Operation of Expressway Weaving Sections under Variable Marking Intervention
-
摘要:
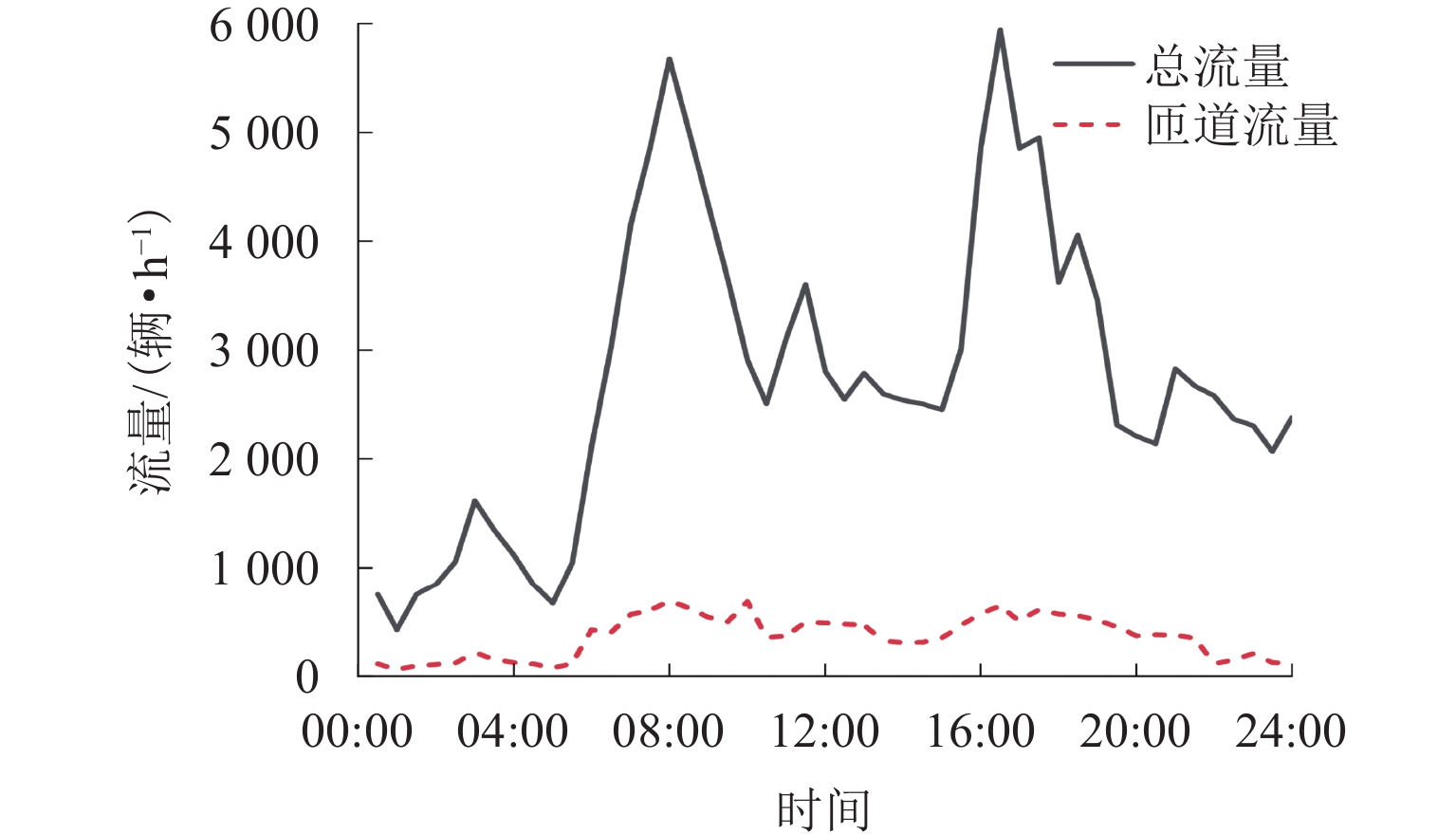
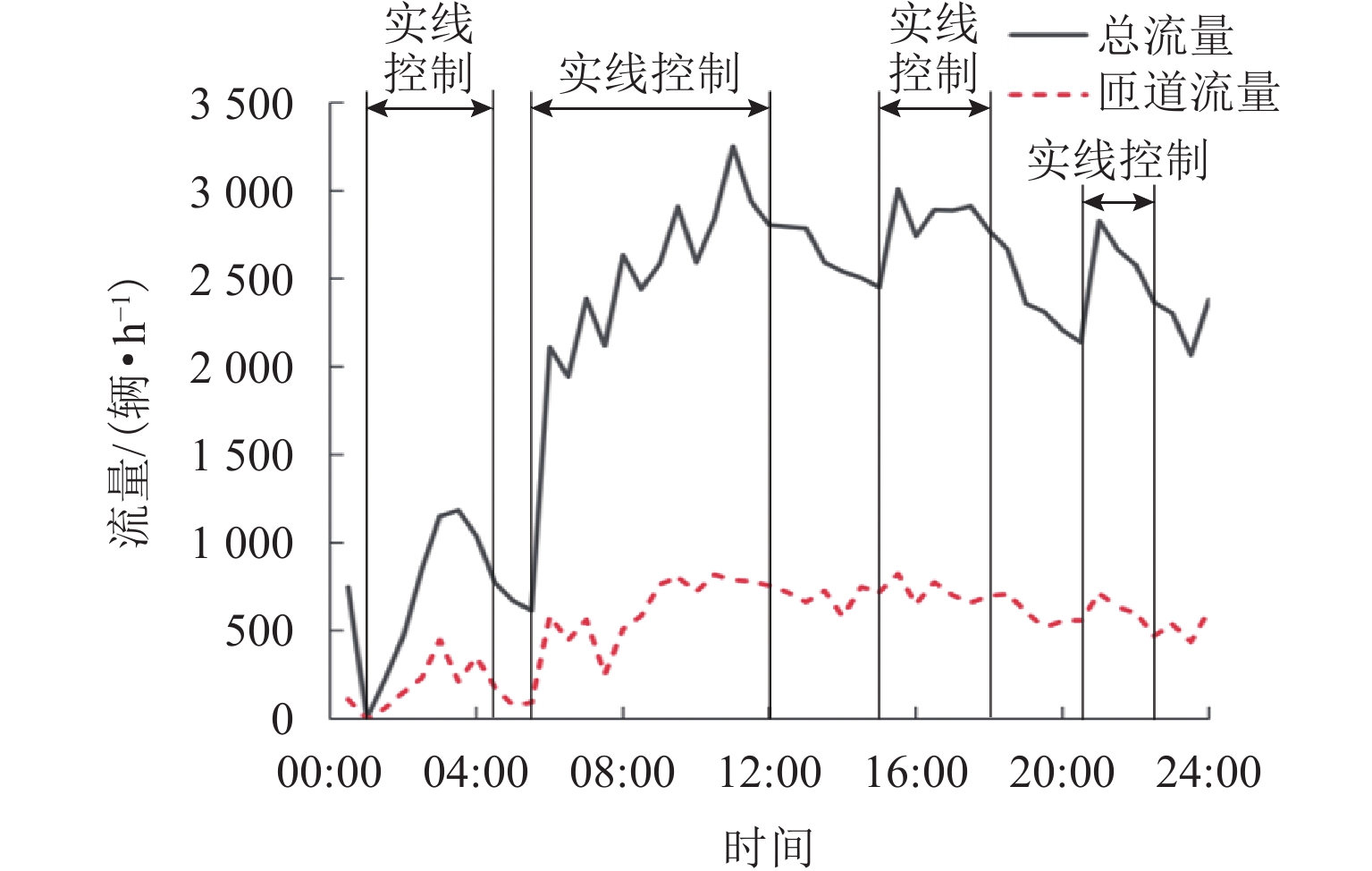
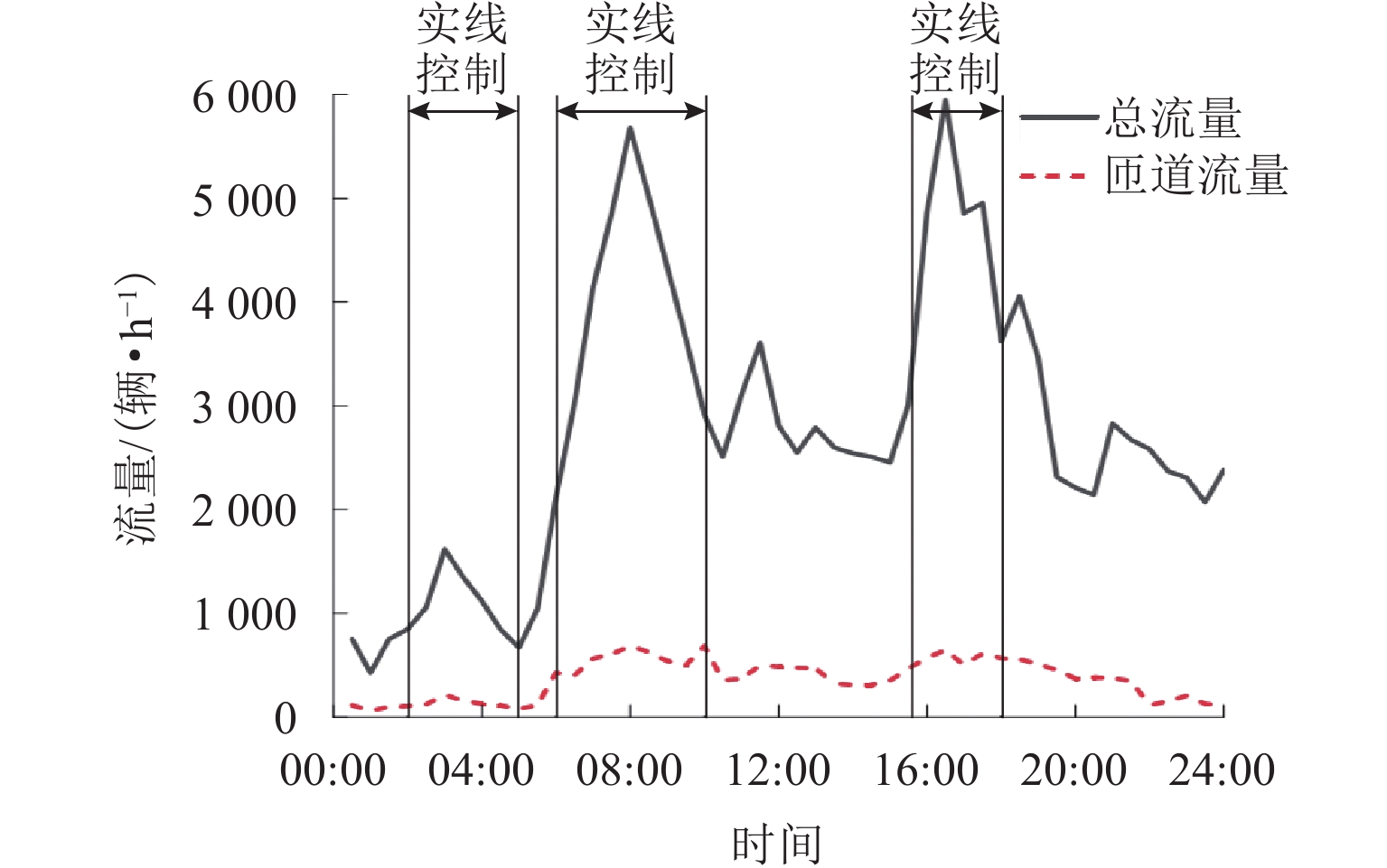
针对城市快速路交织区内固定标线控制存在的缺陷,本文提出基于元胞自动机的快速路交织区可变标线干预,以根据交通场景需要灵活变换标线形式,体现多标线控制策略的优势. 首先,基于三相交通流理论建立元胞自动机模型,为模糊控制器的建立提供基础;其次,生成可变标线主动干预的策略库并构建模糊控制器,以实现可变标线控制下交织区场景的全时段仿真;然后,通过选取上海市交织区线圈数据和典型高峰期交通流量数据作为交通流输入进行全时段仿真,输出得到标线控制方案;最后,从运行效率、潜在事故风险和污染物排放共3个方面对干预效果进行评价. 研究结果表明:在可变标线干预下,现实工况与设计工况场景的平均延误相比普通标线显著降低,其中,设计工况从71 s降低至48 s;现实工况中可变标线干预下的危险场景数量相比普通标线降低了23.4%;车辆排放的几类重要污染物均值均有明显减小.
Abstract:Variable marking intervention in expressway weaving sections based on the cellular automaton was proposed by combining the advantage that variable markings can flexibly change the marking form according to the needs of traffic scenarios and provide more marking control strategies to solve the problems of fixed marking control in the weaving sections of urban expressways, with the intervention effect evaluated. First, the cellular automaton model was built based on the three-phase traffic flow theory to provide a basis for fuzzy controller building. Second, the strategy library of active variable marking intervention was generated, and the fuzzy controller was constructed to realize the full-time simulation of weaving section scenarios under variable marking control. By selecting the coil data of weaving sections and typical traffic flow data during peak periods in Shanghai as the traffic flow input for full-time simulation, the output was obtained for the marking control scheme. Finally, the intervention effect was evaluated in terms of operation efficiency, potential accident risk and pollutant emission. The results show that the average delays of the scenarios of real working conditions and designed working conditions are significantly reduced under variable marking intervention compared with ordinary markings, with the average delay of the designed working conditions decreasing from 71 to 48 s. The number of hazardous scenarios under variable marking intervention in real working conditions is reduced by 23.4% compared with ordinary markings. The mean values of several important pollutants emitted by the vehicles are significantly reduced.
-
Key words:
- urban traffic /
- variable marking /
- cellular automaton /
- expressway weaving section /
- microsimulation
-
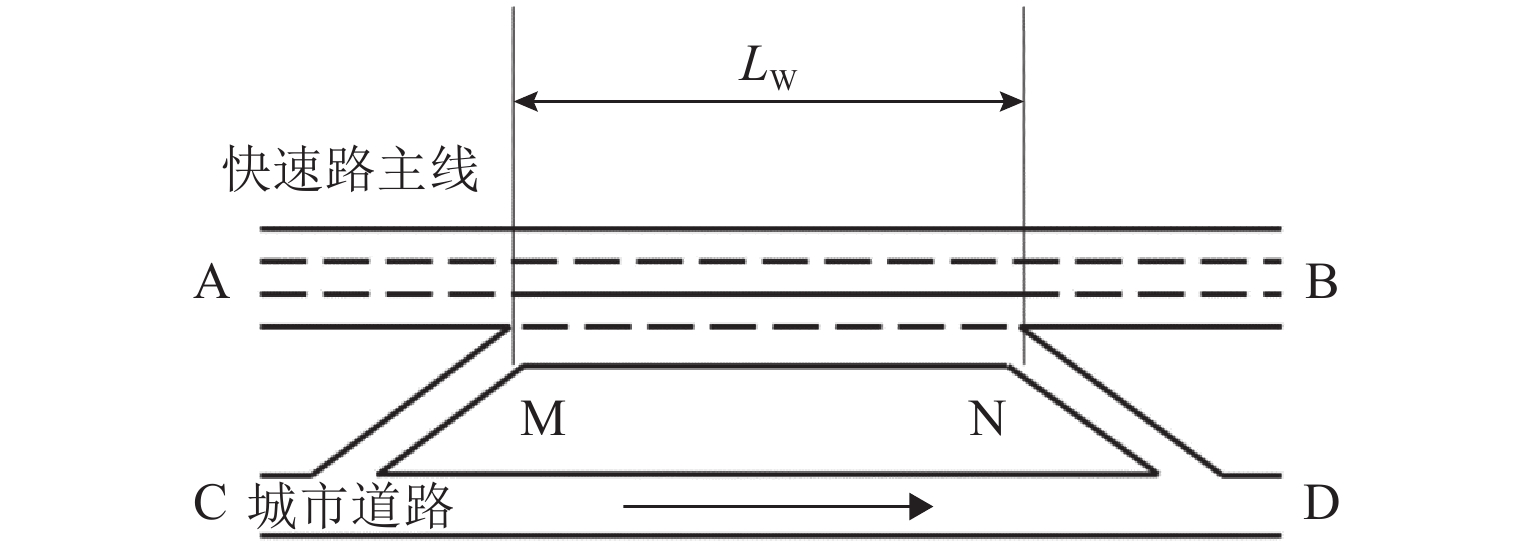
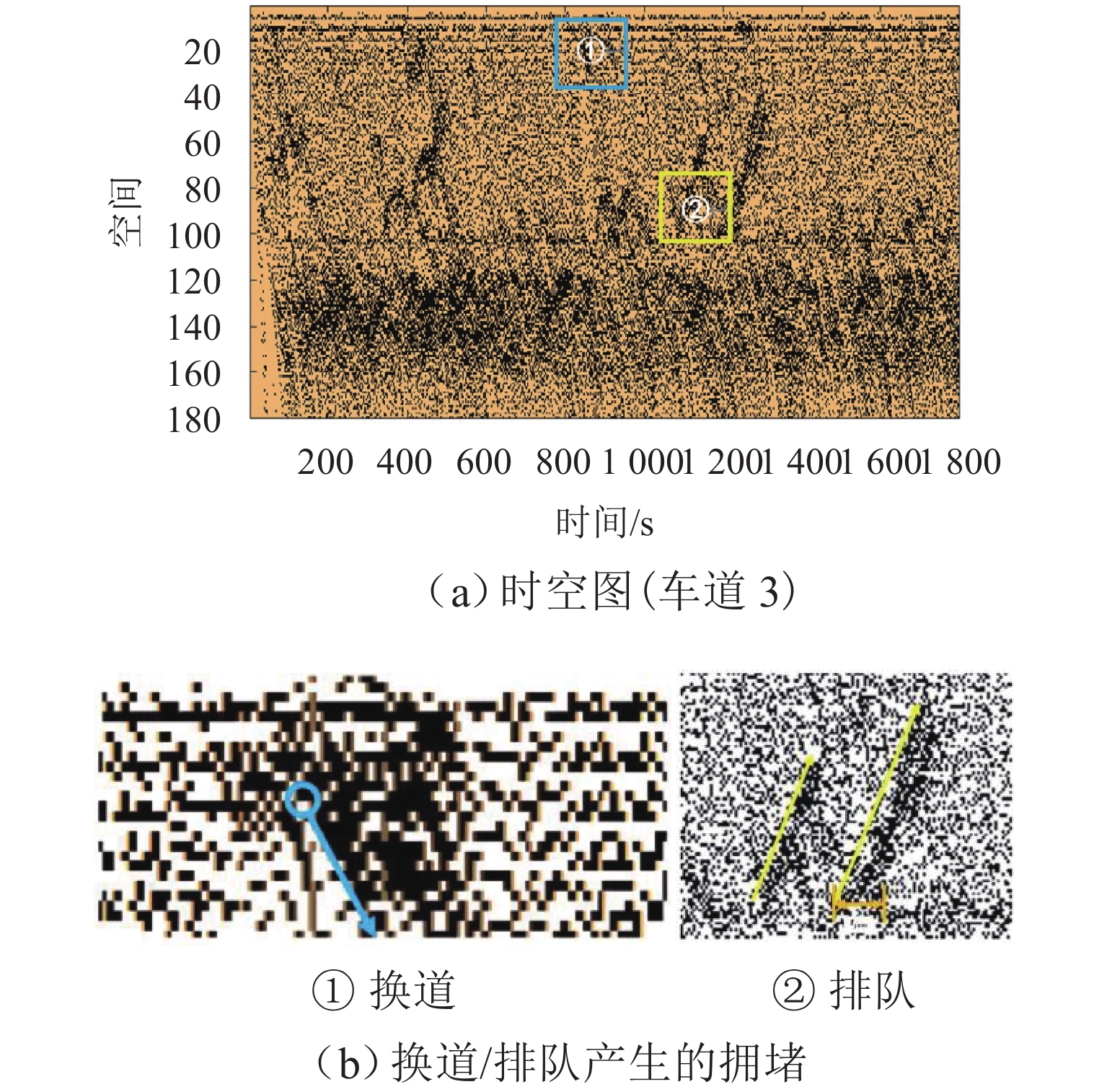
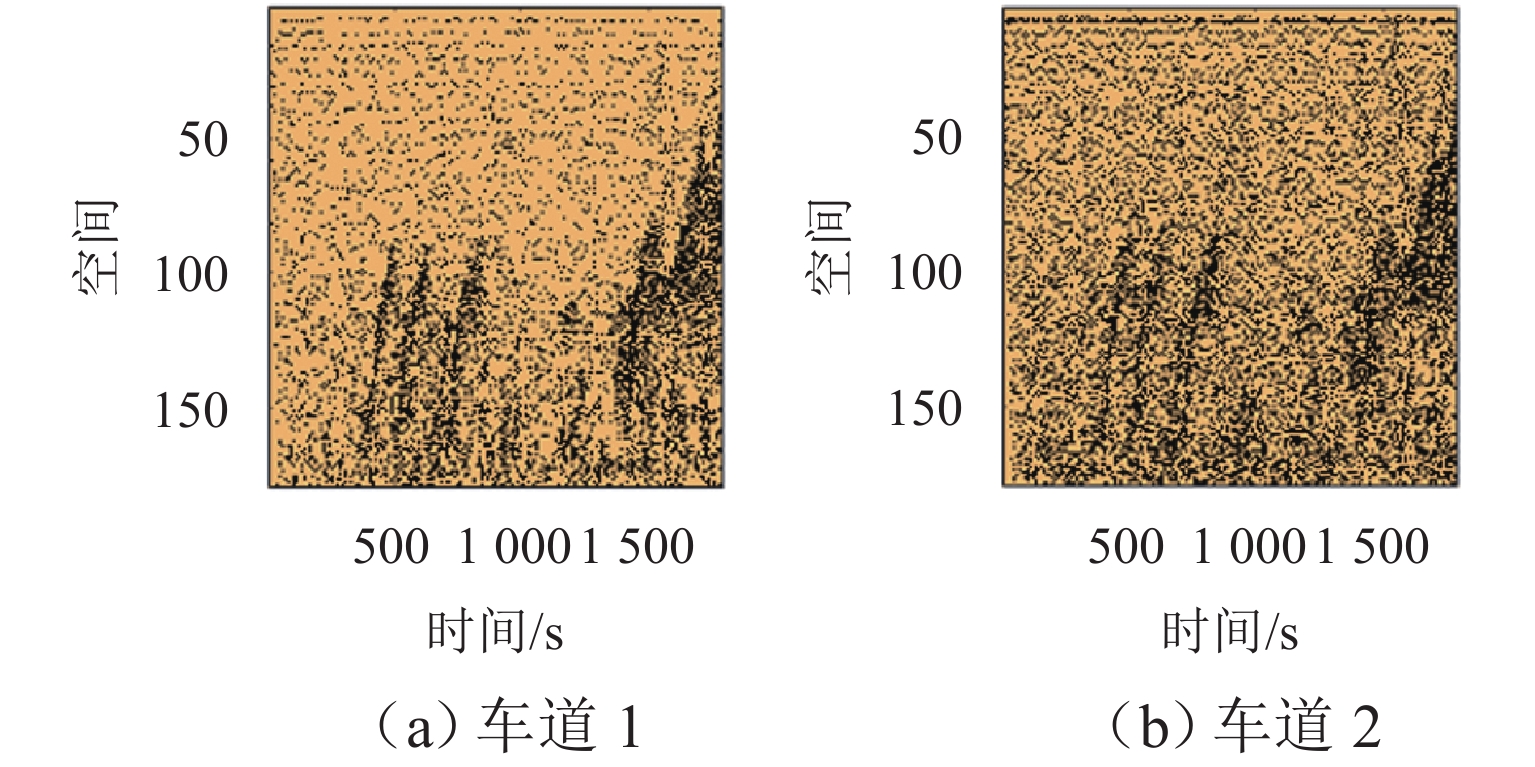
表 1 交通流时空图对比
Table 1. Spatio-temporal map of traffic flow
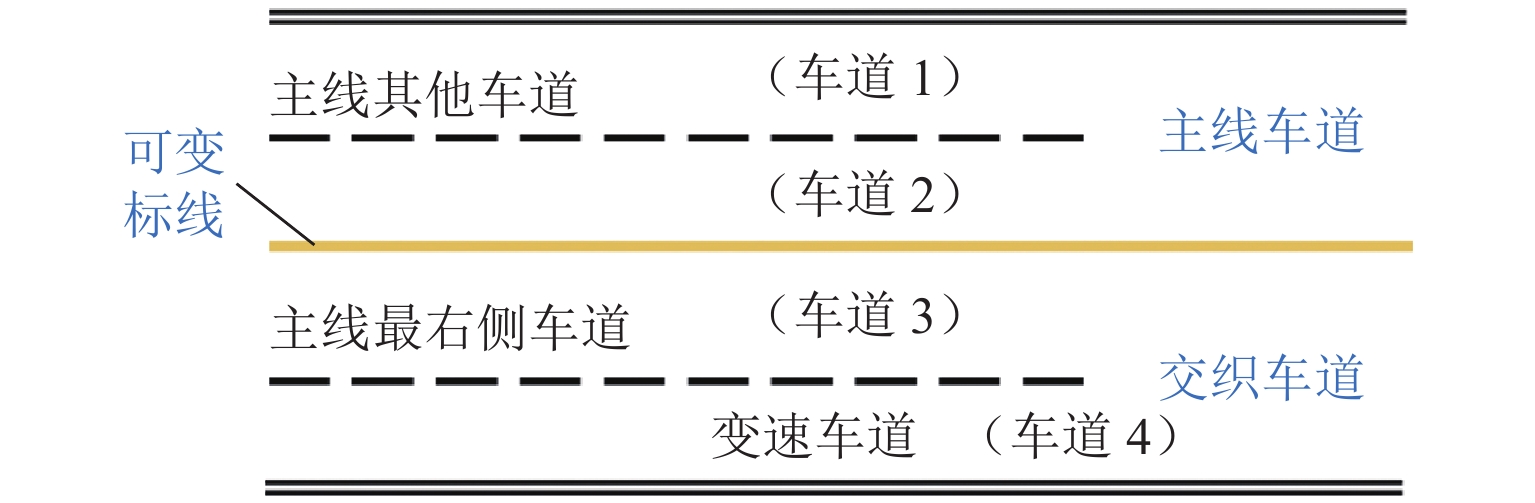
LC/m 标线类型 车道 1 车道 2 车道 3 车道 4 100 传统路面标线 ① ② ③ ④ 可变木标线 ⑤ ⑥ ⑦ ⑧ 500 传统路面标线 ⑨ ⑩ ⑪ ⑫ 可变木标线 ⑬ ⑭ ⑮ ⑯ 

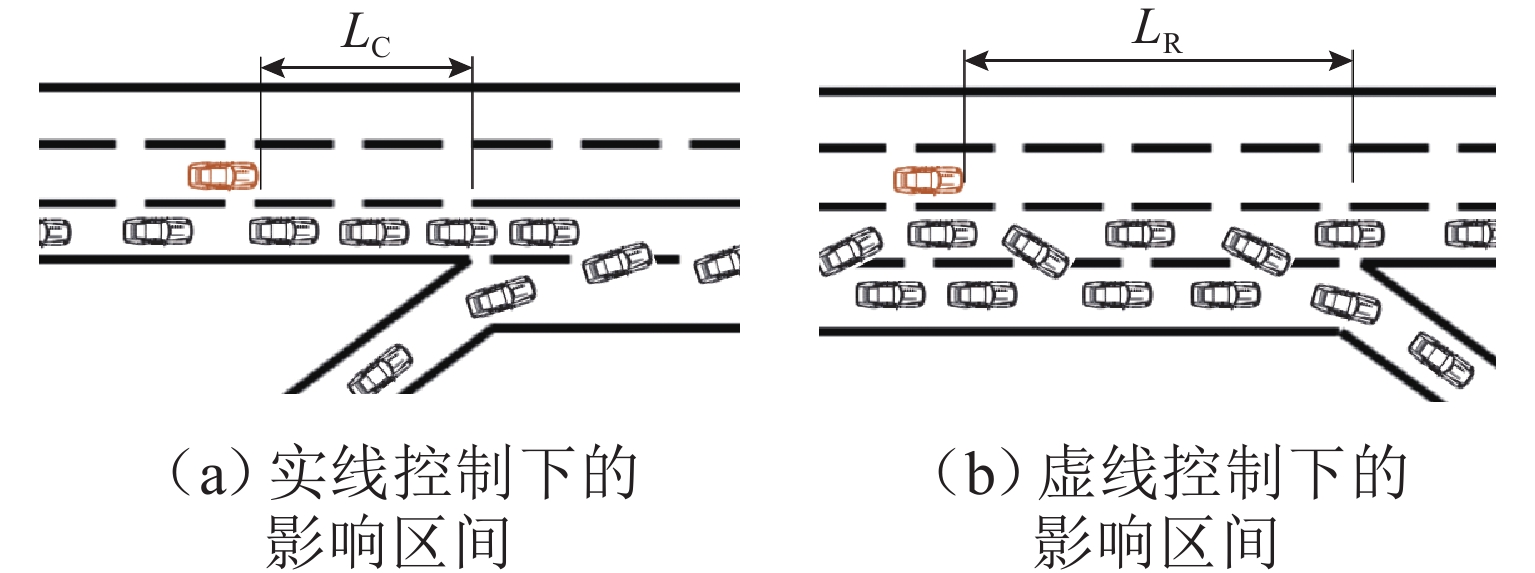
表 2 LR影响下的交通流时空图
Table 2. Spatio-temporal map of traffic flow under influence of LR
随机慢化概率 车道 1 车道 2 车道 3 车道 4 传统路面标线(0.3) ① ② ③ ④ 可变木标线(0.4) ⑤ ⑥ ⑦ ⑧ 传统路面标线(0.3) ⑨ ⑩ ⑪ ⑫ 可变木标线(0.4) ⑬ ⑭ ⑮ ⑯ 
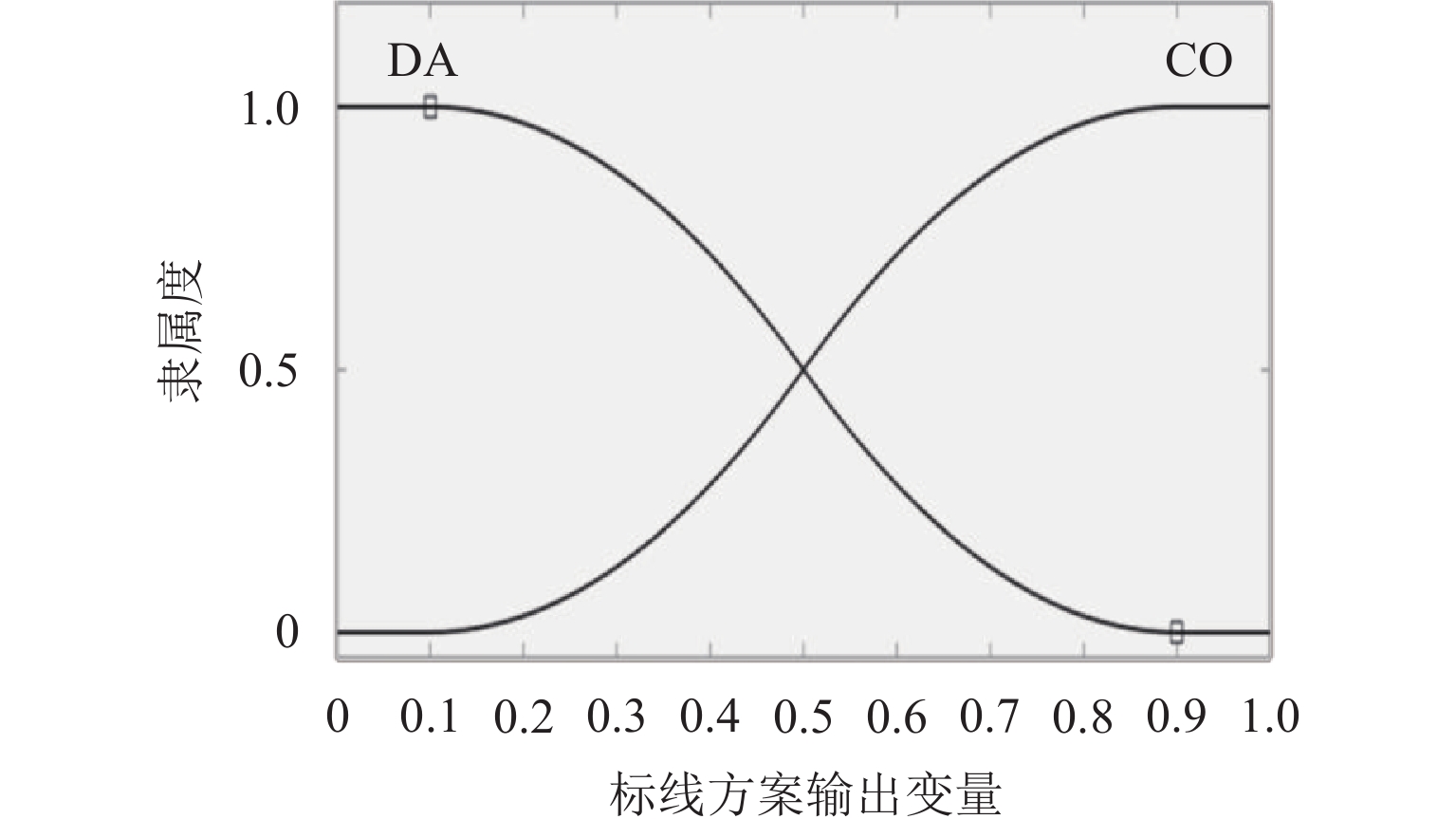
表 3 模糊变量$\beta_{\mathrm{express}} $赋值表
Table 3. Fuzzy variable $\beta_{\mathrm{express}} $ assignment
$ \beta_{\mathrm{express}} $ $ \beta_{\text{ramp}} $ US VS QS QL VL UL $ {p}_{{\mathrm{DR}}} $ US 1 1 1 0 0 0 VS 1 1 0/1/1/1/1 0 0 0 QS 1 1 0/1/0/1/0 0 0 0 QL 1 1 0 0 0 0 VL 1 1/0/0/1/0 0 0 0 0 UL 0/0/0/1/0 0 0 0 0 0 表 4 平均延误计算结果
Table 4. Average delay calculations
交通流类型 平均延误/s 可变标线干预 普通标线(实线) 现实交通流 12 18 设计交通流 48 71 表 5 现实交通流工况下冲突场景统计
Table 5. Conflict scenarios statistics for realistic traffic flow
标线类型 场景数量/个 危险 严重冲突 轻度冲突 可变标线干预 341 229 912 普通标线 445 341 771 表 6 设计交通流工况下冲突场景统计
Table 6. Conflict scenario statistics for designed traffic flow
标线类型 场景数量/个 危险 严重冲突 轻度冲突 可变标线干预 883 748 1 967 普通标线 775 992 2 094 表 7 现实交通流工况下污染物排放率
Table 7. Pollutant emission rates for r realistic traffic flow
标线类型 污染物排放率/(mg·s−1) CO HC NOx 可变标线干预 97.625 8 5.342 5 19.513 6 普通标线 105.698 4 6.220 6 22.301 1 表 8 设计交通流工况下污染物排放率
Table 8. Pollutant emission rates for designed traffic flow
标线类型 污染物排放率/(mg·s−1) CO HC NOx 可变标线干预 100.298 7 6.790 5 20.531 7 普通标线 117.117 0 7.012 2 24.910 5 -
[1] 谢济铭, 夏玉兰, 秦雅琴, 等. 基于双向长短期记忆网络的城市快速路合流区车速预测[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2024, 59(5): 1235-1244. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20220005XIE Jiming, XIA Yulan, QIN Yaqin, et al. Traffic speed prediction in merging zone of urban expressway based on bidirectional long short-term memory network[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2024, 59(5): 1235-1244. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20220005 [2] 季托, 周颖, 吕能超. 多车道高速公路分流交织区交通流特性与交通组织策略[J]. 交通信息与安全, 2021, 39(2): 126-136, 152. doi: 10.3963/j.jssn.1674-4861.2021.02.016JI Tuo, ZHOU Ying, LYU Nengchao. Traffic flow characteristics and traffic organization strategy in a diversion and interleaving area of multi-lane freeways[J]. Journal of Transport Information and Safety, 2021, 39(2): 126-136,152. doi: 10.3963/j.jssn.1674-4861.2021.02.016 [3] OUYANG P Y, WU J M, XU C C, et al. Traffic safety analysis of inter-tunnel weaving section with conflict prediction models[J]. Journal of Transportation Safety & Security, 2022, 14(4): 630-654. doi: 10.1080/19439962.2020.1801924 [4] 中华人民共和国公安部, 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 城市道路交通标志和标线设置规范: GB 51038-2015 [S]. 北京: 中国计划出版, 2015. [5] 李琛, 陈丰, 林子鉴, 等. 越江越海隧道入口处自发光标线应用效果[J]. 长安大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 44(2): 101-114. doi: 10.19721/j.cnki.1671-8879.2024.02.010LI Chen, CHEN Feng, LIN Zijian, et al. Application effect of self-luminous road markings at entrance of cross-river and cross-sea tunnel[J]. Journal of Chang’an University (Natural Science Edition), 2024, 44(2): 101-114. doi: 10.19721/j.cnki.1671-8879.2024.02.010 [6] HENRY K. Reducing road congestion with dynamic road marking[J]. Lighting Journal, 2004, 69(6): 34-38. [7] LENDERINK E, RAAIJMAKERS A. Dynamic road marking module using chip-on-board phosphor-converted white LEDs with application-specific primary optics[C]// Light Sources 2004 Proceedings of the 10th International Symposium on the Science and Technology of Light Sources, Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2004: 1-2. [8] LEE S, PARK W, JIN M, et al. Study on effects of dynamic road marking on reduction in drivers workload under rainy conditions[J]. International Journal of Highway Engineering, 2020, 22(3): 41-47. doi: 10.7855/IJHE.2020.22.3.041 [9] CAPATO S, COCONEA L, HELMREICH B, et al. Intelligent Road Marking Systems enabling future connected mobility[C]// Proceedings of the 25th ITS World Congress, Copenhagen: [s. n.], 2018: 2540962. [10] 李璜, 陈奕韬, 潘晓东, 等. 基于元胞自动机的地下停车场内自动导引运输车选址研究[J]. 交通与运输, 2022, 38(4): 37-42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3400.2022.04.009LI Huang, CHEN Yitao, PAN Xiaodong, et al. AGV parking area site selection based on cellular automata[J]. Traffic & Transportation, 2022, 38(4): 37-42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3400.2022.04.009 [11] 李珣, 程硕, 吴丹丹, 等. 车路协同下基于元胞自动机的精细交通流模型[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2025, 60(01): 225-232. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20220830LI Xun, CHENG Shuo, WU Dandan, et al. Refined traffic flow model based on cellular automaton under cooperative vehicle infrastructure system[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2025, 60(01): 225-232. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20220830 [12] 赵超, 谢天, 辛国容, 等. 基于Seq2Seq自编码器模型的交通事故实时检测与评价[J]. 控制与决策, 2022, 37(8): 2141-2148. doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2020.1742ZHAO Chao, XIE Tian, XIN Guorong, et al. Real-time traffic accident detection and evaluation based on Seq2Seq and autoencode model[J]. Control and Decision, 2022, 37(8): 2141-2148. doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2020.1742 [13] 战勇斌. 基于换道需求的快速路交织区可变限速与匝道协同控制策略研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2022. [14] 侯宁昊. 考虑混合交通流货车占比的城市快速路事故预测方法[D]. 武汉: 武汉理工大学, 2022. [15] 朱俊杰. 基于元胞自动机的高速公路车辆协同控制建模研究[D]. 广州: 广东工业大学, 2024 [16] 陈永恒, 杨绥程, 李世豪, 等. 基于元胞自动机的城市快速路长距离交织区运行仿真[J]. 浙江大学学报(工学版), 2024, 58(12): 2575-2585. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-973X.2024.12.017CHEN Yongheng, YANG Suicheng, LI Shihao, et al. Operation simulation of urban expressway long-distance interweaving zones based on cellular automata[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University(Engineering Science), 2024, 58(12): 2575-2585. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-973X.2024.12.017 [17] 屠强, 郑中义, 靳彪. 基于元胞自动机的航道交通流仿真[J]. 合肥工业大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 46(3): 364-370. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-5060.2023.03.013TU Qiang, ZHENG Zhongyi, QI Biao. Simulation of traffic flow in channel based on cellular automaton[J]. Journal of Hefei Jiaotong University of Technology (Natural Science), 2023, 46(3): 364-370. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-5060.2023.03.013 [18] 刘克毅. 考虑驾驶风格的异质交通流元胞自动机模型研究[D]. 长春: 吉林建筑大学, 2024. [19] 裴玉龙, 李馨. 基于动态强制清空及协同换道策略的BLIP设置[J]. 长安大学学报(自然科学版), 2025, 45(1): 125-137 doi: 10.19721/j.cnki.1671-8879.2025.01.011PEI Yulong, LI Xi. BLIP setting based on dynamic forced clearance and cooperative lane change strategy[J]. Journal of Chang’an University (Natural Science Edition), 2025, 45(1): 125-137 doi: 10.19721/j.cnki.1671-8879.2025.01.011 [20] 徐婷, 邓恺龙, 刘永涛, 等. 基于航测数据的不同风格换道轨迹规划[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2024, 59(3): 720-728. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20230392XU Ting, Deng Kailong, Liu Yongtao, et al. Different styles of lane changing trajectory planning based on aerial survey data[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2024, 59(3): 720-728 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20230392 [21] 叶颖俊, 孙剑. 快速路汇入区瓶颈交通流早发性失效研究(第1部分): 建模仿真[J]. 中国公路学报, 2023, 36(8): 240-256. doi: 10.19721/j.cnki.1001-7372.2023.08.022YE Yingjun, SUN Jian. Early-onset breakdown of bottleneck traffic at expressway merging area, part 1: modeling and simulation[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2023, 36(8): 240-256. doi: 10.19721/j.cnki.1001-7372.2023.08.022 [22] 张方方, 王长君, 王俊骅. 城市快速路匝道合流区车辆交互行为模式[J]. 中国公路学报, 2022, 35(9): 66-79. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2022.09.006ZHANG Fangfang, WANG Changjun, WANG Junhua. Vehicle interaction patterns at on-ramp merging area of urban expressway[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2022, 35(9): 66-79. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2022.09.006 [23] Palacios J, Luis J. Understanding and quantifying motor vehicle emissions with vehicle specific power and TILDAS remote sensing[J]. Massachusetts Institute Of Technology, 1999: 345-361. [24] 宋国华, 于雷. 城市快速路上机动车比功率分布特性与模型[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2010, 10(6): 133-140. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6744.2010.06.020SONG Guohua, YU Lei. Distribution characteristics and models of vehicle specific power on urban expressways[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2010, 10(6): 133-140. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6744.2010.06.020 [25] 郭栋, 赵韩涛, 高松, 等. 不同比功率分区下轻型车排放特征分析[J]. 武汉理工大学学报, 2013, 35(3): 84-87.GUO Dong, ZHAO Hantao, GAO Song, et al. Study on light-duty vehicle emission models based on different VSP bins[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology, 2013, 35(3): 84-87. -





 下载:
下载: