMAPE R2 零均值函数 10.2247 9.8318 × 10−40.99794 常数均值函数 9.7055 9.8746 × 10−40.99813 线性均值函数 8.7959 8.7661 × 10−40.99847 二次多项式均值函数 11.3238 9.2346 × 10−40.99746 表 5 不同核函数下的预测结果评价指标
Table 5. Evaluation indexes of prediction results for different kernel functions
函数 ρRMSE ρMAPE R2 SEiso 8.7959 8.7661 × 10−40.99847 RQard 4.6668 3.4779 × 10−40.99957 Maternard_3/2 6.6684 5.7328 × 10−40.99912 Maternard_5/2 5.3705 4.6916 × 10−40.99943 -
[1] HAN T, SINGH R, LAVOIE G, et al. Multiple injection for improving knock, gaseous and particulate matter emissions in direct injection SI engines[J]. Applied Energy, 2020, 262: 114578. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2020.114578 [2] 赵建辉, 徐煜, 杨贵春, 等. 基于喷雾动量法的共轨喷油器喷油稳定性试验研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2025, 60(3): 665-670. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20230335ZHAO Jianhui, XU Yu, YANG Guichun, et al. Experimental study on injection stability of common rail injector based onsSpray momentum method[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2025, 60(3): 665-670. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20230335 [3] MORETTO G, SCHNELL N, FREY J, et al. Fast model-based calibration of multiple injections for a CI engine using nonlinear optimal control[J]. Control Engineering Practice, 2024, 145: 105848. doi: 10.1016/j.conengprac.2024.105848 [4] 夏天峰, 陶文辉, 王晓艳, 等. 微量柴油引燃高压直喷天然气的碳烟体积分数分布[J]. 内燃机学报, 2025, 43(2): 117-126. doi: 10.16236/j.cnki.nrjxb.202502014XIA Tianfeng, TAO Wenhui, WANG Xiaoyan, et al. Distribution of soot volume fraction of high pressure direct injection natural gas ignited by trace diesel[J]. Transactions of CSICE, 2025, 43(2): 117-126 doi: 10.16236/j.cnki.nrjxb.202502014 [5] 杨津韬, 张恒, 赵建辉, 等. 多次喷射下喷油器结构参数对喷油量波动影响[J]. 哈尔滨工程大学学报, 2025, 46(2): 276-282. doi: 10.11990/jheu.202307011YANG Jintao, ZHANG Heng, ZHAO Jianhui, et al. Influence of injector structure parameters on fuel injection quantity fluctuation under multiple injections[J]. Journal of Harbin Engineering University, 2025, 46(2): 276-282. doi: 10.11990/jheu.202307011 [6] JIA G H, GAO S, SHU X, et al. Multi-objective optimization of emission parameters of a diesel engine using oxygenated fuel and pilot injection strategy based on RSM-NSGA Ⅲ[J]. Energy, 2024, 293: 130661. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2024.130661 [7] XUAN T M, LI H J, WANG Y T, et al. A conceptual model of polyoxymethylene dimethyl ether 3 (PODE3) spray combustion under compression ignition engine-like conditions[J]. Combustion and Flame, 2024, 261: 113296. doi: 10.1016/j.combustflame.2024.113296 [8] KIM J, LEE J, KIM K. Numerical study on the effects of fuel viscosity and density on the injection rate performance of a solenoid diesel injector based on AMESim[J]. Fuel, 2019, 256: 115912. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2019.115912 [9] XU J, FAN L Y, LI B, et al. Research on pressure wave decoupling method for the nozzle of common rail electronically controlled injector based on water hammer theory[J]. International Journal of Engine Research, 2024, 25(5): 882-895. doi: 10.1177/14680874231210715 [10] ROJAS-REINOSO E V, MORALES-CHAUCA K, LARA-LARA J, et al. Adaptation and validation of injection rate predictive model for solenoid type injectors with different nozzle geometry[J]. Applied Sciences, 2024, 14(8): 3394. doi: 10.3390/app14083394 [11] LI R C, YUAN W T, XU J K, et al. Study of the optimization of rail pressure characteristics in the high-pressure common rail injection system for diesel engines based on the response surface methodology[J]. Processes, 2023, 11(9): 2626. doi: 10.3390/pr11092626 [12] TORRES-JIMENEZ E, DORADO R, KEGL B, et al. One-dimensional modeling and simulation of injection processes of bioethanol-biodiesel and bioethanol-diesel fuel blends[J]. Fuel, 2018, 227: 334-344. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2018.04.118 [13] FINESSO R, SPESSA E. A control-oriented approach to estimate the injected fuel mass on the basis of the measured in-cylinder pressure in multiple injection diesel engines[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2015, 105: 54-70. doi: 10.1016/j.enconman.2015.07.053 [14] DONG Q, YANG X Y, NI H, et al. An on-line measurement method of injection rate of high pressure common rail system[J]. Measurement, 2021, 170: 108716. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2020.108716 [15] FEI H Z, LIU B X, WANG L P, et al. Optimal estimation of injection rate for high-pressure common rail system using the extended Kalman filter[J]. Measurement, 2023, 220: 113385. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2023.113385 [16] SILVAGNI G, RAVAGLIOLI V, PONTI F, et al. Development of a predictive pressure waves model for high-pressure common rail injection systems[J]. SAE International Journal of Engines, 2021, 15(5): 719-741. doi: 10.4271/03-15-05-0039 [17] SORIANO J A, MATA C, ARMAS O, et al. A zero-dimensional model to simulate injection rate from first generation common rail diesel injectors under thermodynamic diagnosis[J]. Energy, 2018, 158: 845-858. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2018.06.054 [18] GAO Z G, LI G X, XU C L, et al. A calculation method and experiment study of high-pressure common rail injection rate with solenoid injectors[J]. Science Progress, 2021, 104(2): 368504211026157. [19] PLAMONDON E, SEERS P. Development of a simplified dynamic model for a piezoelectric injector using multiple injection strategies with biodiesel/diesel-fuel blends[J]. Applied Energy, 2014, 131: 411-424. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2014.06.039 [20] ATAC O F, LEE S, MOON S. Development of simplified model for injection rate prediction of diesel injectors during transient and steady operation[J]. Fuel, 2022, 324: 124655. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2022.124655 [21] ZHANG T T. An estimation method of the fuel mass injected in large injections in common-rail diesel engines based on system identification using artificial neural network[J]. Fuel, 2022, 310: 122404. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2021.122404 [22] OH H, HWANG J, PICKETT L M, et al. Machine-learning based prediction of injection rate and solenoid voltage characteristics in GDI injectors[J]. Fuel, 2022, 311: 122569. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2021.122569 [23] ZHAO J H, ZIRKA S E, MOROZ Y I. Duality-derived models of high-speed electromagnetic valves[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2021, 68(10): 9876-9884. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2020.3022510 [24] ZHAO J H, ZIRKA S E, MOROZ Y I, et al. Physical Cauer circuits in nonlinear eddy-current modeling[J]. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 2020, 508: 166850. doi: 10.1016/j.jmmm.2020.166850 [25] 张付英, 高勇新, 张原浩, 等. 基于响应面法和正交试验的旋转轴唇形密封的可靠性分析[J]. 机械设计, 2024, 41(10): 41-49. doi: 10.13841/j.cnki.jxsj.2024.10.003ZHANG Fuying, GAO Yongxin, ZHANG Yuanhao, et al. Reliability analysis of rotary shaft lip seal based on response surface method and orthogonal test[J]. Journal of Machine Design, 2024, 41(10): 41-49. doi: 10.13841/j.cnki.jxsj.2024.10.003 -




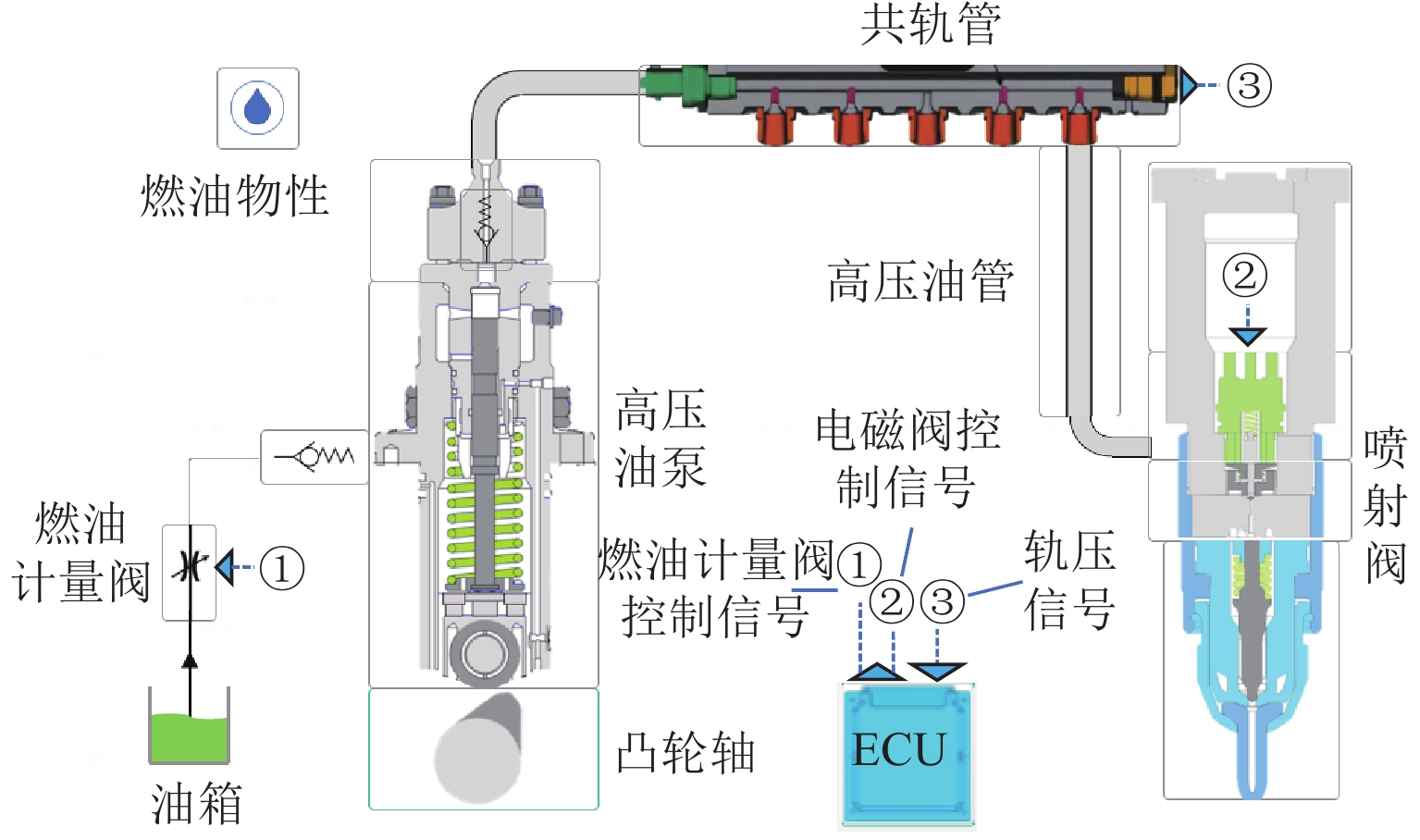
 下载:
下载: