InSAR Tropospheric Correction Method Incorporating Baarda Data Snooping and Its Application
-
摘要:
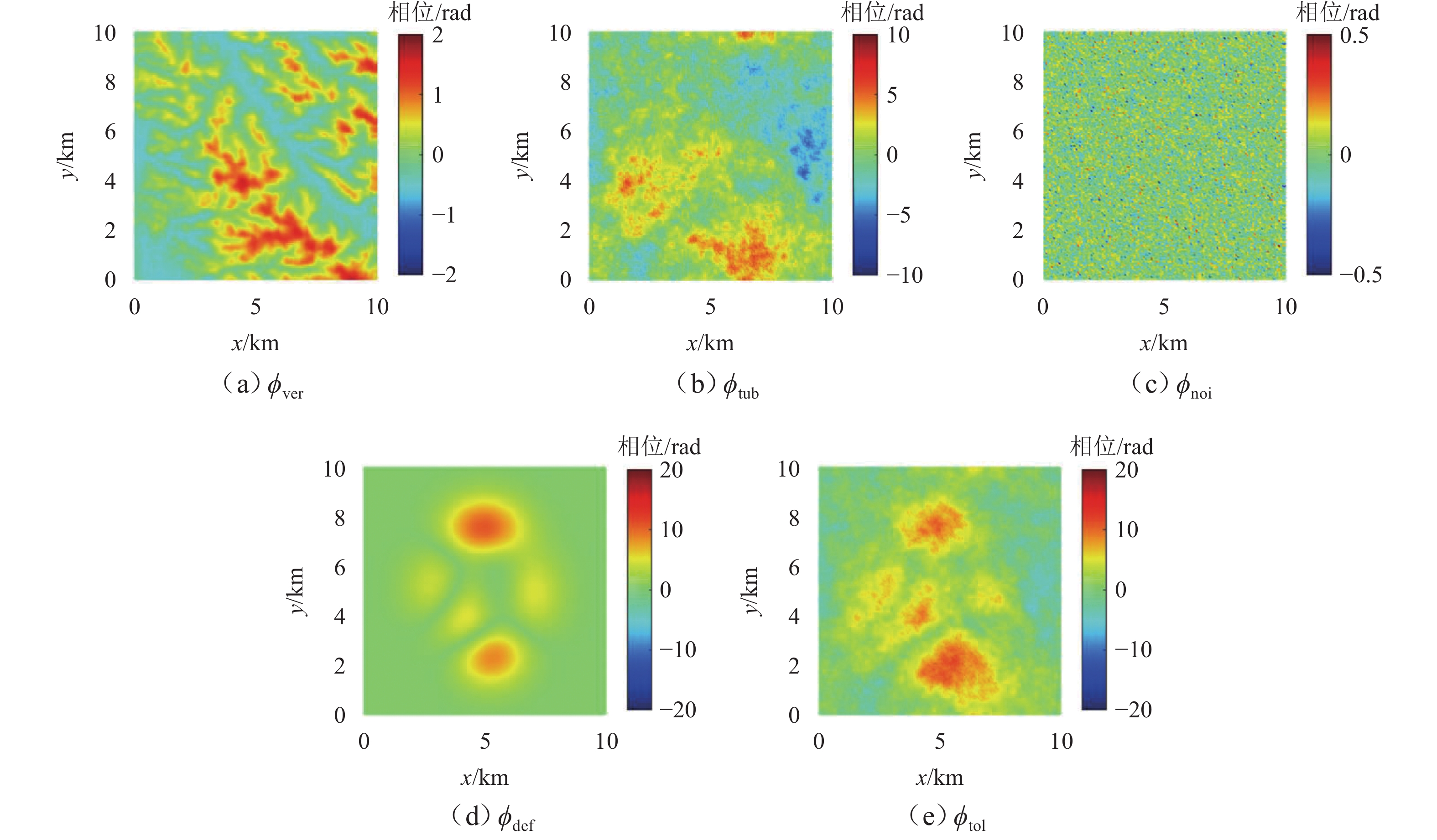
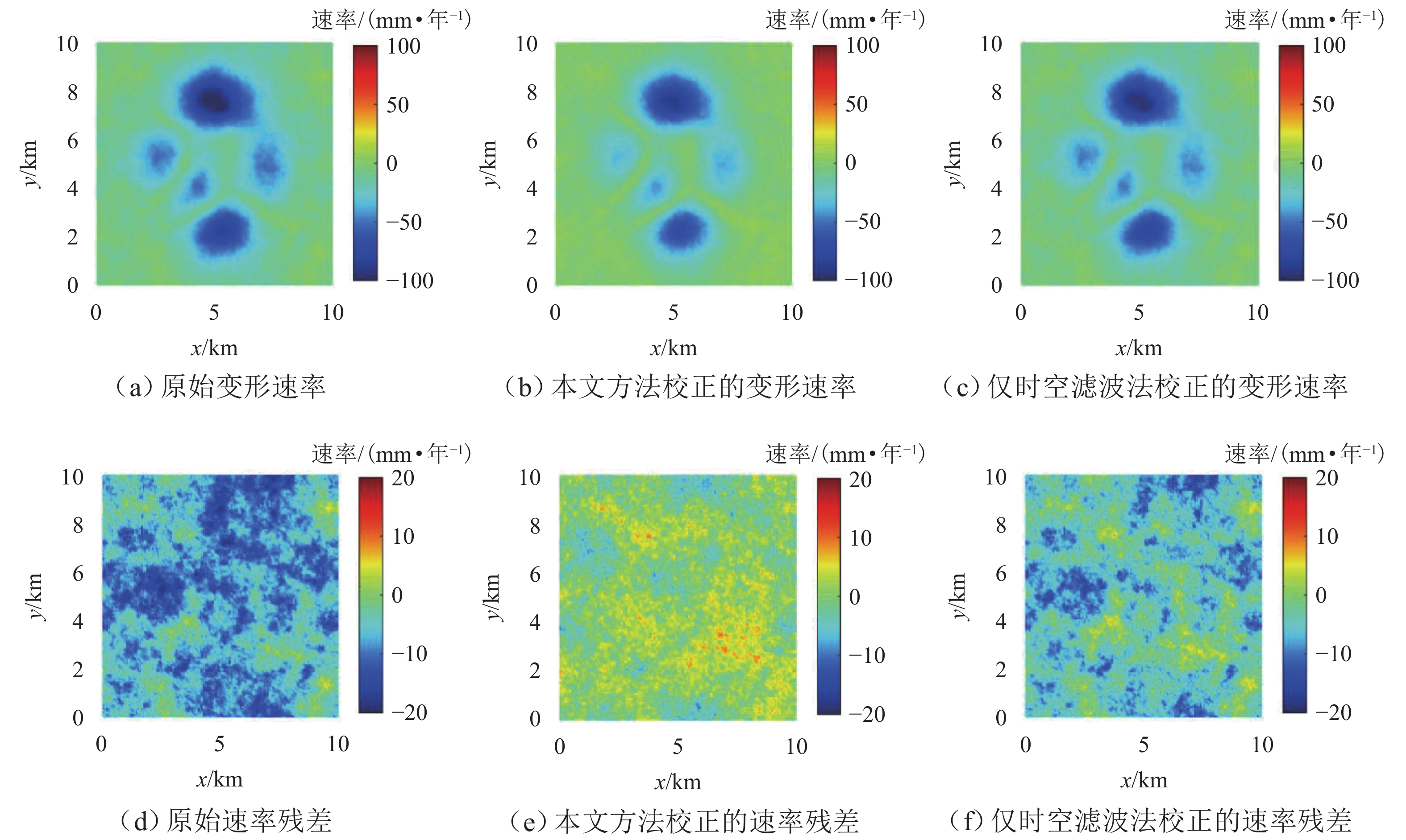
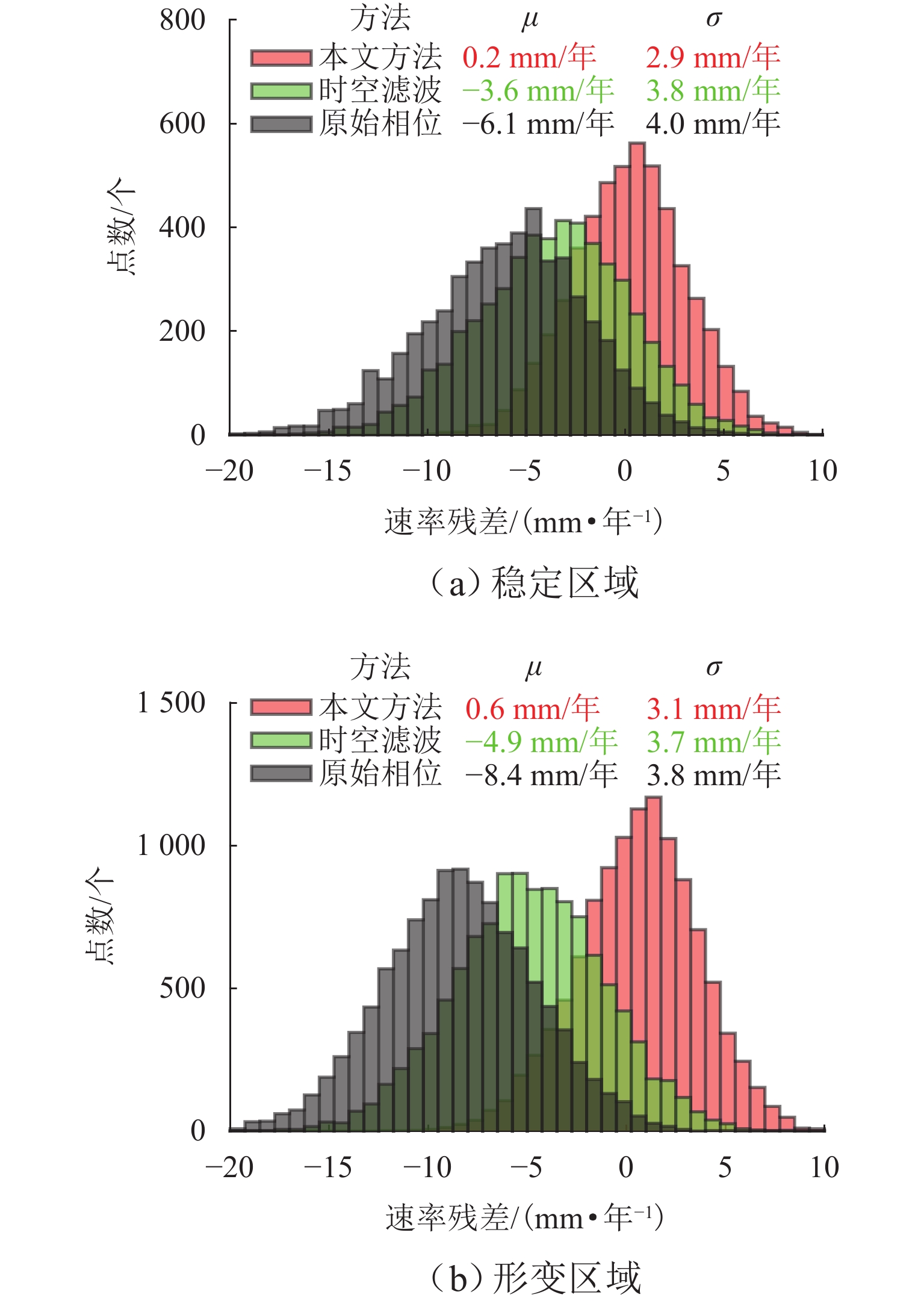
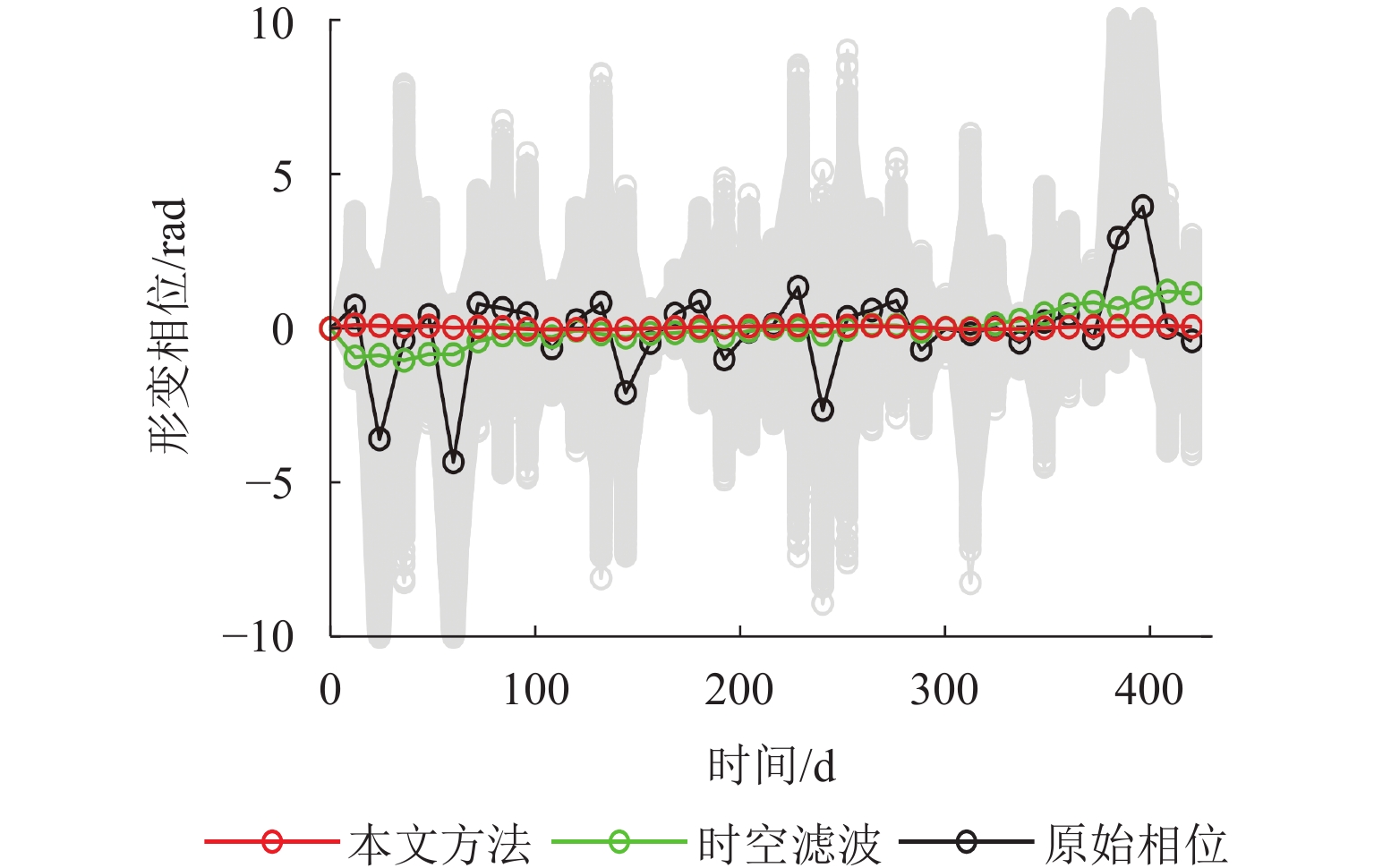
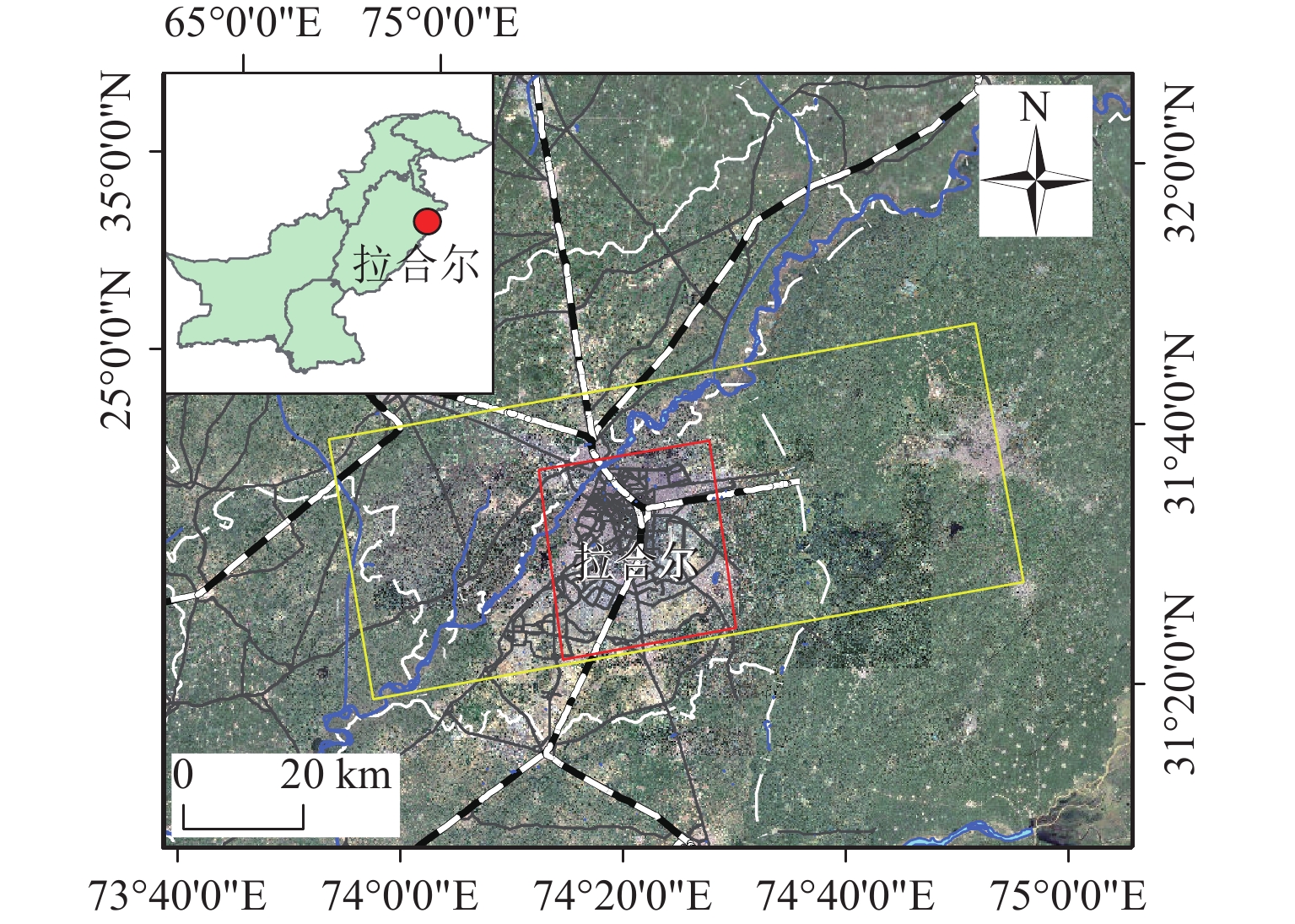
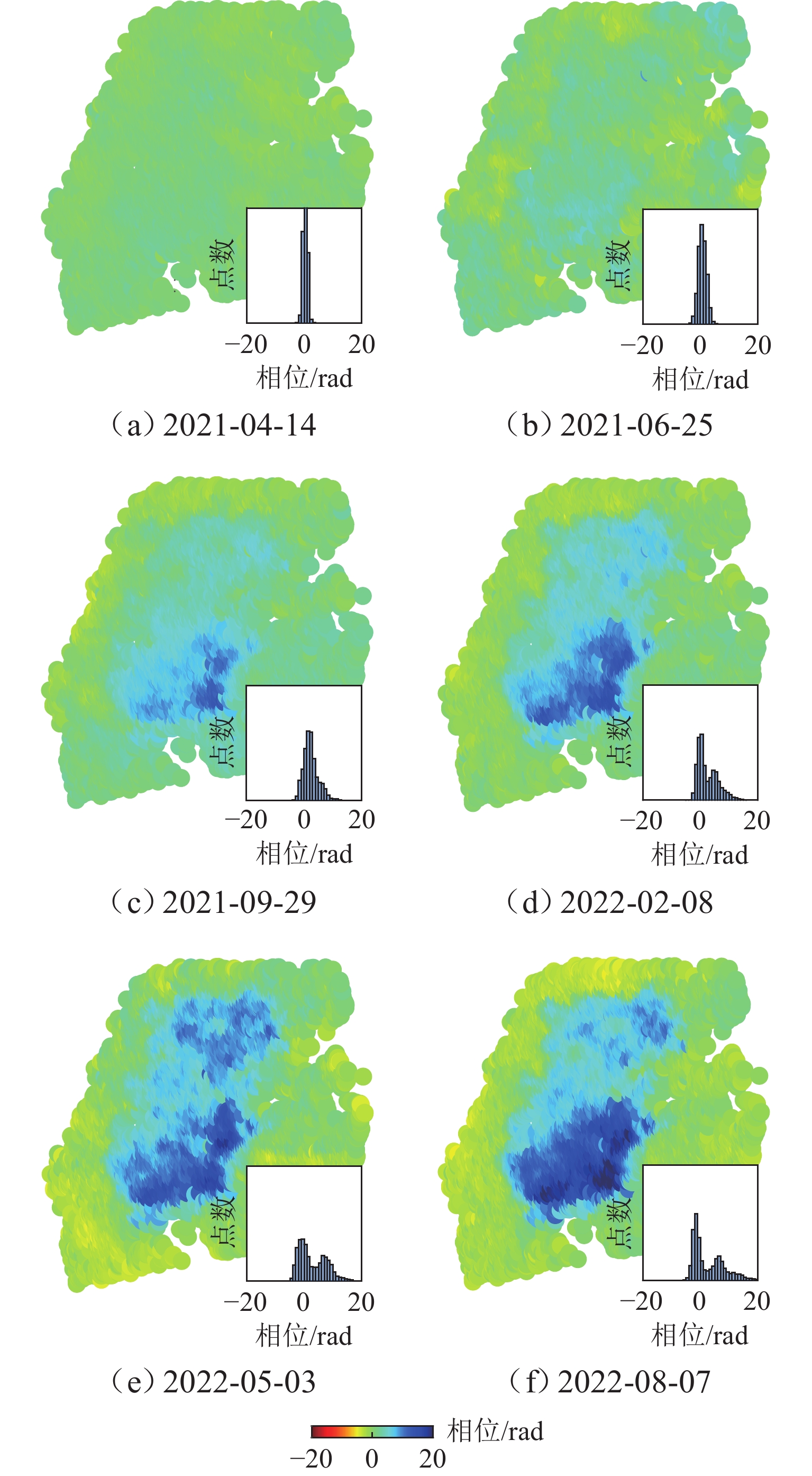
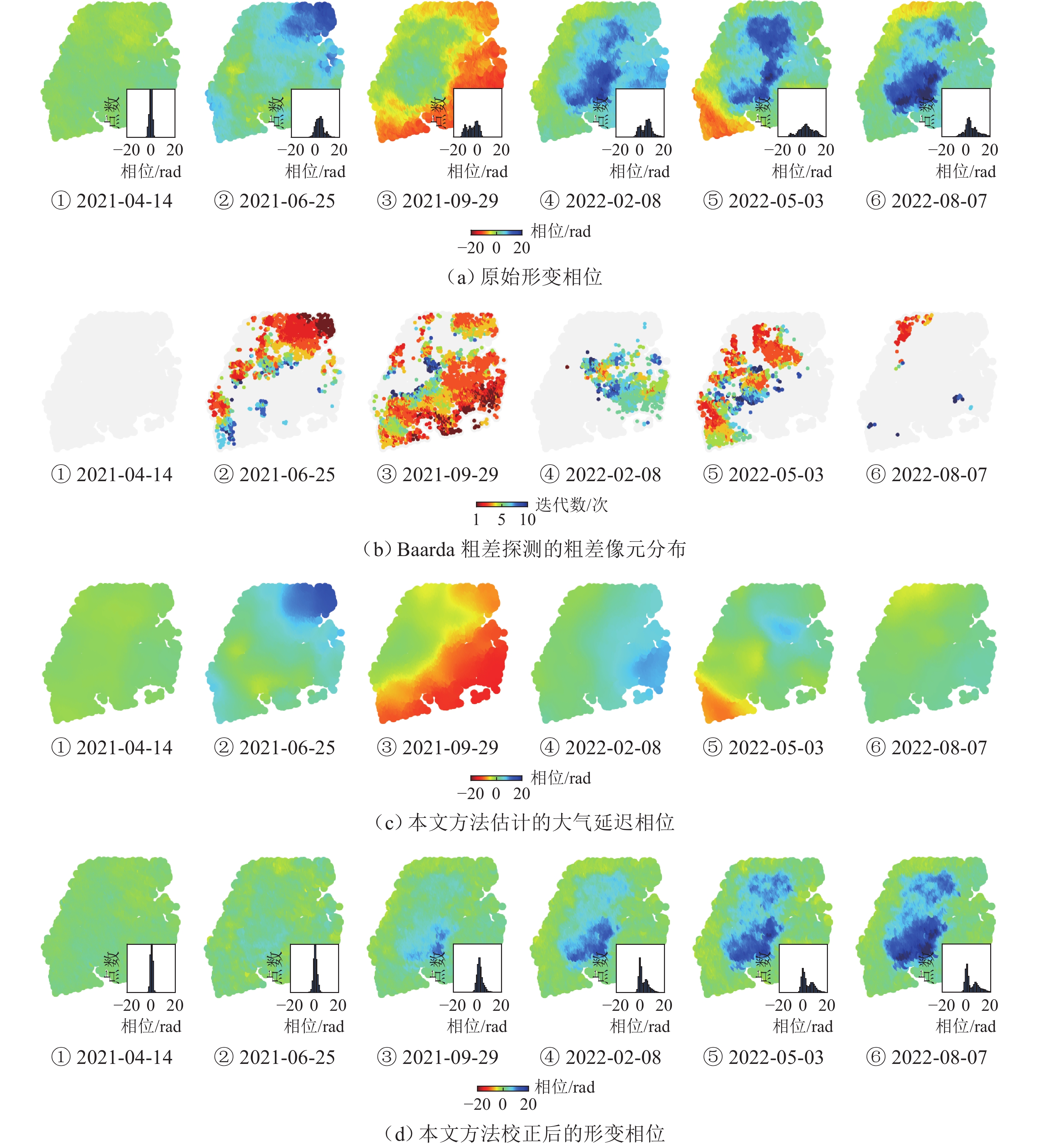
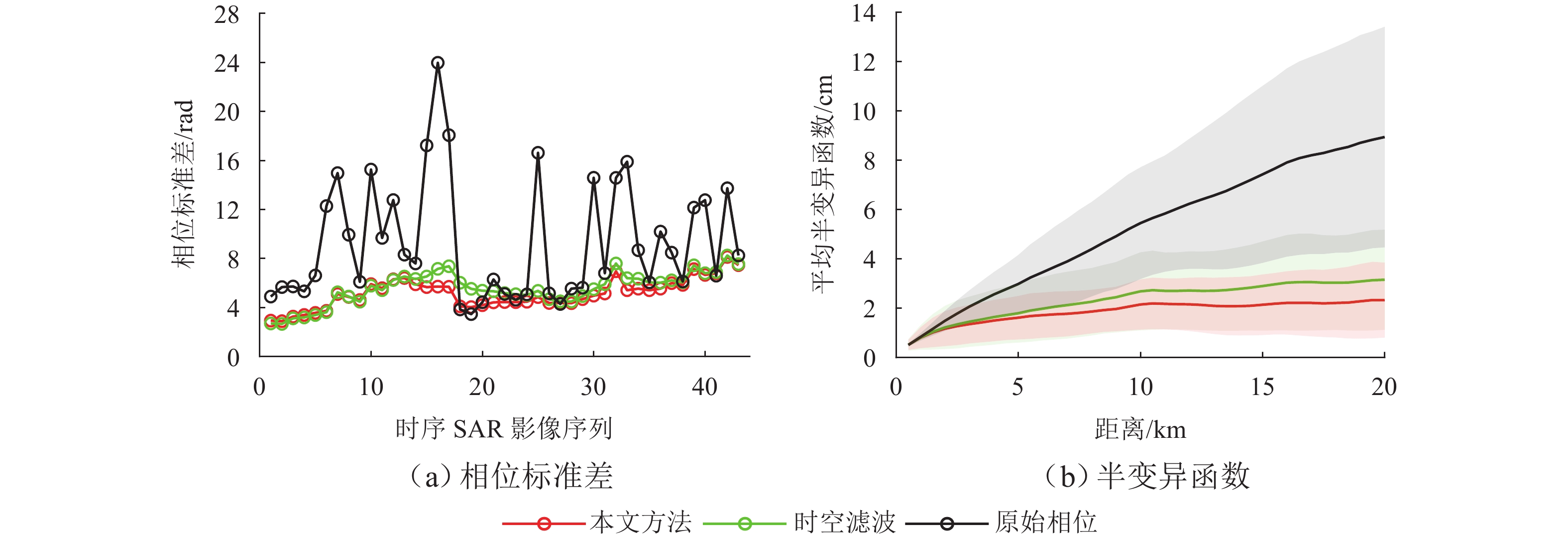
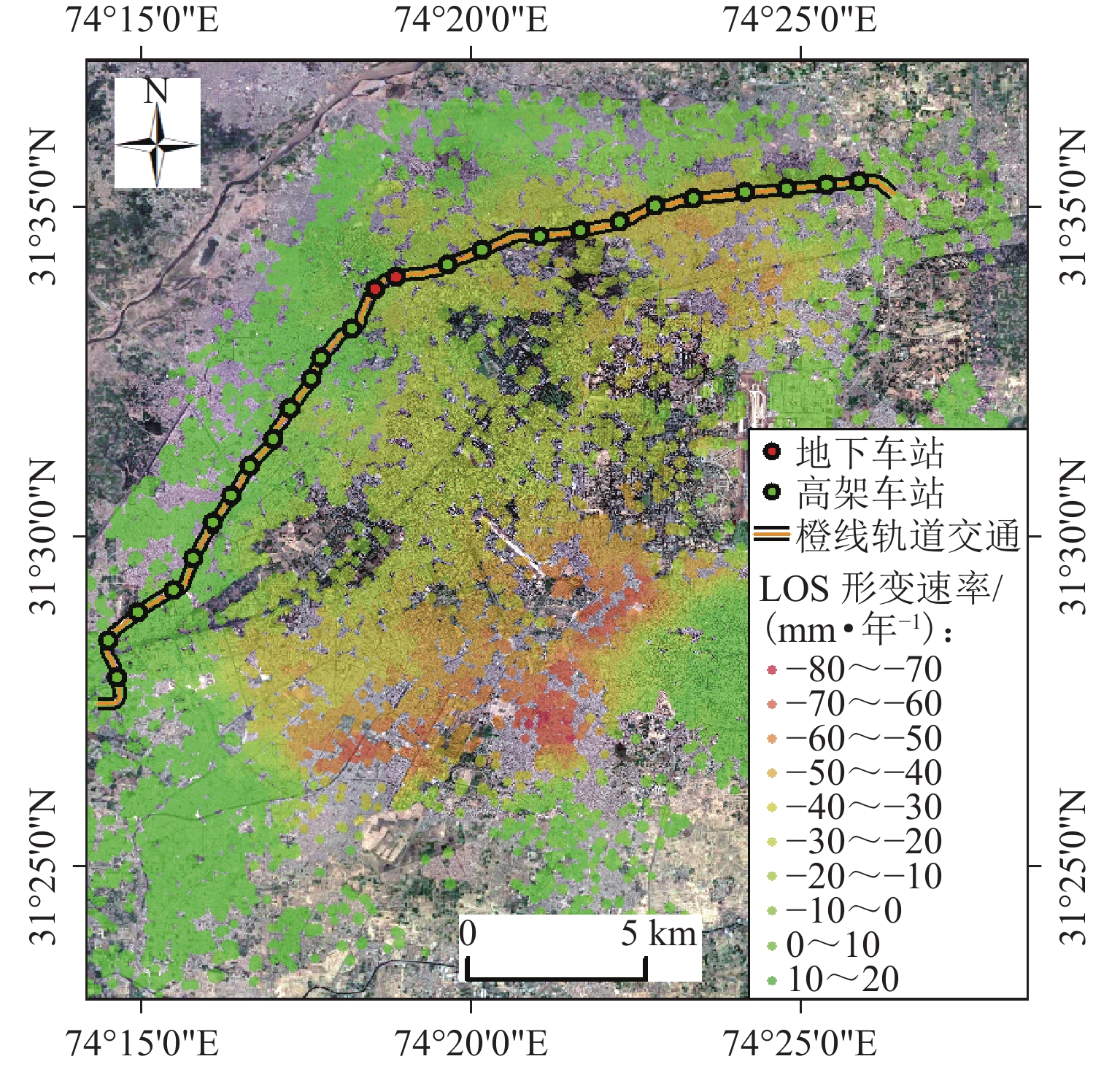
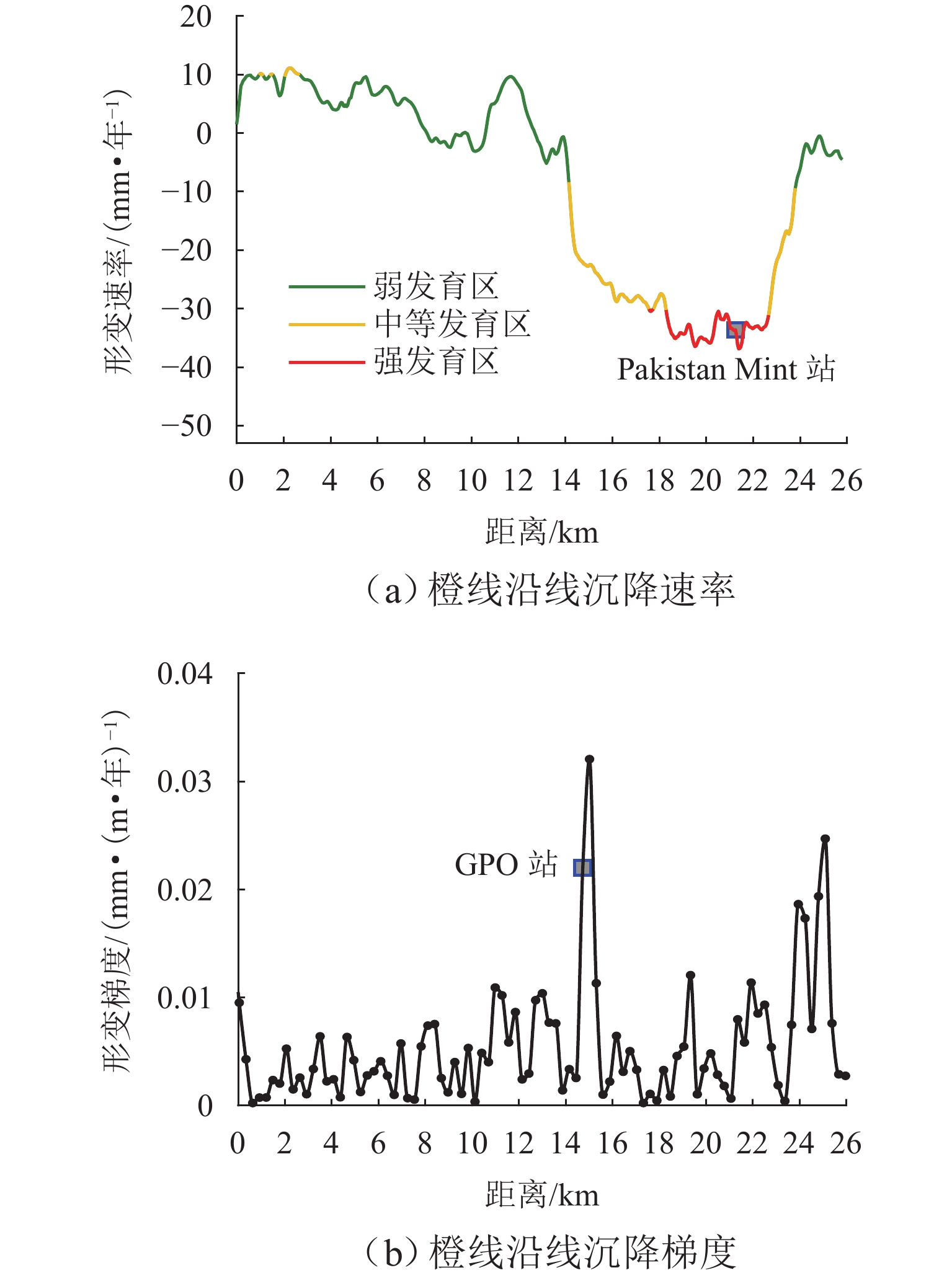
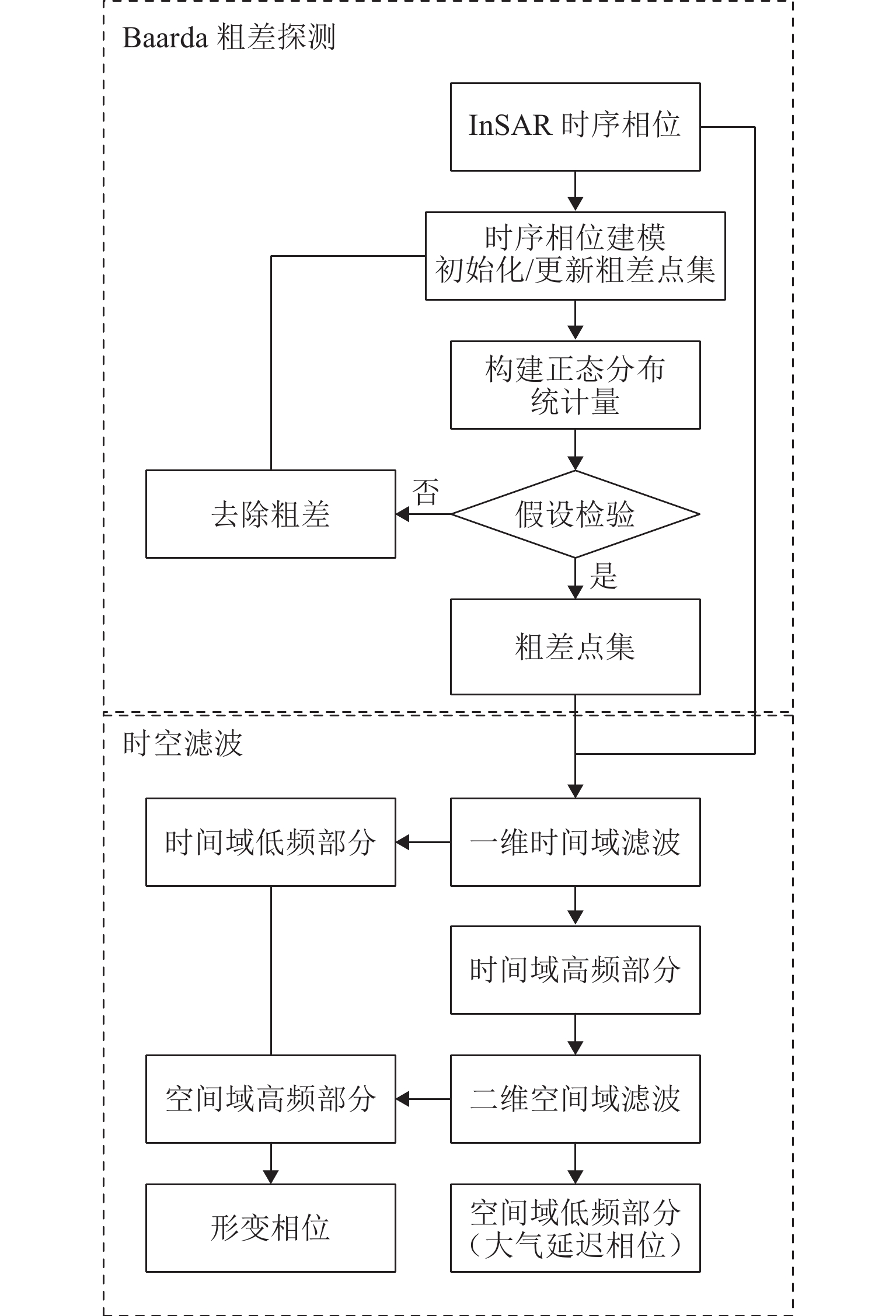
为研究湍流大气延迟对时序InSAR(合成孔径雷达干涉测量)高精度精细化变形提取的影响,基于湍流大气延迟在时空域上的随机特性和对形变相位的剧烈影响特征,将湍流大气延迟视为时间序列上的粗差,采用Baarda粗差探测方法予以识别和去除,随后利用时空滤波法提取高精度形变信息,并通过模拟和Sentinel-1 SAR实测数据验证方法的有效性. 研究结果表明:与仅使用时空滤波法相比,本文方法获取的模拟数据形变速率残差标准差在稳定区域和形变区域分别降低约25.8%和16.0%;Sentinel-1 SAR数据获取的半变异函数相较于同空间尺度下的原始相位结果降低约74%,优于仅使用时空滤波法的65%. 该方法成功应用于巴基斯坦拉合尔市橙线轨道交通的精细化监测,发现橙线全线约17.6%处于地面沉降强发育区.
-
关键词:
- 时序InSAR /
- 大气校正 /
- Baarda粗差探测 /
- 变形监测
Abstract:To investigate the impact of turbulent atmospheric delay on high-precision and fine-scale deformation extraction using time-series InSAR (Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar), the turbulent atmospheric delay was considered as a gross error in the time series, based on its random characteristics in the spatiotemporal domain and its significant impact on deformation phase. The Baarda data snooping method was first applied to identify and remove the turbulent atmospheric delay, followed by spatiotemporal filtering to extract high-precision deformation information. Simulation and Sentinel-1 SAR data have confirmed the effectiveness of the proposed method. Results show that compared to using only spatiotemporal filtering, the standard deviation of displacement rate residuals obtained from the simulated data using the proposed method is decreased by about 25.8% and 16.0% in the stable and deformation regions, respectively. For Sentinel-1 SAR data, the semi-variograms of the results are reduced by about 74% compared to the original phase at the same spatial scale, outperforming the 65% reduction achieved by spatiotemporal filtering alone. The proposed method has been successfully applied to the fine-scale monitoring of the Orange Line rail transit in Lahore, Pakistan, with 17.6% of the entire line found to be located in areas experiencing strong ground subsidence.
-
-
[1] 姜兆英, 于胜文, 陶秋香. StaMPS-MTI技术在地面沉降监测中的应用[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2017, 52(2): 295-302. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2017.02.012JIANG Zhaoying, YU Shengwen, TAO Qiuxiang. Application of StaMPS-MTI technology in monitoring ground subsidence[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2017, 52(2): 295-302. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2017.02.012 [2] 黄其欢, 丁幼亮, 王一安, 等. 基于InSAR的南京大胜关大桥纵向位移监测与分析[J]. 东南大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 47(3): 584-589. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0505.2017.03.028HUANG Qihuan, DING Youliang, WANG Yian, et al. InSAR-based longitudinal displacement monitoring and analysis on Nanjing Dashengguan bridge[J]. Journal of Southeast University (Natural Science Edition), 2017, 47(3): 584-589. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0505.2017.03.028 [3] 叶勇超, 闫超德, 罗先学, 等. 时序InSAR郑州地铁沿线地面沉降分析[J]. 遥感学报, 2022, 26(7): 1342-1353. doi: 10.11834/jrs.20211246YE Yongchao, YAN Chaode, LUO Xianxue, et al. Analysis of ground subsidence along Zhengzhou metro based on time series InSAR[J]. National Remote Sensing Bulletin, 2022, 26(7): 1342-1353. doi: 10.11834/jrs.20211246 [4] 李名语, 李政, 姚京川, 等. 基于ISBAS-InSAR的京雄城际铁路建设期区域沉降监测及气候因子相关性分析[J]. 铁道学报, 2022, 44(11): 71-81. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2022.11.009LI Mingyu, LI Zheng, YAO Jingchuan, et al. ISBAS-InSAR-based ground subsidence monitoring and climatic correlation analysis during construction period of Beijing−Xiongan intercity railway[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2022, 44(11): 71-81. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2022.11.009 [5] BEKAERT D P S, WALTERS R J, WRIGHT T J, et al. Statistical comparison of InSAR tropospheric correction techniques[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2015, 170: 40-47. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2015.08.035 [6] 李永生. 高级时序InSAR地面形变监测及地震同震震后形变反演[D]. 哈尔滨: 中国地震局工程力学研究所, 2014. [7] LIANG H Y, ZHANG L, DING X L, et al. Toward mitigating stratified tropospheric delays in multitemporal InSAR: a quadtree aided joint model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(1): 291-303. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2853706 [8] WANG Y A, DONG J, ZHANG L, et al. Refined InSAR tropospheric delay correction for wide-area landslide identification and monitoring[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2022, 275: 113013.1-113013.18. [9] 占文俊, 李志伟, 韦建超, 等. 一种InSAR大气相位建模与估计方法[J]. 地球物理学报, 2015, 58(7): 2320-2329. doi: 10.6038/cjg20150710ZHAN Wenjun, LI Zhiwei, WEI Jianchao, et al. A strategy for modeling and estimating atmospheric phase of SAR interferogram[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2015, 58(7): 2320-2329. doi: 10.6038/cjg20150710 [10] LI Z W, DUAN M, CAO Y M, et al. Mitigation of time-series InSAR turbulent atmospheric phase noise: a review[J]. Geodesy and Geodynamics, 2022, 13(2): 93-103. doi: 10.1016/j.geog.2021.12.002 [11] 唐伟, 廖明生, 张丽, 等. 基于全球气象再分析资料的InSAR对流层延迟改正研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 2017, 60(2): 527-540. doi: 10.6038/cjg20170208TANG Wei, LIAO Mingsheng, ZHANG Li, et al. Study on InSAR tropospheric correction using global atmospheric reanalysis products[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2017, 60(2): 527-540. doi: 10.6038/cjg20170208 [12] YU W Y, JIANG M, CHENG X. Integrating MODIS LST and Sentinel-1 InSAR to monitor frozen soil deformation in the Qumalai−Zhiduo area, Qinghai−Tibet Plateau[J]. International Journal of Digital Earth, 2023, 16(1): 1923-1943. doi: 10.1080/17538947.2023.2218116 [13] HOOPER A, ZEBKER H, SEGALL P, et al. A new method for measuring deformation on volcanoes and other natural terrains using InSAR persistent scatterers[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2004, 31(23): L23611.1-L23611.5. [14] 武帅莹, 刘国祥, 贾洪果, 等. 一种基于GNSS和机器学习的InSAR大气改正方法[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2025, 50(9): 1864-1877. doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20220191Wu Shuaiying, LlU Guoxiang, JlA Hongguo, et al. An InSAR atmospheric correction method based on GNSS and machine learning[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2025, 50(9): 1864-1877. doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20220191 [15] 崔喜爱, 曾琪明, 童庆禧, 等. 重轨星载InSAR测量中的大气校正方法综述[J]. 遥感技术与应用, 2014, 29(1): 9-17.CUI Xiai, ZENG Qiming, TONG Qingxi, et al. Overview of the atmospheric correction methods in repeat-pass InSAR measurements[J]. Remote Sensing Technology and Application, 2014, 29(1): 9-17. [16] LI Z W, CAO Y M, WEI J C, et al. Time-series InSAR ground deformation monitoring: Atmospheric delay modeling and estimating[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2019, 192: 258-284. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2019.03.008 [17] JUNG J, KIM D J, PARK S E. Correction of atmospheric phase screen in time series InSAR using WRF model for monitoring volcanic activities[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(5): 2678-2689. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2264532 [18] KIRUI P K, REINOSCH E, ISYA N, et al. Mitigation of atmospheric artefacts in multi temporal InSAR: a review[J]. PFG – Journal of Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Geoinformation Science, 2021, 89(3): 251-272. doi: 10.1007/s41064-021-00138-z [19] GONG W Y, MEYER F J, LIU S Z, et al. Temporal filtering of InSAR data using statistical parameters from NWP models[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(7): 4033-4044. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2015.2389143 [20] 杨玲, 喻杨康. Baarda数据探测法中的粗差误判分析[J]. 同济大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 46(10): 1440-1447.YANG Ling, YU Yangkang. Separability analysis for baarda data snooping method[J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science), 2018, 46(10): 1440-1447. [21] KAMPES B. Radar interferometry—persistent scatterer technique[M]. Dordrecht: Springer, 2006: 71-85. [22] AHMAD A, WANG C, TANG Y X, et al. SAR-based subsidence monitoring and assessment of the factors involved in the occurrence of subsidence, Lahore City[J]. Journal of Resources and Ecology, 2022, 13(5): 826-841. [23] HUSSAIN M A, CHEN Z L, ZHENG Y, et al. PS-InSAR based monitoring of land subsidence by groundwater extraction for Lahore metropolitan city, Pakistan[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14: 3950.1-3950.22. [24] TAO Q X, WANG F Y, GUO Z J, et al. Accuracy verification and evaluation of small baseline subset (SBAS) interferometric synthetic aperture radar (InSAR) for monitoring mining subsidence[J]. European Journal of Remote Sensing, 2021, 54(1): 642-663. doi: 10.1080/22797254.2021.2002197 [25] CROSETTO M, MONSERRAT O, CUEVAS M, et al. Spaceborne differential SAR interferometry: data analysis tools for deformation measurement[J]. Remote Sensing, 2011, 3(2): 305-318. doi: 10.3390/rs3020305 [26] 李鹏, 高梦瑶, 李振洪, 等. 阿尔金断裂带宽幅InSAR对流层延迟估计方法评估[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2020, 45(6): 879-887.LI Peng, GAO Mengyao, LI Zhenhong, et al. Evaluation of wide-swath InSAR tropospheric delay estimation methods over the Altyn tagh fault[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2020, 45(6): 879-887. [27] MURRAY K D, BEKAERT D P S, LOHMAN R B. Tropospheric corrections for InSAR: statistical assessments and applications to the central United States and Mexico[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2019, 232: 111326.1-111326.12. [28] 孙海富, 朱万方. 中国地铁标准在巴基斯坦的适应性分析[J]. 铁道工程学报, 2022, 39(4): 95-98. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2022.04.018SUN Haifu, ZHU Wanfang. Adaptability analysis of China’s metro standards in Pakistan[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society, 2022, 39(4): 95-98. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2022.04.018 [29] 林辉, 董继峰, 冯硕, 等. 基于性能的巴基斯坦橙线地铁桥梁安全运维体系研究[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报, 2022, 19(8): 2313-2319.LIN Hui, DONG Jifeng, FENG Shuo, et al. Research on performance based safety operation and maintenance system of metro bridge on Orange Line in Pakistan[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2022, 19(8): 2313-2319. -




 下载:
下载: