Impact of Horizontal Ribs on Aerodynamic Characteristics of High-Rise Buildings
-
摘要:
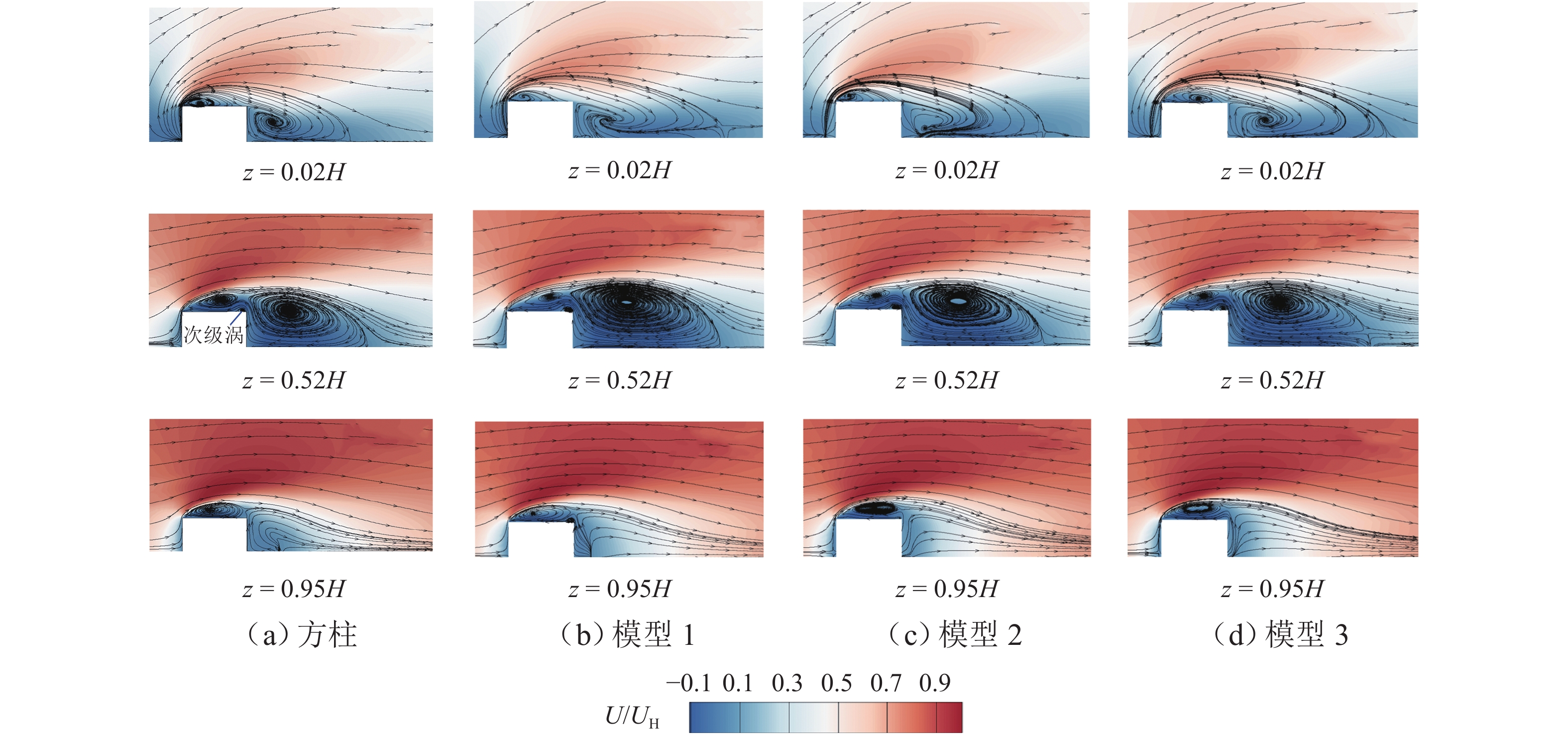
为分析高层建筑上外伸肋板的抗风工作机理,利用大涡模拟(LES)评估大气边界层来流下水平肋板对高层建筑的流场和风荷载的影响,对比不同类型水平肋板的抗风效果. 结果表明:水平肋板明显抑制了侧风面分离涡的形成,并拉长尾涡;肋板会显著抑制建筑附近的竖向流,并在肋板附近诱导形成局部旋涡,最终导致近壁流动形式明显变化;流场的变化会影响风压分布和风荷载,水平肋板使建筑表面平均风压系数沿高度呈“之”字形分布,水平板明显降低侧壁面上平均和脉动风压,最大降幅分别约为20%和17%;对总荷载而言,水平肋板对平均阻力无明显影响,但能明显降低建筑上的脉动升力,最大降幅为27%;肋板的布置形式对气动特性的影响有明显差异,连续水平板通过改变近壁流、涡结构来影响风压分布和风荷载,而间隔水平板对风荷载的影响相对较弱.
Abstract:To analyze the wind-resistance working mechanism of facade ribs mounted on high-rise buildings, the impact of horizontal ribs on the flow field and wind load of high-rise buildings under atmospheric boundary layer flow was evaluated by using the large eddy simulation (LES), and the wind-resistance effect of different types of horizontal ribs was compared. The results show that the horizontal ribs significantly inhibit the formation of the separated vortex near the sidewall and elongate the wake vortex. The ribs obviously suppress the vertical flow near the buildings and induce a local vortex near the ribs, which eventually causes significant changes in the pattern of near-wall flow. The changes in the flow field will lead to corresponding alterations in wind pressure distribution and wind load. The horizontal ribs can cause a “zigzag” pattern distribution of the mean wind pressure coefficient along the altitude of the buildings, and the ribs significantly reduce the mean and fluctuating wind pressure on the sidewall. The maximum reductions are about 20% and 17%, respectively. With regard to total wind load, the horizontal ribs have negligible impact on the mean drag, while they can significantly mitigate the fluctuating lift on the buildings, with a maximum reduction of 27%. The effect of the rib arrangement on the aerodynamic characteristics is also significantly different. The continuous horizontal ribs affects the wind pressure distribution and wind load by changing the near-wall flow and the vortex structure, while the influence of discontinuous ribs on wind load is relatively weak.
-
Key words:
- high-rise building /
- horizontal ribs /
- LES /
- flow field /
- aerodynamic forces
-
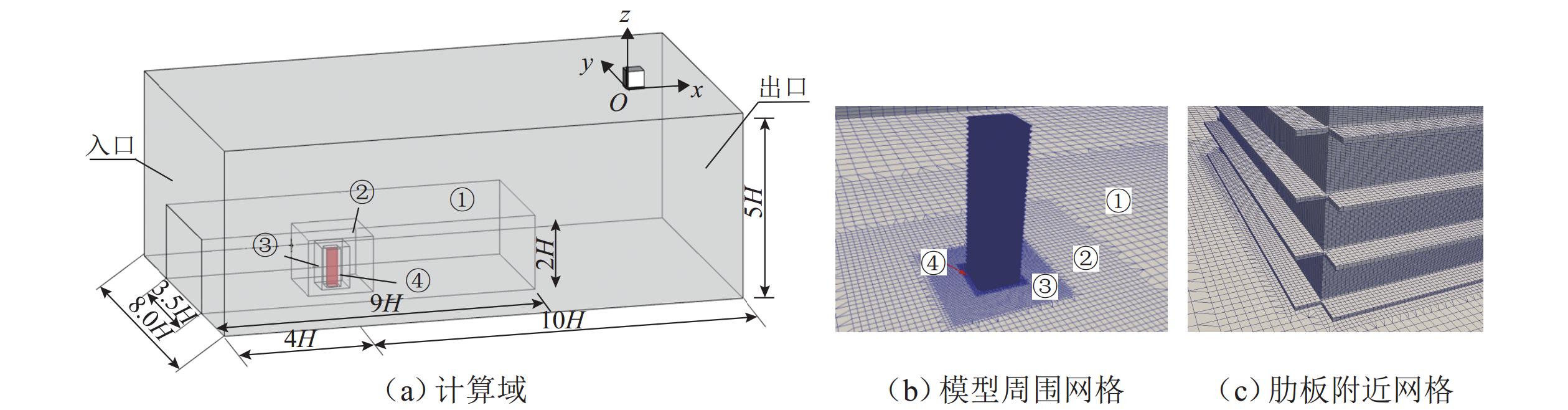
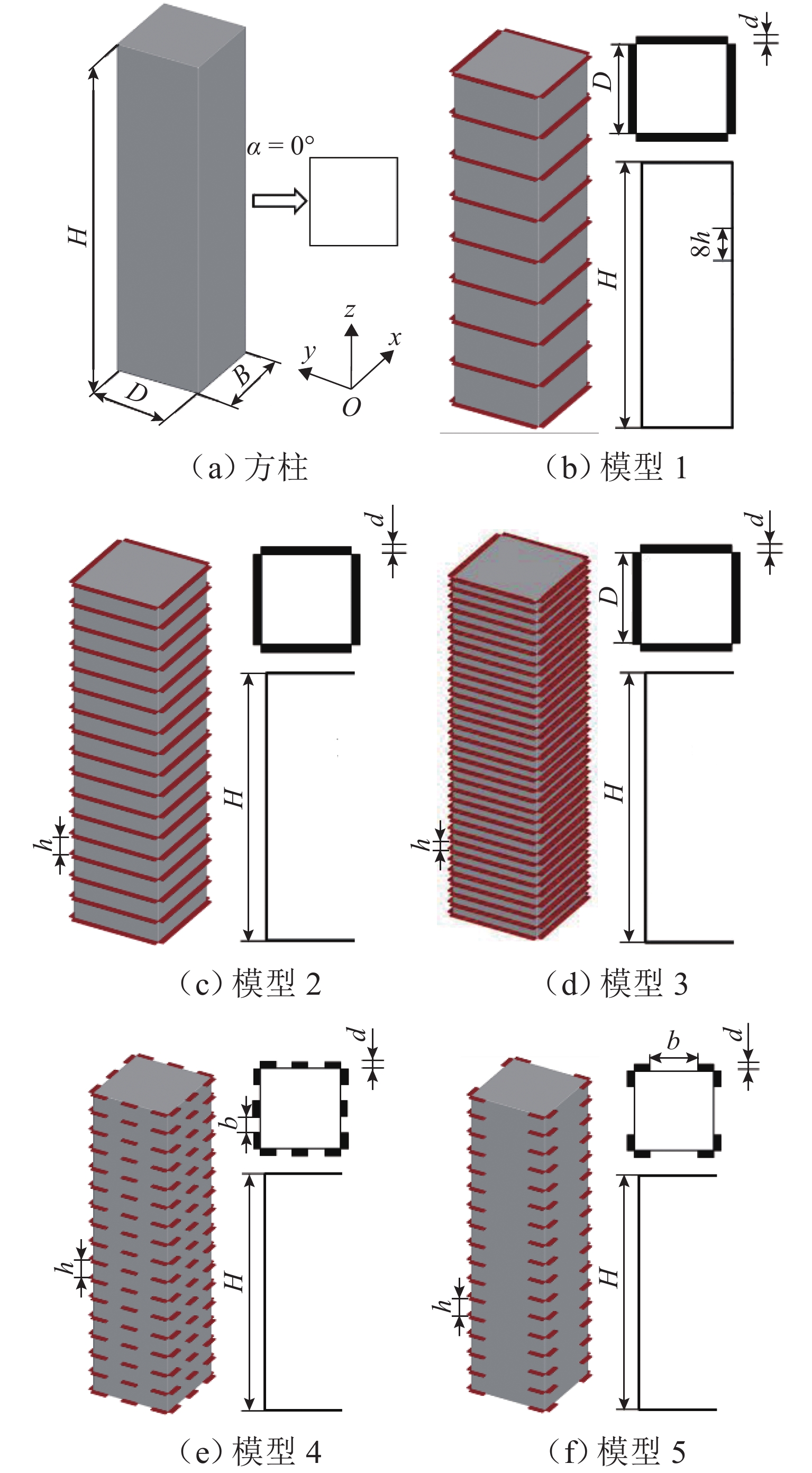
表 1 肋板尺寸信息
Table 1. Dimension information of ribs
模型编号 d/D b/D h/D 1 0.06 0.500 2 0.06 0.250 3 0.06 0.125 4 0.06 0.2 0.250 5 0.06 0.6 0.250 表 2 网格信息
Table 2. Mesh information
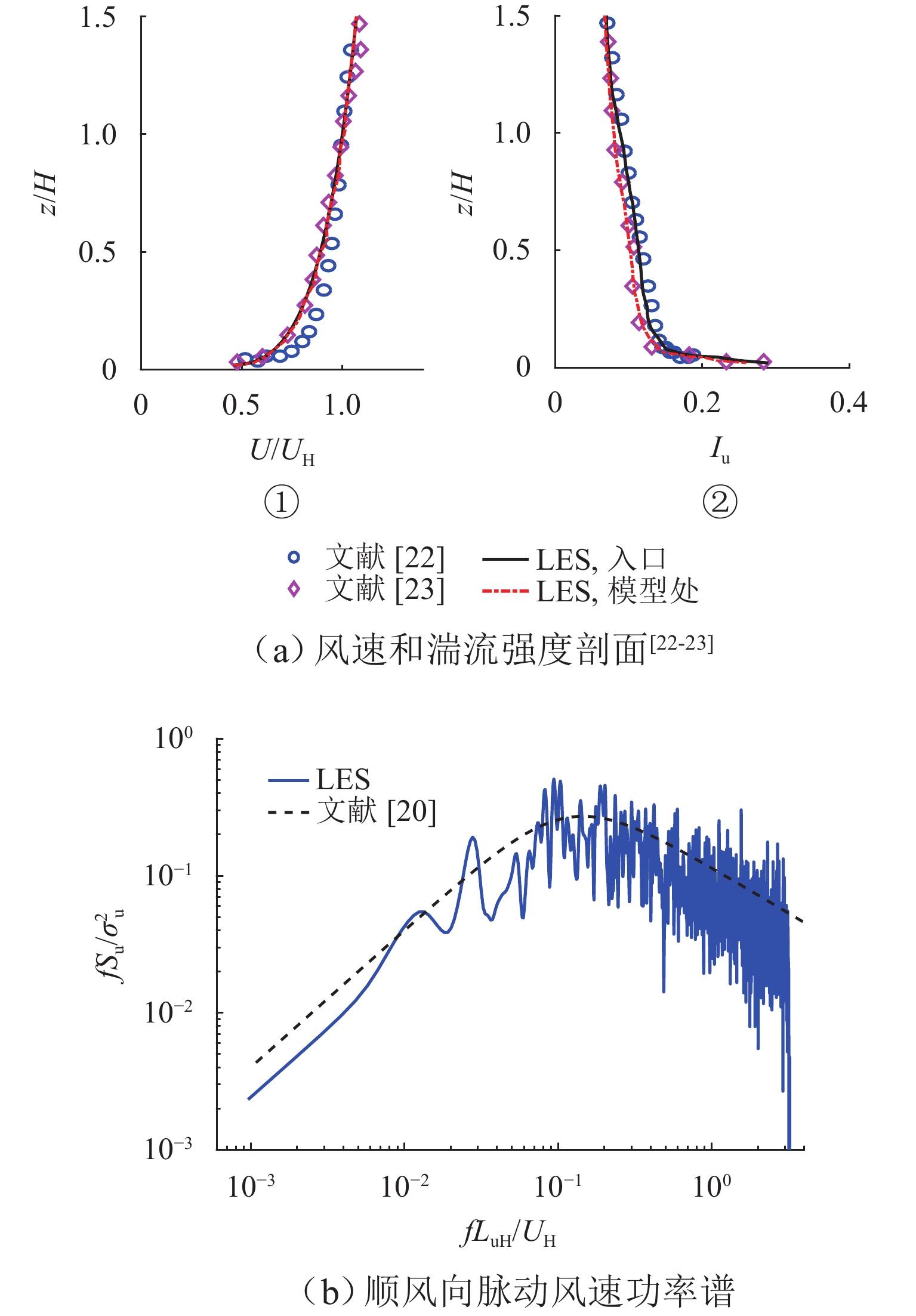
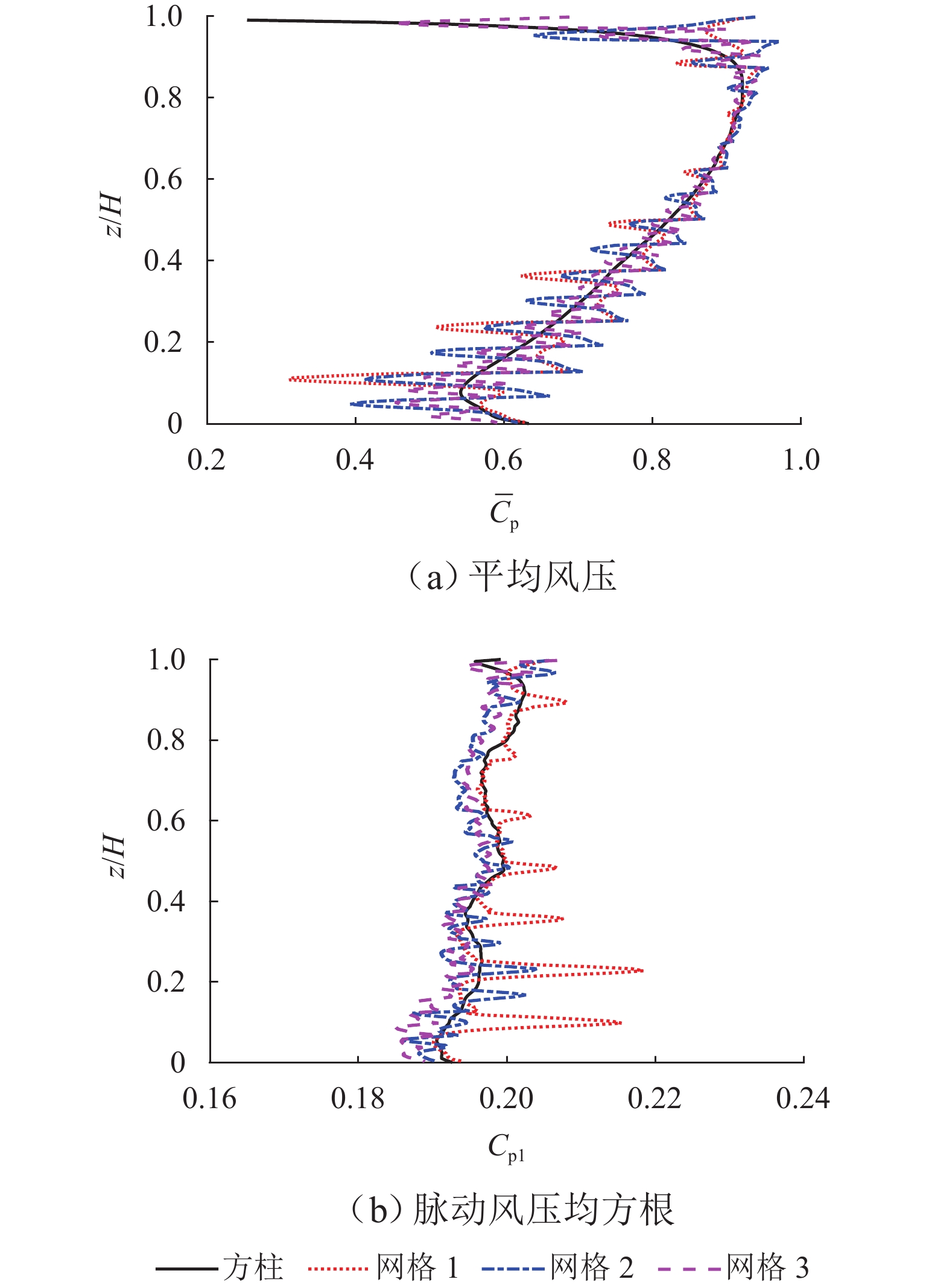
网格 最小网格 最大网格 数量/百万个 x/y z x/y z 网格 1 1/62.5D 1/300D 0.6D 1D 3.7 网格 2 1/125.0D 1/600D 0.6D 1D 7.2 网格 3 1/250.0D 1/ 1200 D0.6D 1D 13.6 表 3 参考方柱LES结果及验证
Table 3. LES results of square column and verification
方法 文献 Re/×104 AR ${\overline C}_{\mathrm{d}} $ ${C}_{{\mathrm{d}}1} $ ${C}_{{\mathrm{l}}1} $ St LES 网格 1 5.5 4 1.220 0.09 0.330 0.100 网格 2 5.5 4 1.147 0.10 0.300 0.096 网格 3 5.5 4 1.156 0.11 0.310 0.094 试验 文献 [22] 5.5 4 1.200 0.410 0.100 文献 [23] 5.0 4 1.280 0.13 0.320 0.085 文献 [24] 6.0 4 1.270 0.08 0.296 0.097 文献 [25] 7.3 3 1.290 0.102 文献 [11] 5.5 5 0.930 0.350 0.100 文献 [10] 5.5 5 1.080 表 4 参考方柱和模型1~3的风荷载系数
Table 4. Wind load coefficients for square cylinder and models 1–3
名称 ${\overline C}_{\mathrm{d}} $ ${ C}_{{\mathrm{d}}1} $ ${ C}_{{\mathrm{l}}1} $ 方柱 1.147 0.100 0.300 模型 1 0.146 0.102 0.232 模型 2 0.149 0.102 0.219 模型 3 0.145 0.101 0.218 表 5 模型2、4、5的风荷载
Table 5. Wind loads of models 2, 4, 5
名称 ${\overline C}_{\mathrm{d}} $ ${C}_{{\mathrm{d}}1} $ ${C}_{{\mathrm{l}}1} $ 模型 2 1.149 0.102 0.219 模型 4 1.156 0.106 0.229 模型 5 1.153 0.103 0.261 -
[1] 张正维, 全涌, 顾明, 等. 锥度化方形截面高层建筑的气动力特性[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2014, 49(5): 772-778. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2014.05.005ZHANG Zhengwei, QUAN Yong, GU Ming, et al. Aerodynamic characteristics of tapered tall buildings with square section[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2014, 49(5): 772-778. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2014.05.005 [2] 曾加东, 李明水. 矩形断面高层建筑脉动风荷载频谱特性研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2017, 52(1): 83-90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2017.01.012ZENG Jiadong, LI Mingshui. Experimental study of spectral characteristics of fluctuating wind loads on high-rise building with rectangular section[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2017, 52(1): 83-90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2017.01.012 [3] 黄东梅, 何世青, 朱学, 等. 表面粗糙度对超高层建筑风荷载与风振响应的影响[J]. 湖南大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 44(9): 41-51.HUANG Dongmei, HE Shiqing, ZHU Xue, et al. Influence of surface roughness on wind load and wind-induced response of super-tall building[J]. Journal of Hunan University (Natural Sciences), 2017, 44(9): 41-51. [4] MARUTA E, KANDA M, SATO J. Effects on surface roughness for wind pressure on glass and cladding of buildings[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 1998, 74/75/76: 651-663. [5] CHAND I, BHARGAVA P K, KRISHAK N L V. Effect of balconies on ventilation inducing aeromotive force on low-rise buildings[J]. Building and Environment, 1998, 33(6): 385-396. doi: 10.1016/S0360-1323(97)00054-1 [6] ZHENG X, MONTAZERI H, BLOCKEN B. CFD analysis of the impact of geometrical characteristics of building balconies on near-façade wind flow and surface pressure[J]. Building and Environment, 2021, 200: 107904.1-107904.19. [7] MONTAZERI H, BLOCKEN B. CFD simulation of wind-induced pressure coefficients on buildings with and without balconies: validation and sensitivity analysis[J]. Building and Environment, 2013, 60: 137-149. doi: 10.1016/j.buildenv.2012.11.012 [8] YUAN K, HUI Y, CHEN Z Q. Effects of facade appurtenances on the local pressure of high-rise building[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2018, 178: 26-37. doi: 10.1016/j.jweia.2018.05.004 [9] HUI Y, YUAN K, CHEN Z Q, et al. Characteristics of aerodynamic forces on high-rise buildings with various façade appurtenances[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2019, 191: 76-90. doi: 10.1016/j.jweia.2019.06.002 [10] CHENG X, HUANG G Q, YANG Q S, et al. Influence of architectural facades on wind pressures and aerodynamic forces of tall buildings[J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 2021, 147(1): 04020303.1-04020303.14. [11] YANG Q S, LIU Z H, HUI Y, et al. Modification of aerodynamic force characteristics on high-rise buildings with arrangement of vertical plates[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2020, 200: 104155.1-104155.18. [12] AI Z T, MAK C M, NIU J L. Numerical investigation of wind-induced airflow and interunit dispersion characteristics in multistory residential buildings[J]. Indoor Air, 2013, 23(5): 417-429. doi: 10.1111/ina.12041 [13] ZHENG X, MONTAZERI H, BLOCKEN B. CFD simulations of wind flow and mean surface pressure for buildings with balconies: comparison of RANS and LES[J]. Building and Environment, 2020, 173: 106747.1-106747.17. [14] KUMAR A, RAHUL P S, KUMAR S. Performance optimization of tall buildings subjected to wind—an Indian scenario[C]//Proceedings of the Eighth Asia-Pacific Conference on Wind Engineering. Singapore: Research Publishing Services, 2013: 817-826. [15] LIU J Y, HUI Y, YANG Q S, et al. Flow field investigation for aerodynamic effects of surface mounted ribs on square-sectioned high-rise buildings[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2021, 211: 104551.1-104551.9. [16] LIU J Y, HUI Y, WANG J X, et al. LES study of windward-face-mounted-ribs’ effects on flow fields and aerodynamic forces on a square cylinder[J]. Building and Environment, 2021, 200: 107950.1-107950.14. [17] LIU J Y, HUI Y, LI S K, et al. Numerical studies on aerodynamic forces and flow control regimes of square cylinder with four surface ribs[J]. Computers & Fluids, 2022, 245: 105609.1-105609.13. [18] HUI Y, LIU J Y, WANG J X, et al. Effects of facade rib arrangement on aerodynamic characteristics and flow structure of a square cylinder[J]. Building and Environment, 2022, 214: 108924.1-108924.13. [19] LAM K, LIN Y F. Large eddy simulation of flow around wavy cylinders at a subcritical Reynolds number[J]. International Journal of Heat and Fluid Flow, 2008, 29(4): 1071-1088. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatfluidflow.2008.01.006 [20] YANG Q S, ZHOU T, YAN B W, et al. LES study of turbulent flow fields over hilly terrains—comparisons of inflow turbulence generation methods and SGS models[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2020, 204: 104230.1-104230.22. [21] ABOSHOSHA H, ELSHAER A, BITSUAMLAK G T, et al. Consistent inflow turbulence generator for LES evaluation of wind-induced responses for tall buildings[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2015, 142: 198-216. doi: 10.1016/j.jweia.2015.04.004 [22] MARUYAMA Y, TAMURA T, OKUDA Y, et al. LES of fluctuating wind pressure on a 3D square cylinder for PIV-based inflow turbulence[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2013, 122: 130-137. doi: 10.1016/j.jweia.2013.07.001 [23] CAO Y, TAMURA T, KAWAI H. Investigation of wall pressures and surface flow patterns on a wall-mounted square cylinder using very high-resolution Cartesian mesh[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2019, 188: 1-18. doi: 10.1016/j.jweia.2019.02.013 [24] SAKAMOTO H, OIWAKE S. Fluctuating forces on a rectangular prism and a circular cylinder placed vertically in a turbulent boundary layer[J]. Journal of Fluids Engineering, 1984, 106(2): 160-166. doi: 10.1115/1.3243093 [25] MCCLEAN J F, SUMNER D. An experimental investigation of aspect ratio and incidence angle effects for the flow around surface-mounted finite-height square prisms[J]. Journal of Fluids Engineering, 2014, 136(8): 081206.1-081206.10. -




 下载:
下载: