Prediction of Discrete Element Breakage Parameter for Ballast Particles Based on Genetic Algorithm-Back Propagation Neural Network Model
-
摘要:
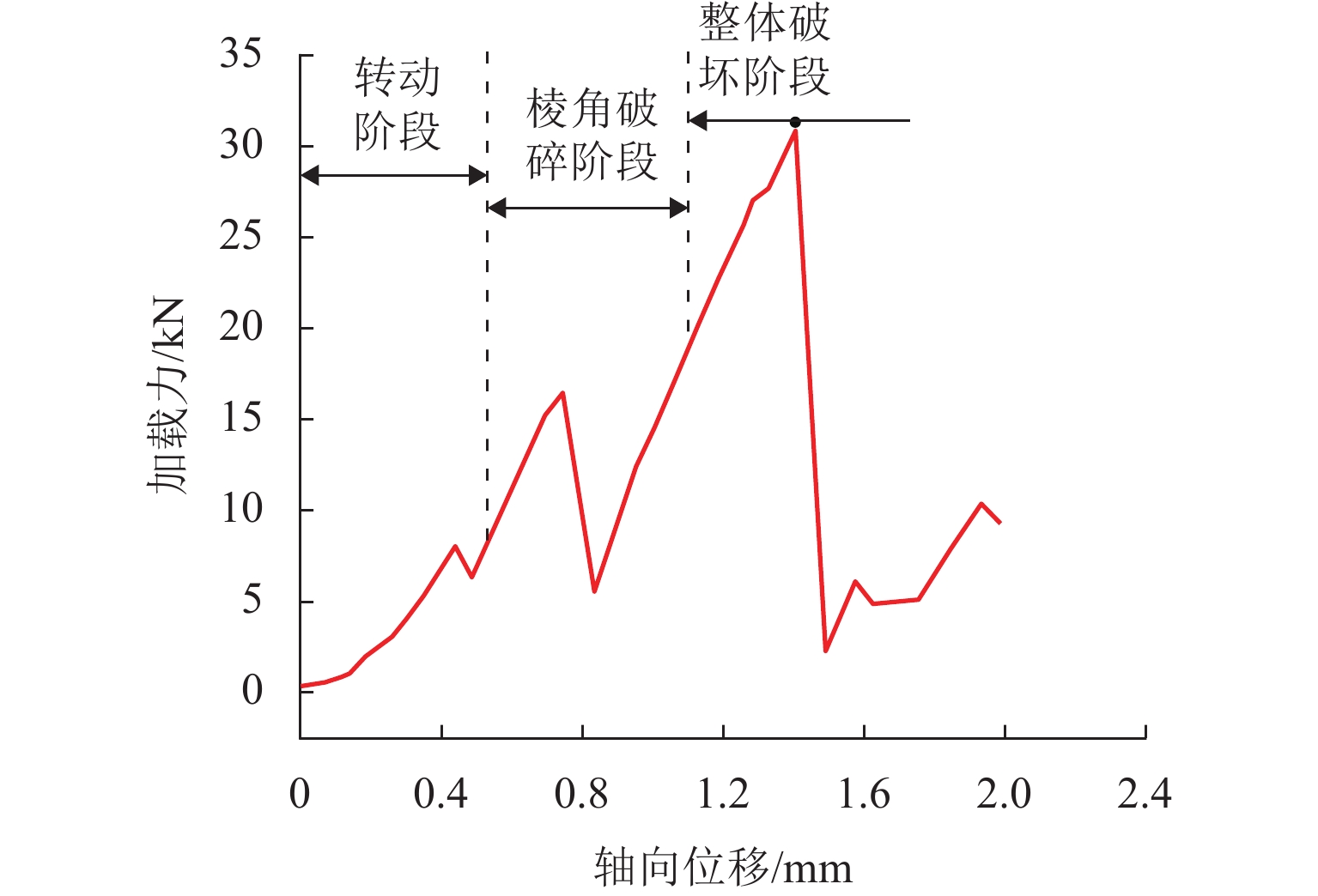
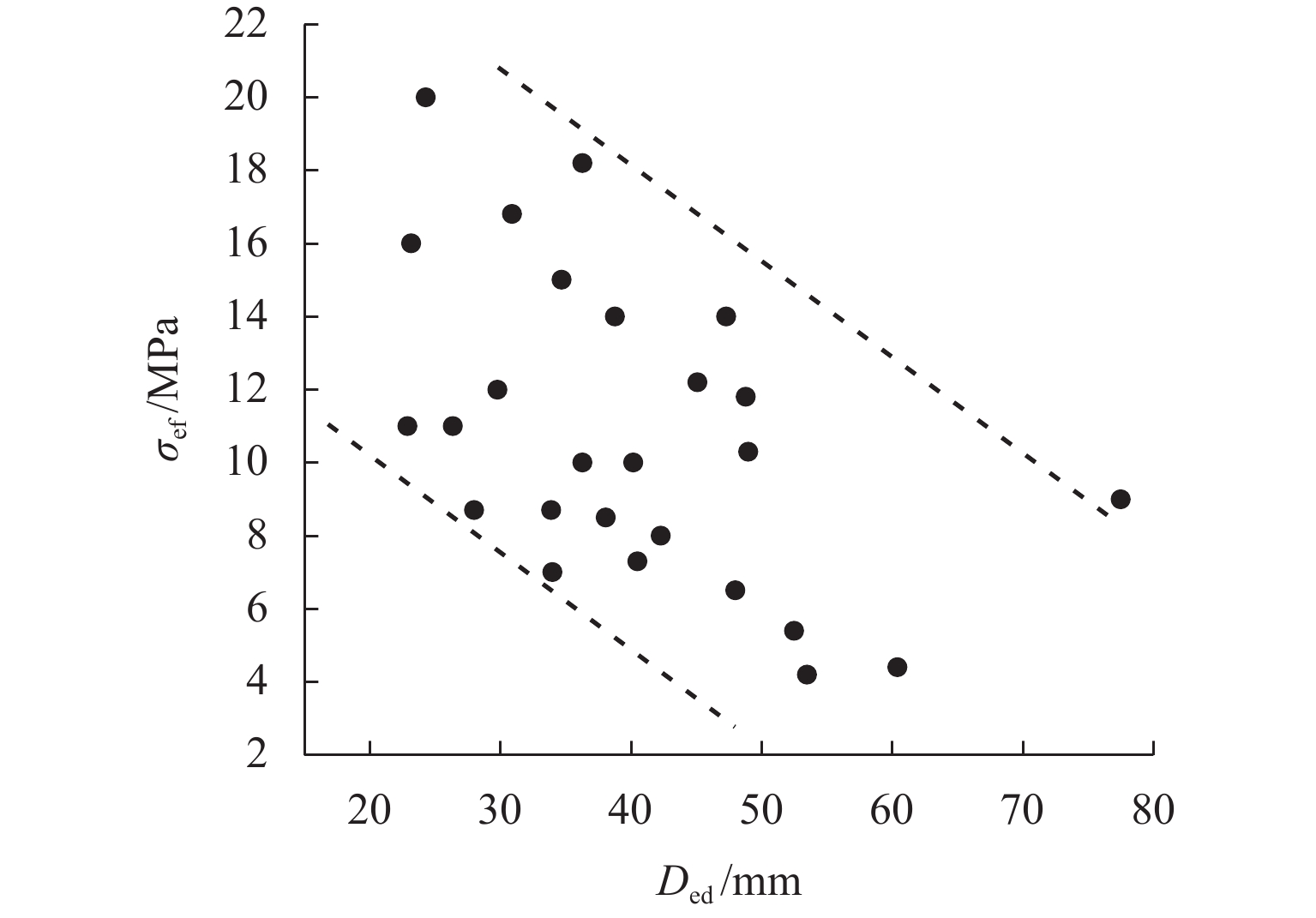
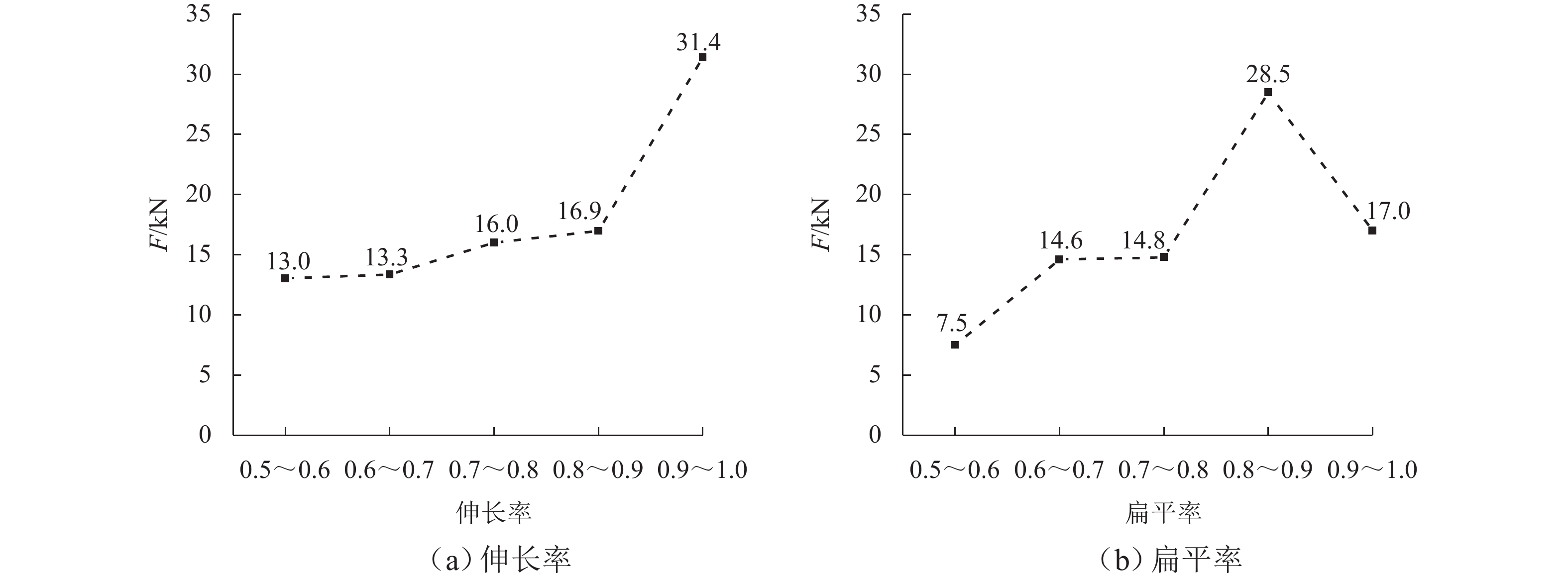
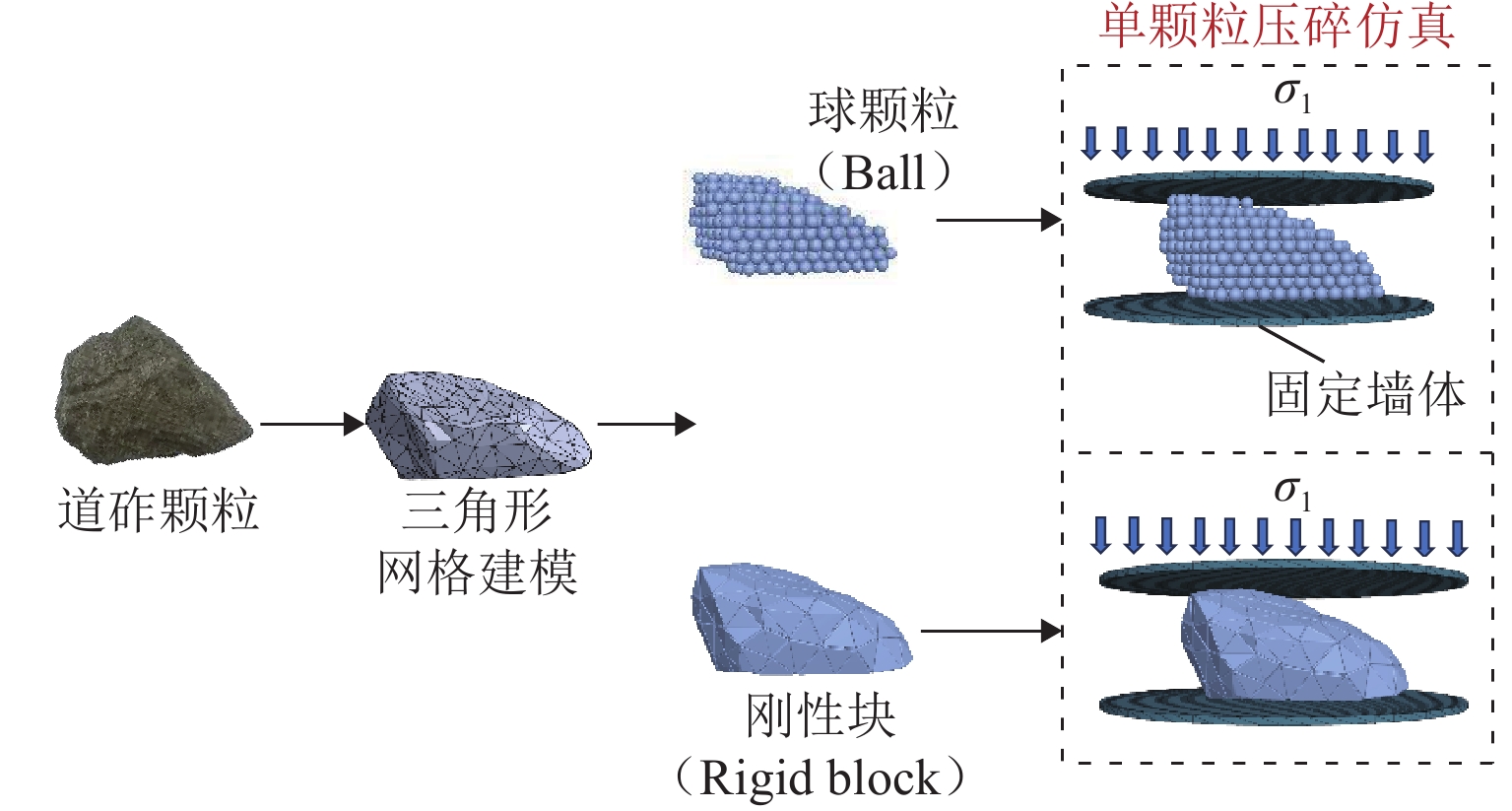
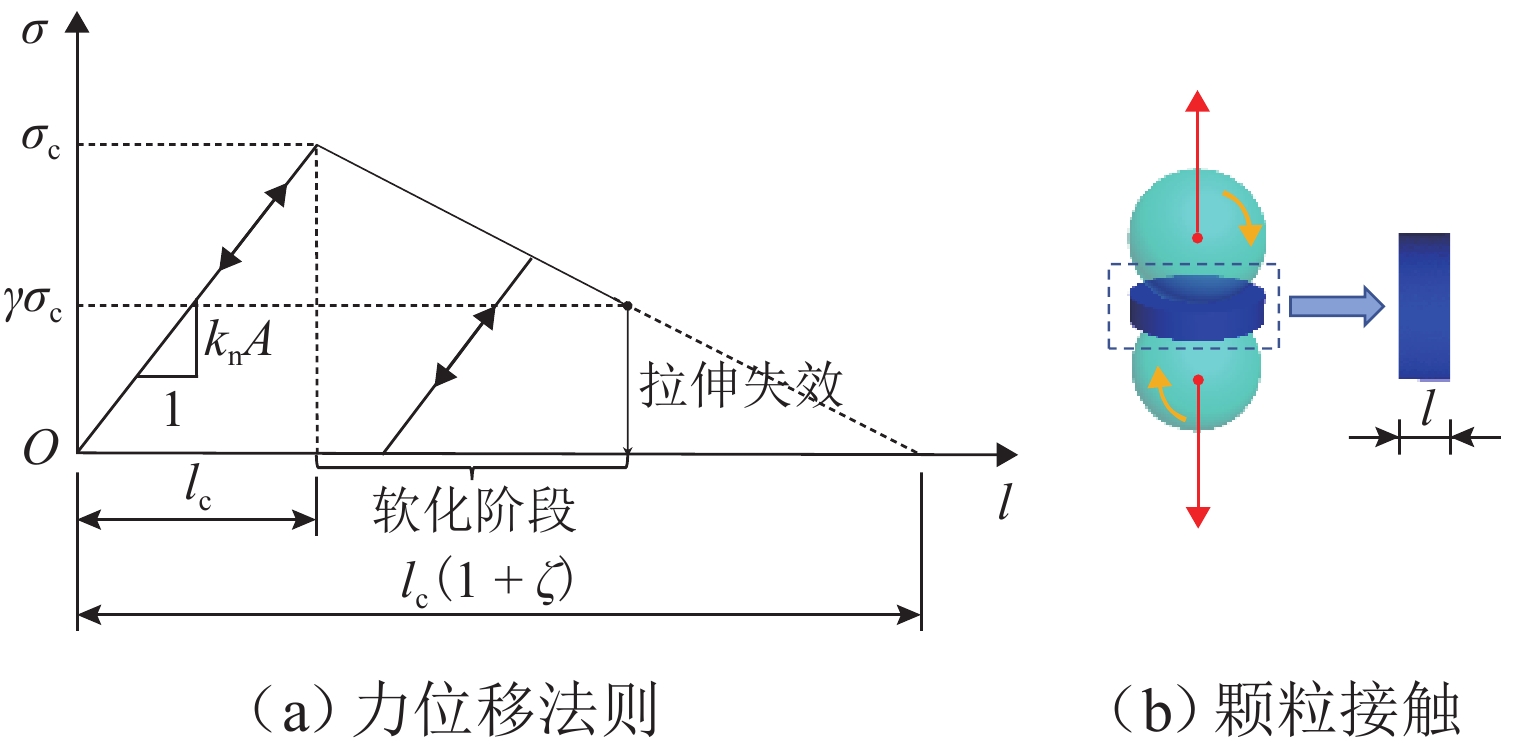
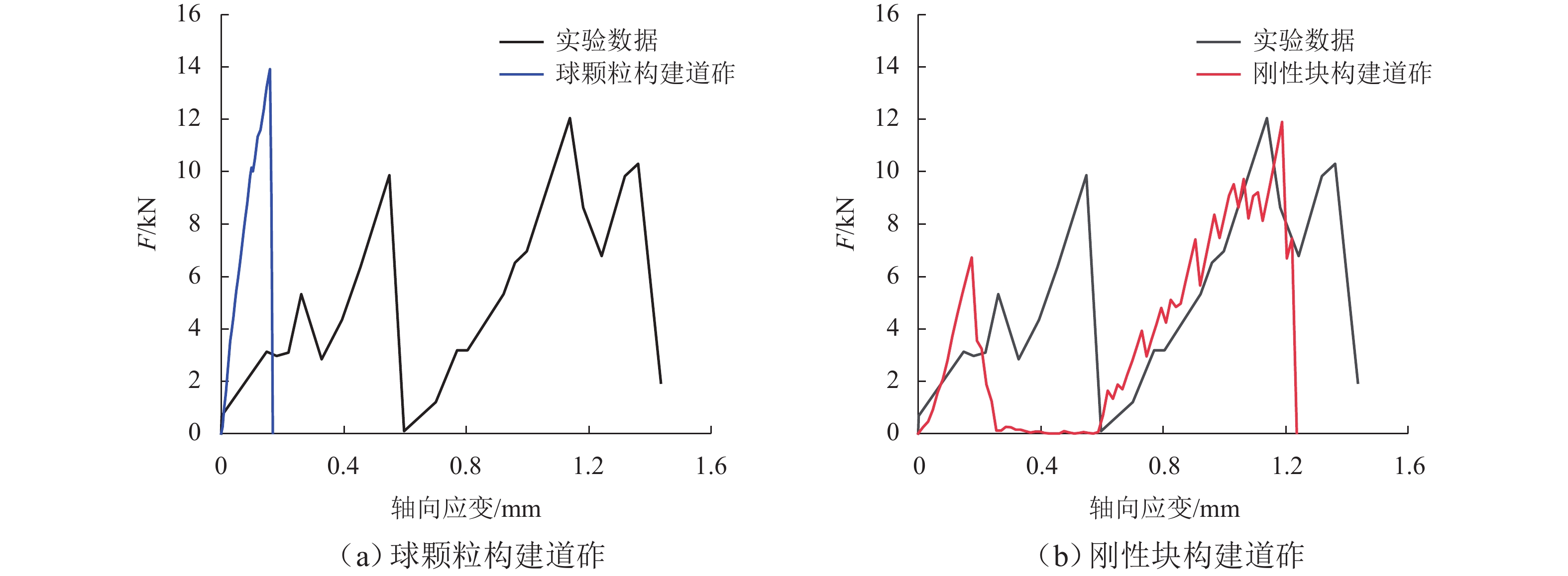
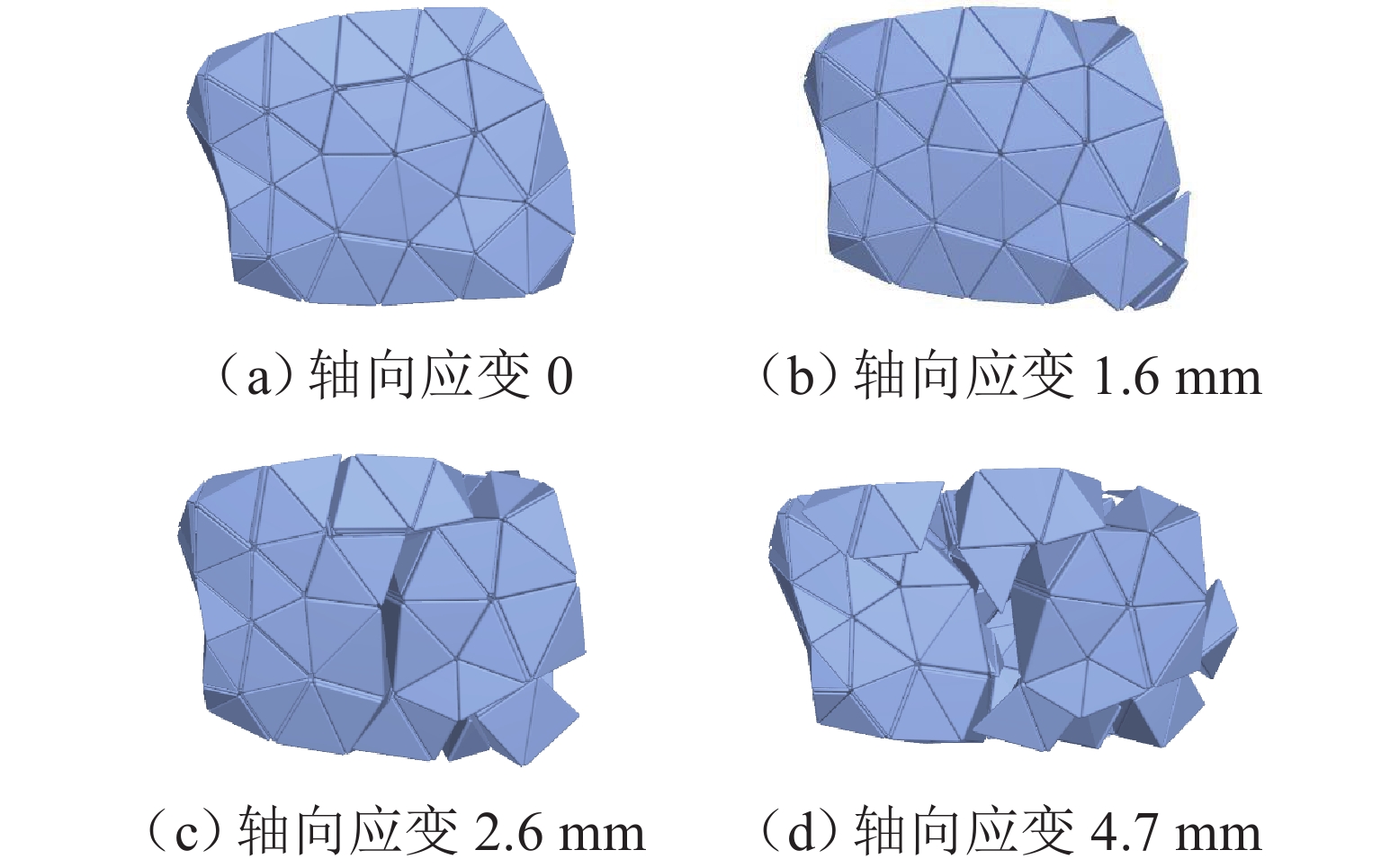
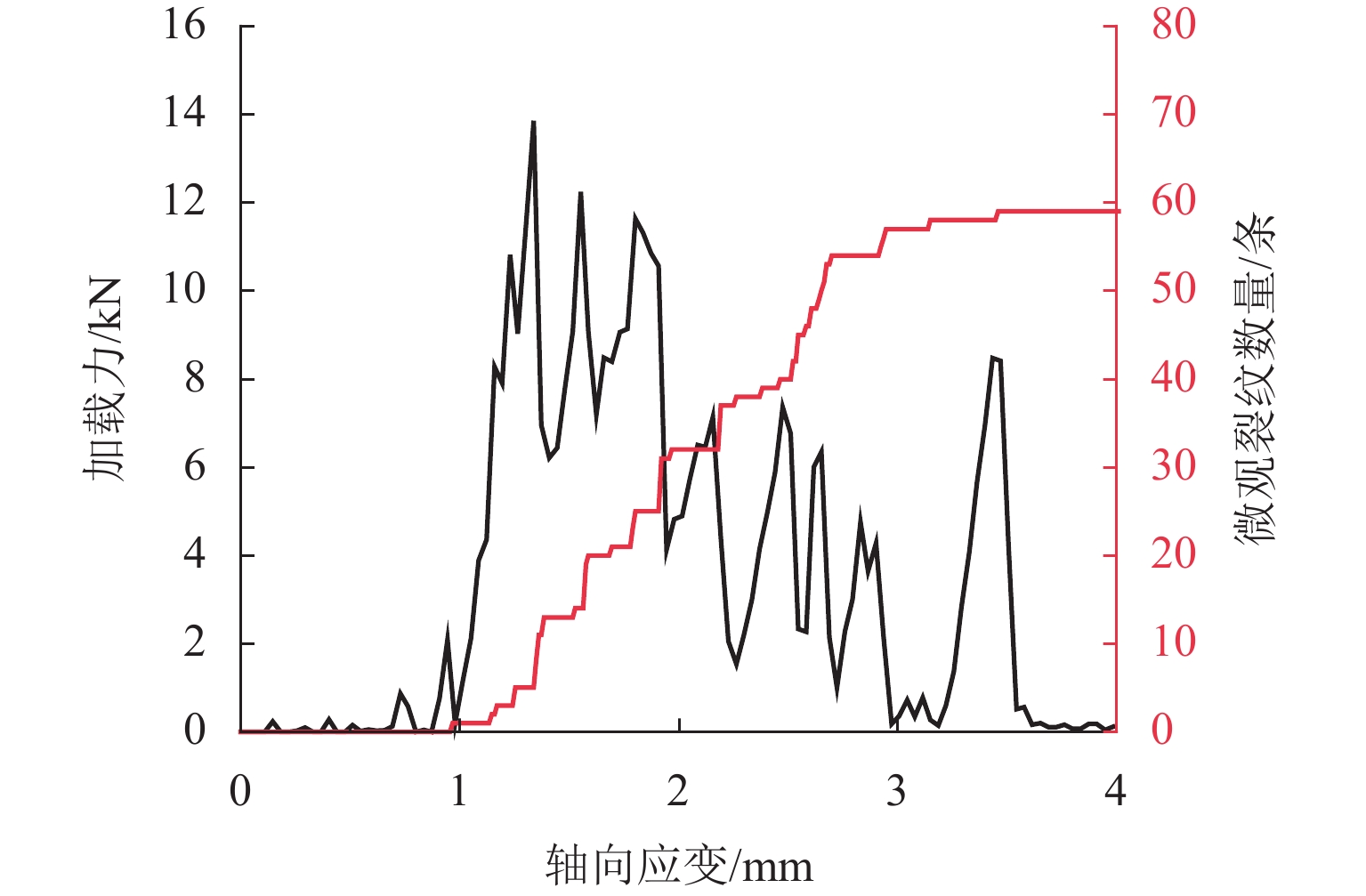
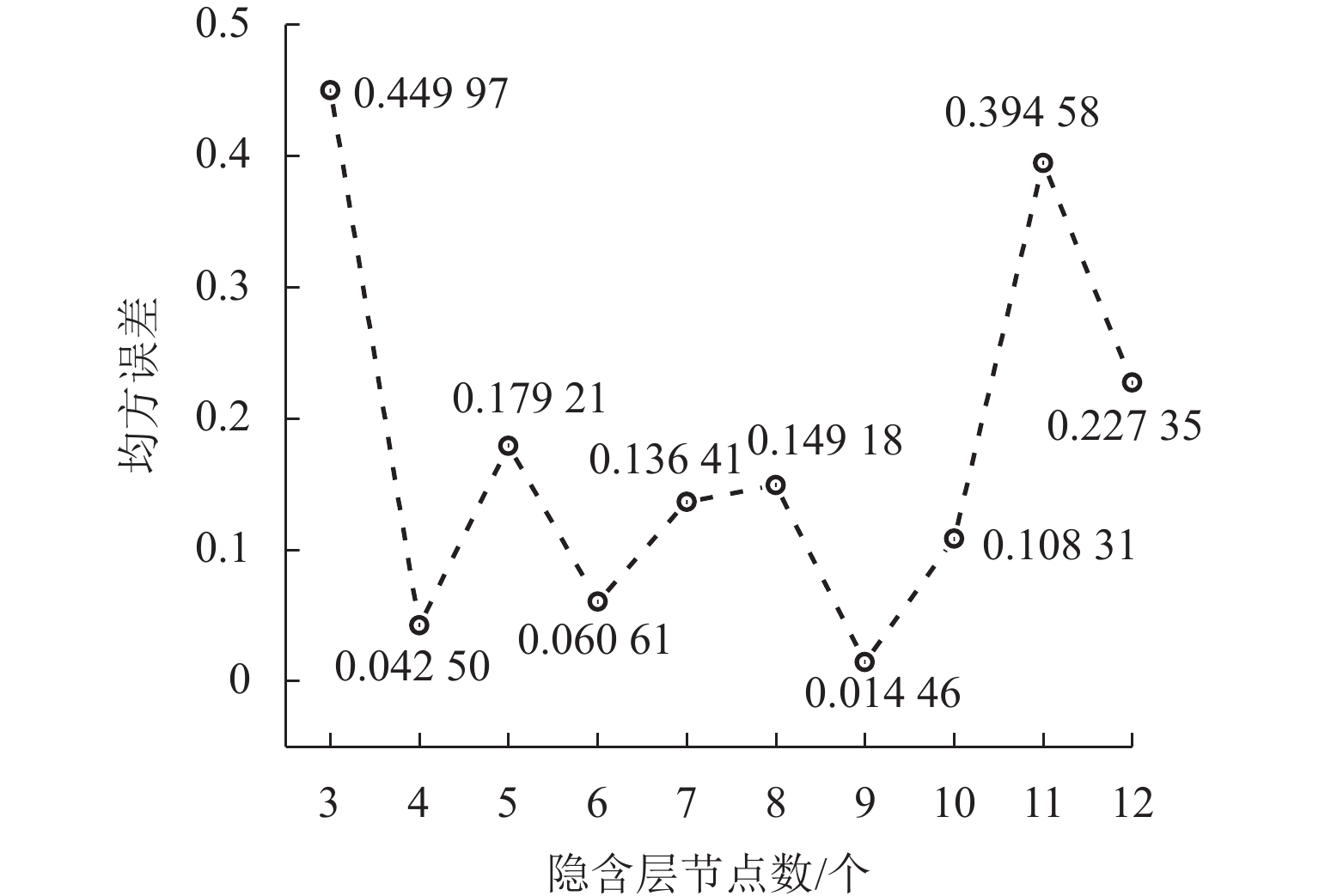
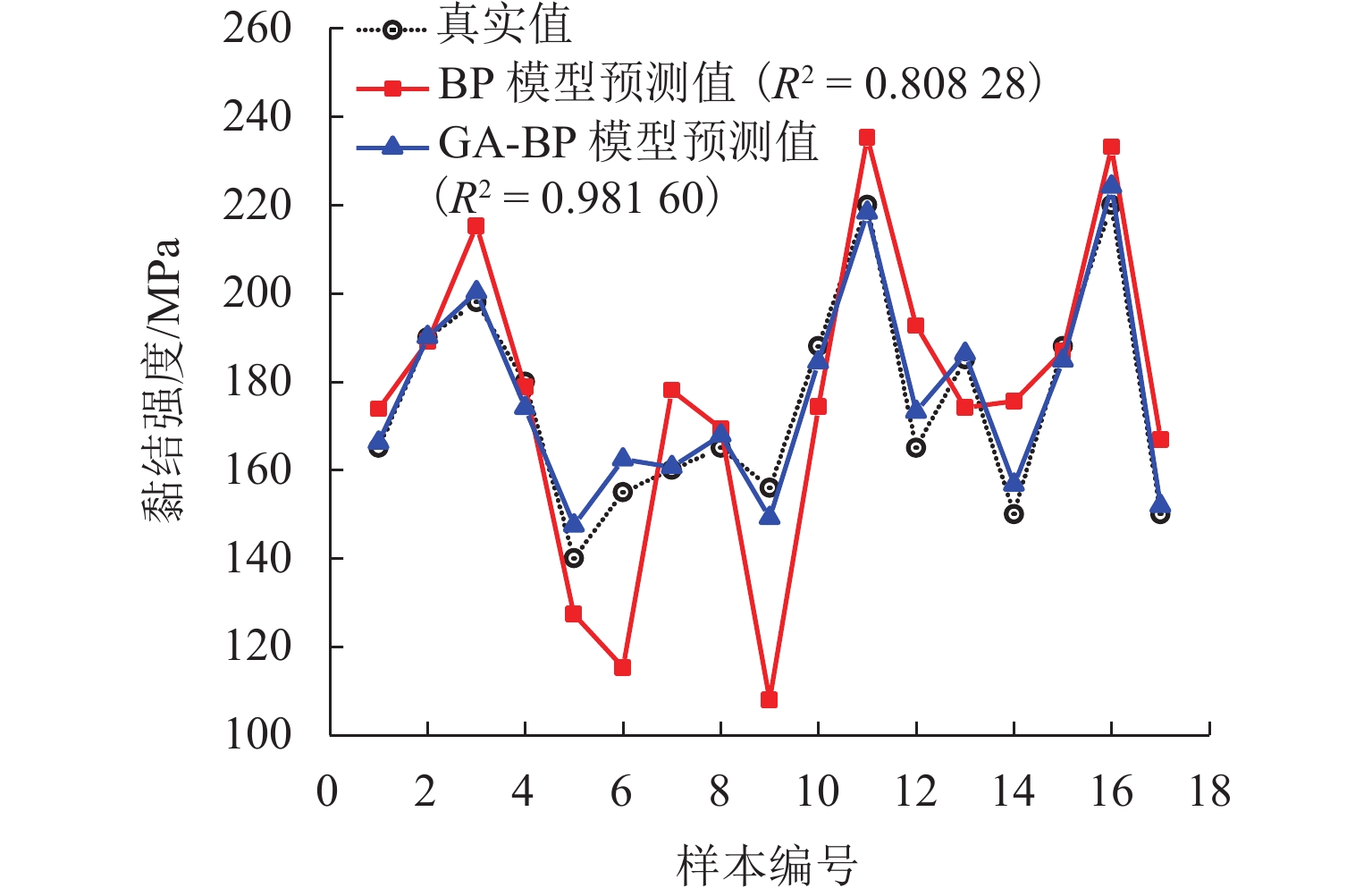
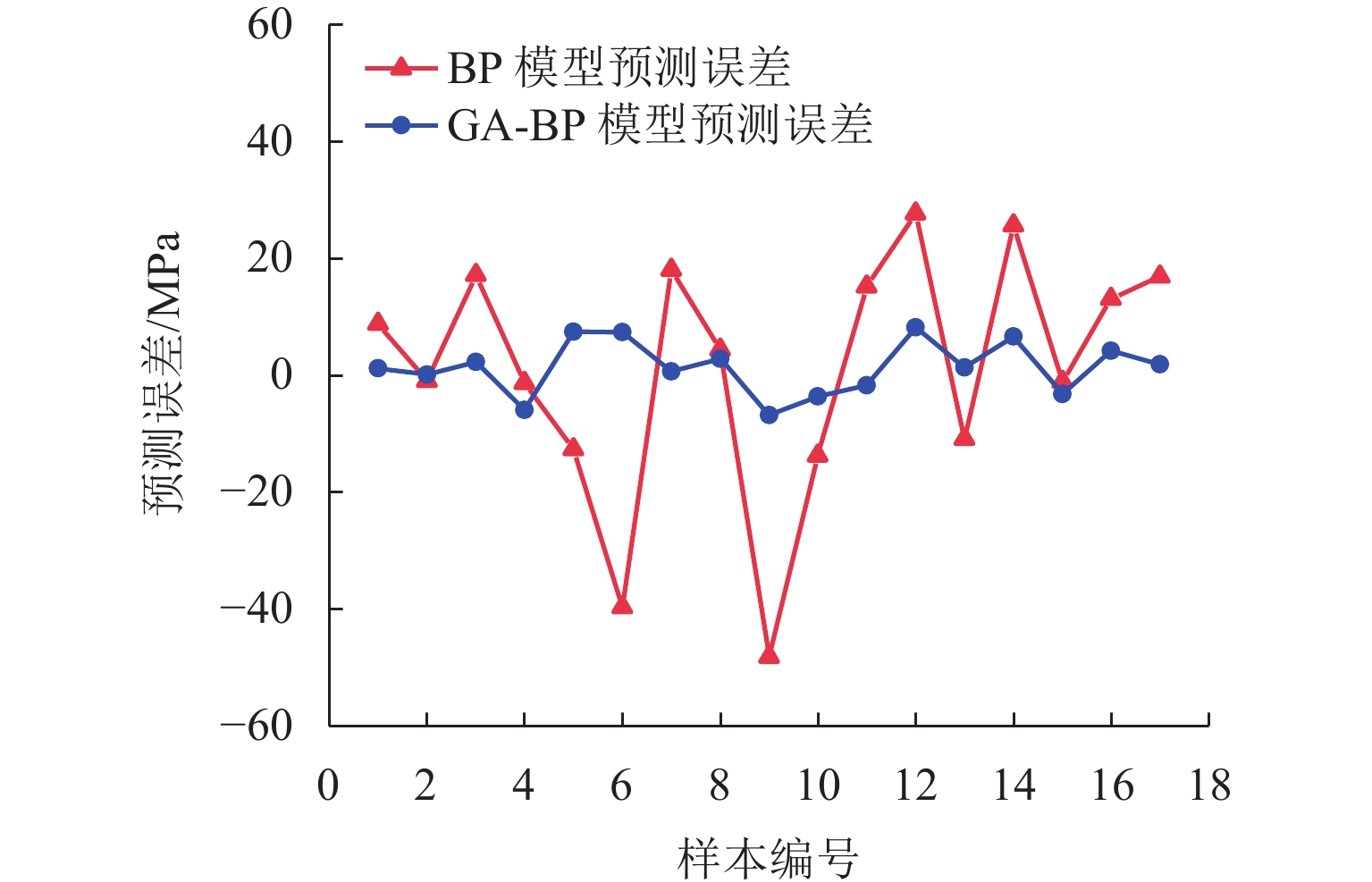
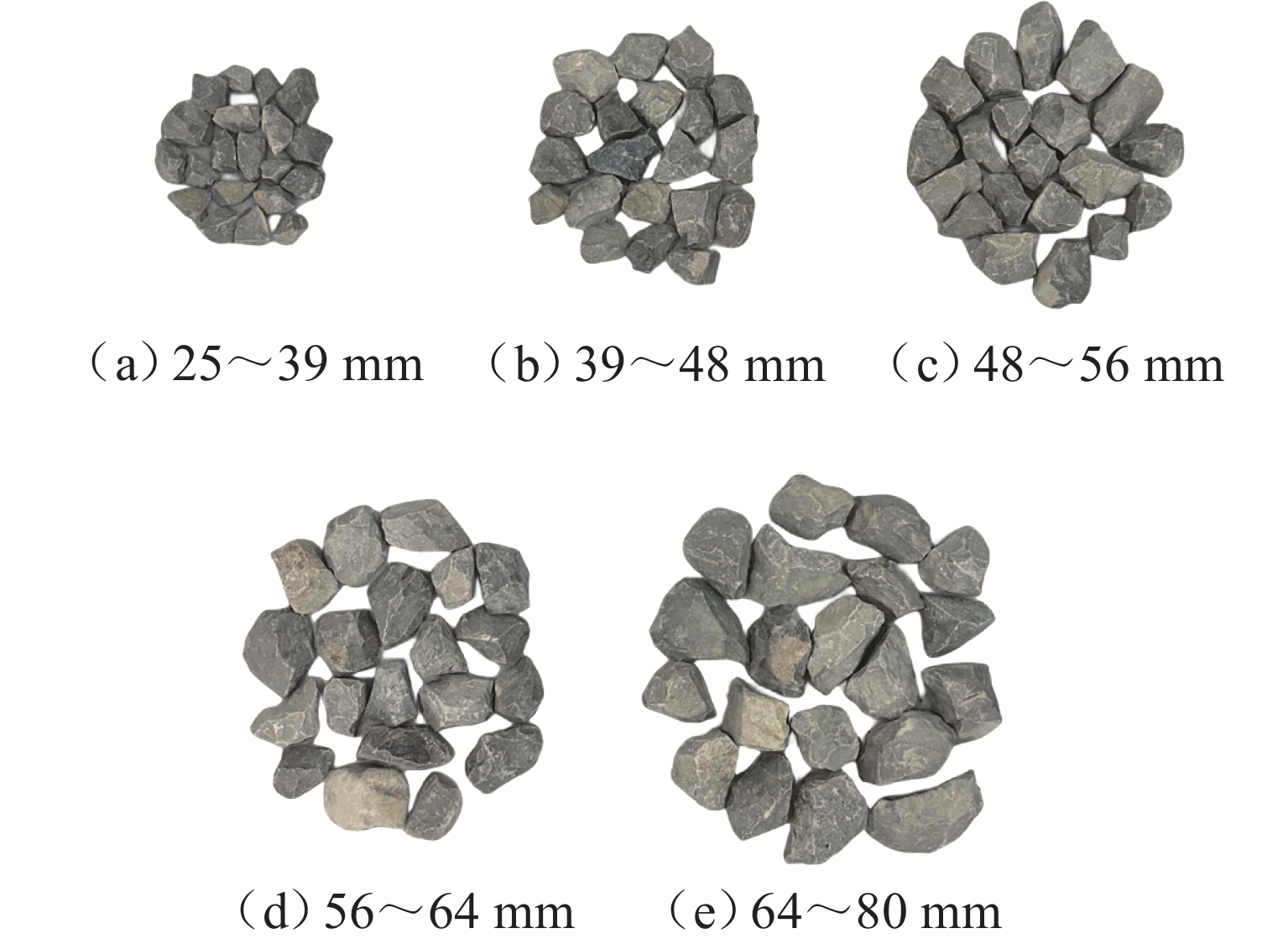
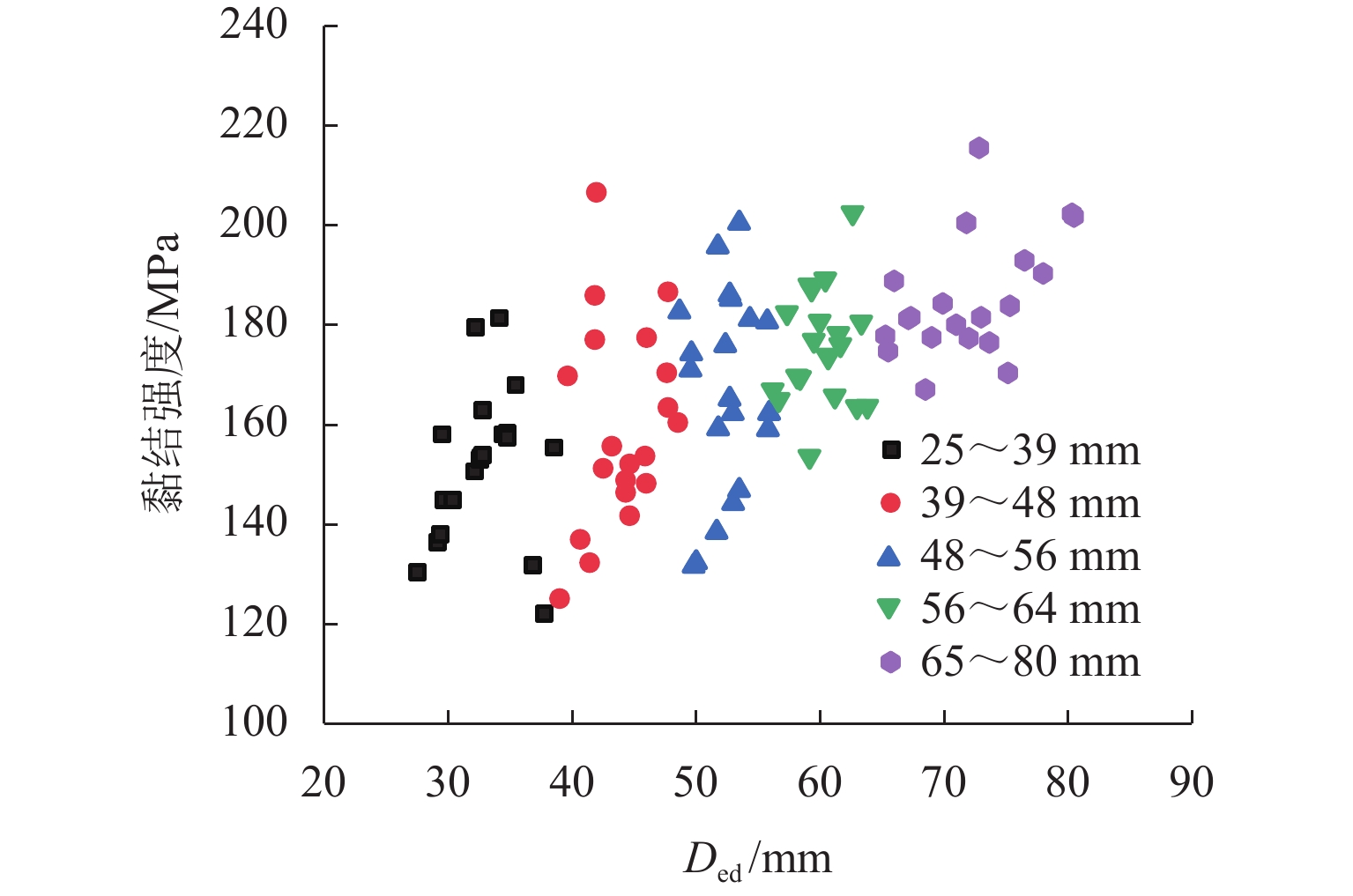
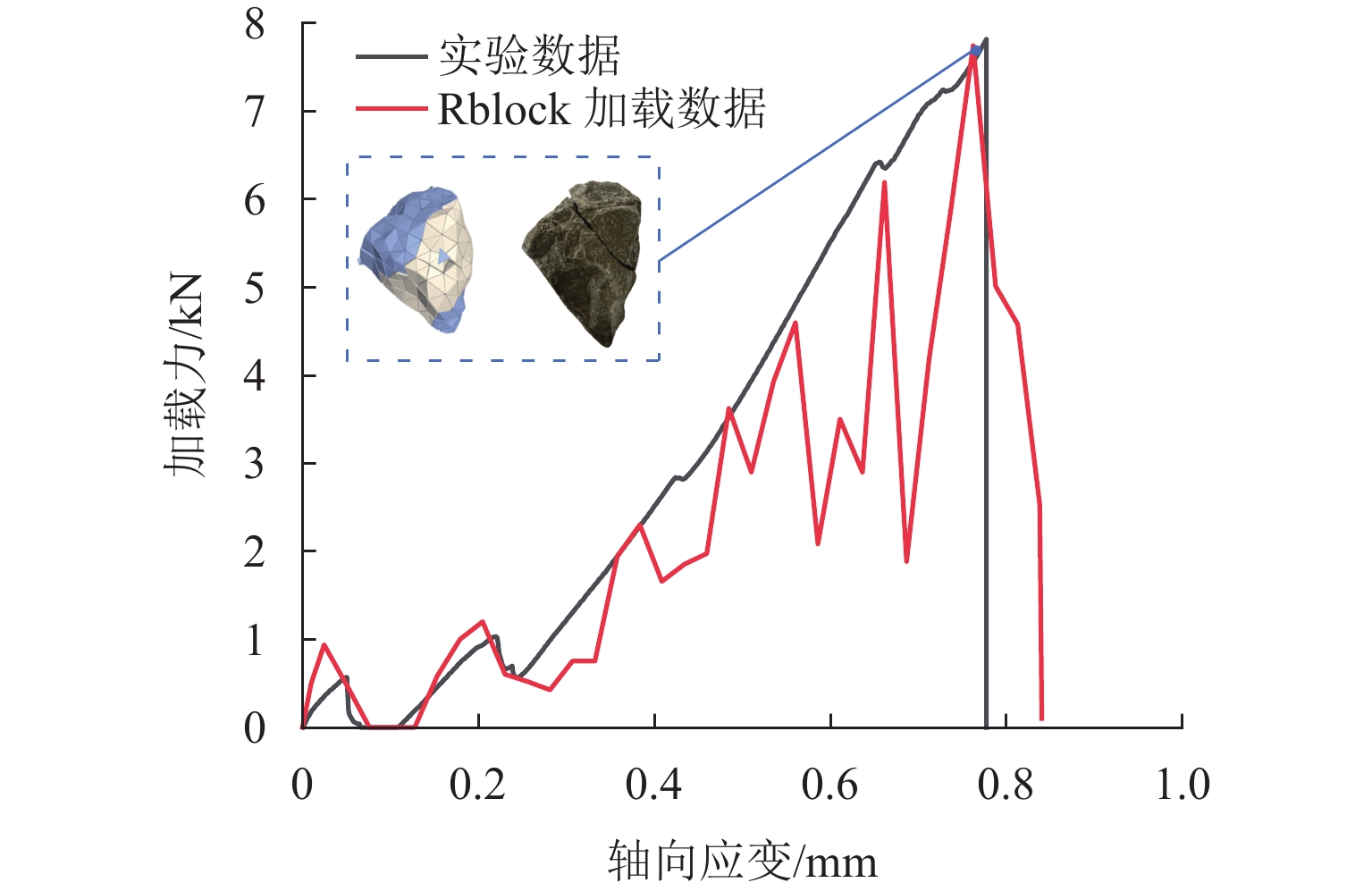
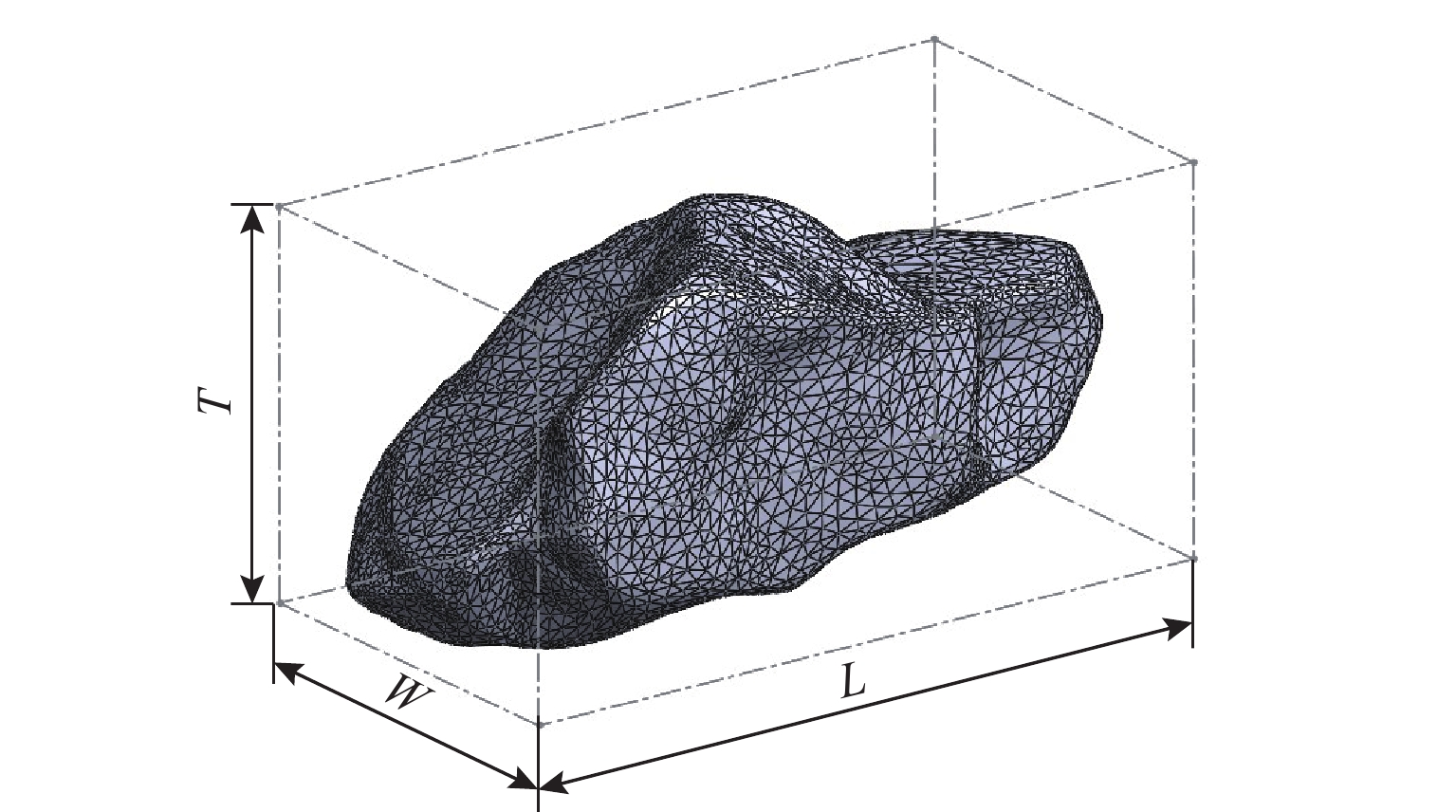
为优化有砟道床的劣化评估与养护维修,针对道砟颗粒破碎过程及破碎机理的研究具有重要价值. 通过对单个道砟颗粒进行单轴压碎实验,确定破坏所需的等效应力,依据道砟颗粒的破碎过程和加载力对其受载变形行为进行分析;通过激光光栅扫描道砟颗粒的几何外形,使用最小外接矩形法对其进行规定,同时,采用刚性块进行道砟颗粒填充,并与传统球颗粒填充方式作对比,分析了使用刚性块所构造道砟颗粒的破碎过程以及道砟颗粒内部微裂纹萌生情况;此外,研究不同几何外形道砟颗粒的离散元接触参数,采用遗传算法优化的神经网络模型(GA-BP)预测不同等效粒径道砟颗粒对应的黏结强度. 研究结果表明:在离散元中,道砟颗粒的黏结强度随着等效粒径的增加而增加, 当等效粒径为25~39、39~48、 48~56、56~64、64~80 mm时,对应的平均黏结强度分别为151.85、159.45、166.71、175.29、185.29 MPa.
Abstract:To optimize the deterioration assessment and maintenance of ballasted tracks, it is of great value to study the breakage process and mechanism of ballast particles. Through a uniaxial breakage test on the single ballast particle, the equivalent stress required for its failure was determined. The deformation behavior under load was analyzed based on the ballast particle breakage process and loading force. Laser grating scanning of the ballast particle geometry was performed, and a minimum bounding rectangle method was used for specification. Rigid blocks were used for ballast particle packing, and a comparison was made with the traditional spherical particle packing method. The breakage process of ballast particles constructed with rigid blocks and the initiation of microcracks within the ballast particles were analyzed. In addition, the discrete element contact parameters for ballast particles with different geometries were studied, and a neural network model optimized by a genetic algorithm, namely GA-BP was used to predict the bond strength for ballast particles with different equivalent particle sizes. The results show that in the discrete element model, the bond strength of the ballast particles increases with the increase in its equivalent particle sizes. Specifically, for equivalent particle sizes in the ranges of 25–39, 39–48, 48–56, 56–64, and 64–80 mm, the corresponding average bond strengths are 151.85, 159.45, 166.71, 175.29, and 185.29 MPa, respectively.
-
Key words:
- discrete element method /
- rigid block /
- neural network /
- bond strength /
- ballast particle breakage
-
表 1 道砟颗粒棱角特性仿真接触参数
Table 1. Simulation contact parameters for angular characteristics of ballast particle
微观参数 数值 杨氏模量/GPa 70 剪切刚度比 0.18 软化系数 1.0 软化阈值 0.8 摩擦系数 0.1 表 2 依据等效粒径分组的道砟颗粒黏结强度
Table 2. Bond strength of ballast particles grouped according to equivalent particle size
等效粒径
范围/mm黏结强度
范围/MPa黏结强度
均值/MPa25~39 130.37~155.34 151.85 39~48 132.22~186.58 159.45 48~56 138.58~195.69 166.71 56~64 164.99~202.46 175.29 64~80 177.84~201.76 185.29 -
[1] 张徐, 赵春发, 翟婉明. 铁路碎石道砟静态压碎行为数值模拟[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2015, 50(1): 137-143. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2015.01.020ZHANG Xu, ZHAO Chunfa, ZHAI Wanming. Numerical analysis of static crushed behavior of railway ballast[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2015, 50(1): 137-143. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2015.01.020 [2] YANG X, YU L Y, WANG X J, et al. Analysis of mesoscopic mechanical dynamic characteristics of ballast bed with under sleeper pads[J]. Railway Engineering Science, 2024, 32(1): 107-123. doi: 10.1007/s40534-023-00319-z [3] MCDOWELL G R, BOLTON M D. On the micromechanics of crushable aggregates[J]. Géotechnique, 1998, 48(5): 667-679. [4] INDRARATNA B, THAKUR P K, VINOD J S. Experimental and numerical study of railway ballast behavior under cyclic loading[J]. International Journal of Geomechanics, 2010, 10(4): 136-144. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)GM.1943-5622.0000055 [5] LIM W. Mechanics of railway baUast behaviour [D] . United Kingdom: University of Nottingham, 2004. [6] 严颖, 赵春发, 李勇俊, 等. 铁路道砟破碎特性的离散元分析[J]. 计算力学学报, 2017, 34(5): 615-622.YAN Ying, ZHAO Chunfa, LI Yongjun, et al. Discrete element analysis of breakage characteristics of railway ballast[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Mechanics, 2017, 34(5): 615-622. [7] XIAO J H, ZHANG X, ZHANG D, et al. Morphological reconstruction method of irregular shaped ballast particles and application in numerical simulation of ballasted track[J]. Transportation Geotechnics, 2020, 24: 100374.1-100374.12. [8] GUO Y L, MARKINE V, ZHANG X H, et al. Image analysis for morphology, rheology and degradation study of railway ballast: a review[J]. Transportation Geotechnics, 2019, 18: 173-211. doi: 10.1016/j.trgeo.2018.12.001 [9] POTYONDY D O, CUNDALL P A. A bonded-particle model for rock[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2004, 41(8): 1329-1364. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2004.09.011 [10] SIMPSON T W, BOOKER A J, GHOSH D, et al. Approximation methods in multidisciplinary analysis and optimization: a panel discussion[J]. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization, 2004, 27(5): 302-313. [11] 冯浩, 何鸿云, 米祖强. 基于改进遗传算法的递归神经网络非线性系统辨识[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2002, 37(4): 404-407. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2002.04.011FENG Hao, HE Hongyun, MI Zuqiang. Nonlinear system identification with recurrent neural network based on genetic algorithm[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2002, 37(4): 404-407. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2002.04.011 [12] REN J, XIAO M, LIU G. Rock Macro–Meso Parameter Calibration and Optimization Based on Improved BP Algorithm and Response Surface Method in PFC 3D[J]. Energies, 2022, 15(17): 6290.1-6290.26. [13] WANG H, ZHOU M. Finding minimum contain cuboid of polyhedron with genetic algorithm[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2004, 21(1): 32-34. [14] RUSSELL A R, MUIR WOOD D. Point load tests and strength measurements for brittle spheres[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2009, 46(2): 272-280. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2008.04.004 [15] SCHOLT\`ES L, DONZ\'E F V. A DEM model for soft and hard rocks: role of grain interlocking on strength[J]. Journal of Mechanics Physics of Solids, 2013, 61(2): 352-369. doi: 10.1016/j.jmps.2012.10.005 [16] ZINGG T. Beitrag zur schotteranalyse[D]. Zürich: ETH Zurich, 1935. [17] LU R, LUO Q, WANG T F, et al. Comparison of clumps and rigid blocks in three-dimensional DEM simulations: curvature-based shape characterization[J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2022, 151: 104991.1-104991.13. [18] 赵正佳, 黄洪钟, 陈新. 优化设计求解的遗传神经网络新算法研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2000, 35(1): 65-68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2000.01.016ZHAO Zhengjia, HUANG Hongzhong, CHEN Xin. A genetic neural network algorithm in optimum design[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2000, 35(1): 65-68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2000.01.016 [19] 张相文, 范晨光, 何安, 等. 基于GA-BP神经网络对控制棒水力缓冲器的性能预测和结构参数优化[J]. 核动力工程, 2023, 44(6): 162-169.ZHANG Xiangwen, FAN Chenguang, HE An, et al. Performance prediction and structural parameter optimization of control rod hydraulic buffer based on GA-BP neural network[J]. Nuclear Power Engineering, 2023, 44(6): 162-169. -




 下载:
下载: