Optimal Configuration of Photovoltaic and Hybrid Energy Storage System Capacity in Multi-Substation Interconnected Traction Power Supply System
-
摘要:
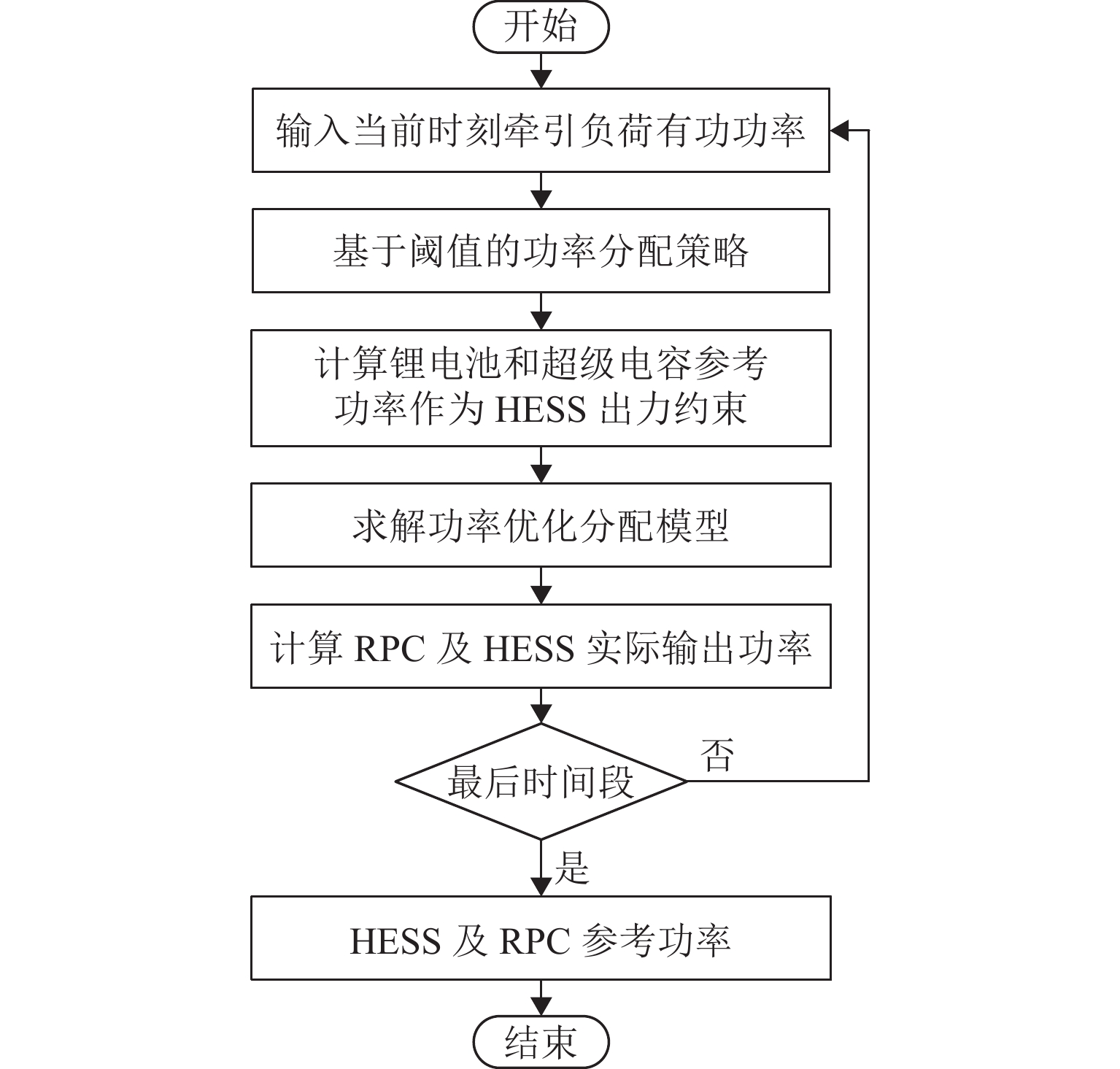
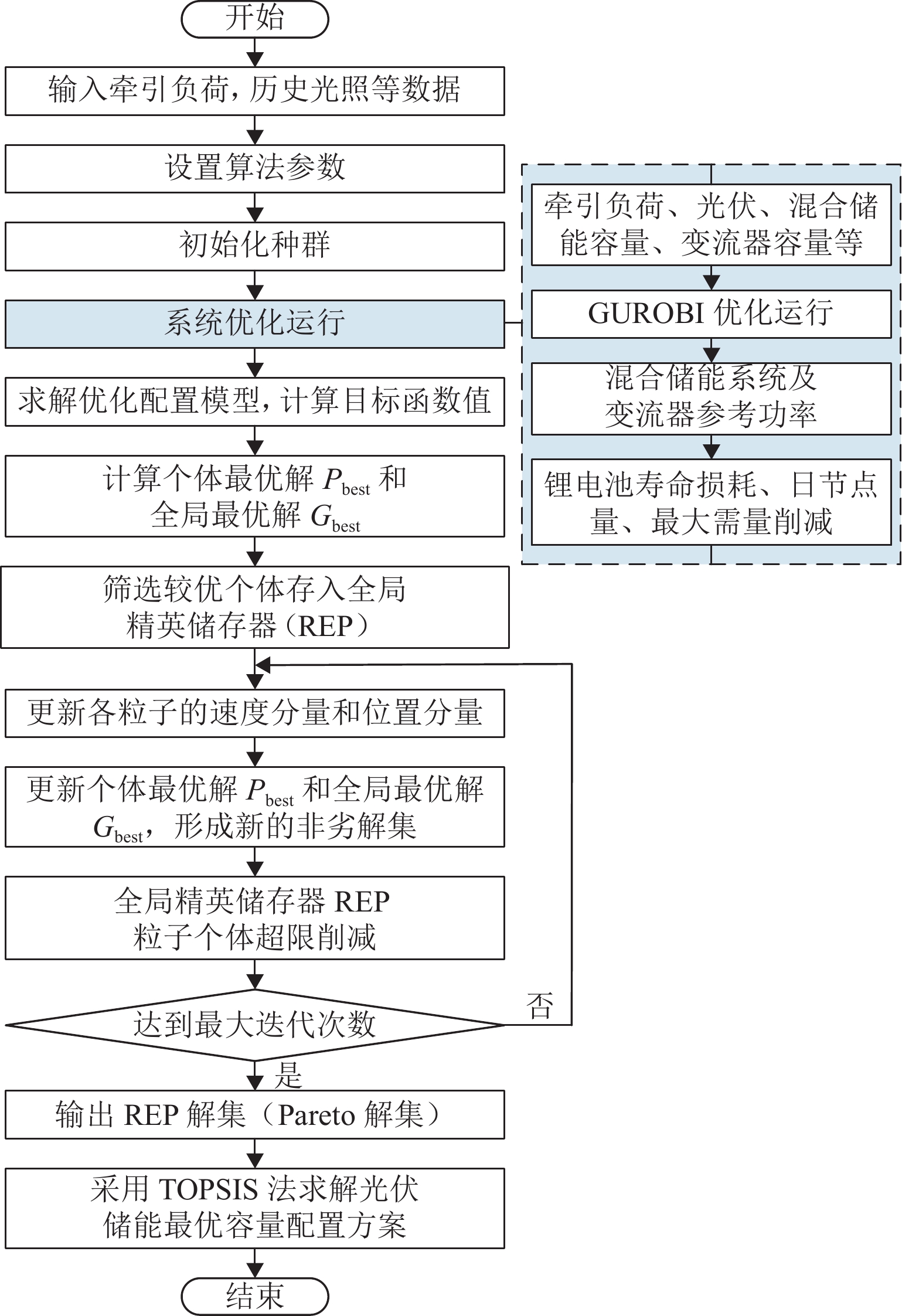
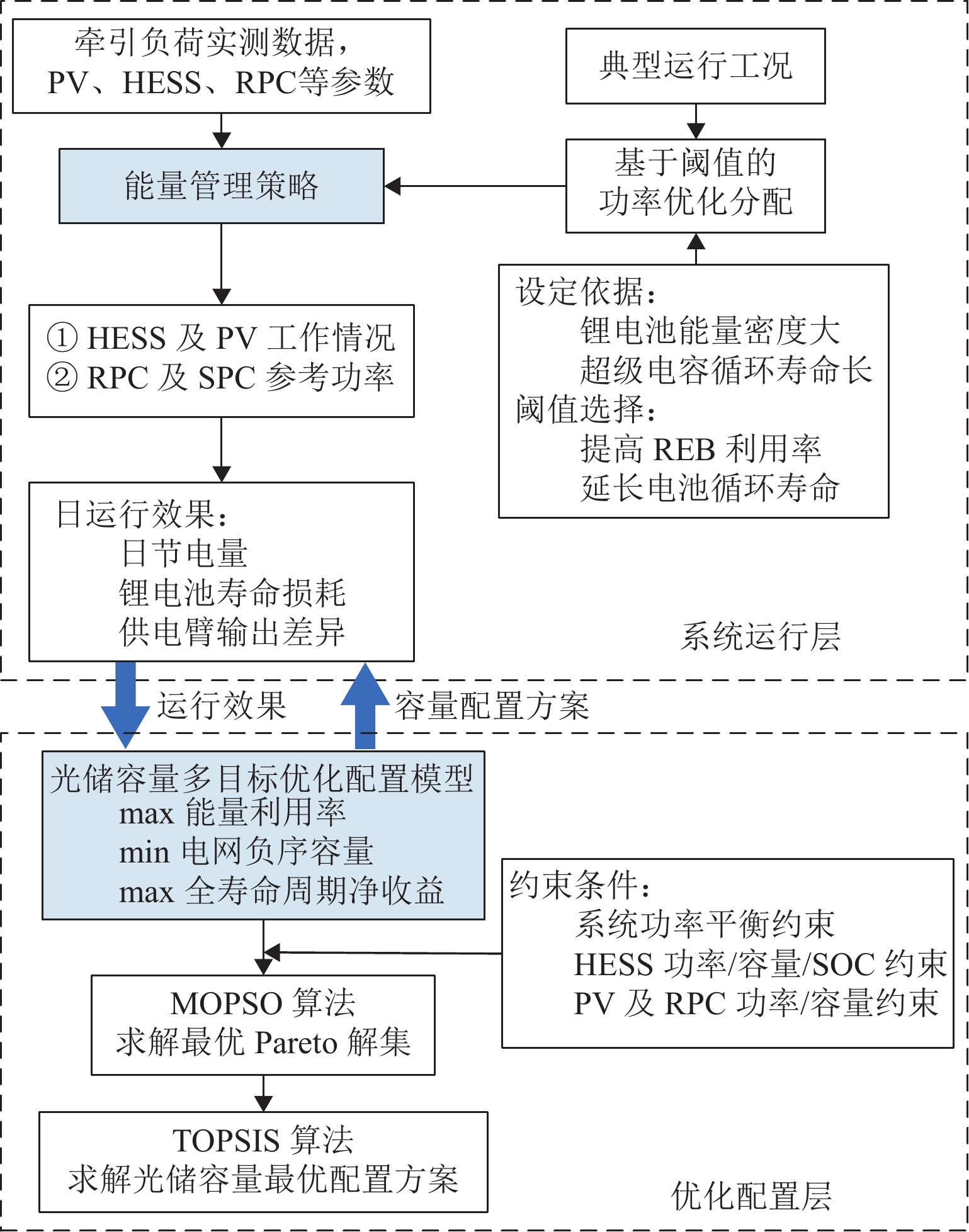
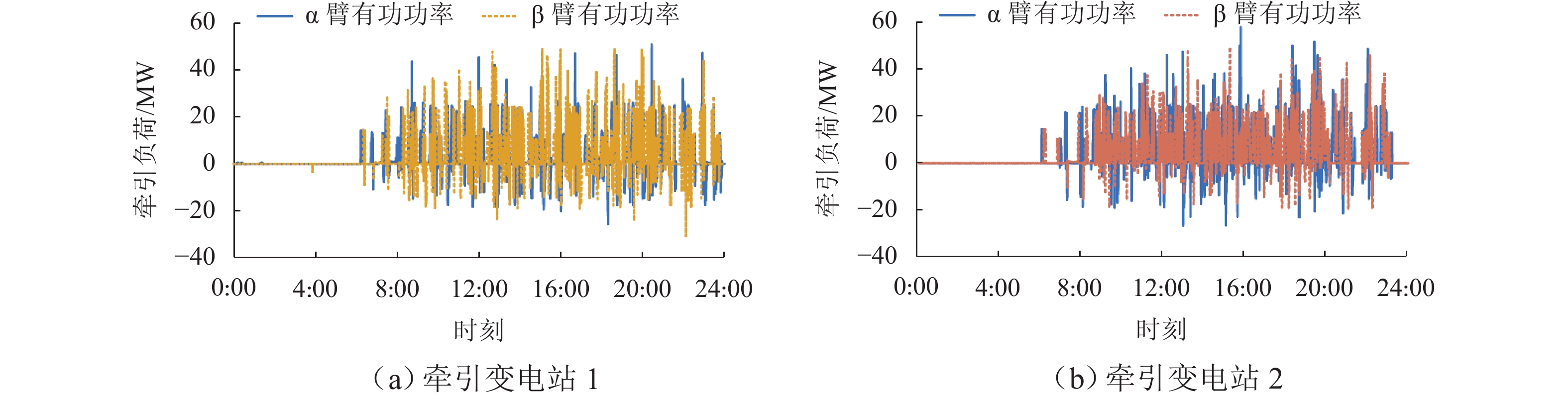
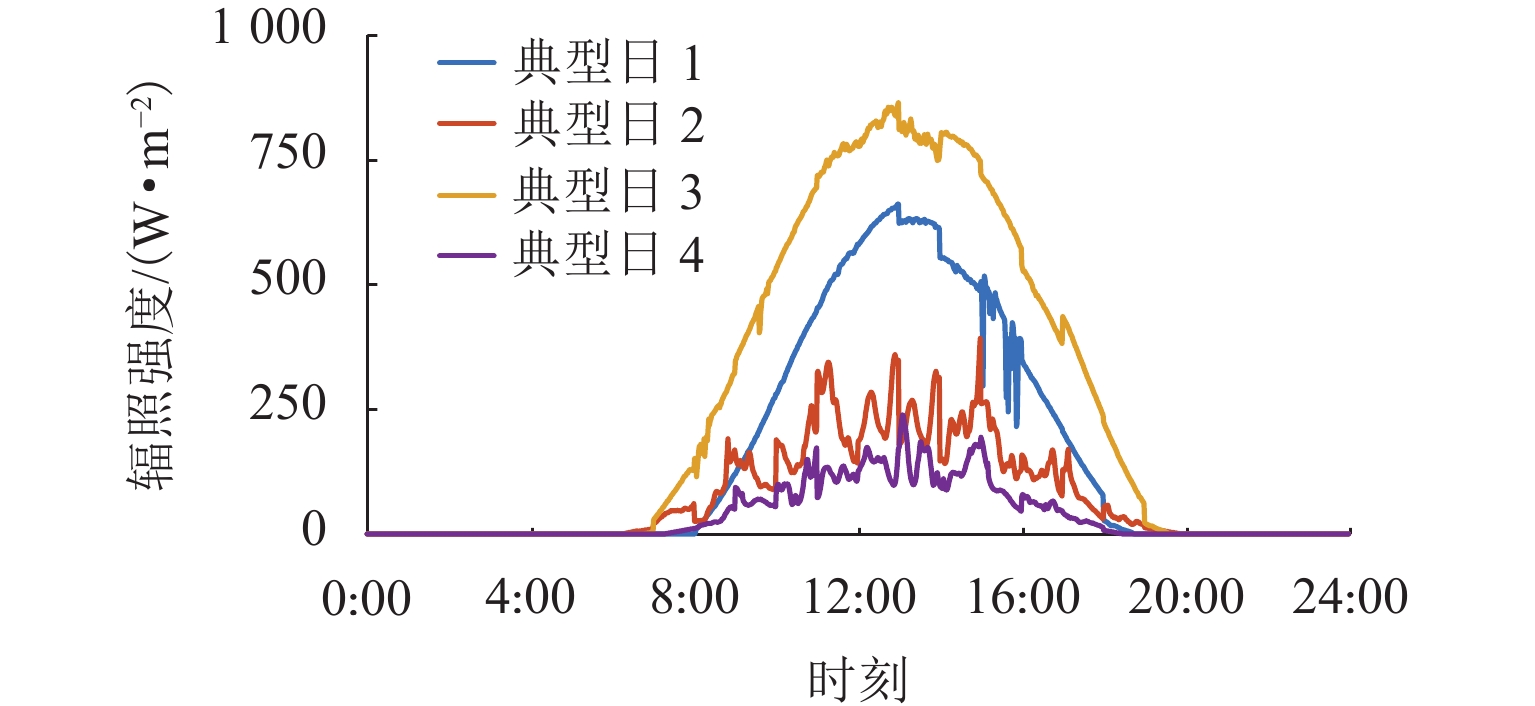
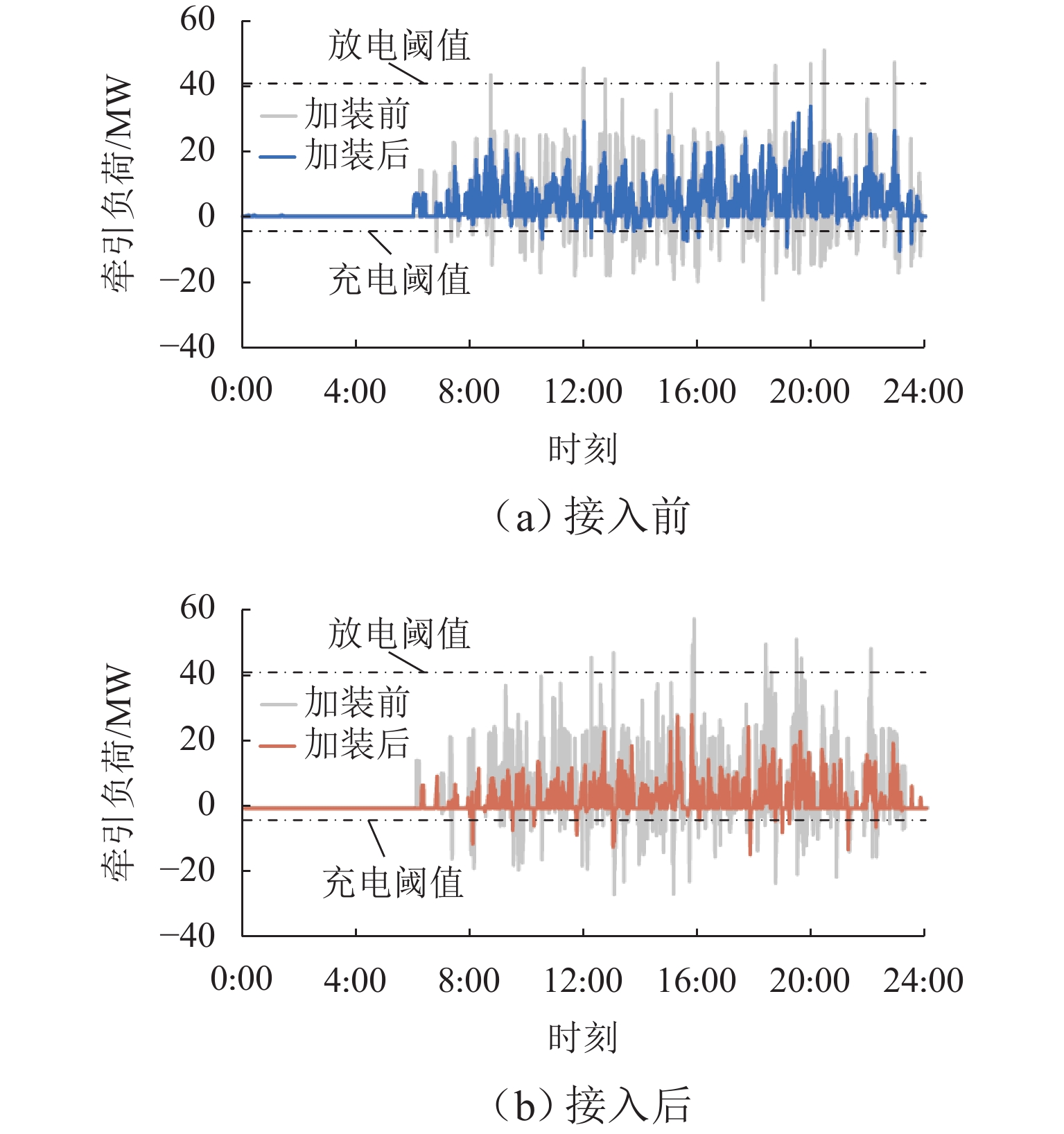
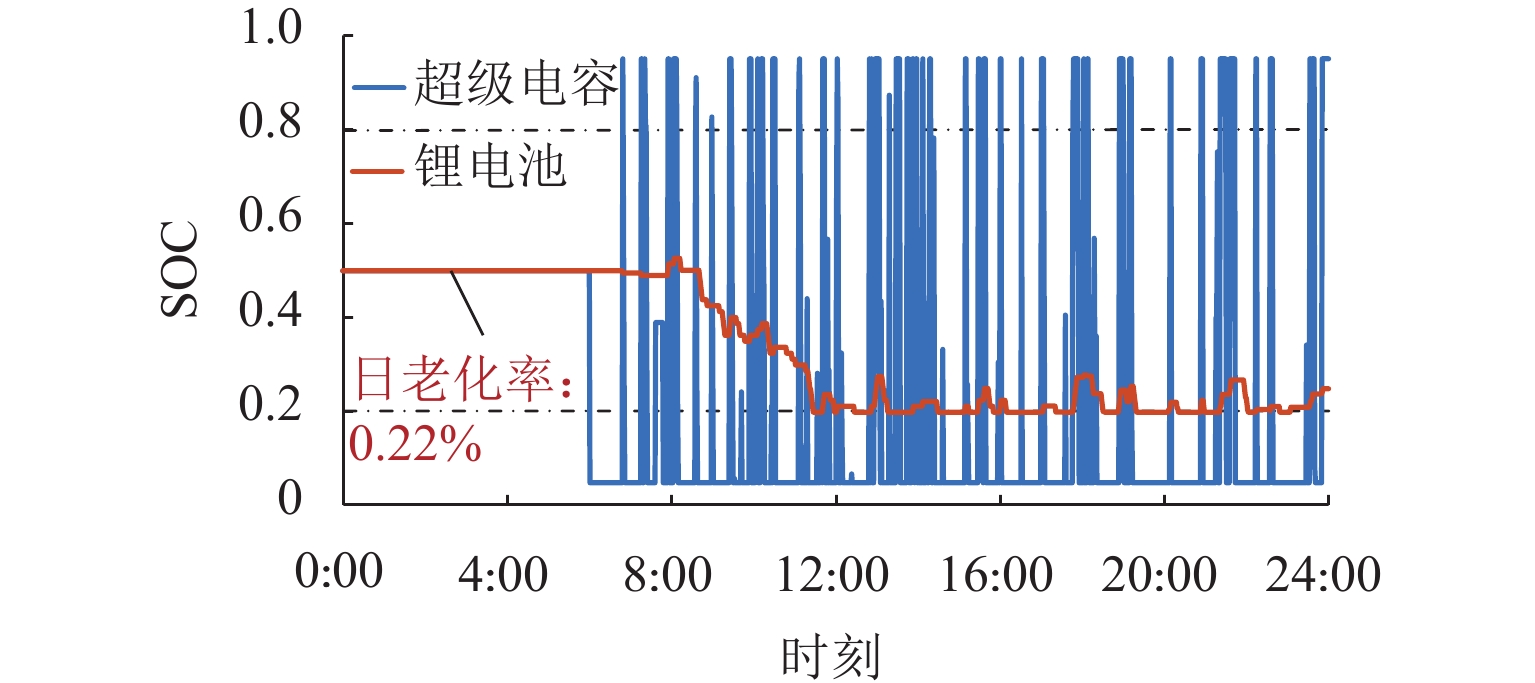
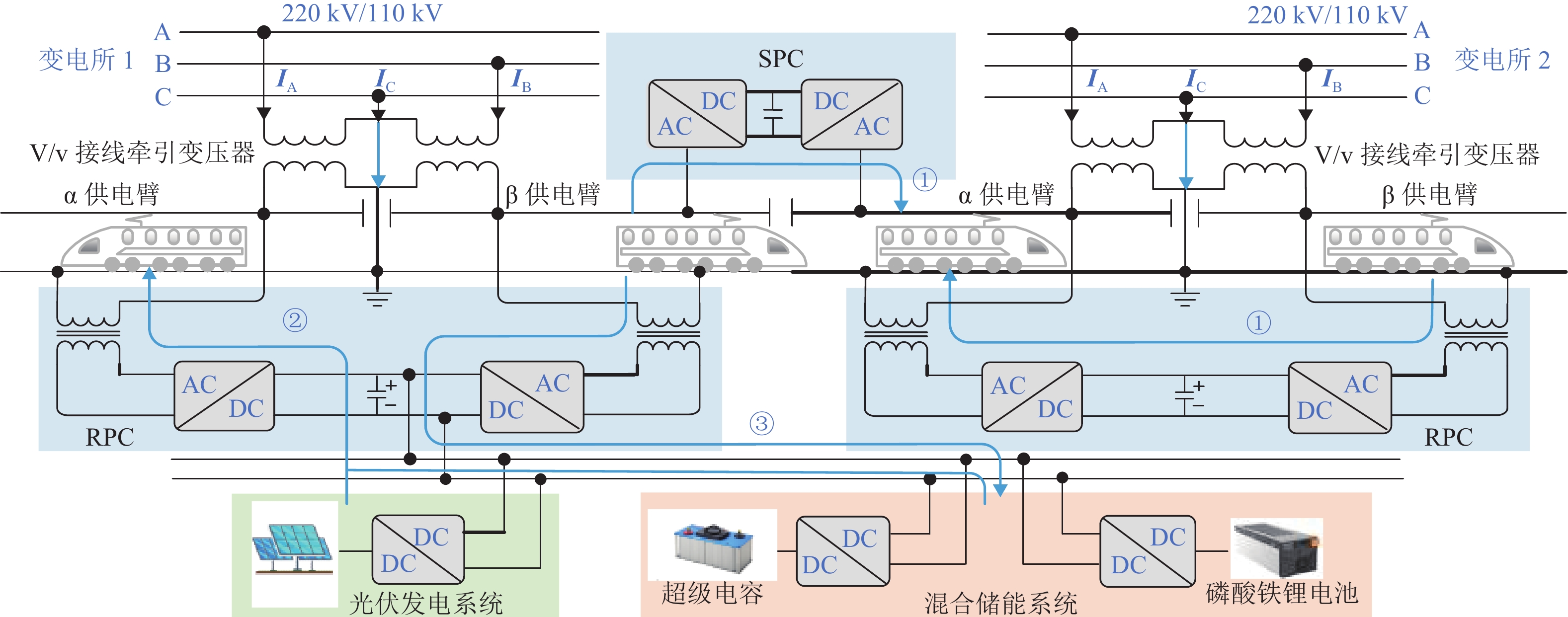
随着我国电气化铁路规模持续扩大,光伏-储能装置接入牵引供电系统逐渐成为实现电气化铁路节能减排的有效方式. 为保障多变电所互联牵引供电系统能够平稳且经济地运行,提出一种基于技术-经济评价体系的光伏-储能系统容量优化配置方法. 该方法首先对牵引负荷运行特性与混合储能介质充放电特性开展分析,据此划分系统的运行工况,并对不同工况下的功率分配进行控制,进而给出考虑节能和三相电压不平衡度的能量管理策略;其次,在综合考虑系统稳定运行边界及经济效益的基础上,以全寿命周期净收益、能量利用率和负序容量为优化目标,定量评价系统运行的技术-经济效果;进一步建立基于所提能量管理策略的光伏-储能系统容量配置双层优化模型,以能量管理层日运行效果对容量优化配置层参数进行迭代修正;最后,以国内某高速铁路为例开展算例分析. 仿真结果显示:所提出方法能有效实现光伏-储能系统在多个互联变电所间的最优配置,总成本降低21.18%,能量利用率达74.61%,且三相电压不平衡度符合国标2%的上限要求.
Abstract:With the continuous expansion of China’s electrified railways, the integration of photovoltaic (PV) and hybrid energy storage systems (HESS) into the traction power supply system (TPSS) has gradually become an effective approach to achieve energy conservation and emission reduction in electrified railways. In order to ensure the stable and economical operation of multi-substation interconnected TPSS, the optimal configuration method of PV and HESS capacity based on a techno-economic evaluation system was proposed. By analyzing the operation characteristics of traction load and the charging and discharging characteristics of mixed energy storage media, the operation conditions of the system were divided, and the energy management strategy considering energy conservation and three-phase voltage imbalance was given by controlling the power allocation under different conditions. On the basis of comprehensively considering the boundaries of stable operation and economic benefits of the system, the technical and economic effects of the system operation were quantitatively evaluated with the net benefit throughout the full life cycle, energy utilization rate, and negative-sequence capacity as optimization objectives. Furthermore, a two-layer optimization model for PV and HESS capacity configuration based on the proposed energy management strategy was established, and the parameters of the capacity optimization layer were iteratively modified according to the daily operation effect of the energy management layer. China’s high-speed railway was taken as an example for analysis. Simulation results have shown that the proposed method can effectively realize the optimal configuration of PV and HESS in multiple interconnected substations, where the total cost is reduced by 21.18%; the energy utilization rate is up to 74.61%, and the three-phase voltage unbalance meets the upper limit of 2% in the national standard.
-
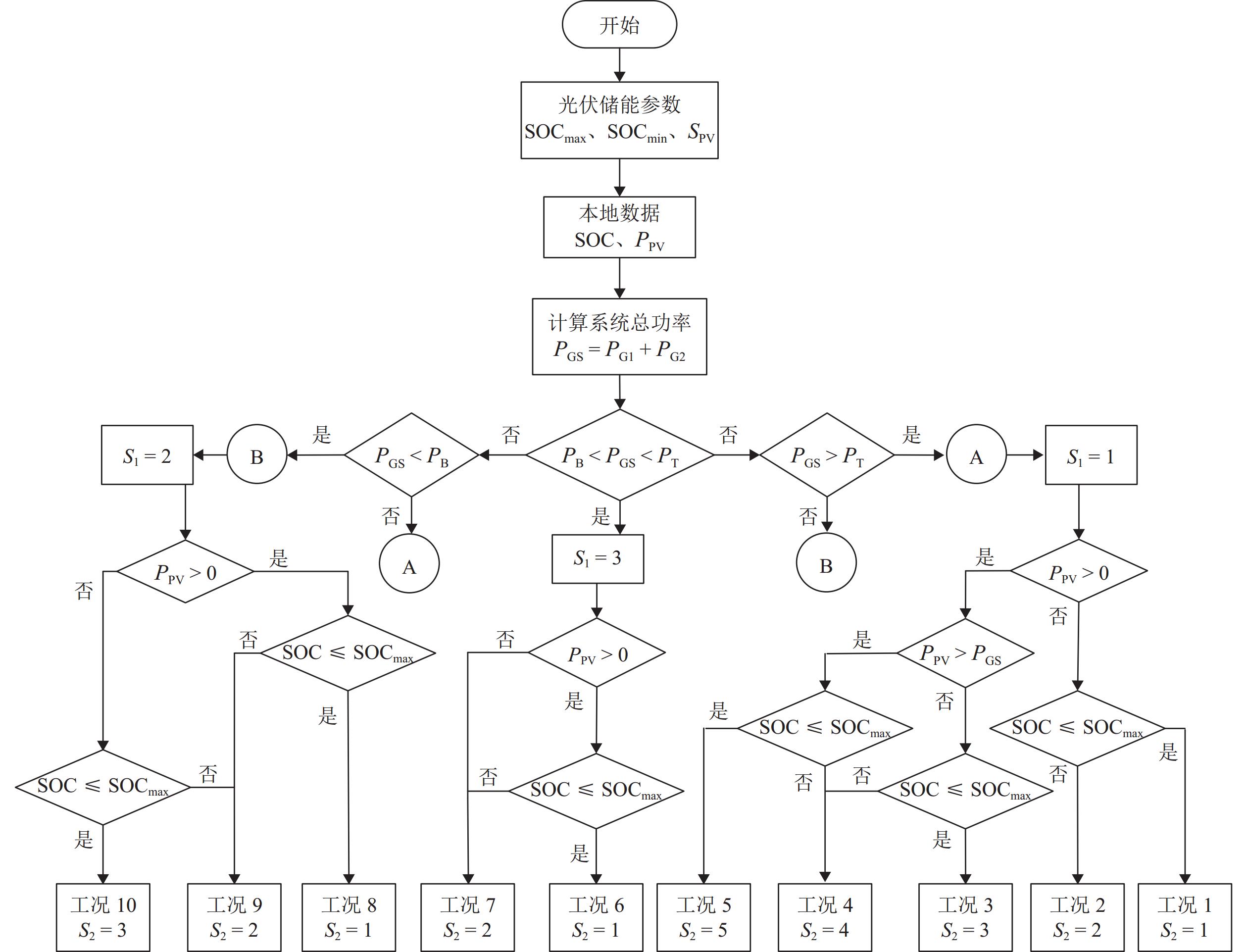
表 1 系统运行模式
Table 1. System operation modes
运行模式 判据 变电所 1 变电所 2 功率缺额 ${P_{{\text{GS}}}} \gt {P_{\text{T}}}$ 牵引 牵引 牵引 制动 制动 牵引 功率过剩 ${P_{{\text{GS}}}} \lt {P_{\text{B}}}$ 制动 制动 牵引 制动 功率平衡 ${P_{\text{B}}} \lt {P_{{\text{GS}}}} \lt {P_{\text{T}}}$ 牵引 制动 制动 牵引 表 2 各运行工况能量流
Table 2. Energy flow of each operation condition
工况 运行状态 能量流 1 ${S_1} = 1,{S_2} = 1$ PV 不工作,HESS 放电供能 2 ${S_1} = 1,{S_2} = 2$ PV 和 HESS 不工作,电网供能 3 ${S_1} = 1,{S_2} = 3$ HESS 和 PV 同时供能 4 ${S_1} = 1,{S_2} = 4$ HESS 不工作,限制 PV 供能 5 ${S_1} = 1,{S_2} = 5$ 限制 PV 供能,HESS 吸收 PV 6 ${S_1} = 3,{S_2} = 1$ HESS 吸收 PV 能量 7 ${S_1} = 3,{S_2} = 2$ HESS 和 PV 均不工作 8 ${S_1} = 2,{S_2} = 1$ HESS 吸收 RBE 和 PV 能量 9 ${S_1} = 2,{S_2} = 2$ HESS 不工作,RBE 反送电网 10 ${S_1} = 2,{S_2} = 3$ PV 不工作,HESS 吸收 RBE 表 3 HESS工作状态
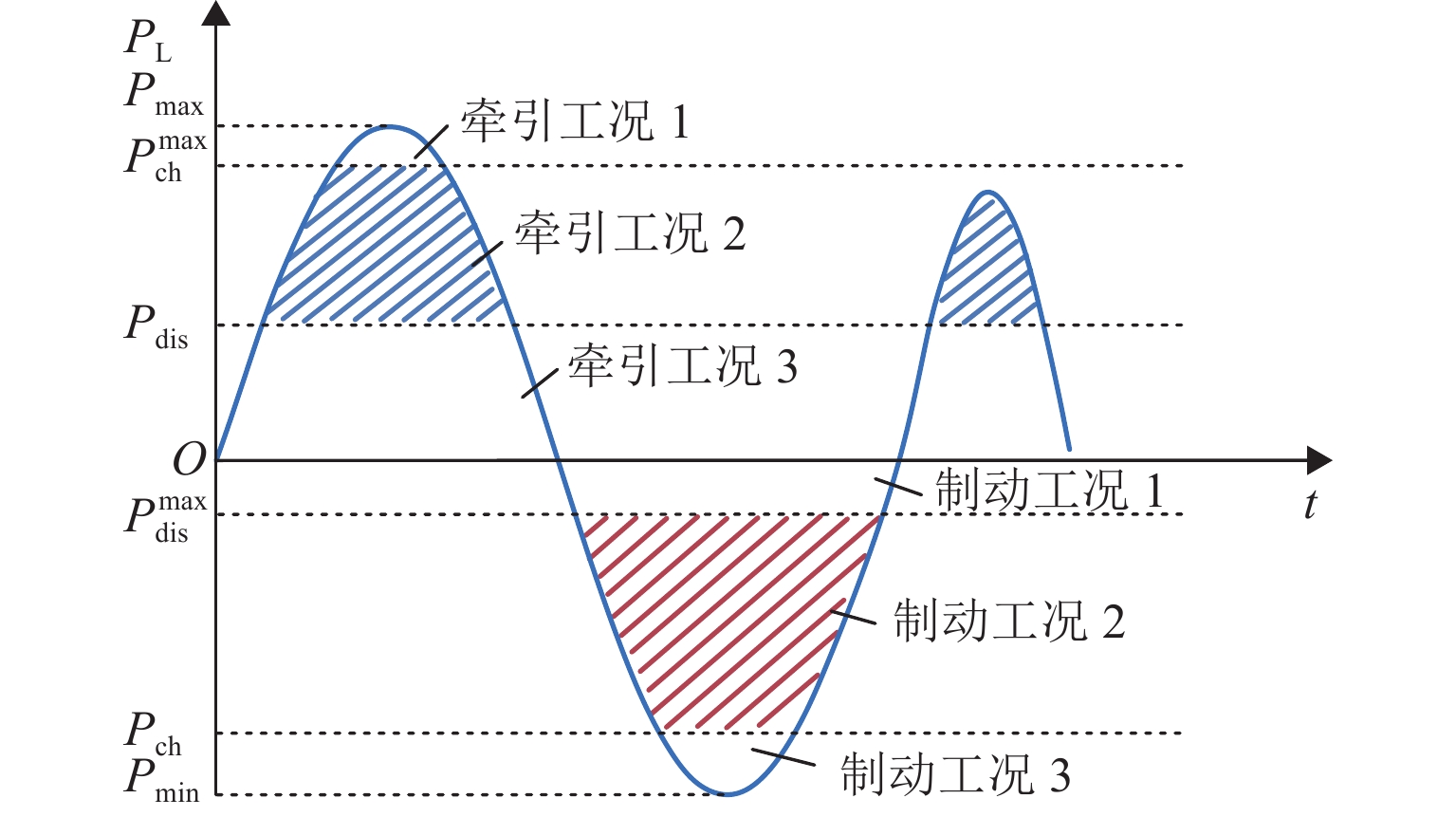
Table 3. Operative modes of HESS
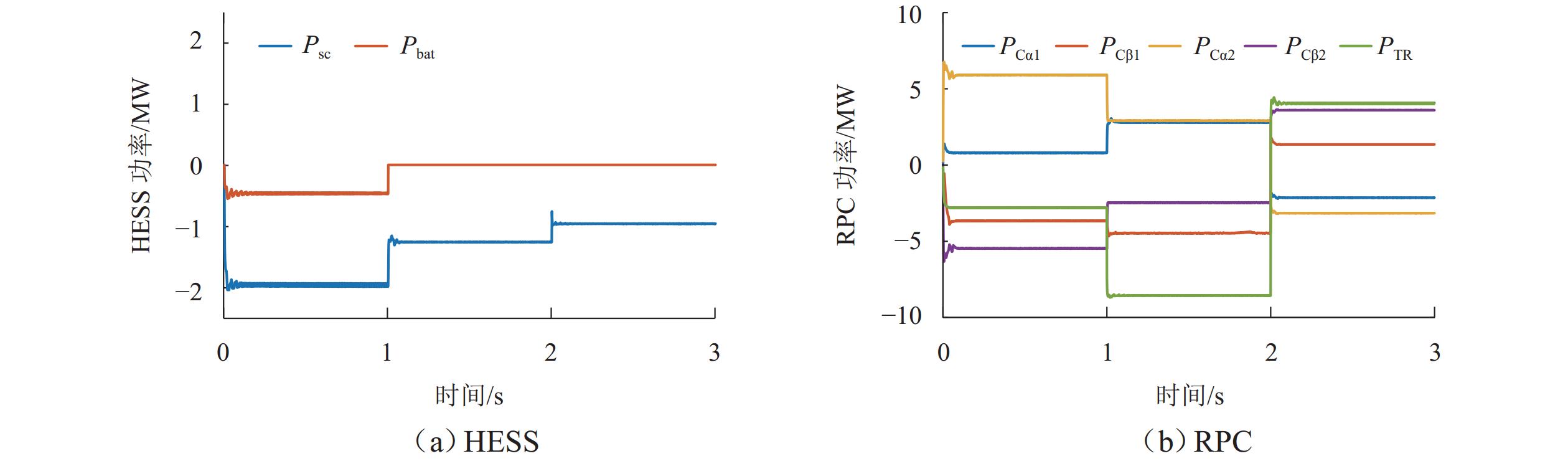
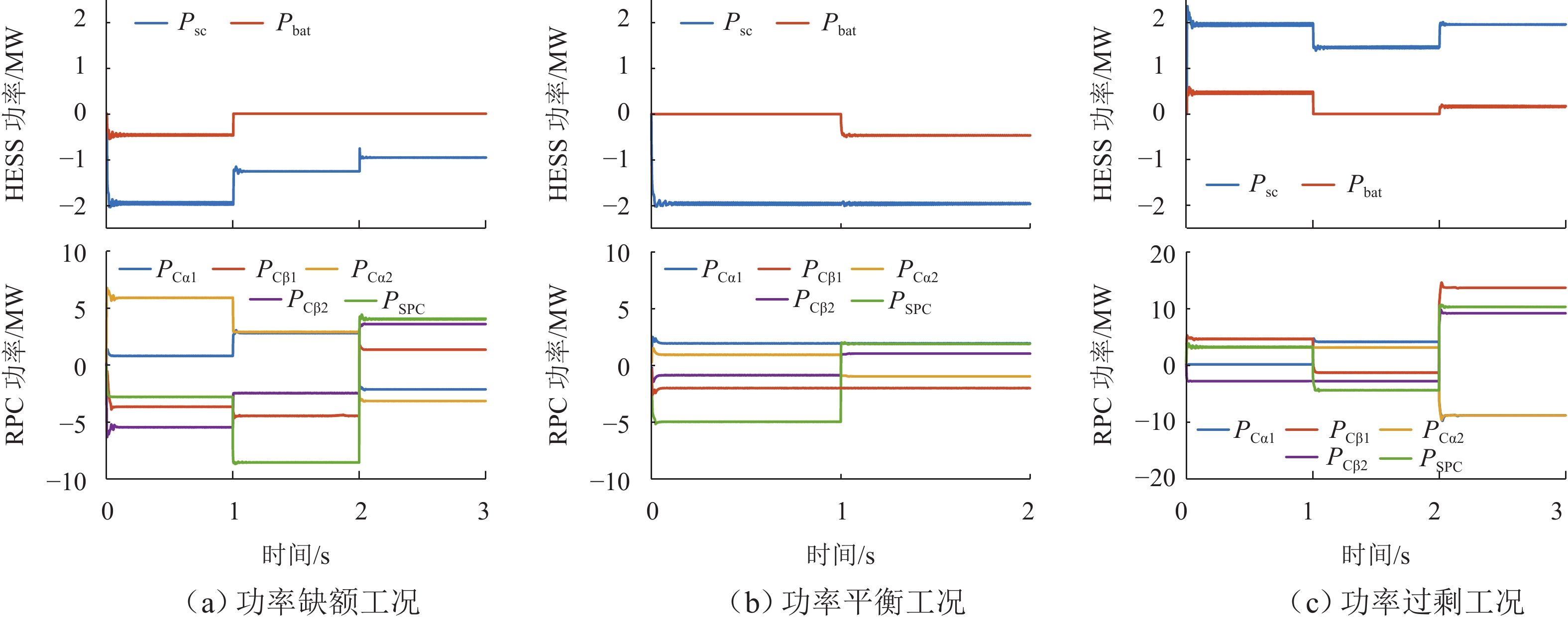
区域工况 HESS 工作状态 牵引工况 1 电池和超级电容均可最大功率放电 牵引工况 2 电池和超级电容均可放电 牵引工况 3 仅超级电容放电 制动工况 1 仅超级电容充电 制动工况 2 电池和超级电容均可充电 制动工况 3 电池和超级电容均可最大功率充电 表 4 系统仿真参数
Table 4. Simulation parameters of system
类别 参数 数值 类别 参数 数值 超级电容 SOC 范围 [0.05,0.95] 收益参数 电度电费/(元·(kW·h)−1) 0.6 功率成本/(元·kW−1) 600 需量电费/(元·(kWh·月)−1) 40 充放电效率 0.95 附加电费/(元·(kW·h)−1) 0.1 锂电池 SOC 范围 [0.2,0.8] 其他参数 设备残值率/% 7 功率成本/(元·kW−1) 1000 通货膨胀率/% 5 容量成本/(元·(kW·h)−1) 1200 资本贴现率/% 3.5 充放电效率 0.85 项目全寿命周期/年 15 成本参数 PV 投资成本/(元·kW−1) 9000 决策变量
限制参数超级电容功率/kW [ 1000 ,15000 ]PV 运维成本/(元·(kW·年)−1) 45 锂电池功率/kW [ 1000 ,6000 ]RPC 投资成本/(元·kW−1) 460 锂电池容量/(kW·h) [ 2000 ,10000 ]配套设备成本/(元·(kW·月)−1) 200 PV 装机容量/kW [ 2000 ,10000 ]HESS 运维成本/(元·(kW·月)−1) 0.1 放电阈值/kW [ 2000 ,6000 ]充电阈值/kW [− 5000 ,−500]表 5 多目标优化配置方案
Table 5. Schemes of multi-objective optimization configuration
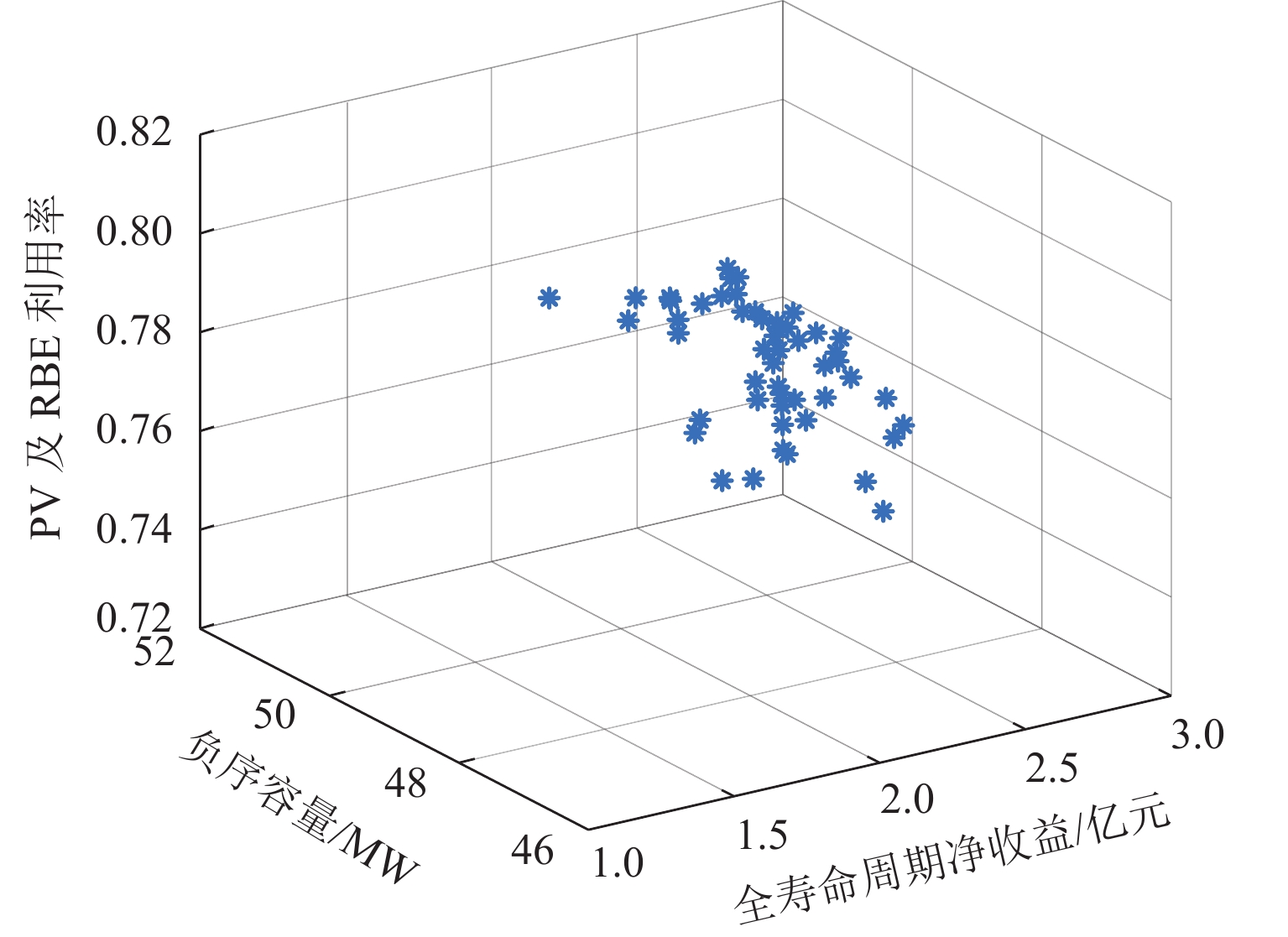
参数 方案 1 方案 2 方案 3 方案 4 超级电容功率/MW 5.96 11.56 12.57 13.37 超级电容容量/(kW·h−1) 59.62 115.68 125.72 133.77 锂电池功率/MW 2.19 4.85 5.50 5.16 锂电池容量/(MW·h) 2.89 4.26 5.27 10.00 PV 装机容量/MW 10.00 9.85 10.00 9.91 RPC 容量/MW 13.81 14.47 14.59 14.21 放电阈值/MW 40.74 42.89 43.33 42.07 能量利用率/% 74.61 79.94 80.14 81.28 总负序容量/MW 48.51 48.81 48.39 47.70 变电所 1 负序容量/MW 27.33 27.14 27.13 27.35 变电所 2 负序容量/MW 21.18 21.67 21.26 20.35 净收益/万元 25695 21986 20447 12441 表 6 4种方案效果对比
Table 6. Comparison of effect of four schemes
方案 $ \eta $/% $ {S^{( - )}} $/MW $ {C_{{\text{total}}}} $/万元 $ R $/万元 方案 A 0 74.89 23.56 0 方案 B 60.96 50.78 21.50 1.41 方案 C 65.75 51.55 21.34 2.37 本文方案 74.61 48.51 18.57 4.69 优化率/% 35.22 21.18 -
[1] 发展和改革部. 中国国家铁路集团有限公司2022年统计公报[N/OL]. 人民铁道, 2023-03-17[2024-01-16]. http://www.china-railway.com.cn/xwzx/zhxw/202303/t20230317_126718.html. [2] 耿安琪, 胡海涛, 张育维, 等. 基于阶梯能量管理的电气化铁路混合储能系统控制策略[J]. 电工技术学报, 2021, 36(23): 4916-4925.GENG Anqi, HU Haitao, ZHANG Yuwei, et al. Control strategy of hybrid energy storage system for electrified railway based on increment energy management[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2021, 36(23): 4916-4925. [3] 陈维荣, 王小雨, 韩莹, 等. 基于RPC的光储接入牵引供电系统协调控制方法[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2024, 59(1): 1-10.CHEN Weirong, WANG Xiaoyu, HAN Ying, et al. Coordinated control method of photovoltaic and battery system connected to traction power supply system based on railway power conditioner[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2024, 59(1): 1-10. [4] 邓文丽, 戴朝华, 陈维荣. 轨道交通能源互联网背景下光伏在交/直流牵引供电系统中的应用及关键问题分析[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2019, 39(19): 5692-5702, 5897.DENG Wenli, DAI Chaohua, CHEN Weirong. Application of PV generation in AC/DC traction power supply system and the key problem analysis under the background of rail transit energy Internet[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2019, 39(19): 5692-5702, 5897. [5] 张丽艳, 贾瑛, 韩笃硕, 等. 电气化铁路同相储能供电系统能量管理及容量配置策略[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2023, 58(1): 22-29.ZHANG Liyan, JIA Ying, HAN Dushuo, et al. Energy management and capacity allocation scheme for co-phase traction power supply and energy storage system in electrified railways[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2023, 58(1): 22-29. [6] JI L, YU Z W, MA J, et al. The potential of photovoltaics to power the railway system in China[J]. Energies, 2020, 13(15): 3844. doi: 10.3390/en13153844 [7] 贾利民, 程鹏, 张蜇, 等. “双碳” 目标下轨道交通与能源融合发展路径和策略研究[J]. 中国工程科学, 2022, 24(3): 173-183. doi: 10.15302/J-SSCAE-2022.03.018JIA Limin, CHENG Peng, ZHANG Zhe, et al. Integrated development of rail transit and energies in China: development paths and strategies[J]. Strategic Study of CAE, 2022, 24(3): 173-183. doi: 10.15302/J-SSCAE-2022.03.018 [8] 黄小红, 赵艺, 李群湛, 等. 电气化铁路同相储能供电技术[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2020, 55(4): 856-864. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20181083HUANG Xiaohong, ZHAO Yi, LI Qunzhan, et al. Co-phase traction power supply and energy storage technology for electrified railway[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2020, 55(4): 856-864. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20181083 [9] 胡海涛, 陈俊宇, 葛银波, 等. 高速铁路再生制动能量储存与利用技术研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2020, 40(1): 246-256, 391.HU Haitao, CHEN Junyu, GE Yinbo, et al. Research on regenerative braking energy storage and utilization technology for high-speed railways[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2020, 40(1): 246-256,391. [10] 刘元立, 李群湛. 含光伏和混合储能的同相牵引供电系统日前优化调度[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2023, 58(1): 30-39.LIU Yuanli, LI Qunzhan. Day-ahead optimal scheduling of co-phase traction power supply system with photovoltaic and hybrid energy storage[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2023, 58(1): 30-39. [11] AGUADO J A, SÁNCHEZ RACERO A J, DE LA TORRE S. Optimal operation of electric railways with renewable energy and electric storage systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2018, 9(2): 993-1001. doi: 10.1109/TSG.2016.2574200 [12] LIU Y L, CHEN M W, LU S F, et al. Optimized sizing and scheduling of hybrid energy storage systems for high-speed railway traction substations[J]. Energies, 2018, 11(9): 2199. doi: 10.3390/en11092199 [13] 郑政. 含光伏发电的牵引供电系统混合储能优化配置研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2018. [14] 邓文丽, 戴朝华, 韩春白雪, 等. 计及再生制动能量回收和电能质量改善的铁路背靠背混合储能系统及其控制方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2019, 39(10): 2914-2924.DENG Wenli, DAI Chaohua, HAN Chunbaixue, et al. Back-to-back hybrid energy storage system of electric railway and its control method considering regenerative braking energy recovery and power quality improvement[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2019, 39(10): 2914-2924. [15] 李群湛, 王喜军, 黄小红, 等. 电气化铁路飞轮储能技术研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2019, 39(7): 2025-2033.LI Qunzhan, WANG Xijun, HUANG Xiaohong, et al. Research on flywheel energy storage technology for electrified railway[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2019, 39(7): 2025-2033. [16] 袁佳歆, 曲锴, 郑先锋, 等. 高速铁路混合储能系统容量优化研究[J]. 电工技术学报, 2021, 36(19): 4161-4169, 4182.YUAN Jiaxin, QU Kai, ZHENG Xianfeng, et al. Optimizing research on hybrid energy storage system of high speed railway[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2021, 36(19): 4161-4169, 4182. [17] 张育维, 胡海涛, 耿安琪, 等. 考虑削峰填谷的电气化铁路混合储能系统容量优化配置[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2023, 43(2): 44-50.ZHANG Yuwei, HU Haitao, GENG Anqi, et al. Capacity optimization configuration of hybrid energy storage system for electrified railway considering peak load shifting[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2023, 43(2): 44-50. [18] CHEN J Y, GE Y B, WANG K, et al. Integrated regenerative braking energy utilization system for multi-substations in electrified railways[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2023, 70(1): 298-310. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2022.3146563 [19] 邓文丽, 戴朝华, 陈维荣, 等. 铁路功率调节器研究进展[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2020, 40(14): 4640-4655, 4742.DENG Wenli, DAI Chaohua, CHEN Weirong, et al. Research progress of railway power conditioner[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2020, 40(14): 4640-4655, 4742. [20] 罗嘉明, 韦晓广, 高仕斌, 等. 高速铁路储能系统容量配置与能量管理技术综述与展望[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2022, 42(19): 7028-7051.LUO Jiaming, WEI Xiaoguang, GAO Shibin, et al. Summary and outlook of capacity configuration and energy management technology of high-speed railway energy storage system[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2022, 42(19): 7028-7051. [21] 杨浩丰, 刘冲, 李彬, 等. 基于列车运行工况的城轨地面式混合储能系统控制策略研究[J]. 电工技术学报, 2021, 36(增1): 168-178.YANG Haofeng, LIU Chong, LI Bin, et al. Research on control strategy of urban rail ground hybrid energy storage device based on train operating condition[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2021, 36(S1): 168-178. [22] GE Y B, HU H T, CHEN J Y, et al. Combined active and reactive power flow control strategy for flexible railway traction substation integrated with ESS and PV[J]. IEEE Transactions on Sustainable Energy, 2022, 13(4): 1969-1981. doi: 10.1109/TSTE.2022.3178095 [23] 吴小刚, 刘宗歧, 田立亭, 等. 基于改进多目标粒子群算法的配电网储能选址定容[J]. 电网技术, 2014, 38(12): 3405-3411.WU Xiaogang, LIU Zongqi, TIAN Liting, et al. Energy storage device locating and sizing for distribution network based on improved multi-objective particle swarm optimizer[J]. Power System Technology, 2014, 38(12): 3405-3411. [24] 胡元潮, 阮羚, 阮江军, 等. 基于改进逼近理想点法的变电站智能化改造评估[J]. 电网技术, 2012, 36(10): 42-48.HU Yuanchao, RUAN Ling, RUAN Jiangjun, et al. Evaluation on intelligent renovation of substations based on improved TOPSIS[J]. Power System Technology, 2012, 36(10): 42-48. [25] 李相俊, 马锐, 王上行, 等. 考虑电池寿命的商业园区储能电站运行控制策略[J]. 高电压技术, 2020, 46(1): 62-70.LI Xiangjun, MA Rui, WANG Shangxing, et al. Operation control strategy for energy storage station after considering battery life in commercial park[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2020, 46(1): 62-70. -




 下载:
下载: