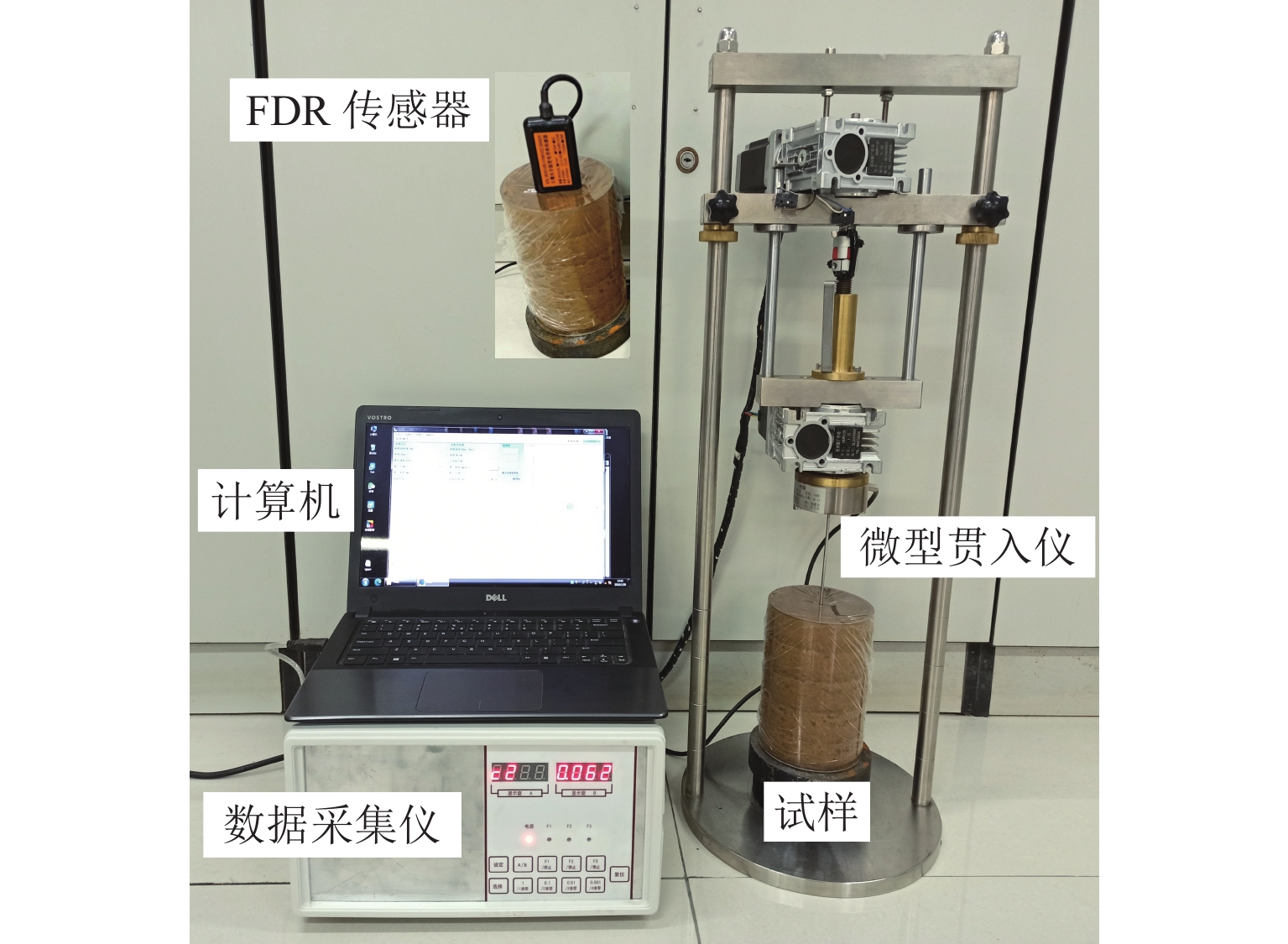
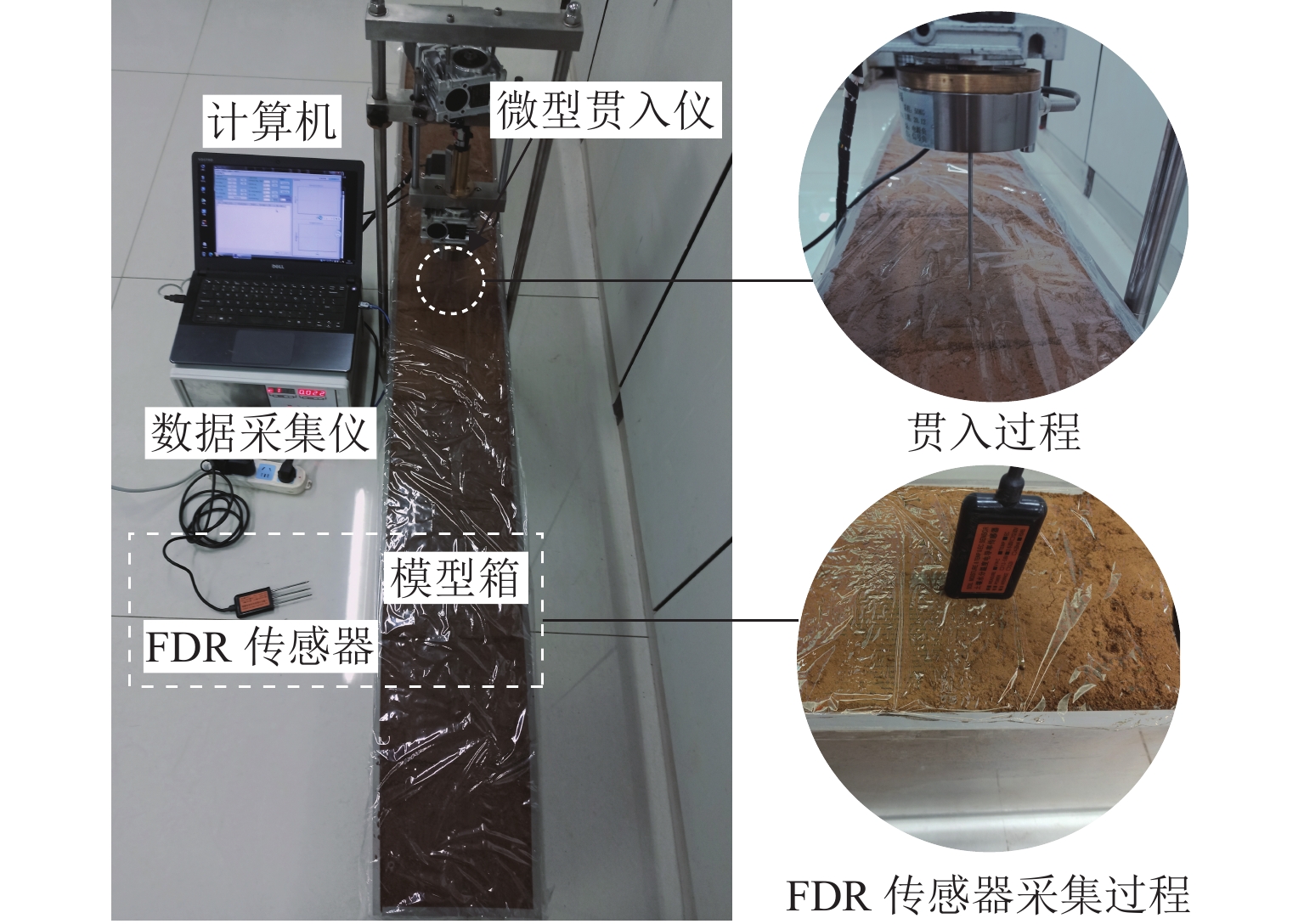
Experimental Study on Rapid Determination of Soil Gravimetric Water Content and Dry Density Based on Frequency Domain Reflectometry Combined with Static Penetration
-
摘要:
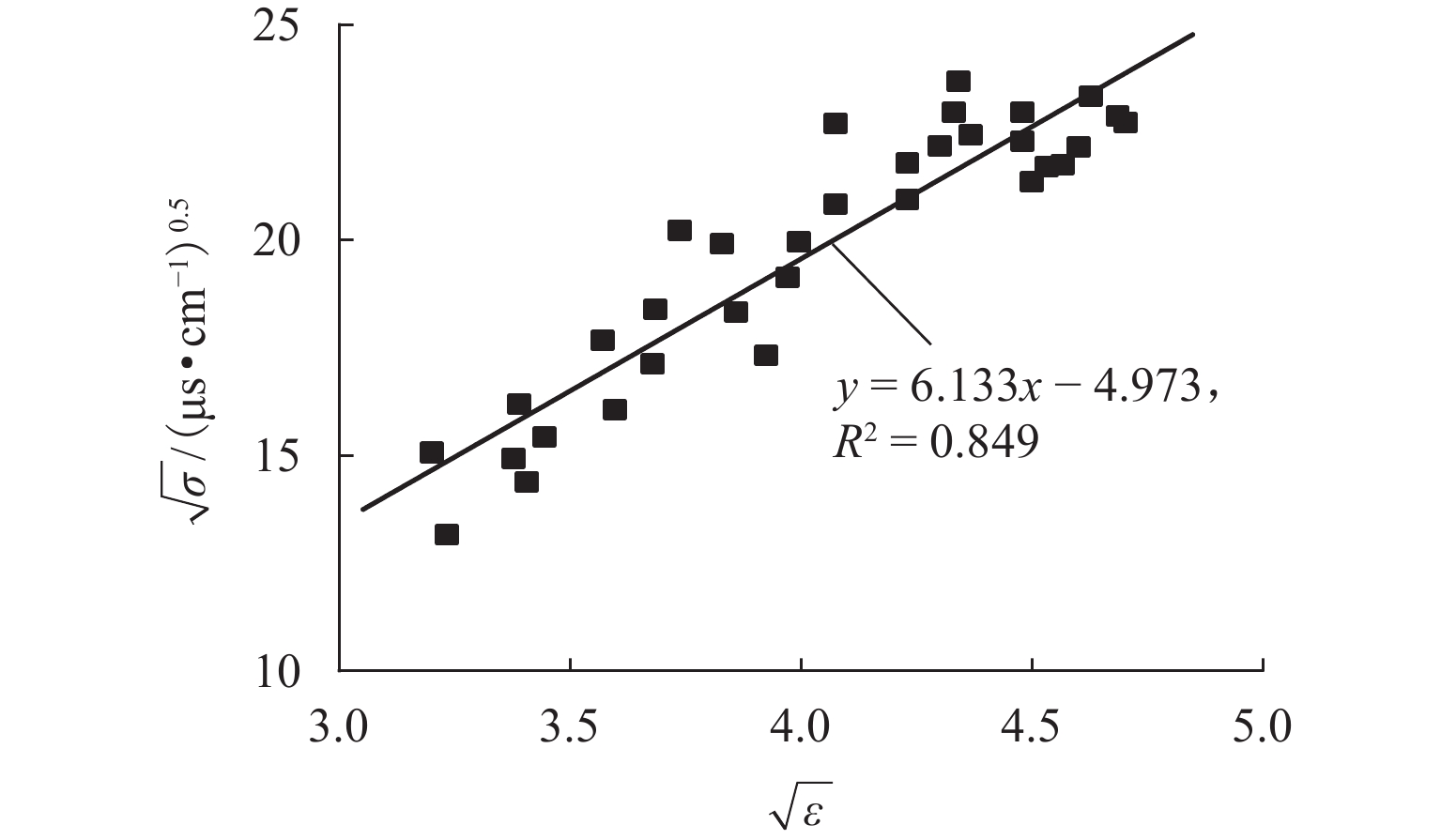
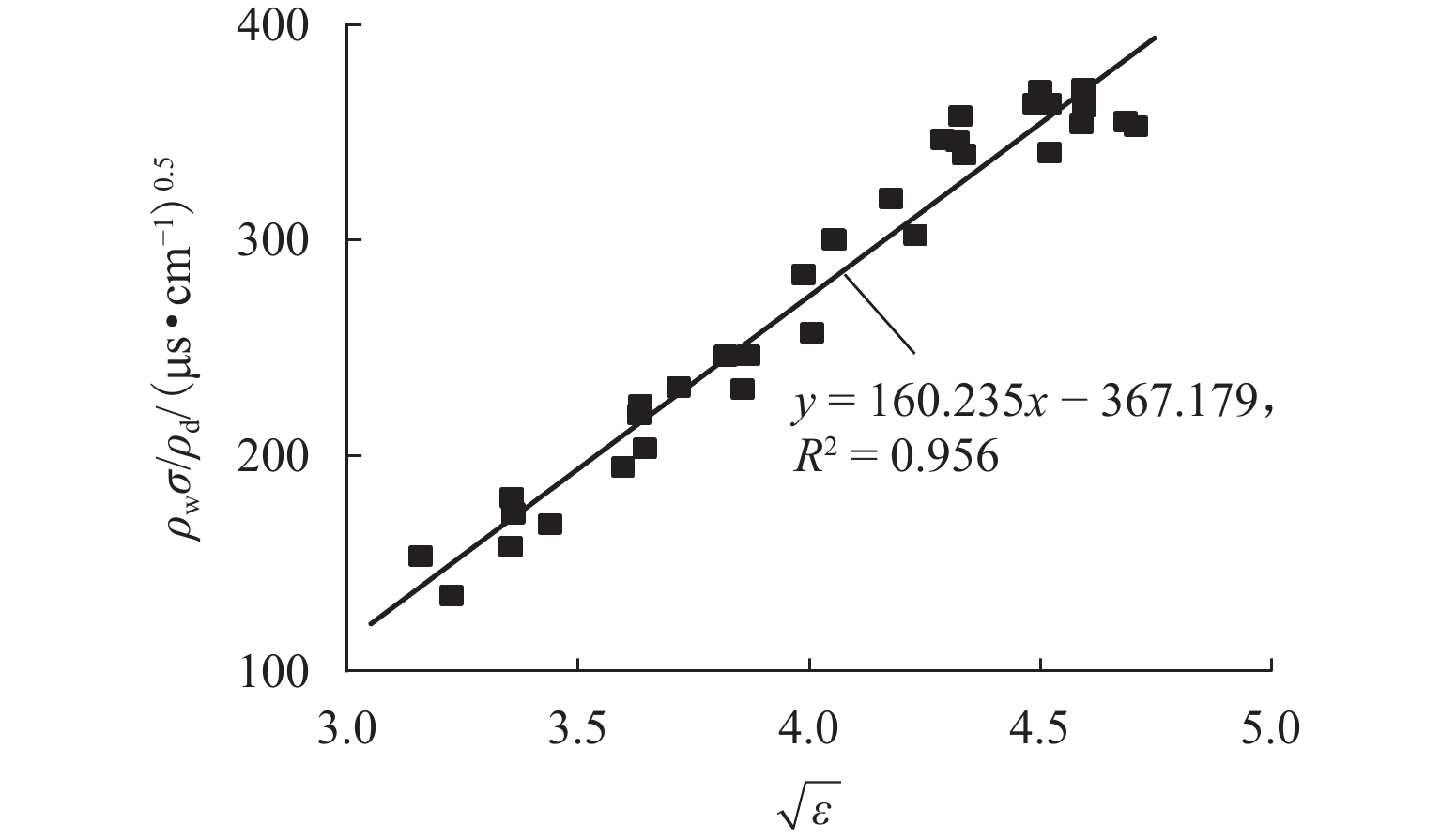
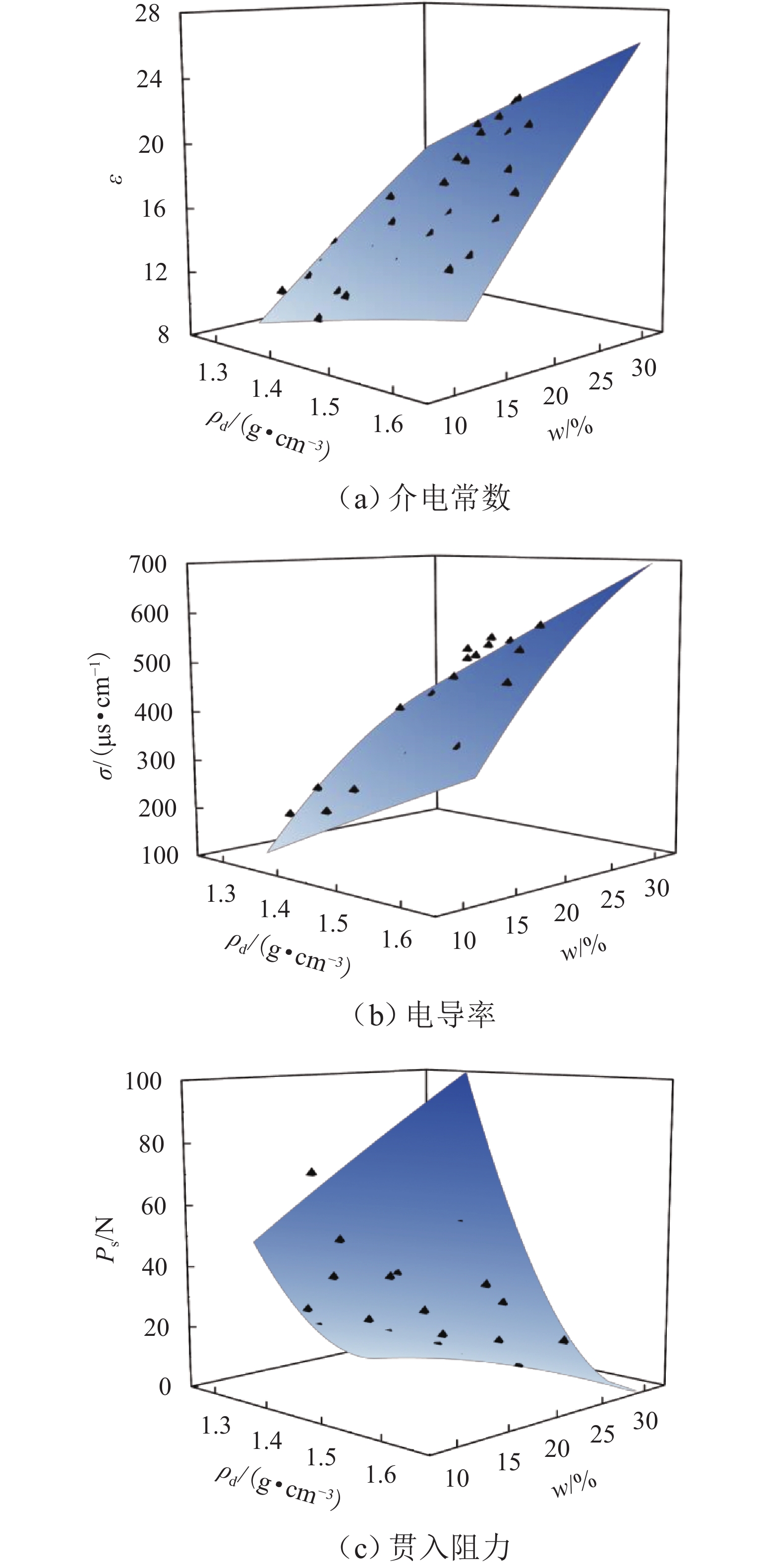
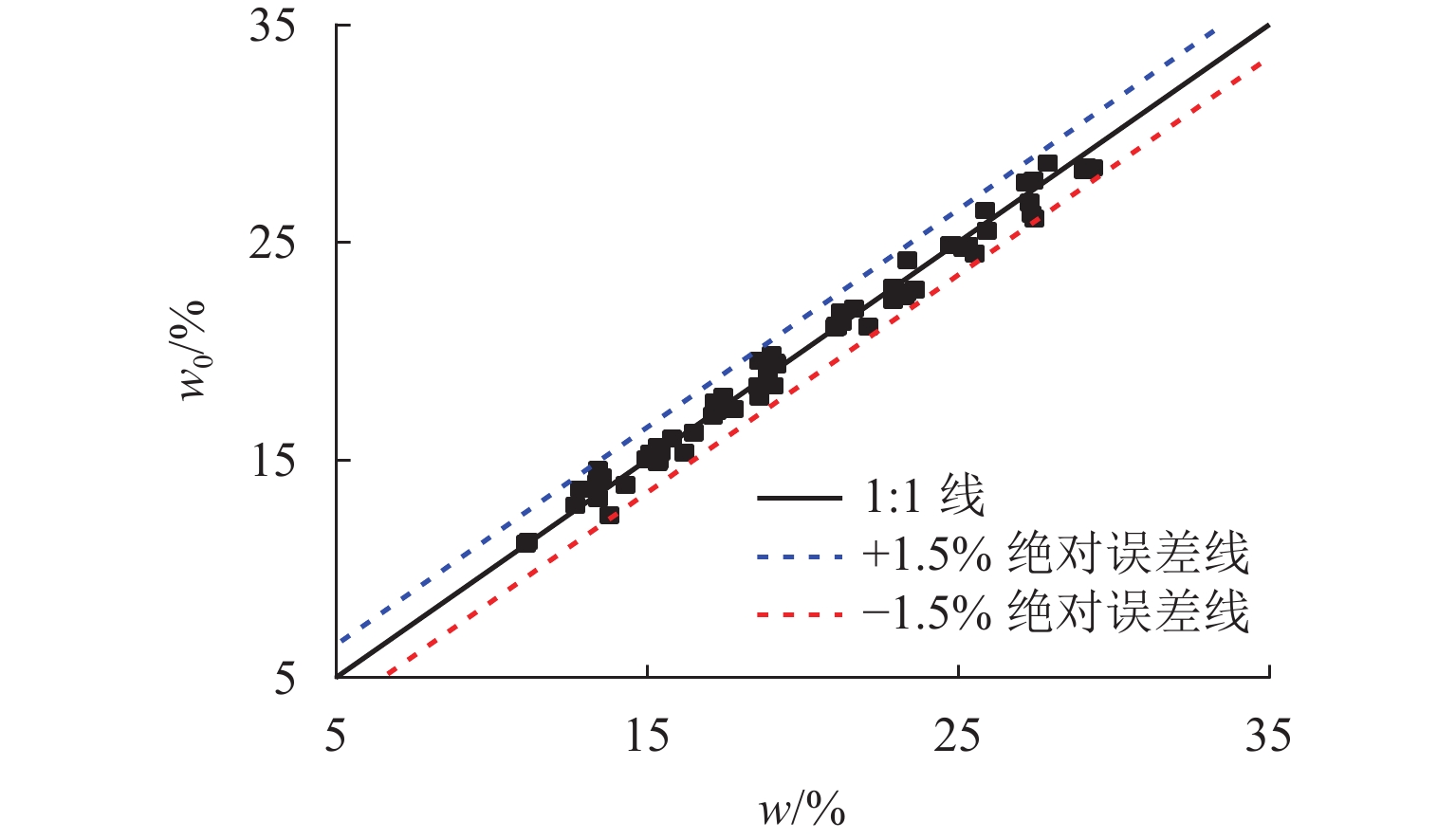
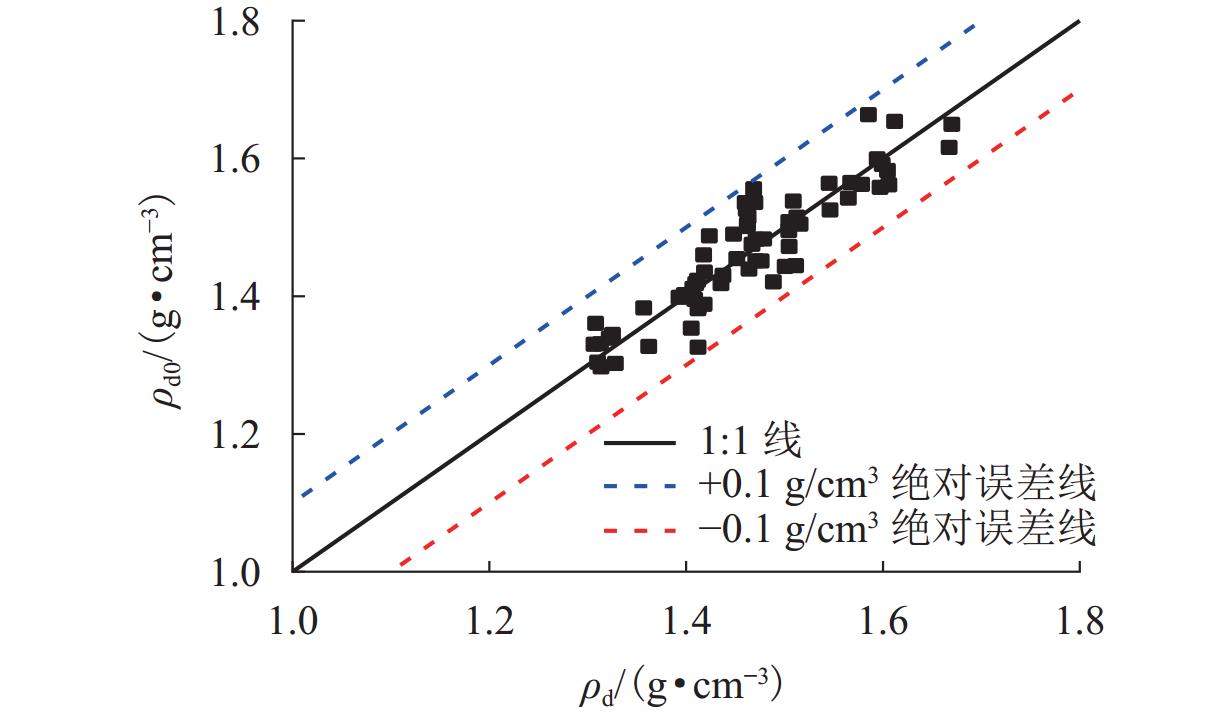
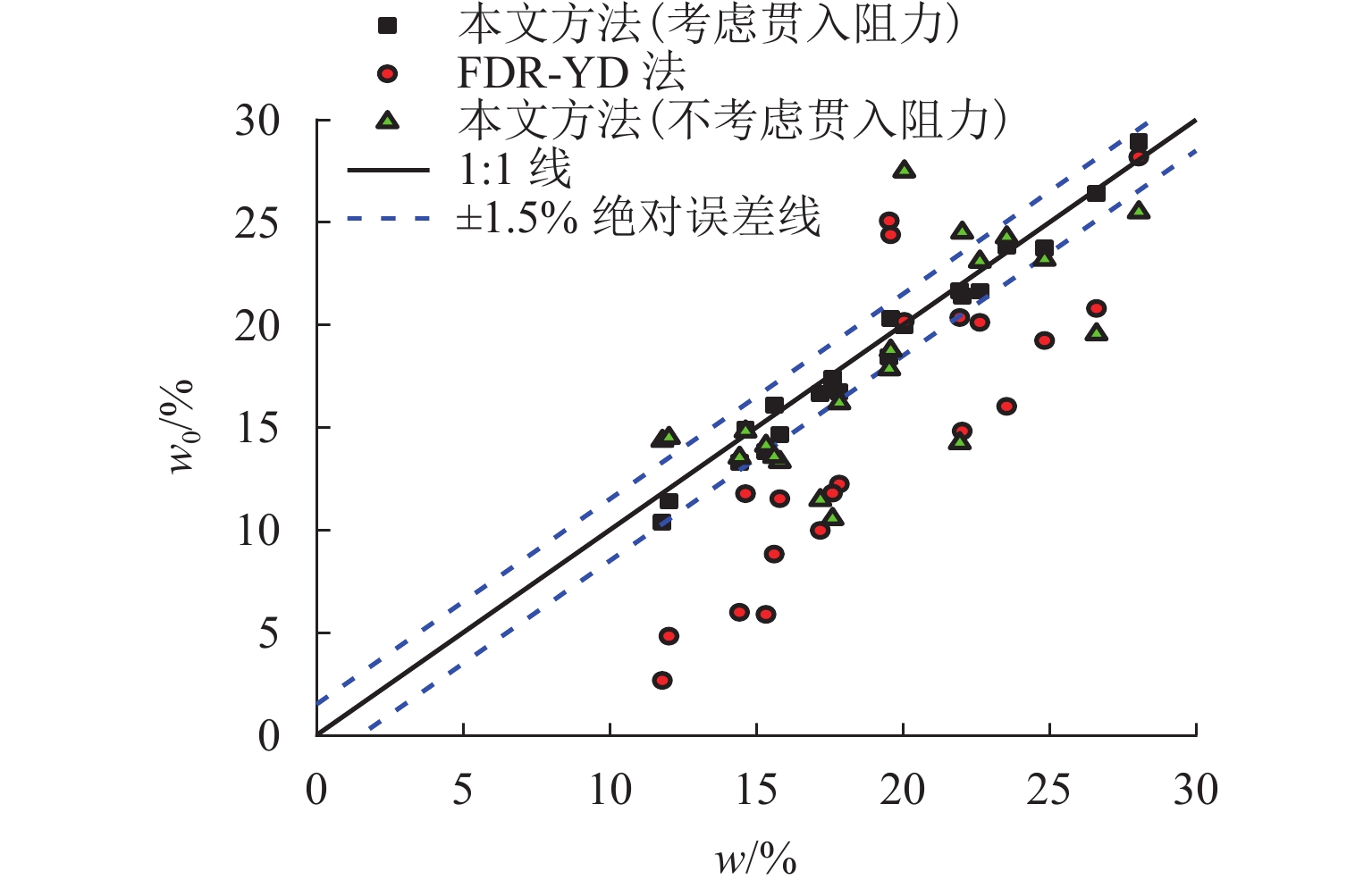
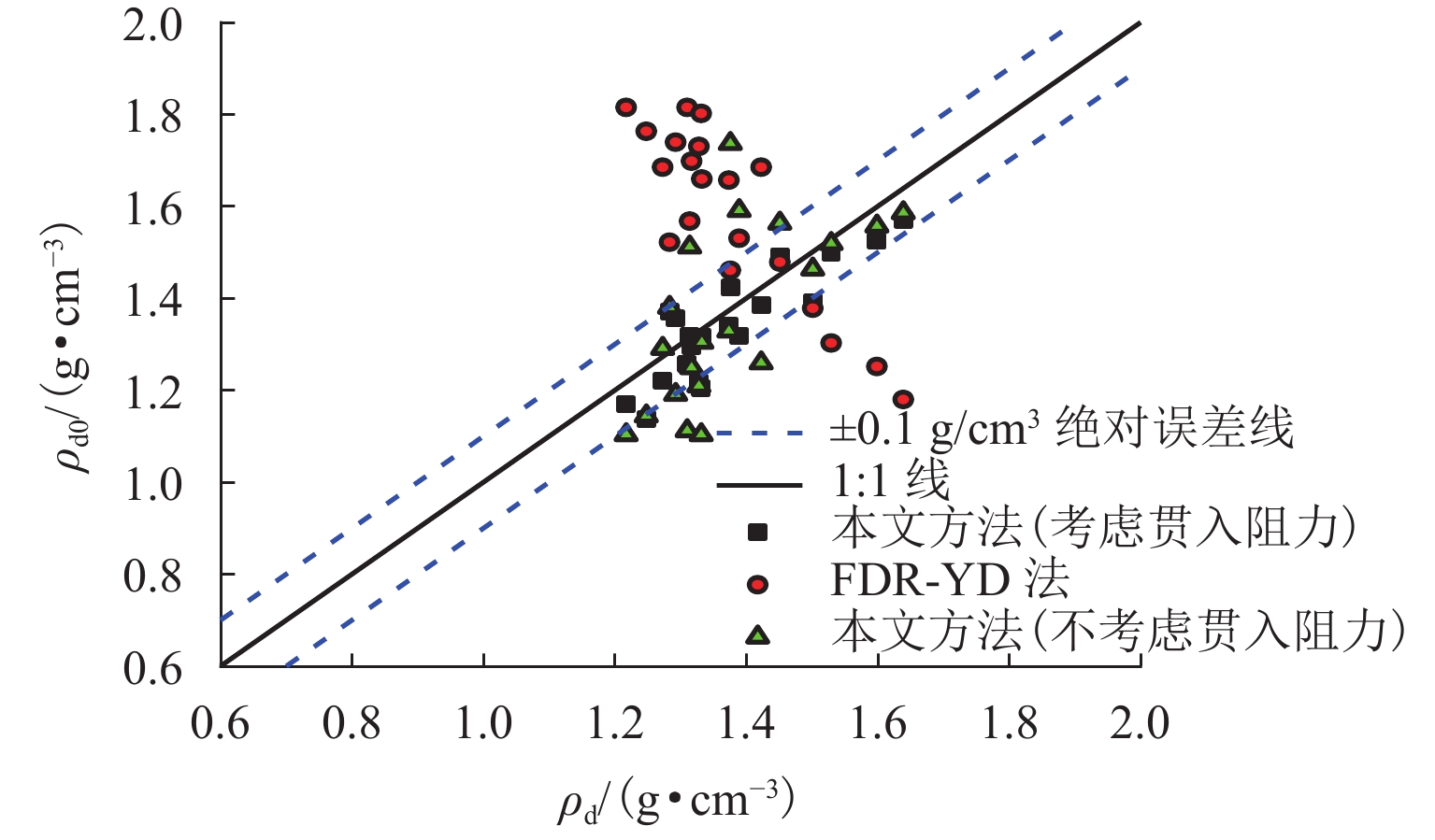
为解决传统土体质量含水率和干密度检测方法存在人工劳动强度高、检测时间长等问题,提出一种基于频域反射法(frequency domain reflectometry, FDR)与静力贯入的土体质量含水率和干密度快速检测方法. 通过开展参数标定试验,构建介电常数、电导率和贯入阻力相对于质量含水率和干密度的二阶响应曲面模型,并提出电导率修正模型;在此基础上,开展初步验证试验和室内模型试验,并结合粒子群优化算法进行反演计算,对该方法的适用性及优势进行系统验证. 结果表明:所采用的二阶响应曲面模型能够较好地拟合土体介电常数、电导率、贯入阻力与土体质量含水率和干密度之间的关系,相关系数均在0.950以上;在FDR法基础上增加贯入阻力测试,有效避免了仅测试介电常数和电导率引起的反演结果不唯一和异常值问题,土体质量含水率和干密度的均方根误差分别由3.838和0.143降低至0.853和0.069;相较传统FDR法,该方法的检测精度显著提升,土体质量含水率和干密度的最大误差分别在 [−1.5%,1.5%]和 [−0.1,0.1] g/cm3以内.
Abstract:To overcome the labor-intensive and time-consuming limitations of conventional methods for determining soil gravimetric water content (
w ) and dry density (ρ d), a rapid determination method integrating frequency domain reflectometry (FDR) and static penetration was developed. Parameter calibration tests were conducted to establish a second-order response surface model describing the relationships between dielectric constant, electrical conductivity, and penetration resistance with respect tow andρ d, along with the introduction of a conductivity correction model. Systematic validation was subsequently performed on the applicability and advantages of this method through preliminary verification tests, laboratory model tests, and inversion calculations utilizing particle swarm optimization. The results indicate that the second-order response surface model effectively captures the complex multivariate relationships between soil dielectric constant, electrical conductivity, and penetration resistance with respect tow andρ d, with correlation coefficients exceeding 0.950. The integration of penetration resistance measurements into the FDR method effectively mitigates issues of non-unique inversion solutions and anomalies associated with measuring only dielectric constant and electrical conductivity, reducing the root mean square errors forw andρ d from 3.838 and 0.143 to 0.853 and 0.069, respectively. Compared to the traditional FDR method, the proposed method significantly improves detection accuracy, with maximum errors forw andρ d limited within [−1.5%,1.5%] and [−0.1,0.1] g/cm3, respectively. -
表 1 试验黏土的基本物理指标
Table 1. Basic physical indicators of clay used in test
参数 比重 塑限/% 液限/% 塑性指数 天然含水率/% 取值 2.68 21.7 39.5 17.8 28.4 表 2 试验方案
Table 2. Experimental design
编号 目标含
水率/%目标干密度/(g•cm−3) 编号 目标含
水率/%目标干密度/(g•cm−3) 1-1 12 1.40 6-1 22 1.35 2-1 14 1.30 6-2 22 1.45 2-2 14 1.40 6-3 22 1.55 2-3 14 1.50 6-4 22 1.65 2-4 14 1.60 7-1 24 1.40 3-1 16 1.30 7-2 24 1.45 3-2 16 1.40 7-3 24 1.50 3-3 16 1.50 7-4 24 1.55 3-4 16 1.60 8-1 26 1.40 4-1 18 1.30 8-2 26 1.45 4-2 18 1.40 8-3 26 1.50 4-3 18 1.50 9-2 28 1.45 4-4 18 1.60 9-1 28 1.40 5-1 20 1.30 9-3 28 1.50 5-2 20 1.40 10-1 30 1.45 5-3 20 1.50 10-2 30 1.50 5-4 20 1.60 表 3 响应曲面模型拟合参数
Table 3. Fitting parameters of response surface model
参数 拟合值 参数 拟合值 α0 −9.568 β12 8.457 α1 −0.325 β11 −0.508 α2 14.770 β22 −80.742 α12 0.733 γ0 −241.819 α11 −0.002 γ1 −0.769 α22 −4.561 γ2 344.080 β0 − 1179.581 γ12 −9.430 β1 26.705 γ11 0.265 β2 813.866 γ22 −27.266 -
[1] 沈英朋,陆海玉,刘猛,等. 土料的击实特性及其击实后的力学性质[J]. 济南大学学报(自然科学版),2022,36(5): 566-570.SHEN Yingpeng, LU Haiyu, LIU Meng, et al. Compaction characteristics of soil and its mechanical properties after compaction[J]. Journal of University of Jinan (Science and Technology), 2022, 36(5): 566-570. [2] 张炎飞,刘先峰,袁胜洋,等. 过渡型细粒土击实特性及基质吸力试验研究[J]. 应用基础与工程科学学报,2023,31(4): 935-945.ZHANG Yanfei, LIU Xianfeng, YUAN Shengyang, et al. Experimental investigation of compaction behavior and matric suction of transitional fine-grained soil[J]. Journal of Basic Science and Engineering, 2023, 31(4): 935-945. [3] 钱劲松,庞劲松,费伦林,等. 路基智能压实评价指标研究进展综述[J]. 同济大学学报(自然科学版),2024,52(3): 388-397.QIAN Jinsong, PANG Jinsong, FEI Lunlin, et al. A review of research progress on intelligent compaction measurement values for subgrade[J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science), 2024, 52(3): 388-397. [4] KODIKARA J, ISLAM T, SOUNTHARARAJAH A. Review of soil compaction: history and recent developments[J]. Transportation Geotechnics, 2018, 17: 24-34. doi: 10.1016/j.trgeo.2018.09.006 [5] 张婵青,何凤飞,姜顺航,等. 土体含水率监测的移动点热源法研究[J]. 岩土力学,2022,43(7): 2025-2033.ZHANG Chanqing, HE Fengfei, JIANG Shunhang, et al. A mobile point heat source method for soil moisture monitoring[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2022, 43(7): 2025-2033. [6] 徐翔,姬业钦,陈志坚,等. 基于分焦平面偏振成像的冬青卫矛含水率快速无损检测[J]. 农业工程学报,2024,40(3): 219-226. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.202307204XU Xiang, JI Yeqin, CHEN Zhijian, et al. Rapid nondestructive detection of the moisture content of holly leaves using focal plane polarization imaging[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2024, 40(3): 219-226. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.202307204 [7] 刘洁,孙梦雅,施斌,等. 基于主动加热型FBG的土体干密度原位测量方法研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2021,43(2): 390-396. doi: 10.11779/CJGE202102020LIU Jie, SUN Mengya, SHI Bin, et al. Feasibility study on actively heated FBG methods for dry density measurement[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2021, 43(2): 390-396. doi: 10.11779/CJGE202102020 [8] 赵云,凌道盛,王云龙,等. 改进一步法模型及TDR自适应方法研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2016,38(5): 818-827. doi: 10.11779/CJGE201605007ZHAO Yun, LING Daosheng, WANG Yunlong, et al. Modified one-step method and its adaptive system of TDR[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2016, 38(5): 818-827. doi: 10.11779/CJGE201605007 [9] TOPP G C, DAVIS J L, ANNAN A P. Electromagnetic determination of soil water content: measurements in coaxial transmission lines[J]. Water Resources Research, 1980, 16(3): 574-582. doi: 10.1029/WR016i003p00574 [10] BHUYAN H, SCHEUERMANN A, BODIN D, et al. Soil moisture and density monitoring methodology using TDR measurements[J]. International Journal of Pavement Engineering, 2020, 21(10): 1263-1274. doi: 10.1080/10298436.2018.1537491 [11] MU Q Y, ZHAN L T, LIN C P, et al. Non-invasive time domain reflectometry probe for transient measurement of water retention curves in structured soils[J]. Engineering Geology, 2020, 264: 105335.1-105335.8. [12] ROTH K, SCHULIN R, FLÜHLER H, et al. Calibration of time domain reflectometry for water content measurement using a composite dielectric approach[J]. Water Resources Research, 1990, 26(10): 2267-2273. [13] SIDDIQUI S I, DRNEVICH V P. A new method of measuring density and moisture content of soil using the technique of time domain reflectometry[R]. West Lafayette: Purdue University, 1995. [14] YU X, DRNEVICH V P. Soil water content and dry density by time domain reflectometry[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2004, 130(9): 922-934. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2004)130:9(922) [15] 陈云敏,陈赟,陈仁朋,等. 滑坡监测TDR技术的试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2004,23(16): 2748-2755. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2004.16.018CHEN Yunmin, CHEN Yun, CHEN Renpeng, et al. Testing study on applications of time domain reflectometry to slope monitoring[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2004, 23(16): 2748-2755. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2004.16.018 [16] 陈仁朋,许伟,汤旅军,等. 地下水位及电导率TDR测试探头研制与应用[J]. 岩土工程学报,2009,31(1): 77-82. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2009.01.013CHEN Renpeng, XU Wei, TANG Lüjun, et al. Development and application of TDR probes to monitor water level and electrical conductivity[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2009, 31(1): 77-82. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2009.01.013 [17] 陈赟,陈云敏,周群建. 基于TDR技术的多种岩土介质含水量试验研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2011,46(1): 42-48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2011.01.007CHEN Yun, CHEN Yunmin, ZHOU Qunjian. Measurement of water content of multiple geomaterials by time-domain reflectometry technique[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2011, 46(1): 42-48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2011.01.007 [18] 陈仁朋,吴进,亓帅,等. 高铁路基粗颗粒土水力学参数测试方法研究[J]. 岩土力学,2015,36(12): 3365-3372.CHEN Renpeng, WU Jin, QI Shuai, et al. A method for measuring hydraulic parameters of coarse-grained soils for high-speed railway subgrade[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2015, 36(12): 3365-3372. [19] 陈仁朋,陈卓,陆明,等. 基于频率步进原理的TDR研制及在土体含水率测试中的应用[J]. 岩土工程学报,2019,41(7): 1191-1199. doi: 10.11779/CJGE201907002CHEN Renpeng, CHEN Zhuo, LU Ming, et al. Development of TDR based on stepped-frequency principle and its application in measurement of volumetric water content of soils[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2019, 41(7): 1191-1199. doi: 10.11779/CJGE201907002 [20] 江朝晖,檀春节,支孝勤,等. 基于频域反射法的便携式土壤水分检测仪研制[J]. 传感器与微系统,2013,32(1): 79-82. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9787.2013.01.023JIANG Zhaohui, TAN Chunjie, ZHI Xiaoqin, et al. Development of portable soil moisture detector based on principle of frequency domain reflectometry[J]. Transducer and Microsystem Technologies, 2013, 32(1): 79-82. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9787.2013.01.023 [21] BILSKIE J. Using dielectric properties to measure soil water content[J]. Sensors, 1997, 14(7): 26-33. [22] CAMPBELL G S, ANDERSON R Y. Evaluation of simple transmission line oscillators for soil moisture measurement[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 1998, 20(1): 31-44. doi: 10.1016/S0168-1699(98)00006-4 [23] 周建平,李银,臧耀辉,等. 基于FDR技术的土体质量含水率和干密度快速检测方法[J]. 河海大学学报(自然科学版),2022,50(6): 123-129. doi: 10.3876/j.issn.1000-1980.2022.06.016ZHOU Jianping, LI Yin, ZANG Yaohui, et al. Fast detection method of soil mass moisture content and dry density based on FDR technology[J]. Journal of Hohai University (Natural Sciences), 2022, 50(6): 123-129. doi: 10.3876/j.issn.1000-1980.2022.06.016 [24] 王德银,唐朝生,李建,等. 基于超微型贯入试验的黏性土干燥过程中结构强度演化规律研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2014,22(5): 818-823.WANG Deyin, TANG Chaosheng, LI Jian, et al. Super miniature penetration test on structural strength of clayey soil during evaporation[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2014, 22(5): 818-823. [25] 段伟,蔡国军,刘松玉,等. 基于多功能CPTU测试的无黏性土状态参数评价研究[J]. 中国公路学报,2022,35(1): 200-209. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2022.01.018DUAN Wei, CAI Guojun, LIU Songyu, et al. Evaluation of state parameter of cohesion less soils based on multifunctional CPTU data[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2022, 35(1): 200-209. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2022.01.018 [26] KENNEDY J, EBERHART R. Particle swarm optimization[C]//Proceedings of ICNN’95-International Conference on Neural Networks. Perth: IEEE, 1995: 1942-1948. [27] 占玉林,许江辉,许俊,等. 基于响应面法和粒子群算法的桥梁高耸临时提升支架优化[J]. 中国铁道科学,2022,43(6): 39-46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4632.2022.06.05ZHAN Yulin, XU Jianghui, XU Jun, et al. Optimization of bridge high temporary lifting support based on response surface method and particle swarm algorithm[J]. China Railway Science, 2022, 43(6): 39-46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4632.2022.06.05 [28] 占玉林,侯之瑶,邵俊虎,等. 基于响应面法及粒子群算法的异形斜拉桥索力优化[J]. 桥梁建设,2022,52(3): 16-23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-4722.2022.03.003ZHAN Yulin, HOU Zhiyao, SHAO Junhu, et al. Cable force optimization of irregular cable-stayed bridge based on response surface method and particle swarm optimization algorithm[J]. Bridge Construction, 2022, 52(3): 16-23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-4722.2022.03.003 [29] 杨道学,赵奎,曾鹏,等. 基于粒子群优化算法的未知波速声发射定位数值模拟[J]. 岩土力学,2019,40(增1): 494-502.YANG Daoxue, ZHAO Kui, ZENG Peng, et al. Numerical simulation of unknown wave velocity acoustic emission localization based on particle swarm optimization algorithm[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2019, 40(S1): 494-502. [30] 吕春妍,蒲浩,宋陶然,等. 基于粒子群算法的复杂山区铁路土方调配与取弃土场选址协同优化[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报,2024,21(3): 1202-1212.LÜ Chunyan, PU Hao, SONG Taoran, et al. Concurrent optimization of earthwork allocation and borrow/waste site selection of complex mountain railway alignments based on particle swarm optimization algorithm[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2024, 21(3): 1202-1212. [31] 王志强,郭伟鹏,桑孜良,等. 高速磁浮列车导向系统优化控制方法研究[J/OL]. 西南交通大学学报,1-10[2025-04-18]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/51.1277.U.20240605.1249.002.html.U.20240605.1249.002.5. [32] 崔晓璐,唐传平,包鹏羽,等. 高速列车制动区段钢轨波磨抑制方法[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2023,58(3): 656-664. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20220256CUI Xiaolu, TANG Chuanping, BAO Pengyu, et al. Rail corrugation suppressing method on braking sections of high-speed trains[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2023, 58(3): 656-664. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20220256 [33] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 土工试验方法标准:GB/T 50123—2019[S]. 北京:中国计划出版社,2019. -





 下载:
下载: