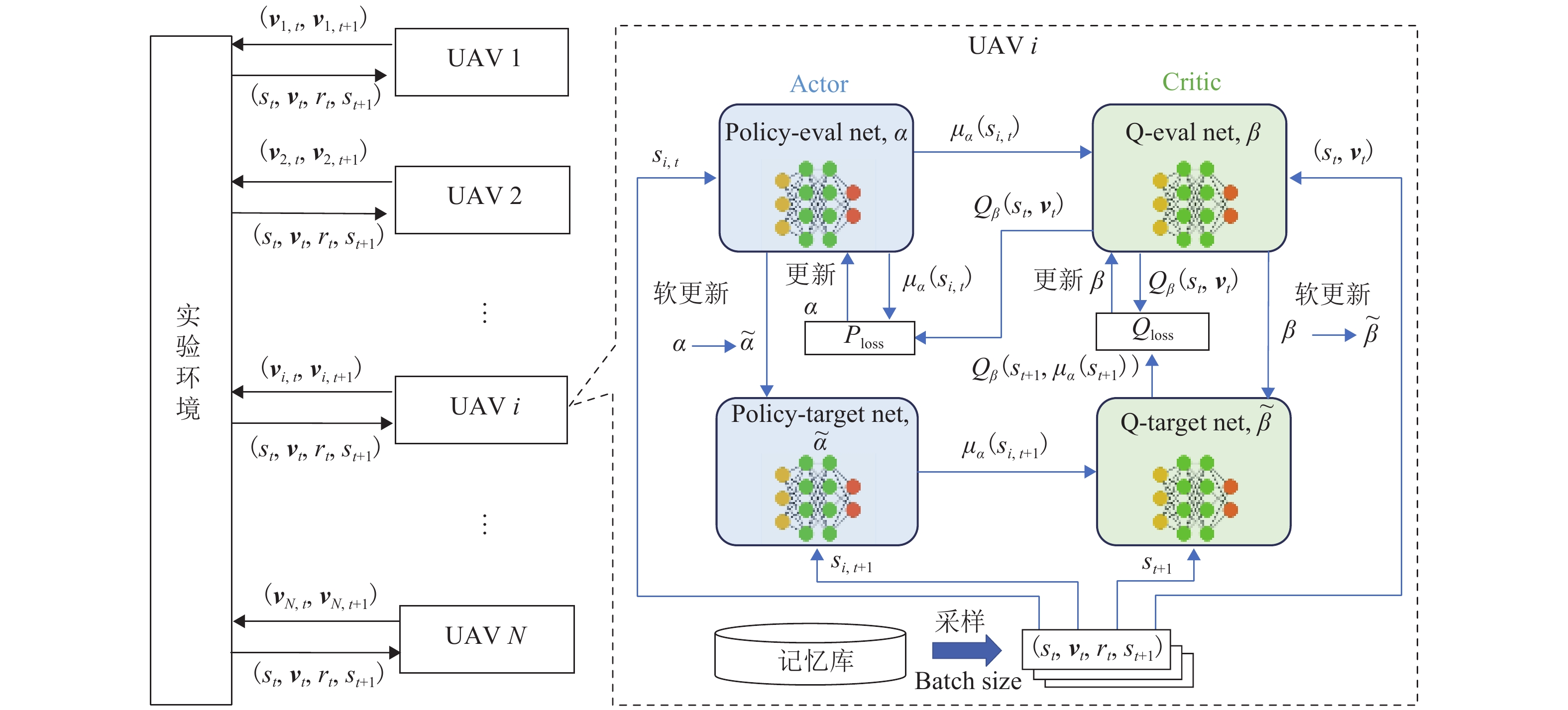
Optimization Control Strategy for Low-Altitude and Single-Layer Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Network Coverage
-
摘要:
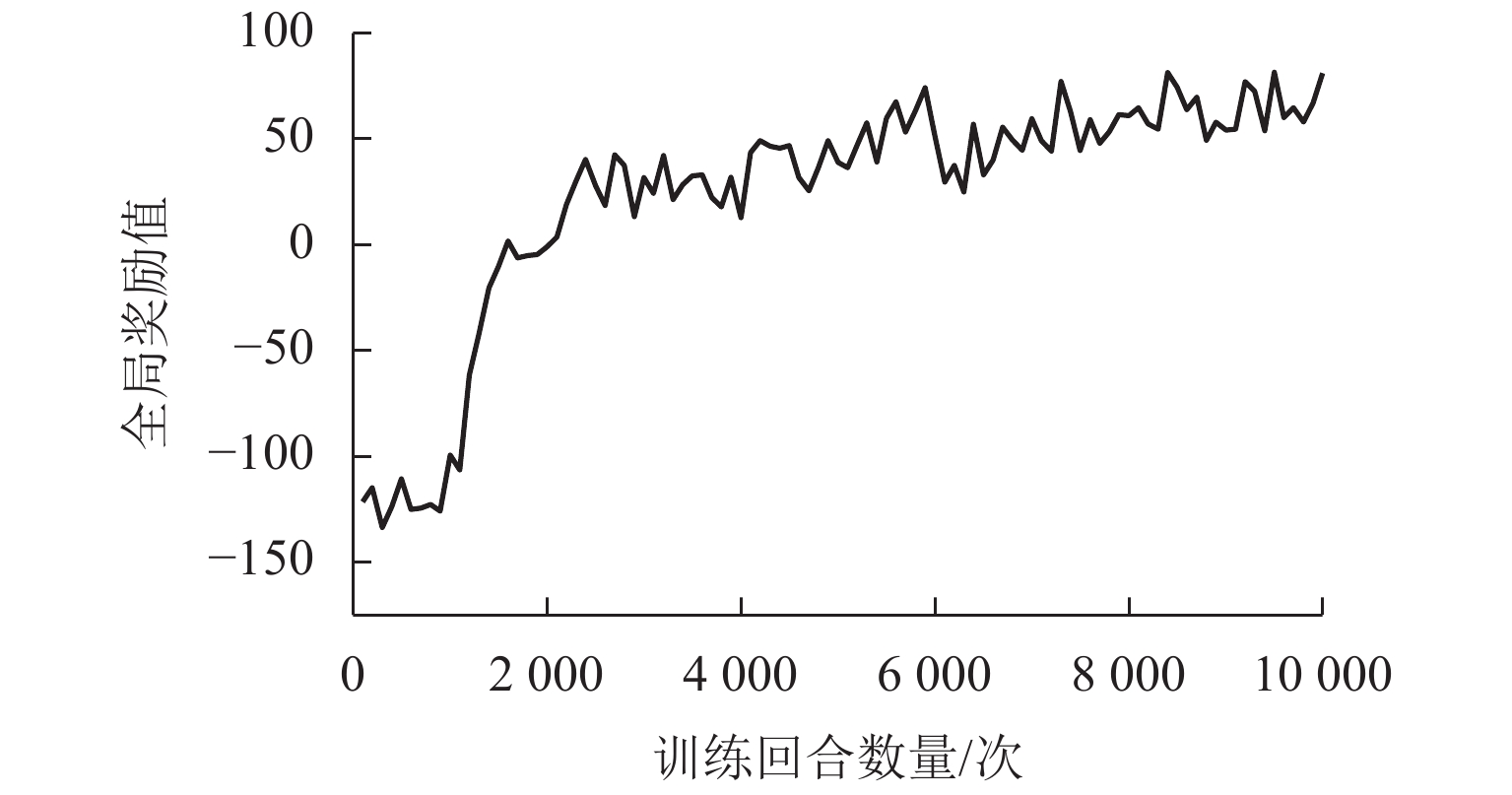
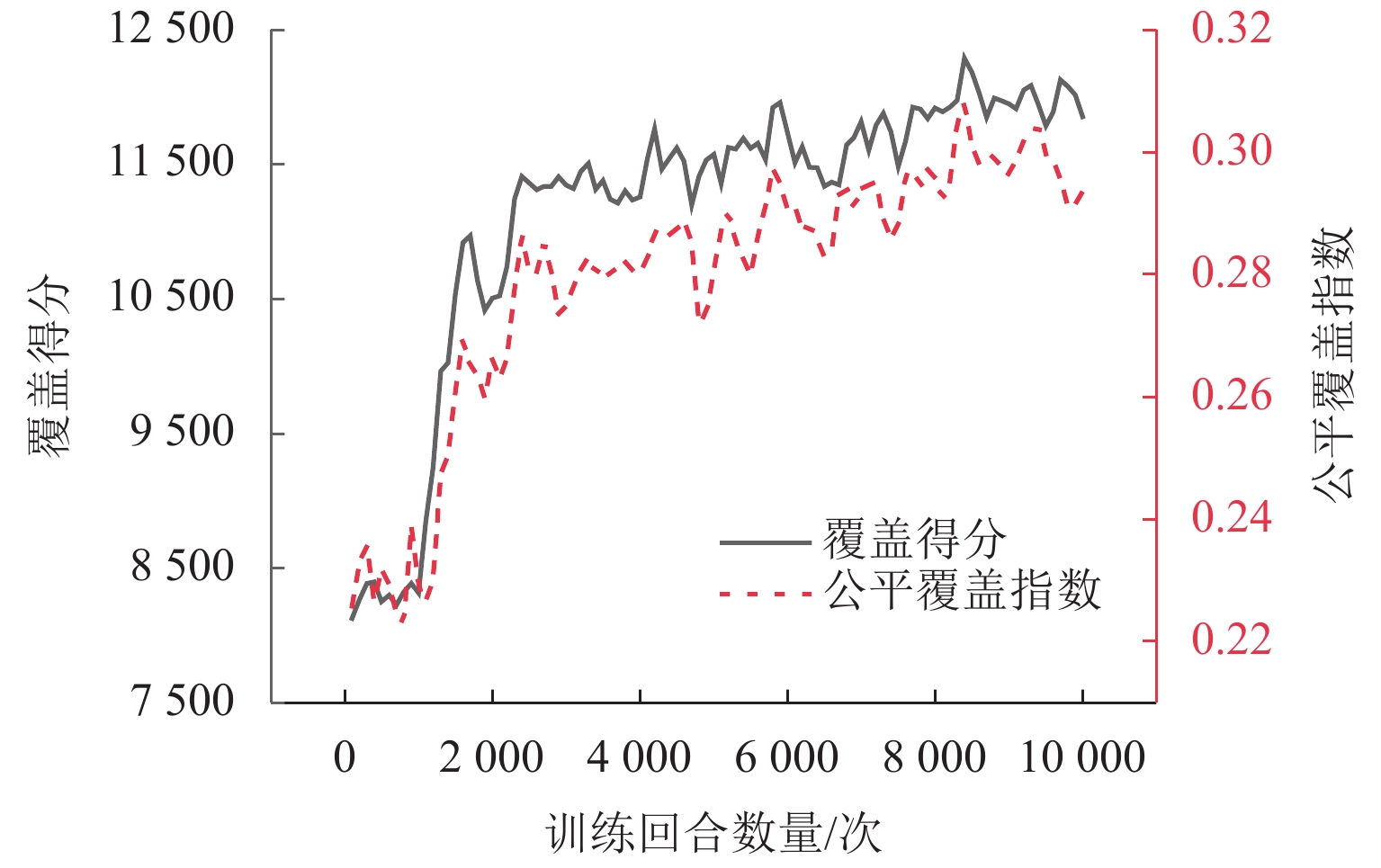
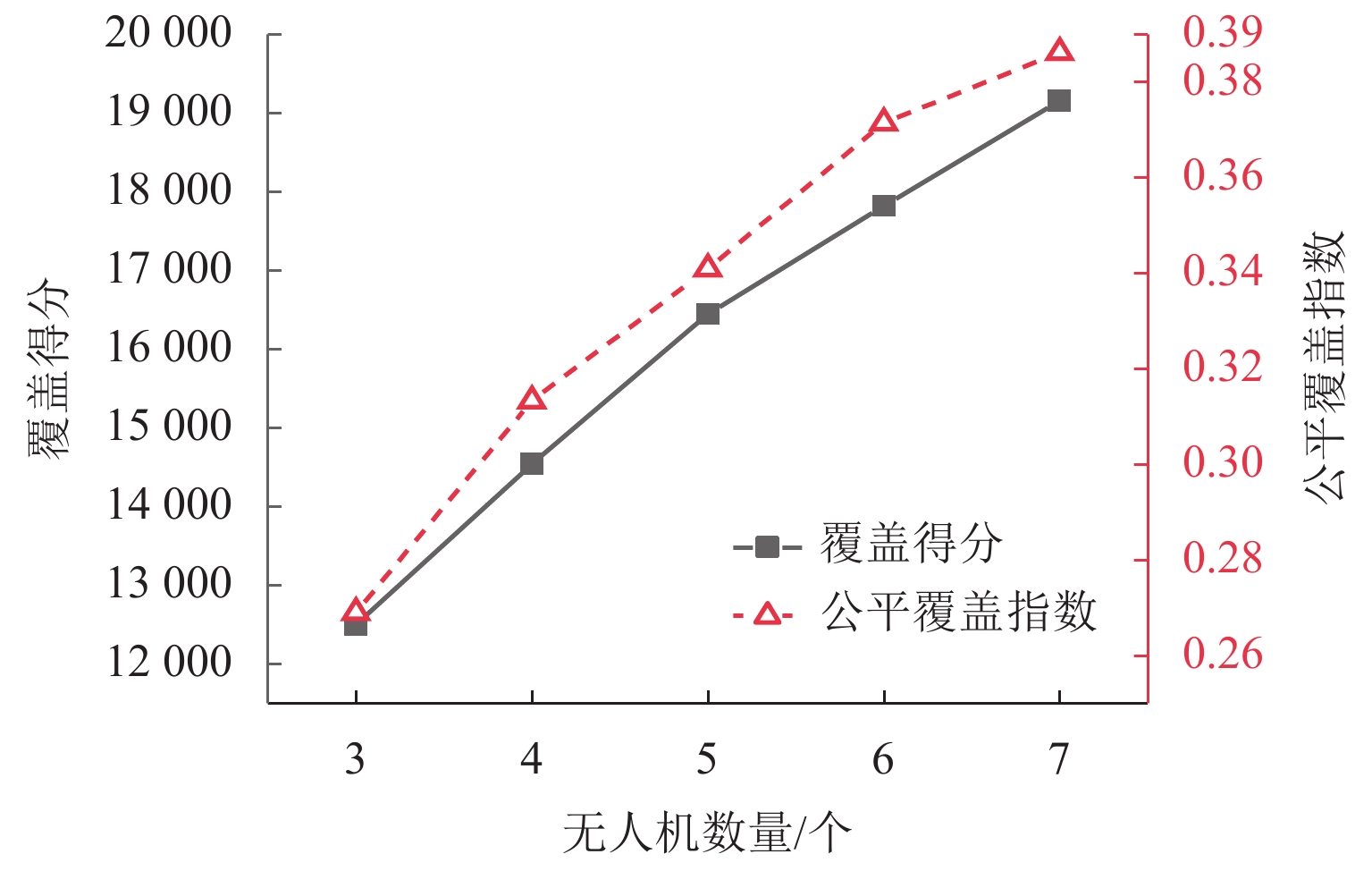
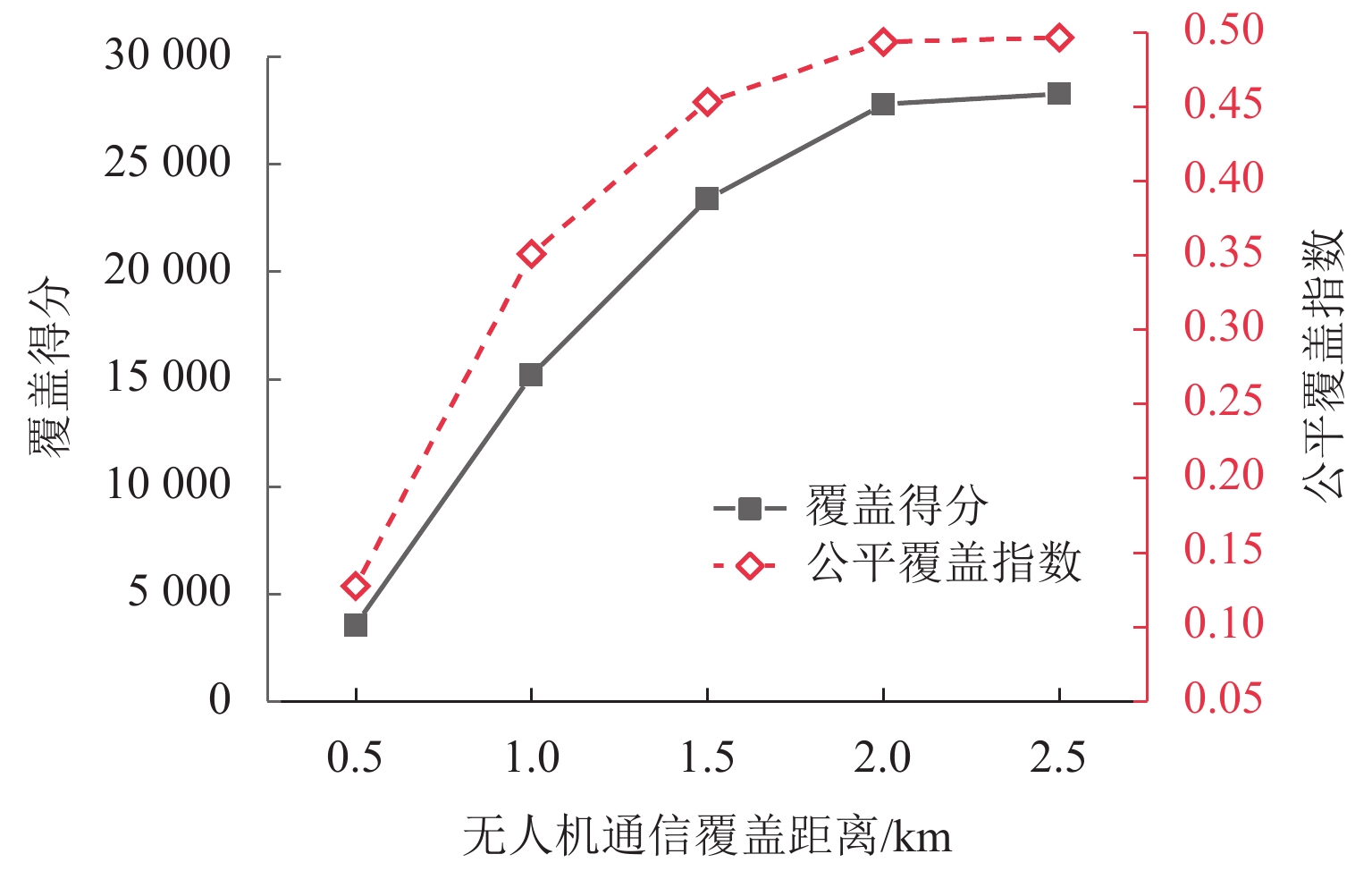
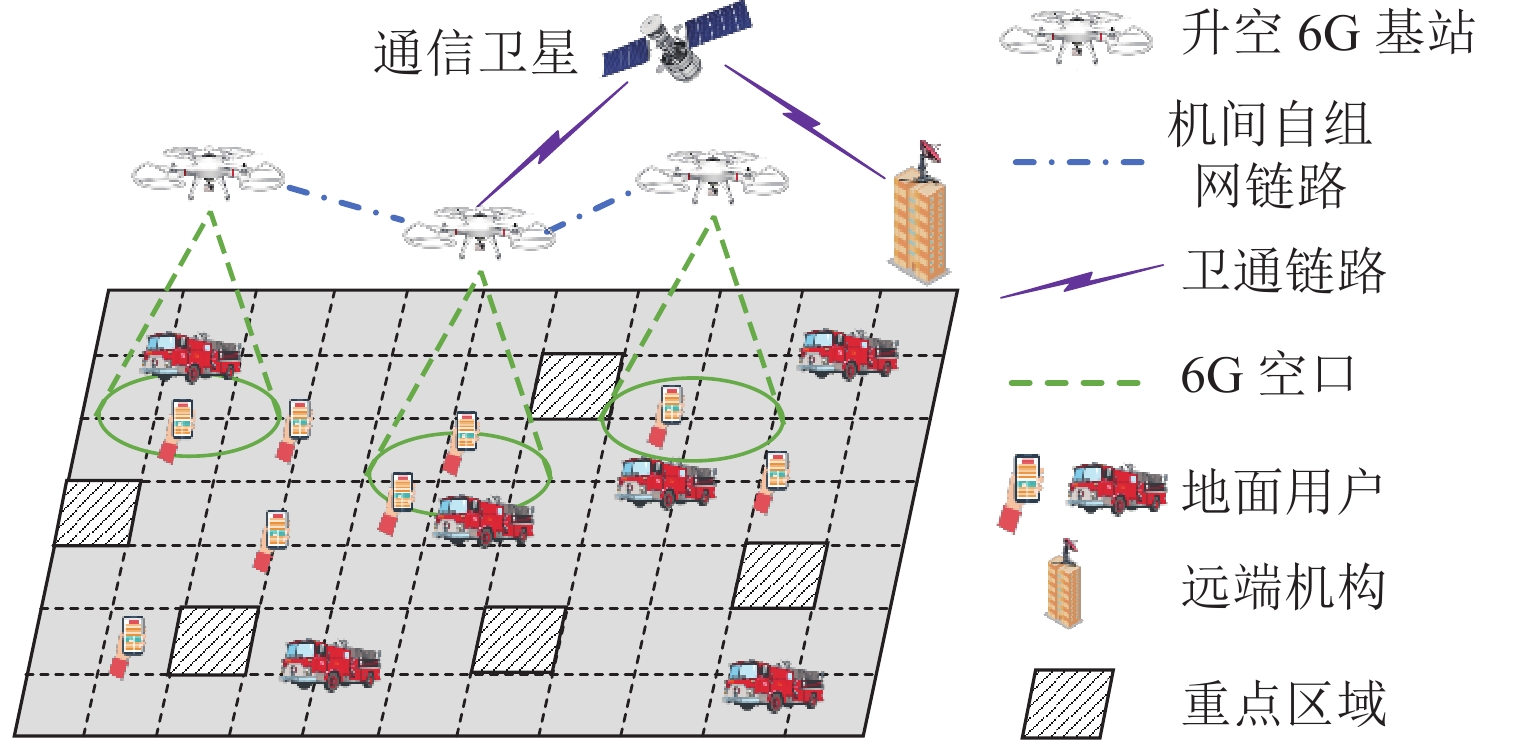
为研究应急通信场景中无人机网络自主控制问题,采用多架旋翼无人机搭载6G一体化基站,通过机间组网形成低空单层无人机网络,对地面任务区域内的用户提供无线网络服务;针对典型场景构建数值模型,利用多智能体强化学习方法求解无人机网络的优化控制策略,并分析无人机基站数量、无人机基站通信距离对于任务地域无线网络覆盖效果的影响. 研究结果表明:利用强化学习方法得到的优化控制策略收敛效果较好;无人机网络覆盖得分和公平覆盖指数的学习曲线变化趋势相似,在第1000~2 000个episode之间快速增长,随后进入平台区;在无人机基站通信覆盖距离1.0 km、飞行高度300 m条件下,将无人机基站数量从3个增加到7个,网络覆盖得分提高53.28%,公平覆盖指数提高43.57%;当无人机基站数5个、飞行高度300 m条件下,基站通信距离从1.0 km增加到2.5 km时,无人机网络覆盖得分提高86.01%,公平覆盖指数提高41.47%.
Abstract:In order to study the autonomous control problem of unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) networks in emergency communication scenarios, multiple rotary-wing UAVs equipped with 6G base stations were used, and a low-altitude and single-layer UAV network was formed through the interconnection between UAVs, thus providing wireless network services to users in the ground task area. A numerical model was constructed for typical scenarios, and a multi-agent reinforcement learning method was used to solve the optimization control strategy of the UAV network. The effects of the number of UAV base stations and the communication distance of UAV base stations on the wireless network coverage in the task area were investigated. The research results indicate that the optimization control strategy obtained by using reinforcement learning methods can converge well. The learning curves of the UAV network coverage score and fairness coverage index have similar trends. The curves rapidly increase between the 1000th and 2000th episode and then change slowly. Under the conditions of a communication coverage distance of 1 km and a flight altitude of 300 m for UAV base stations, the UAV network coverage score increases by 53.28%, and the fairness coverage index increases by 43.57% when the number of UAV base stations increases from 3 to 7. Under the condition of five UAV base stations and a flight altitude of 300 m, the UAV network coverage score increases by 86.01%, and the fairness coverage index increases by 41.47% when the communication distance of the base stations increases from 1.0 km to 2.5 km.
-
表 1 仿真实验参数数值
Table 1. Parameters for simulation experiment
参数名称 数值 无人机基站数量/个 3 任务地域的长、宽/km 4、4 任务地域划分的方格数量/个 100 重点保障方格数量/个 5 无人机基站覆盖距离/km 1 无人机基站飞行高度/m 300 无人机基站最大飞行速度/(m·s−1) 20 重点方格覆盖得分 10 一般方格覆盖得分 1 无人机基站飞出边界处罚值 1 无人机基站间碰撞处罚值 1 表 2 强化学习主要参数
Table 2. Main parameters for reinforcement learning
参数名称 数值 神经网络层数/层 2 隐藏网络节点数/个 64 学习率 0.01 折扣因子 0.95 $\tau $ 0.99 batch size 1000 -
[1] 陈新颖,盛敏,李博,等. 面向6G的无人机通信综述[J]. 电子与信息学报,2022,44(3): 781-789. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210789CHEN Xinying, SHENG Min, LI Bo, et al. Survey on unmanned aerial vehicle communications for 6G[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(3): 781-789. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210789 [2] 向庭立,王红军,杨刚,等. 分布式无人机网络覆盖优化算法[J]. 空军工程大学学报(自然科学版),2019,20(4): 59-65.XIANG Tingli, WANG Hongjun, YANG Gang, et al. Research on distributed UAV network coverage optimization algorithm[J]. Journal of Air Force Engineering University (Natural Science Edition), 2019, 20(4): 59-65. [3] 王巍,梁雅静,刘阳,等. 城市灾区无人机网络自适应覆盖优化算法[J]. 计算机工程与应用,2022,58(14): 258-268. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2010-0211WANG Wei, LIANG Yajing, LIU Yang, et al. Adaptive coverage optimization algorithm for drone network in urban disaster areas[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2022, 58(14): 258-268. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2010-0211 [4] 王超. 基于强化学习的无线网络移动性管理技术研究[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学,2021. [5] 靳晓洁,石建迈,伍国华,等. 无人机基站部署问题综述:模型与算法[J]. 控制理论与应用,2022,39(12): 2219-2232.JIN Xiaojie, SHI Jianmai, WU Guohua, et al. Review of the UAV base station deployment problem: models and algorithms[J]. Control Theory & Applications, 2022, 39(12): 2219-2232. [6] 郭艺轩,贾向东,曹胜男,等. 三维动态无人机网络覆盖性能与信道容量分析[J]. 重庆邮电大学学报(自然科学版),2022,34(4): 662-668. doi: 10.3979/j.issn.1673-825X.202101080012GUO Yixuan, JIA Xiangdong, CAO Shengnan, et al. Analysis of 3D dynamic UAV network coverage performance and channel capacity[J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications (Natural Science Edition), 2022, 34(4): 662-668. doi: 10.3979/j.issn.1673-825X.202101080012 [7] 吕忠昊. 基于强化学习的无人机通信系统容量优化研究[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学,2021. [8] 蒋逸凡,郭婧,费泽松. 多层高度的无人机-地面异构网络的覆盖性能[J]. 无线电通信技术,2021,47(5): 649-654. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3114.2021.05.020JIANG Yifan, GUO Jing, FEI Zesong. Coverage performance of UAV-terrestrial heterogeneous network with multiple altitudes[J]. Radio Communications Technology, 2021, 47(5): 649-654. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3114.2021.05.020 [9] 崔壮壮. 面向空地通信的无线信道特性和建模研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学,2022. [10] 马张枫. 面向B5G/6G无线网络的无人机信道建模研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学,2022. [11] 王莉,魏青,徐连明,等. 面向通信-导航-感知一体化的应急无人机网络低能耗部署研究[J]. 通信学报,2022,43(7): 1-20.WANG Li, WEI Qing, XU Lianming, et al. Research on low-energy-consumption deployment of emergency UAV network for integrated communication-navigating-sensing[J]. Journal on Communications, 2022, 43(7): 1-20. [12] 夏景明,刘玉风,谈玲. 基于蜂窝网络的多无人机能量消耗最优化算法研究[J]. 通信学报,2023,44(2): 185-197.XIA Jingming, LIU Yufeng, TAN Ling. Research on multi-UAV energy consumption optimization algorithm for cellular-connected network[J]. Journal on Communications, 2023, 44(2): 185-197. [13] 窦邵婷. 无人机辅助移动边缘计算的空地能耗折衷研究[D]. 南昌: 南昌大学,2022. [14] LIU C H, CHEN Z Y, TANG J, et al. Energy-efficient UAV control for effective and fair communication coverage: a deep reinforcement learning approach[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2018, 36(9): 2059-2070. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2018.2864373 [15] LIU C H, MA X X, GAO X D, et al. Distributed energy-efficient multi-UAV navigation for long-term communication coverage by deep reinforcement learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2020, 19(6): 1274-1285. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2019.2908171 [16] QI H, HU Z Q, HUANG H, et al. Energy efficient 3-D UAV control for persistent communication service and fairness: a deep reinforcement learning approach[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 53172-53184. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2981403 [17] JAIN R K, CHIU D M W, HAWE W R. A quantitative measure of fairness and discrimination for resource allocation in shared computer system[R]. Hudson MA: Digital Equipment Corporation, 1984. [18] LOWE R, WU Y, TAMAR A, et al. Multi-agent actor-critic for mixed cooperative-competitive environments [C]//Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Long Beach: ACM, 2017: 6382-6393. -




 下载:
下载: