Non-Singular Fast Terminal Sliding Mode Rotor Position Control of Active Magnetic Bearings
-
摘要:
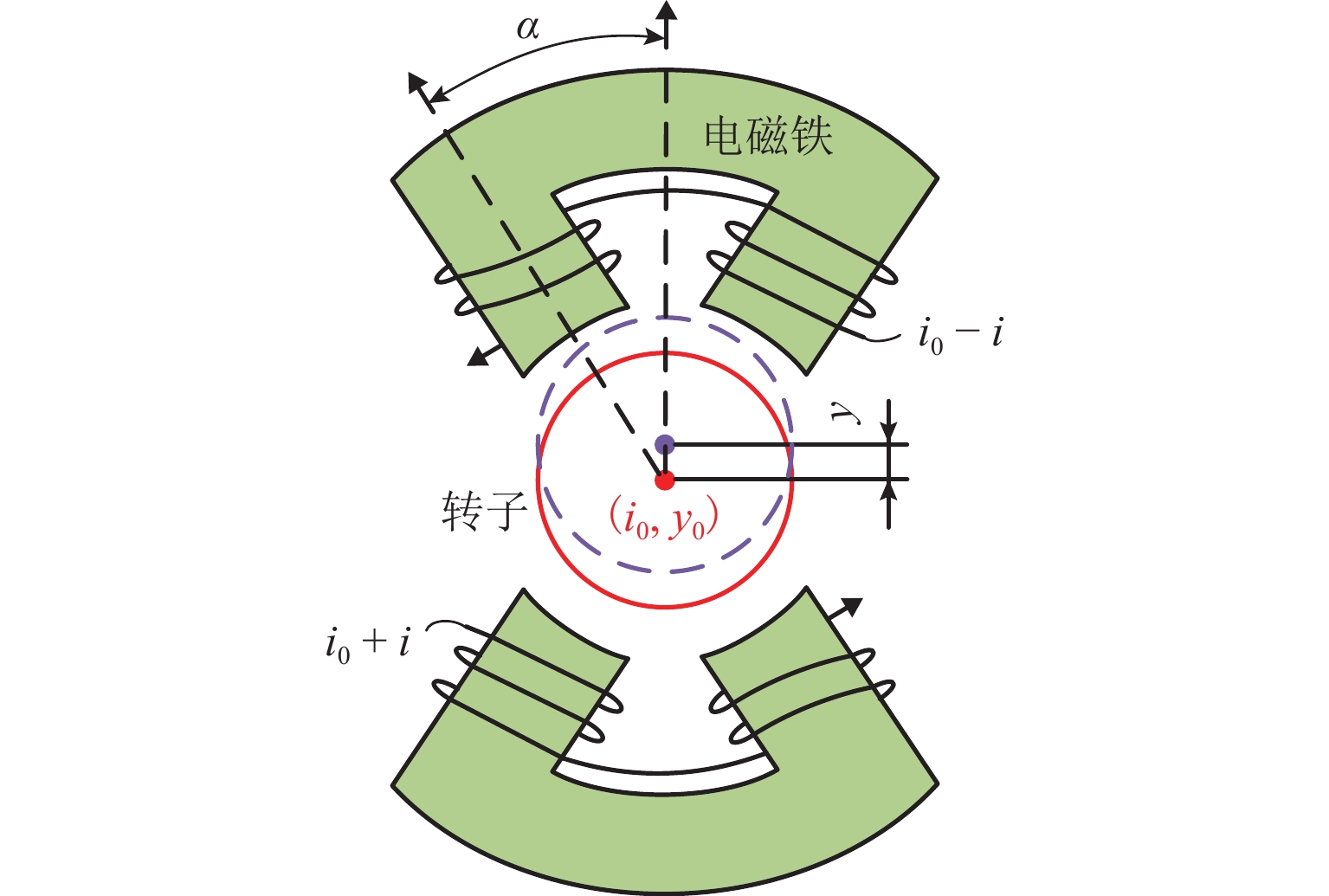
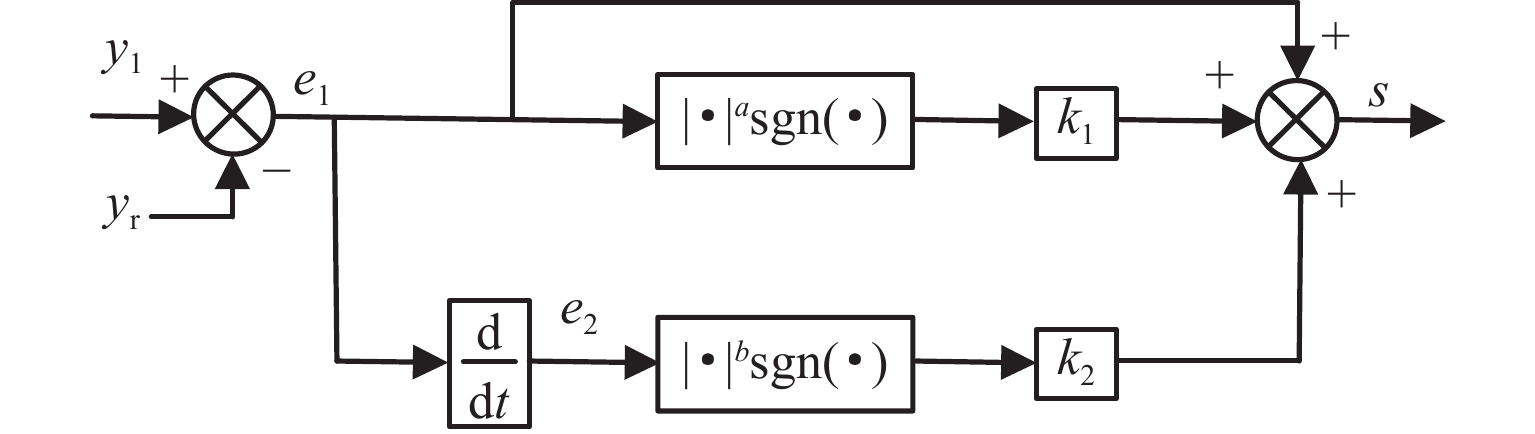
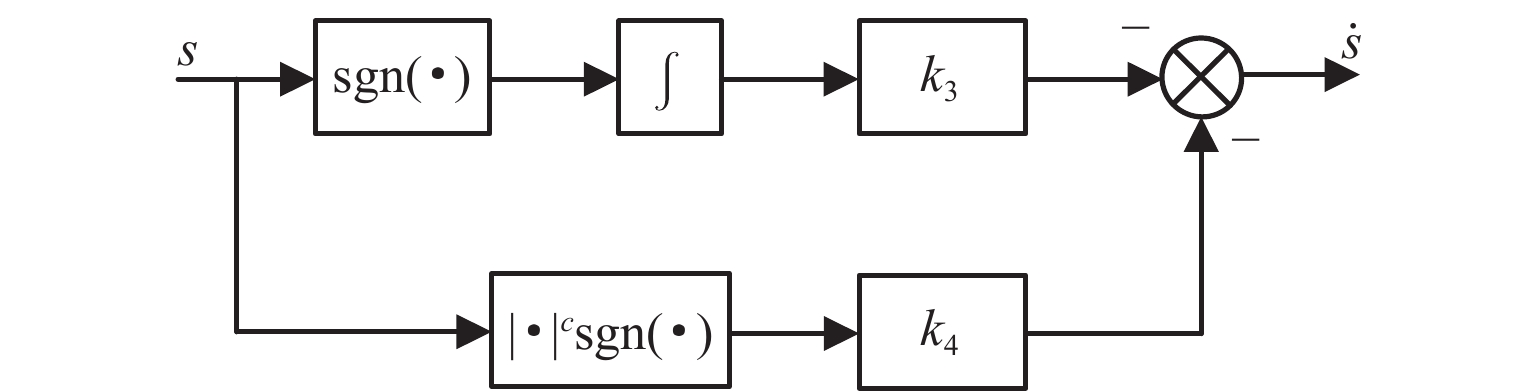
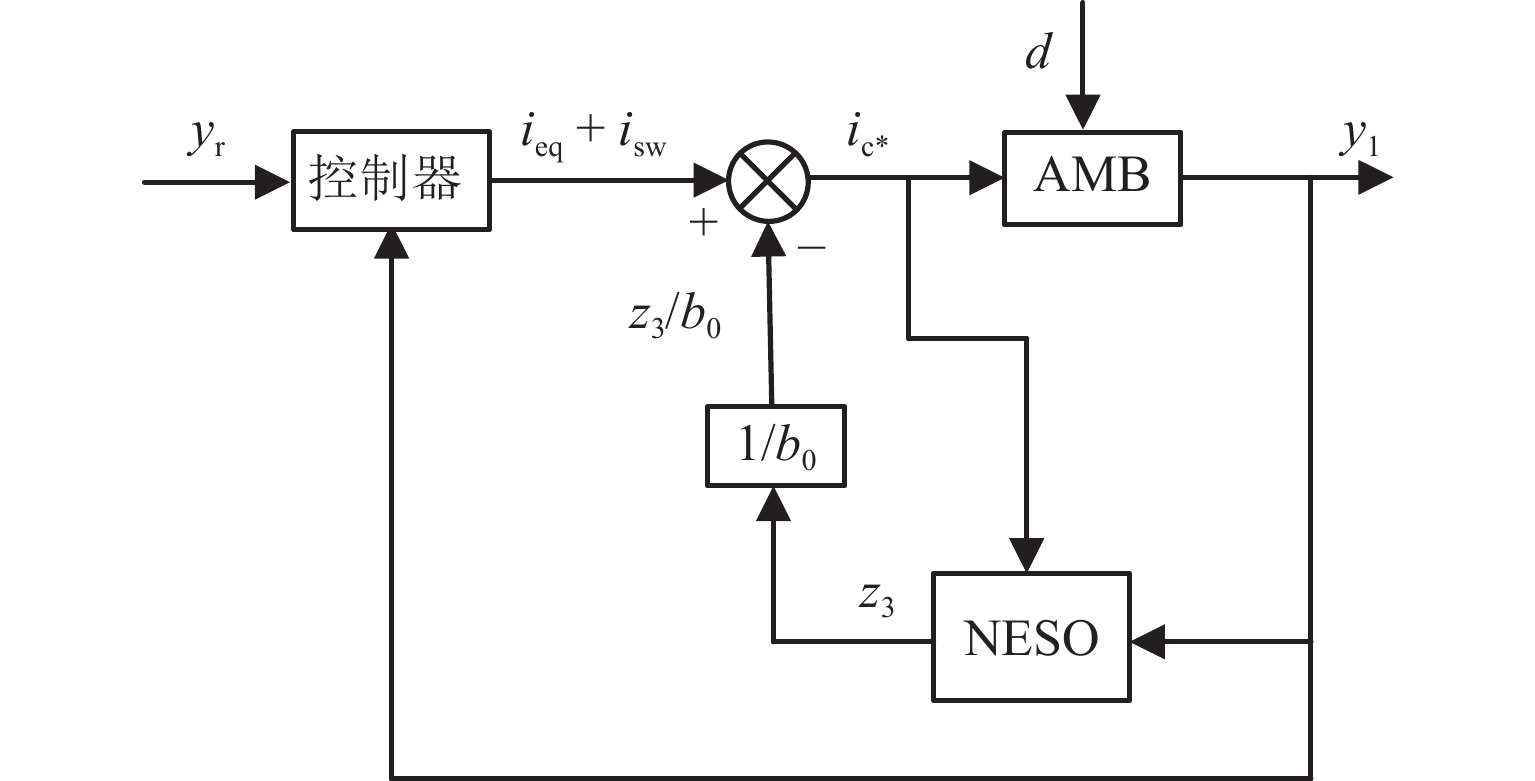
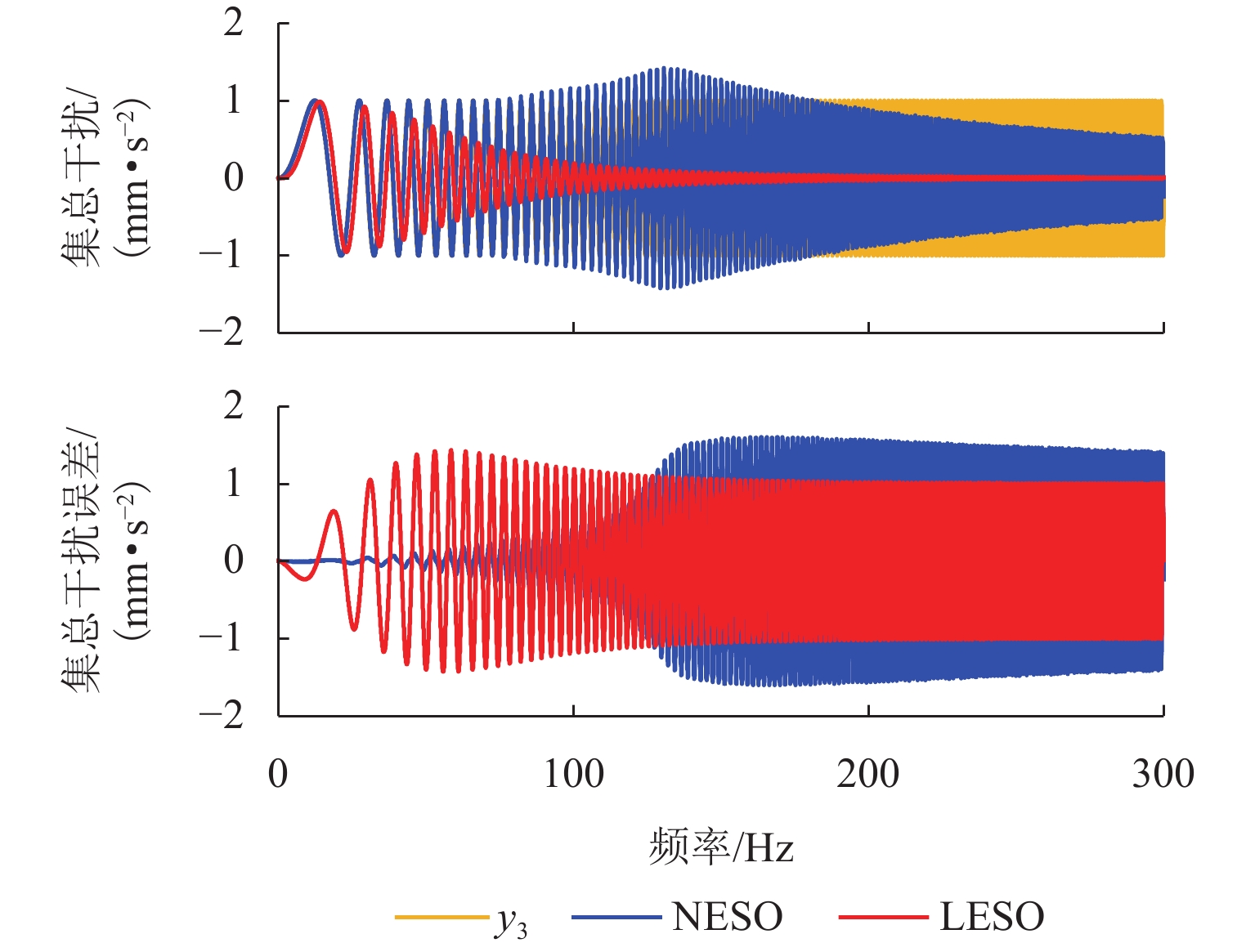
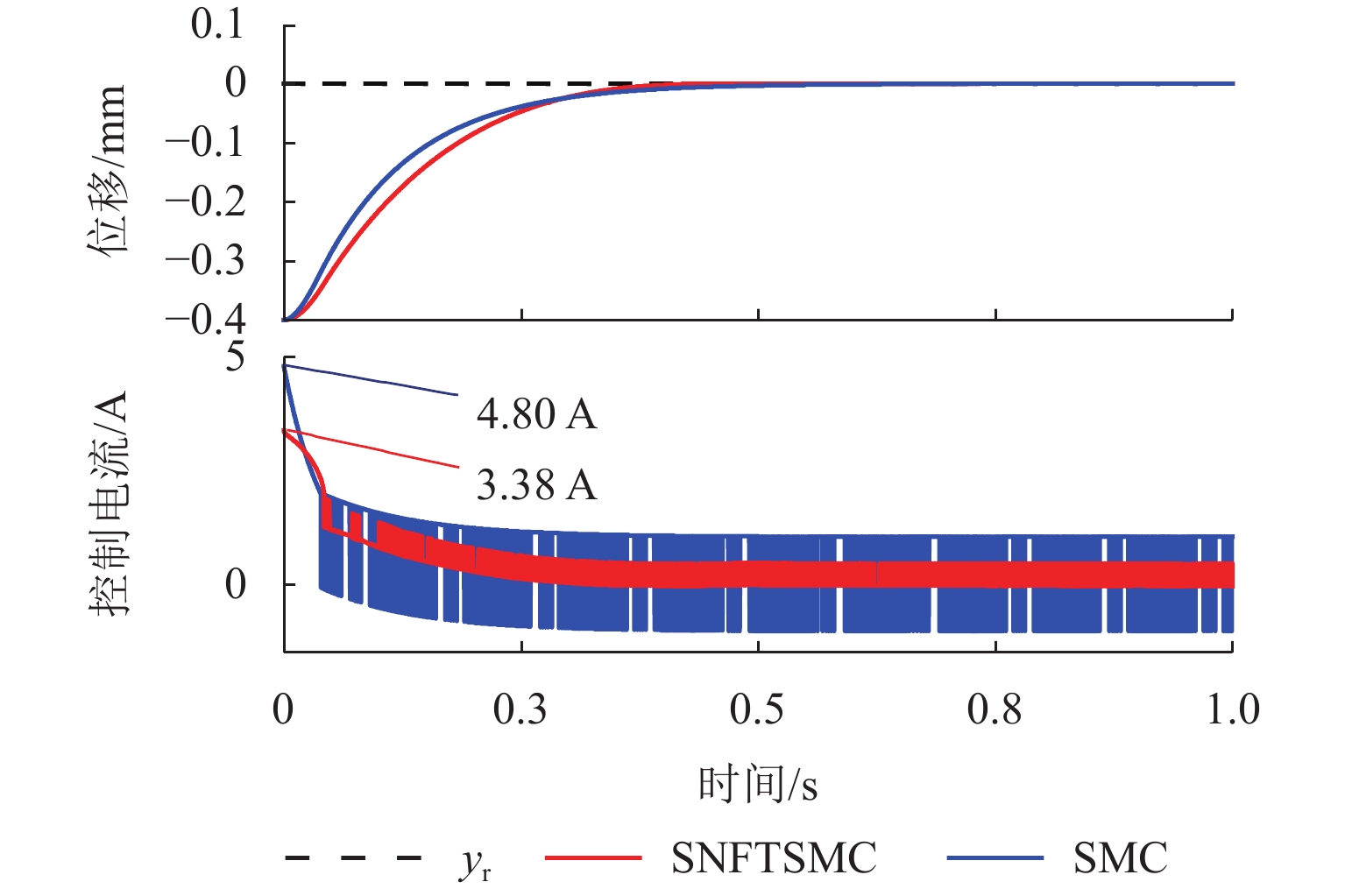
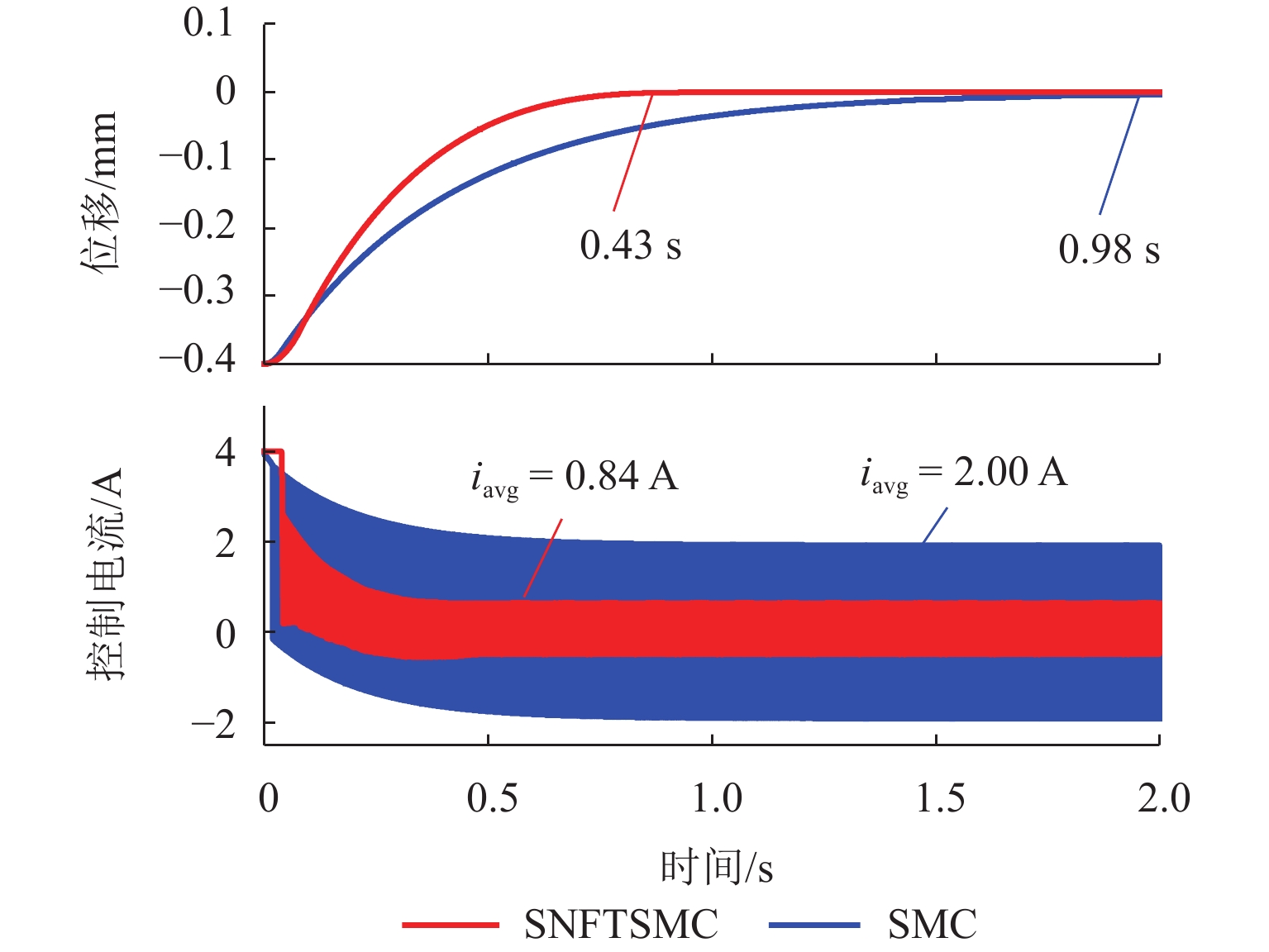
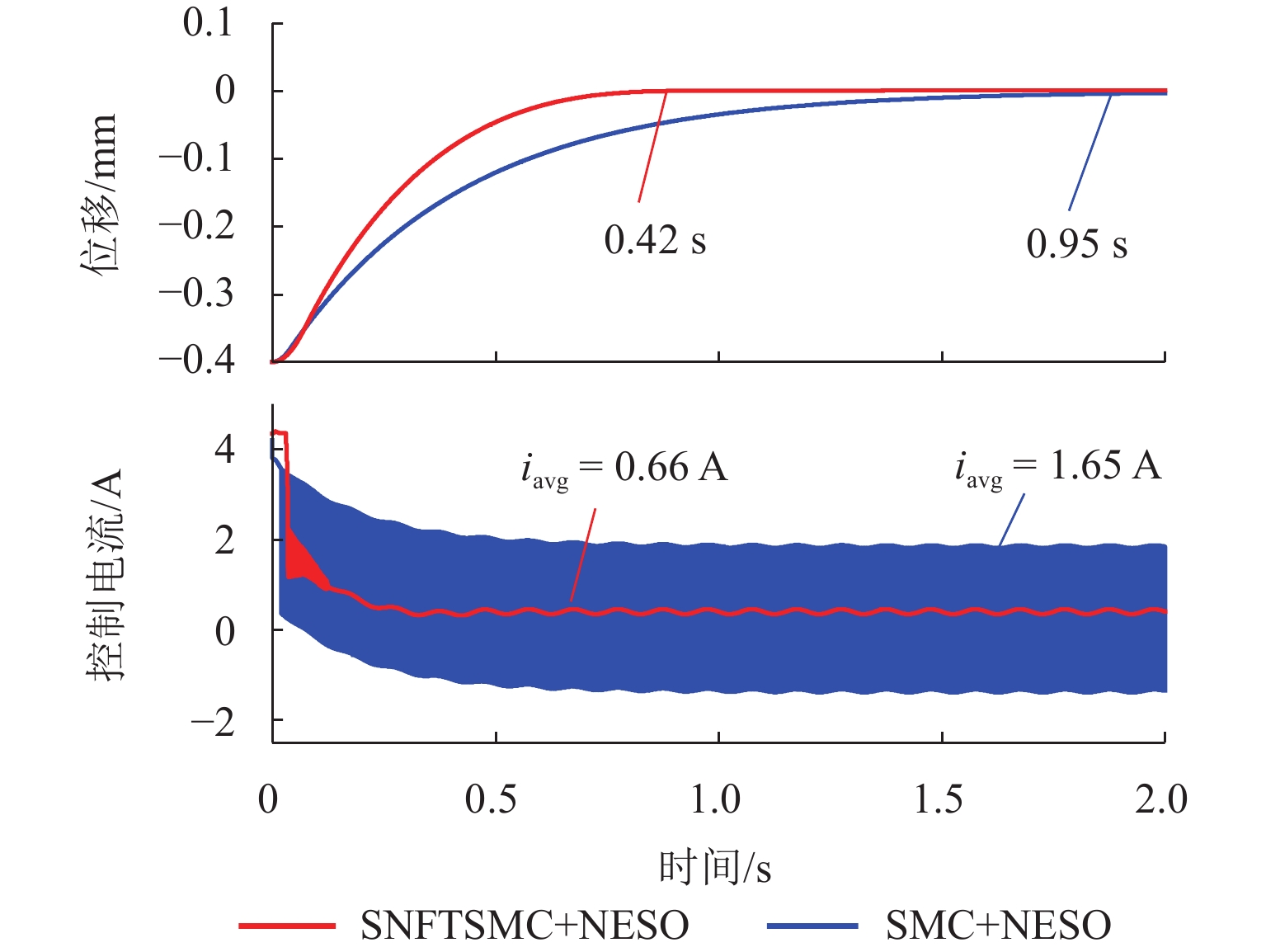
针对主动磁悬浮轴承转子位置控制中系统响应速度慢、抗干扰能力弱等问题,本文提出将非奇异快速终端滑模函数与改进超螺旋趋近律相结合的位置控制方法,以获得快速、精确的动态响应控制效果. 由于系统内扰和外扰的存在,需要对滑模趋近律增加常值切换增益以保证系统的强鲁棒性,但会使得系统抖振进一步变大,本文通过采用非线性扩张状态观测器对干扰进行实时观测并动态补偿,折衷了抖振与抗干扰性之间的矛盾;通过李雅普诺夫稳定性理论证明了所提方法的稳定性,并对提出的控制方法进行仿真与实验验证. 研究结果表明:与传统的滑模控制器相比,所设计的控制器具有更快的响应速度和更强的抖振抑制能力,转子达到目标位置的时间缩短了56.4%,系统动态性能得到改善;控制电流的平均值减小了68.5%,系统抑制抖振的能力增强,即算法具有较强的鲁棒性.
Abstract:In order to solve problems of slow system response speed and poor anti-interference ability in the position control of the rotor of active magnetic bearings (AMB), a position control method combining the non-singular fast terminal sliding function with the improved super-twisting reaching law was proposed to obtain fast and accurate control effects of dynamic responses. In addition, due to internal and external interference in the system, constant switching gain was added to the sliding mode reaching law, so as to ensure the robustness of the system, but it could exacerbate the system chattering. Therefore, the interference was observed and compensated by a nonlinear extended state observer, which alleviated the contradiction between chattering and anti-interference. Then, the stability of the proposed method was proven Lyapunov stability theory, and the proposed control method was verified by simulation and experiment. The results show that compared with the traditional sliding mode controller, the designed controller has faster response speed and stronger chattering suppression ability, and the time for the rotor to reach the target position is shortened by 56.4%. The dynamic performance of the system is improved, and the average control current is reduced by 68.5%. The chattering suppression ability of the system is enhanced, indicating that the proposed algorithm has strong robustness.
-
表 1 AMB参数
Table 1. Parameters of AMB
参数 值 磁极面积/mm2 720 匝数/圈 150 气隙长度/mm 0.4 偏置电流/A 2 转子质量/kg 15 电流刚度系数/(N·A−1) 939.5 位移刚度系数/(N·mm−1) 4697.5 表 2 控制器参数
Table 2. Parameters of controller
控制器 值 SNFTSMC k1=1、k2=0.1、k3=80、k4=50、a=2.5、
b=1.5、γ=1.5、λ=1、η=0.5、M=15SMC k1=30、k2=50、c=10、M=15 -
[1] ZHENG S Q, WANG C. Rotor balancing for magnetically levitated TMPs integrated with vibration self-sensing of magnetic bearings[J]. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2021, 26(6): 3031-3039. doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2021.3051372 [2] WANG K, MA X, LIU Q, et al. Multiphysics global design and experiment of the electric machine with a flexible rotor supported by active magnetic bearing[J]. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2019, 24(2): 820-831. doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2019.2892392 [3] HUTTERER M, WIMMER D, SCHRÖDL M. Stabilization of a magnetically levitated rotor in the case of a defective radial actuator[J]. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2020, 25(6): 2599-2609. doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2020.2985623 [4] DU L, CUI P L, ZHOU X X, et al. Unbalance vibration control for MSCMG based on high-precision synchronous signal detection method[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(16): 17917-17925. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2021.3082695 [5] 刘贺. 主动磁悬浮轴承的H∞控制研究[D]. 大连:大连理工大学,2021. [6] ZHANG X Y, CHEN X K, ZHU G Q, et al. Output feedback adaptive motion control and its experimental verification for time-delay nonlinear systems with asymmetric hysteresis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2020, 67(8): 6824-6834. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2019.2938460 [7] 王忠博,毛川,祝长生. 主动电磁轴承-刚性转子系统PID控制器设计方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2018,38(20): 6154-6163.WANG Zhongbo, MAO Chuan, ZHU Changsheng. A design method of PID controller for active magnetic bearings-rigid rotor systems[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2018, 38(20): 6154-6163. [8] 周天豪,杨智,祝长生,等. 电磁轴承高速电机转子系统的内模-PID控制[J]. 电工技术学报,2020,35(16): 3414-3425.ZHOU Tianhao, YANG Zhi, ZHU Changsheng, et al. Internal model control-PID control of an active magnetic bearing high-speed motor rotor system[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2020, 35(16): 3414-3425. [9] MU C X, HE H B. Dynamic behavior of terminal sliding mode control[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2018, 65(4): 3480-3490. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2017.2764842 [10] 任萍,朱景伟,赵燕,等. 基于双滑模控制器的开关磁阻电机调速策略[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2024,44(11): 4501-4513.REN Ping, ZHU Jingwei, ZHAO Yan, et al. Speed control strategy for switched reluctance motor based on dual sliding mode controller[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2024, 44(11): 4501-4513. [11] HOU H Z, YU X H, XU L, et al. Finite-time continuous terminal sliding mode control of servo motor systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2020, 67(7): 5647-5656. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2019.2931517 [12] XU D Z, DING B, JIANG B, et al. Nonsingular fast terminal sliding mode control for permanent magnet linear synchronous motor via high-order super-twisting observer[J]. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2022, 27(3): 1651-1659. doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2021.3086527 [13] 李冰林,曾励,张鹏铭,等. 主动磁悬浮轴承的滑模自抗扰解耦控制[J]. 电机与控制学报,2021,25(7): 129-138.LI Binglin, ZENG Li, ZHANG Pengming, et al. Sliding mode active disturbance rejection decoupling control for active magnetic bearings[J]. Electric Machines and Control, 2021, 25(7): 129-138. [14] 靖永志,冯伟,王森,等. 基于自适应非奇异终端滑模的悬浮控制策略[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2022,57(3): 566-573. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20210743JING Yongzhi, FENG Wei, WANG Sen, et al. Levitation control strategy based on adaptive non-singular terminal sliding mode[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2022, 57(3): 566-573. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20210743 [15] WANG J X, RONG J Y, YANG J. Adaptive fixed-time position precision control for magnetic levitation systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2023, 20(1): 458-469. doi: 10.1109/TASE.2022.3156943 [16] 赵静,林智昌,姜斌,等. 永磁同步直线电机的分数阶超螺旋滑模控制[J]. 控制理论与应用,2023,40(7): 1224-1232. doi: 10.7641/CTA.2022.20162ZHAO Jing, LIN Zhichang, JIANG Bin, et al. Fractional order super-twisting sliding mode control of permanent magnet synchronous linear motor[J]. Control Theory & Applications, 2023, 40(7): 1224-1232. doi: 10.7641/CTA.2022.20162 [17] KALI Y, AYALA M, RODAS J, et al. Time delay estimation based discrete-time super-twisting current control for a six-phase induction motor[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2020, 35(11): 12570-12580. doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2020.2995773 [18] WANG J X, ZHAO L, YU L. Adaptive terminal sliding mode control for magnetic levitation systems with enhanced disturbance compensation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2021, 68(1): 756-766. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2020.2975487 [19] 东野亚兰,杨淑英,王奇帅,等. 基于增强型扩张状态观测器的永磁同步电机低抖振高抗扰二阶终端滑模电流控制[J]. 电工技术学报,2024,39(8): 2434-2448.DONGYE Yalan, YANG Shuying, WANG Qishuai, et al. Enhanced extended state observer based second order terminal sliding mode current control for permanent magnet synchronous machine with low chattering and improved disturbance rejection[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2024, 39(8): 2434-2448. [20] 朱良红,张国强,李宇欣,等. 基于级联扩张观测器的永磁电机无传感器自抗扰控制策略[J]. 电工技术学报,2022,37(18): 4614-4624.ZHU Lianghong, ZHANG Guoqiang, LI Yuxin, et al. Active disturbance rejection control for position sensorless permanent magnet synchronous motor drives based on cascade extended state observer[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2022, 37(18): 4614-4624. [21] XU W, DIAN R J, LIU Y, et al. Robust flux estimation method for linear induction motors based on improved extended state observers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2019, 34(5): 4628-4640. doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2018.2865800 [22] ZHANG T R, XU Z, GERADA C. A nonlinear extended state observer for sensorless IPMSM drives with optimized gains[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 2020, 56(2): 1485-1494. doi: 10.1109/TIA.2019.2959537 -




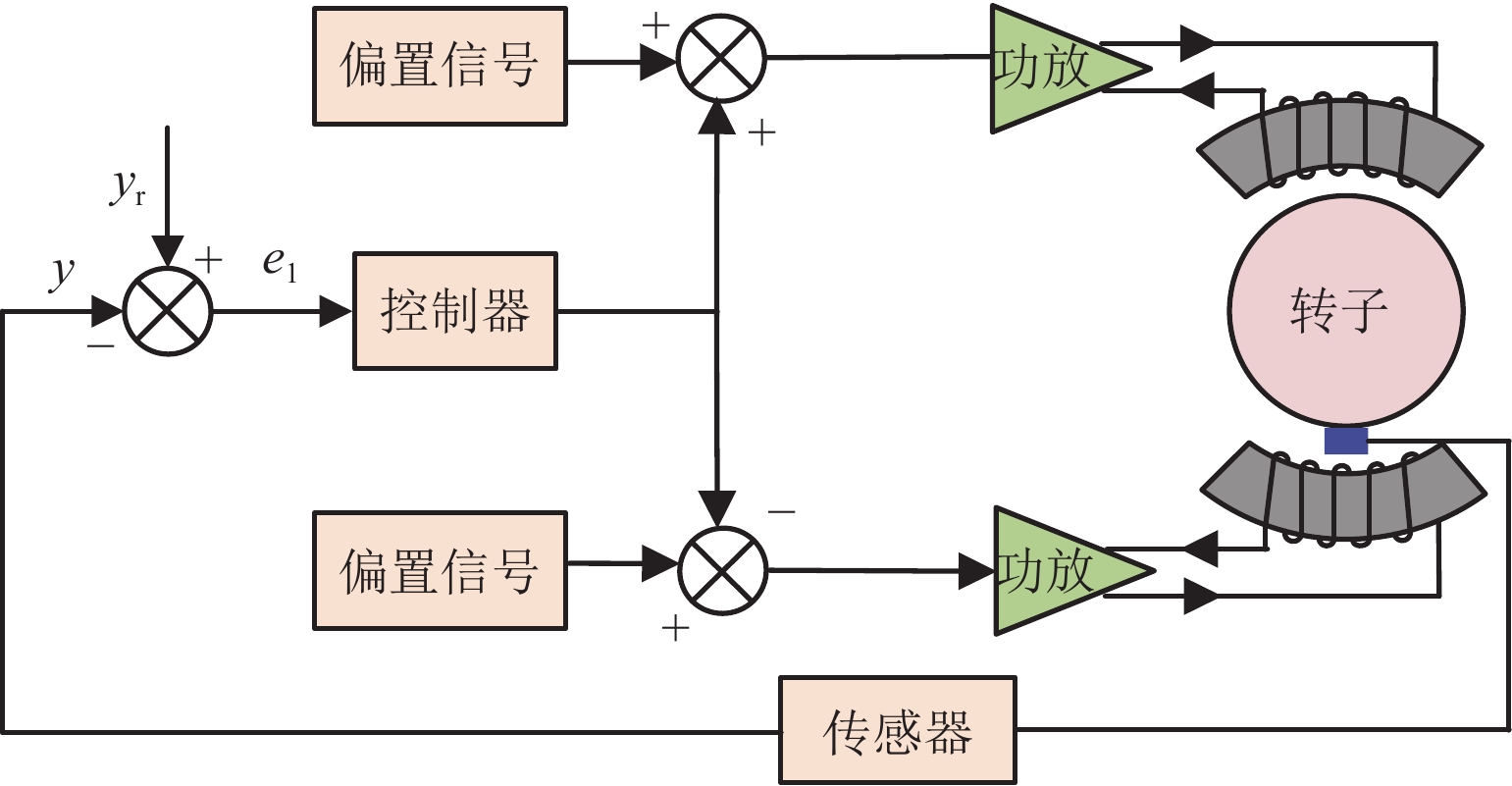
 下载:
下载: