Node Deployment Algorithm for Wireless Sensor Network in Rolling Terrain
-
摘要:
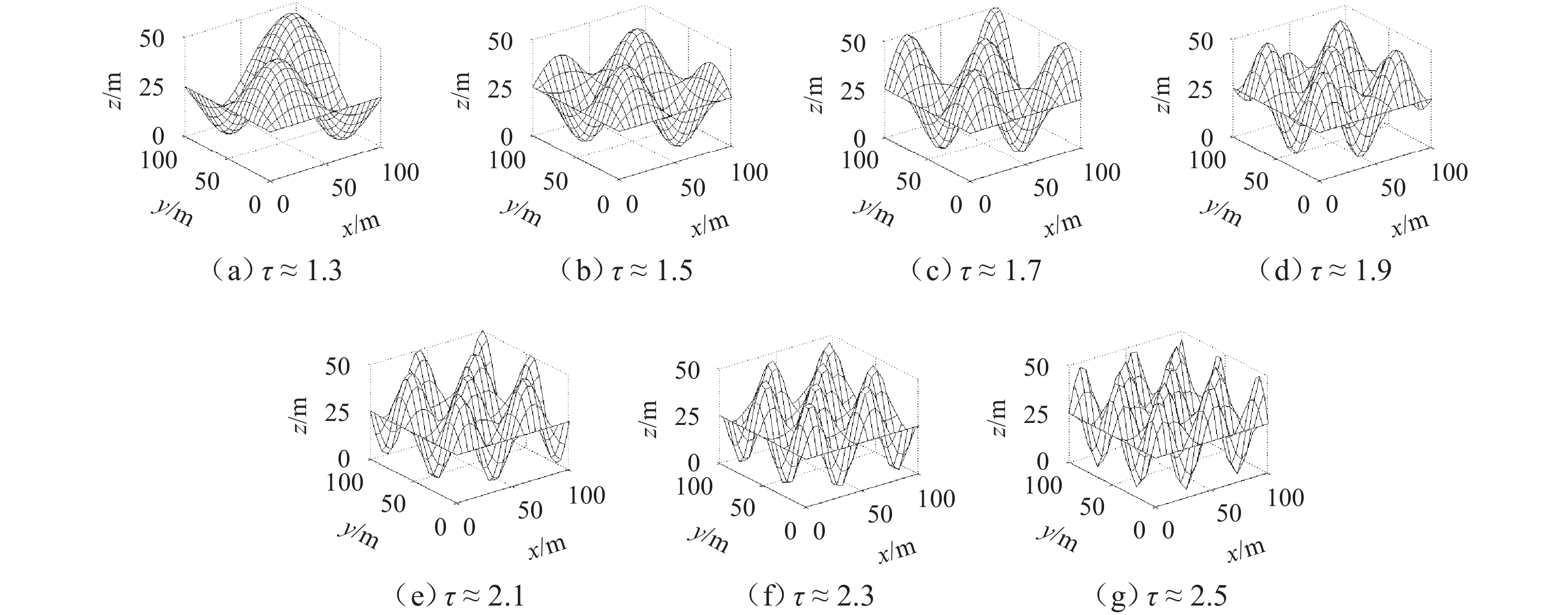
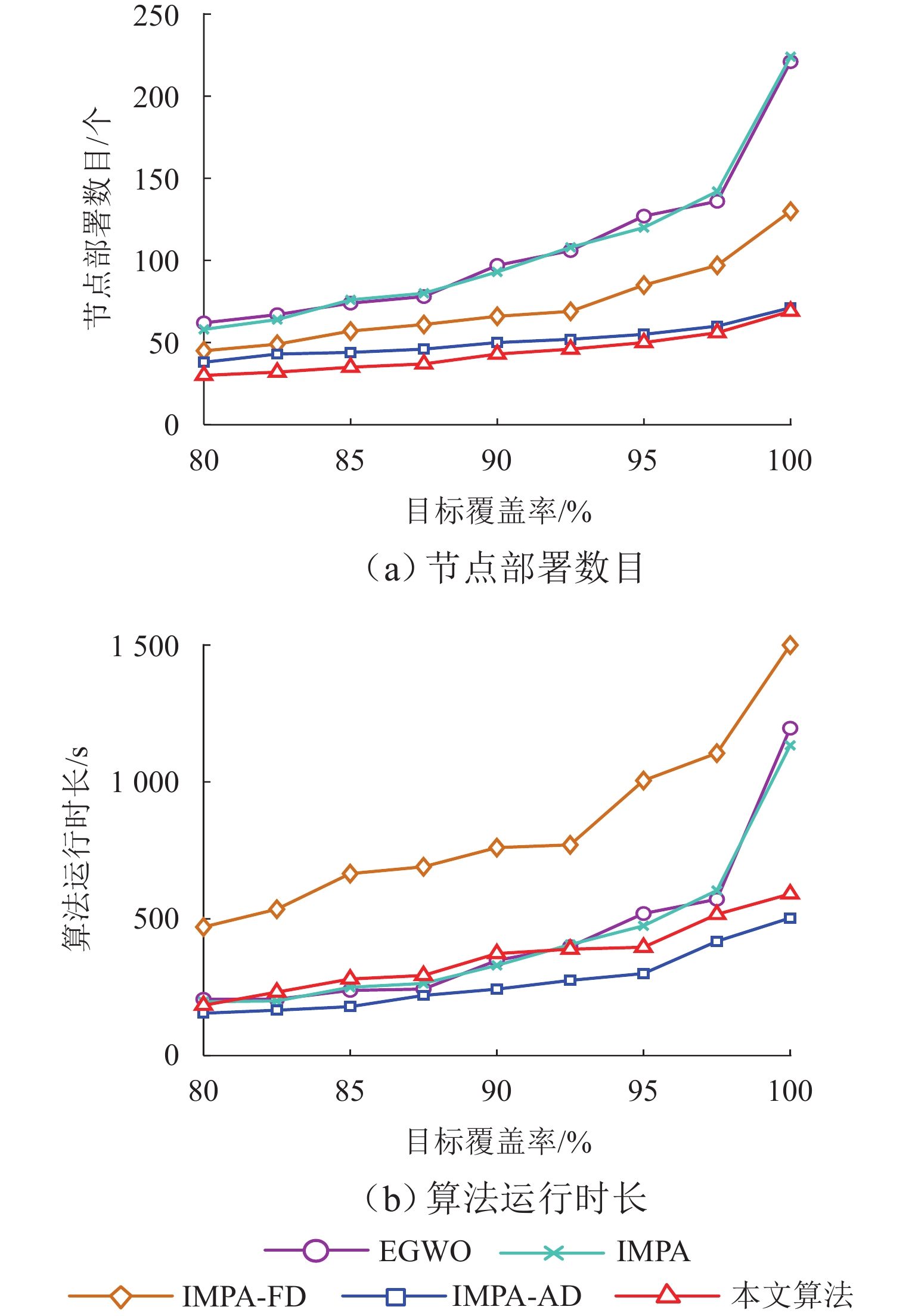
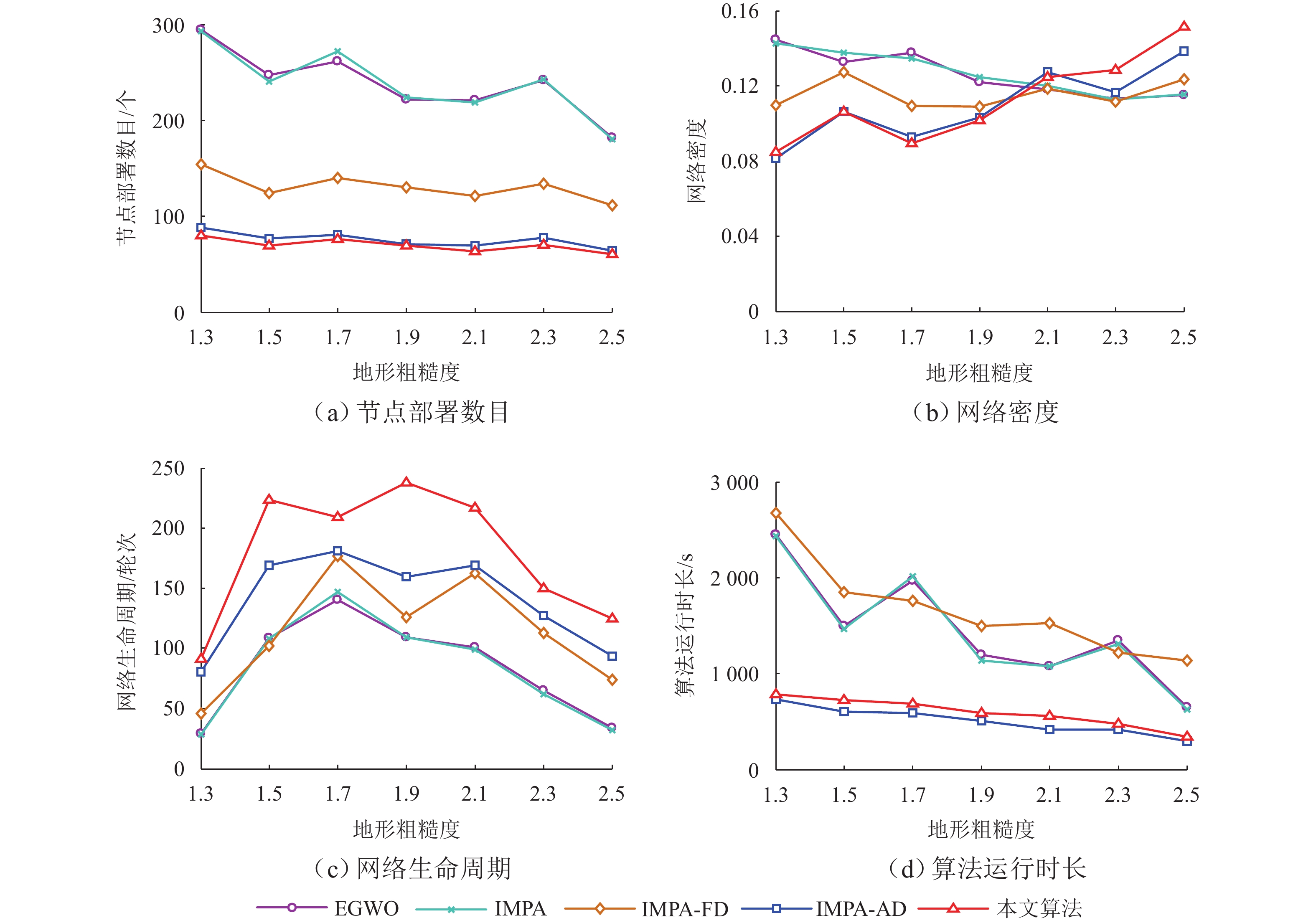
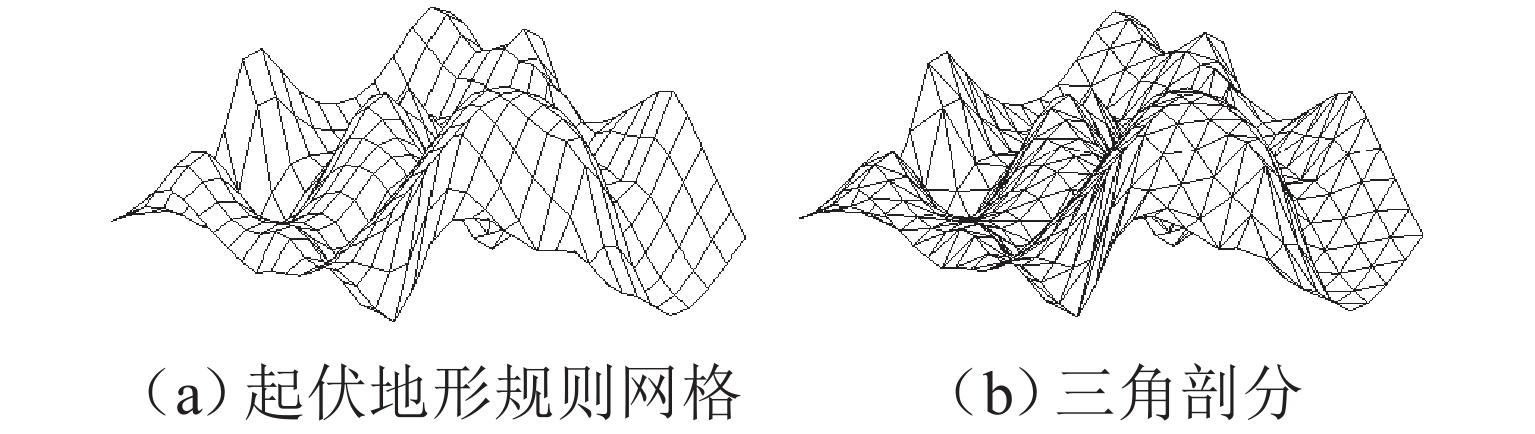
为减少起伏地形下传感器节点的部署数量,首先,采用数字高程模型与Delaunay三角剖分对起伏地形表面建模,确定节点部署问题解空间;然后,建立节点部署算法搜索维度与网络覆盖率之间的函数关系,以网络连通为约束、网络覆盖率最大化为目标,并基于改进海洋捕食者算法,搜索形成候选个体集;再以收益遗憾最小化为准则,使用候选个体衍生新个体;最后,将网络覆盖率、网络密度作为指标构建筛选函数,选出最佳新个体并纳入到部署节点集合. 仿真结果表明:在地形粗糙度为1.9、目标覆盖率为80.0%~100.0%时,与同类部署算法相比,所提算法的节点部署数量降低2.9%~69.1%;在地形粗糙度为1.3~2.5、目标覆盖率为100.0%时,所提算法的节点部署数量降低3.1%~74.0%,网络生命周期有所延长.
Abstract:To reduce the number of sensor nodes deployed in rolling terrains, firstly, the digital elevation model and Delaunay triangulation were used to model the rolling terrain surface and determine the solution space of the node deployment problem. Secondly, the functional relationship between the node deployment algorithm search dimension and network coverage rate was established. A candidate individual set was searched and formed based on the proposed improved marine predator algorithm, with the constraints of network connectivity and the goal of maximizing network coverage rate. The utility regret minimization criterion was used to derive new individuals from the candidate individuals. Finally, the filtering function was constructed using network coverage rate and network density as indicators to select the best new individual and incorporate it into the deployed node set. Simulation results show that compared with similar deployment algorithms, the proposed algorithm reduces the number of deployed nodes by 2.9%–69.1% for terrain roughness at 1.9 and target coverage rate at 80.0%–100.0% and that by 3.1%–74.0% for the terrain roughness at 1.3–2.5 and the target coverage rate at 100.0%, and the network lifetime is prolonged.
-
Key words:
- wireless sensor network /
- node deployment /
- terrain roughness /
- network lifetime
-
表 1 仿真参数及取值
Table 1. Simulation parameters and values
参数 取值 起伏地形:长/宽/高/m 100/100/50 DEM 网格精度 21 × 21 IMPA 种群大小 50 权重$ \theta _0 $ 0.9 节点初始能量/J 1 数据包大小/bit 3200 电路能耗$ E_{\text{elec}} $/(nJ•bit−1) 50 功放参数$ \varepsilon _{\text{fs}} $/( pJ•bit−1•m−2) 10 功放参数$ \varepsilon _{\text{amp}} $/(pJ•bit−1•m−4) 0.0013 距离阈值$ d_0 $/m 87 -
[1] 张海柱, 黎荣, 丁国富, 等. 高速列车顶层设计指标分解研究现状与展望[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2024, 59(2): 456-466. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20220188ZHANG Haizhu, LI Rong, DING Guofu, et al. Research status and prospect of decomposition of top-level design indicators for high-speed trains[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2024, 59(2): 456-466. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20220188 [2] 徐正宣, 林之恒, 刘云鹏, 等. 复杂孕灾环境下隧道进口斜坡稳定性分析与评价[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2024, 59(5): 1068-1077, 1085. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20220361XU Zhengxuan, LIN Zhiheng, LIU Yunpeng, et al. Stability analysis and evaluation of a tunnel entrance slope under complex disaster-prone environments[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2024, 59(5): 1068-1077, 1085. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20220361 [3] JOSHI A, KANUNGO D P, PANIGRAHI R K. WSN-based smart landslide monitoring device[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2023, 72: 5501912.1-5501912.12. [4] 李翠然, 杨茜, 谢健骊, 等. 基于SWIPT的能量收集WSN吞吐量性能分析及优化[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2024, 59(5): 1014-1022. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20220625LI Cuiran, YANG Qian, XIE Jianli, et al. Throughput performance analysis and optimization of energy harvesting wireless sensor network based on simultaneous wireless information and power transfer[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2024, 59(5): 1014-1022. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20220625 [5] GIRI P, NG K, PHILLIPS W. Wireless sensor network system for landslide monitoring and warning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2019, 68(4): 1210-1220. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2018.2861999 [6] CHOWDHURY A, DE D. Energy-efficient coverage optimization in wireless sensor networks based on Voronoi-Glowworm Swarm Optimization-K-means algorithm[J]. Ad Hoc Networks, 2021, 122: 102660.1-102660.16. [7] WANG J, LIU Y, RAO S Y, et al. A novel self-adaptive multi-strategy artificial bee colony algorithm for coverage optimization in wireless sensor networks[J]. Ad Hoc Networks, 2023, 150: 103284.1-103284.13. [8] LI Y, YAO Y D, HU S S, et al. Coverage enhancement strategy for WSNs based on multiobjective ant lion optimizer[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2023, 23(12): 13762-13773. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2023.3267459 [9] KONG L H, ZHAO M C, LIU X Y, et al. Surface coverage in sensor networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2014, 25(1): 234-243. [10] DU Y Z. Method for the optimal sensor deployment of WSNs in 3D terrain based on the DPSOVF algorithm[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 140806-140821. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3013106 [11] ANAND N, RANJAN R, RAI B S, et al. A novel computational geometry-based node deployment scheme in 3D wireless sensor network[J]. International Journal of Sensor Networks, 2017, 25(3): 135-145. doi: 10.1504/IJSNET.2017.087708 [12] FENG L, QIU T, SUN Z L, et al. A coverage strategy for wireless sensor networks in a three-dimensional environment[J]. International Journal of Ad Hoc and Ubiquitous Computing, 2014, 15(1/2/3): 83-94. doi: 10.1504/IJAHUC.2014.059904 [13] FU W D, YANG Y, HONG G Q, et al. WSN deployment strategy for real 3D terrain coverage based on greedy algorithm with DEM probability coverage model[J]. Electronics, 2021, 10(16): 2028.1-2028.16. [14] WANG Z D, XIAO H, YANG S X, et al. Multistrategy integrated marine predator algorithm applied to 3D surface WSN coverage optimization[J]. Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing, 2022, 2022(1): 9593103.1-9593103.32. [15] WANG Z D, XIE H M. Wireless sensor network deployment of 3D surface based on enhanced grey wolf optimizer[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 57229-57251. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2982441 [16] 李振洪, 李鹏, 丁咚, 等. 全球高分辨率数字高程模型研究进展与展望[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2018, 43(12): 1927-1942.LI Zhenhong, LI Peng, DING Dong, et al. Research progress of global high resolution digital elevation models[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2018, 43(12): 1927-1942. [17] 蒋球伟. 地形分析中一个基础算法的研究与改进[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2007, 43(34): 95-97, 104. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-8331.2007.34.030JIANG Qiuwei. Research and improvement of basic algorithm over terrain analysis[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2007, 43(34): 95-97, 104. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-8331.2007.34.030 [18] 李明, 胡江平, 曹晓莉. 异构有向传感器网络连通覆盖调度算法[J]. 电子科技大学学报, 2022, 51(4): 572-579. doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2022001LI Ming, HU Jiangping, CAO Xiaoli. Connected coverage scheduling algorithm for heterogeneous directional sensor networks[J]. Journal of University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2022, 51(4): 572-579. doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2022001 [19] 徐公国, 单甘霖, 段修生. 基于改进d-Xdraw算法的起伏地形下异构多传感器分簇部署方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2019, 41(7): 1516-1524. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2019.07.12XU Gongguo, SHAN Ganlin, DUAN Xiusheng. Cluster deployment method of heterogeneous multi-sensor on rolling terrains based on improved d-Xdraw algorithm[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2019, 41(7): 1516-1524. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2019.07.12 [20] FARAMARZI A, HEIDARINEJAD M, MIRJALILI S, et al. Marine predators algorithm: a nature-inspired metaheuristic[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2020, 152: 113377.1-113377.28. [21] 曾斌, 王睿, 李厚朴, 等. 海上基地攻防博弈模型及纳什均衡策略研究[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2022, 44(8): 2570-2580. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2022.08.22ZENG Bin, WANG Rui, LI HouPu, et al. Nash equilibrium strategy and attack-defense game model for naval support base[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(8): 2570-2580. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2022.08.22 [22] ZHANG D C, SHI W, ELHABYAN R, et al. A coverage and obstacle-aware clustering protocol for wireless sensor networks in 3D terrain[J]. Computer Communications, 2019, 146: 48-54. doi: 10.1016/j.comcom.2019.07.011 [23] 段宇英, 汤军, 刘远刚, 等. 基于随机森林的山西省柳林县黄土滑坡空间敏感性评价[J]. 地理科学, 2022, 42(2): 343-351.DUAN Yuying, TANG Jun, LIU Yuangang, et al. Spatial sensitivity evaluation of loess landslide in Liulin County, Shanxi based on random forest[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2022, 42(2): 343-351. [24] TAM N T, BINH H T T, DAT V T, et al. Towards optimal wireless sensor network lifetime in three dimensional terrains using relay placement metaheuristics[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2020, 206: 106407.1-106407.12. [25] DONG S, SAREM M, ZHOU W G. Distributed data gathering algorithm based on spanning tree[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2020, 15(1): 289-296. -




 下载:
下载: