DEM Study About Influence of Fabric Anisotropy on Formation Disturbance
-
摘要:
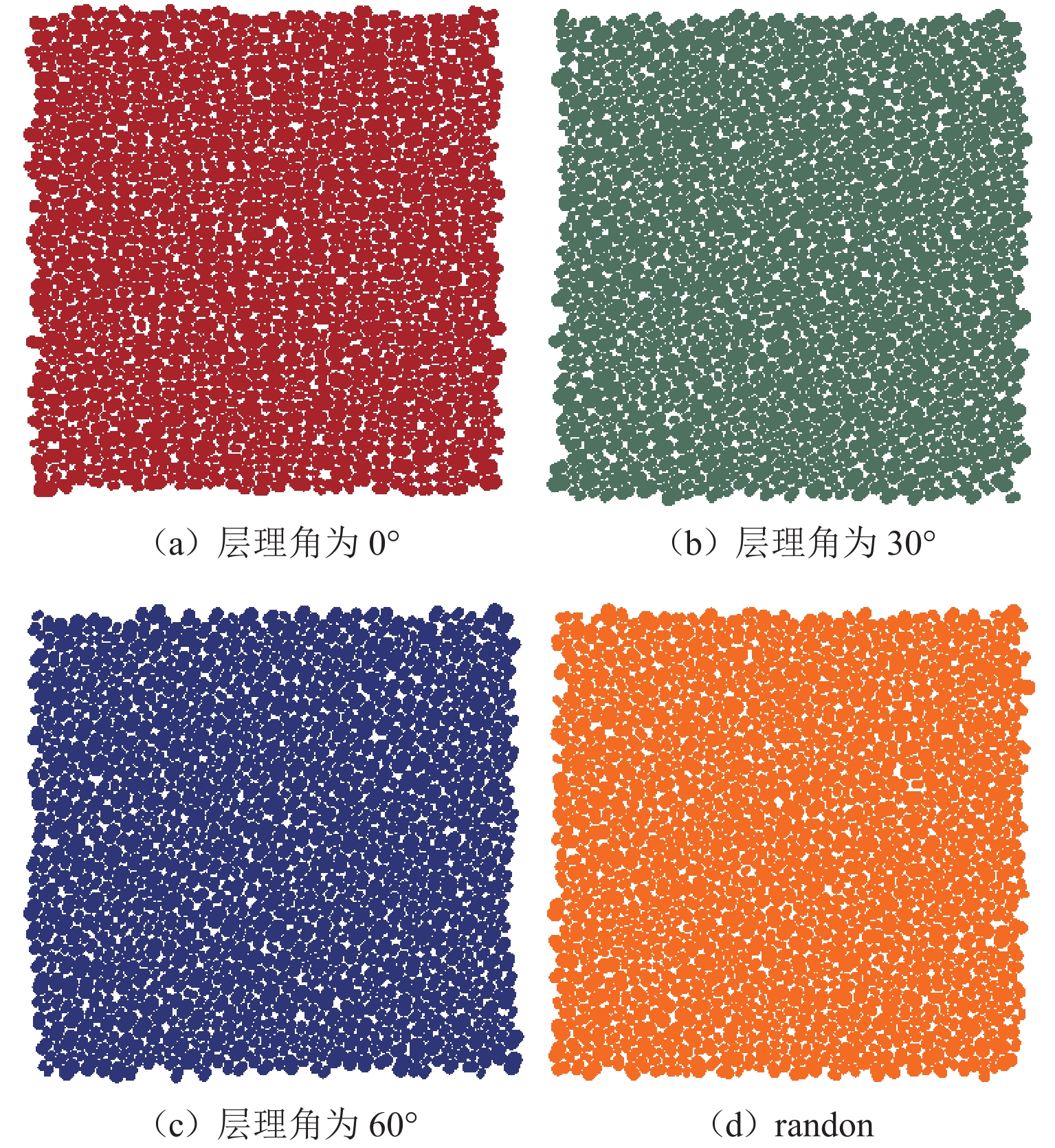
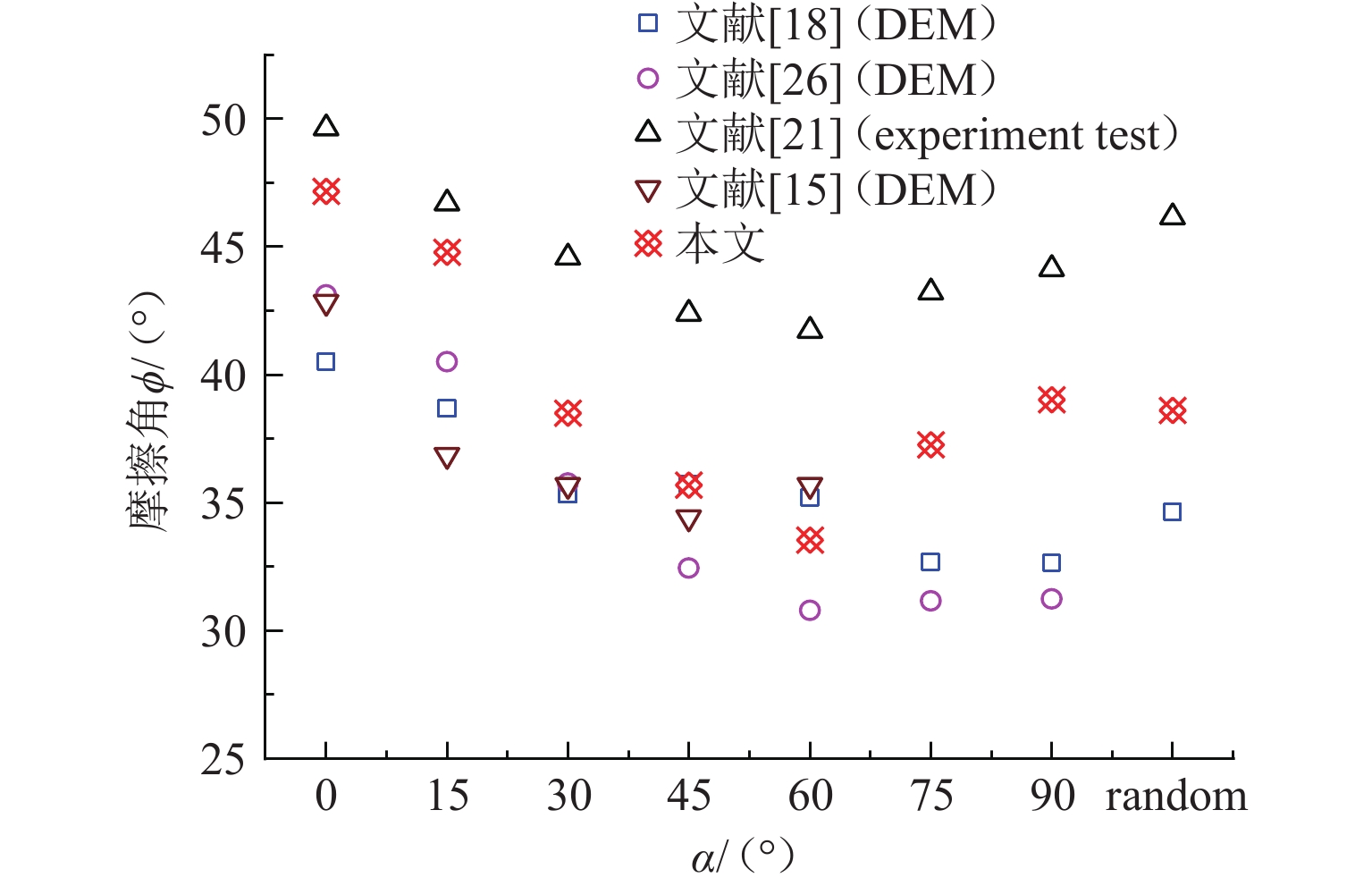
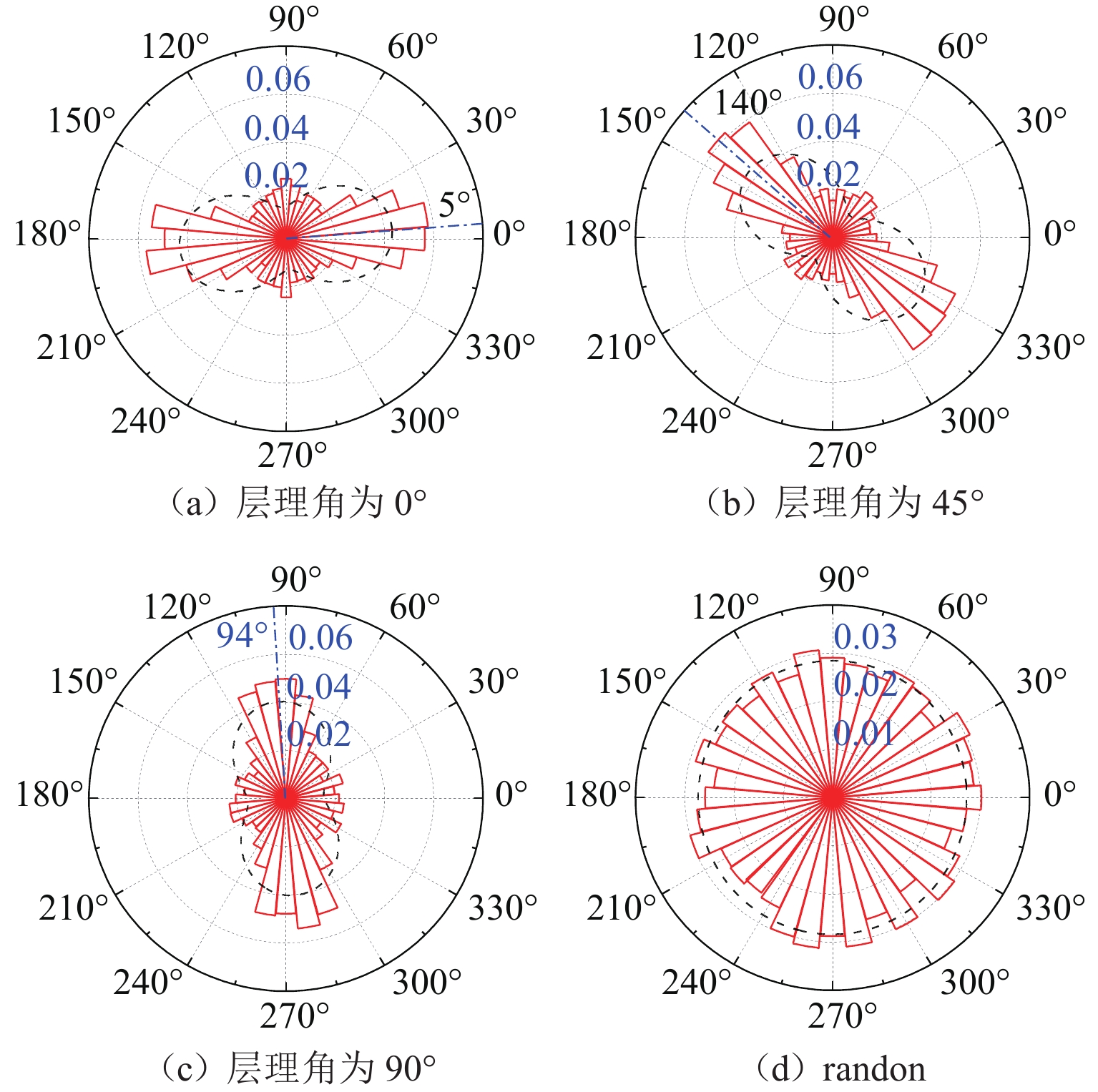
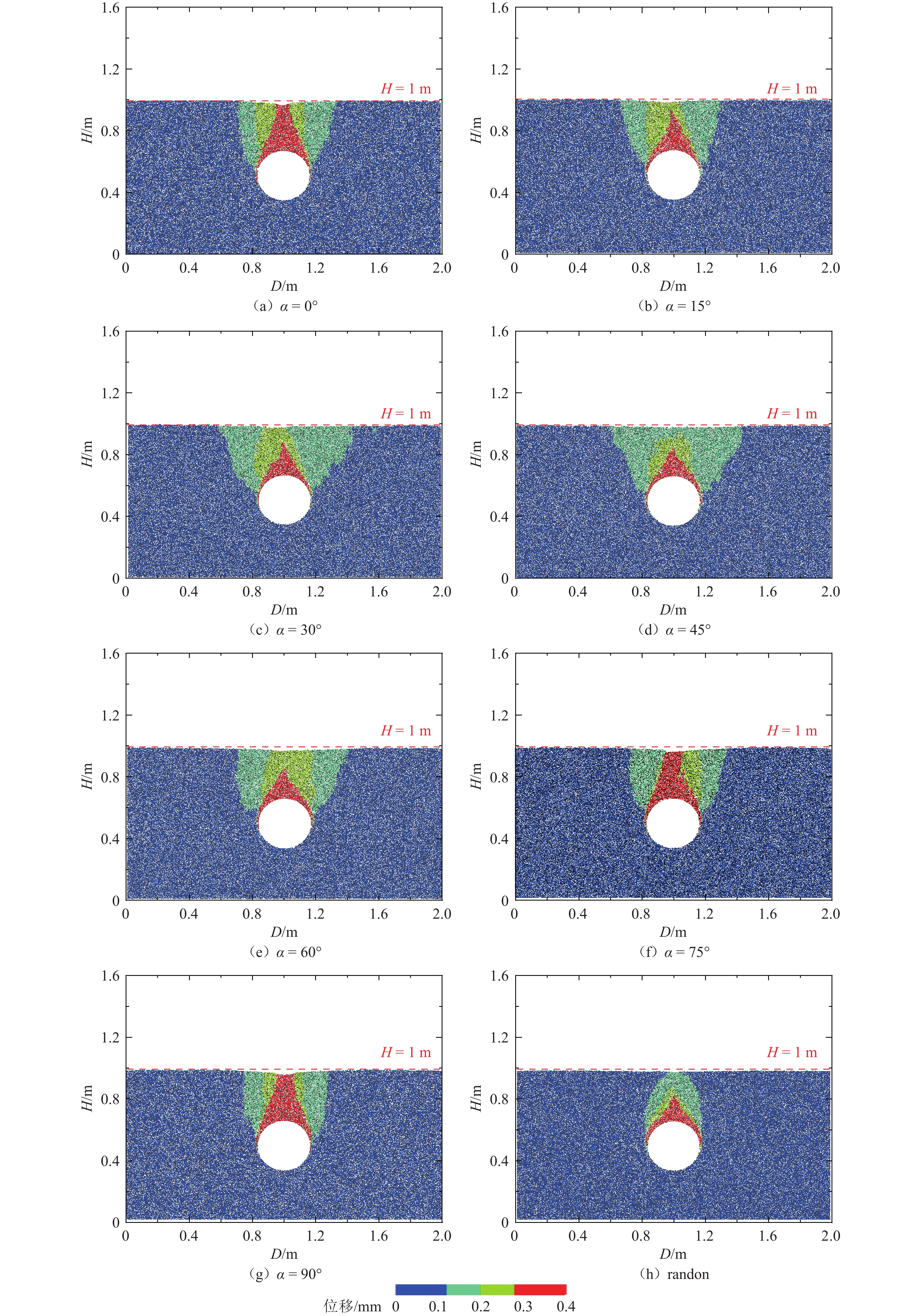
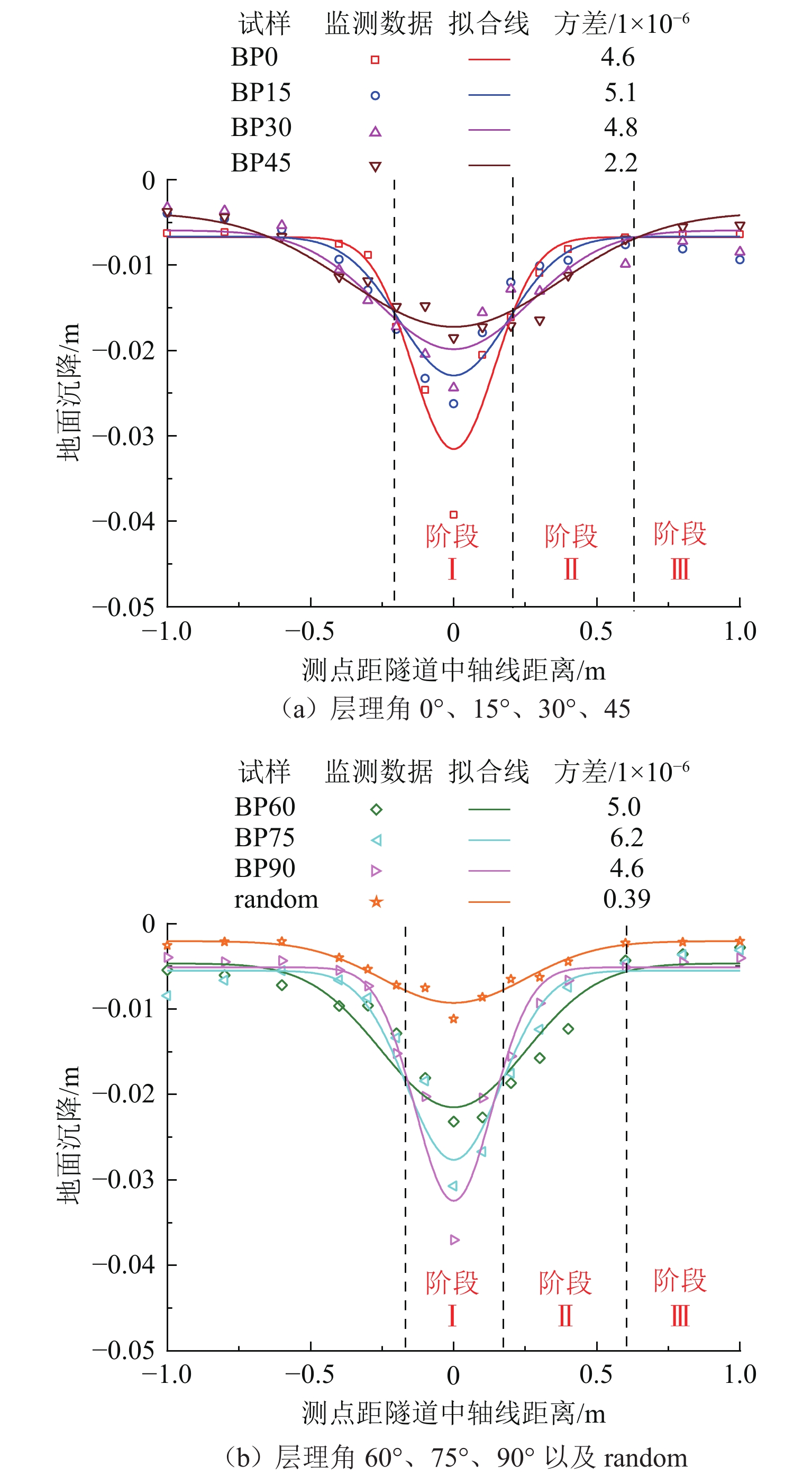
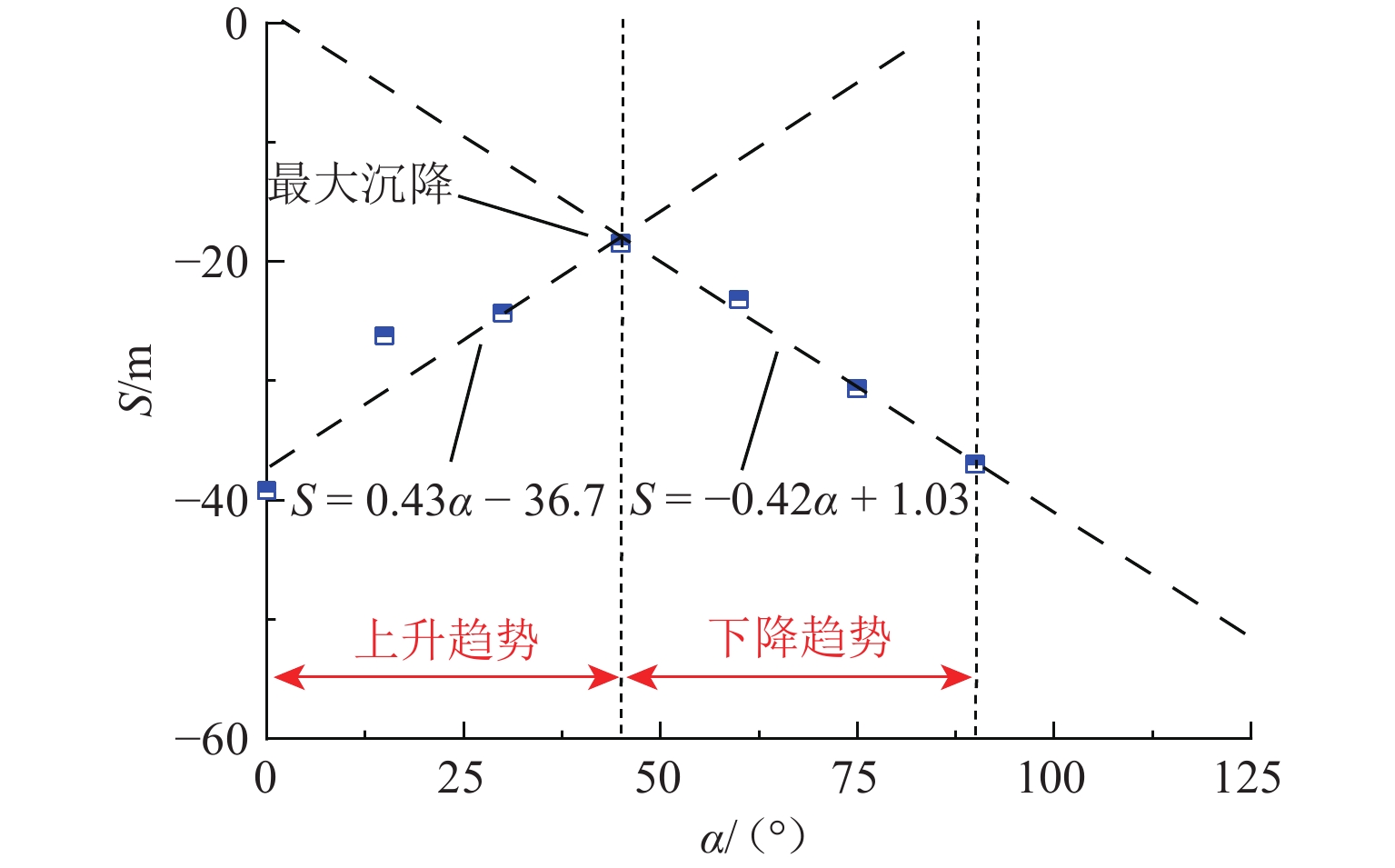
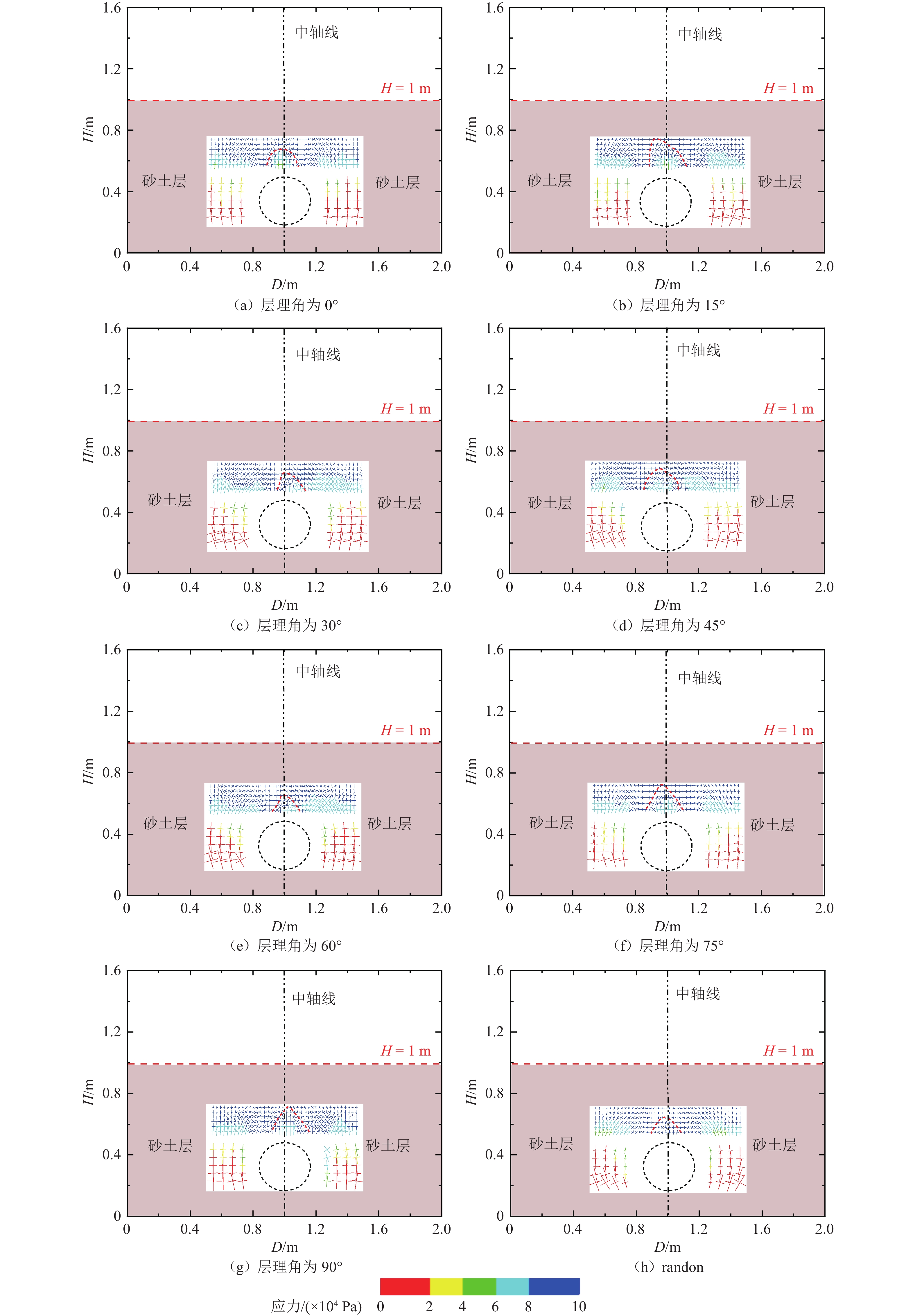
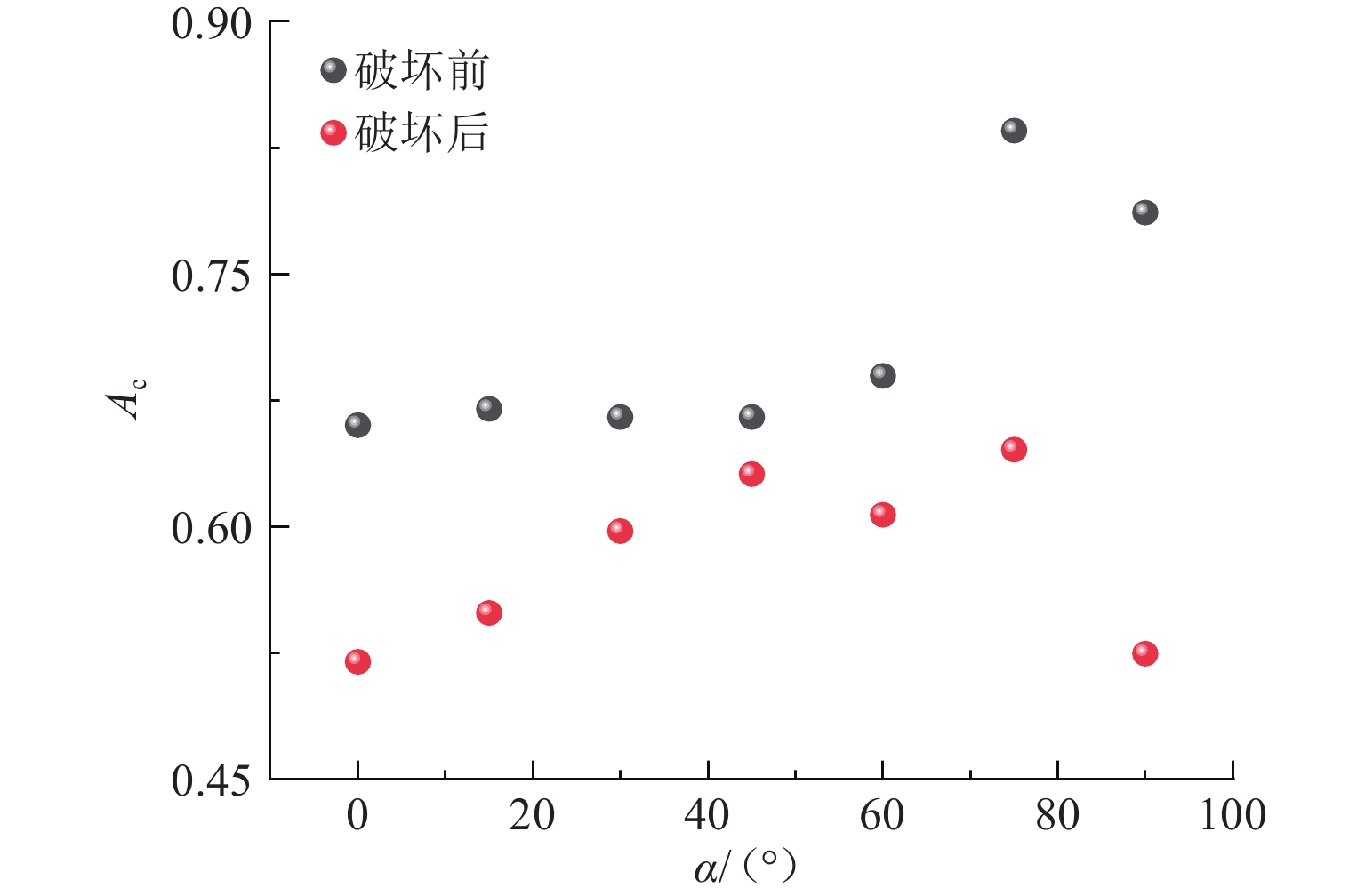
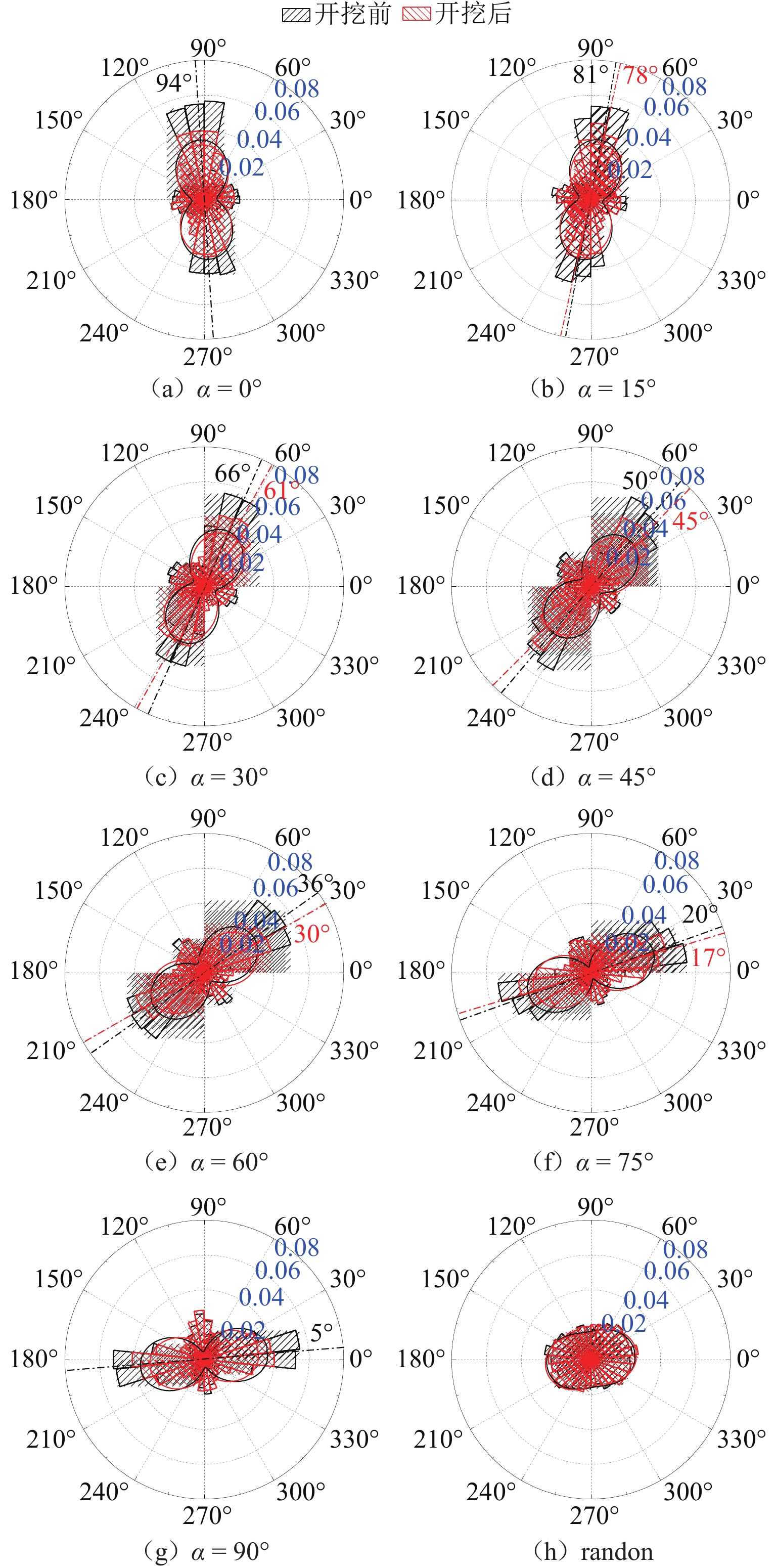
组构各向异性是影响砂土力学特性的重要因素,进而对盾构隧道开挖过程中地层扰动产生显著影响. 为探究组构各向异性对砂土地层扰动特性的影响,基于二维离散元方法,创建具有重叠的类椭圆簇颗粒,长轴取向被特定排列以形成不同各向异性的砂土试样,长轴取向与水平沉积方向为层理角;进行二维代表性体积单元(RVE)代表单元体双轴实验,并将数值模拟所得到的峰值摩擦角与已有文献中的实验结果进行对比验证;生成具有不同层理角的地层,隧道开挖地层损失依据Park地层损失假定. 模拟结果表明:当在各向异性地层中进行盾构隧道开挖时,隧道中轴线两侧扰动范围出现不对称效应;地表沉降曲线分为影响区、扩展区与削弱区,层理角对地表沉降的影响仅表现在影响区、扩展区;地表沉降槽中最大沉降的最大值出现在层理角为0°的试样中,为0.037 m;层理角为45°的试样中最大沉降最小,为0.011 m;随着层理角增大,45°左侧的最大沉降呈线性上升趋势,右侧呈线性下降趋势;隧道主应力的偏转与位移偏转造成的不对称效应一致;层理角为0°和90°的试样中,接触法向分布的主方向未发生改变.
Abstract:Fabric anisotropy is an important factor affecting the mechanical properties of sandy soil, and the formation disturbance caused by shield tunnel excavation in sandy soil is largely affected by the mechanical properties of the overlying sandy soil. This study utilizes the two-dimensional discrete element method to model particles as overlapping ellipse-like clusters, specifically arranging the long-axis orientation to create sand samples with varying anisotropy. The long-axis orientation and horizontal deposition direction form the bedding plane. A two-dimensional RVE biaxial test shows that the peak friction angle initially decreases and then increases with the bedding angle, aligning with experimental findings. Subsequently, strata with different bedding angles are generated, and tunnel excavation is analyzed based on Park's stratum loss model. In anisotropic strata, the disturbance range exhibits asymmetry about the tunnel's central axis. The surface settlement curve divides into three zones: influence, expansion, and weakening. The effect of bedding angle is evident only in the influence and expansion zones. Maximum settlement occurs at a bedding angle of 0°, while it is minimized at 45°. As the bedding angle increases, maximum settlement trends upward on the left side and downward on the right side of 45°. The principal stress deflection of the tunnel correlates with the displacement-induced asymmetry. In the samples with bedding angles of 0° and 90°, the main direction of the distribution of the contact normal did not change.
-
Key words:
- sandy soil /
- fabric anisotropy /
- shield tunneling /
- formation disturbance /
- ground settlement /
- discrete element method
-
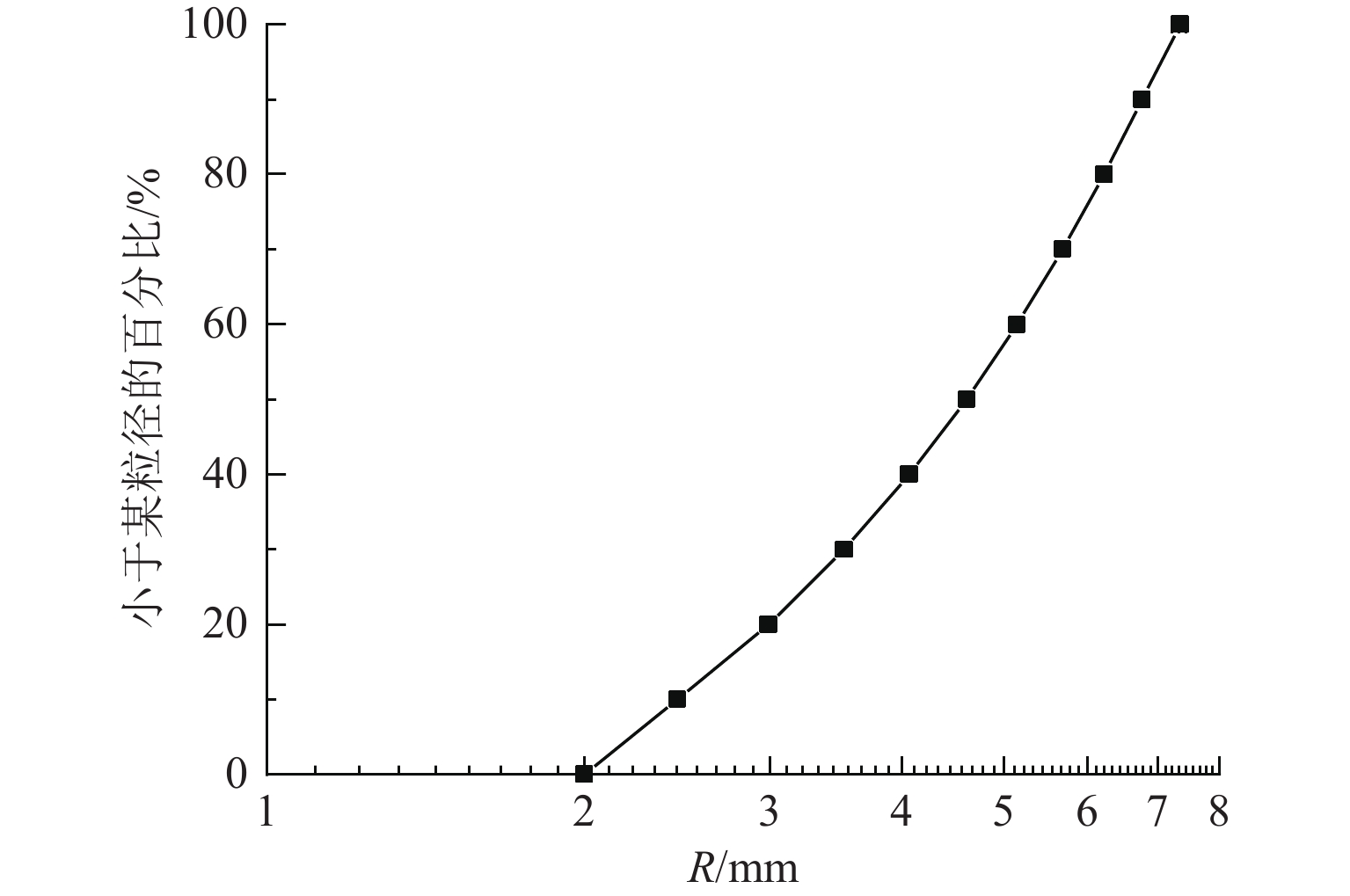
表 1 试样的微观参数
Table 1. Micro parameter of samples
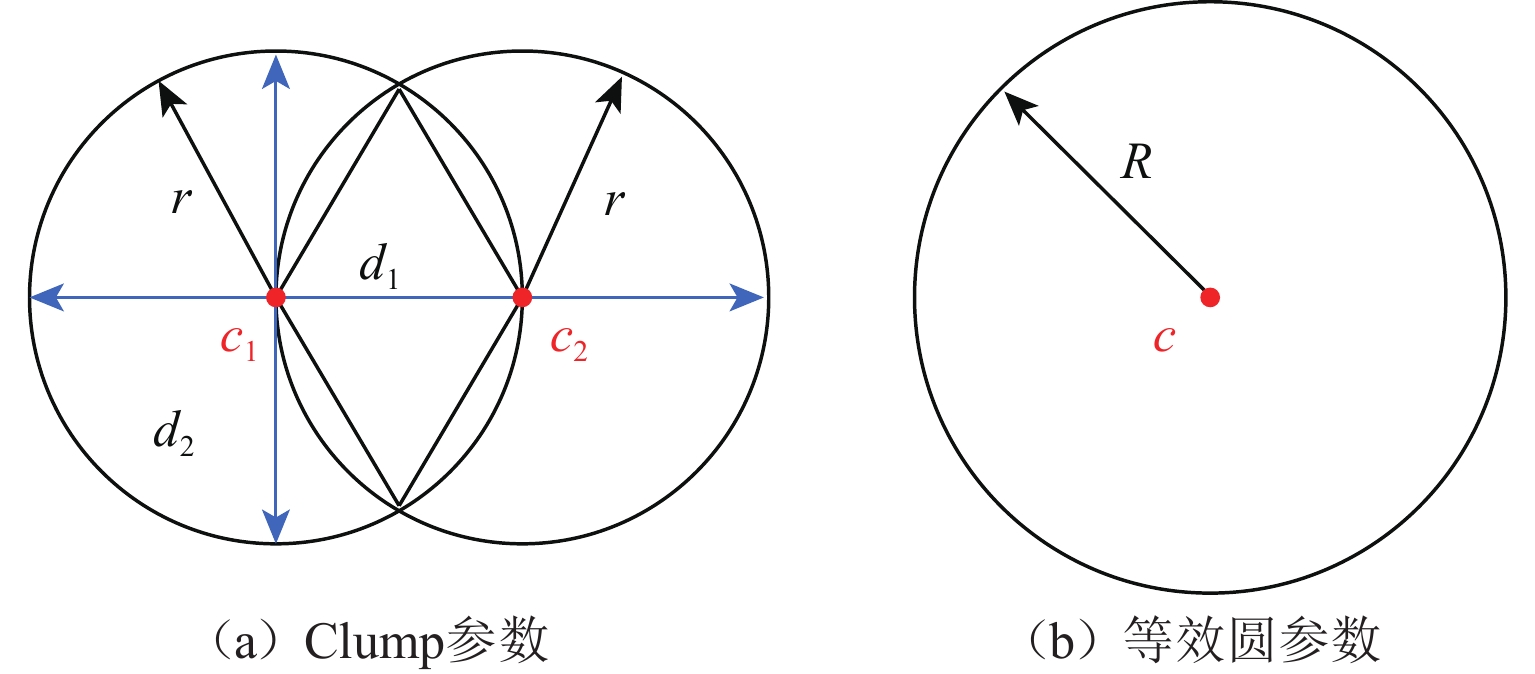
微观参数 取值 $ r $/mm 2.5~7.5 $ {d}_{1} $ 3r $ {d}_{2} $ 2r 法向刚度$ {k}_{{\mathrm{n}}} $/(GN·m−1) 4.0 刚度比$ {k}_{{\mathrm{n}}} $/$ {k}_{{\mathrm{s}}} $ 1.5 $ \mu $ 0.5 阻尼$ \rho $ 0.7 表 2 详细的试样方案
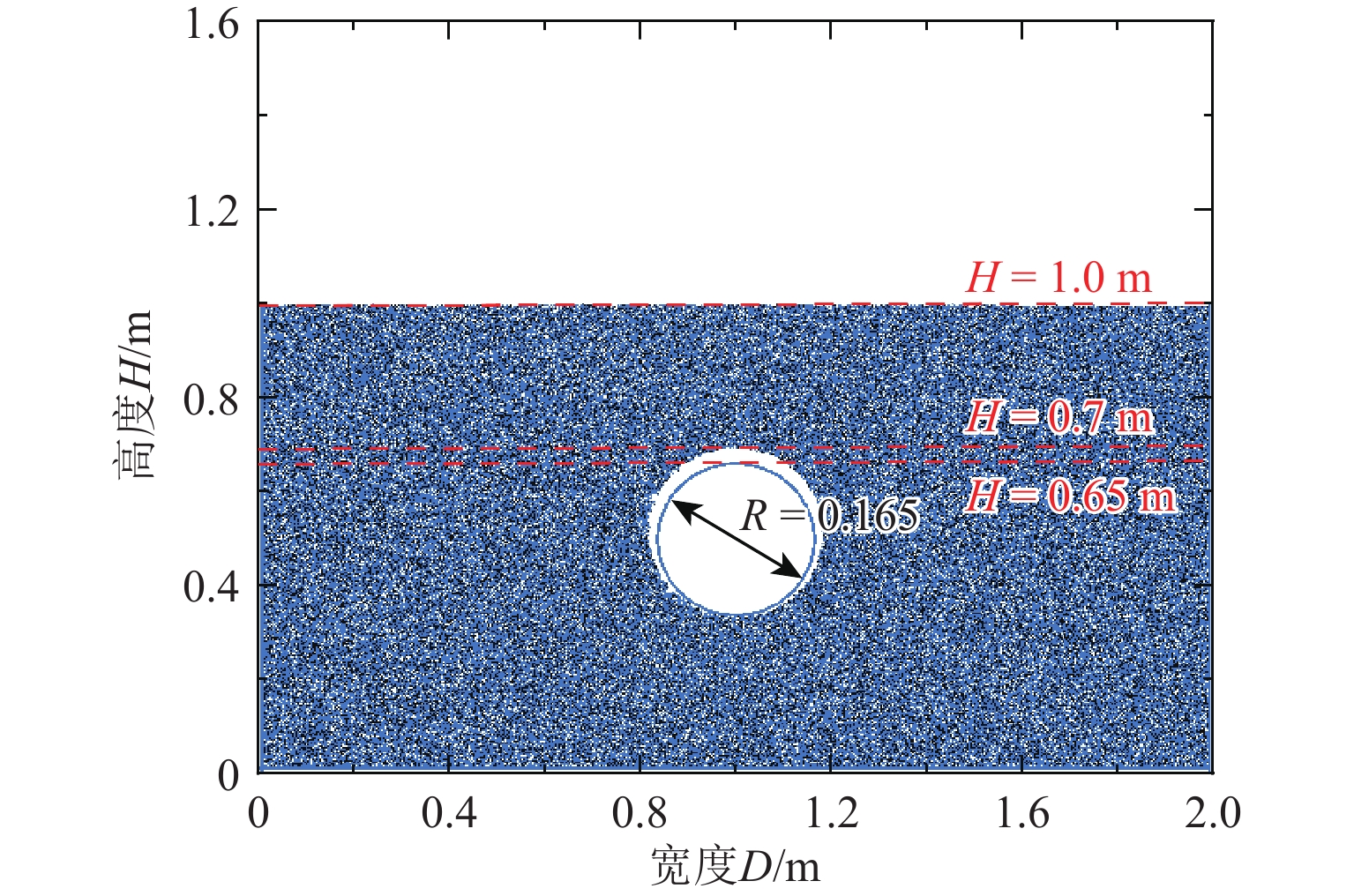
Table 2. Experiment planning in detail
试样 α(°) H/m D/m R/m 地层损失率/% S0 0 1 2 0.165 0.2 S15 15 1 2 0.165 0.2 S30 30 1 2 0.165 0.2 S45 45 1 2 0.165 0.2 S60 60 1 2 0.165 0.2 S75 75 1 2 0.165 0.2 S90 90 1 2 0.165 0.2 随机分布 随机分布 1 2 0.165 0.2 -
[1] CUI J G, ALLAN A, LIN D. The development of grade separation pedestrian system: a review[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2013, 38: 151-160. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2013.06.004 [2] CUI J Q, BROERE W, LIN D. Underground space utilisation for urban renewal[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2021, 108: 103726.1-103726.10. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2020.103726 [3] HU X Y, HE C, LAI X H, et al. A DEM-based study of the disturbance in dry sandy ground caused by EPB shield tunneling[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2020, 101: 103410.1-103410.16. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2020.103410 [4] YIN Z Y, WANG P, ZHANG F S. Effect of particle shape on the progressive failure of shield tunnel face in granular soils by coupled FDM-DEM method[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2020, 100: 103394.1-103394.16. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2020.103394 [5] 韩旭, 张冰利, 洪小星, 等. 砂土地层小曲率半径盾构隧道施工引起的地层变形规律——以南通地铁1号线为例[J]. 隧道建设(中英文), 2022, 42(增刊2): 114-123. doi: 10.3973/j.issn.2096-4498.2022.S2.014HAN Xu, ZHANG Bingli, HONG Xiaoxing, et al. Strata deformation law caused by shield tunnel construction with small curvature radius in sandy soil: taking Nantong metro line 1 as an example[J]. Tunnel Construction, 2022, 42(S2): 114-123. doi: 10.3973/j.issn.2096-4498.2022.S2.014 [6] 梁连, 方焘, 方立建, 等. 基于PIV技术的隧道施工引起的地层变形规律试验研究[J]. 隧道建设(中英文), 2023, 43(4): 625-633. doi: 10.3973/j.issn.2096-4498.2023.04.009LIANG Lian, FANG Tao, FANG Lijian, et al. Experimental study on deformation law of stratum caused by tunnel construction based on particle image velocimetry technique[J]. Tunnel Construction, 2023, 43(4): 625-633. doi: 10.3973/j.issn.2096-4498.2023.04.009 [7] 胡雄玉, 晏启祥, 何川, 等. 土压平衡盾构掘进对散粒体地层扰动和开挖面破坏特性研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2016, 35(8): 1618-1627. doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2016.0075HU Xiongyu, YAN Qixiang, HE Chuan, et al. Study on the disturbance and excavation face failure feature of granular mixtures stratum due to EPB shield tunneling[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2016, 35(8): 1618-1627. doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2016.0075 [8] 王俊, 方勇, 何川, 等. 盾构隧道施工对砂性地层的扰动及管片受荷特征[J]. 地下空间与工程学报, 2015, 11(1): 156-162, 170. doi: 10.20174/j.juse.2015.01.024WANG Jun, FANG Yong, HE Chuan, et al. Disturbance of shield tunnel construction to sandy stratum and load bearing characteristics of segment lining[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering, 2015, 11(1): 156-162,170. doi: 10.20174/j.juse.2015.01.024 [9] 张箭, 王树英, 阳军生, 等. 北京地铁敞口式盾构掘进对砂层土体扰动规律研究[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 37(4): 572-577. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3026.2016.04.025ZHANG Jian, WANG Shuying, YANG Junsheng, et al. Soil disturbance of Beijing subway constructed by open-face shield tunneling method in sandy stratum[J]. Journal of Northeastern University (Natural Science), 2016, 37(4): 572-577. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3026.2016.04.025 [10] 尹光志, 李星, 鲁俊, 等. 真三轴应力条件下层状复合岩石破坏准则[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2017, 36(2): 261-269. doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2016.0682YIN Guangzhi, LI Xing, LU Jun, et al. A failure criterion for layered composite rock under true triaxial stress conditions[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2017, 36(2): 261-269. doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2016.0682 [11] SONG I, SUH M. Effects of foliation and microcracks on ultrasonic anisotropy in retrograde ultramafic and metamorphic rocks at shallow depths[J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 2014, 109: 27-35. doi: 10.1016/j.jappgeo.2014.07.011 [12] XU G W, HE C, SU A, et al. Experimental investigation of the anisotropic mechanical behavior of phyllite under triaxial compression[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2018, 104: 100-112. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2018.02.017 [13] 卢海峰, 魏爱超, 邹星辰. 层状板裂组合结构岩体力学特性试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2022, 41(增2): 3282-3293. LU Haifeng, WEI Aichao, ZHOU Xingchen, et al. Experimental study on mechanical properties of layered slab-crack composite structure rock mass[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, , 2022, 41(增2): 3282-3293. [14] DEWHURST D N, SIGGINS A F. Impact of fabric, microcracks and stress field on shale anisotropy[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2006, 165(1): 135-148. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2006.02834.x [15] GUO N, CHEN L F, YANG Z X. Multiscale modelling and analysis of footing resting on an anisotropic sand[J]. Géotechnique, 2022, 72(4): 364-376. doi: 10.1680/jgeot.20.p.306 [16] GUO P J. Modified direct shear test for anisotropic strength of sand[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2008, 134(9): 1311-1318. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2008)134:9(1311) [17] 张坤勇, 李威, 罗兴军, 等. 基于PFC2D的砂土原生各向异性微观机理数值试验[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2017, 39(3): 518-524. doi: 10.11779/CJGE201703016ZHANG Kunyong, LI Wei, LUO Xingjun, et al. Numerical experiments of microscopic mechanism of inherent anisotropy for sand based on PFC2D[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2017, 39(3): 518-524. doi: 10.11779/CJGE201703016 [18] LIANG W J, ZHAO S W, WU H R, et al. Bearing capacity and failure of footing on anisotropic soil: a multiscale perspective[J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2021, 137: 104279.1-104279.15. doi: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2021.104279 [19] ARTHUR J R F, MENZIES B K. Inherent anisotropy in a sand[J]. Géotechnique, 1972, 22(1): 115-128. [20] CASAGRANDE A, CARILLO N. Shear failure of anisotropic materials[J]. Proc. Boston Soc. civ. Engrs J. Boston Soc. Civ. Eng., 1944, 31(4): 74-87 [21] ODA M, KOISHIKAWA I, HIGUCHI T. Experimental study of anisotropic shear strength of sand by plane strain test[J]. Soils and Foundations, 1978, 18(1): 25-38. doi: 10.3208/sandf1972.18.25 [22] LAM W K, TATSUOKA F. Effects of initial anisotropic fabric and σ2 on strength and deformation characteristics of sand[J]. Soils and Foundations, 1988, 28(1): 89-106. doi: 10.3208/sandf1972.28.89 [23] AZAMI A, PIETRUSZCZAK S, GUO P. Bearing capacity of shallow foundations in transversely isotropic granular media[J]. International Journal for Numerical and Analytical Methods in Geomechanics, 2010, 34(8): 771-793. doi: 10.1002/nag.827 [24] TATSUOKA F, NAKAMURA S, HUANG C C, et al. Strength anisotropy and shear band direction in plane strain tests of sand[J]. Soils and Foundations, 1990, 30(1): 35-54. doi: 10.3208/sandf1972.30.35 [25] LADE P V, NAM J, HONG W P. Shear banding and cross-anisotropic behavior observed in laboratory sand tests with stress rotation[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 2008, 45(1): 74-84. doi: 10.1139/T07-078 [26] FU P C, DAFALIAS Y F. Study of anisotropic shear strength of granular materials using DEM simulation[J]. International Journal for Numerical and Analytical Methods in Geomechanics, 2011, 35(10): 1098-1126. [27] ZHAO J, GUO N. The interplay between anisotropy and strain localisation in granular soils: a multiscale insight[J]. Géotechnique, 2015, 65(8): 642-656. [28] WEI J T. DEM exploration of confining stress effect in cyclic liquefaction of granular soils[J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2021, 136: 104214.1-104214.9. doi: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2021.104214 [29] ODA M. Fabric tensor for discontinuous geological materials[J]. Soils and Foundations, 1982, 22(4): 96-108. doi: 10.3208/sandf1972.22.4_96 [30] ODA M, NEMAT-NASSER S, KONISHI J. Stress-induced anisotropy in granular masses[J]. Soils and Foundations, 1985, 25(3): 85-97. doi: 10.3208/sandf1972.25.3_85 -




 下载:
下载: