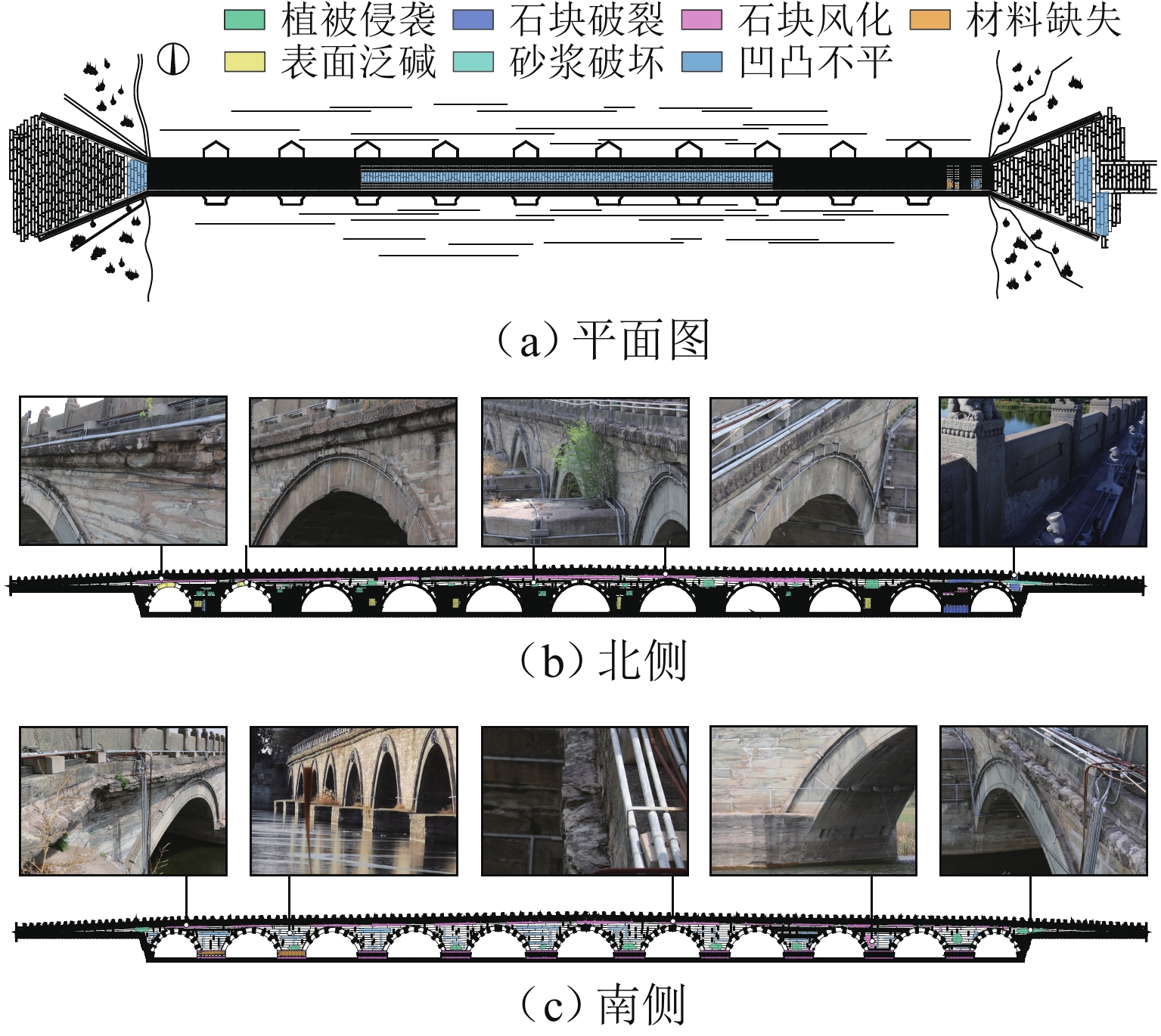
Optimal Sensor Placement and Evaluation Method of Stone Arch Bridge Based on Meta-Genetic Algorithm
-
摘要:
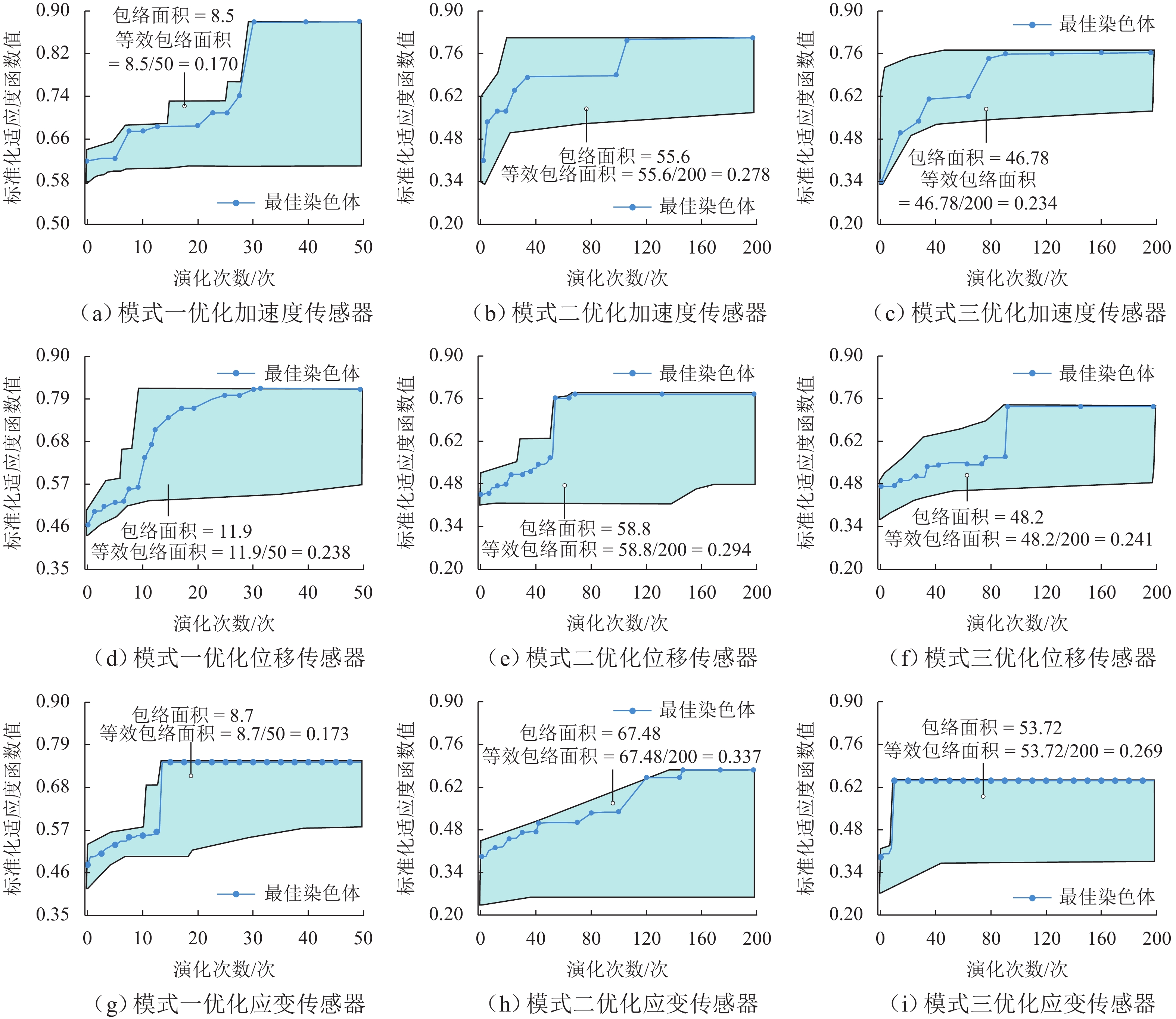
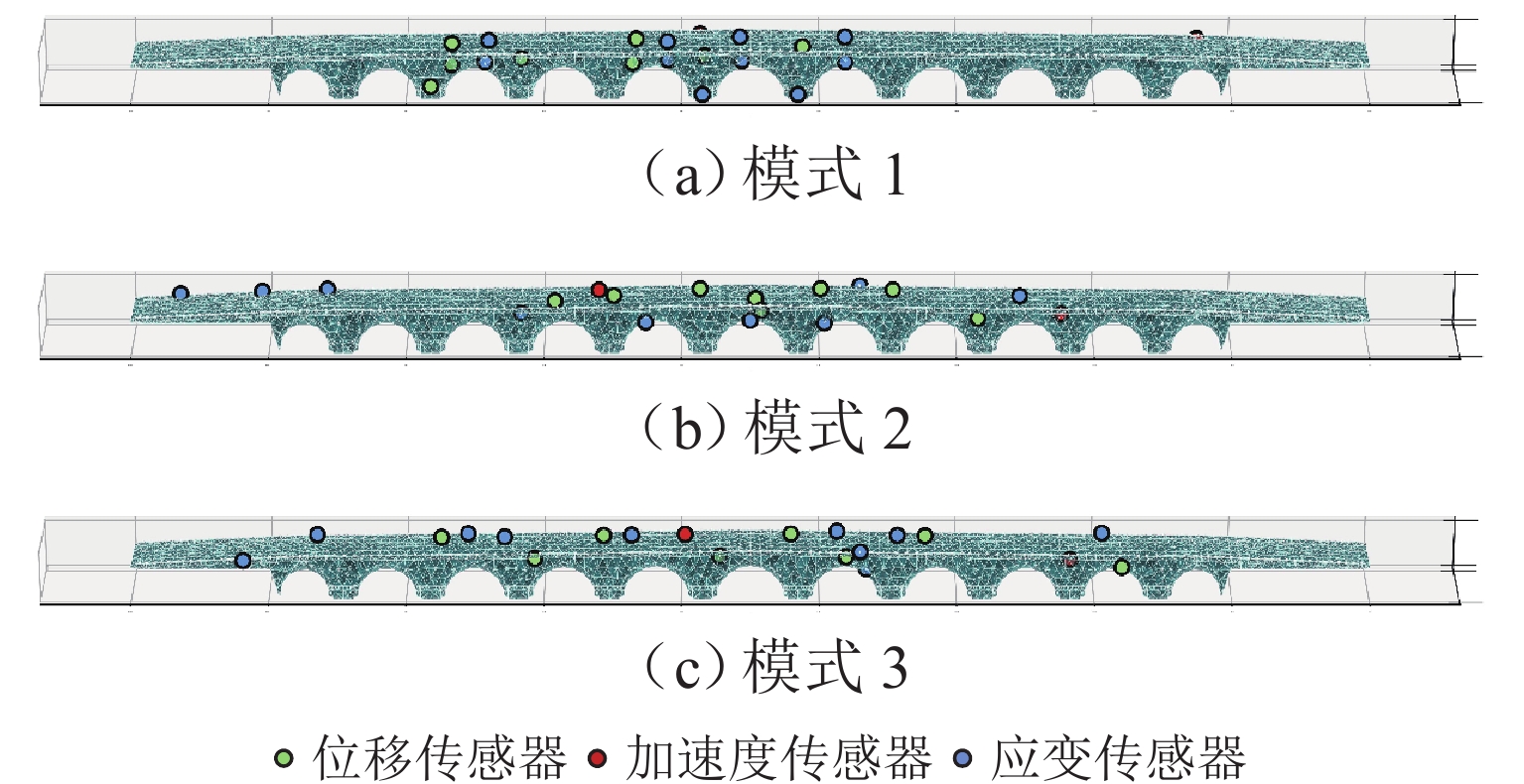
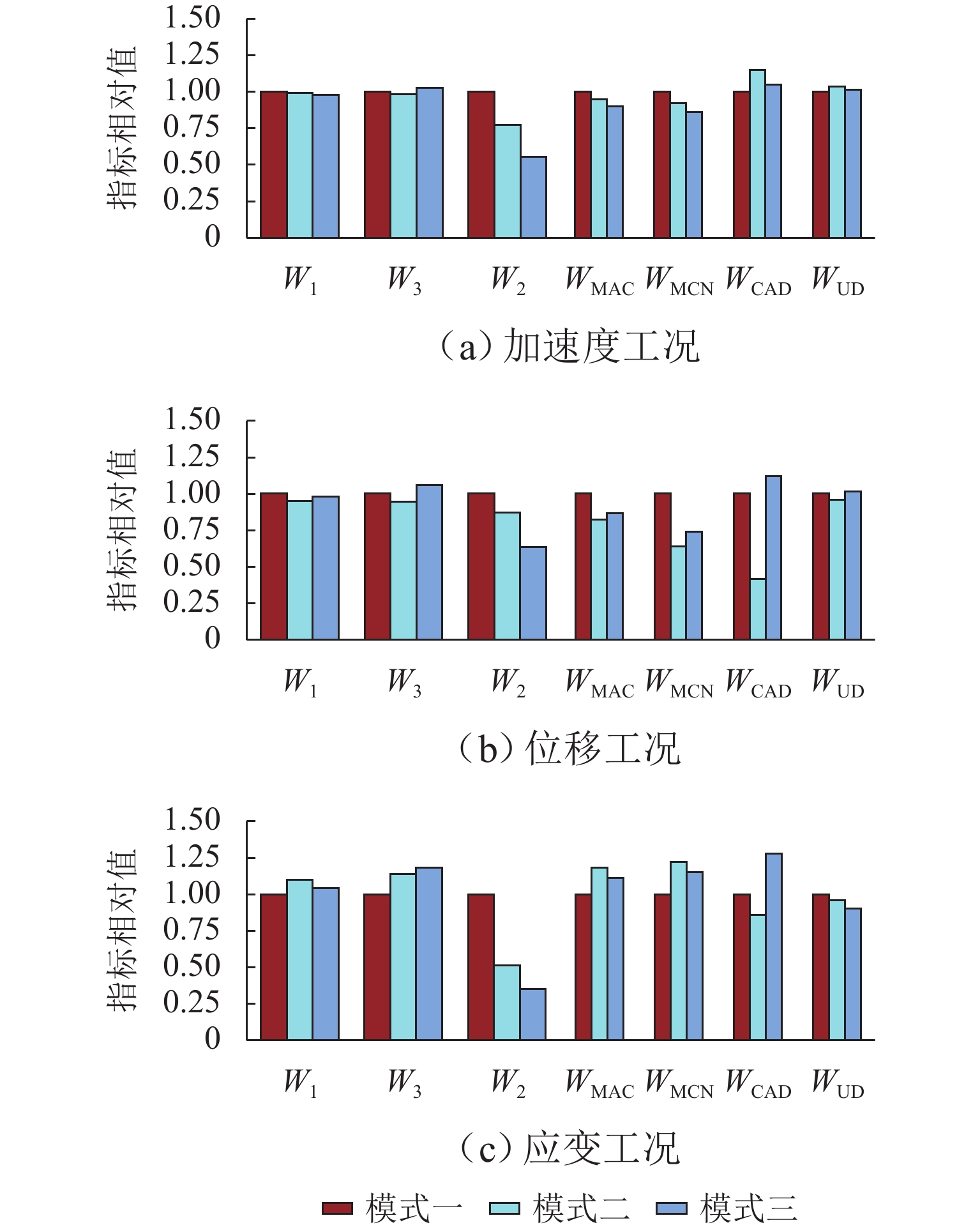
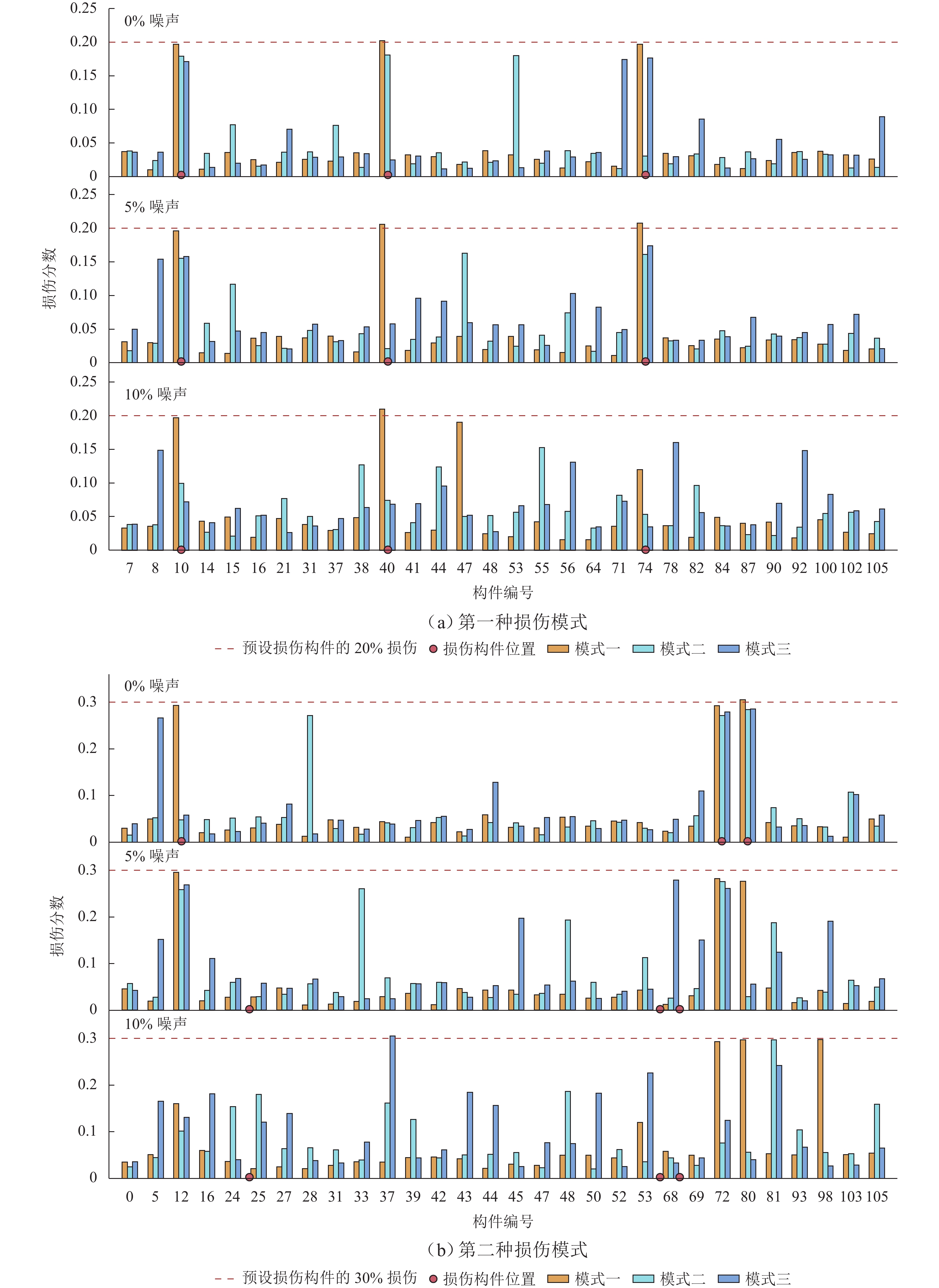
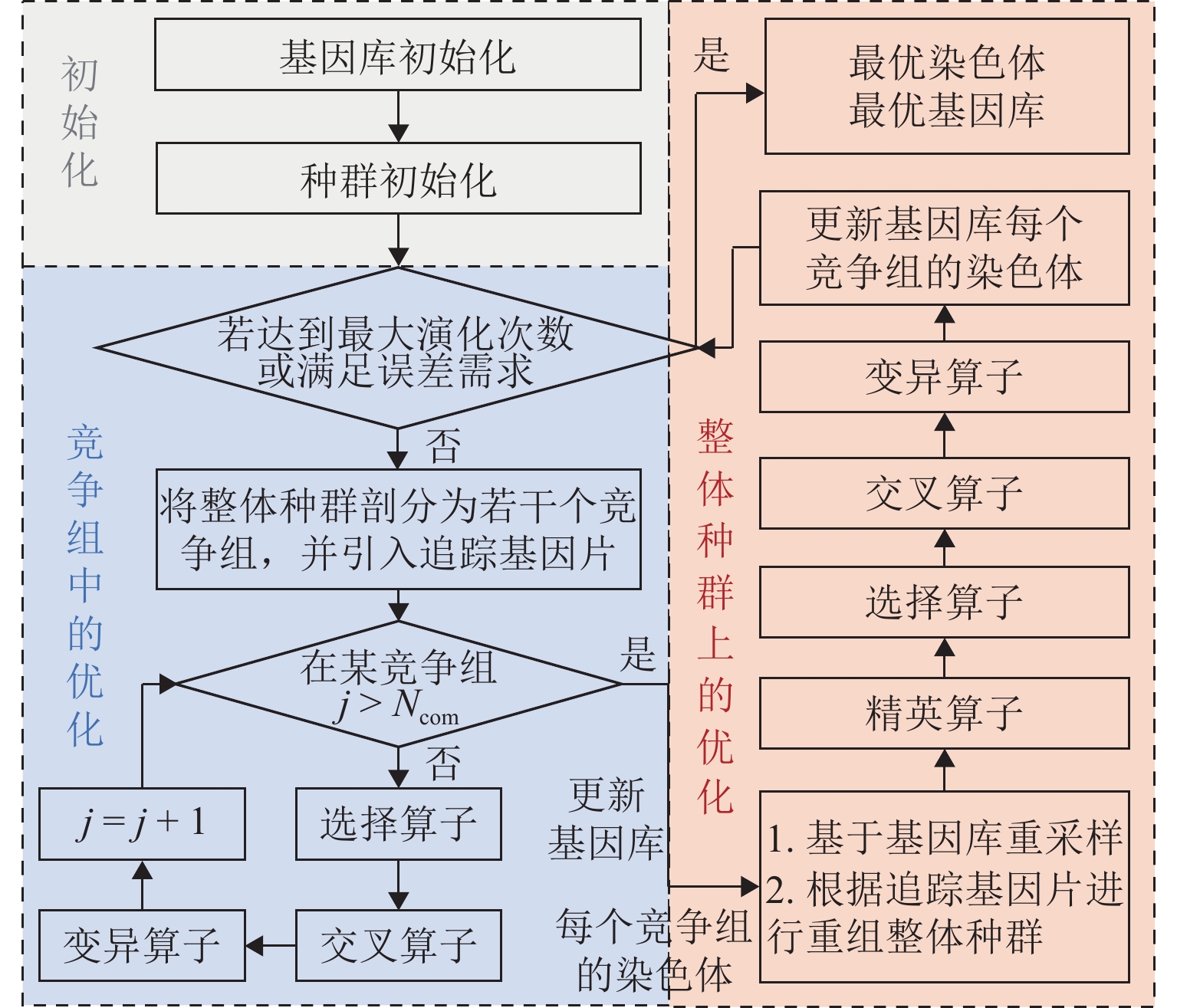
为开发古代石拱桥传感器优化布置方法,本文以全国重点文物保护单位北京卢沟桥为例,建立考虑初始残损和材料参数随机的传感器优化计算模型;提出考虑复杂监测目标的适应度函数设计与求解方法、以元学习思想为基础的元遗传算法,对传感器优化布置问题进行搜优;并将提出方法与2种基于传统遗传算法的优化模式进行对比,实现了面向古代石拱桥的高效传感器优化布置. 研究结果表明:所提出方法具有更好的参数识别能力、损伤灵敏度与信息冗余水平;当噪声水平在5%以内时,元遗传算法给出的方案均可成功检测损伤,而另外2种方案的损伤检测成功率仅60.0%;当噪声水平达到10%时,元遗传算法给出方案可以检测出60.0%的损伤,而其他2种方案无法有效检测出损伤.
Abstract:To develop an optimal sensor placement method for ancient stone arch bridges, by taking the Beijing Lugou Bridge, a national key cultural relics protection unit, as an example, a sensor optimization model considering initial damage and random material parameters was established. A fitness function design and solution method considering complex monitoring targets was proposed, along with a meta-genetic algorithm based on the concept of meta-learning for solving the sensor placement optimization problem. The proposed method was compared with two optimization methods based on conventional genetic algorithms, achieving optimal sensor placement for ancient stone arch bridges. The results show that the proposed method offers better parameter identification capability, damage sensitivity, and information redundancy level. When the noise level is within 5%, the sensor placement scheme given by the meta-genetic algorithm can successfully detect the damage, while the other two methods achieve only a 60.0% success rate. When the noise level reaches 10%, the meta-genetic algorithm can detect 60.0% of the damage, while the other two methods fail to detect damage effectively.
-
表 1 材料信息
Table 1. Information on materials
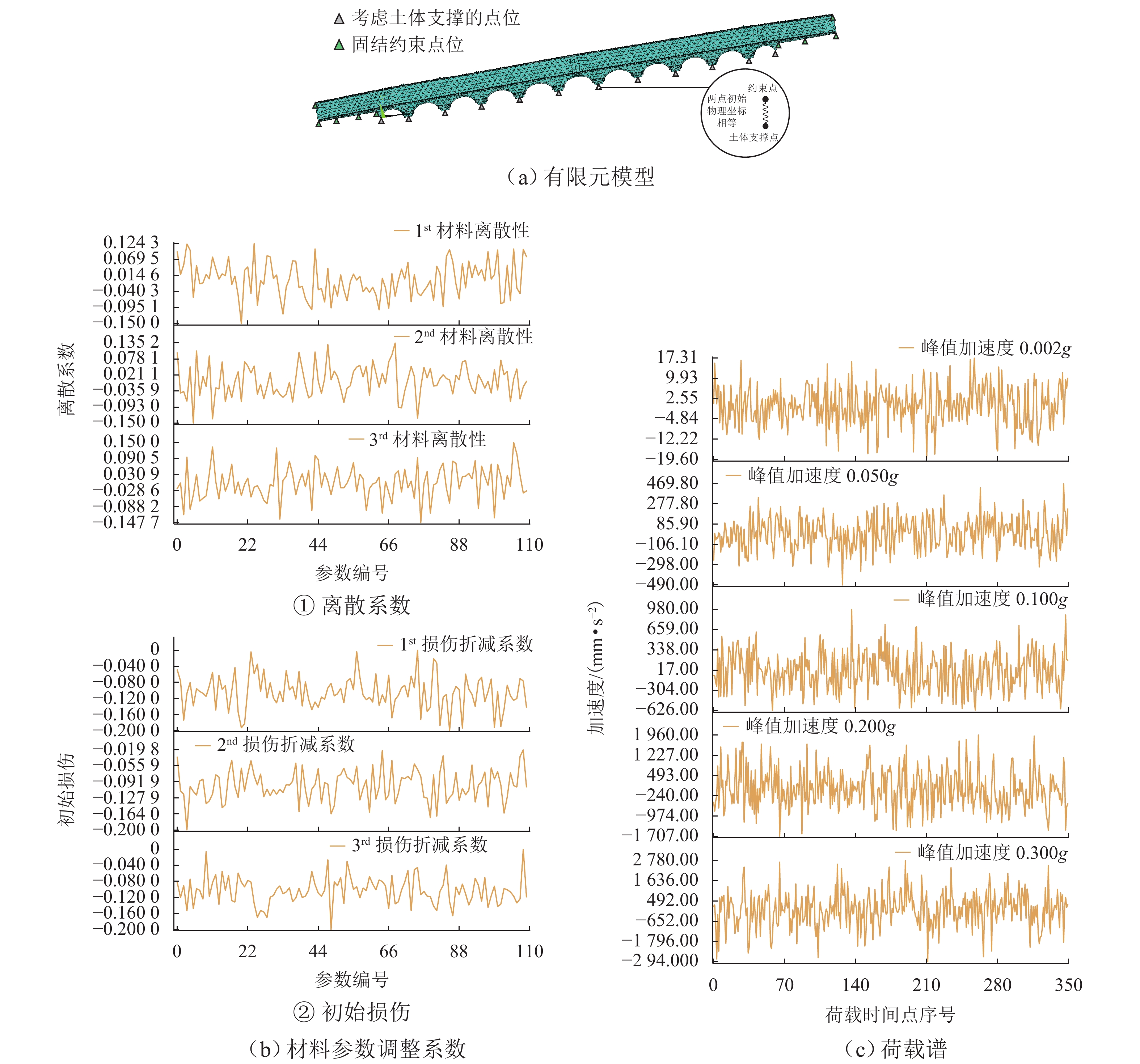
材料 弹性模量/ MPa 密度/(kg·m−3) 泊松比 石砌体 2450 2556 0.15 内填土 1000 1938 0.20 表 2 荷载信息
Table 2. Information on loads
噪声峰值/(×g) 权重 权重设置 0.002 1.000 实测服役峰值加速度,g 为重力加速度,假定其发生概率为 100% 0.050 0.815 扫频白噪声峰值,概率设定为 0.001g 与 0.100g 工况的均值 0.100 0.630 50年一遇多遇地震的加速度峰值,发生概率为 63% 0.200 0.100 50年一遇设防地震的加速度峰值,发生概率为 10% 0.300 0.030 50年一遇罕遇地震的加速度峰值,发生概率为 3% -
[1] AN H C, YOUN B D, KIM H S. Optimal sensor placement considering both sensor faults under uncertainty and sensor clustering for vibration-based damage detection[J]. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization, 2022, 65(3): 1-32. [2] ZINI G, BETTI M, BARTOLI G. A pilot project for the long-term structural health monitoring of historic city gates[J]. Journal of Civil Structural Health Monitoring, 2022, 12(3): 537-556. doi: 10.1007/s13349-022-00563-7 [3] YANG C, XIA Y Q. A novel two-step strategy of non-probabilistic multi-objective optimization for load-dependent sensor placement with interval uncertainties[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2022, 176: 109173.1-109173.15. [4] CARNE T G, DOHRMANN C R. A modal test design strategy for model correlation [C]//International modal analysis conference. Nashville: [s.n.], 1995: 927-933. [5] KAMMER D C. Sensor placement for on-orbit modal identification and correlation of large space structures[C]//1990 American Control Conference. San Diego: IEEE, 1990: 2984-2990. [6] HOLLAND J H. Adaptation in natural and artificial systems: an introductory analysis with applications to biology, control, and artificial intelligence[M]. Ann Arbor: University of Michigan Press, 1975. [7] 伊廷华, 张旭东, 李宏男. 基于自适应猴群算法的传感器优化布置方法研究[J]. 振动与冲击, 2013, 32(23): 57-63. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3835.2013.23.011YI Tinghua, ZHANG Xudong, LI Hongnan. Optimal sensor placement based on adaptive monkey algorithm[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2013, 32(23): 57-63. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3835.2013.23.011 [8] 伊廷华, 张旭东, 李宏男. 基于异步爬猴群算法的传感器优化布置方法研究[J]. 计算力学学报, 2013, 30(5): 599-604. doi: 10.7511/jslx201305001YI Tinghua, ZHANG Xudong, LI Hongnan. Asynchronous-climb monkey algorithm for optimal sensor placement[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Mechanics, 2013, 30(5): 599-604. doi: 10.7511/jslx201305001 [9] 伊廷华, 张旭东, 李宏男. 基于改进猴群算法的传感器优化布置方法研究[J]. 计算力学学报, 2013, 30(2): 218-223. doi: 10.7511/jslx201302008YI Tinghua, ZHANG Xudong, LI Hongnan. Research on optimal sensor placement based on improved monkey algorithm[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Mechanics, 2013, 30(2): 218-223. doi: 10.7511/jslx201302008 [10] 伊廷华, 张旭东, 李宏男. 基于分布式猴群算法的传感器优化布置方法研究[J]. 工程力学, 2014, 31(3): 93-100.YI Tinghua, ZHANG Xudong, LI Hongnan. Distributed monkey algorithm for optimal sensor placement[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2014, 31(3): 93-100. [11] 伊廷华, 张旭东, 李宏男. 基于小生境猴群算法的传感器优化布置方法研究[J]. 工程力学, 2014, 31(9): 112-119. doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2013.04.0323YI Tinghua, ZHANG Xudong, LI Hongnan. The niching monkey algorithm for optimal sensor placement[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2014, 31(9): 112-119. doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2013.04.0323 [12] 赵建华, 张陵, 孙清. 利用粒子群算法的传感器优化布置及结构损伤识别研究[J]. 西安交通大学学报, 2015, 49(1): 79-85. doi: 10.7652/xjtuxb201501013ZHAO Jianhua, ZHANG Ling, SUN Qing. Optimal placement of sensors for structural damage identification using improved particle swarm optimization[J]. Journal of Xi’an Jiaotong University, 2015, 49(1): 79-85. doi: 10.7652/xjtuxb201501013 [13] 王志宇, 陈华钊, 施袁锋, 等. 模态测试不确定性影响因素分析及传感器布置应用[J]. 湖南大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 51(7): 62-71.WANG Zhiyu, CHEN Huazhao, SHI Yuanfeng, et al. Analysis of influencing factors on uncertainty in modal testing and its application on sensor layout scheme[J]. Journal of Hunan University (Natural Sciences), 2024, 51(7): 62-71. [14] 董学超, 郭明伟, 王水林. 基于LightGBM的超大沉井下沉状态预测及传感器优化布置[J]. 岩土力学, 2023, 44(6): 1789-1799.DONG Xuechao, GUO Mingwei, WANG Shuilin. Sinking state prediction and optimal sensor placement of super large open caissons based on LightGBM[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2023, 44(6): 1789-1799. [15] 李英民, 秦阳, 刘纲. 基于行波理论的桁架结构传感器优化布设方法研究[J/OL]. 工程力学, 2023: 1-12. (2023-03-06). https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2595.o3.20230303.1255.006.html.LI Yingmin, QIN Yang, LIU Gang. Research on optimal placement method of truss structure sensors based on traveling wave theory[J/OL]. Engineering Mechanics, 2023: 1-12. (2023-03-06). https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2595.o3.20230303.1255.006.html. [16] 刘杰, 王海龙, 张志国, 等. 斜拉桥损伤可识别性传感器的优化布置方法[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2018, 53(1): 173-181. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2018.01.021LIU Jie, WANG Hailong, ZHANG Zhiguo, et al. Optimum sensor placement method for cable-stayed bridges based on damage identifiability[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2018, 53(1): 173-181. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2018.01.021 [17] 张明金, 李永乐, 余显全, 等. 桥塔上风传感器安装位置对测量结果的影响[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2015, 50(4): 617-622. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2015.04.007ZHANG Mingjin, LI Yongle, YU Xianquan, et al. Influence of wind sensor location on bridge tower on measurement results[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2015, 50(4): 617-622. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2015.04.007 [18] OTTOSEN N S, PETERSSON H. Introduction to the Finite Element Methods[M]. New York: Prentice Hall, 1992. [19] ZHANG C W, CHUN Q, LENG J W, et al. Optimal placement method of multi-objective and multi-type sensors for courtyard-style timber historical buildings based on Meta-genetic algorithm[J]. Structural Health Monitoring, 2024, 23(3): 1468-1497. doi: 10.1177/14759217231181724 [20] YANG C, LIANG K, ZHANG X P. Strategy for sensor number determination and placement optimization with incomplete information based on interval possibility model and clustering avoidance distribution index[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2020, 366: 113042.1-113042.21. [21] LIN J F, XU Y L, LAW S S. Structural damage detection-oriented multi-type sensor placement with multi-objective optimization[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2018, 422: 568-589. doi: 10.1016/j.jsv.2018.01.047 [22] FINN C, ABBEEL P, LEVINE S. Model-agnostic meta-learning for fast adaptation of deep networks [M]. [S.l.]: International Conference on Machine Learning, 2017. [23] ZHANG C W, CHUN Q, SUN A, et al. Improved meta-learning neural network for the prediction of the historical reinforced concrete bond–slip model using few test specimens[J]. International Journal of Concrete Structures and Materials, 2022, 16: 41.1-41.29. [24] DOWNEY A, HU C, LAFLAMME S. Optimal sensor placement within a hybrid dense sensor network using an adaptive genetic algorithm with learning gene pool[J]. Structural Health Monitoring, 2018, 17(3): 450-460. doi: 10.1177/1475921717702537 [25] GÜNAYDIN M, DEMIRKIR C, ALTUNIŞIK A C, et al. Diagnosis and monitoring of historical timber velipaşa Han building prior to restoration[J]. International Journal of Architectural Heritage, 2023, 17(2): 285-309. doi: 10.1080/15583058.2021.1919239 [26] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 砌体结构设计规范: GB 50003—2011[S]. 北京: 中国计划出版社, 2012. [27] 国家市场监督管理总局, 国家标准化管理委员会. 古建筑砖石结构维修与加固技术规范: GB/T 39056—2020[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2020. [28] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 建筑结构荷载规范: GB 50009—2012[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2012. [29] HE L J, LIAN J J, MA B, et al. Optimal multiaxial sensor placement for modal identification of large structures[J]. Structural Control and Health Monitoring, 2014, 21(1): 61-79. doi: 10.1002/stc.1550 [30] STEPHAN C. Sensor placement for modal identification[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2012, 27: 461-470. doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2011.07.022 -




 下载:
下载: