Stochastic Vibration Analysis of Maglev Train-Bridge Coupling System Based on Pseudo Excitation Method
-
摘要:
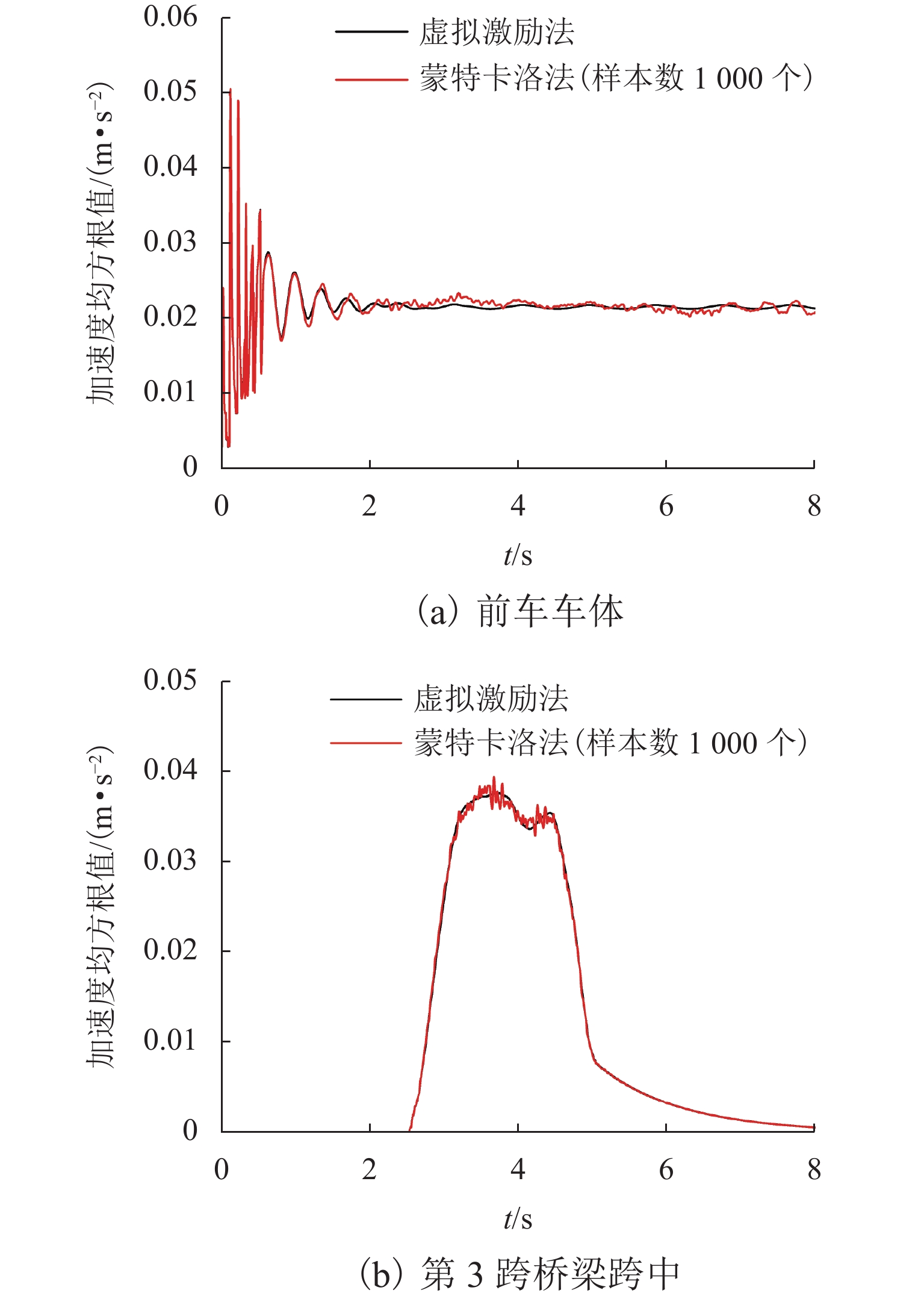
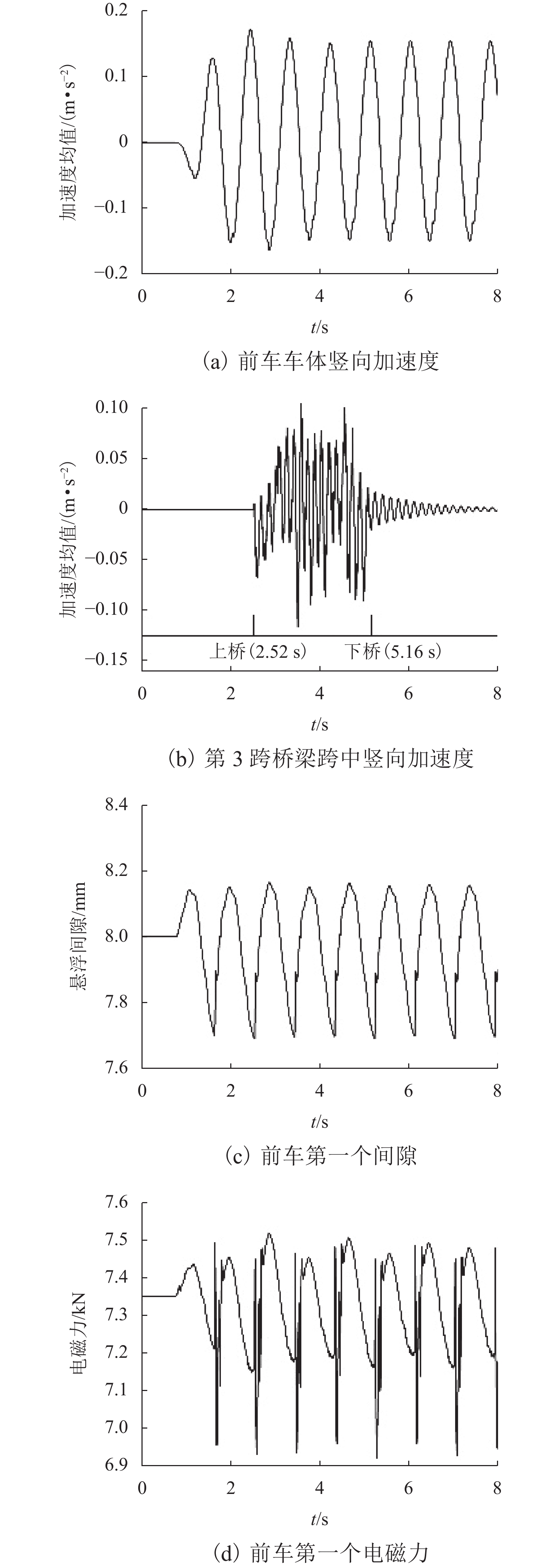
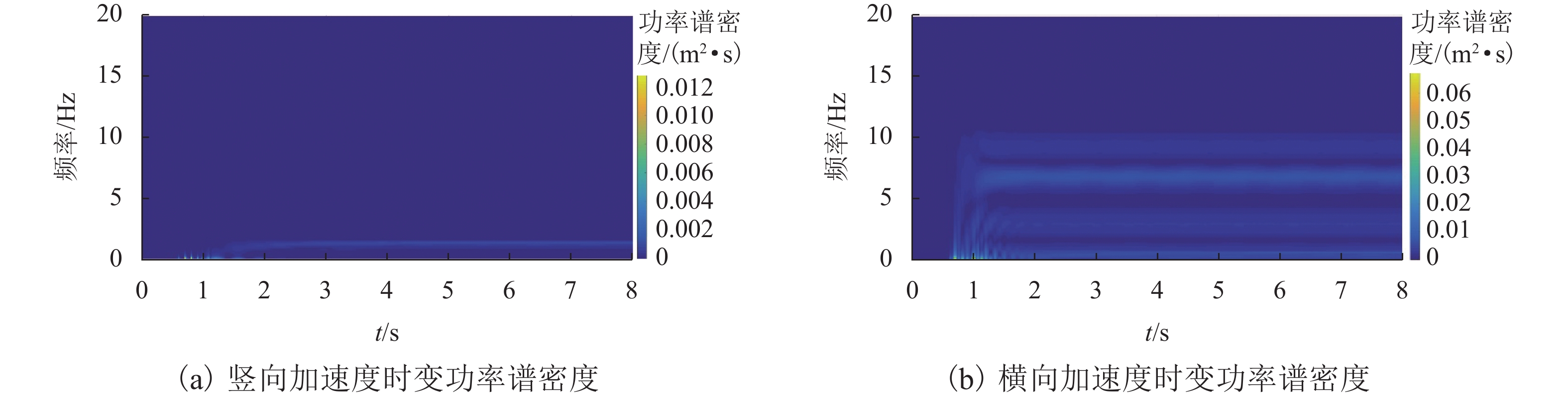
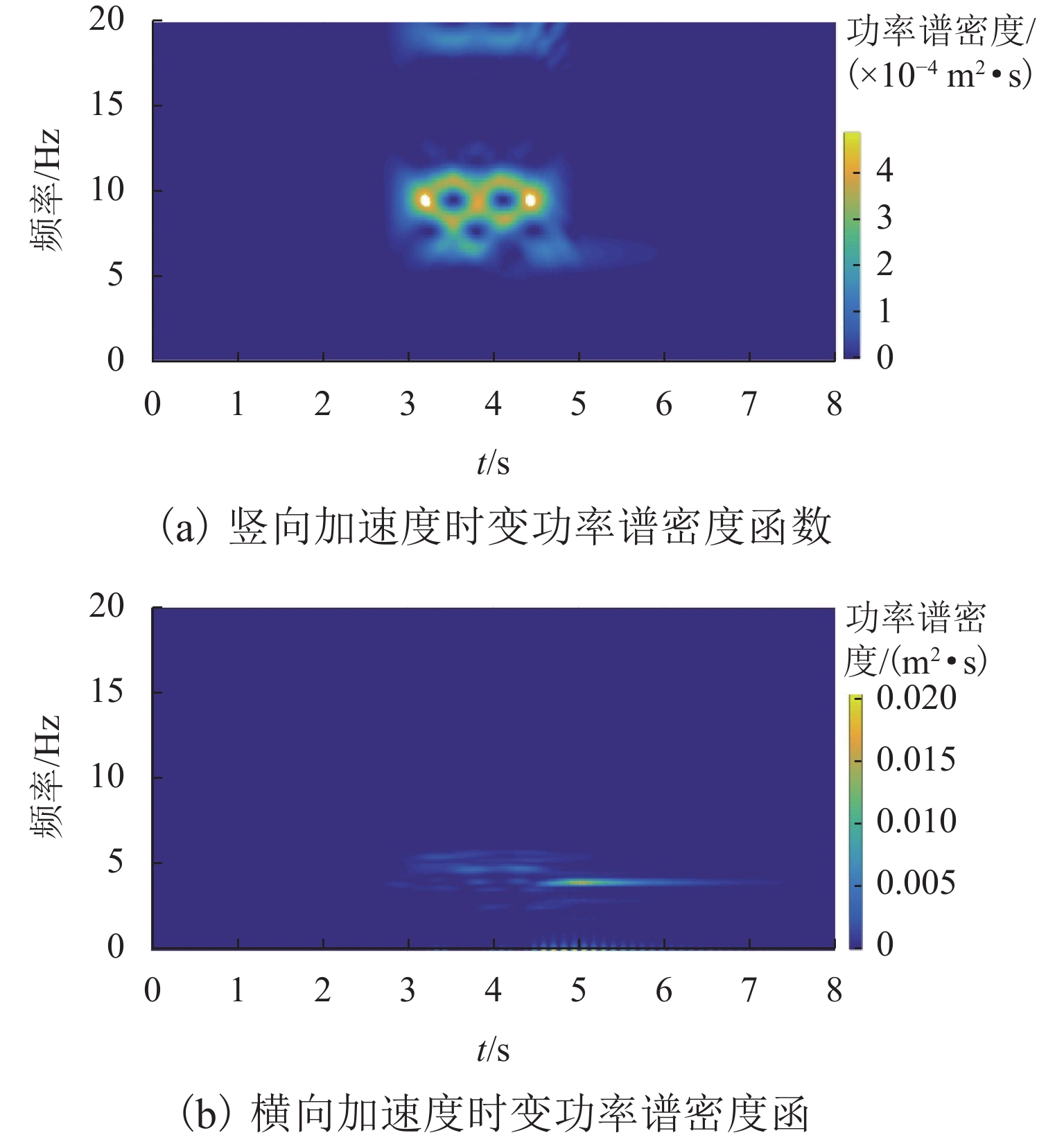
为探讨随机轨道不平顺作用下中低速磁浮列车和桥梁的动力响应,将虚拟激励法引入磁浮车桥振动分析中,提出中低速磁浮车辆-悬浮控制系统-桥梁耦合系统随机振动分析方法. 将中低速磁浮列车简化为弹簧阻尼器连接的多刚体,悬浮系统中电流使用比例-微分(PD)控制方法进行主动控制,采用有限元方法对桥梁进行建模,将随机轨道不平顺转换为一系列简谐波构成的虚拟激励;编制中低速磁浮车桥动力系统随机振动分析程序,自动生成系统随机振动方程,利用分离迭代方法对磁浮车辆控制方程和桥梁动力方程进行求解计算. 研究结果表明:虚拟激励法能够高效计算中低速磁浮车桥系统随机动力响应,其计算效率约为蒙特卡洛方法的1/11,基于虚拟激励法能够获得中低速磁浮车桥动力系统均值、标准差和时变功率谱密度等统计结果.
Abstract:To explore the dynamic responses of medium-low speed maglev trains and bridges under stochastic track irregularities, the pseudo excitation method was introduced into the vibration analysis of the maglev train-bridge system. A stochastic vibration analysis method for the medium-low speed maglev train, suspension control system, and bridge coupling system was proposed. The medium-low speed maglev train was simplified as rigid bodies connected by spring dampers, and the current in the suspension system was actively controlled using the proportional-differential (PD) control method. The bridge was modeled by using a finite element method, and the stochastic track irregularity was converted into a pseudo excitation composed of a series of simple harmonic waves. The stochastic vibration analysis program for the medium-low speed maglev train-bridge dynamic system was developed, which could automatically generate the stochastic vibration equations of the system, and the separation iteration method was used to solve the control equation of the maglev train and the dynamic equation of the bridge. The research results indicate that the pseudo excitation method can efficiently calculate the stochastic dynamic response of the medium-low speed maglev train-bridge system, with a calculation efficiency of about 1/11 of the Monte Carlo method. Based on the pseudo excitation method, statistical results such as mean, standard deviation, and time-varying power spectral density of the medium-low speed maglev train-bridge dynamic system can be obtained.
-
Key words:
- maglev train /
- train-bridge interaction /
- stochastic vibration /
- pseudo excitation method
-
表 1 磁浮车辆主要参数
Table 1. Main parameters of maglev train
参数 取值 车体质量/kg 20 000 悬浮模块质量/kg 1 000 车体绕 x 轴转动惯量/(kg·m2) 66 800 车体绕 y 轴转动惯量/ (kg·m2) 210 000 车体绕 z 轴转动惯量/(kg·m2) 193 000 悬浮模块绕 x 轴转动惯量/(kg·m2) 1 030 悬浮模块绕 y 轴转动惯量/(kg·m2) 1 800 悬浮模块绕 z 轴转动惯量/(kg·m2) 2 680 二系悬挂弹簧纵向刚度/(N·m−1) 900 000 二系悬挂弹簧竖向刚度/(N·m−1) 80 000 二系悬挂弹簧横向刚度/(N·m−1) 80 000 二系悬挂弹簧纵向阻尼/(N·s·m−1) 50 000 二系悬挂弹簧竖向阻尼/(N·s·m−1) 2 000 二系悬挂弹簧横向阻尼/(N·s·m−1) 4 000 线圈匝数/匝 96 磁导率/(× 10−6 H·m−1) 1.26 铁芯极面积/m2 0.383 额定气隙/mm 8 车体长度/m 16 -
[1] 罗英昆,赵春发,梁鑫,等. 小半径竖曲线上磁浮车辆空气弹簧动态响应分析[J]. 振动与冲击,2020,39(17): 99-105.LUO Yingkun, ZHAO Chunfa, LIANG Xin, et al. Dynamic responses of air-spring suspension of a maglev vehicle negotiating a small-radius vertical curved track[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2020, 39(17): 99-105. [2] LIU W, GUO W H. Vibration analysis of EMS-type maglev vehicles traveling over a long-span bridge with double lines[J]. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering, 2020, 24(5): 1531-1544. doi: 10.1007/s12205-020-0816-5 [3] 付善强,梁鑫,丁叁叁. 高速磁浮车-轨耦合系统动态机理与振动响应[J]. 同济大学学报(自然科学版),2023,51(3): 314-320,384.FU Shanqiang, LIANG Xin, DING Sansan. Dynamic mechanism and vibration response of high-speed maglev vehicleguideway coupling system[J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science), 2023, 51(3): 314-320,384. [4] 李小珍,王渝文,胡启凯,等. 不同桥跨对中低速磁浮列车-简支梁系统竖向耦合振动影响机理研究[J]. 振动与冲击,2022,41(19): 8-15.LI Xiaozhen, WANG Yuwen, HU Qikai, et al. Influence mechanisms of different bridge spans on vertical coupled vibration of low and medium speed maglev train-simply supported beam system[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2022, 41(19): 8-15. [5] ZHAO C F, ZHAI W M. Maglev vehicle/guideway vertical random response and ride quality[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2002, 38(3): 185-210. doi: 10.1076/vesd.38.3.185.8289 [6] 时瑾,魏庆朝. 线路不平顺对高速磁浮铁路动力响应特性的影响[J]. 工程力学,2006,23(1): 154-159,86. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4750.2006.01.028SHI Jin, WEI Qingchao. The effect of guideway irregularity on the dynamic characteristics of high-speed maglev railway[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2006, 23(1): 154-159,86. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4750.2006.01.028 [7] 时瑾,魏庆朝,冯雅薇. 高速磁浮车桥系统随机振动特性仿真研究[J]. 系统仿真学报,2005,17(7): 1577-1579.SHI Jin, WEI Qingchao, FENG Yawei. Analysis of random vibration responses characteristics of maglev and elevated-beam guideway[J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2005, 17(7): 1577-1579. [8] MIN D J, JUNG M R, KIM M Y, et al. Dynamic interaction analysis of maglev-guideway system based on a 3D full vehicle model[J]. International Journal of Structural Stability and Dynamics, 2017, 17(1): 1750006.1-1750006.39. [9] TALUKDAR R P, TALUKDAR S. Dynamic analysis of high-speed MAGLEV vehicle–guideway system: an approach in block diagram environment[J]. Urban Rail Transit, 2016, 2: 71-84. doi: 10.1007/s40864-016-0039-8 [10] HAN J B, HAN H S, KIM S S, et al. Design and validation of a slender guideway for maglev vehicle by simulation and experiment[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2016, 54(3): 370-385. doi: 10.1080/00423114.2015.1137957 [11] 张鹏. 磁浮列车-轨道-桥梁耦合系统随机振动分析[D]. 长沙:中南大学,2022. [12] 余志武,张鹏,丁叁叁,等. 基于概率密度演化理论的磁浮列车-轨道梁耦合系统随机动力分析[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版),2022,53(7): 2544-2554.YU Zhiwu, ZHANG Peng, DING Sansan, et al. Stochastic vibration analysis of maglev vehicle-guideway coupling system based on PDEM[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2022, 53(7): 2544-2554. [13] 陆周瑞,陈冉,苏成. 磁浮车辆-桥梁耦合系统随机振动分析的时域显式方法研究[J]. 工程力学,2022,39(8): 19-30. doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2021.04.0321LU Zhourui, CHEN Ran, SU Cheng. Random vibration analysis of maglev vehicle-bridge coupled systems with the explicit time-domain method[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2022, 39(8): 19-30. doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2021.04.0321 [14] 周劲松,李大光,沈钢,等. 磁浮车辆运行平稳性的虚拟激励分析方法[J]. 交通运输工程学报,2008,8(1): 5-9.ZHOU Jinsong, LI Daguang, SHEN Gang, et al. Pseudo-excitation analysis method of riding quality for maglev vehicle[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2008, 8(1): 5-9. [15] SU X J, YANG X Z, SHI P, et al. Fuzzy control of nonlinear electromagnetic suspension systems[J]. Mechatronics, 2014, 24(4): 328-335. doi: 10.1016/j.mechatronics.2013.08.002 [16] KONG E, SONG J S, KANG B B, et al. Dynamic response and robust control of coupled maglev vehicle and guideway system[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2011, 330(25): 6237-6253. doi: 10.1016/j.jsv.2011.05.031 [17] 赵春发. 磁悬浮车辆系统动力学研究[D]. 成都:西南交通大学,2002. [18] FENG Y, ZHAO C F, ZHOU W, et al. Maglev vehicle-switch girder coupled vibration characteristics analysis based on distributed co-simulation[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2023, 61(5): 1345-1366. doi: 10.1080/00423114.2022.2074470 [19] 曾庆元,杨平. 形成矩阵的“对号入座” 法则与桁梁空间分析的桁段有限元法[J]. 铁道学报,1986,8(2): 48-59.ZENG Qingyuan, YANG Ping. The “set-in-right-position” rule for forming structural matrices and the finite truss-element method for space analysis of truss bridges[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 1986, 8(2): 48-59. [20] 胡帛茹. 两种中低速EMS磁浮车辆动力学性能的对比分析[D]. 成都:西南交通大学,2021. [21] FRÝBA L. Dynamics of railway bridges[M]. London: Thomas Telford Publishing, 1996. [22] YANG Y B, YAO Z D, WU Y S. Vehicle-bridge interaction dynamics: with applications to high-speed railways[M]. Singapore: World Scientific, 2004. [23] 林家浩. 随机地震响应的确定性算法[J]. 地震工程与工程振动,1985,5(1): 89-94.LIN Jiahao. A deterministic method for the computation of stochastic earthquake response[J]. Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration, 1985, 5(1): 89-94. -





 下载:
下载: