Energy Evolution Mechanism and Constitutive Model of Sandstone Subjected to Different Temperatures
-
摘要:
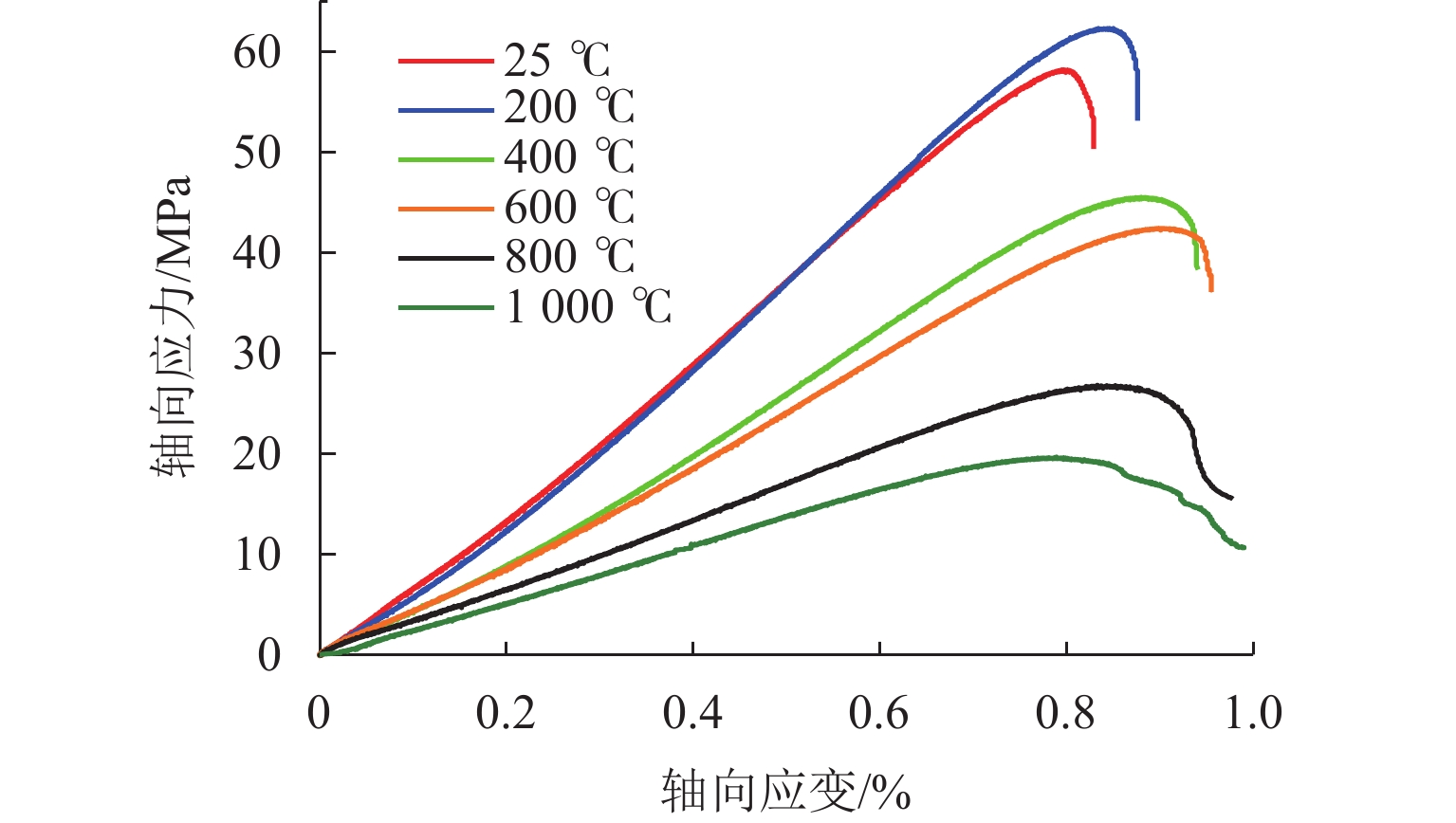
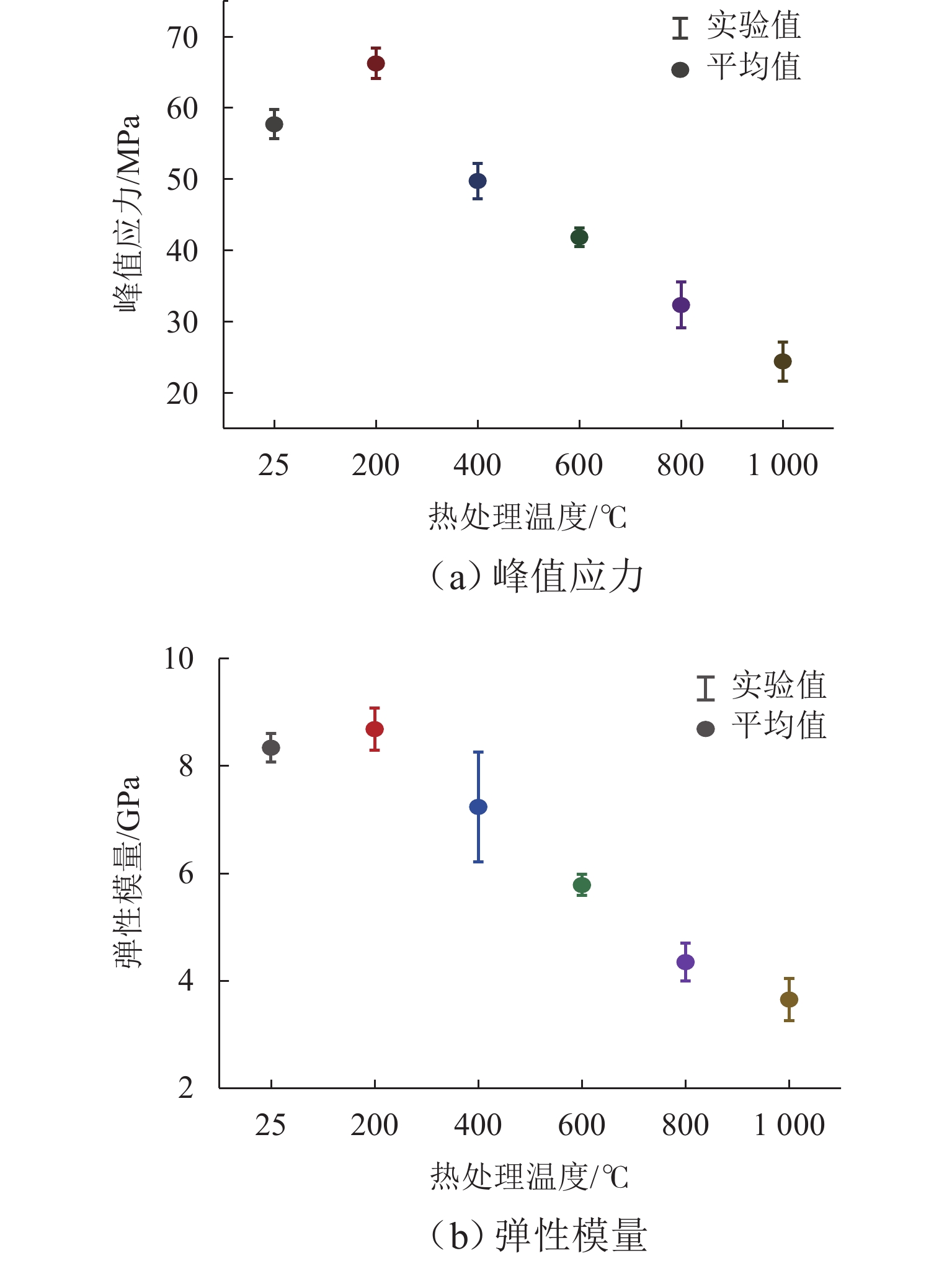
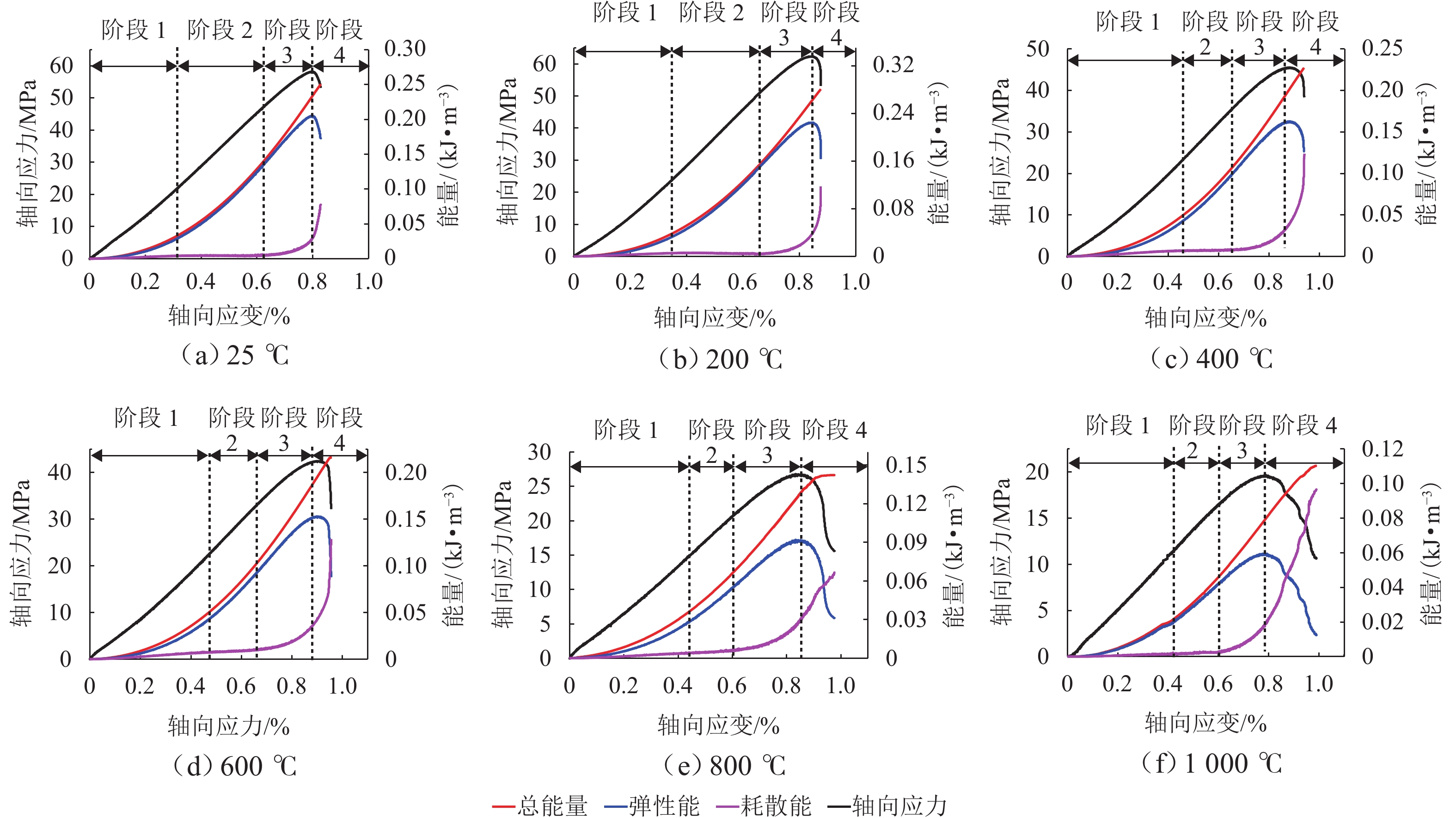
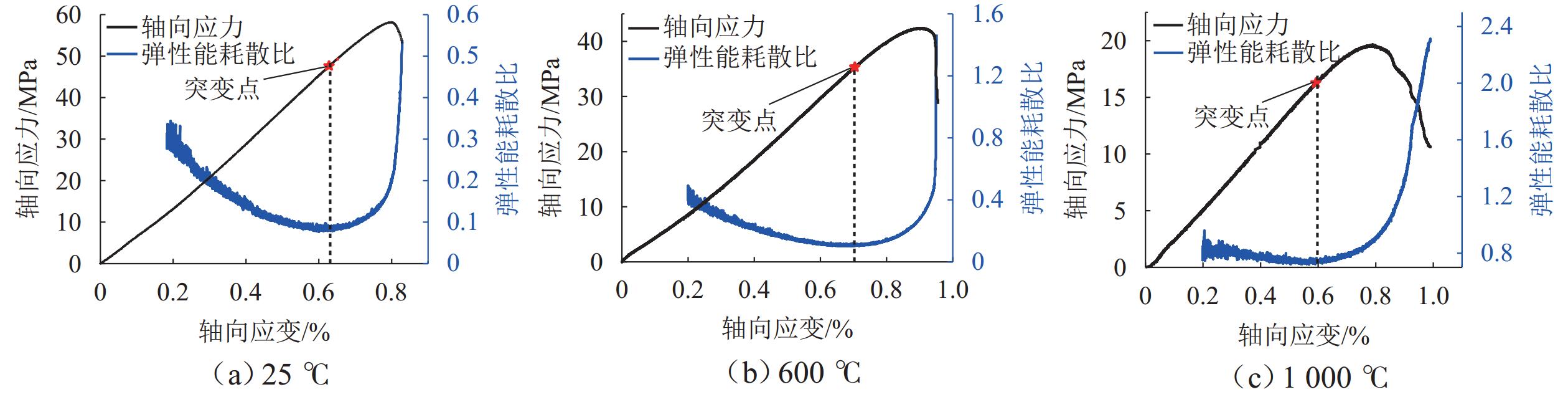
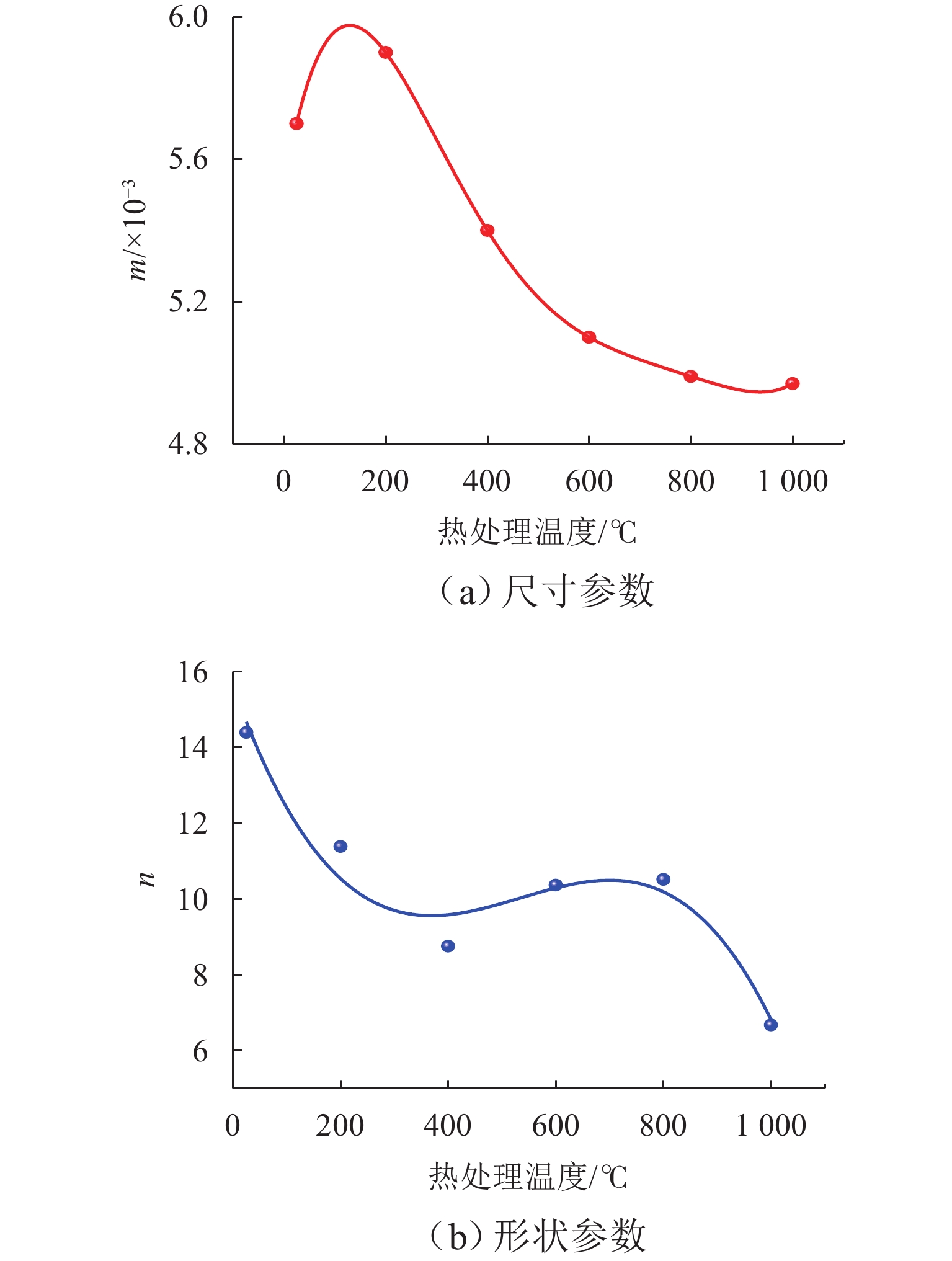
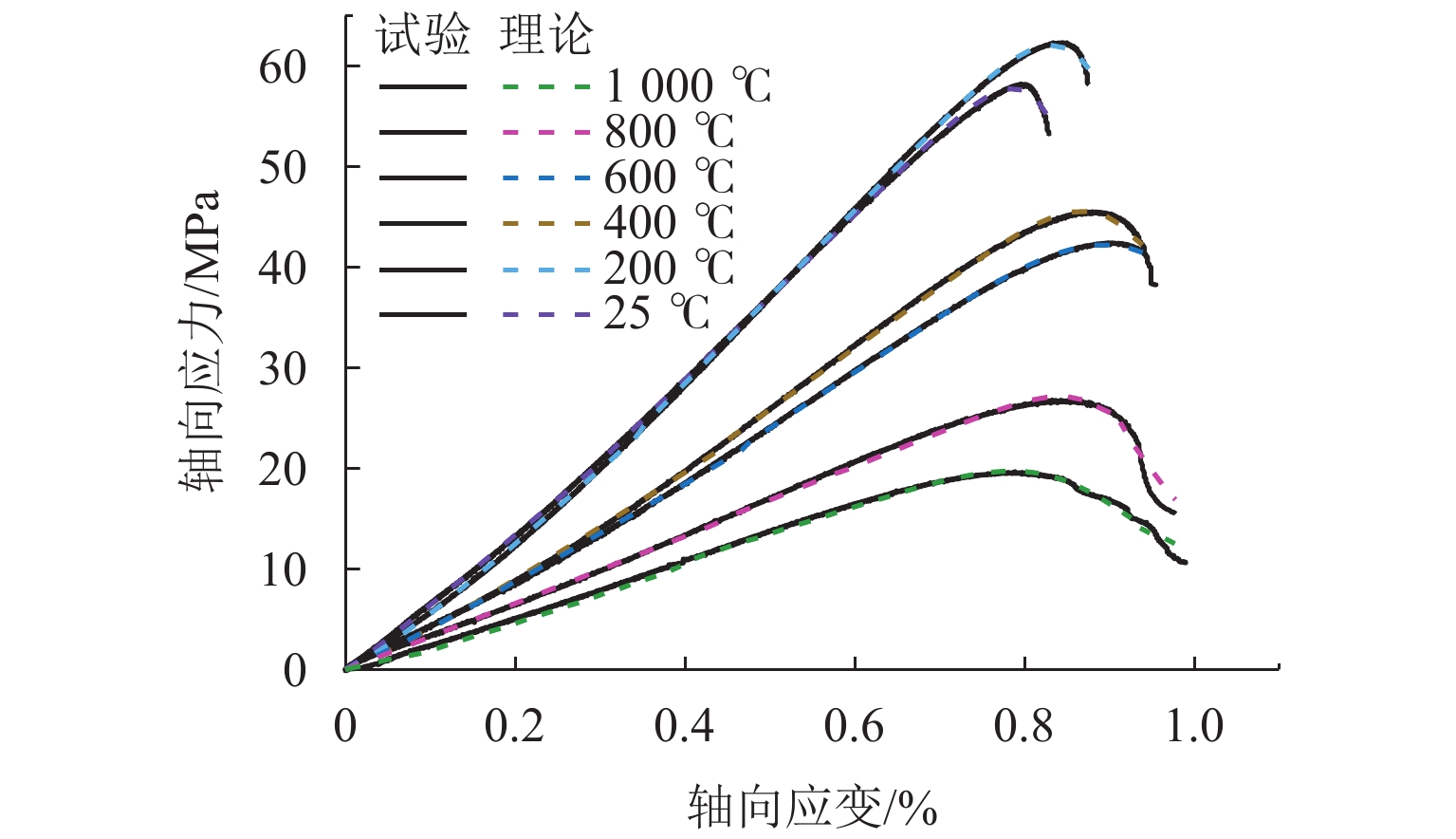
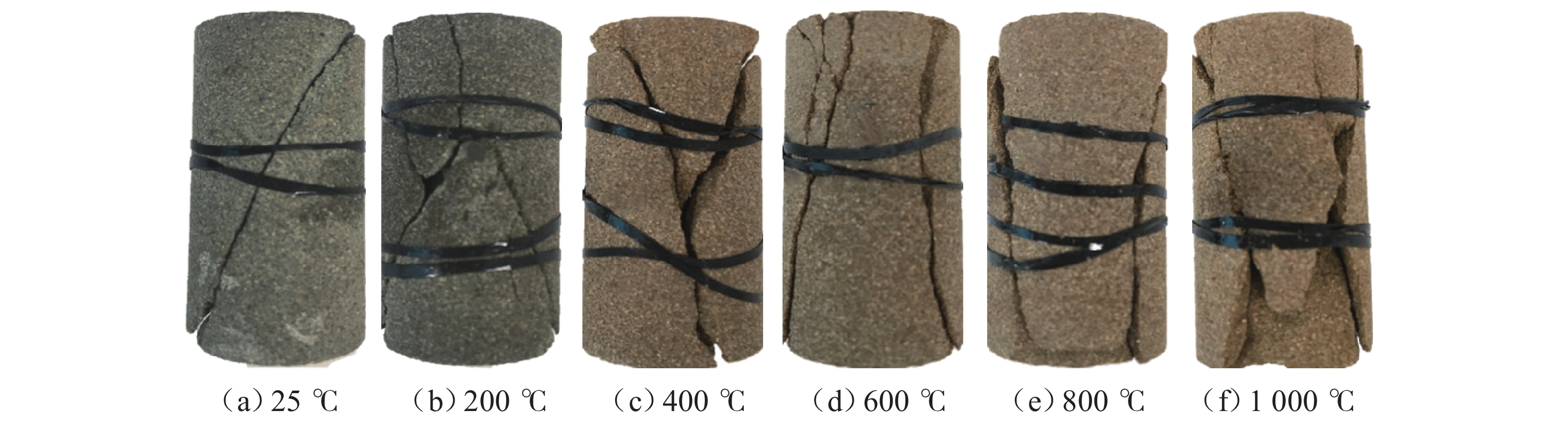
为研究高温对砂岩物理力学性能劣化的影响,本文开展不同温度热处理砂岩的单轴压缩试验. 首先,分析力学强度和破断模式,获得砂岩宏观力学参数的劣化特征;其次,研究不同温度对砂岩能量演化机制及弹性能耗比的影响;最后,基于温度和荷载损伤因子,采用分段函数方法构建考虑裂纹闭合阶段的热-力耦合损伤本构模型. 研究结果表明:随着温度的增加,砂岩峰值强度和弹性模量先增加后减小,在200 ℃时达到最大值;破断模式由倾斜剪切破坏向“Y”型共轭拉-剪混合破坏转变,脆-延性转变的临界温度阈值为400 ℃;根据耗散能演化特征将整个变形破裂过程划分为裂纹闭合阶段、弹性阶段、宏观裂纹扩展阶段和峰后阶段;弹性能耗比(
K )的拐点可作为砂岩由弹性向塑性转变的突变点;模型尺寸参数(m )随温度升高先上升后下降,形状参数(n )逐渐降低,参数m 和n 分别反映砂岩的强度和塑性特征,理论模型与室内试验结果吻合度较高,说明本模型能够反演热-力耦合下砂岩损伤演化全过程.Abstract:To investigate the effect of high temperature on the deterioration of the physical and mechanical properties of sandstone, uniaxial compression tests were conducted on thermally-treated sandstone subjected to different temperatures. Firstly, the deterioration characteristics of macroscopic mechanical parameters of sandstone were obtained through the analysis of mechanical strength and failure modes. Secondly, the influence of different temperatures on the energy evolution mechanism and elastic energy dissipation ratio of sandstone was studied. Finally, combined with the temperature and load damage factor, the piecewise function method was applied to develop a thermo-mechanical coupling damage constitutive model, considering the crack closure stage. The results show that as temperature increases, the peak strength and elastic modulus of thermally-treated sandstone increase first and then decrease, reaching a maximum value at 200 ℃. The failure mode transforms from oblique shear to “Y”-shaped conjugate tension–shear mixed failure, with the critical temperature threshold for the brittle and ductile transition occurring at 400 ℃. Based on dissipated energy evolution characteristics, the deformation and failure process is primarily divided into crack closure, elastic, macro-crack extension, and post-peak stages. The turning point of the elastic energy dissipation ratio (
K ) serves as the critical point where sandstone transitions from elastic to plastic behavior. The model’s size parameter (m ) first increases and then decreases with increasing temperature, while the shape parameter (n ) gradually decreases, reflecting the strength and plasticity of sandstone. The good agreement between the theoretical model and the laboratory results indicates that the model can invert the whole process of damage development of sandstone under thermo-mechanical coupling conditions.-
Key words:
- rock mechanics /
- thermally-treated sandstone /
- dissipated energy /
- constitutive model
-
-
[1] BAI F T, SUN Y H, LIU Y M, et al. Evaluation of the porous structure of Huadian oil shale during pyrolysis using multiple approaches[J]. Fuel, 2017, 187: 1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2016.09.012 [2] SAIF T, LIN Q Y, BIJELJIC B, et al. Microstructural imaging and characterization of oil shale before and after pyrolysis[J]. Fuel, 2017, 197: 562-574. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2017.02.030 [3] KUMARI W G P, RANJITH P G, PERERA M S A, et al. Mechanical behaviour of Australian Strathbogie granite under in situ stress and temperature conditions: an application to geothermal energy extraction[J]. Geothermics, 2017, 65: 44-59. doi: 10.1016/j.geothermics.2016.07.002 [4] LEI R D, WANG Y, ZHANG L, et al. The evolution of sandstone microstructure and mechanical properties with thermal damage[J]. Energy Science & Engineering, 2019, 7(6): 3058-3075. [5] 赵亚永, 魏凯, 周佳庆, 等. 三类岩石热损伤力学特性的试验研究与细观力学分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2017, 36(1): 142-151.ZHAO Yayong, WEI Kai, ZHOU Jiaqing, et al. Laboratory study and micromechanical analysis of mechanical behaviors of three thermally damaged rocks[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2017, 36(1): 142-151. [6] 苏海健, 聂银江, 蔚立元, 等. 高温作用后砂岩-混凝土黏结界面拉伸力学特性研究[J]. 土木工程学报, 2023, 56(7): 157-167.SU Haijian, NIE Yinjiang, YU Liyuan, et al. Study on tensile mechanical properties of sandstone-concrete bonding interface after high-temperature treatment[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2023, 56(7): 157-167. [7] 李天斌, 高美奔, 陈国庆, 等. 基于热-力-损伤本构参数的硬岩脆性评价方法[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2022, 41(增1): 2593-2602.LI Tianbin, GAO Meiben, CHEN Guoqing, et al. Brittleness evaluation method of hard rock based on thermal-mechanical-damage constitutive parameters[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2022, 41(S1): 2593-2602. [8] 贾宝新, 陈国栋, 刘丰溥. 高温下岩石损伤本构模型及其验证[J]. 岩土力学, 2022, 43(增2): 63-73.JIA Baoxin, CHEN Guodong, LIU Fengpu. Constitutive model of rock damage at high temperature and its verification[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2022, 43(增2): 63-73. [9] LIU X S, NING J G, TAN Y L, et al. Damage constitutive model based on energy dissipation for intact rock subjected to cyclic loading[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2016, 85: 27-32. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2016.03.003 [10] GONG F Q, ZHANG P L, XU L. Damage constitutive model of brittle rock under uniaxial compression based on linear energy dissipation law[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2022, 160: 105273.1-105273.10. [11] 孙梦成, 徐卫亚, 王苏生, 等. 基于最小耗能原理的岩石损伤本构模型研究[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 49(8): 2067-2075. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2018.08.029SUN Mengcheng, XU Weiya, WANG Susheng, et al. Study on damage constitutive model of rock based on principle of minimum dissipative energy[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2018, 49(8): 2067-2075. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2018.08.029 [12] 寇昊, 何川, 陈子全, 等. 考虑残余强度的层状岩体损伤演化规律[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2023, 58(5): 1064-1072. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20211083KOU Hao, HE Chuan, CHEN Ziquan, et al. Damage evolution law of layered rock mass considering residual strength[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2023, 58(5): 1064-1072. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20211083 [13] 王飞, 钱永久, 许金余, 等. 高温作用后混凝土损伤动态本构模型研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2017, 52(6): 1075-1081. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2017.06.006WANG Fei, QIAN Yongjiu, XU Jinyu, et al. Analysis of dynamic damage constitutive model for concrete exposed to high temperature[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2017, 52(6): 1075-1081. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2017.06.006 [14] 刘之喜, 孟祥瑞, 赵光明, 等. 真三轴压缩下砂岩的能量和损伤分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2023, 42(2): 327-341.LIU Zhixi, MENG Xiangrui, ZHAO Guangming, et al. Energy and damage analysis of sandstone under true triaxial compression[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2023, 42(2): 327-341. [15] 候超, 靳晓光, 何杰, 等. 基于最大拉应变准则的冻融岩石损伤模型研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2023, 58(5): 1045-1055. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20210493HOU Chao, JIN Xiaoguang, HE Jie, et al. Research on damage model of rock under freeze-thaw cycles based on maximum tensile strain criterion[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2023, 58(5): 1045-1055. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20210493 [16] LI M, LIU X S. Effect of thermal treatment on the physical and mechanical properties of sandstone: insights from experiments and simulations[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2022, 55(6): 3171-3194. doi: 10.1007/s00603-022-02791-1 [17] ISRM Testing Commission. Suggested method for determining tensile strength of rock materials[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 1978, 15(3): 99-103. [18] XU X L, GAO F, ZHANG Z Z. Thermo-mechanical coupling damage constitutive model of rock based on the Hoek-Brown strength criterion[J]. International Journal of Damage Mechanics, 2018, 27(8): 1213-1230. doi: 10.1177/1056789517726838 [19] WANG C L, HE B B, HOU X L, et al. Stress-energy mechanism for rock failure evolution based on damage mechanics in hard rock[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2020, 53(3): 1021-1037. doi: 10.1007/s00603-019-01953-y [20] 邓华锋, 胡安龙, 李建林, 等. 水岩作用下砂岩劣化损伤统计本构模型[J]. 岩土力学, 2017, 38(3): 631-639.DENG Huafeng, HU Anlong, LI Jianlin, et al. Statistical damage constitutive model of sandstone under water-rock interaction[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2017, 38(3): 631-639. [21] PAN X H, GUO W, WU S F, et al. An experimental approach for determination of the Weibull homogeneity index of rock or rock-like materials[J]. Acta Geotechnica, 2020, 15(2): 375-391. doi: 10.1007/s11440-019-00803-z [22] XU X L, YUE C Q, XU L Q. Thermal damage constitutive model and brittleness index based on energy dissipation for deep rock[J]. Mathematics, 2022, 10(3): 410.1-410.16. -




 下载:
下载: