Mechanical Model of Downhole Debris Flow Mechanism Based on Key Block Theory
-
摘要:
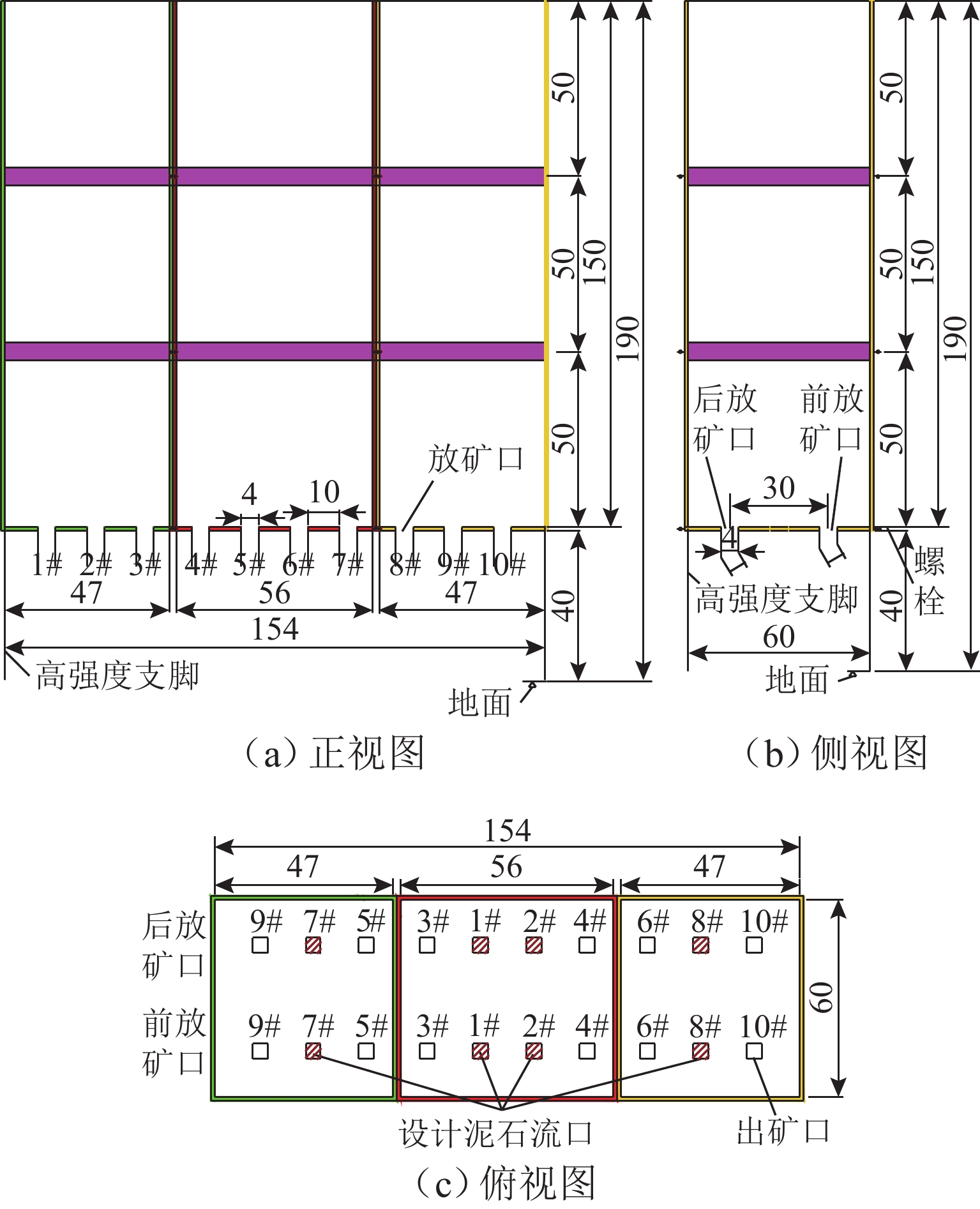
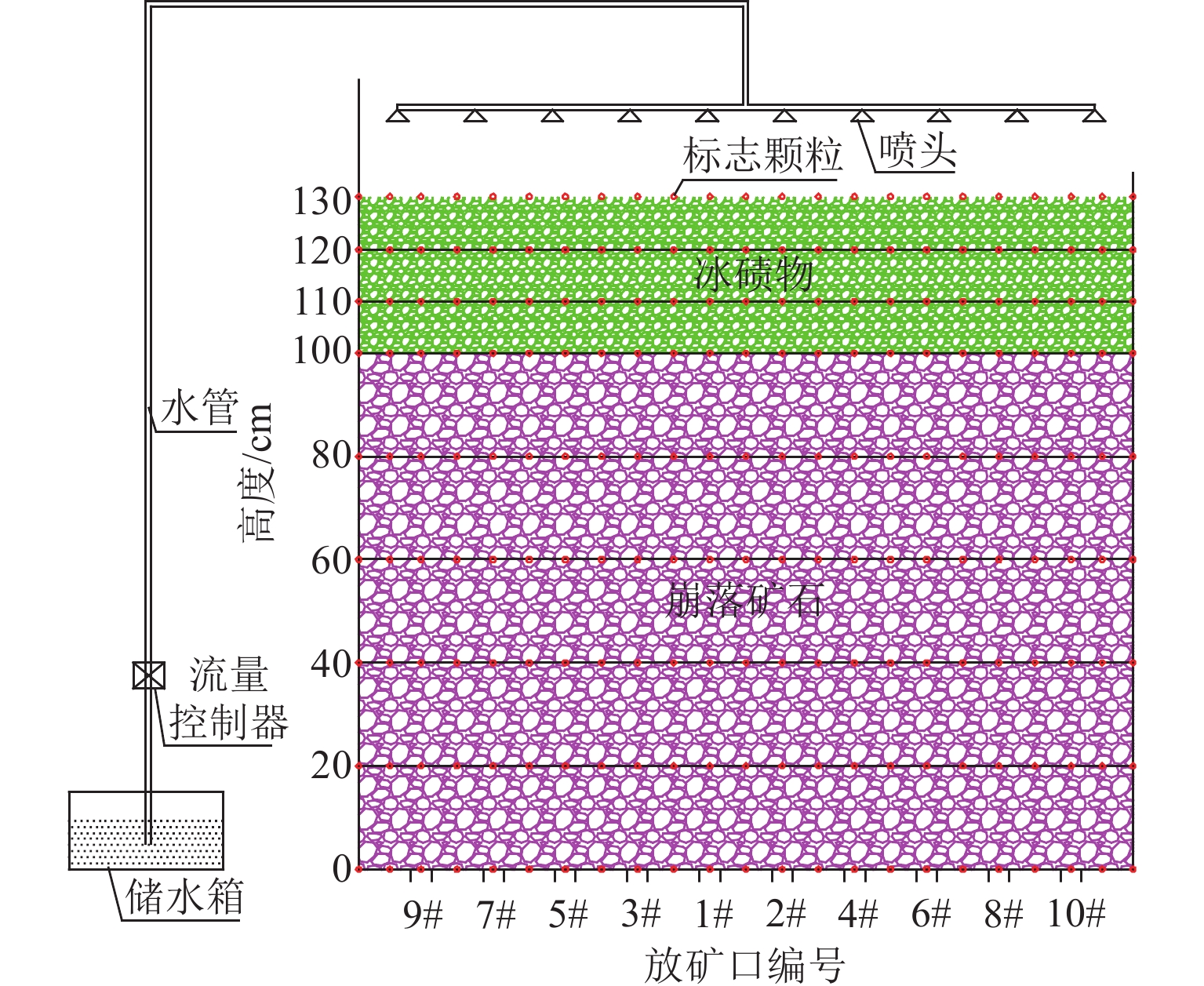
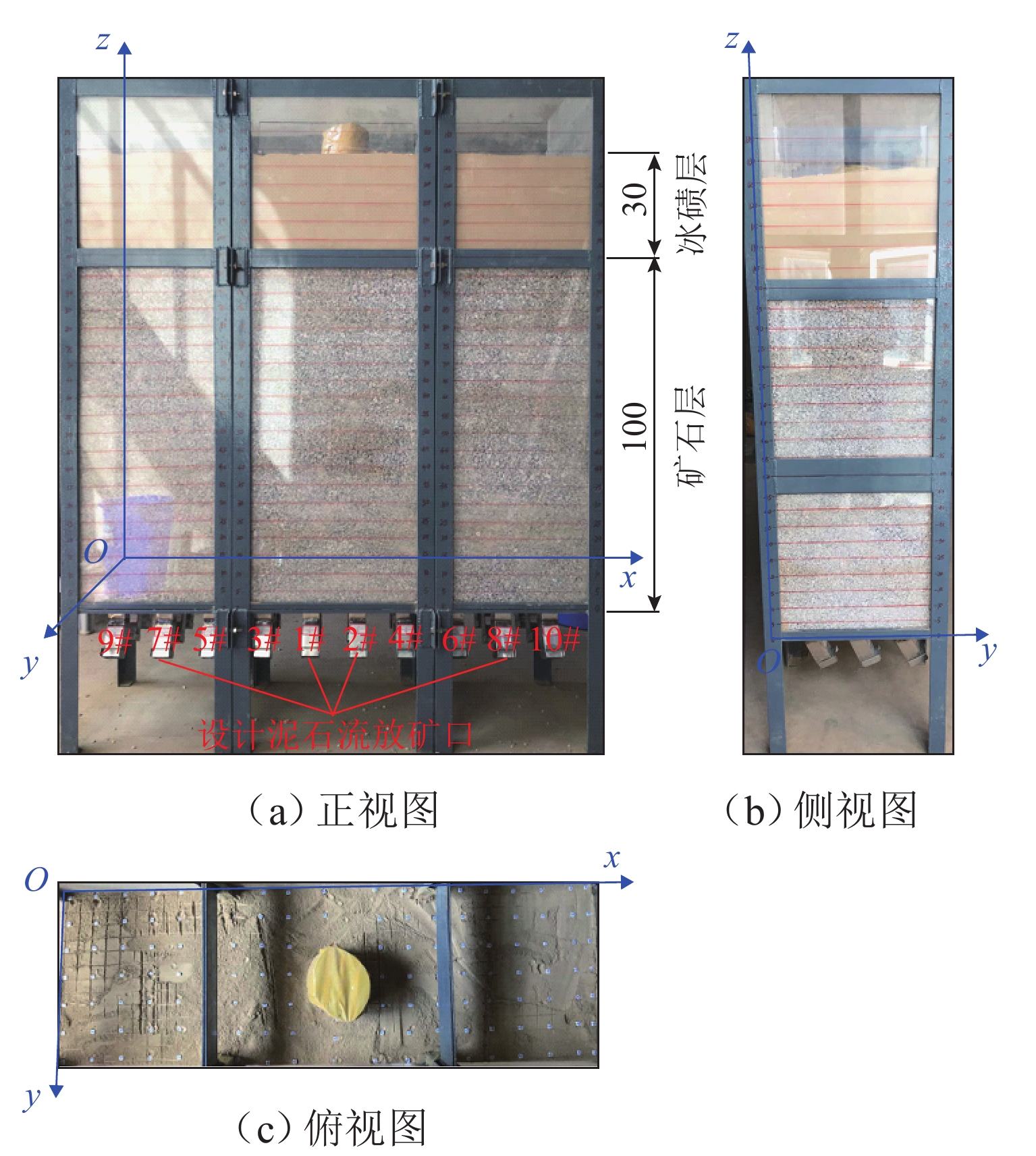
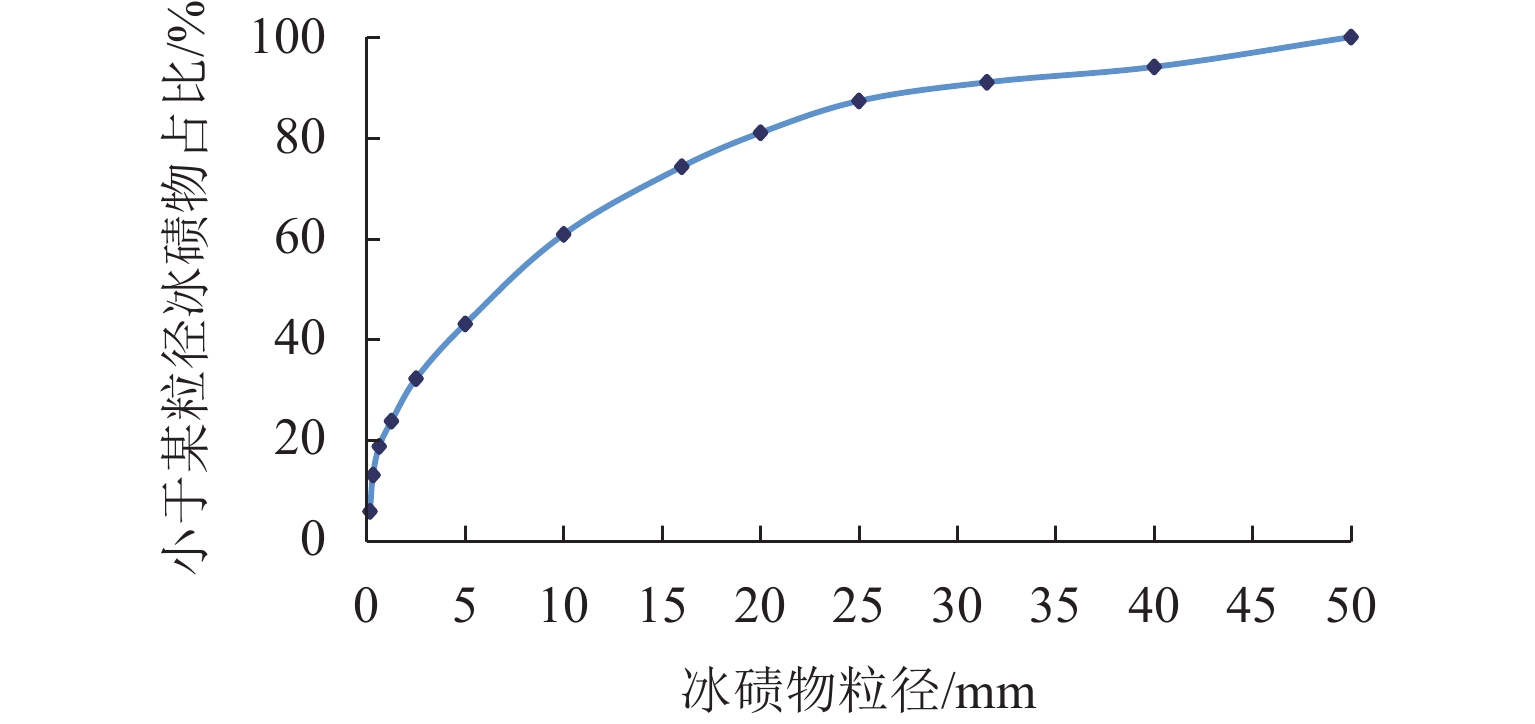
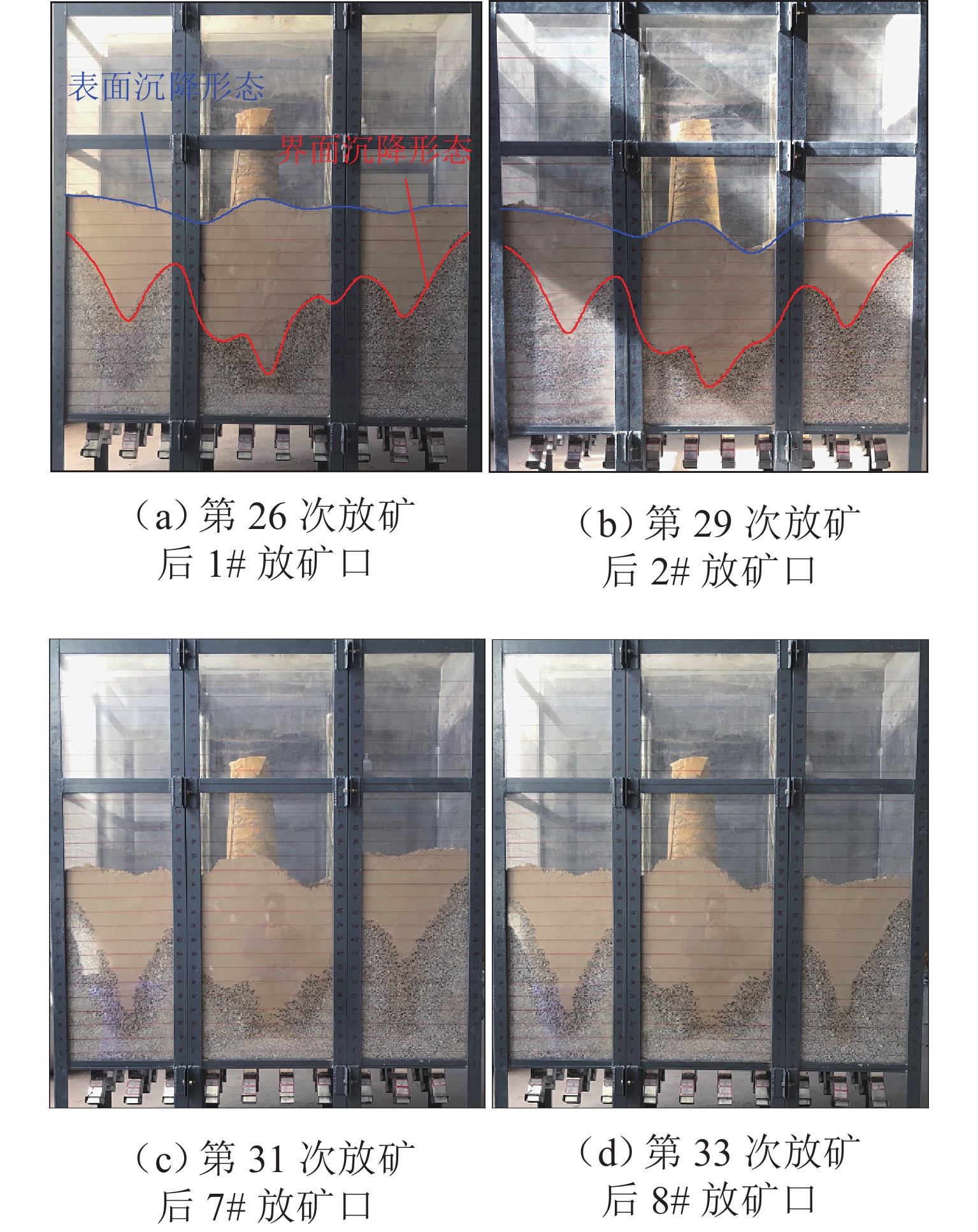
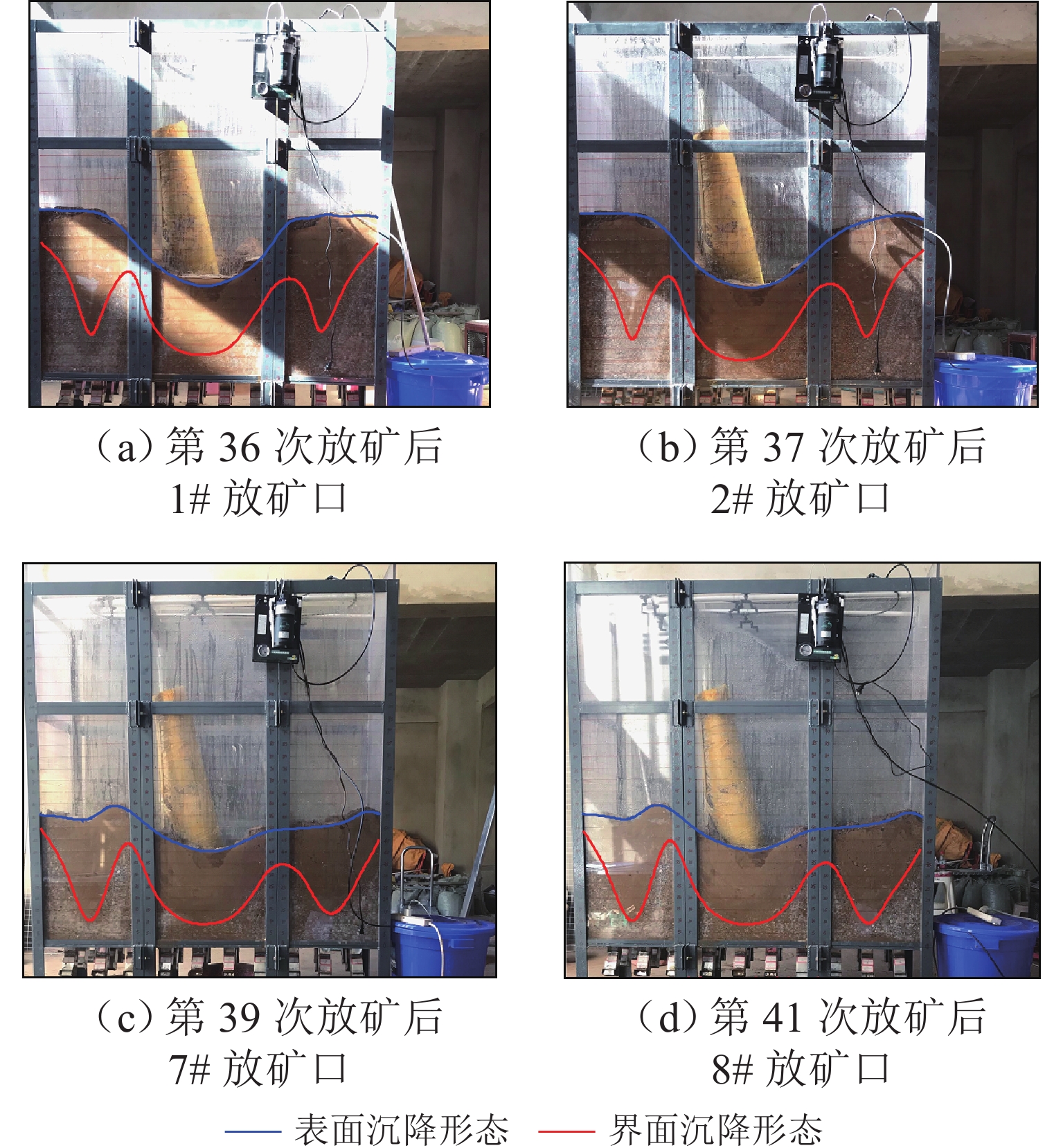
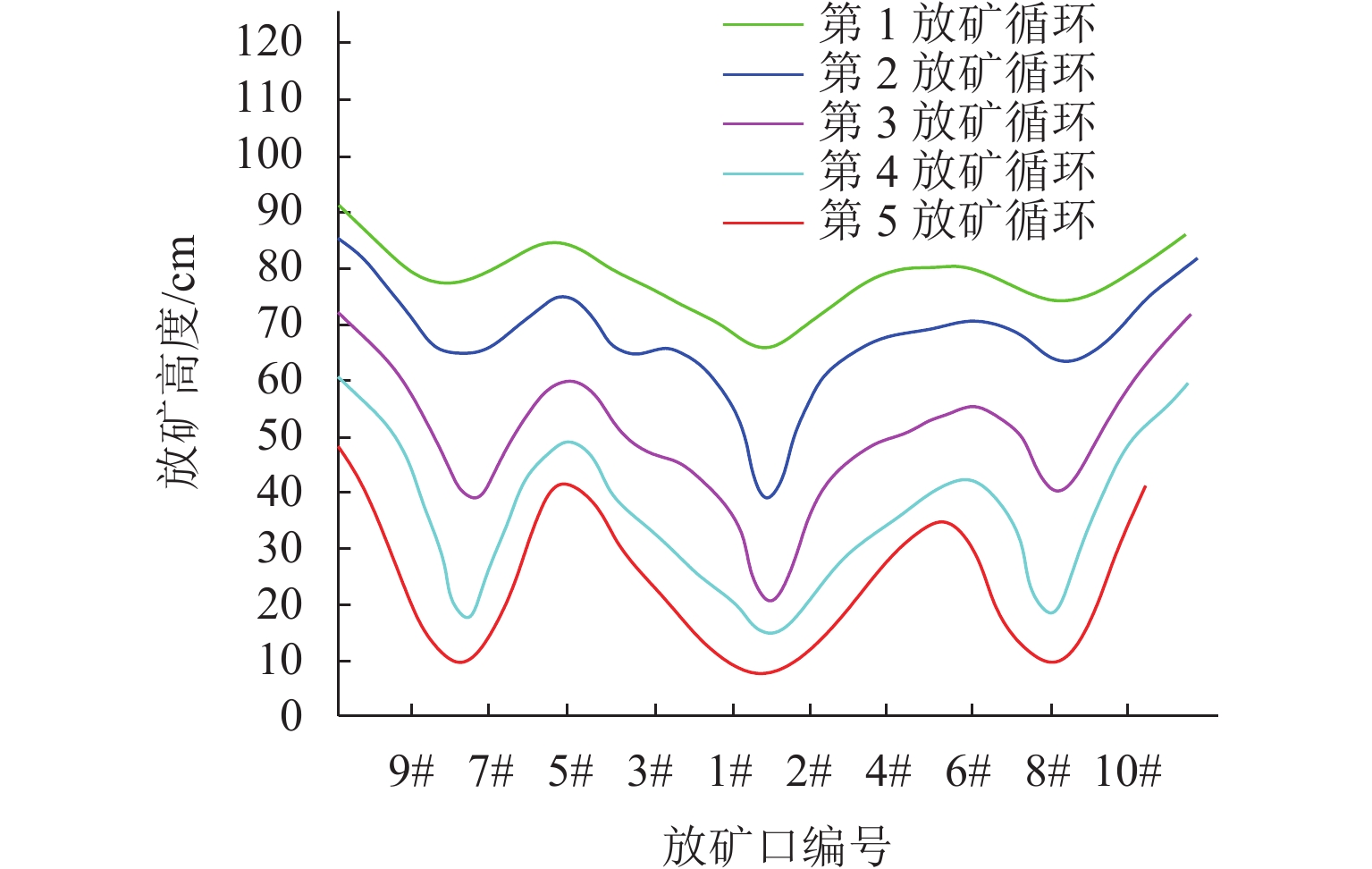
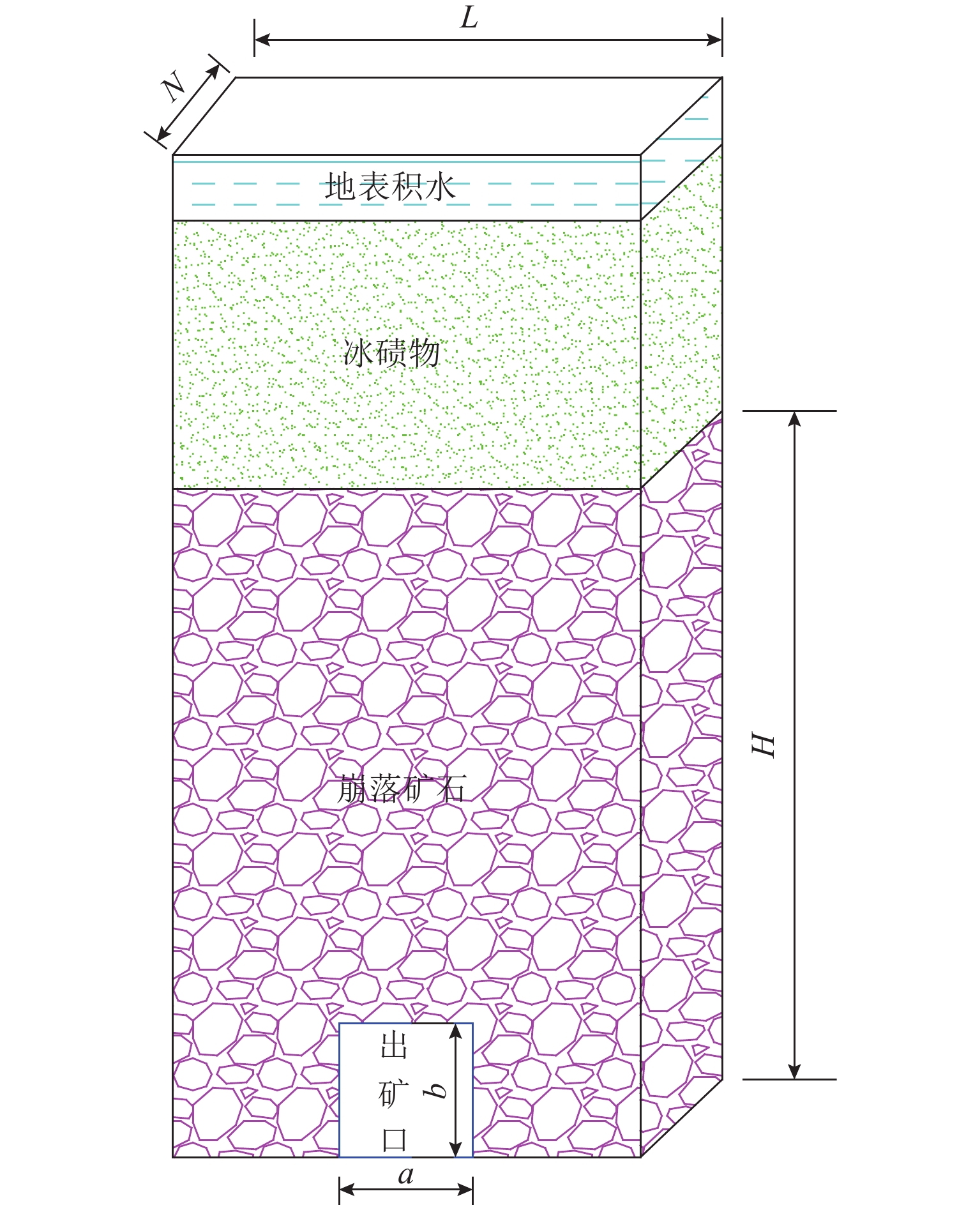
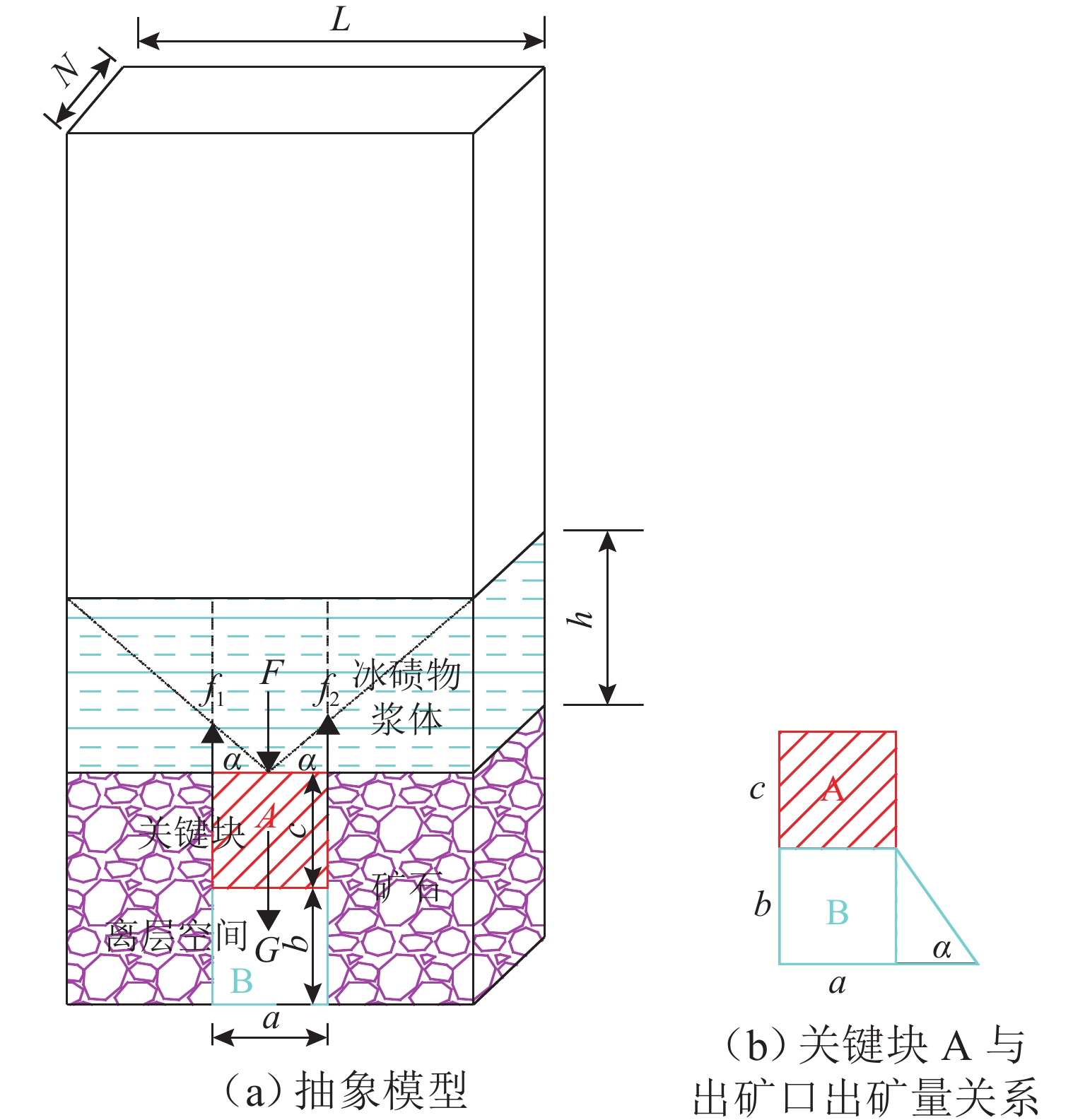
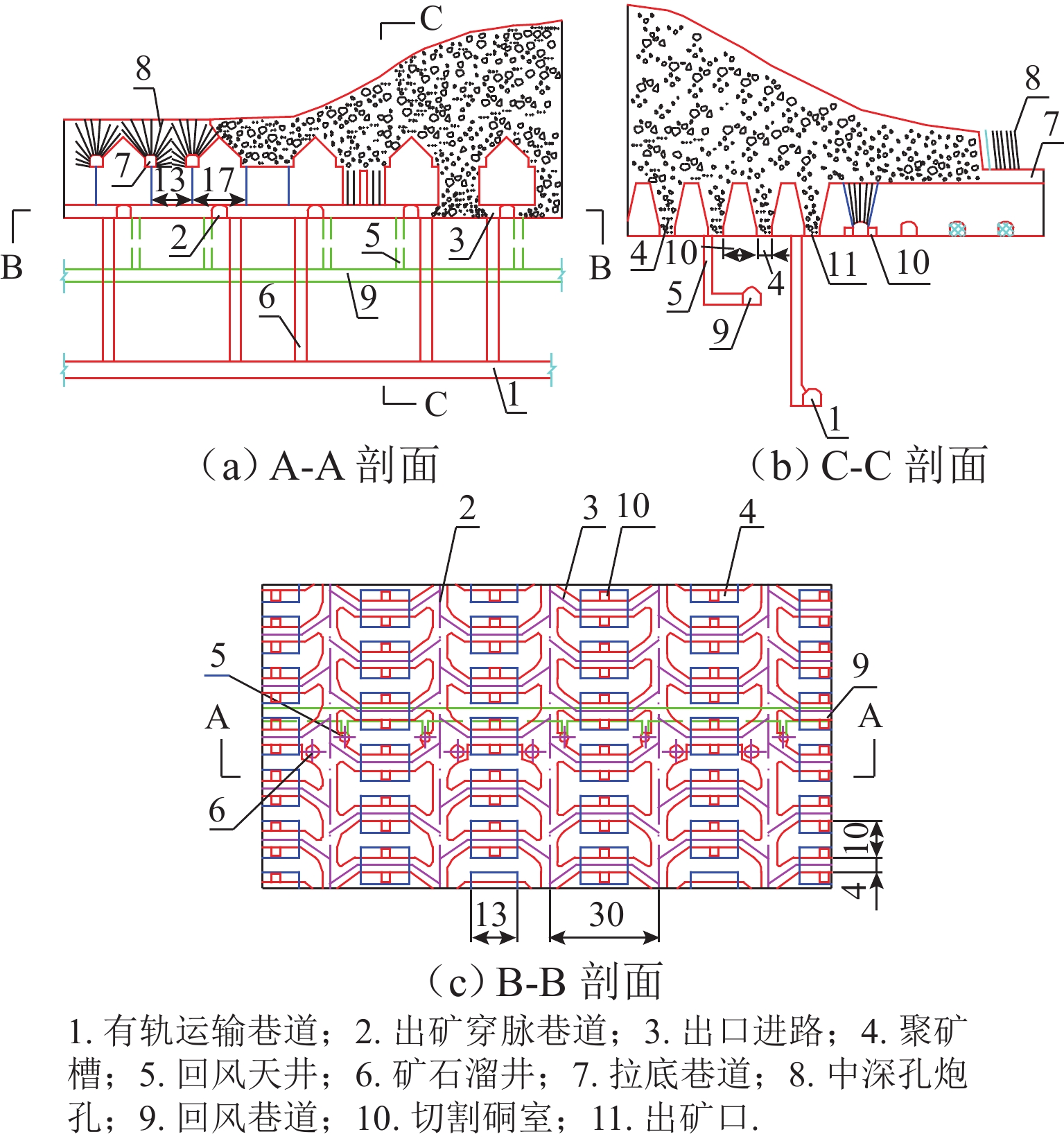
为实现对自然崩落法开采矿山井下泥石流定量的精准防控,利用室内大型井下泥石流试验方法,以普朗铜矿井下泥石流为研究对象,对形成井下泥石流的通道类型及诱发机理进行分析,得出井下泥石流诱发的临界条件;基于关键块理论,对处于临界条件下井下泥石流关键块体进行力学分析,构建井下泥石流诱发机理的力学模型,推导出井下泥石流诱发的理论临界出矿量. 研究结果表明:不均匀放矿条件下,易在崩落矿石层中形成3种类型的泥石流通道(放矿直通道、离层通道和弯曲通道);井下泥石流形成时空演化机理需要经历4个发展阶段(泥石流通道形成扩展阶段、物源运移聚集阶段、降雨径流积水阶段和震动因子诱发阶段);井下泥石流诱发临界条件是冰碛层和矿石层界面出现离层空间,并利用普朗铜矿2019—2022年间井下泥石流发生次数及降低率验证此力学模型的准确性和可靠性.
Abstract:To achieve quantitative and precise prevention and control of downhole debris flows in mines mined by the natural caving method, a large-scale laboratory experimental method for downhole debris flow was employed by taking the Plan copper mine as a case study. The channel types and inducing mechanism of the downhole debris flow formation were analyzed, revealing the critical conditions for the occurrence of downhole debris flow. The key block theory was applied to conduct a mechanical analysis of the key block of downhole debris flows under critical conditions. A mechanical model of the inducing mechanism of the downhole debris flow was constructed, and the theoretical critical ore yield induced by the natural caving method was deduced. The results show that under non-uniform ore drawing conditions, three types of debris flow channels are prone to form in the caved ore layer: straight ore drawing channels, separated layer channels, and curved channels. The spatiotemporal evolution mechanism of the formation of a downhole debris flow involves four stages: formation and expansion of the debris flow channel, migration and accumulation of source material, accumulation of runoff water from rainfall, and induction through vibration factors. The critical condition for inducing downhole debris flow is the formation of a certain separation space at the interface between the moraine layer and the ore layer. The accuracy and reliability of the model were verified by the occurrence frequency and reduction rate of underground debris flow in the Plan copper mine from 2019 to 2022.
-
-
[1] 牛向东, 谢晋谊, 侯克鹏, 等. 普朗铜矿井下冰碛补给型泥石流启动机理试验研究[J]. 有色金属工程, 2020, 10(7): 100-106. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1744.2020.07.016NIU Xiangdong, XIE Jinyi, HOU Kepeng, et al. Experimental study on the start-up mechanism of moraine-supplied debris flow in the prang copper mine[J]. Nonferrous Metals, 2020, 10(7): 100-106. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1744.2020.07.016 [2] 陈宁生, 佘德彬. 基于弃渣综合利用的矿山泥石流灾害防治新模式——以冕宁盐井沟泸沽铁矿为例[J]. 山地学报, 2019, 37(1): 78-85.CHEN Ningsheng, SHE Debin. A new approach to debris flow disaster control based on comprehensive utilization of waste slag—a case study of Lugu iron mine at the yanjing valley of Mianning County, Sichuan, China[J]. Mountain Research, 2019, 37(1): 78-85. [3] NIU X D, ZHE Y L, SUN H F, et al. Study on the effect of ore-drawing shear factor on underground debris flow in the block caving method[J]. Water, 2023, 15(20): 3563. [4] NIU X D, HOU K P , SUN H F. Study on the prevention and control of downhole debris flows based on disaster chain theory[J]. Water, 2023, 15(13): 2367. [5] 张丽萍, 唐克丽, 陈文亮. 人为泥石流起动及产沙放水冲刷实验——以神府-东胜矿区为例[J]. 自然灾害学报, 2000, 9(4): 94-98.ZHANG Liping, TANG Keli, CHEN Wenliang. Experiments of artificial simulation setting water on initiation and sediment of man-made debris now—taking Shenfu-Dongsheng minesite as an example[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 2000, 9(4): 94-98. [6] MAHSA S K, MOHAMMAD E B, JABER S. A hybrid SVR-PSO model to predict concentration of sediment in typical and debris floods[J]. Earth Science Informatics, 2021, 14: 365-376. doi: 10.1007/s12145-021-00570-0 [7] SAJID A, RASHID H, WAHID A, et al. Empirical assessment of rockfall and debris flow risk along the Karakoram Highway, Pakistan[J]. Nonferrous Metals Engineering, 2020, 10(7): 2437-2460. [8] 胡以德, 余海东, 杨涛. 基于固相沉积法的大型排土场暴雨泥石流流动特性预测研究——以四川某矿山泥石流为例[J]. 岩土工程技术, 2016, 30(6): 275-278. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2993.2016.06.002HU Yide, YU Haidong, YANG Tao. The prediction of raintorm debris flows characteristics about large dump based on solid sedimentary analysis—take the mine debris flow in Sichuan as an example[J]. Geotechnical Engineering Technique, 2016, 30(6): 275-278. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2993.2016.06.002 [9] 祝鑫, 胡斌, 李京, 等. 黄山矿区潜在泥石流发生机理与冲起高度的模拟研究[J]. 矿业研究与开发, 2021, 41(8): 108-113.ZHU Xin, HU Bin, LI Jing, et al. Simulation research on occurrence mechanism and rising height of potential debris flow in Huangshan mining area[J]. Mining Research and Development, 2021, 41(8): 108-113. [10] 倚江星. 基于颗粒流的寺沟矿区泥石流动力特征预测研究[D]. 西安: 西安科技大学, 2020. [11] 李朋伟. 秦岭南麓赵家沟矿山泥石流发育特征及风险评价[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2020. [12] SUENG W J. Geotechnical and rheological characteristics of waste rock deposits influencing potential debris flow occurrence at the abandoned Imgi Mine, Korea[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2015, 73(12): 8299-8310. doi: 10.1007/s12665-014-3991-1 [13] 邓俊平. 基于事故致因理论的某矿井下突泥事故原因及防控研究[J]. 采矿技术, 2019, 19(5): 98-101. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2900.2019.05.031DENG Junping. Study on the cause and prevention of mud outburst accident in a mine based on accident causation theory[J]. Mining Technology, 2019, 19(5): 98-101. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2900.2019.05.031 [14] 宋卫东, 王艳辉, 杜建华, 等. 井下泥石流影响因素指标体系研究[J]. 金属矿山, 2009(9): 155-159.SONG Weidong, WANG Yanhui, DU Jianhua, et al. Study on the indicator system of influencing factors on the underground debris flow[J]. Metal Mine, 2009(9): 155-159. [15] 牛向东, 侯克鹏, 孙华芬. 均匀放矿过程中细粒冰碛物穿流机理试验研究[J]. 采矿与岩层控制工程学报发, 2023, 5(3): 24-31.NIU Xinagdong, HOU Kepeng, SUN Huafen. Experimental study on the flow mechanism of fine-grained moraine in the process of uniform ore drawing[J]. Journal of Mining and Strata Control Engineering, 2023, 5(3): 24-31. [16] XUE Y G, KONG F M, LI S C, et al. Water and mud inrush hazard in underground engineering Genesis, evolution and prevention[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2021, 114: 103987. [17] 杜建华, 匡忠祥, 宋卫东, 等. 井下泥石流发生机理数值模拟研究[J]. 金属矿山, 2008(4): 18-22.DU Jianhua, KUANG Zhongxiang, SONG Weidong, et al. Numerical simulation study on occurrence mechanism of underground mud-rock slides[J]. Metal Mine, 2008(4): 18-22. [18] 欧阳治华, 王胜开, 全中学. 矿山井下泥石流形成机理与固液耦合数值模拟研究[J]. 金属矿山, 2008(10): 21-24, 31.OUYANG Zhihua, WANG Shengkai, QUAN Zhongxue. Investigation on the formation mechanism of mine underground mud-stone flow and numerical simulation with coupled solid-liquid model[J]. Metal Mine, 2008(10): 21-24, 31. [19] 樊圆圆, 宋玲, 孙雯. 基于PFC的冰碛土泥石流起动过程模拟研究[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2021, 35(3): 140-146.FAN Yuanyuan, SONG Ling, SUN Wen. A simulation study on the starting process of moraine debris flow based on PFC[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2021, 35(3): 140-146. [20] HU X D, ZHANG L, HU K H, et al. Modelling the evolution of propagation and runout from a gravel-silty clay landslide to a debris flow in Shaziba, southwestern Hubei Provin, China[J]. Landslides, 2022, 19: 2199-2212. [21] RAY A, VERMA H, BHARATI A K, et al. Numerical modeling of rheological properties of landslide debris[J]. Natural Hazards, 2021, 110(3): 2303-2327. [22] CHENG X L, LIU L P, XIAO J, et al. A general block stability analysis algorithm for arbitrary block shapes[J]. Frontiers in Earth Science, 2021, 9: 723320. [23] DONG Z H, DING X L, LU B, et al. Anchorage design analysis and field monitoring of large key blocks in high and steep rock slope[J]. IOP Conference Series Earth and Environmental Science, 2021, 869(6): 062019. [24] 何富连, 吕凯, 许旭辉, 等. 近距离煤层综放末采关键块体回转机制及其应用[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2023, 42(8): 1832-1846.HE Fulian, LV Kai, XU Xuhui, et al. Rotation mechanism of key blocks during end-mining period of fully mechanized caving in close distance coal seams and its application[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2023, 42(8): 1832-1846. [25] 杨东升, 费秉宏, 孙春华. 基于BIM技术的水电站地下洞室定位关键块体分析方法[J]. 西北水电, 2022(2): 81-85.YANG Dongsheng, FEI Binghong, SUN Chunhua. Analysis method of key blocks for the location of underground caverns of hydropower stations based on BIM technology[J]. Northwest Hydropower, 2022(2): 81-85. [26] WANG H D, SONG F F, CHEN Y, et al. Stability analysis of fractured rock masses based on an extended key block theory considering the forces between blocks and block rotation[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2023, 132: 104895. -




 下载:
下载: