Steel Caisson Lowering Process for Cross-Sea Bridges Under Complex Marine Conditions and Influence Optimization
-
摘要:
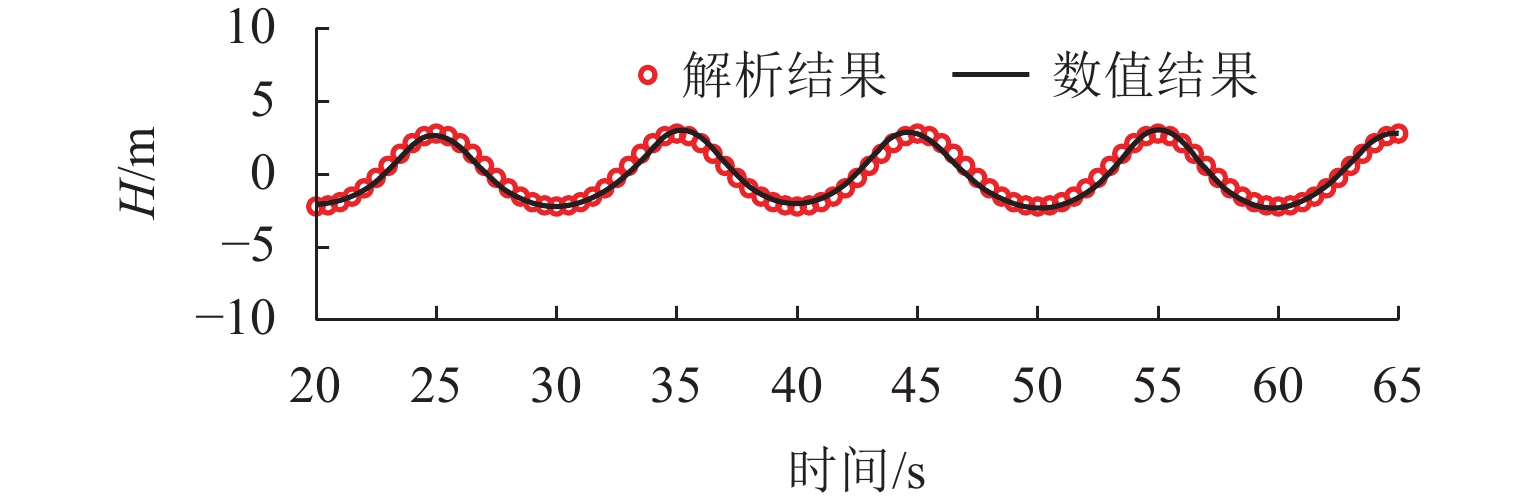
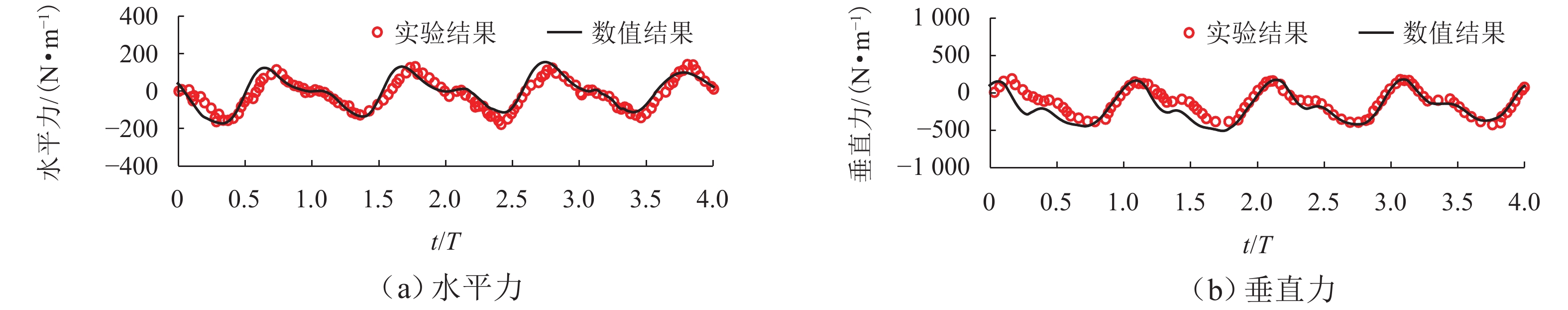
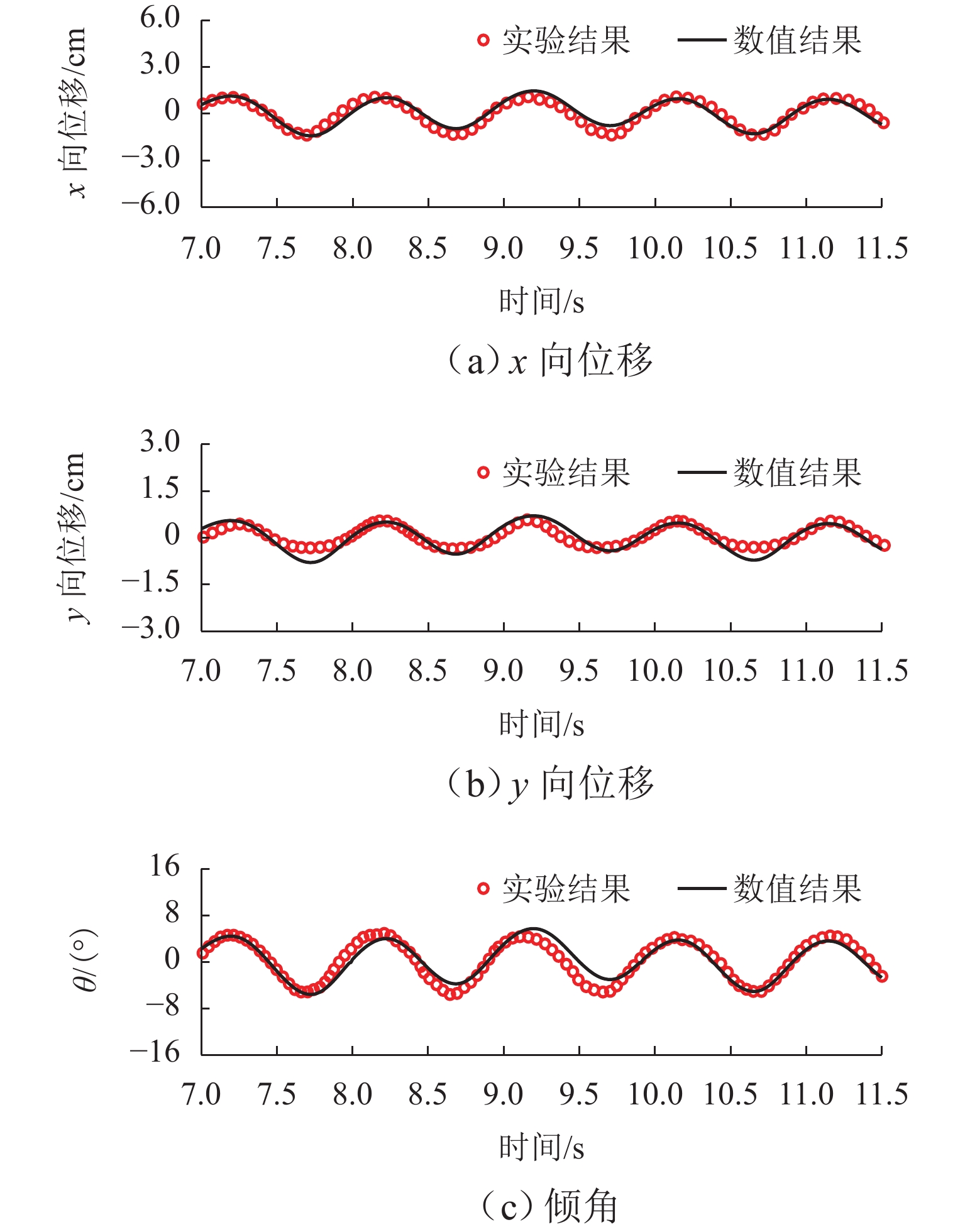
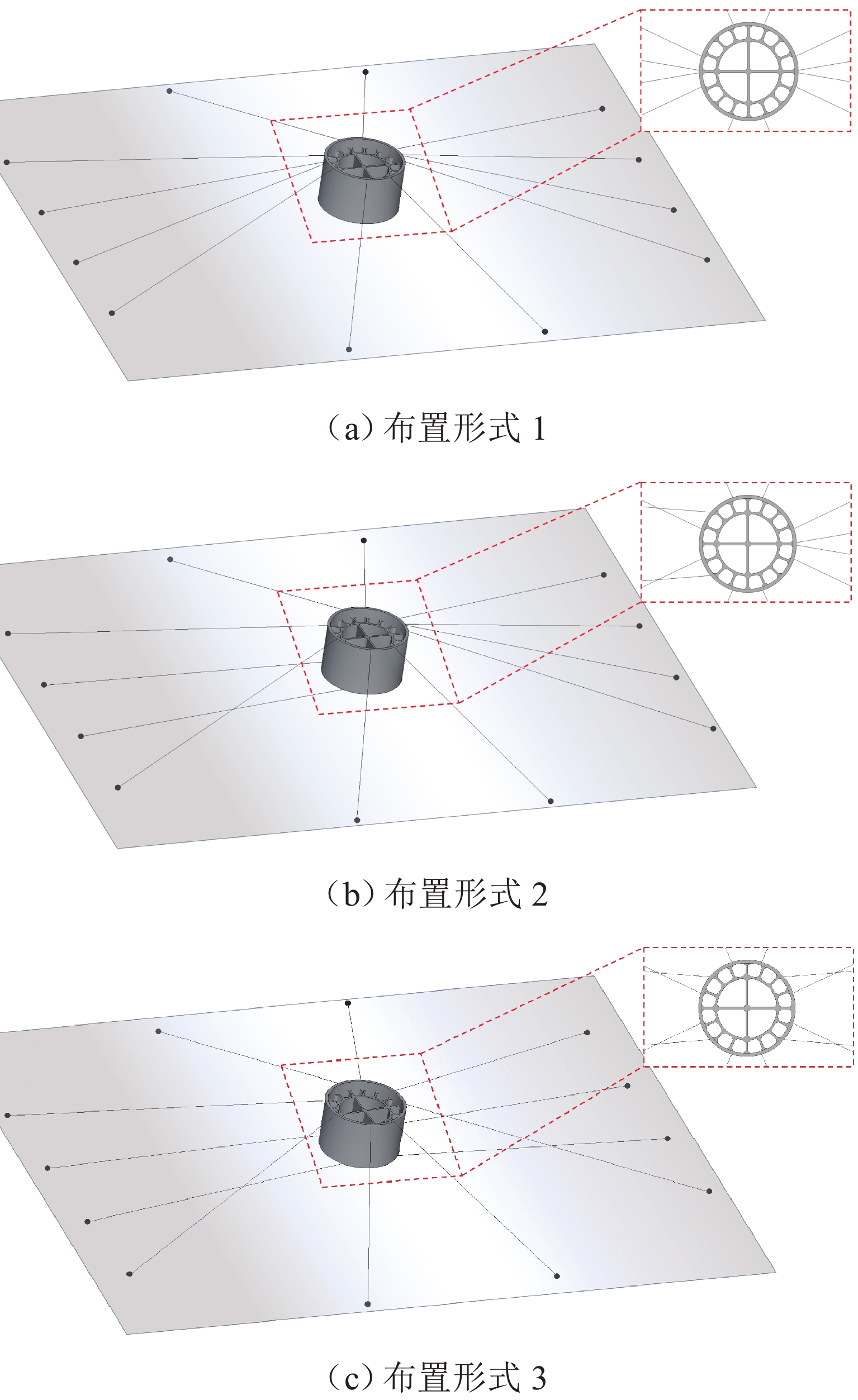
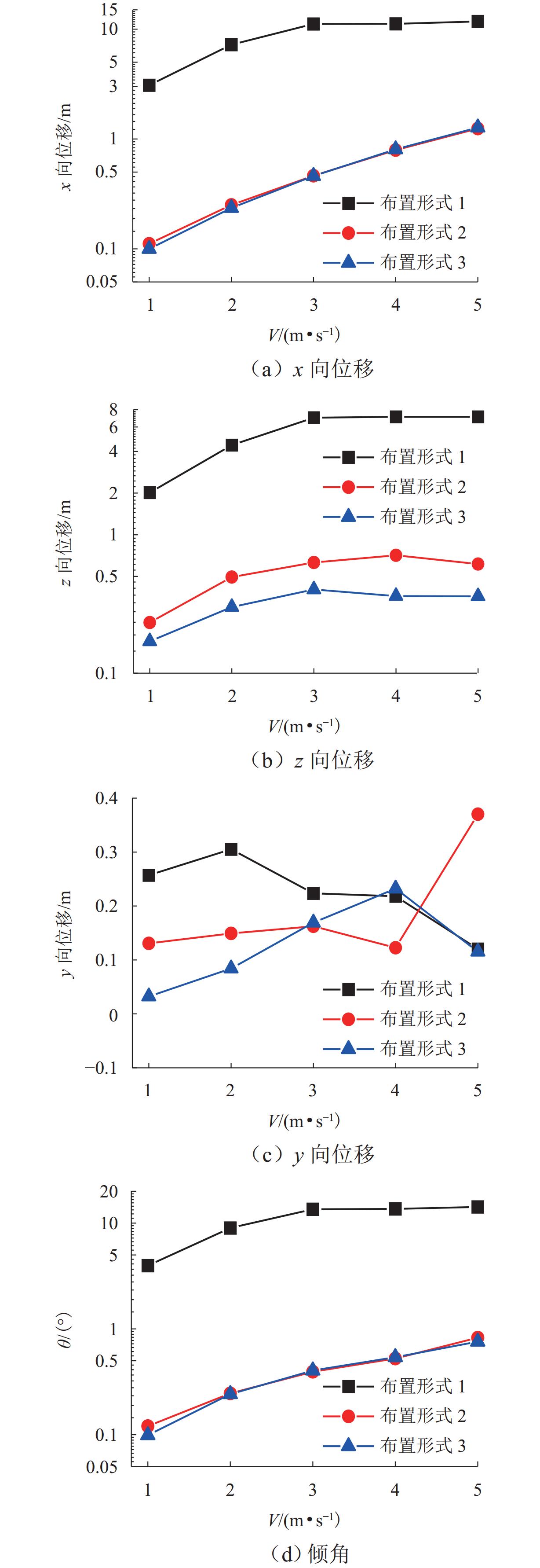
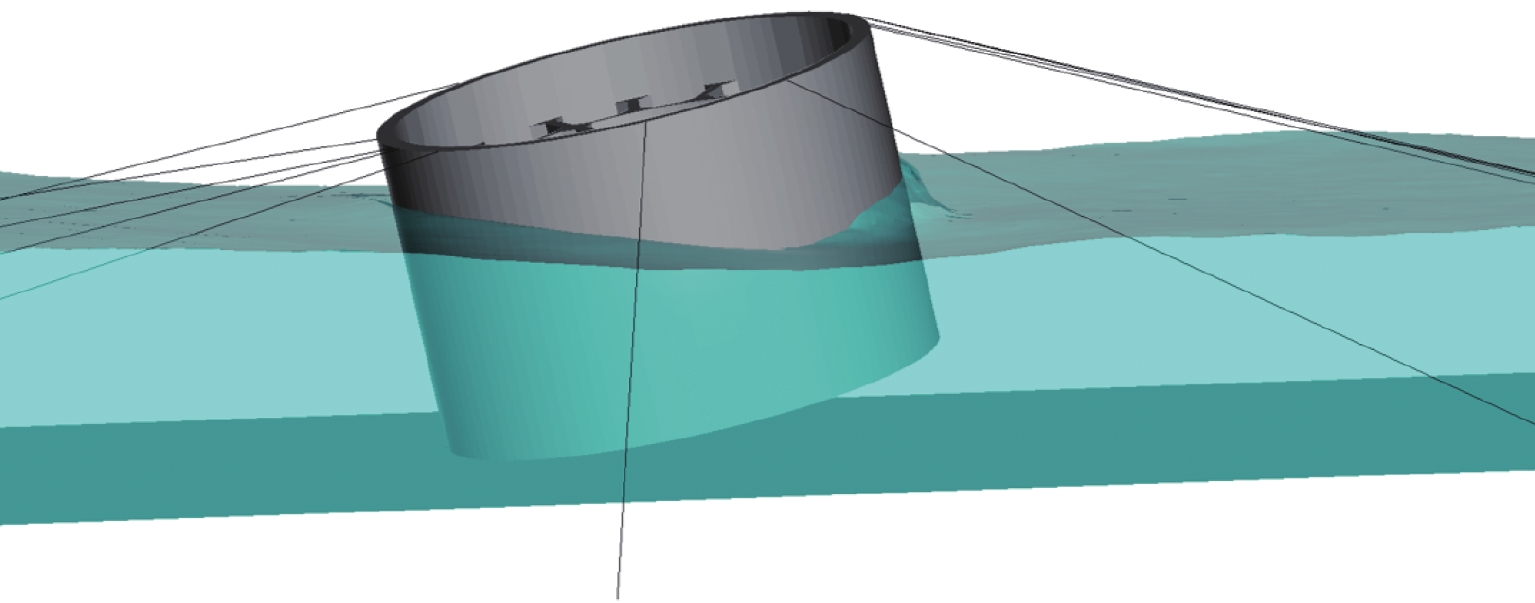
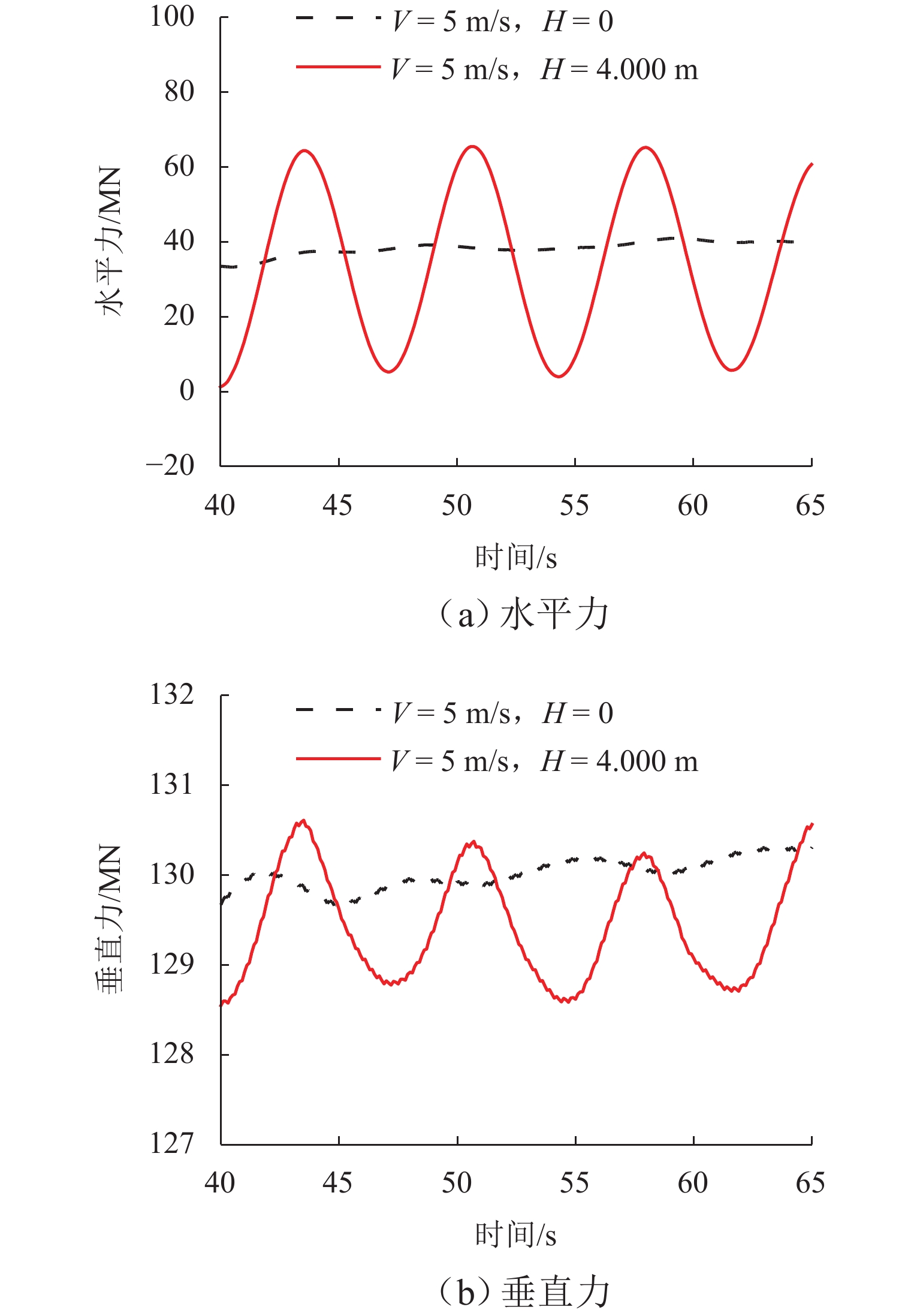
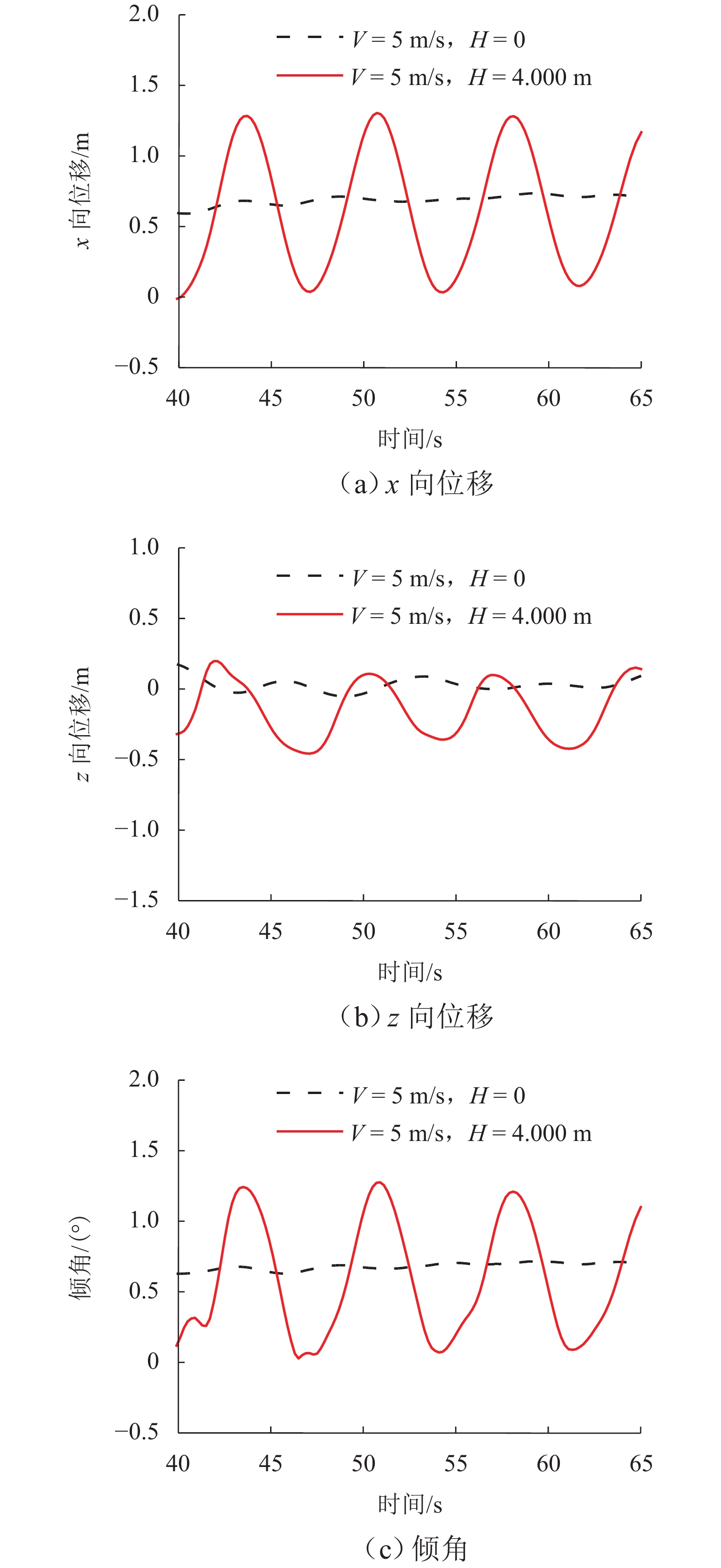
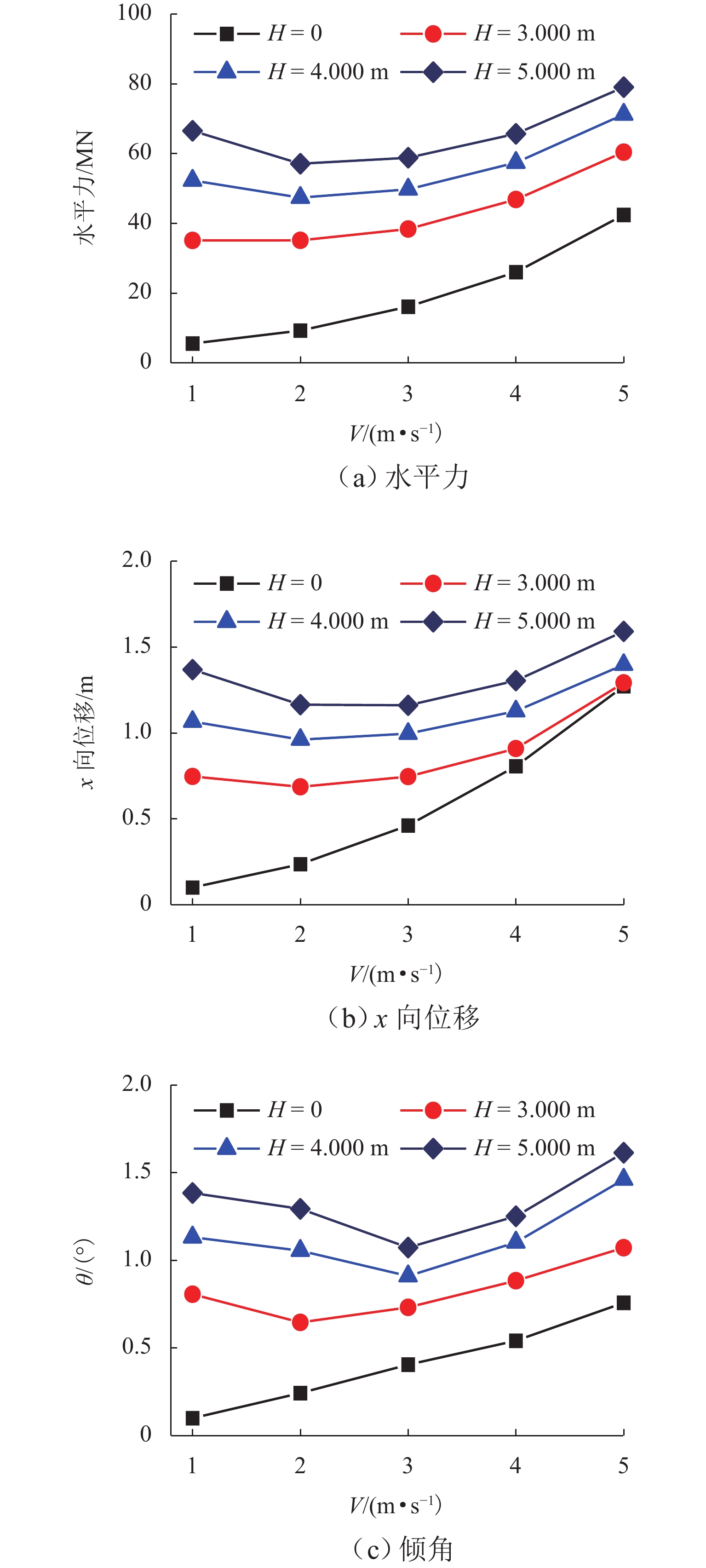
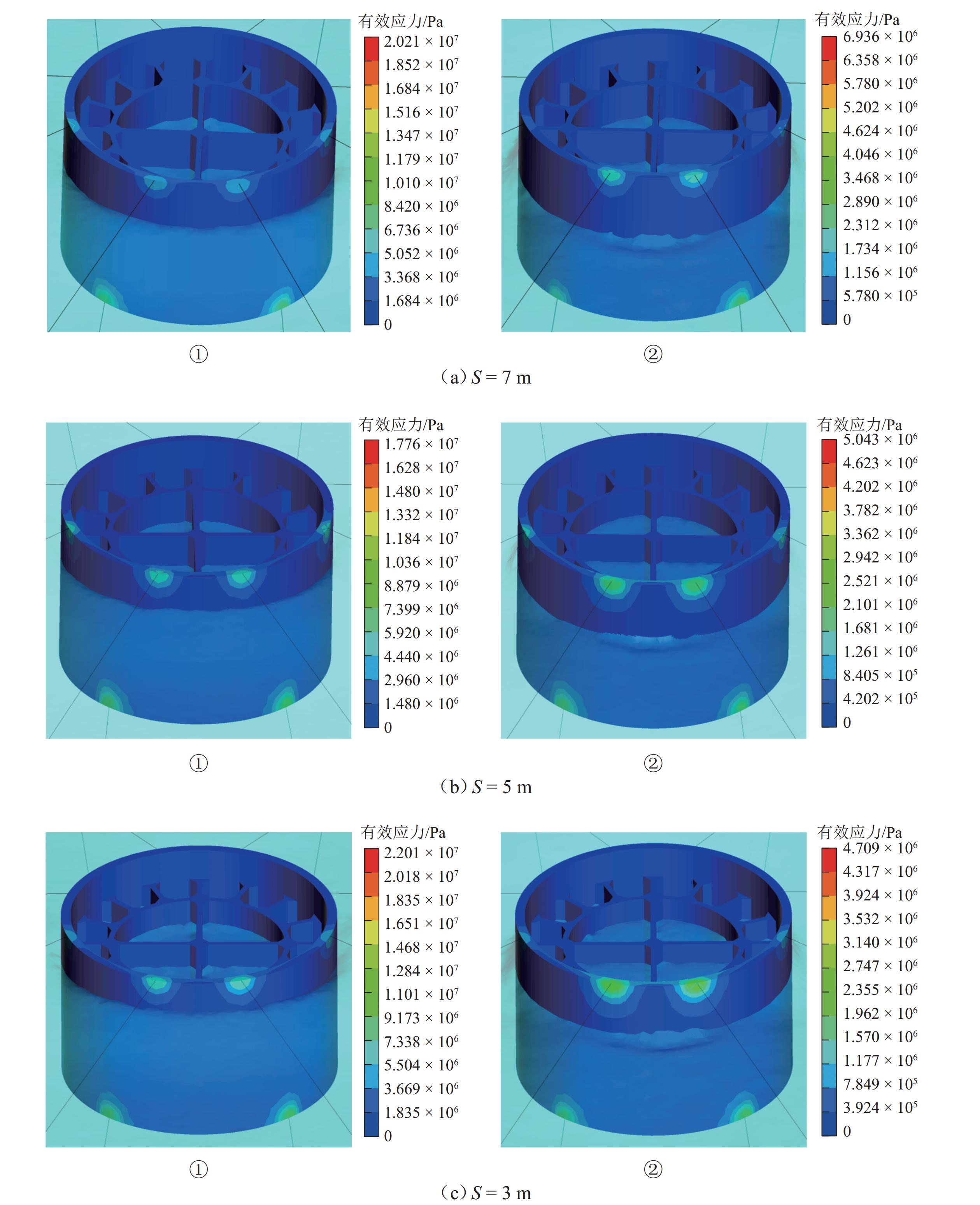
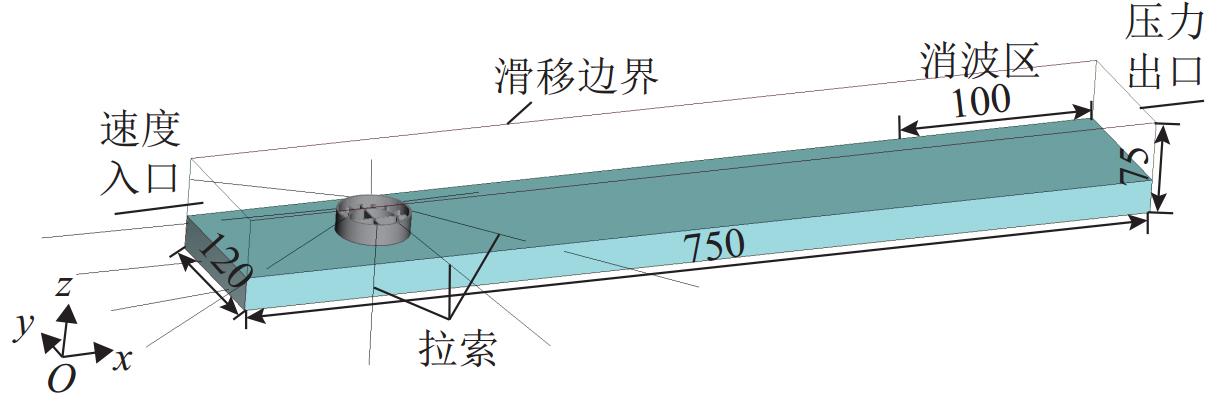
跨海桥梁大型预制钢沉井的定位下放施工面临着海洋复杂环境中极端波浪和水流的巨大威胁,深入研究波流作用下钢沉井定位下放过程中的动力特性,对钢沉井的定位准确性、下放稳定性及施工安全性具有重要意义. 基于LS-DYNA有限元程序构建波流作用下三维全尺寸钢沉井流固耦合模型,通过与Stokes二阶波浪解析解和已有水槽耦合实验结果进行对比,验证该三维流固耦合模型的准确性;使用已验证模型探究波浪参数、水流参数、锚缆布置形式以及结构下放位置等对钢沉井定位下放过程中所受的波流荷载和动力特性影响规律. 研究结果表明:所提出的锚缆布置形式可以有效降低钢沉井结构在不同波流作用下的位移和倾角,最大倾角不超过2°;相较于水流单独作用,波流共同作用对钢沉井造成的最大水平力、水平位移和倾角至少分别增加了约86.34%、25.15%和112.96%;随着钢沉井淹没深度的增加,钢沉井所受最大水平力和水平位移分别增大了约41.90%和50.62%,钢沉井的最大倾角却减小了约31.06%;在钢沉井定位下放研究中,应充分考虑结构在不同下放深度时所受的波流荷载和位移等的影响,为分析钢沉井下放过程中的稳定性提供可靠的理论基础.
Abstract:The positioning and lowering construction of large prefabricated steel caissons for cross-sea bridges is facing significant threats from the complex marine environment, including extreme waves and currents. In-depth research on the dynamic characteristics of the steel caisson during the positioning and lowering process under wave and current effects is of great importance for the positioning accuracy, lowering stability, and construction safety of steel caissons. Based on the LS-DYNA finite element program, a three-dimensional full-scale steel caisson fluid-structure coupling model under the action of wave and current was established. By comparing with the second-order Stokes wave analytical solution and the experimental results of the existing flume coupling experiment, the accuracy of the three-dimensional fluid-structure coupling model was verified. Subsequently, the validated model was used to investigate the influence of wave parameters, flow parameters, anchor cable arrangement, and structure lowering position on the wave and current loads and dynamic characteristics during the positioning and lowering process of the steel caisson. The research results indicate that the proposed anchor cable arrangement can effectively reduce the displacement and inclination of the steel caisson structure under different wave and current conditions, with a maximum inclination angle of no more than 2°. Compared with the individual effect of currents, the maximum horizontal force, horizontal displacement, and inclination angle of the steel caisson caused by the combined effect of waves and currents are increased by at least about 86.34%, 25.15%, and 112.96%, respectively. As the submergence depth of the steel caisson increases, the maximum horizontal force and horizontal displacement experienced by the steel caisson increase by approximately 41.90% and 50.62%, respectively, while the maximum inclination angle of the steel caisson decreases by approximately 31.06%. In the study of the positioning and lowering process of the steel caisson, the influence of wave and current loads and displacements on the structure at different lowering depths should be fully considered, so as to provide a reliable theoretical basis for analyzing the stability of the steel caisson in the process of positioning and lowering.
-
-
[1] 祝兵,黄博,康啊真,等. 跨海桥梁上部结构极端波浪(流)作用2019年度研究进展[J]. 土木与环境工程学报(中英文),2020,42(5): 106-114.ZHU BING, HUANG BO, KANG AZHEN, et al. State-of-the-art review of the action of extreme wave (wave-current) on the superstructure of sea-crossing bridges in 2019[J]. Journal of Civil and Environmental Engineering, 2020, 42(5): 106-114. [2] 项海帆. 21世纪世界桥梁工程的展望[J]. 土木工程学报,2000,33(3): 1-6.XIANG Haifan. Prospect of world’s bridge projects in 21st century[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2000, 33(3): 1-6. [3] CHEN M L, HUANG B, YANG Z Y, et al. Study on the mechanical characteristics and failure mechanism of the coastal bridge with a box-girder superstructure under the action of breaking solitary waves[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2023, 287(1): 115834.1-115834.18. [4] XU G J, CAI C S. Numerical investigation of the lateral restraining stiffness effect on the bridge deck-wave interaction under Stokes waves[J]. Engineering Structures, 2017, 130: 112-123. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2016.10.007 [5] 魏凯,杨雄欣,刘强,等. 大型桥梁沉井下沉过程中的水流力数值模拟[J]. 铁道标准设计,2020,64(11): 62-67.WEI Kai, YANG Xiongxin, LIU Qiang, et al. Numerical analyses of current load of large bridge Caisson during its sinking process[J]. Railway Standard Design, 2020, 64(11): 62-67. [6] 自然资源部. 2022年中国海洋灾害公报(摘登)[N]. 中国自然资源报,2023-04-14. [7] 董学超,郭明伟,蒋振雄,等. 基于土压力监测值的超大沉井下沉端阻力计算与分析[J]. 桥梁建设,2022,52(5): 78-84.DONG Xuechao, GUO Mingwei, JIANG Zhenxiong, et al. End resistance calculation and analysis of super-large open caisson during soil excavation sinking based on monitored soil pressure data[J]. Bridge Construction, 2022, 52(5): 78-84. [8] 蒋凡,刘华,岳青,等. 超大沉井基础取土下沉刃脚土压力变化规律研究[J]. 岩土力学,2022,43(增2): 431-442.JIANG Fan, LIU Hua, YUE Qing, et al. Variation trend of soil pressure under cutting edges of the super large caisson during sinking stage[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2022, 43(S2): 431-442. [9] 李维生,杨彤薇. 锚碇沉井排水下沉期应力特性研究[J]. 公路交通科技,2022,39(7): 106-114.LI Weisheng, YANG Tongwei. Study on stress characteristics of anchorage caisson during drainage subsidence period[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2022, 39(7): 106-114. [10] DONG X C, GUO M W, WANG S L. Inclination prediction of a giant open caisson during the sinking process using various machine learning algorithms[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2023, 269: 113587.1-113587.14. [11] XU Y, XU G J, XUE S H, et al. Failure mechanism and vulnerability assessment of coastal box-girder bridge with laminated rubber bearings under extreme waves[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2022, 266(2): 112834.1-112834.13. [12] 黄博,唐尧,杨志莹,等. 极端波浪作用下跨海箱形桥梁上部结构流固耦合特性研究[J]. 振动与冲击,2023,42(17): 210-219.HUANG Bo, TANG Yao, YANG Zhiying, et al. Fluid-structure interaction characteristics of superstructure of a cross-sea box bridge under extreme wave action[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2023, 42(17): 210-219. [13] CHEN X B, XU G J, LIN C, et al. A comparative study on lateral displacements of movable T-deck and Box-deck under solitary waves[J]. Structures, 2021, 34:1614-1635. [14] XU G J, CAI C S. Numerical simulations of lateral restraining stiffness effect on bridge deck–wave interaction under solitary waves[J]. Engineering Structures, 2015, 101:337-351. [15] LI J Z, KONG X, YANG Y L, et al. Computer vision-based measurement of wave force on the rectangular structure[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2023, 270: 113624.1-113624.15. [16] RAHMAN M A, MIZUTANI N, KAWASAKI K. Numerical modeling of dynamic responses and mooring forces of submerged floating breakwater[J]. Coastal Engineering, 2006, 53(10): 799-815. doi: 10.1016/j.coastaleng.2006.04.001 -




 下载:
下载: