Multi-Skilled Multi-Manned Assembly Line Rebalancing Problem Based on Two-Stage Algorithm
-
摘要:
为提高装配线的生产效率和灵活性,考虑多人共站与工人熟练度差异,分析多技能工人共站装配线再平衡问题,并对相应的求解算法进行设计. 首先,提出工人熟练度和综合影响系数的概念,分别用于量化工人差异和多人共站的效应,并以此建立多目标优化模型;其次,针对不同规模的算例,提出
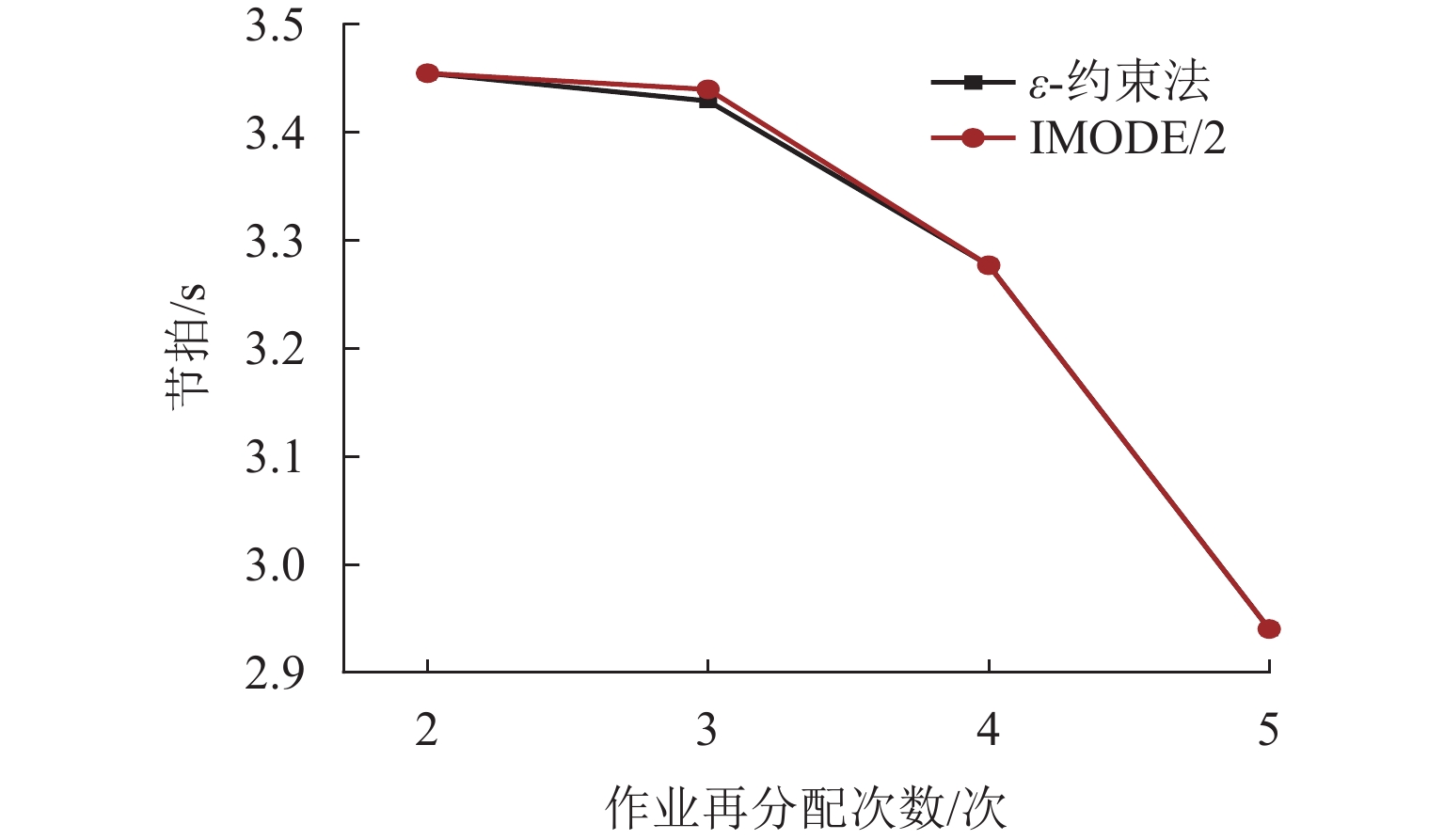
ε -约束法和一种贪婪启发式与邻域搜索相结合的两阶段算法进行求解;最后,通过消融实验与算法对比实验进行验证. 研究结果显示:在小规模问题的测试中,模型的2种求解结果仅在一个数据上相差0.3%,验证了模型的准确性;在消融实验中,任意一种策略的舍弃均会导致求解结果变差,证明了各算法策略的有效性;而在大规模问题的对比中,所提算法相较于经典的多目标优化算法NSGA-Ⅱ和MOEA/D,在多数算例上均显示出显著优势,证明了所提算法在解决该问题上的优越性.Abstract:To improve the production efficiency and flexibility of assembly lines, based on the consideration of multi-manned stations and variations in worker proficiency, an analysis and design of the rebalancing problem for multi-skilled multi-manned assembly lines and corresponding solution algorithms have been conducted. Firstly, the concepts of worker proficiency and comprehensive influence coefficient are proposed to quantify the differences among workers and the effects of multi-manned stations, and a multi-objective optimization model is established accordingly. Secondly, the ε-constraint method and a two-stage algorithm combining greedy heuristic and neighborhood search are proposed to solve problems of different scales. Finally, ablation study and algorithm comparison experiments are designed for validation. The research results show that in the testing of small-scale problems, the solutions of the model only differ by 0.3% in one data point, demonstrating the accuracy of the model. In the ablation study, abandoning any algorithm strategy leads to worse results, indicating the effectiveness of each strategy. Furthermore, in the comparison of large-scale problems, the proposed algorithm exhibits significant advantages over the classical multi-objective optimization algorithms NSGA-Ⅱ and MOEA/D in most cases, thus proving the superiority of the proposed algorithm in solving this problem.
-
表 1 工人熟练度数据示例
Table 1. Example of worker proficiency data
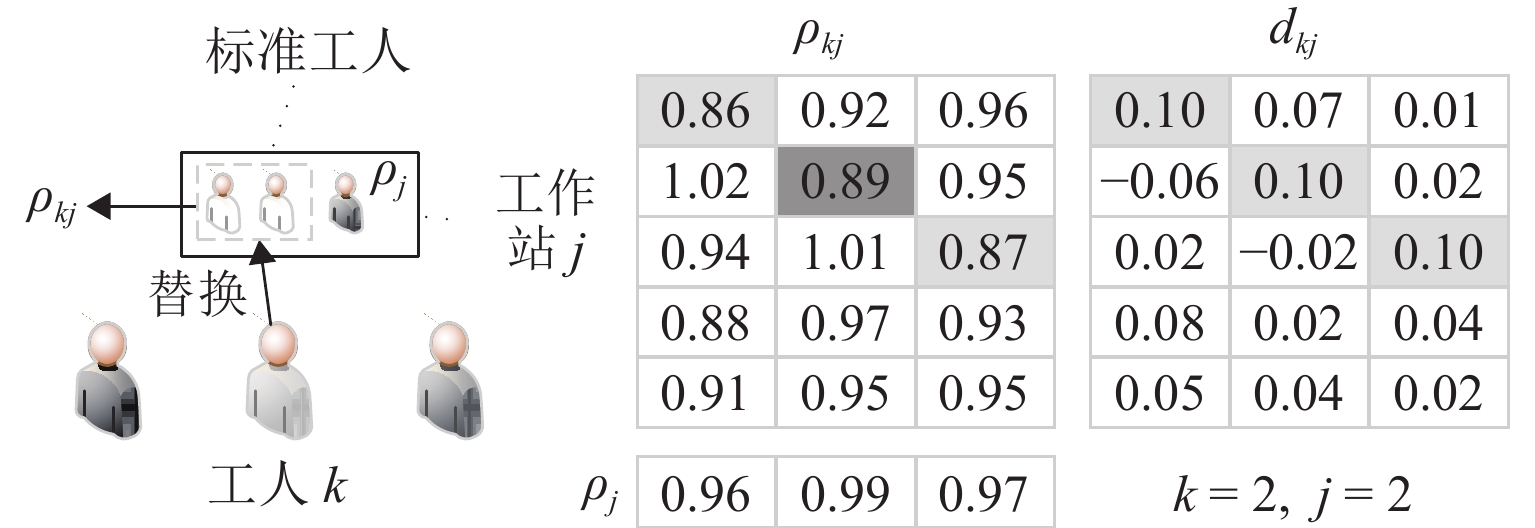
作业 ski 工人 1 工人 2 工人 3 作业 1 0.90 1.10 1.05 作业 2 1.06 1.02 0.87 作业 3 1.12 0.98 1.11 表 2 综合影响系数数据示例
Table 2. Example of comprehensive influence coefficient data
人数 r βr 1 1.00 2 0.98 $ \vdots $ $\vdots $ 10 1.05 表 3 算例描述
Table 3. Description of benchmark example
问题 作业数量/项 工人数量/人 工作站
数量/个关闭工作
站数/个Jaeschke 9 10 4 1 Mitchell 21 12 5 1 Roszieg 25 15 6 1 Buxey 29 50 8 2 Sawyer 30 25 9 2 Gunther 35 20 7 1 Kilbridge 45 27 8 1 Warnecke 58 50 16 3 Tonge 70 60 9 1 Wee-Mag 75 35 12 2 Lutz2 89 50 15 3 Arcus2 111 42 13 3 Barthold 148 60 22 4 表 4 消融实验策略与参数设置
Table 4. Strategies and parameter settings of ablation study
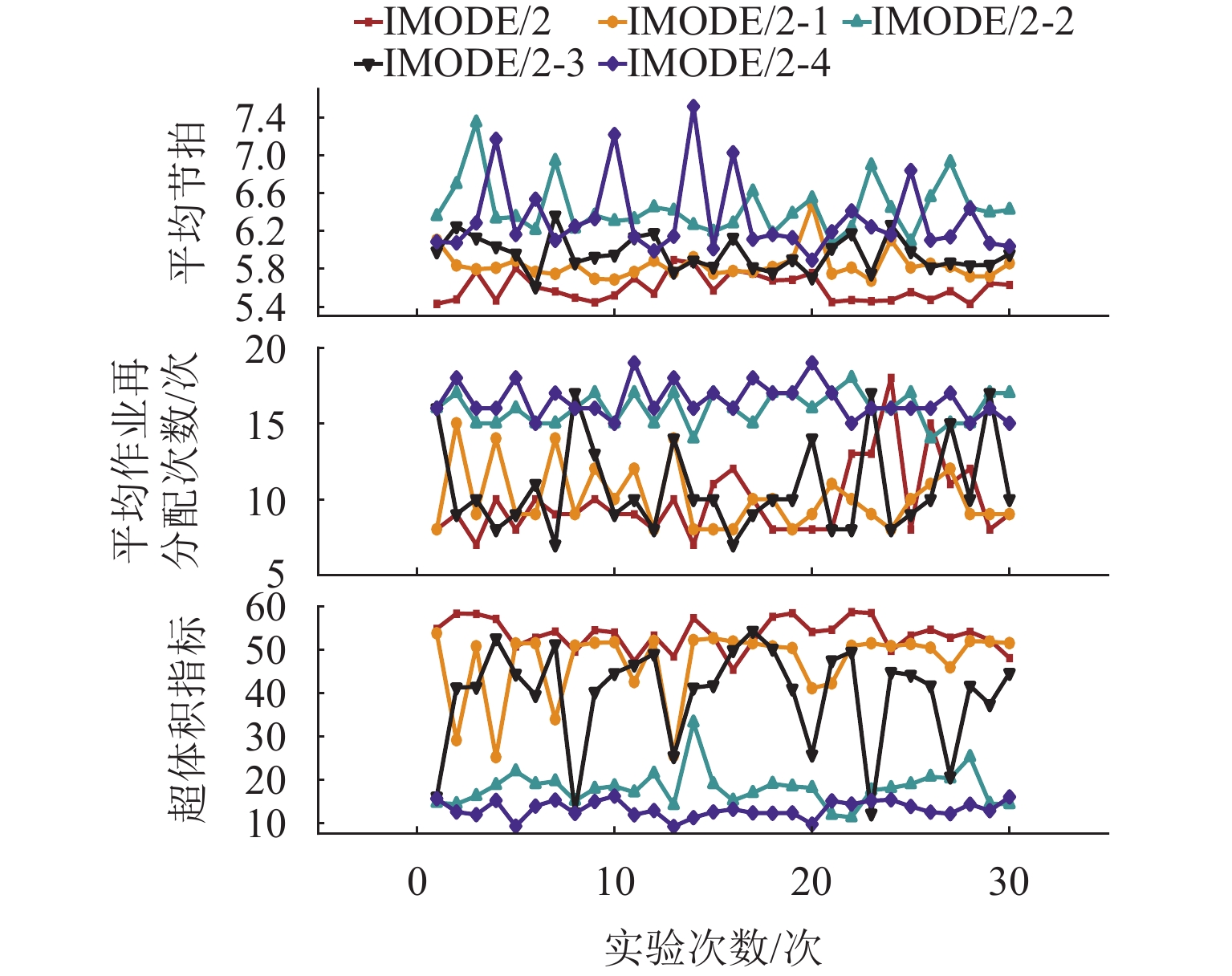
算法 变异参数 选择策略 邻域搜索 IMODE/2 自适应,p0=20,pG=5 非支配排序 有 IMODE/2-1 固定,p=10,F1=F2=0.5,R=0.5 非支配排序 有 IMODE/2-2 自适应,p0=20,pG=5 贪婪 有 IMODE/2-3 自适应,p0=20,pG=5 非支配排序 无 IMODE/2-4 固定,p=10,F1=F2=0.5,R=0.5 贪婪 无 表 5 算法对比统计结果
Table 5. Statistical comparison of algorithms' results
算例 IMODE/2 NSGA-Ⅱ MOEA/D 平均节拍/s 平均再分配次数/次 HV 平均节拍/s 平均再分配次数/次 HV 平均节拍/s 平均再分配次数/次 HV Mitchell 7.57 8.10 11.77 8.12 9.40 9.23 8.42 9.70 7.37 Roszieg 7.57 5.90 19.92 8.10 6.80 14.75 8.31 10.60 7.29 Buxey 5.58 8.90 53.24 6.16 16.00 18.10 6.37 15.60 19.28 Sawyer 11.96 9.20 107.24 12.83 18.10 59.64 14.05 18.60 34.00 Gunther 21.95 12.60 119.12 23.21 17.00 72.10 24.14 20.10 41.63 Kilbridge 19.14 12.40 161.60 21.08 24.30 26.25 22.06 21.50 50.79 Warnecke 33.27 23.90 338.14 33.17 36.10 123.64 33.92 37.20 80.93 Tonge 54.77 27.20 464.21 56.50 54.20 112.01 60.40 46.60 141.16 Wee-Mag 41.73 35.20 748.21 42.66 46.70 550.93 43.45 48.70 407.64 Lutz2 9.74 36.70 452.41 10.13 55.40 199.12 10.40 54.20 214.70 Arcus2 3431.04 53.70 10033.80 3588.47 62.80 3486.20 3615.96 59.70 4139.97 Barthold 70.00 108.50 555.62 73.72 123.50 186.02 73.35 131.10 72.86 表 6 95%置信度指标均值t检验
Table 6. 95% confidence interval mean t-test
算例 指标 IMODE/2-NSGA-Ⅱ IMODE/2-MOEA/D 置信下限 置信上限 置信下限 置信上限 Mitchell 节拍/s −1.0 0.0 −1.3 −0.4 再分配次数/次 −2.4 −0.2 −2.5 −0.7 HV 1.4 3.6 3.5 5.3 Roszieg 节拍/s −0.9 −0.2 −1.0 −0.5 再分配次数/次 −1.8 0.0 −5.3 −4.1 HV 3.3 7.0 11.0 14.3 Buxey 节拍/s −1.2 0.0 −1.5 −0.1 再分配次数/次 −9.4 −4.8 −8.5 −4.9 HV 31.1 39.1 30.6 37.3 Sawyer 节拍/s −1.8 0.1 −2.8 −1.4 再分配次数/次 −11.4 −6.4 −11.5 −7.3 HV 39.8 55.4 66.1 80.4 Gunther 节拍/s −2.6 0.1 −3.6 −0.8 再分配次数/次 −7.1 −1.7 −10.0 −5.0 HV 41.2 52.8 72.7 82.3 Kilbridge 节拍/s −2.9 −1.0 −3.8 −2.0 再分配次数/次 −15.5 −8.3 −11.4 −6.8 HV 118.6 152.1 100.2 121.4 Warnecke 节拍/s −1.6 1.7 −1.9 0.6 再分配次数/次 −15.3 −9.1 −16.1 −10.5 HV 177.6 251.4 222.3 292.0 Tonge 节拍/s −3.1 −0.4 −6.7 −4.6 再分配次数/次 −30.3 −23.6 −22.0 −16.8 HV 304.7 399.8 276.5 369.6 Wee-Mag 节拍/s −2.1 0.2 −3.0 −0.4 再分配次数/次 −16.9 −6.1 −17.8 −9.2 HV 138.9 255.8 299.9 381.2 Lutz2 节拍/s −1.1 0.3 −1.3 0.0 再分配次数/次 −23.6 −13.8 −22.4 −12.6 HV 210.0 296.3 202.0 273.3 Arcus2 节拍/s −164.7 −150.3 −189.7 −180.1 再分配次数/次 −13.4 −4.8 −9.9 −2.1 HV 5874.3 7220.9 5379.5 6408.1 Barthold 节拍/s −7.2 −0.2 −4.6 −2.1 再分配次数/次 −22.5 −7.5 −29.8 −15.4 HV 295.2 444.0 425.4 540.1 -
[1] GRANGEON N, LECLAIRE P, NORRE S. Heuristics for the re-balancing of a vehicle assembly line[J]. International Journal of Production Research, 2011, 49(22): 6609-6628. doi: 10.1080/00207543.2010.539025 [2] MAKSSOUD F, BATTAÏA O, DOLGUI A, et al. Re-balancing problem for assembly lines: new mathematical model and exact solution method[J]. Assembly Automation, 2015, 35(1): 16-21. doi: 10.1108/AA-07-2014-061 [3] SAMADHI T, SUMIHARTATI A. Model for assembly line re-balancing considering additional capacity and outsourcing to face demand fluctuations[C]//IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering. Nanjing: [s.n.], 2016: 814-823. [4] SANCI E, AZIZOĞLU M. Rebalancing the assembly lines: exact solution approaches[J]. International Journal of Production Research, 2017, 55(20): 5991-6010. doi: 10.1080/00207543.2017.1319583 [5] BELASSIRIA I, MAZOUZI M, ELFEZAZI S, et al. An integrated model for assembly line re-balancing problem[J]. International Journal of Production Research, 2018, 56(16): 5324-5344. doi: 10.1080/00207543.2018.1467061 [6] LI Y C, LI Z X, SALDANHA-DA-GAMA F. New approaches for rebalancing an assembly line with disruptions[J]. International Journal of Computer Integrated Manufacturing, 2022, 35(10/11): 1059-1076. [7] ZHANG Y H, HU X F, WU C X. Improved imperialist competitive algorithms for rebalancing multi-objective two-sided assembly lines with space and resource constraints[J]. International Journal of Production Research, 2020, 58(12): 3589-3617. doi: 10.1080/00207543.2019.1633023 [8] LIU R F, LIU M, CHU F, et al. Eco-friendly multi-skilled worker assignment and assembly line balancing problem[J]. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2021, 151: 106944.1-106944.12. [9] GIRIT U, AZIZOĞLU M. Rebalancing the assembly lines with total squared workload and total replacement distance objectives[J]. International Journal of Production Research, 2021, 59(22): 6702-6720. doi: 10.1080/00207543.2020.1823027 [10] 张于贤, 梁师文, 杨梦珂. 多目标约束下装配线再平衡研究[J]. 兵器装备工程学报, 2019, 40(1): 214-219.ZHANG Yuxian, LIANG Shiwen, YANG Mengke. Research on rebalancing of multi-objective constraints assembly line[J]. Journal of Ordnance Equipment Engineering, 2019, 40(1): 214-219. [11] 张亚辉, 胡小锋, 吴传珣. 基于ε-约束法的多目标双边装配线再平衡问题[J]. 计算机集成制造系统, 2016, 22(11): 2551-2562.ZHANG Yahui, HU Xiaofeng, WU Chuanxun. Multi-objective two-sided assembly line rebalancing problem based on ε-constraint method[J]. Computer Integrated Manufacturing Systems, 2016, 22(11): 2551-2562. [12] ZHANG Y H, HU X F, WU C X. A modified multi-objective genetic algorithm for two-sided assembly line re-balancing problem of a shovel loader[J]. International Journal of Production Research, 2018, 56(9): 3043-3063. doi: 10.1080/00207543.2017.1402136 [13] KATIRAEE N, CALZAVARA M, FINCO S, et al. Consideration of workforce differences in assembly line balancing and worker assignment problem[J]. IFAC-Papers OnLine, 2021, 54(1): 13-18. doi: 10.1016/j.ifacol.2021.08.002 [14] BUDAK G, CHEN X. Pace making and worker reassignment for assembly line rebalancing[J]. SN Applied Sciences, 2020, 2(9): 1-15. [15] MICHELS A S, COSTA A M. Conserving workforce while temporarily rebalancing assembly lines under demand disruption[J]. International Journal of Production Research, 2022, 60(21): 6616-6636. doi: 10.1080/00207543.2021.1998694 [16] 邓超, 胡瑞飞, 蒋捷峰, 等. 考虑工人分配的多目标装配线平衡优化[J]. 组合机床与自动化加工技术, 2021(6): 116-121, 126.DENG Chao, HU Ruifei, JIANG Jiefeng, et al. Multi-objective assembly line balancing optimization considering worker assignment[J]. Modular Machine Tool & Automatic Manufacturing Technique, 2021(6): 116-121, 126. [17] 徐责, 宋小欣, 付建林, 等. 考虑人员能力差异的多人共站混流装配线平衡研究[J]. 现代制造工程, 2020(11): 33-40.XU Ze, SONG Xiaoxin, FU Jianlin, et al. Study on the balance of multi-person stage-sharing mixed-flow assembly line considering the difference of personnel ability[J]. Modern Manufacturing Engineering, 2020(11): 33-40. [18] 李金霖, 陈晓红, 高杰. 用多能工应对需求波动的混流装配线平衡问题[J]. 系统工程理论与实践, 2016, 36(4): 923-933.LI Jinlin, CHEN Xiaohong, GAO Jie. Designing a mixed model assembly line with utility workers to satisfy uncertain demands[J]. Systems Engineering-Theory & Practice, 2016, 36(4): 923-933. [19] ÇIMEN T, BAYKASOĞLU A, AKYOL S D. Assembly line rebalancing and worker assignment considering ergonomic risks in an automotive parts manufacturing plant[J]. International Journal of Industrial Engineering Computations, 2022, 13(3): 363-384. doi: 10.5267/j.ijiec.2022.2.001 [20] PÉREZ-WHEELOCK R M, OU W, YENRADEE P, et al. A demand-driven model for reallocating workers in assembly lines[J]. IEEE Access, 2022, 10: 80300-80320. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3194658 [21] KARAS A, OZCELIK F. Assembly line worker assignment and rebalancing problem: a mathematical model and an artificial bee colony algorithm[J]. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2021, 156: 107195.1-107195.16. [22] YANG C J, GAO J, SUN L Y. A multi-objective genetic algorithm for mixed-model assembly line rebalancing[J]. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2013, 65(1): 109-116. [23] 杨红光, 胡小锋, 张亚辉, 等. 考虑多技能人员的装配线再平衡问题研究[J]. 组合机床与自动化加工技术, 2015(7): 131-134.YANG Hongguang, HU Xiaofeng, ZHANG Yahui, et al. Research on assembly line rebalancing with mixed-skill workers[J]. Modular Machine Tool & Automatic Manufacturing Technique, 2015(7): 131-134. [24] KATIRAEE N, CALZAVARA M, FINCO S, et al. Assembly line balancing and worker assignment considering workers’ expertise and perceived physical effort[J]. International Journal of Production Research, 2023, 61(20): 6939-6959. doi: 10.1080/00207543.2022.2140219 [25] MICHELS A S, LOPES T C, SIKORA C G S, et al. A Benders’ decomposition algorithm with combinatorial cuts for the multi-manned assembly line balancing problem[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2019, 278(3): 796-808. doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2019.05.001 [26] MARTIGNAGO M, BATTAÏA O, BATTINI D. Workforce management in manual assembly lines of large products: a case study[J]. IFAC-Papers OnLine, 2017, 50(1): 6906-6911. doi: 10.1016/j.ifacol.2017.08.1215 [27] ZHANG J Q, SANDERSON A C. JADE: adaptive differential evolution with optional external archive[J]. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2009, 13(5): 945-958. doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2009.2014613 [28] 王丽萍, 任宇, 邱启仓, 等. 多目标进化算法性能评价指标研究综述[J]. 计算机学报, 2021, 44(8): 1590-1619.WANG Liping, REN Yu, QIU Qicang, et al. Survey on performance indicators for multi-objective evolutionary algorithms[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2021, 44(8): 1590-1619. -




 下载:
下载: