Progress and Prospects of Landslide Multi-Source Monitoring Technology and Early Warning Model
-
摘要:
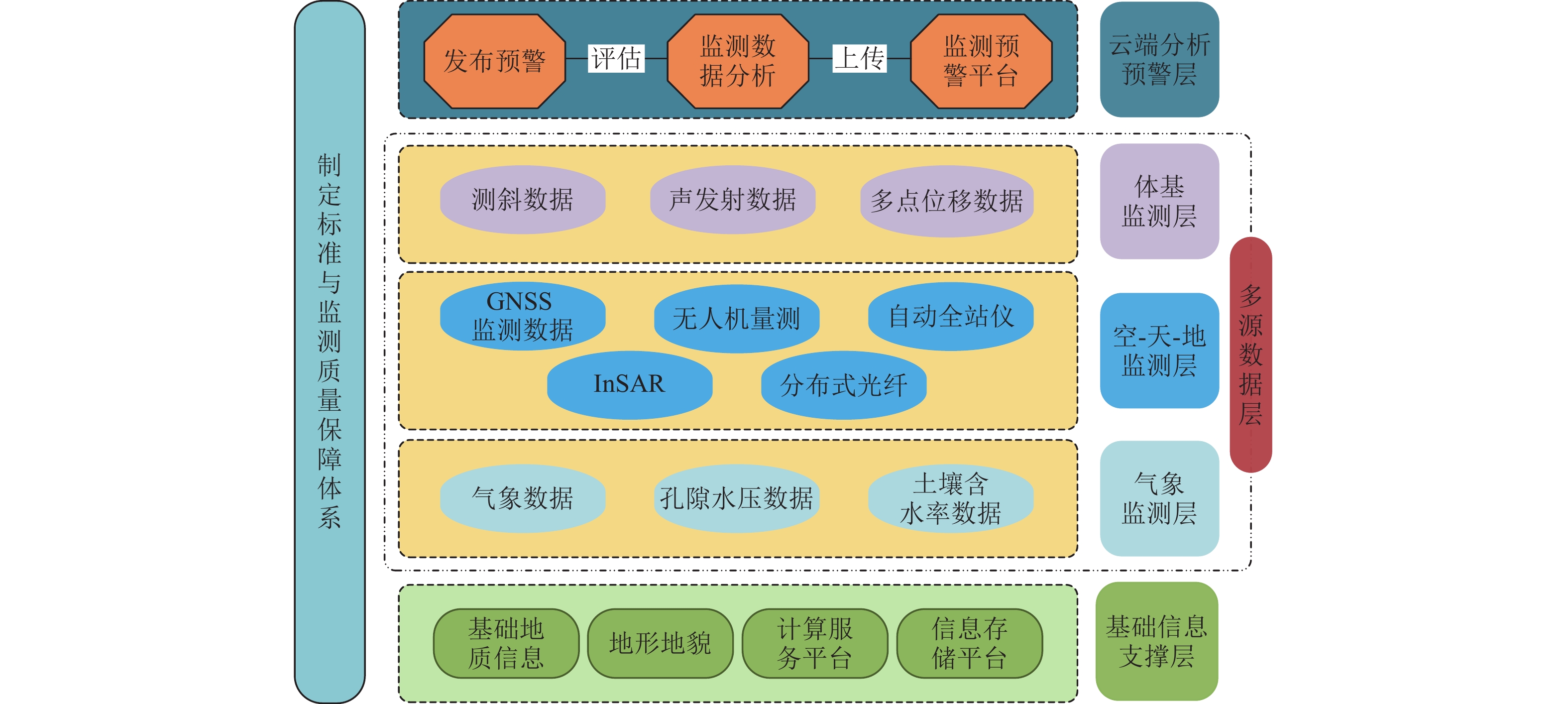
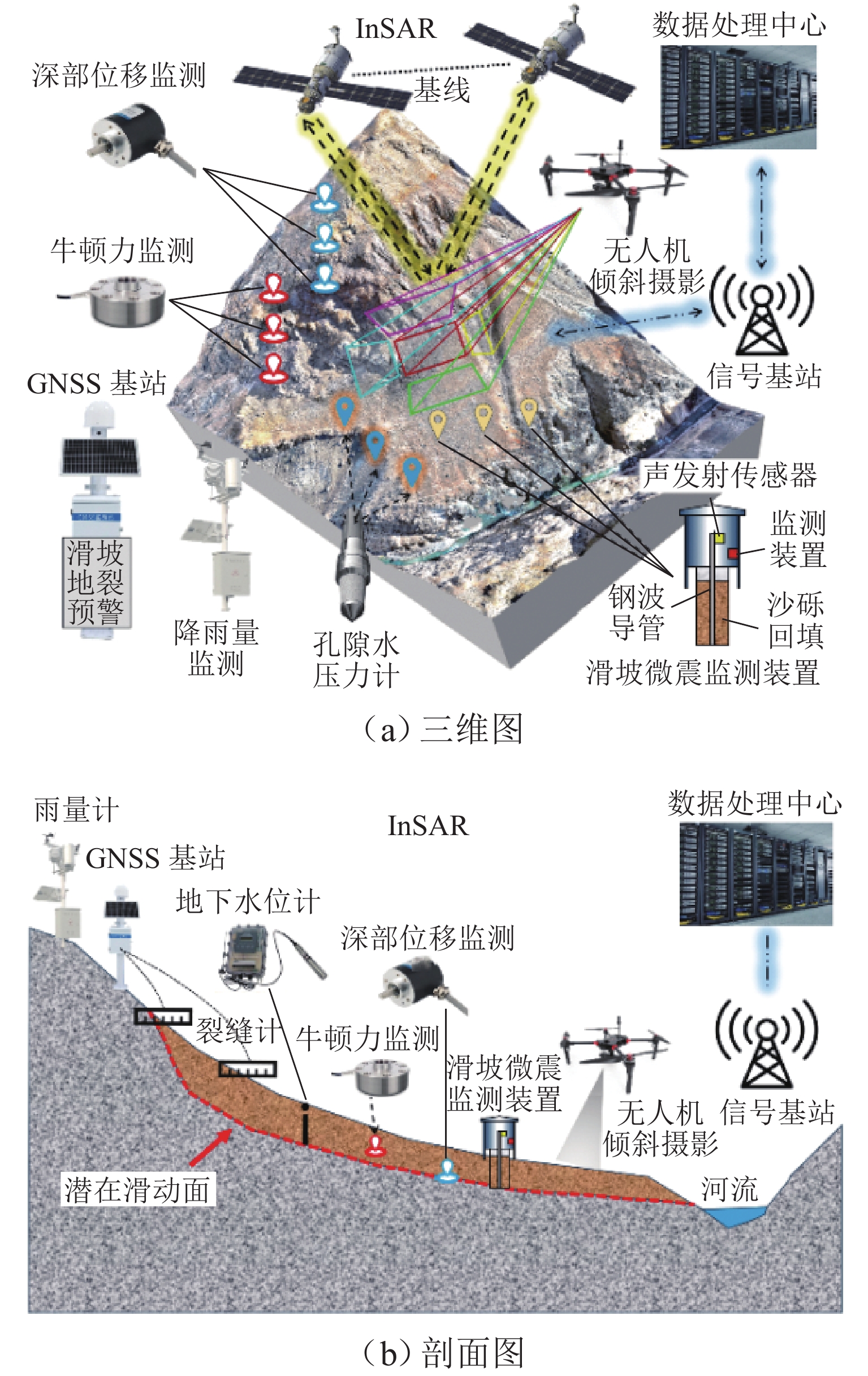
我国地质灾害频发,滑坡灾害因其种类多、察觉难、分布广、危害大等特点,造成的人员伤亡和财产损失位于各类地质灾害之首. 多源监测技术在滑坡预警、防灾减灾过程中起着至关重要的作用. 简要回顾多种滑坡监测技术的产生及发展历程;系统梳理近年来从滑坡的表观长期安全评估、深部牛顿力监测到微震信号感知的多源数据融合监测方法应用等一系列重要进展;概述了卫星监测智能识别技术、空天地一体化复合光纤滑坡监测技术以及NPR (negative poisson’s ratio anchor)深部牛顿力实时监测技术在滑坡识别解译、长期监测、应急响应等方面的应用研究;总结学者在滑坡预警模型的最新成果和主要研究方向,对其评估方法及主要结论进行分类评述;分析讨论以现有滑坡监测数据为驱动,融合各类深度学习方法来预测滑坡的优势和主要存在的问题. 前沿的深度学习算法与滑坡灾变多参量高精度演化特征信息的深度融合,将引领智能化滑坡预警模型的研究迈向新的高度,成为未来探索的核心焦点.
Abstract:Geological disasters occur frequently in China, among which landslide disasters, due to their multiple types, difficult detection, wide distribution, great harm, and other characteristics, result in casualties and property losses and are ranked as the first of all types of geological disasters. Multi-source monitoring technology plays a vital role in the process of landslide early warning, disaster prevention, and disaster mitigation. The emergence and development of a variety of landslide monitoring technologies were briefly reviewed. A series of important advances in recent years ranging from apparent long-term safety assessment of landslides and deep Newtonian force monitoring to the application of multi-source data fusion monitoring methods for micro-seismic signal sensing were systematized. The research applications of satellite monitoring-based intelligent identification technology, space-air-ground integrated composite fiber-optic landslide monitoring technology, and negative poisson’s ratio anchor (NPR) deep Newtonian force real-time monitoring technology in landslide identification and deciphering, long-term monitoring, and emergency response were outlined. The latest achievements and main research directions of scholars in landslide early warning models were summarized, and their assessment methods and main conclusions were classified and reviewed. The advantages and major problems of integrating various deep learning methods to predict landslides driven by existing landslide monitoring data were analyzed. The deep integration of cutting-edge deep learning algorithms with the multi-parameter high-precision evolutionary feature information of landslide catastrophes will lead the research of intelligent landslide warning models to a new level and become the core focus of future exploration.
-
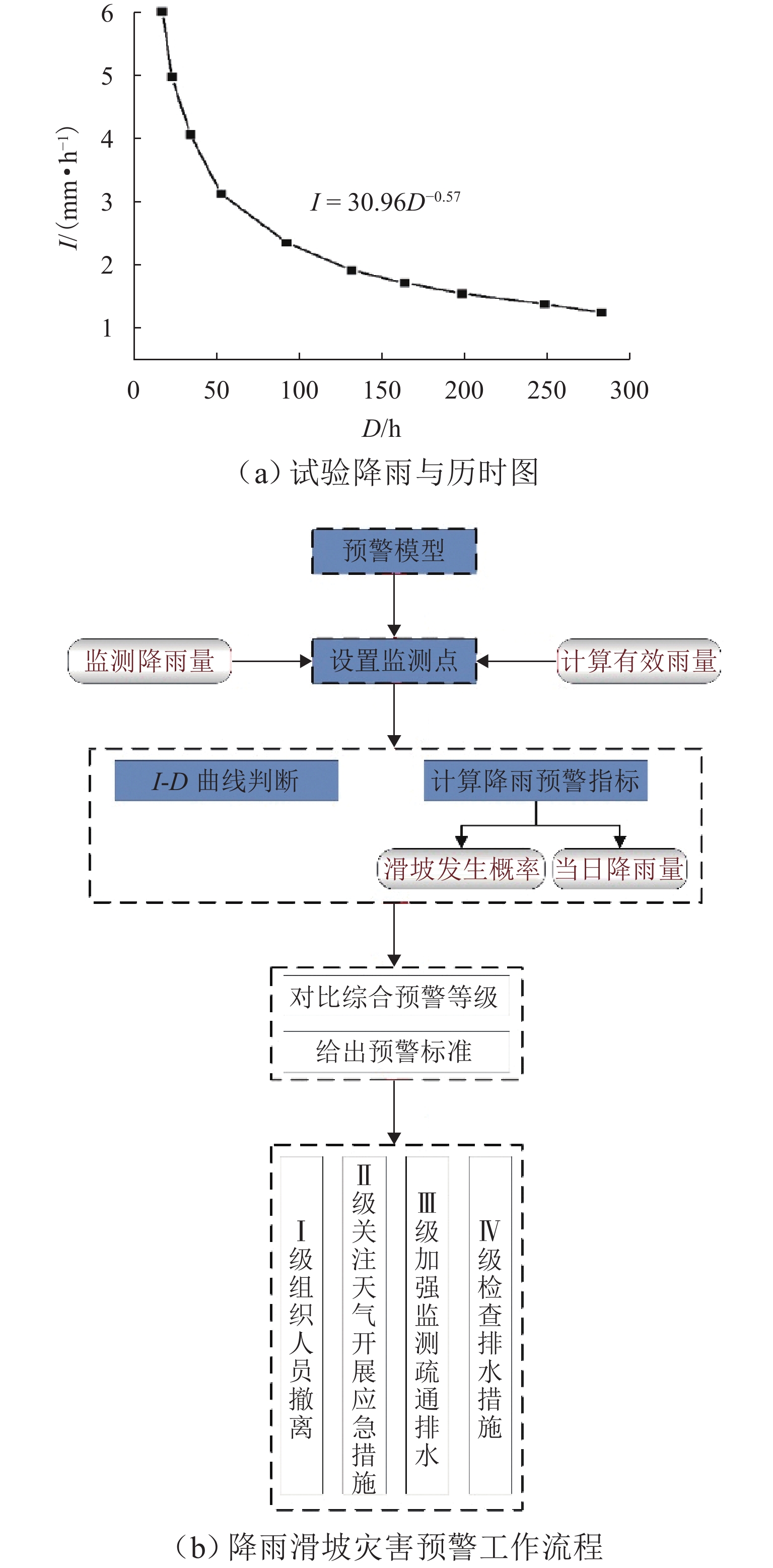
表 1 昆明铁路局威红线附近区段边坡降雨警戒值[26]
Table 1. Rainfall warning value of slopes near Weihong Line for Kunming Railway Bureau[26]
警戒值 K 采取措施 3 d 连续累计
降雨量/mm降雨强度/
(mm•h−1)38 11 1.15≤K<1.20 加强巡守 56 16 1.10≤K<1.15 固定看守 89 25 1.05≤K<1.10 固定看守(限速) 113 32 K<1.05 固定看守(限速) 表 2 地表变形监测技术及其特点
Table 2. Surface deformation-based monitoring technology and characteristics
监测技术 测量精度 适用条件 优缺点 天基 GNSS[29] mm~cm 级 适用于较大区域滑坡的长期观测 受飞行高度、地形、植被和大气延迟误差等影响,数据后处理较复杂 InSAR[30] mm~cm 级 大范围、长周期观测包括坡表沉降、裂缝等 空基 航空摄影[31] mm~m 级 小区域的三维快速测量 受到复杂地形条件影响 机载LiDAR[32] mm~m 级 小区域精确测量 受植被影响小,测量精准 地基 GB-InSAR[33] 亚 mm 级 全天候、实时监测滑坡区域的变形 受环境对监测结果的影响较大 自动全站仪[34] 0.5~5.0 mm 适于较小范围内处于加速变形阶段前的滑坡 受通视条件、大气条件和植被影响 裂缝计[35] 适于较小范围内处于加速变形阶段的滑坡 埋深过程较为繁琐 分布式光纤[22] 0.01 mm 级 适于长距离、大范围滑坡体宏观实时监测 连续监测,灵敏度高,成本较高 三维激光
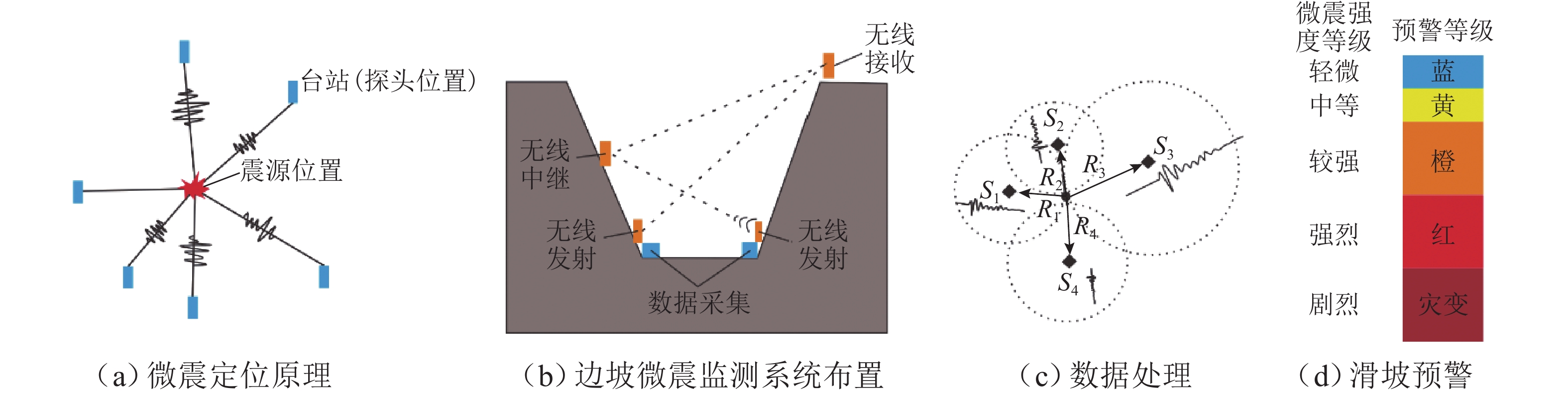
扫描[36]mm 级 适于滑坡不同变形阶段 地表三维空间位移与沉降等地貌变形监测 成本高,数据处理复杂 地震仪微震
监测[37]cm~m 级 区域性大范围岩质边坡局部破裂 信号分析较为繁琐,地震事件和滑坡变形的关系有待明确 表 3 滑坡深部变形监测技术及其特点
Table 3. Deep deformation-based landslide monitoring technology and characteristics
表 4 常用滑坡预测解译机器学习模型
Table 4. Common machine learning models for landslide prediction and interpretation
常用滑坡解译模型 优点 缺点 逻辑回归 学习成本较低、易于理解和实现 发生欠拟合现象、分类精度可能不高 决策树 适合评价离散小规模样本 评价大量连续变量和多类别样本效果欠佳 人工神经网络 准确度高、学习能力强 需要大量参数,学习时间过长,评价结果不稳定 支持向量机 结果易解释 崩塌滑坡易发性,存在运行时间较长、存在过拟合的问题 集成算法(bagging、随机森林、boosting、stacking) 对样本数量要求较低 在某些噪音值较大的样本来进行危险性评价时可能会发生过拟合现象 深度学习 学习能力强、覆盖范围广 准确性受样本数量的影响较大 -
[1] 自然资源部地质灾害技术指导中心. 全国地质灾害通报(2012-2021)[Z]. [2023-10-01]. [2] 彭建兵, 崔鹏, 庄建琦. 川藏铁路对工程地质提出的挑战[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2020, 39(12): 2377-2389.PENG JianBing, CUI Peng, ZHUANG Jianqi. Challenges to engineering geology of Sichuan—Tibet railway[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2020, 39(12): 2377-2389. [3] 孙云强, 邱鑫鹏, 陈常勇, 等. GNSS和InSAR约束的2023积石山Ms6.2地震同震滑动分布[J]. 地震工程学报, 2024, 46(4): 867-879.SUN Yunqiang, QIU Xinpeng, CHEN Changyong, et al. GNSS and InSAR derived coseismic slip distribution of the 2023 Jishishan Ms6.2 earthquake[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal, 2024, 46(4): 867-879. [4] 徐靓, 程刚, 朱鸿鹄. 基于空天地内一体化的滑坡监测技术研究[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2021, 58(9): 0900006.1-0900006.14.XU Liang, CHENG Gang, ZHU Honghu. Research review of landslide monitoring methods based on integration of space-air-ground-interior[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2021, 58(9): 0900006.1-0900006.14. [5] 张凯翔. 基于“3S”技术的地质灾害监测预警系统在我国应用现状[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2020, 31(6): 1-11.ZHANG Kaixiang. Review on geological disaster monitoring and early warning system based on “3S” technology in China[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2020, 31(6): 1-11. [6] LIU Z J, QIU H J, ZHU Y R, et al. Efficient identification and monitoring of landslides by time-series InSAR combining single- and multi-look phases[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(4): 1026.1-1026.24. [7] CASAGLI N, INTRIERI E, TOFANI V, et al. Landslide detection, monitoring and prediction with remote-sensing techniques[J]. Nature Reviews Earth & Environment, 2023, 4: 51-64. [8] XU Q, ZHAO B, DAI K R, et al. Remote sensing for landslide investigations: a progress report from China[J]. Engineering Geology, 2023, 321: 107156.1-107156.26. [9] 刘斌, 张丽, 葛大庆, 等. 陆地探测-1号卫星滑坡大变形InSAR监测应用[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2024, 49(10): 1753-1762.LIU Bin, ZHANG Li, GE Daqing, et al. Application of InSAR monitoring large deformation of landslides using lutan-1 constellation[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2024, 49(10): 1753-1762. [10] 杨正荣, 喜文飞, 史正涛, 等. 基于SBAS-InSAR技术的白鹤滩水电站库岸潜在滑坡变形分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2022, 33(5): 83-92.YANG Zhengrong, XI Wenfei, SHI Zhengtao, et al. Deformation analysis in the bank slopes in the reservoir area of Baihetan Hydropower Station based on SBAS-InSAR technology[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2022, 33(5): 83-92. [11] WANG D Y, ZHU H H, WANG J, et al. Characterization of sliding surface deformation and stability evaluation of landslides with fiber–optic strain sensing nerves[J]. Engineering Geology, 2023, 314: 107011.1-107011.16. [12] GIORDAN D, ADAMS M S, AICARDI I, et al. The use of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) for engineering geology applications[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 2020, 79(7): 3437-3481. doi: 10.1007/s10064-020-01766-2 [13] SHI B, XU X J, WANG D, et al. Study on BOTDR-based distributed optical fiber strain measurement for tunnel health diagnosis[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2005, 24(15): 2622-2628. [14] ZHANG Y G, TANG J, HE Z Y, et al. A novel displacement prediction method using gated recurrent unit model with time series analysis in the Erdaohe landslide[J]. Natural Hazards, 2021, 105(1): 783-813. doi: 10.1007/s11069-020-04337-6 [15] ZHANG W G, LI H R, TANG L B, et al. Displacement prediction of Jiuxianping landslide using gated recurrent unit (GRU) networks[J]. Acta Geotechnica, 2022, 17(4): 1367-1382. doi: 10.1007/s11440-022-01495-8 [16] YANG B B, YIN K L, LACASSE S, et al. Time series analysis and long short-term memory neural network to predict landslide displacement[J]. Landslides, 2019, 16(4): 677-694. doi: 10.1007/s10346-018-01127-x [17] 李高, 谭建民, 王世梅, 等. 滑坡对降雨响应的多指标监测及综合预警探析: 以赣南罗坳滑坡为例[J]. 地学前缘, 2021, 28(6): 283-294.LI Gao, TAN Jianmin, WANG Shimei, et al. Multi-index monitoring and comprehensive early warning of landslides in response to rainfall: An example of the Luoao landslide in southern Jiangxi Province[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2021, 28(6): 283-294. [18] 程刚, 张昊宇, 朱鸿鹄, 等. 边坡全维度监测技术与模型试验研究[J]. 高校地质学报, 2024, 30(2): 207-217.CHENG Gang, ZHANG Haoyu, ZHU Honghu, et al. Research progress of full dimension monitoring technology and model test of slope[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2024, 30(2): 207-217. [19] 杜源. 高连续性GNSS实时滑坡监测算法与应用研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2021. [20] 董岳, 丁明涛, 李鑫泷, 等. 基于光学遥感像素偏移量的金沙江流域2018年白格滑坡演变过程[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2022, 44(6): 1002-1015.DONG Yue, DING Mingtao, LI Xinlong, et al. Evolution of the 2018 baige landslides revealed by optical remote sensing pixel offsets in Jinsha River Basin, China[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 2022, 44(6): 1002-1015. [21] 姚鑫, 邓建辉, 刘星洪, 等. 青藏高原泛三江并流区活动性滑坡InSAR初步识别与发育规律分析[J]. 工程科学与技术, 2020, 52(5): 16-37.YAO Xin, DENG Jianhui, LIU Xinghong, et al. Primary recognition of active landslides and development rule analysis for pan three-river-parallel territory of Tibet Plateau[J]. Advanced Engineering Sciences, 2020, 52(5): 16-37. [22] 程刚, 施斌, 朱鸿鹄, 等. 光纤和砂土界面耦合性能的分布式感测试验研究[J]. 高校地质学报, 2019, 25(4): 487-494.CHENG Gang, SHI Bin, ZHU Honghu, et al. Experimental study on coupling performance of fiber and sand interface based on distributed sensing[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2019, 25(4): 487-494. [23] 黄润秋, 许强.中国典型灾难性滑坡[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2008. [24] 张利勇. 周至任家城黄土边坡稳定性评价及监测预警研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2014. [25] 黄雯, 方琼, 王国卫, 等. 湖南茶陵滑坡空间预警的降雨临界值初步分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2014, 25(3): 38-42.HUANG Wen, FANG Qiong, WANG Guowei, et al. Preliminary study on the critical rainfall for landslide space early warning in Chaling County of Hunan Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2014, 25(3): 38-42. [26] 张有会, 颜志雄. 威红铁路降雨诱发边坡溜坍预警值的研究[J]. 铁道建筑, 2013, 53(11): 83-86. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1995.2013.11.27ZHANG Youhui, YAN Zhixiong. Study on early warning value of slope slip induced by rainfall in Wei-Hong railway[J]. Railway Engineering, 2013, 53(11): 83-86. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1995.2013.11.27 [27] 孙徐. 降雨型岩质滑坡预警模型与判据研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2014. [28] 戴福初, 邓建辉. 青藏高原东南三江流域滑坡灾害发育特征[J]. 工程科学与技术, 2020, 52(5): 3-15.DAI Fuchu, DENG Jianhui. Development Characteristics of landslide hazards in three-rivers basin of southeast Tibetan Plateau[J]. Advanced Engineering Sciences, 2020, 52(5): 3-15. [29] 张勤, 白正伟, 黄观文, 等. GNSS滑坡监测预警技术进展[J]. 测绘学报, 2022, 51(10): 1985-2000.ZHANG Qin, BAI Zhengwei, HUANG Guanwen, et al. Review of GNSS Landslide Monitoring and Early Warning[J]. ACTA Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2022, 51(10): 1985-2000. [30] SABER R, ISIK V, CAGLAYAN A, et al. Sentinel-1 InSAR observations and time-series analysis of co- and postseismic deformation mechanisms of the 2021 Mw 5.8 Bandar Ganaveh Earthquake, Southern Iran[J]. Journal of Mountain Science, 2023, 20(4): 911-927. doi: 10.1007/s11629-022-7574-4 [31] ZHANG J Y, LI H B, YANG X G, et al. Quantitative assessment of rockfall hazard in post-landslide high rock slope through terrestrial laser scanning[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 2021, 80(10): 7315-7331. doi: 10.1007/s10064-021-02426-9 [32] ISMAIL A, AHMAD SAFUAN A R, SA’ARI R, et al. Application of combined terrestrial laser scanning and unmanned aerial vehicle digital photogrammetry method in high rock slope stability analysis: a case study[J]. Measurement, 2022, 195: 111161.1-111161.17. [33] 段斌, 何加平, 覃事河, 等. 基于GB-InSAR技术的水电工程高边坡变形监测[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2022, 32(增2): 64-69.DUAN Bin, HE Jiaping, QIN Shihe, et al. Surface deformation monitoring of high slope in hydropower project based on GB-InSAR technology[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2022, 32(S2): 64-69. [34] 韩军强, 黄观武, 黄观文, 等. 多种监测手段在滑坡变形中的组合应用[J]. 测绘科学, 2019, 44(11): 116-122.HAN Junqiang, HUANG Guanwu, HUANG Guanwen, et al. Multi-monitoring methods joint application in landslide deformation monitoring[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 2019, 44(11): 116-122. [35] 许强, 彭大雷, 何朝阳, 等. 突发型黄土滑坡监测预警理论方法研究——以甘肃黑方台为例[J]. 工程地质学报, 2020, 28(1): 111-121.XU Qiang, PENG Dalei, HE Chaoyang, et al. Theory and method of monitoring and early warning for sudden loess landslide—a case study at Heifangtai Terrace[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2020, 28(1): 111-121. [36] DONATI D, RABUS B, ENGELBRECHT J, et al. A robust SAR speckle tracking workflow for measuring and interpreting the 3D surface displacement of landslides[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(15): 3048.1-3048.19. doi: 10.3390/rs13153048 [37] 韩侃, 陈贤丰, 杨文斌, 等. 基于微震监测的川藏铁路某隧道岩爆预测研究[J]. 铁道工程学报, 2020, 37(11): 90-95. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2020.11.016HAN Kan, CHEN Xianfeng, YANG Wenbin, et al. Research on the rock burst prediction of a tunnel in Sichuan-Tibet Railway based on microseismic monitoring[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society, 2020, 37(11): 90-95. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2020.11.016 [38] 李振洪, 张成龙, 陈博, 等. 一种基于多源遥感的滑坡防灾技术框架及其工程应用[J]. 地球科学, 2022, 47(6): 1901-1916. doi: 10.3321/j.issn.1000-2383.2022.6.dqkx202206001LI Zhenhong, ZHANG Chenglong, CHEN Bo, et al. A technical framework of landslide prevention based on multi-source remote sensing and its engineering application[J]. Earth Science, 2022, 47(6): 1901-1916. doi: 10.3321/j.issn.1000-2383.2022.6.dqkx202206001 [39] 肖玉钢, 姜卫平, 陈华, 等. 北斗卫星导航系统的毫米级精度变形监测算法与实现[J]. 测绘学报, 2016, 45(1): 16-21.XIAO Yugang, JIANG Weiping, CHEN Hua, et al. Research and realization of deformation monitoring algorithm with millimeter level precision based on BeiDou navigation satellite system[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2016, 45(1): 16-21. [40] 黄观文, 黄观武, 杜源, 等. 一种基于北斗云的低成本滑坡实时监测系统[J]. 工程地质学报, 2018, 26(4): 1008-1016.HUANG Guanwen, HUANG Guanwu, DU Yuan, et al. A lowcost real-time monitoring system for landslide deformaion with Beidou cloud[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2018, 26(4): 1008-1016. [41] 余斌, 李松, 谢凌霄, 等. 改进TS-InSAR方法的白格滑坡灾前-灾后形变演化特征分析[J]. 测绘通报, 2022(11): 8-12.YU Bin, LI Song, XIE Lingxiao, et al. Analysis of deformation evolution characteristics of Baige landslide before and after disaster based on improved TS-InSAR method[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, 2022(11): 8-12. [42] 王德军, 万田宝, 孙晓东, 等. 基于三维激光扫描的植被覆盖边坡监测[J]. 测绘通报, 2023(12): 112-115.WANG Dejun, WAN Tianbao, SUN Xiaodong, et al. Monitoring of vegetation covered slopes based on 3D laser[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, 2023(12): 112-115. [43] 张文, 韩博, 孙昊林, 等. 高陡岩质斜坡的结构面非接触式采集技术与三维裂隙网络模拟研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 2020, 28(2): 221-231.ZHANG Wen, HAN Bo, SUN Haolin, et al. Non-contact collection and 3d fracture network modell-ing for high-steep rock slopes[J]. Journal [44] 许强, 郭晨, 董秀军. 地质灾害航空遥感技术应用现状及展望[J]. 测绘学报, 2022, 51(10): 2020-2033. doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2022.20220302XU Qiang, GUO Chen, DONG Xiujun. Application status and prospect of aerial remote sensing technology for geohazards[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2022, 51(10): 2020-2033. doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2022.20220302 [45] ZHANG L, SHI B, ZHU H H, et al. PSO-SVM-based deep displacement prediction of Majiagou landslide considering the deformation hysteresis effect[J]. Landslides, 2021, 18(1): 179-193. doi: 10.1007/s10346-020-01426-2 [46] ZHANG L, SHI B, ZHU H H, et al. A machine learning method for inclinometer lateral deflection calculation based on distributed strain sensing technology[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 2020, 79(7): 3383-3401. doi: 10.1007/s10064-020-01749-3 [47] 何荣, 陆广. 基于三维激光扫描的矿区地表倾斜值提取方法研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2020, 48(11): 199-205.HE Rong, LU Guang. Study on extraction method of surface deformation tilt based on 3D laser scanning[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2020, 48(11): 199-205. [48] ZAN W B, ZHANG W J, WANG N, et al. Stability analysis of complex terrain slope based on multi-source point cloud fusion[J]. Journal of Mountain Science, 2022, 19(9): 2703-2714. doi: 10.1007/s11629-022-7307-8 [49] 叶飞, 张世明, 孙振勇, 等. 移动背包三维激光扫描系统在陡岸水库测绘中的应用: 以白鹤滩水电站库区典型河段为例[J]. 测绘通报, 2023(10): 173-176.YE Fei, ZHANG Shiming, SUN Zhenyong, et al. Application of the backpack laser scanning on steep reservoir bank monitoring: taking the typical reach of the reservoir area of Baihetan hydropower station[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, 2023(10): 173-176. [50] 梁玉飞, 裴向军, 崔圣华, 等. 基于地面三维激光点云的滑坡破坏边界岩体结构特征分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2021, 40(6): 1209-1225.LIANG Yufei, PEI Xiangjun, CUI Shenghua, et al. Analysis of rock mass structure characteristics of landslide boundaries based on ground 3D laser point cloud[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2021, 40(6): 1209-1225. [51] LI H B, QI S C, YANG X G, et al. Geological survey and unstable rock block movement monitoring of a post-earthquake high rock slope using terrestrial laser scanning[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2020, 53(10): 4523-4537. doi: 10.1007/s00603-020-02178-0 [52] 刘兴宗, 唐春安, 李连崇, 等. 基于渐进微震损伤效应的蓄水期库岸稳定性分析[J]. 人民长江, 2019, 50(3): 151-155.LIU Xingzong, TANG Chun’an, LI Lianchong, et al. Stability analysis of reservoir bank slope during reservoir impoundment based on effect of progressive microseismic damage[J]. Yangtze River, 2019, 50(3): 151-155. [53] 刘秀敏, 王月, 陈从新, 等. 地质结构影响下的金属矿山地压显现机制初探[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2022, 41(12): 2451-2459.LIU Xiumin, WANG Yue, CHEN Congxin, et al. Preliminary study on the occurrence mechanism of ground pressure in iron mines under the influence of geological discontinuities[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2022, 41(12): 2451-2459. [54] 盛敏汉, 储日升, 危自根, 等. 四川省理县西山村滑坡运动变形过程中的微震研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 2018, 61(1): 171-182. doi: 10.6038/cjg2018L0367SHENG Minhan, CHU Risheng, WEI Zigen, et al. Study of microseismicity caused by Xishancun Landslide deformation in Li county, Sichuan Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2018, 61(1): 171-182. doi: 10.6038/cjg2018L0367 [55] 李红刚. TDR技术在滑坡变形监测中的适宜性试验研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学, 2009. [56] 邓李政, 袁宏永, 张鸣之, 等. 滑坡变形监测预警技术研究进展[J]. 清华大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 63(6): 849-864.DENG Lizheng, YUAN Hongyong, ZHANG Mingzhi, et al. Research progress on landslides deformation monitoring and early warning technology[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University (Science and Technology), 2023, 63(6): 849-864. [57] 陈杨, 邓李政, 黄丽达, 等. 基于声发射监测的滑坡过程预警模型[J]. 清华大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 62(6): 1052-1058.CHEN Yang, DENG Lizheng, HUANG Lida, et al. Landslide early warning model based on acoustic emission monitoring[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University (Science and Technology), 2022, 62(6): 1052-1058. [58] SMITH A, DIXON N, FOWMES G J. Early detection of first-time slope failures using acoustic emission measurements: large-scale physical modelling[J]. Géotechnique, 2017, 67(2): 138-152. [59] 何满潮, 任树林, 陶志刚. 滑坡地质灾害牛顿力远程监测预警系统及工程应用[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2021, 40(11): 2161-2172.HE Manchao, REN Shulin, TAO Zhigang. Remote monitoring and forecasting system of Newton force for landslide geological hazards and its engineering application[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2021, 40(11): 2161-2172. [60] 许强, 朱星, 李为乐, 等. “天-空-地”协同滑坡监测技术进展[J]. 测绘学报, 2022, 51(7): 1416-1436. doi: 10.11947/j.issn.1001-1595.2022.7.chxb202207027XU Qiang, ZHU Xing, LI weile, et al. Technical progress of space-air-groung collaborative monitoring of landslide[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2022, 51(7): 1416-1436. doi: 10.11947/j.issn.1001-1595.2022.7.chxb202207027 [61] 许强. 对滑坡监测预警相关问题的认识与思考[J]. 工程地质学报, 2020, 28(2): 360-374.XU Qiang. Understanding the landslide monitoring and early warn-ing: consideration to practical issues[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2020, 28(2): 360-374. [62] 赵会芹, 于博, 陈方, 等. 基于高分辨率卫星遥感影像滑坡提取方法研究现状[J]. 遥感技术与应用, 2023, 38(1): 108-115.ZHAO Huiqin, YU Bo, CHEN Fang, et al. Research Status of Landslide Extraction Methods based on High-resolution Satellite Remote Sensing Images[J]. Remote Sensing Technology and Application, 2023, 38(1): 108-115. [63] ZHANG B, ZHANG M S, SUN P P, et al. Resistivity is used as a tool to evaluate the variability of soil water content[J]. Journal of Mountain Science, 2022, 19(12): 3533-3547. doi: 10.1007/s11629-022-7445-z [64] EKSTRÖM G, STARK C P. Simple scaling of catastrophic landslide dynamics[J]. Science, 2013, 339(6126): 1416-1419. doi: 10.1126/science.1232887 [65] LI Z Y, HUANG X H, YU D, et al. Broadband-seismic analysis of a massive landslide in southwestern China: dynamics and fragmentation implications[J]. Geomorphology, 2019, 336: 31-39. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2019.03.024 [66] ZHANG Z, HE S M, LIU W, et al. Source characteristics and dynamics of the October 2018 Baige landslide revealed by broadband seismograms[J]. Landslides, 2019, 16(4): 777-785. doi: 10.1007/s10346-019-01145-3 [67] 许世民. 基于滑震信号分析的特大崩滑灾害数值模拟研究[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2021. [68] PICIULLO L, CALVELLO M, CEPEDA J M. Territorial early warning systems for rainfall-induced landslides[J]. Earth Science Reviews, 2018, 179: 228-247. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2018.02.013 [69] 宋宇飞, 曹琰波, 范文, 等. 基于贝叶斯方法的降雨诱发滑坡概率型预警模型研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2023, 42(3): 558-574.SONG Yufei, CAO Yanbo, FAN Wen, et al. Probabilistic early warning model for rainfall-induced landslides based on Bayesian approach[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2023, 42(3): 558-574. [70] 刘艳辉, 黄俊宝, 肖锐铧, 等. 基于随机森林的福建省区域滑坡灾害预警模型研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 2022, 30(3): 944-955.LIU Yanhui, HUANG Junbao, XIAO Ruihua, et al. Study on early warning model for regional landslides based on random forest in Fujian Province[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2022, 30(3): 944-955. [71] 张真. 陕北黄土边坡降雨入渗现场试验及其灾害预警[D]. 西安: 西安理工大学, 2018 [72] 吴益平, 张秋霞, 唐辉明, 等. 基于有效降雨强度的滑坡灾害危险性预警[J]. 地球科学, 2014, 39(7): 889-895.WU Yiping, ZHANG Qiuxia, TANG Huiming, et al. Landslide hazard warning based on effective rainfall intensity[J]. Earth Science, 2014, 39(7): 889-895. [73] 朱少帅. 基于监测资料的黄河上游某水电站坝前右岸变形岸坡演化趋势研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2015. [74] 刘传正, 王建新. 自然灾害的基本型式及防控对策研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2023, 42(2): 275-291.LIU Chuanzheng, WANG Jianxin. Basic patterns of natural disasters and some countermeasures for risk mitigation[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2023, 42(2): 275-291. [75] SAITO M. Research on forecasting the time of occurrence of slope failure[C]//Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering, Montreal. TOKYO: Railway Technical Research Institute/Tetsudo Gijutsu Kenkyujo, 1969: 135-142. [76] 李阳春, 刘黔云, 李潇, 等. 基于机器学习的滑坡崩塌地质灾害气象风险预警研究[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2021, 32(3): 118-123.LI Yangchun, LIU Qianyun, LI Xiao, et al. Exploring early warning and forecasting of meteorological risk of landslide and rockfall induced by meteorological factors by the approach of machine learning[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2021, 32(3): 118-123. [77] MYRONIDIS D, PAPAGEORGIOU C, THEOPHANOUS S. Landslide susceptibility mapping based on landslide history and analytic hierarchy process (AHP)[J]. Natural Hazards, 2016, 81(1): 245-263. doi: 10.1007/s11069-015-2075-1 [78] COROMINAS J, MOYA J. A review of assessing landslide frequency for hazard zoning purposes[J]. Engineering Geology, 2008, 102(3/4): 193-213. [79] COROMINAS J, VAN WESTEN C, FRATTINI P, et al. Recommendations for the quantitative analysis of landslide risk[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 2014, 73(2): 209-263. [80] SONG R H, HIROMU D, KAZUTOKI A, et al. Modeling the potential distribution of shallow-seated landslides using the weights of evidence method and a logistic regression model: a case study of the Sabae Area, Japan[J]. International Journal of Sediment Research, 2008, 23(2): 106-118. doi: 10.1016/S1001-6279(08)60010-4 [81] SUN W Y, TIAN Y S, MU X M, et al. Loess landslide inventory map based on GF-1 satellite imagery[J]. Remote Sensing, 2017, 9(4): 314.1-314.17. [82] QIN Y G, YANG G L, LU K P, et al. Performance evaluation of five GIS-based models for landslide susceptibility prediction and mapping: a case study of Kaiyang County, China[J]. Sustainability, 2021, 13(11): 6441.1-6441.20. [83] OTHMAN A A, GLOAGUEN R, ANDREANI L, et al. Improving landslide susceptibility mapping using morphometric features in the Mawat area, Kurdistan Region, NE Iraq: comparison of different statistical models[J]. Geomorphology, 2018, 319: 147-160. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2018.07.018 [84] PAWLUSZEK K. Landslide features identification and morphology investigation using high-resolution DEM derivatives[J]. Natural Hazards, 2019, 96(1): 311-330. doi: 10.1007/s11069-018-3543-1 [85] JI S P, YU D W, SHEN C Y, et al. Landslide detection from an open satellite imagery and digital elevation model dataset using attention boosted convolutional neural networks[J]. Landslides, 2020, 17(6): 1337-1352. doi: 10.1007/s10346-020-01353-2 [86] DOU J, YUNUS A P, BUI D T, et al. Improved landslide assessment using support vector machine with bagging, boosting, and stacking ensemble machine learning framework in a mountainous watershed, Japan[J]. Landslides, 2020, 17(3): 641-658. doi: 10.1007/s10346-019-01286-5 [87] DOU J, YUNUS A P, MERGHADI A, et al. Different sampling strategies for predicting landslide susceptibilities are deemed less consequential with deep learning[J]. The Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 720: 137320.1-137320.16. [88] SATO H P, HARP E L. Interpretation of earthquake-induced landslides triggered by the 12 May 2008, M7.9 Wenchuan earthquake in the Beichuan area, Sichuan Province, China using satellite imagery and Google Earth[J]. Landslides, 2009, 6(2): 153-159. doi: 10.1007/s10346-009-0147-6 [89] TANG H M, WASOWSKI J, JUANG C H. Geohazards in the three Gorges Reservoir Area, China—Lessons learned from decades of research[J]. Engineering Geology, 2019, 261: 105267.1-105267.42. [90] YUAN C, MOAYEDI H. Evaluation and comparison of the advanced metaheuristic and conventional machine learning methods for the prediction of landslide occurrence[J]. Engineering with Computers, 2020, 36(4): 1801-1811. doi: 10.1007/s00366-019-00798-x [91] 窦杰, 向子林, 许强, 等. 机器学习在滑坡智能防灾减灾中的应用与发展趋势[J]. 地球科学, 2023, 48(5): 1657-1674.DOU Jie, XIANG Zilin, XU Qiang, et al. Application and development trend of machine learning in landslide intelligent disaster prevention and mitigation[J]. Earth Science, 2023, 48(5): 1657-1674. [92] SUN D L, GU Q Y, WEN H J, et al. Assessment of landslide susceptibility along mountain highways based on different machine learning algorithms and mapping units by hybrid factors screening and sample optimization[J]. Gondwana Research, 2023, 123: 89-106. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2022.07.013 [93] ZHOU X Z, WEN H J, LI Z W, et al. An interpretable model for the susceptibility of rainfall-induced shallow landslides based on SHAP and XGBoost[J]. Geocarto International, 2022, 37(26): 13419-13450. doi: 10.1080/10106049.2022.2076928 [94] ZHOU C, YIN K L, CAO Y, et al. Application of time series analysis and PSO–SVM model in predicting the Bazimen landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir, China[J]. Engineering Geology, 2016, 204: 108-120. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2016.02.009 [95] MIAO F S, WU Y P, XIE Y H, et al. Prediction of landslide displacement with step-like behavior based on multialgorithm optimization and a support vector regression model[J]. Landslides, 2018, 15(3): 475-488. doi: 10.1007/s10346-017-0883-y [96] HUANG F M, HUANG J S, JIANG S H, et al. Landslide displacement prediction based on multivariate chaotic model and extreme learning machine[J]. Engineering Geology, 2017, 218: 173-186. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.01.016 [97] XU S L, NIU R Q. Displacement prediction of Baijiabao landslide based on empirical mode decomposition and long short-term memory neural network in Three Gorges area, China[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 2018, 111: 87-96. [98] MA J W, TANG H M, LIU X, et al. Establishment of a deformation forecasting model for a step-like landslide based on decision tree C5.0 and two-step cluster algorithms: a case study in the Three Gorges Reservoir area, China[J]. Landslides, 2017, 14(3): 1275-1281. doi: 10.1007/s10346-017-0804-0 [99] GUO Z Z, CHEN L X, GUI L, et al. Landslide displacement prediction based on variational mode decomposition and WA-GWO-BP model[J]. Landslides, 2020, 17(3): 567-583. doi: 10.1007/s10346-019-01314-4 [100] LIU Y, XU C, HUANG B, et al. Landslide displacement prediction based on multi-source data fusion and sensitivity states[J]. Engineering Geology, 2020, 271: 105608.1-105608.11. [101] 张梦涵, 魏进, 卞海丁. 基于机器学习的边坡稳定性分析方法——以国内618个边坡为例[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2022, 44(6): 1083-1095.ZHANG Menghan, WEI Jin, BIAN Haiding. Slope stability analysis method based on machine learning—taking 618 slopes in China as examples[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 2022, 44(6): 1083-1095. [102] 纪守领, 李进锋, 杜天宇, 等. 机器学习模型可解释性方法、应用与安全研究综述[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2019, 56(10): 2071-2096. doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2019.20190540JI Shouling, LI Jinfeng, DU Tianyu, et al. Survey on Techniques, applications and security of machine learning interpretability[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2019, 56(10): 2071-2096. doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2019.20190540 [103] 吕安琪, 李翠然, 谢健骊, 等. 起伏地形下无线传感器网络节点部署算法[J/OL]. 西南交通大学学报, 1-8 [2024-09-11]. [104] JI S P, DAI P Y, LU M, et al. Simultaneous cloud detection and removal from bitemporal remote sensing images using cascade convolutional neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 99: 1-17. [105] SHIRZADI A, SOLAIMANI K, ROSHAN M H, et al. Uncertainties of prediction accuracy in shallow landslide modeling: sample size and raster resolution[J]. CATENA, 2019, 178: 172-188. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2019.03.017 -





 下载:
下载: