Magnetic Force Characteristics Between On-Board Permanent Magnet and Permanent Magnetic Rail Considering Five Pose Parameters
-
摘要:
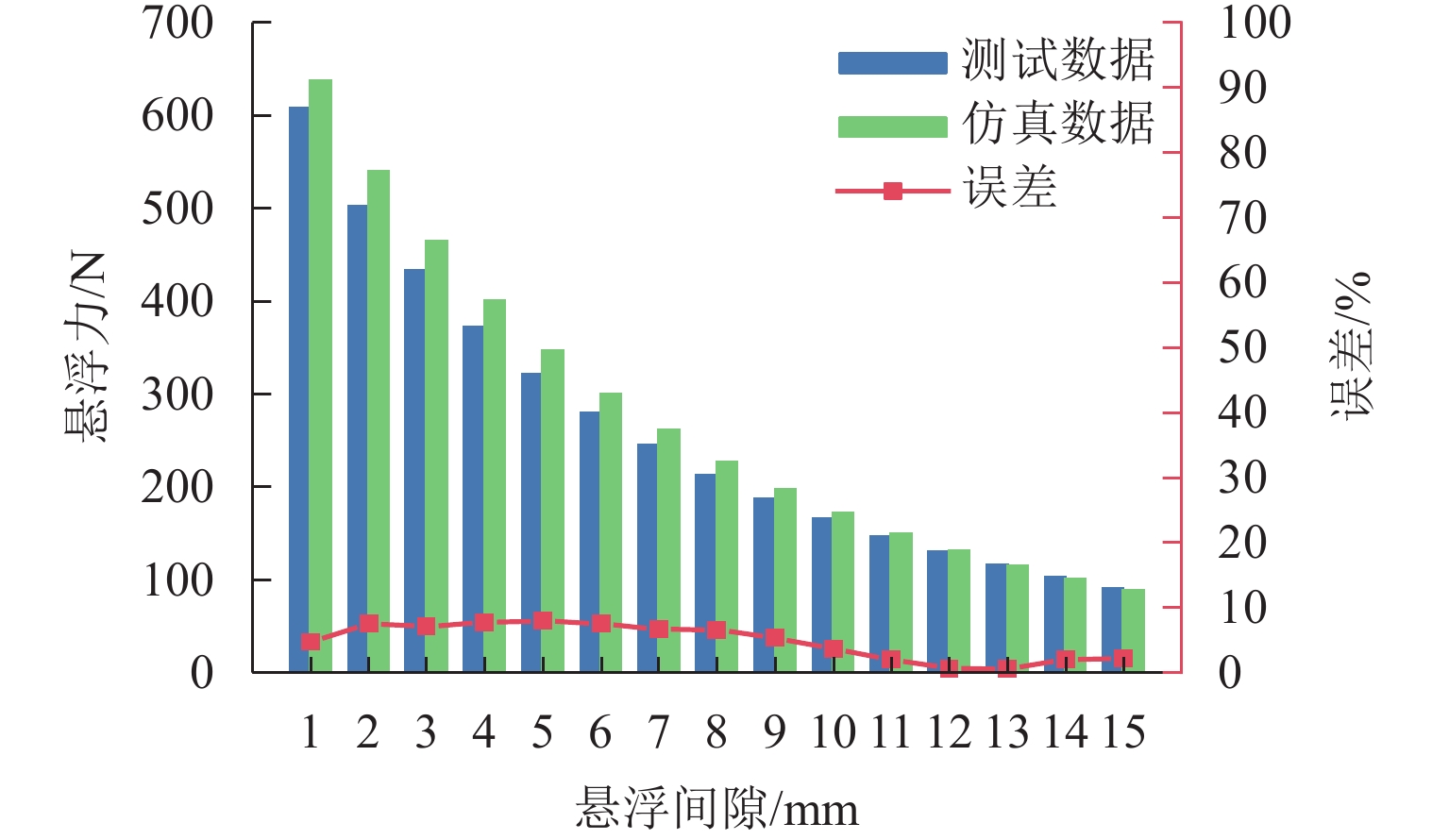
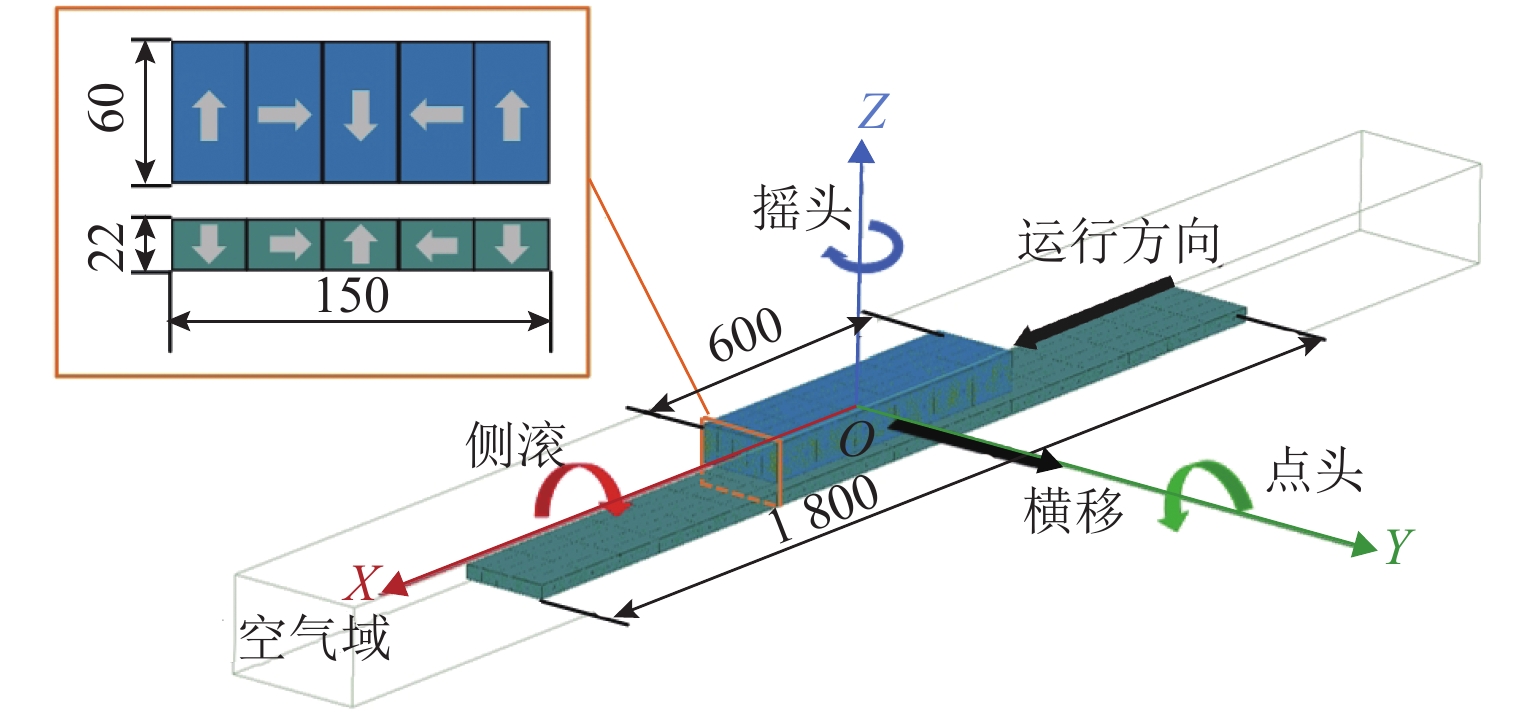
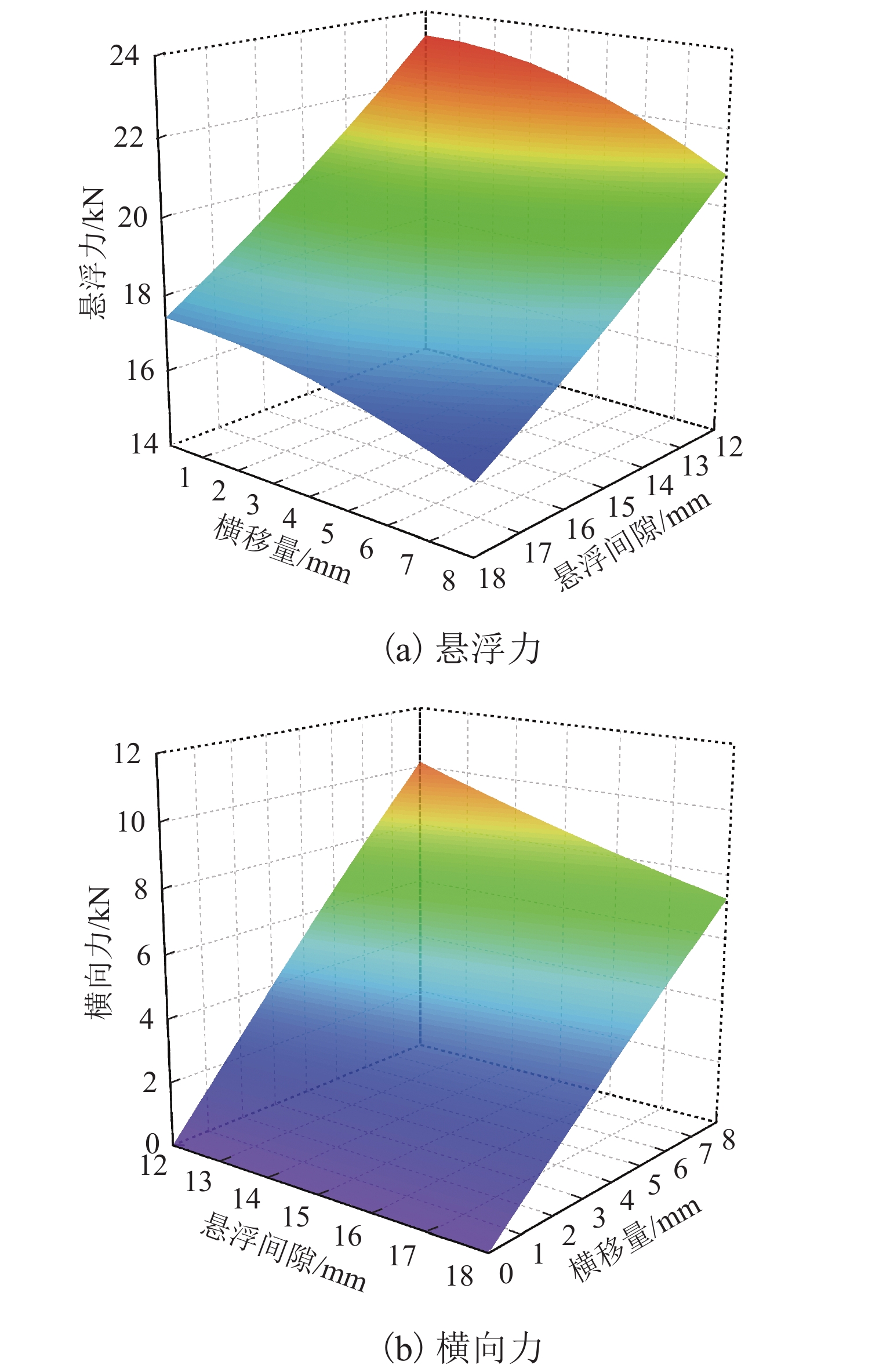
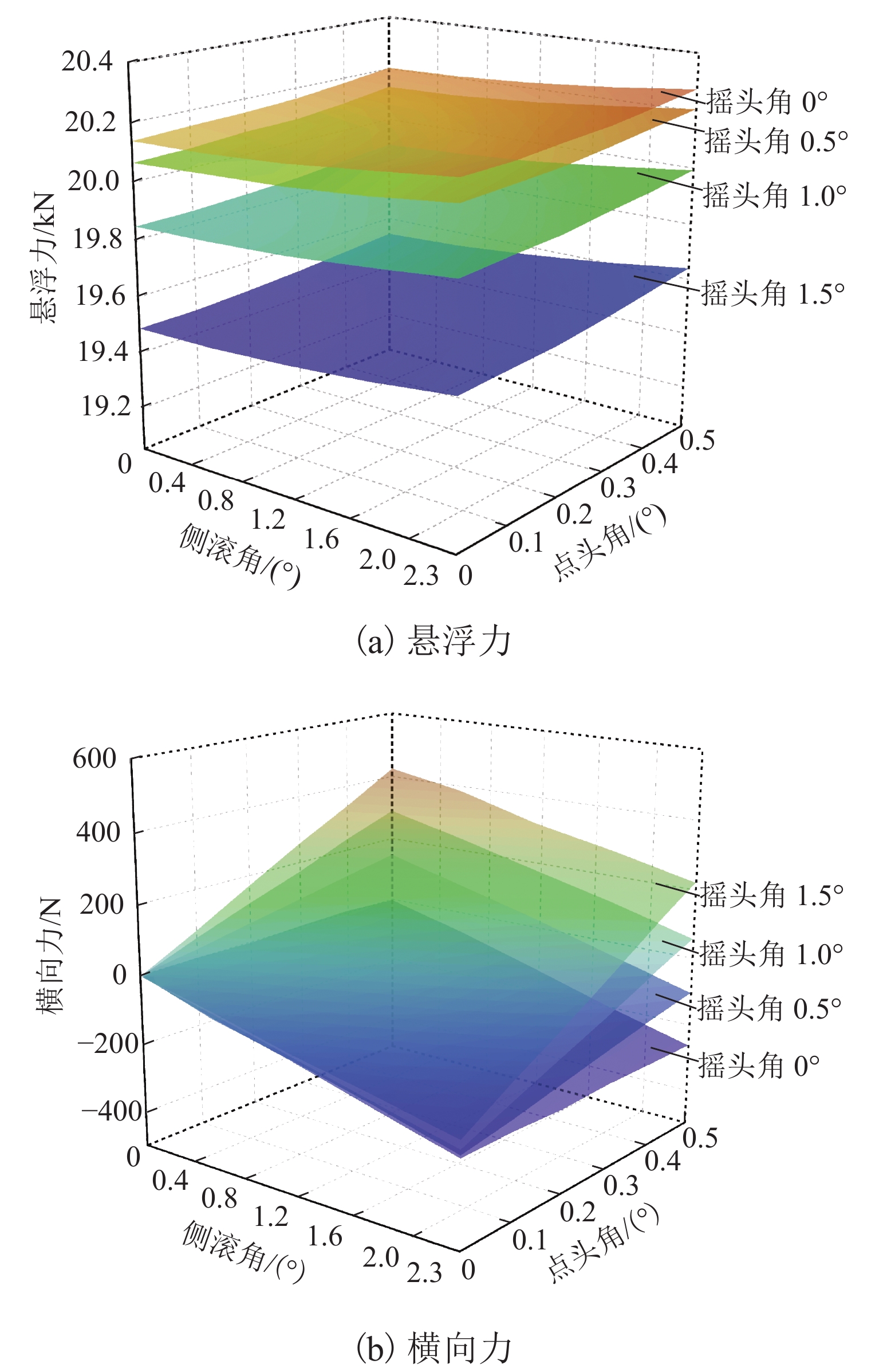
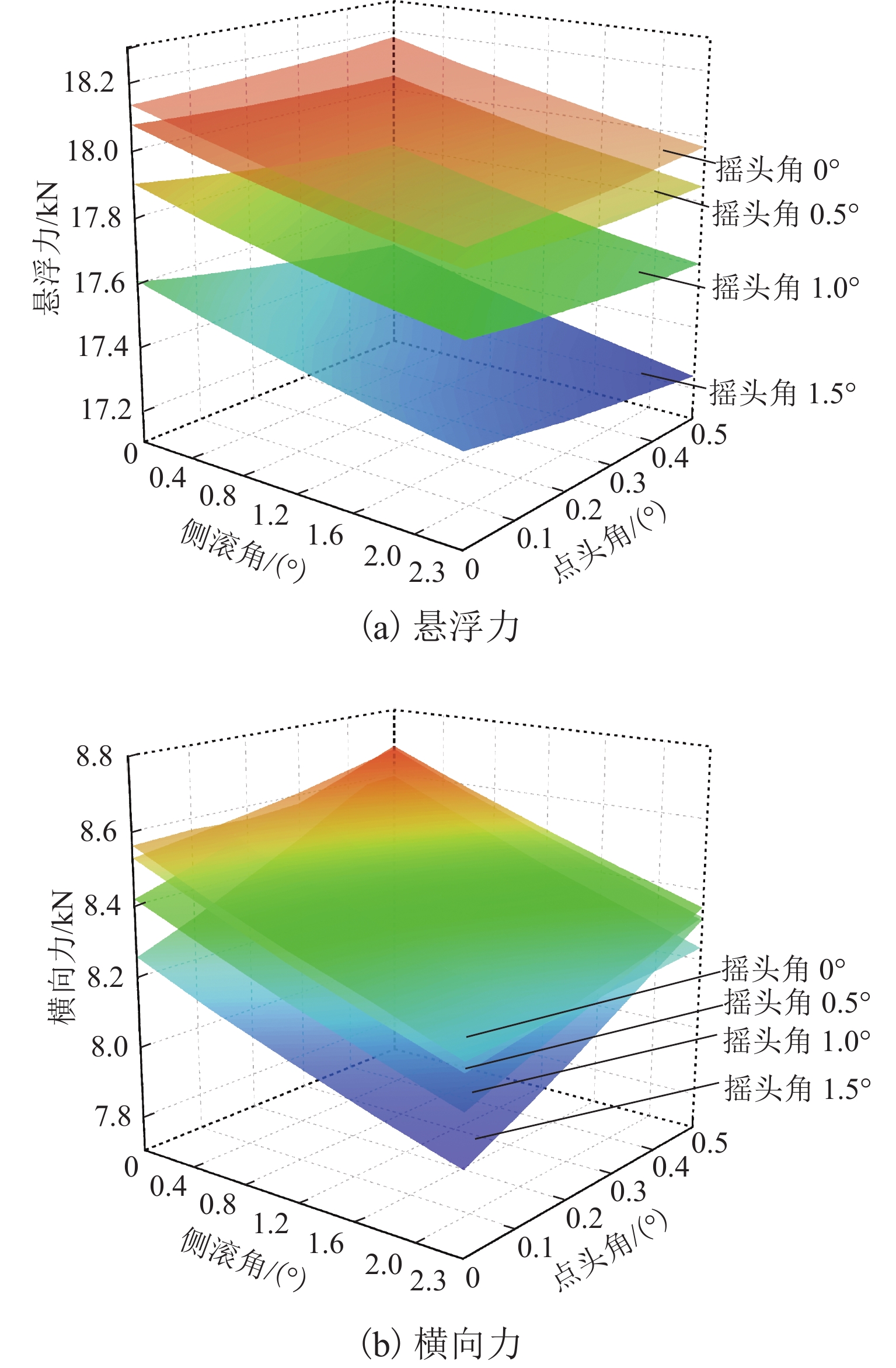
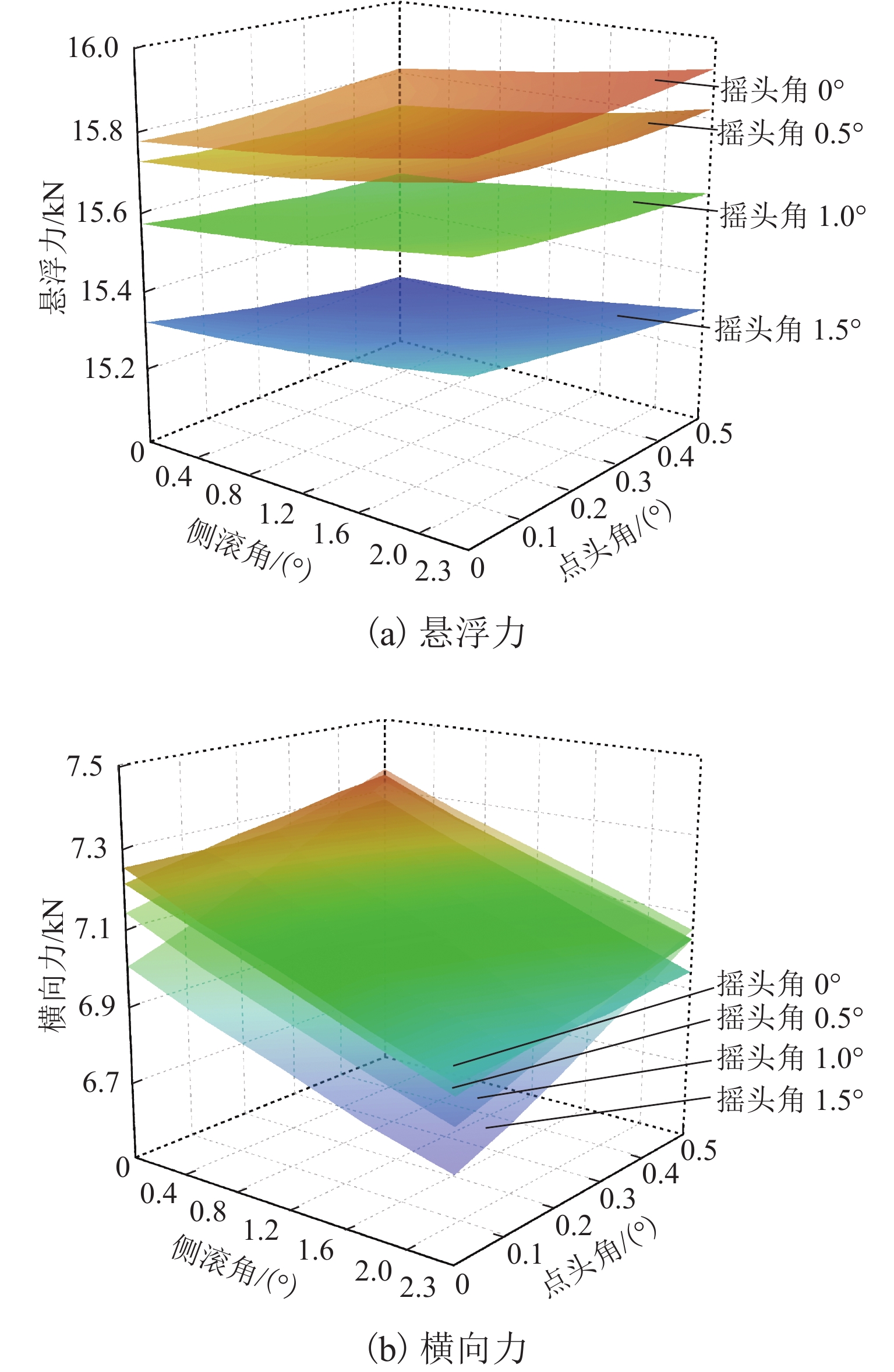
永磁磁浮交通系统利用车载永磁体和永磁轨道间的磁斥力实现悬浮,理解并掌握永磁体磁力与其空间位姿参数的关系对磁浮车辆走行部及轨道结构设计具有重要意义. 参考兴国县永磁磁浮交通系统,建立车载永磁体和永磁轨道的三维磁场有限元模型;计算不同悬浮间隙、横向偏移、点头角、侧滚角和摇头角条件下车载永磁体受到的磁力,重点分析车载永磁体悬浮力和横向力随5个位姿参数的变化规律及其相关程度. 结果表明:车载永磁体的磁力主要受悬浮间隙和横向偏移量的影响,受摇头角的影响较大,受点头角和侧滚角的影响很小;在设定的参数变化范围内,悬浮力最小值和最大值与额定悬浮力之比分别约为0.75和1.16,横向力最大值达到额定悬浮力的50.42%;车载永磁体横向力的方向与其横向偏移方向一致,摇头力矩与其摇头方向相同,需要为永磁悬浮系统设置导向装置,防止车载永磁体横向晃动和偏航运行.
Abstract:The permanent magnet suspension (PMS) transportation system utilizes the magnetic repulsion between the on-board permanent magnet and the permanent magnetic rail to achieve levitation. Understanding and mastering the relationship between the magnetic force of the permanent magnet and its spatial pose parameter are crucial for designing the running gear of the maglev train and track structure. A three-dimensional magnetic field finite element model was developed for the on-board permanent magnet and the permanent magnetic rail based on the PMS transportation system of Xingguo County. The magnetic force on the on-board permanent magnet was calculated under different levitation gaps, lateral offsets, pitching angles, rolling angles, and yawing angles. The variation patterns of levitation force and lateral force of the on-board permanent magnet with respect to these five pose parameters were analyzed, as well as their correlation degree. The results indicate that the magnetic force of the on-board permanent magnet is primarily influenced by the levitation gap and lateral offset, with a greater impact from the yawing angle and minimal effect from the pitching angle and rolling angle. Within the specified range of parameter variations, the ratios of the minimum and maximum values of the levitation force to the rated levitation force are approximately 0.75 and 1.16, respectively. In addition, the maximum value of the lateral force reaches 50.42% of the rated levitation force. The direction of the lateral force of the on-board permanent magnet aligns with its lateral offset direction, while the yawing torque aligns with its yawing angle direction. Consequently, a guiding device is necessary for the PMS system to prevent lateral bobbing and yawing movements of the on-board permanent magnet.
-
Key words:
- maglev train /
- permanent magnetic suspension /
- Halbach array /
- magnetic force /
- finite element method
-
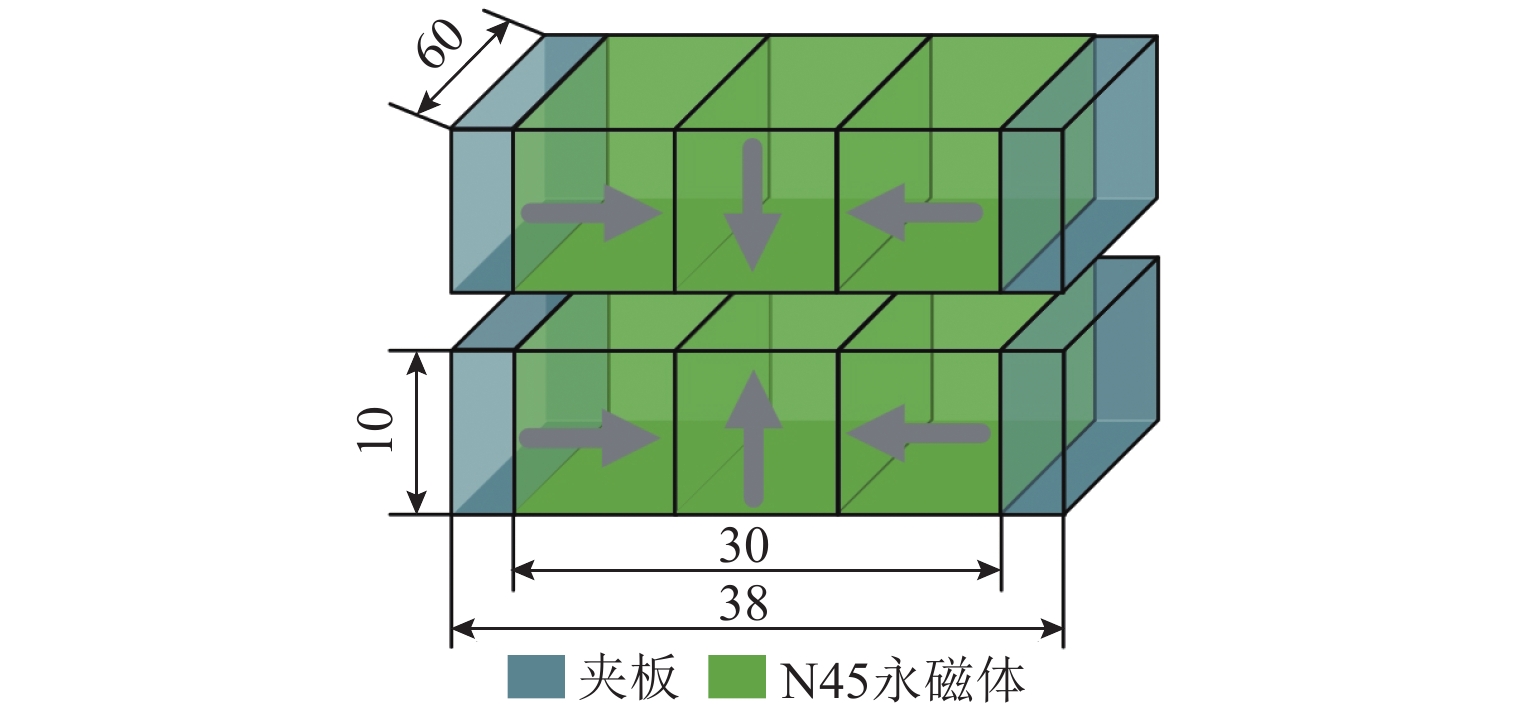
表 1 钕铁硼N45永磁材料参数
Table 1. Parameters of NdFeB N45 permanent magnet materials
材料参数 数值 剩余磁感应强度/T 1.32 矫顽力/(kA·m−1) 890 磁化强度/(kA·m−1) 978.8 相对磁导率 1.22 表 2 磁力与位姿参数的Spearman相关性系数
Table 2. Spearman’s correlation coefficients for magnetic force and pose parameters
位姿参数 悬浮力 横向力 悬浮间隙 −0.884 −0.522 横移量 −0.333 0.806 点头角 −0.073 0.190 侧滚角 −0.058 −0.018 摇头角 −0.282 0.074 -
[1] 翟婉明,赵春发. 现代轨道交通工程科技前沿与挑战[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2016,51(2): 209-226.ZHAI Wanming, ZHAO Chunfa. Frontiers and challenges of sciences and technologies in modern railway engineering[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2016, 51(2): 209-226. [2] 徐飞,罗世辉,邓自刚. 磁悬浮轨道交通关键技术及全速度域应用研究[J]. 铁道学报,2019,41(3): 40-49.XU Fei, LUO Shihui, DENG Zigang. Study on key technologies and whole speed range application of maglev rail transport[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2019, 41(3): 40-49. [3] 邓自刚,刘宗鑫,李海涛,等. 磁悬浮列车发展现状与展望[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2022,57(3): 455-474,530.DENG Zigang, LIU Zongxin, LI Haitao, et al. Development status and prospect of maglev train[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2022, 57(3): 455-474,530. [4] 王滢,张昆仑,张慧娴,等. 高速磁浮交通系统制式特征与适应性[J]. 前瞻科技,2023,2(4): 19-30.WANG Ying, ZHANG Kunlun, ZHANG Huixian, et al. Characteristics and adaptability of different types of high-speed maglev transportation systems[J]. Science and Technology Foresight, 2023, 2(4): 19-30. [5] 杨斌,杨杰,张卫华,等. 悬挂式磁悬浮轨道交通系统:CN109131370B[P]. 2019-06-21. [6] GAO T, YANG J, JIA L M, et al. Design of new energy-efficient permanent magnetic maglev vehicle suspension system[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 1359.17-1359.32. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2939879 [7] 杨杰,高涛,邓永芳,等. 永磁磁浮空轨系统的研究与设计[J]. 铁道学报,2020,42(10): 30-37.YANG Jie, GAO Tao, DENG Yongfang, et al. Study and design on suspended permanent maglev rail transit system[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2020, 42(10): 30-37. [8] ZHANG X T, ZHANG C M, YU J K, et al. Analytical model of magnetic field of a permanent magnet synchronous motor with a trapezoidal halbach permanent magnet array[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2019, 55(7): 8105205.1-8105205.5. [9] HOBURG J F. Modeling maglev passenger compartment static magnetic fields from linear Halbach permanent-magnet arrays[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2004, 40(1): 59-64. doi: 10.1109/TMAG.2003.821559 [10] SUN R X, ZHENG J, ZHENG B T, et al. Study on the magnetic field inhomogeneity of a halbach permanent-magnet guideway due to different defects[J]. IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 2016, 26(1): 3600107.1-3600107.7 [11] 陈殷,张昆仑. Halbach永磁阵列空间磁场的解析计算[J]. 磁性材料及器件,2014,45(1): 1-4,9.CHEN Yin, ZHANG Kunlun. Analytic calculation of the magnetic field created by Halbach permanent magnets array[J]. Journal of Magnetic Materials and Devices, 2014, 45(1): 1-4,9. [12] JIANG Y, DENG Y F, ZHU P H, et al. Optimization on size of halbach array permanent magnets for magnetic levitation system for permanent magnet maglev train[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 44989-45000. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3058124 [13] TANG W B, XIAO L Y, XIA D, et al. 2-D and 3-D analytical calculation of the magnetic field and levitation force between two halbach permanent magnet arrays[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2021, 57(4): 8300208.1-8300208.8. [14] SPEARMAN C. The proof and measurement of association between two things[J]. The American Journal of Psychology, 1987, 100(3/4): 441- 471. -




 下载:
下载: