Experimental Study on Permeability of Soil–Phyllite Mixture in Northwest Sichuan
-
摘要:
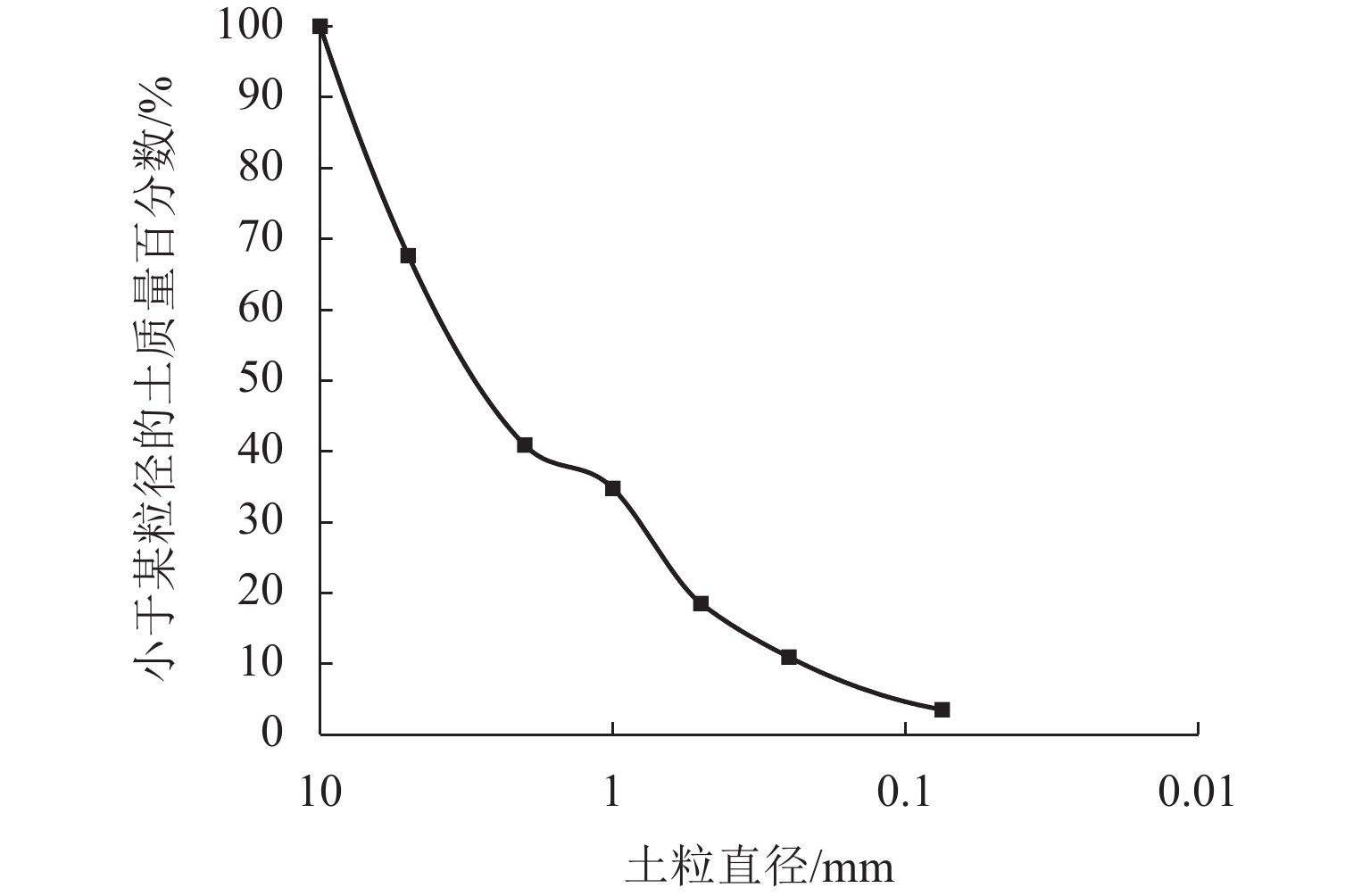
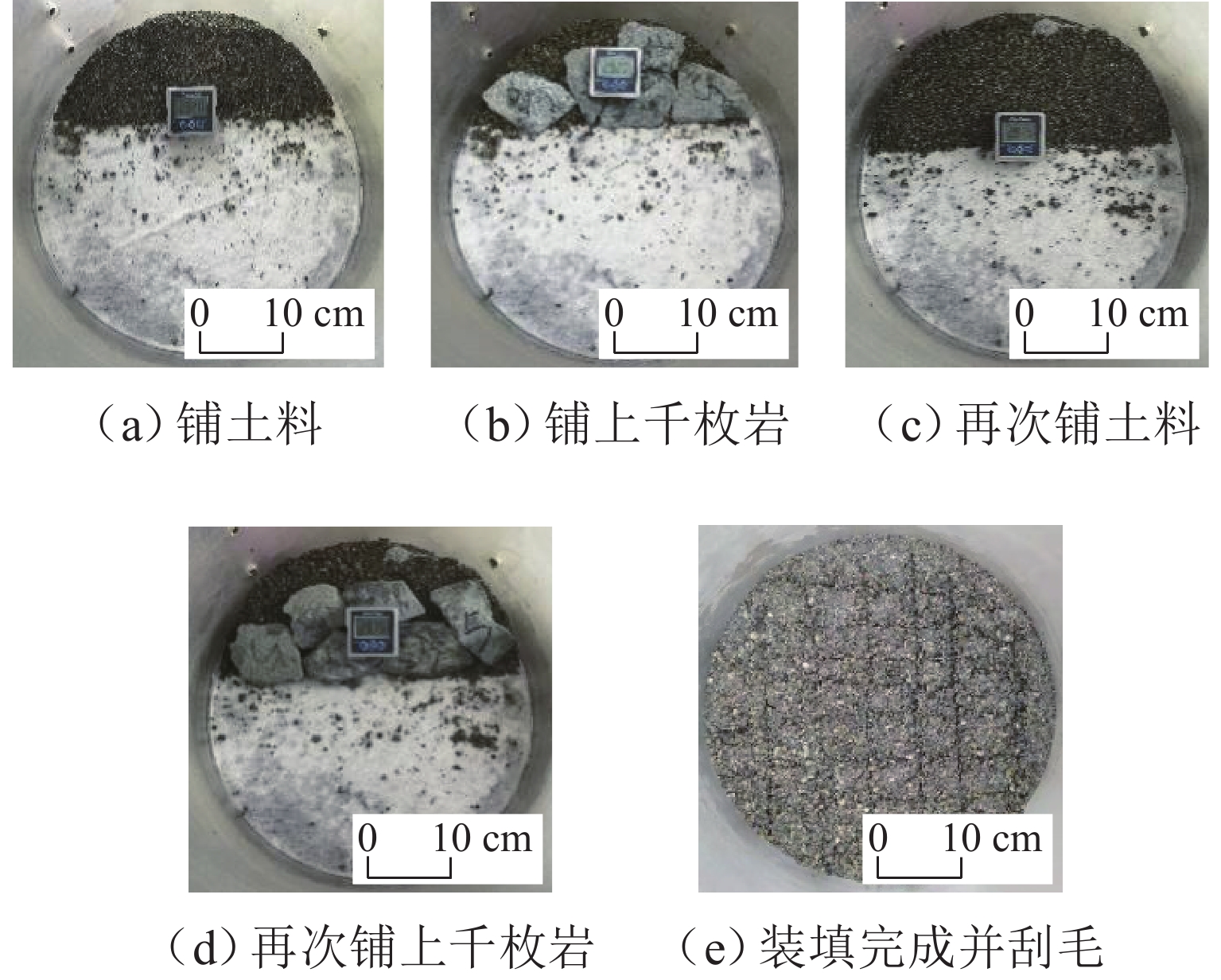
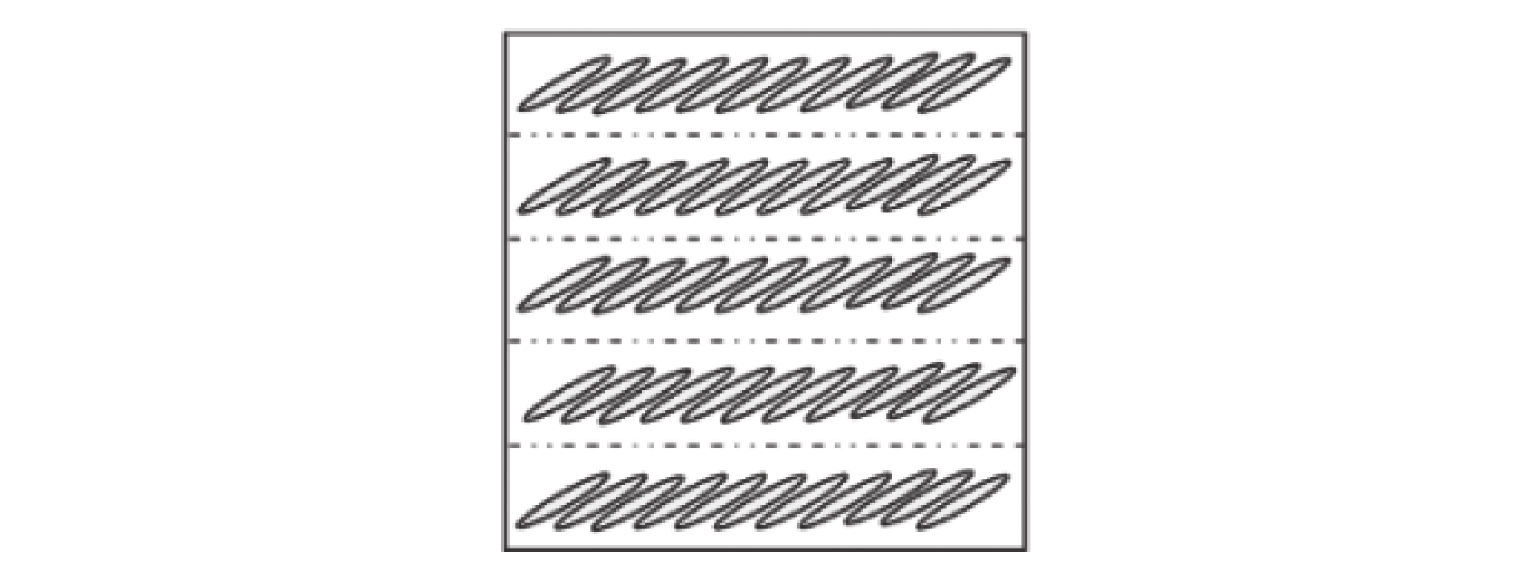
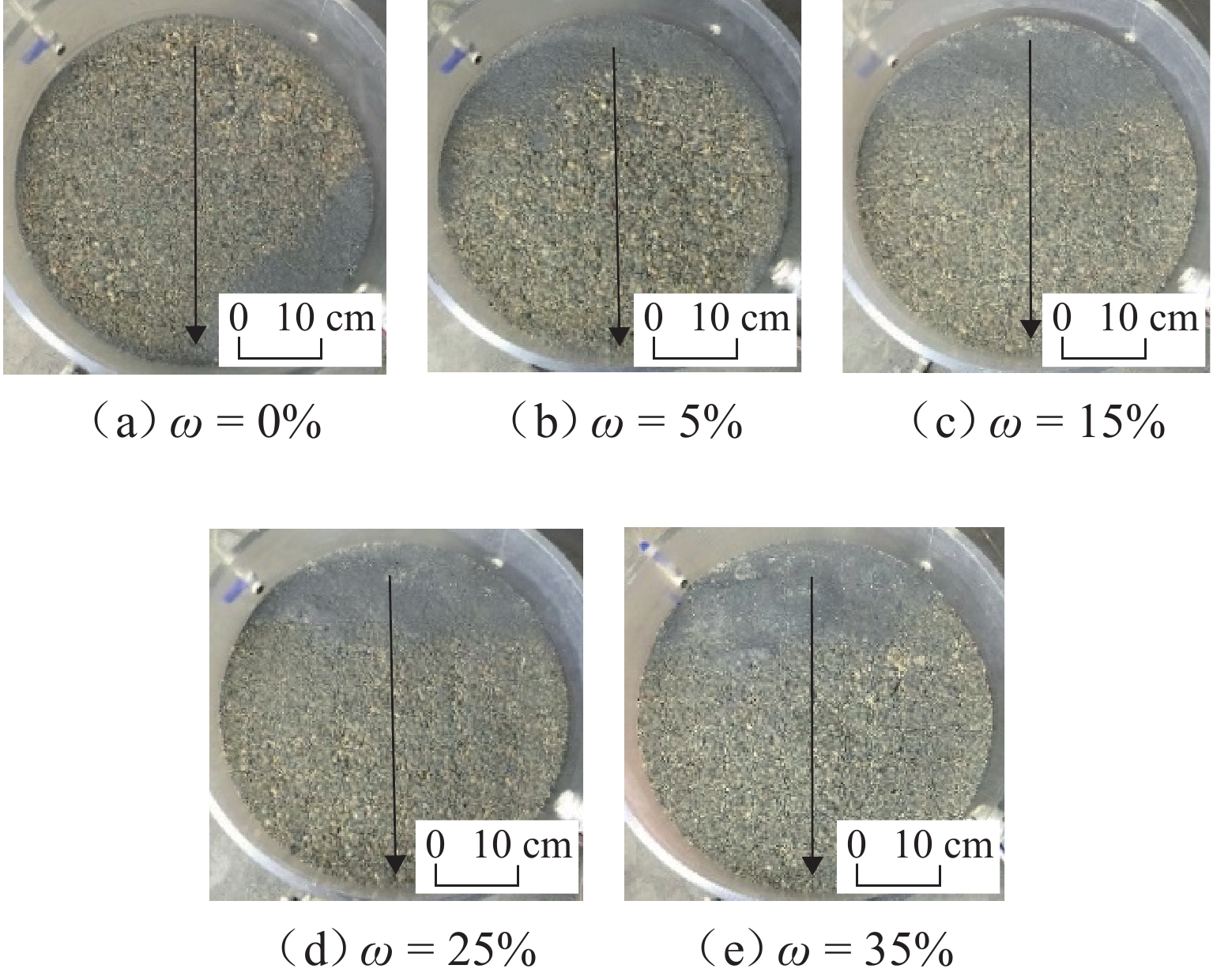
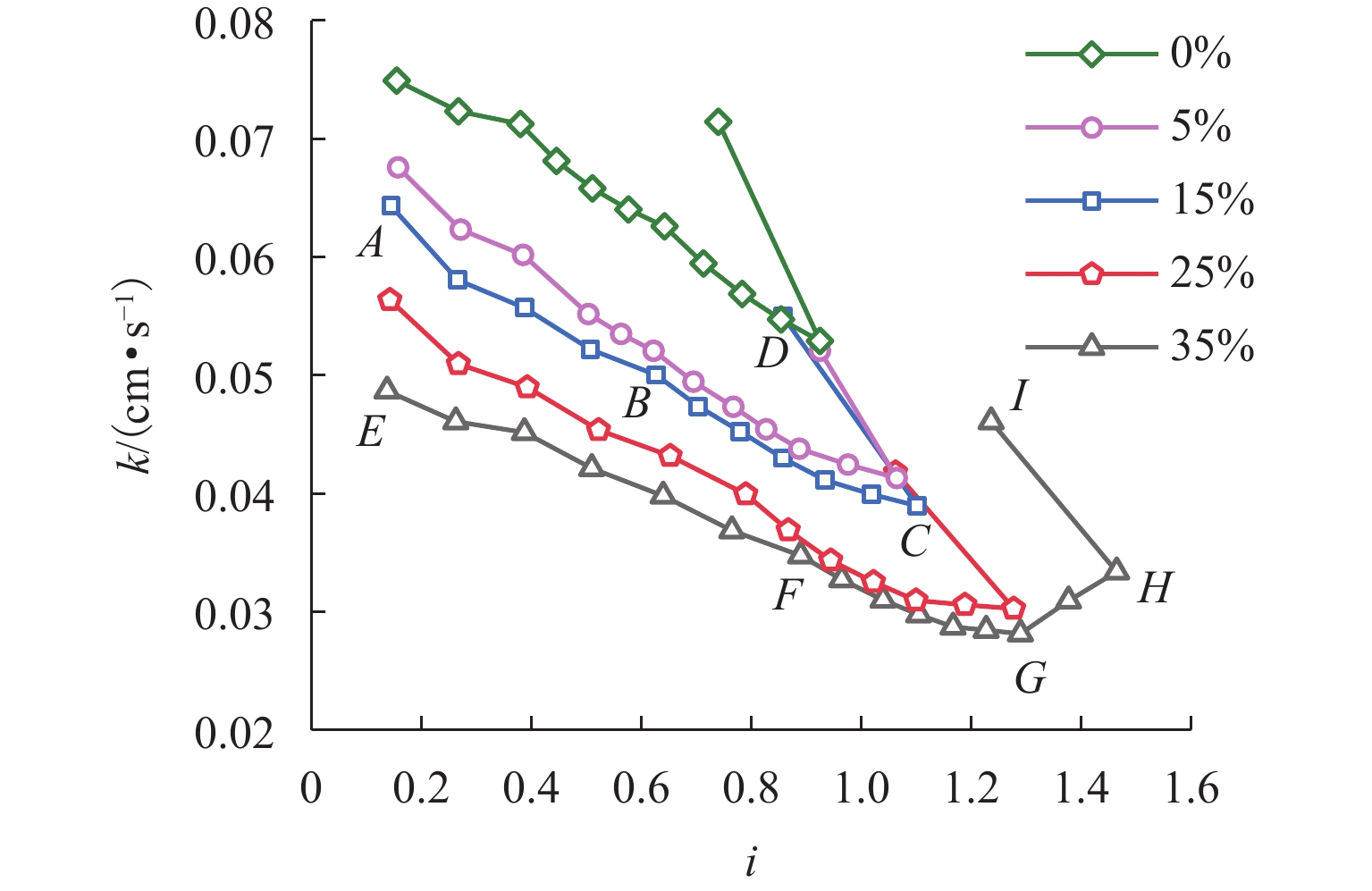
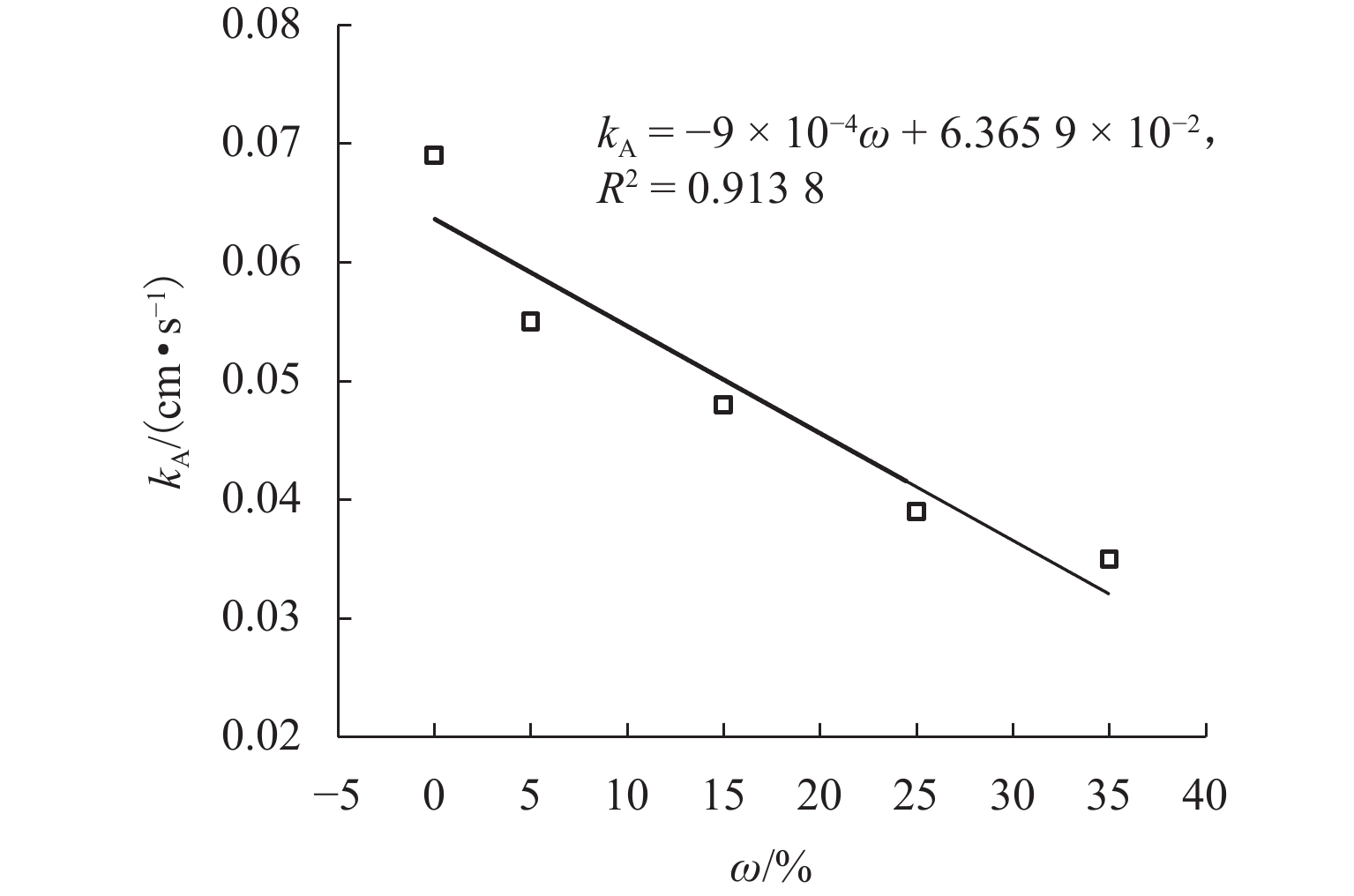
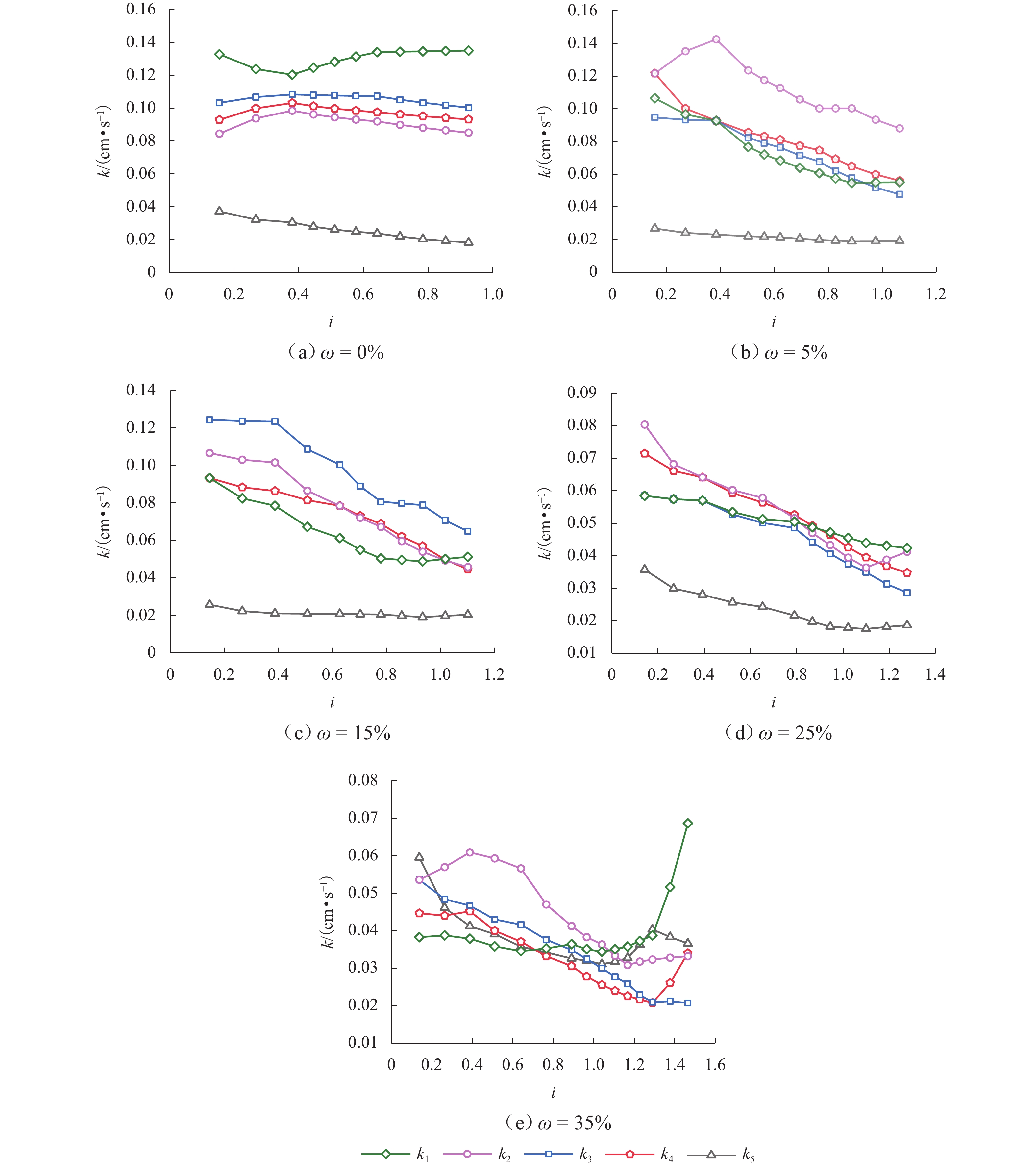
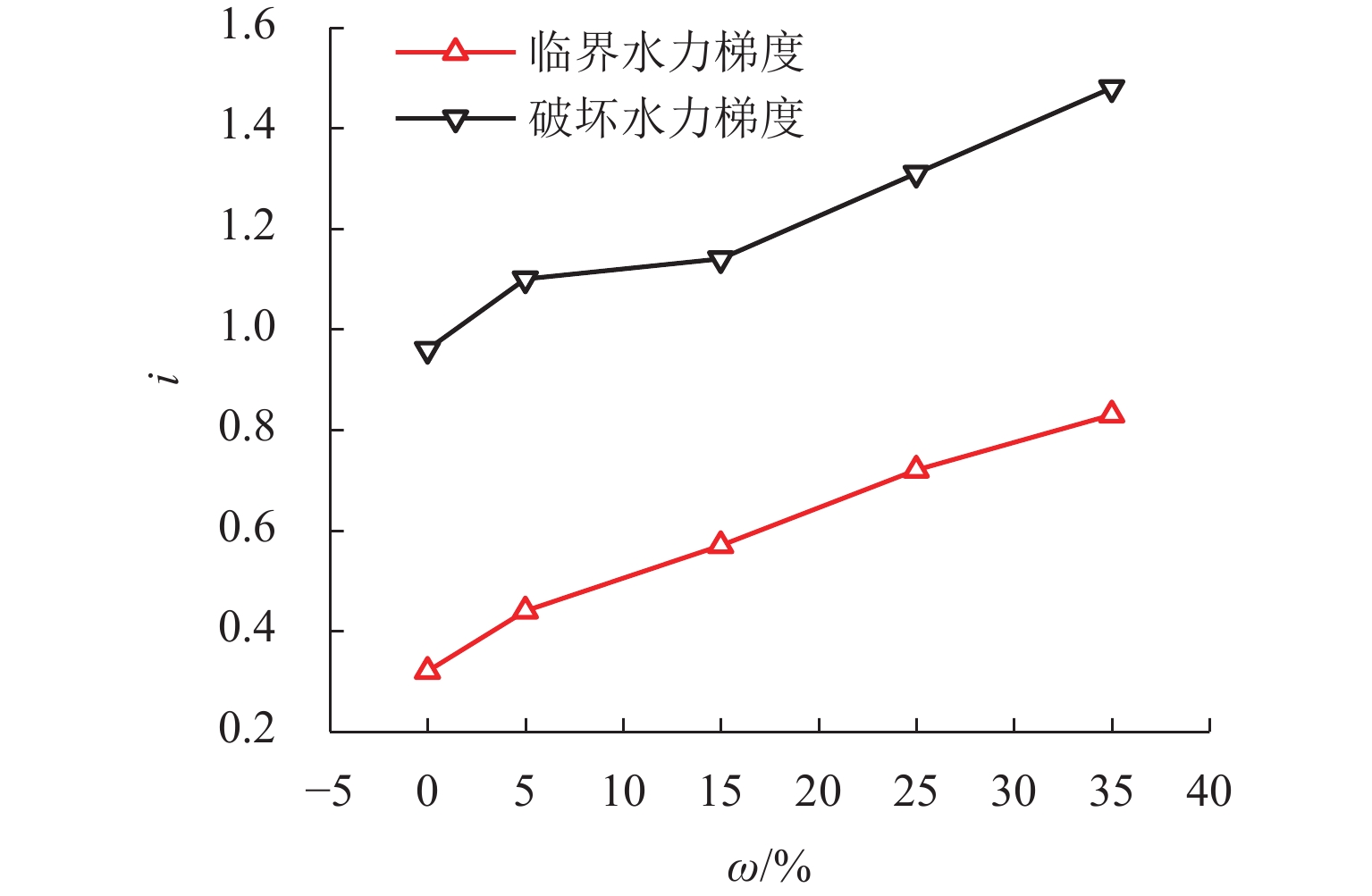
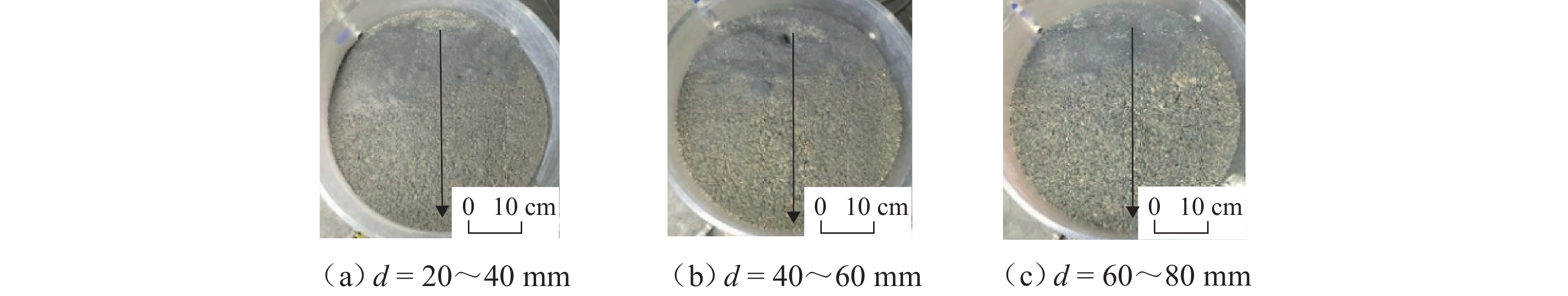
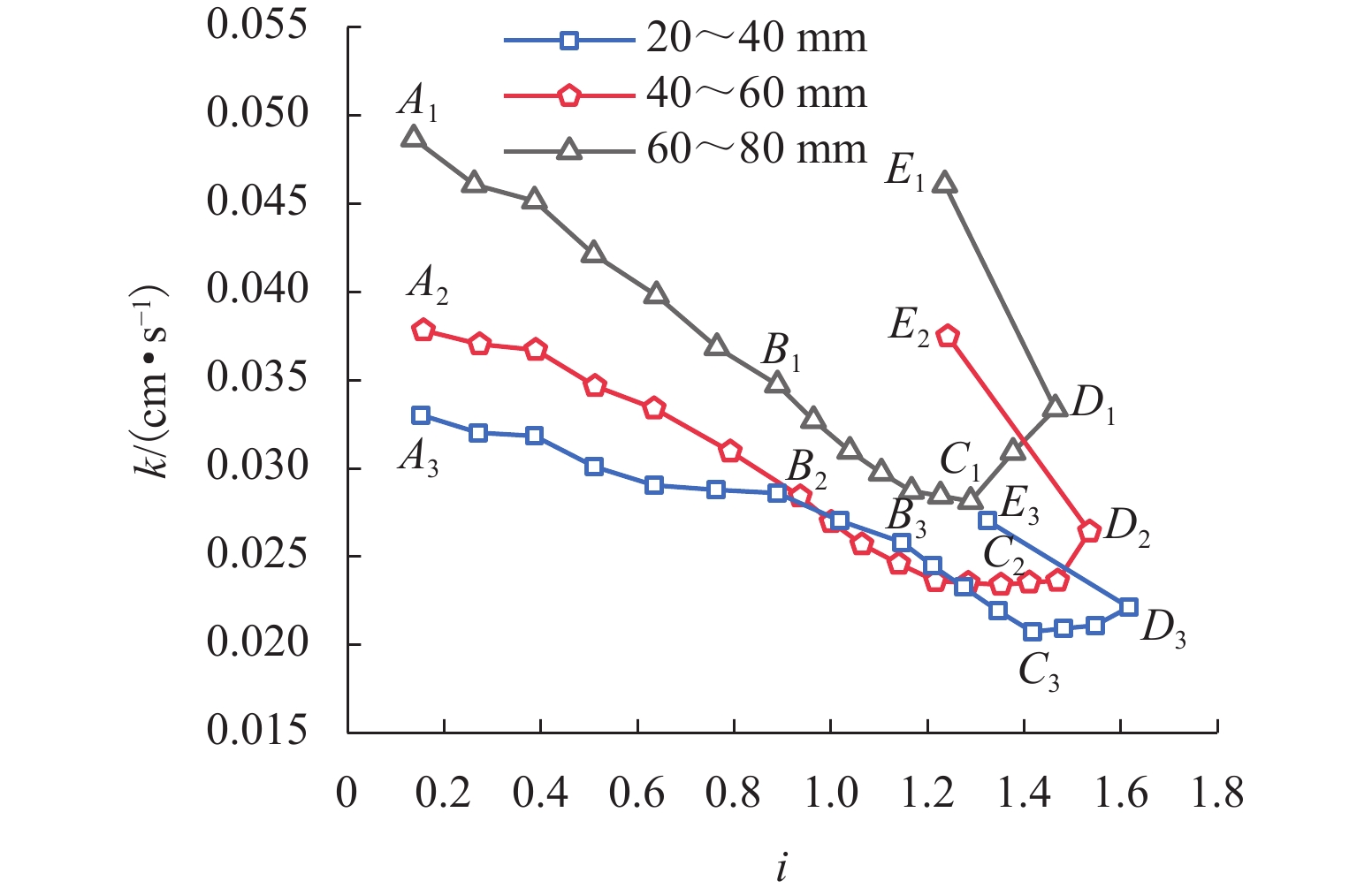
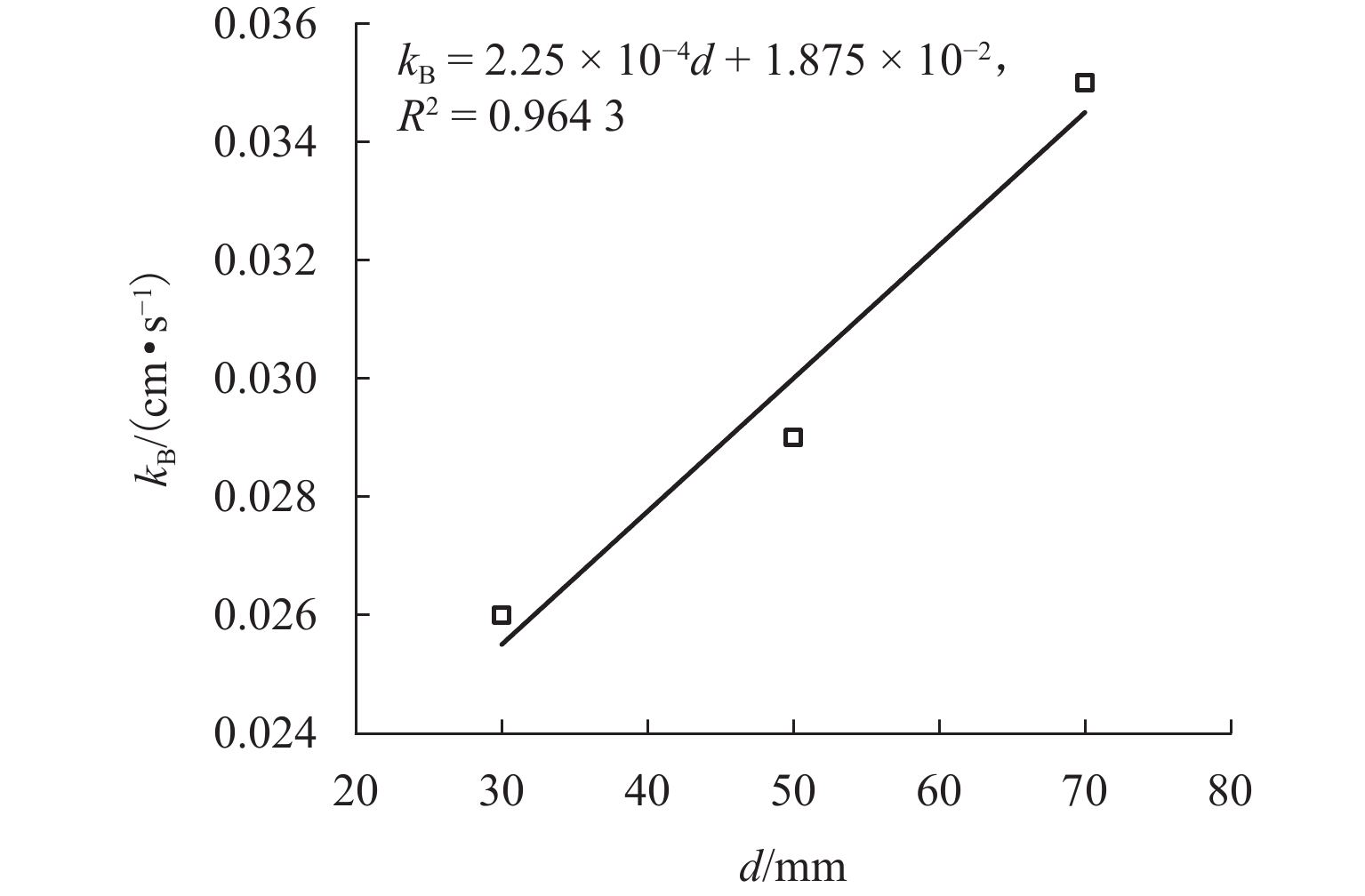
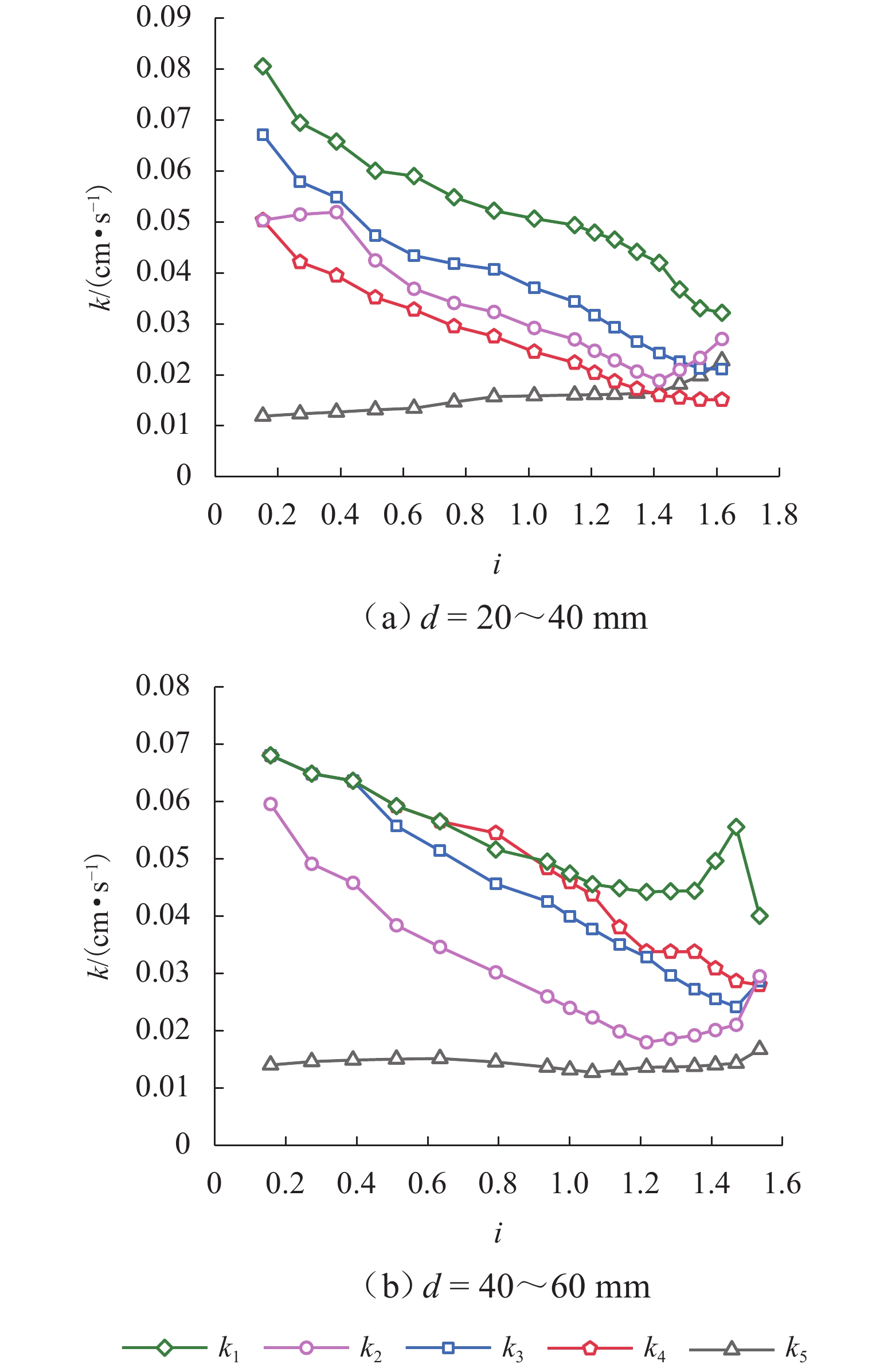
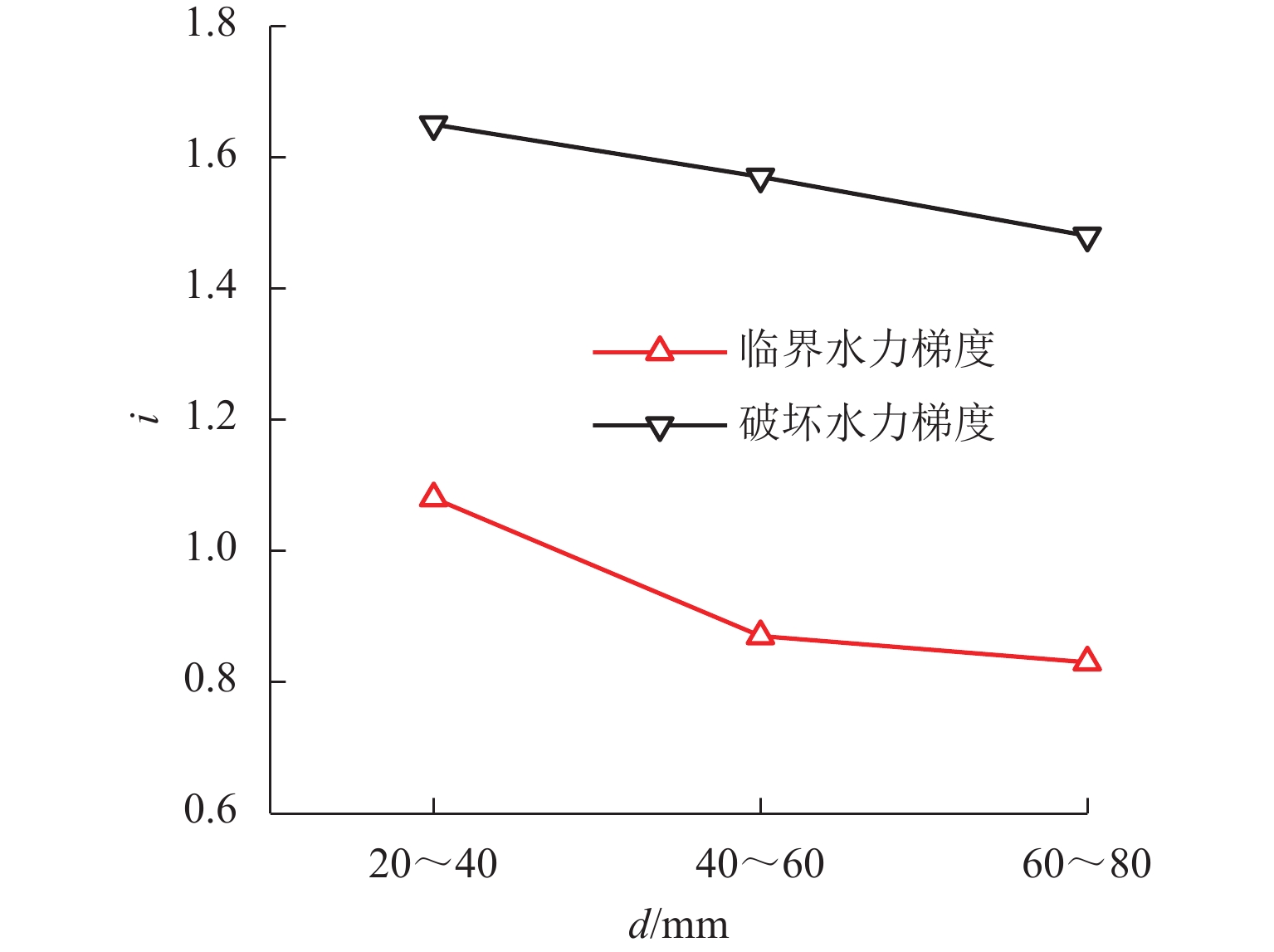
川西北地区千枚岩土石混合体分布广泛,在降雨条件下开挖边坡极易大面积失稳,对该地区交通工程施工和运营安全构成了重要威胁. 土石混合体渗透特性显著影响开挖边坡稳定性,而扁平状千枚岩块的空间定向性是影响千枚岩土石混合体渗透性的关键因素. 本文基于千枚岩岩块的空间定向特征,采用自行研发的大型渗透仪开展不同含石量、岩块粒径等条件下的千枚岩土石混合体渗透特性试验,研究含石量、岩块粒径对此类混合体渗透性的影响. 结果表明:当含石量从0%增至35%时,土石混合体渗透系数降低49.28%,临界和破坏水力梯度分别升高159.38%和54.17%,难以发生管涌破坏现象;当岩块粒径从20~40 mm增至60~80 mm时,其渗透系数增大34.62%,临界和破坏水力梯度分别降低23.15%和10.3%,更易发生管涌破坏等现象;可为川西北地区千枚岩土石混合体的水力特性评价及开挖边坡稳定性分析提供参考.
Abstract:The soil–phyllite mixtures are widely distributed in the northwest of Sichuan, and excavation of slopes in these areas under rainfall conditions can cause large-scale instability, posing threats to the safety of transportation engineering construction and operation. The permeability characteristics of soil–rock mixtures significantly affect the stability of excavated slopes, and the spatial orientation of flat phyllite is the key factor affecting the permeability of soil–phyllite mixtures. Based on the spatial orientation characteristics of phyllite, a self-developed large-scale permeameter was used to examine permeability characteristics of soil–phyllite mixtures under different conditions, including various rock content and particle sizes, and the influence of these factors on the permeability of such mixtures was studied. The results show that when the rock content increases from 0% to 35%, the permeability coefficient of the mixture decreases by 49.28%, while the critical and failure hydraulic gradients increase by 159.38% and 54.17%, respectively, making piping failure less likely to occur. When the rock size increases from 20–40 mm to 60–80 mm, the permeability coefficient increases by 34.62%, and the critical and failure hydraulic gradients decrease by 23.15% and 10.3%, respectively, making piping failure more likely to occur. These findings provide references for evaluating the hydraulic characteristics of soil–phyllite mixtures and assessing the excavated slope stability in northwest Sichuan.
-
Key words:
- soil–phyllite mixture /
- permeability /
- orientation /
- rock content /
- rock particle size
-
-
[1] 赵晓彦, 万宇豪, 张肖兵. 汶马高速公路千枚岩堆积体岩块定向性试验研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2020, 41(1): 175-184.ZHAO Xiaoyan, WAN Yuhao, ZHANG Xiaobing. Experimental study of fragment orientation of phyllite talus at Whenchuan-Maerkang expressway[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2020, 41(1): 175-184. [2] 金磊, 曾亚武, 程涛, 等. 基于格子Boltzmann方法的土石混合体的渗流特性研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2022, 44(4): 669-677. doi: 10.11779/CJGE202204009JIN Lei, ZENG Yawu, CHENG Tao, et al. Seepage characteristics of soil-rock mixture based on lattice Boltzmann method[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2022, 44(4): 669-677. doi: 10.11779/CJGE202204009 [3] CAI P C, MAO X S, DAI Z Y, et al. Lattice Boltzmann simulation and mesoscopic mechanism analysis of permeability in soil-rock mixtures[J]. Computational Particle Mechanics, 2024, 11(2): 789-803. doi: 10.1007/s40571-023-00653-3 [4] WANG T, YAN C Z, ZHENG Y C, et al. Numerical study on the effect of meso-structure on hydraulic conductivity of soil-rock mixtures[J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2022, 146: 104726.1-104726.27. [5] 王月明. 隧道断层带土石混合体渗流特性研究[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2020. [6] WANG Y C, ZHENG S H, WANG Y M, et al. Experimental study on the permeability and seepage characteristics of bimsoils[J]. Geomatics, Natural Hazards and Risk, 2021, 12(1): 3001-3020. doi: 10.1080/19475705.2021.1987341 [7] 李晶晶, 金磊, 程涛. 土石混合体细观渗流场的格子Boltzmann模拟[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2019, 19(29): 235-241. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2019.29.038LI Jingjing, JIN Lei, CHENG Tao. Numerical simulation of mesoscopic seepage field of soil-rock mixture based on lattice boltzmann method[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2019, 19(29): 235-241. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2019.29.038 [8] 罗亦琦. 土石混合体渗流特性的分形研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2019. [9] WANG Y, LI X, ZHENG B, et al. A laboratory study of the effect of confining pressure on permeable property in soil-rock mixture[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2016, 75(4): 284. doi: 10.1007/s12665-015-5193-x [10] ZHOU Z, YANG H, WANG X C, et al. Model development and experimental verification for permeability coefficient of soil–rock mixture[J]. International Journal of Geomechanics, 2017, 17(4): 04016106.1-04016106.10. [11] CHEN T, YANG Y T, ZHENG H, et al. Numerical determination of the effective permeability coefficient of soil–rock mixtures using the numerical manifold method[J]. International Journal for Numerical and Analytical Methods in Geomechanics, 2019, 43(1): 381-414. doi: 10.1002/nag.2868 [12] 胡瑞林, 李晓, 王宇, 等. 土石混合体工程地质力学特性及其结构效应研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 2020, 28(2): 255-281.HU Ruilin, LI Xiao, WANG Yu, et al. Research on engineering geomechanics and structural effect of soil-rock mixture[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2020, 28(2): 255-281. [13] 杨忠平, 李勇华, 李诗琪, 等. 不同含石率土石混合体水力侵蚀分异特征及机制[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2024, 43(1): 133-145.YANG Zhongping, LI Yonghua, LI Shiqi, et al. Differentiation characteristics and mechanism of hydraulic erosion of soil-rock mixtures with different rock contents[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2024, 43(1): 133-145. [14] 中国水电顾问集团成都勘测设计研究院. 水电水利工程粗粒土试验规程: DL/T 5356—2006[S]. 北京: 中国电力出版社, 2006. [15] XU W J, XU Q, HU R L. Study on the shear strength of soil–rock mixture by large scale direct shear test[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2011, 48(8): 1235-1247. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2011.09.018 [16] 曾彩云, 赵晓彦, 万宇豪, 等. 考虑岩块定向性的汶马高速公路千枚岩堆积体渗透特性试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2023, 45(4): 862-868. doi: 10.11779/CJGE20211536ZENG Caiyun, ZHAO Xiaoyan, WAN Yuhao, et al. Experimental study on permeability of phyllite talus in Whenchuan-Maerkang expressway considering fragment orientation[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2023, 45(4): 862-868. doi: 10.11779/CJGE20211536 -




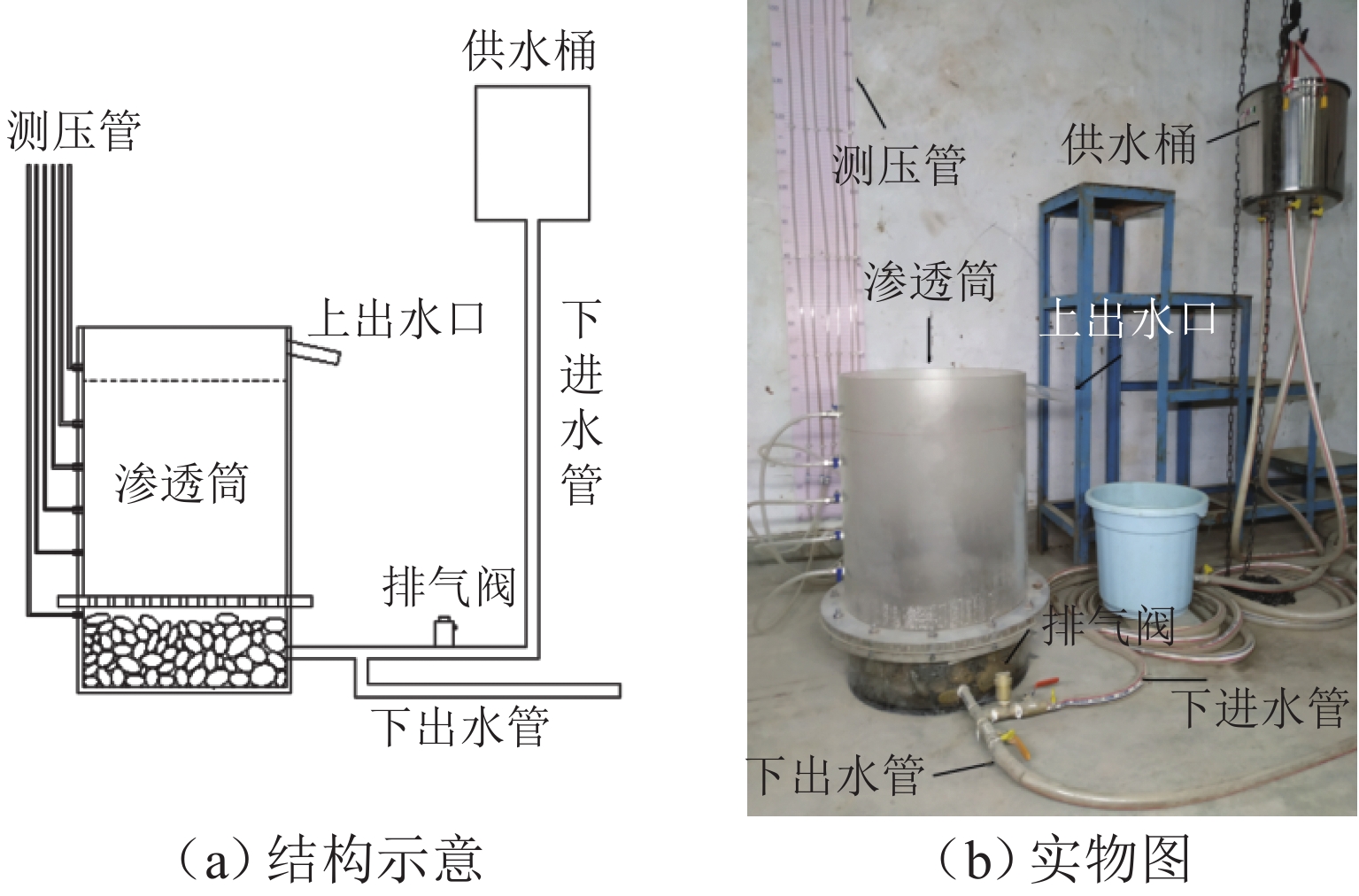
 下载:
下载: