Multi-Task Federated Learning for Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Swarms Based on Encoder-Decoder Architecture
-
摘要:
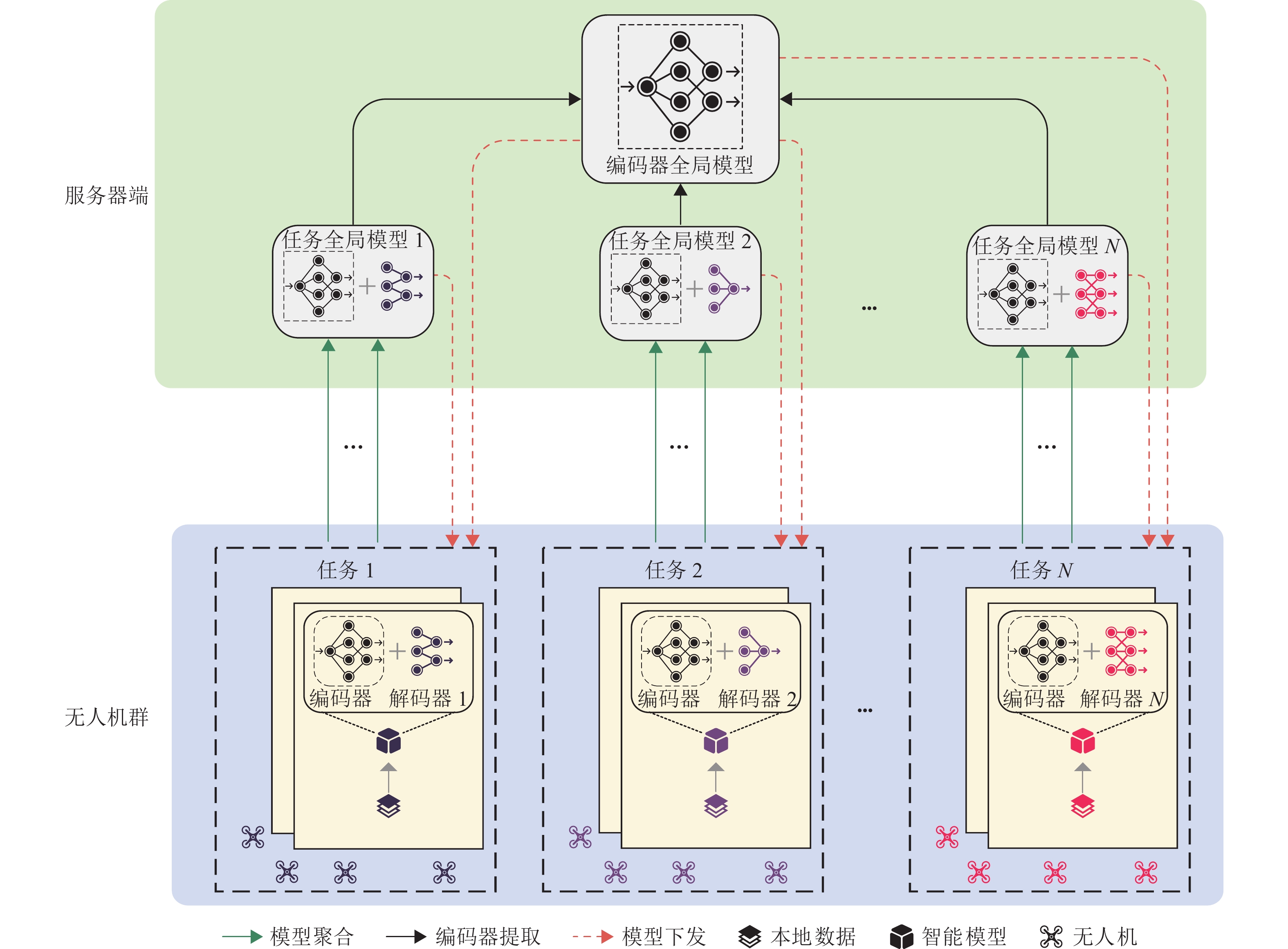
针对传统联邦学习在无人机群应用中的局限性——要求所有参与者执行相同任务并拥有相同的模型结构,本文探索一种适用于无人机群的多任务联邦学习方法,设计一种新的编-解码器架构,以加强执行不同任务的无人机之间的知识共享. 首先,为执行相同任务的无人机建立直接的知识分享机制,通过直接聚合方式实现同任务知识的有效融合;其次,对于执行不同任务的无人机,从所有无人机的编-解码器架构中提取编码器部分,构建一个全局编码器;最后,在训练环节,将本地编码器和全局编码器的信息整合到损失函数中,并通过迭代更新使本地解码器逐步逼近全局解码器,从而实现跨任务间的知识高效共享. 实验结果表明:相较于传统方法,所提出的方法使无人机群在3个单任务上的性能分别提升1.79%、0.37%和2.78%,仅在1个任务上性能略微下降0.38%,但整体性能仍提升2.38%.
Abstract:Traditional federated learning has limitations in unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) swarm applications, which require all participants to perform the same tasks and have the same model structure. Therefore, a multi-task federated learning (M-Fed) method suitable for UAV swarms was explored, and an innovative encoder-decoder architecture was designed to enhance knowledge sharing among UAVs performing different tasks. Firstly, a direct knowledge-sharing mechanism was established for UAVs performing the same tasks, enabling effective knowledge fusion of the same tasks through direct aggregation. Secondly, for UAVs performing different tasks, the encoder parts were extracted from the encoder-decoder architectures of all UAVs to construct a global encoder. Finally, during the training process, the information from both the local encoder and the global encoder was integrated into the loss function. Iterative updates were then performed to gradually align the local decoder with the global decoder, achieving efficient cross-task knowledge sharing. Experimental results demonstrate that compared to traditional methods, the proposed method improves the performance of UAV swarms by 1.79%, 0.37%, and 2.78% on three single tasks, respectively. Although there is a slight decrease of 0.38% in performance on one task, the overall performance is still significantly increased by 2.38%.
-
表 1 PASCAL-Context数据集实验结果
Table 1. Experimental results on PASCAL-Context dataset
方法 编码器 语义分割 人体部位分割 显著性估计 语义边界检测 增量/% 局部训练 ResNet-18 38.36 49.03 55.74 60.90 0 经典联邦学习 ResNet-18 49.71 52.66 59.09 61.20 10.87 M-Fed ResNet-18 50.60 52.46 59.31 62.90 13.25 表 2 PASCAL-Context数据集的量化结果
Table 2. Quantitative results on PASCAL-Context dataset

-
[1] 王志红,程尚. 无人驾驶场景多任务感知算法研究[J]. 武汉理工大学学报,2023,45(8): 140-146. doi: 10.3963/j.issn.1671-4431.2023.08.021WANG Zhihong, CHENG Shang. Research on multitask perception algorithms for unmanned driving scenarios[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology, 2023, 45(8): 140-146. doi: 10.3963/j.issn.1671-4431.2023.08.021 [2] 杜家豪,秦娜,贾鑫明,等. 基于联邦学习的多线路高速列车转向架故障诊断[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2024,59(1): 185-192.DU Jiahao, QIN Na, JIA Xinming, et al. Fault diagnosis of multiple railway high speed train bogies based on federated learning[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2024, 59(1): 185-192. [3] 姚献财,郑建超,郑鑫,等. 面向联邦学习的无人机轨迹与资源联合优化[J/OL]. 计算机工程与应用,2024:1-12 [2024-04-28]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2127.TP.20230 509.1840.007.html. [4] SHEN Y, QU Y B, DONG C, et al. Joint training and resource allocation optimization for federated learning in UAV swarm[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2023, 10(3): 2272-2284. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2022.3152829 [5] MO X P, XU J. Energy-efficient federated edge learning with joint communication and computation design[J]. Journal of Communications and Information Networks, 2021, 6(2): 110-124. doi: 10.23919/JCIN.2021.9475121 [6] PHAM Q V, LE M, HUYNH-THE T, et al. Energy-efficient federated learning over UAV-enabled wireless powered communications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2022, 71(5): 4977-4990. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2022.3150004 [7] HINTON G, VINYALS O, DEAN J. Distilling the knowledge in a neural network[J]. Computer Science, 2015, 14(7): 38-39. [8] XU D, OUYANG W L, WANG X G, et al. PAD-net: multi-tasks guided prediction-and-distillation network for simultaneous depth estimation and scene parsing[C]//2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City: IEEE, 2018: 675-684. [9] CHEN J H, ZHOU J Y, YE J P. Integrating low-rank and group-sparse structures for robust multi-task learning[C]//Proceedings of the 17th ACM SIGKDD international conference on Knowledge discovery and data mining. San Diego: ACM, 2011: 42-50. [10] ARGYRIOU A, EVGENIOU T, PONTIL M. Multi-task feature learning [C]//Conference on Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. [S.l.]: MIT Press, 2007: 41-48. [11] EVGENIOU T, PONTIL M. Regularized multi: task learning[C]//Proceedings of the Tenth ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. Seattle: ACM, 2004: 109-117. [12] KIM S, XING E P. Statistical estimation of correlated genome associations to a quantitative trait network[J]. PLoS Genetics, 2009, 5(8): e1000587.1-e1000587.18. [13] JACOB L, BACH F, VERT J P. Clustered multi-task learning: a convex formulation[C]//Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. New York: Springer-Verlag, 2008: 745-752. [14] ZHANG Y, YEUNG D Y. A convex formulation for learning task relationships in multi-task learning[C]// Proceedings of the Twenty-Sixth Conference on Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence. [S.l.]: AUAI Press, 2010: 733-742. [15] GONALVES A R, VON ZUBEN F J, BANERJEE A. Multi-task sparse structure learning with gaussian copula models[J]. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2016, 17(1): 1205-1234. [16] ZHOU F, SHUI C J, ABBASI M, et al. Task similarity estimation through adversarial multitask neural network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2021, 32(2): 466-480. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2020.3028022 [17] KOKKINOS I. UberNet: training a universal convolutional neural network for low-, mid-, and high-level vision using diverse datasets and limited memory[C]//2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Honolulu: IEEE, 2017: 5454-5463. [18] 赵佳琦,张迪,周勇,等. 基于深度强化学习的遥感图像可解释目标检测方法[J]. 模式识别与人工智能,2021,34(9): 777-786.ZHAO Jiaqi, ZHANG Di, ZHOU Yong, et al. Interpretable object detection method for remote sensing image based on deep reinforcement learning[J]. Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence, 2021, 34(9): 777-786. [19] MARTIN D R, FOWLKES C C, MALIK J. Learning to detect natural image boundaries using local brightness, color, and texture cues[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2004, 26(5): 530-549. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2004.1273918 -





 下载:
下载: