Reinforcement Learning Braking Control of Maglev Trains Based on Self-Learning of Hybrid Braking Features
-
摘要:
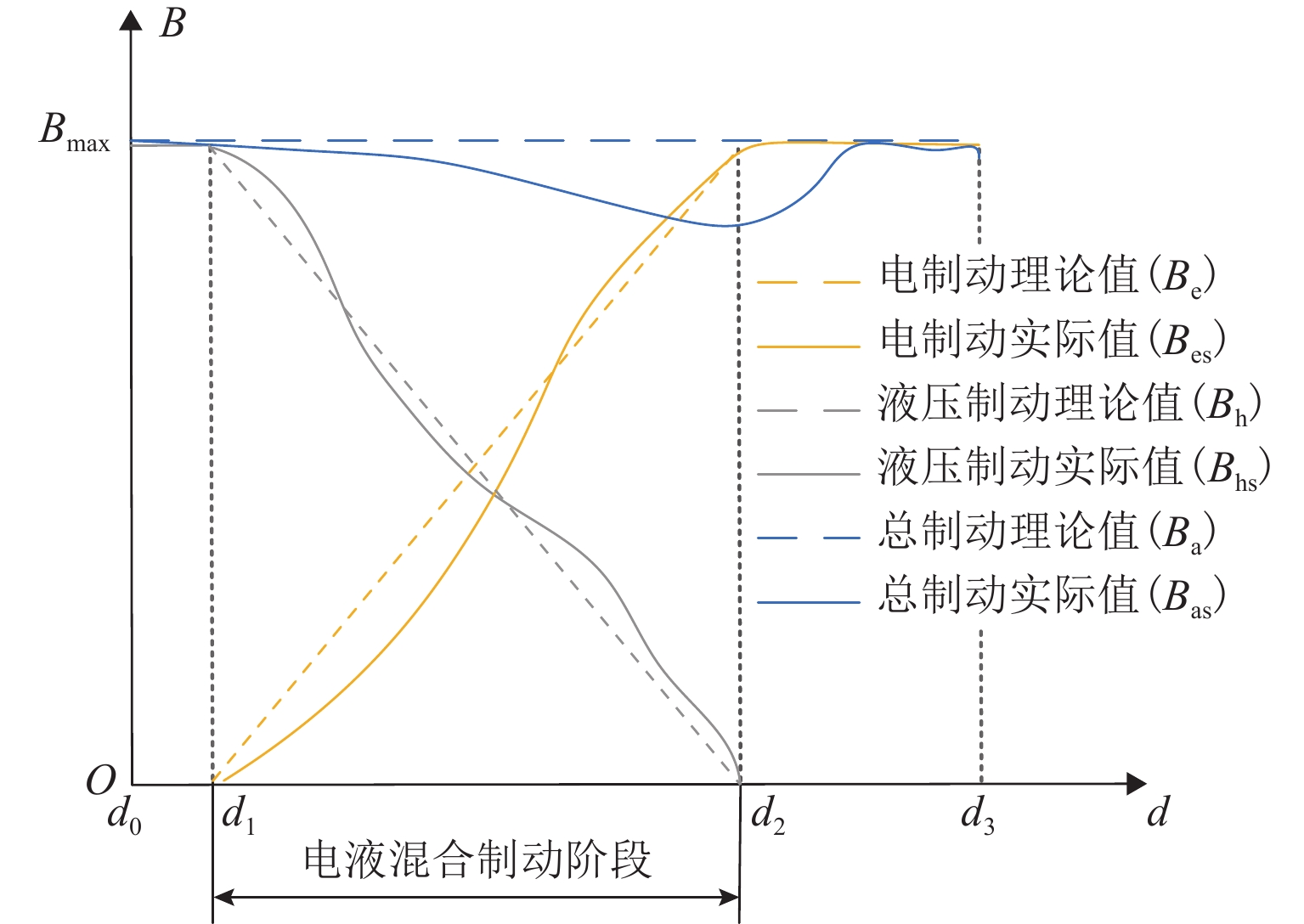
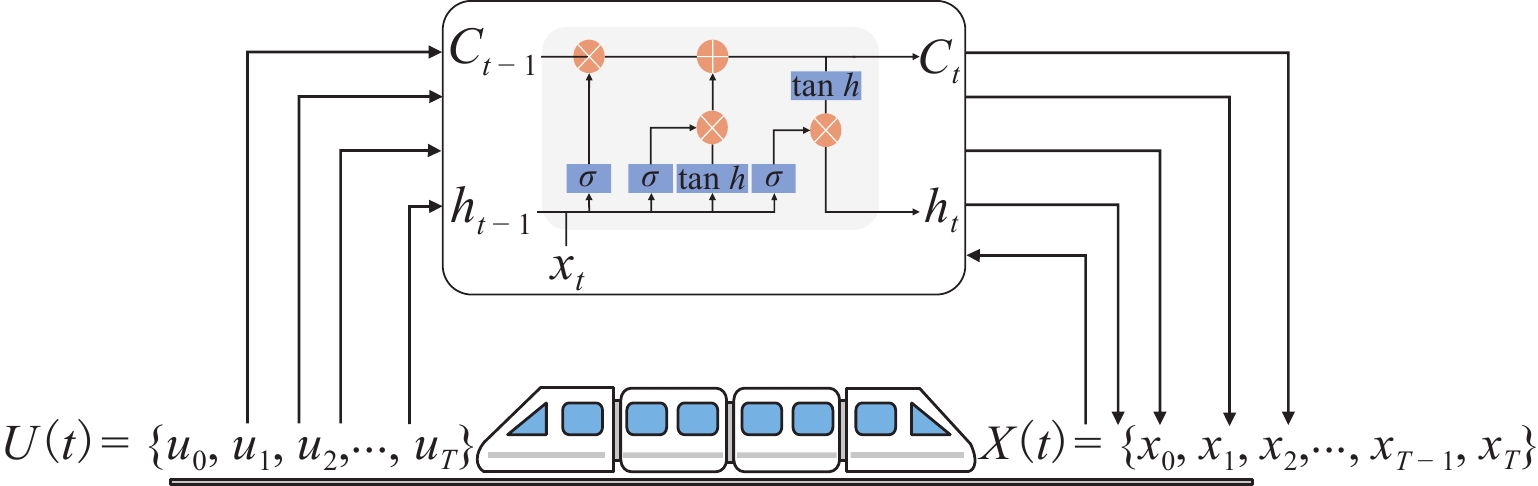
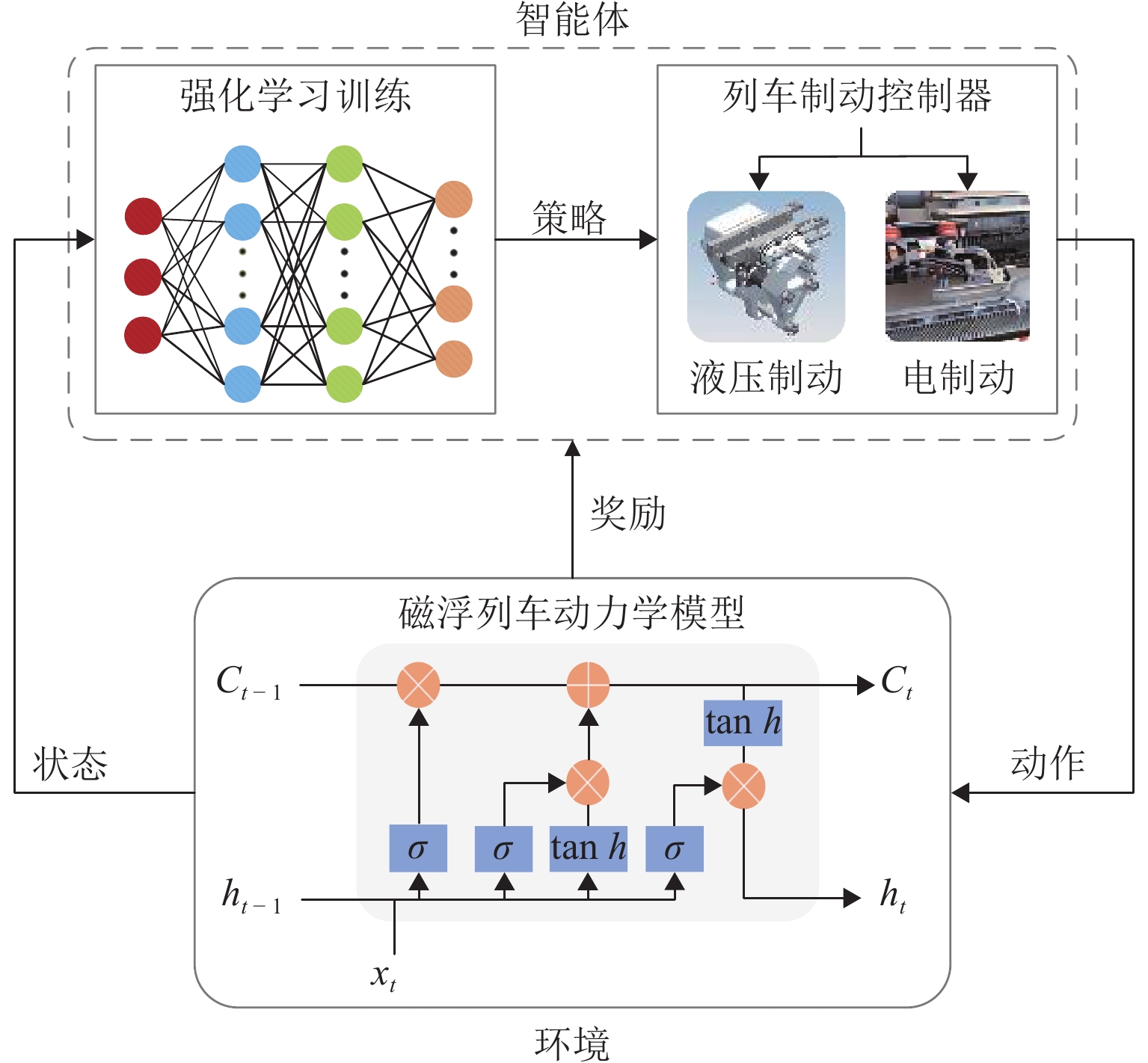
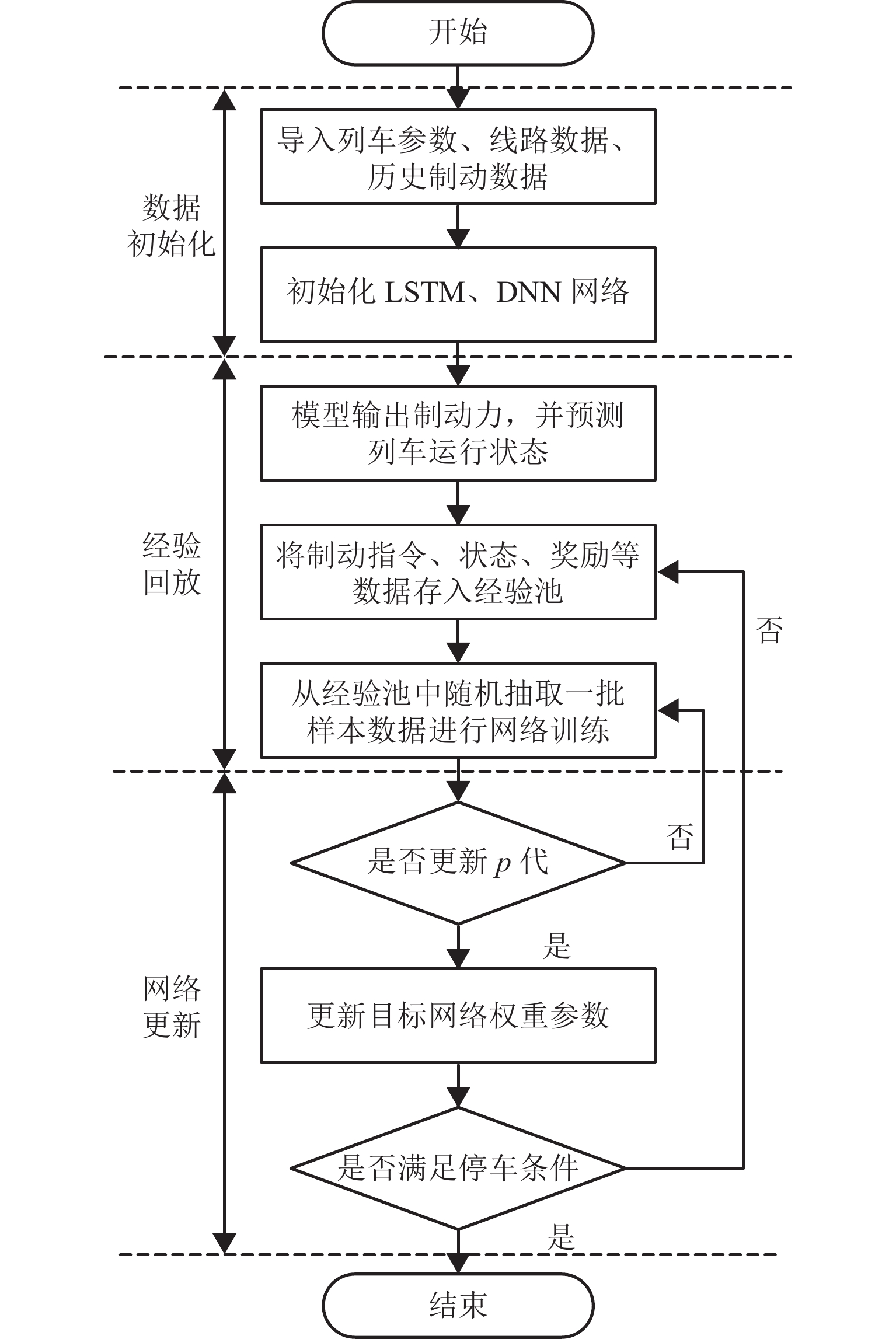
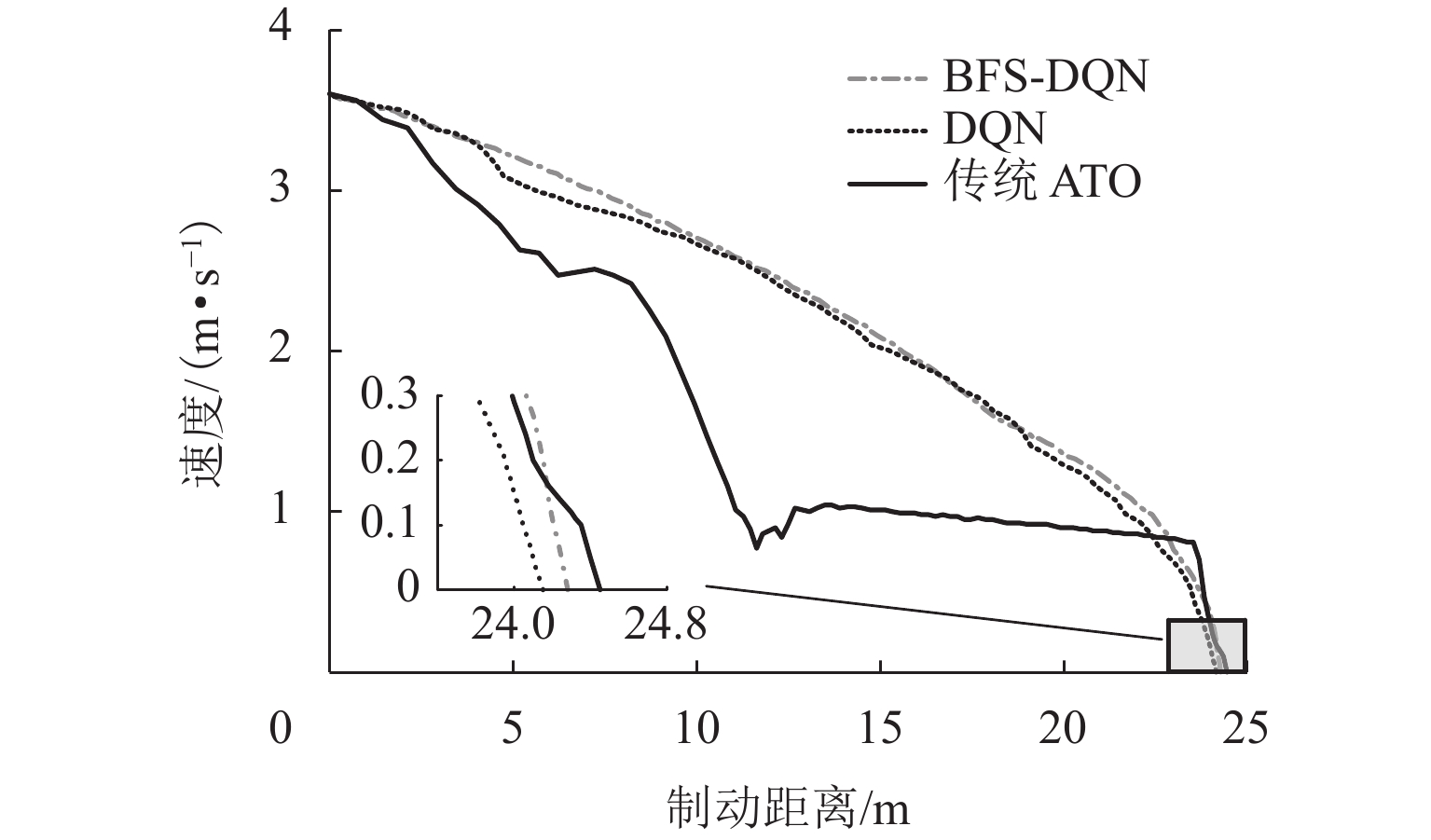
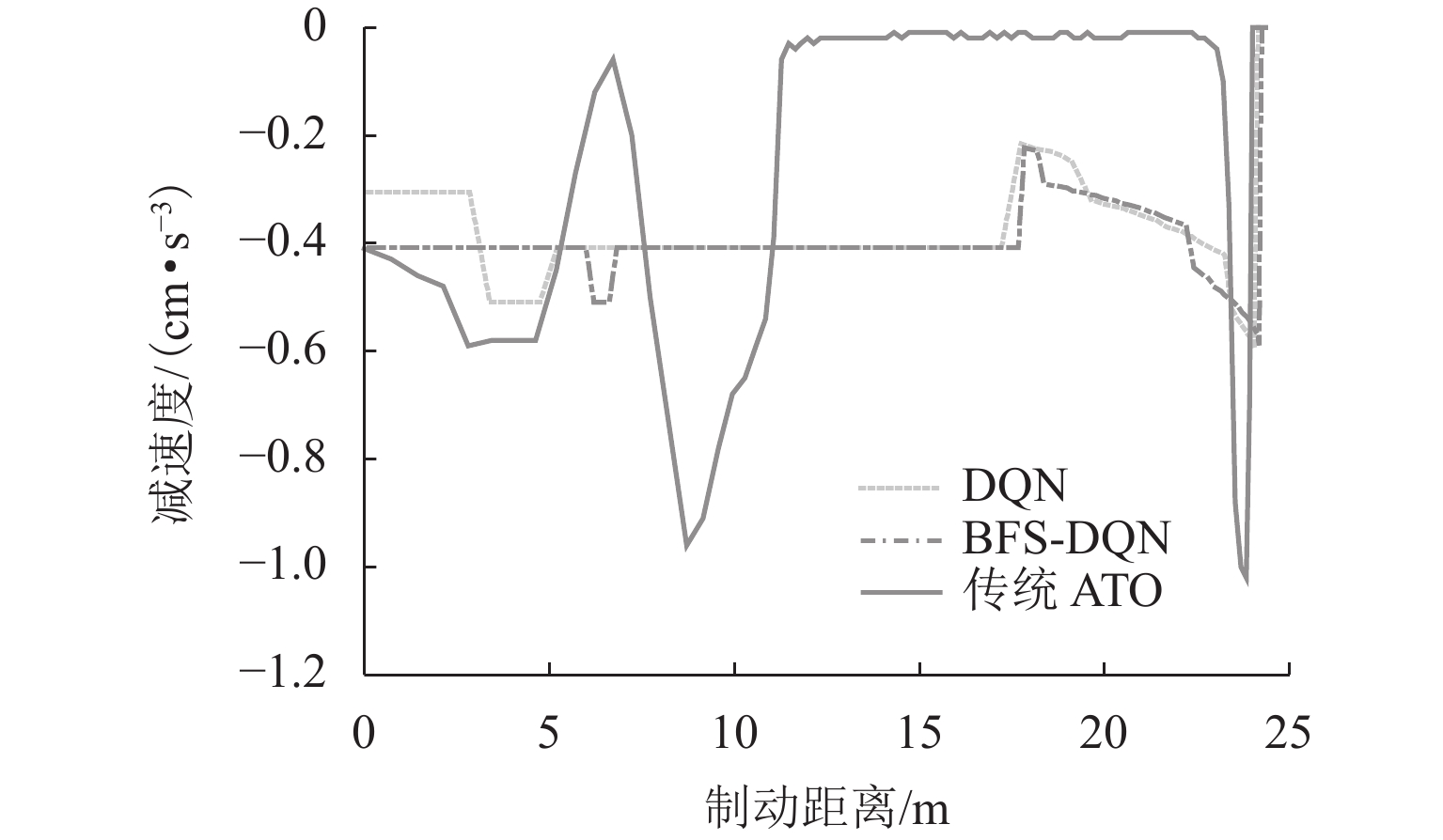
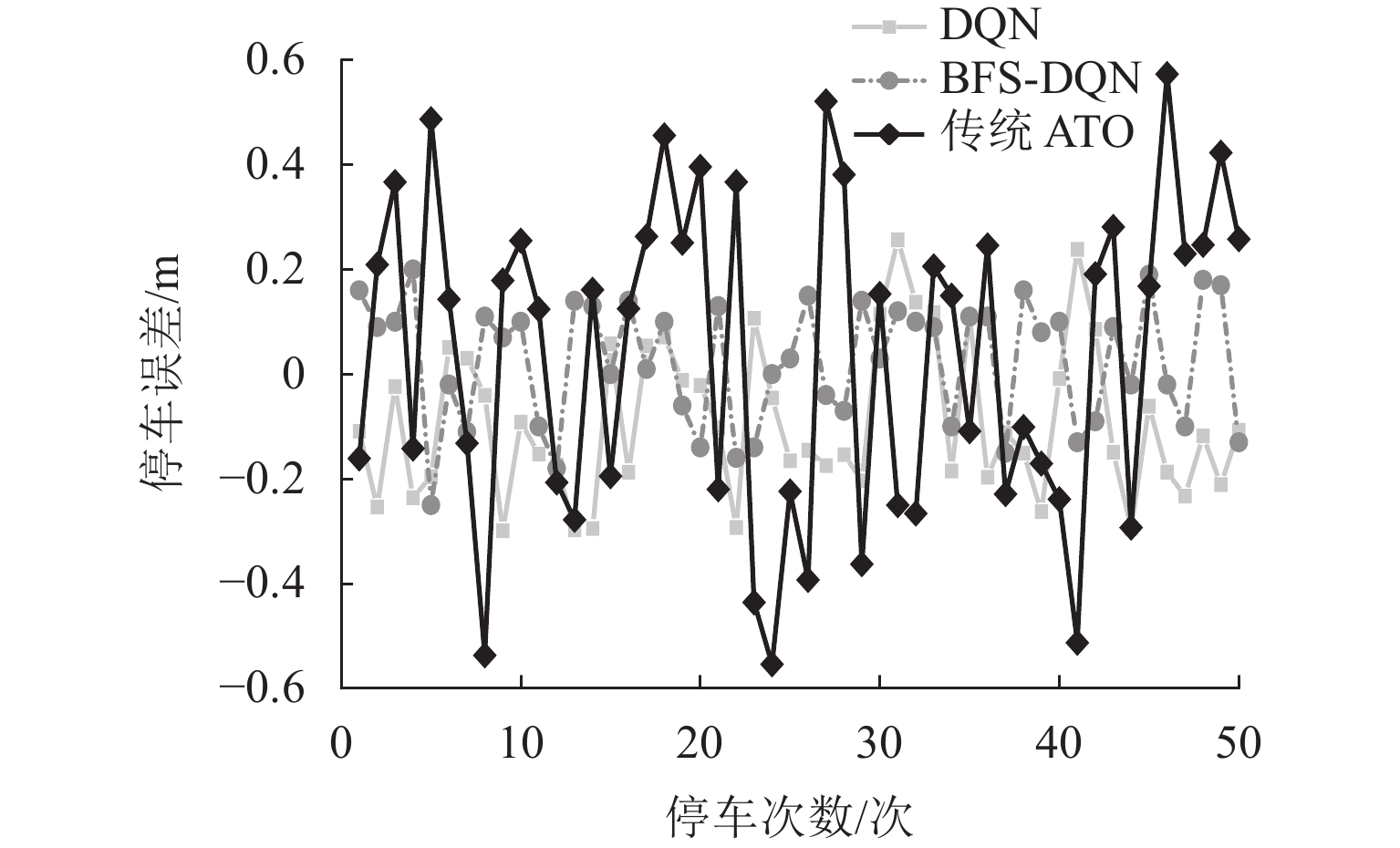
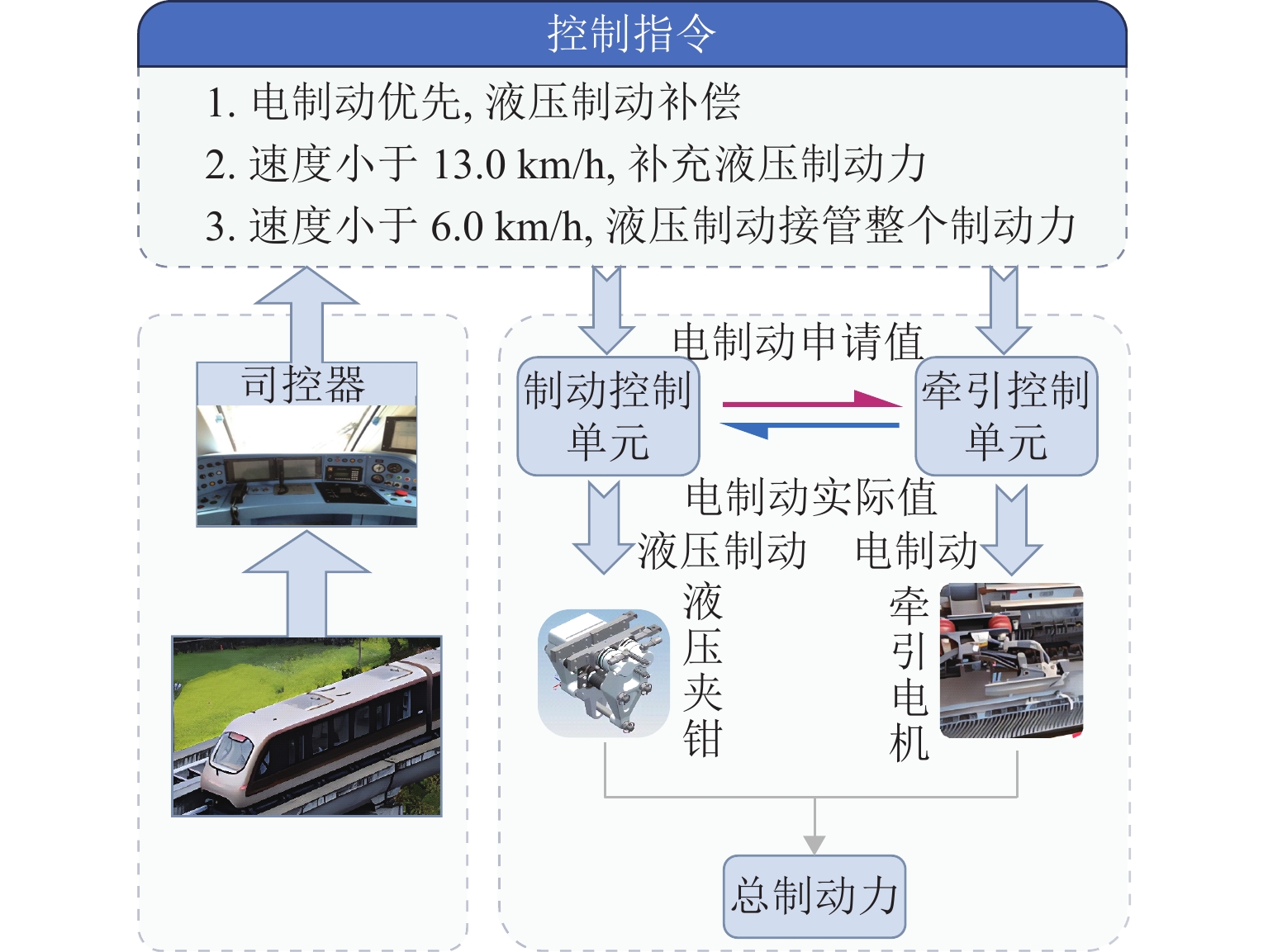
精准、平稳停车是磁浮列车自动驾驶制动控制的重要目标. 中低速磁浮列车停站制动过程受到电-液混合制动状态强耦合等影响,基于制动特性机理模型的传统制动控制方法难以保障磁浮列车的停车精度和舒适性. 本文提出一种基于混合制动特征自学习的磁浮列车强化学习制动控制方法. 首先,采用长短期记忆网络建立磁浮列车混合制动特征模型,结合磁浮列车运行环境和状态数据进行动态制动特征自学习;然后,根据动态特征学习结果更新强化学习的奖励函数与学习策略,提出基于深度强化学习的列车制动优化控制方法;最后,采用中低速磁浮列车现场运行数据开展仿真实验. 实验结果表明:本文所提出的制动控制方法较传统方法的舒适性和停车精度分别提高41.18%和22%,证明了本文建模与制动优化控制方法的有效性.
Abstract:Accurate and smooth parking is an essential goal for automatic driving braking control of maglev trains. The strong coupling of the electro-hydraulic hybrid braking state affects the medium and low-speed maglev trains during the stopping braking process, and the traditional braking control method based on the theoretical model of braking features makes it difficult to guarantee the parking accuracy and comfort of the maglev train. This paper proposed a reinforcement learning braking control method for maglev trains based on self-learning of hybrid braking features. First, a long short-term memory (LSTM) network was used to establish a hybrid braking feature model for maglev trains, and the self-learning of dynamic braking features was performed based on the operating environment and status data of maglev trains. Then, the reward function and learning strategy of reinforcement learning were updated according to the learning results of dynamic features, and a train braking optimization control method based on deep reinforcement learning was proposed. Finally, simulation experiments were carried out by using on-site operation data of medium and low-speed maglev trains. The experimental results show that the braking control method proposed in this paper improves comfort and parking accuracy by 41.18% and 22%, respectively, compared with the traditional method. It proves the effectiveness of the modeling and braking optimization control method in this paper.
-
表 1 仿真列车参数
Table 1. Simulation train parameters
参数类别 参数特性 列车质量/t 75 线路最高限速/(km·h−1) 80 编组数量 3 最大常用制动力/kN 74.23 最大常用减速度/(m·s−2) 0.96 线路最大坡度/‰ 51.01 表 2 算法主要训练参数
Table 2. Main training parameters for algorithm
参数 BFS-DQN DQN LSTM 迭代次数/次 500 LSTM 学习率 0.001 LSTM 样本批量 50 单次训练最大步数/步 80 80 训练最大次数/次 20000 20000 Q 网络学习率 0.001 0.001 Q 网络更新频率 100 100 样本大小 32 32 经验池容量 2000 2000 折扣因子 0.96 0.96 贪婪率初始值 0.9 0.9 贪婪率最终值 0.1 0.1 表 3 算法训练结果
Table 3. Training results for algorithm
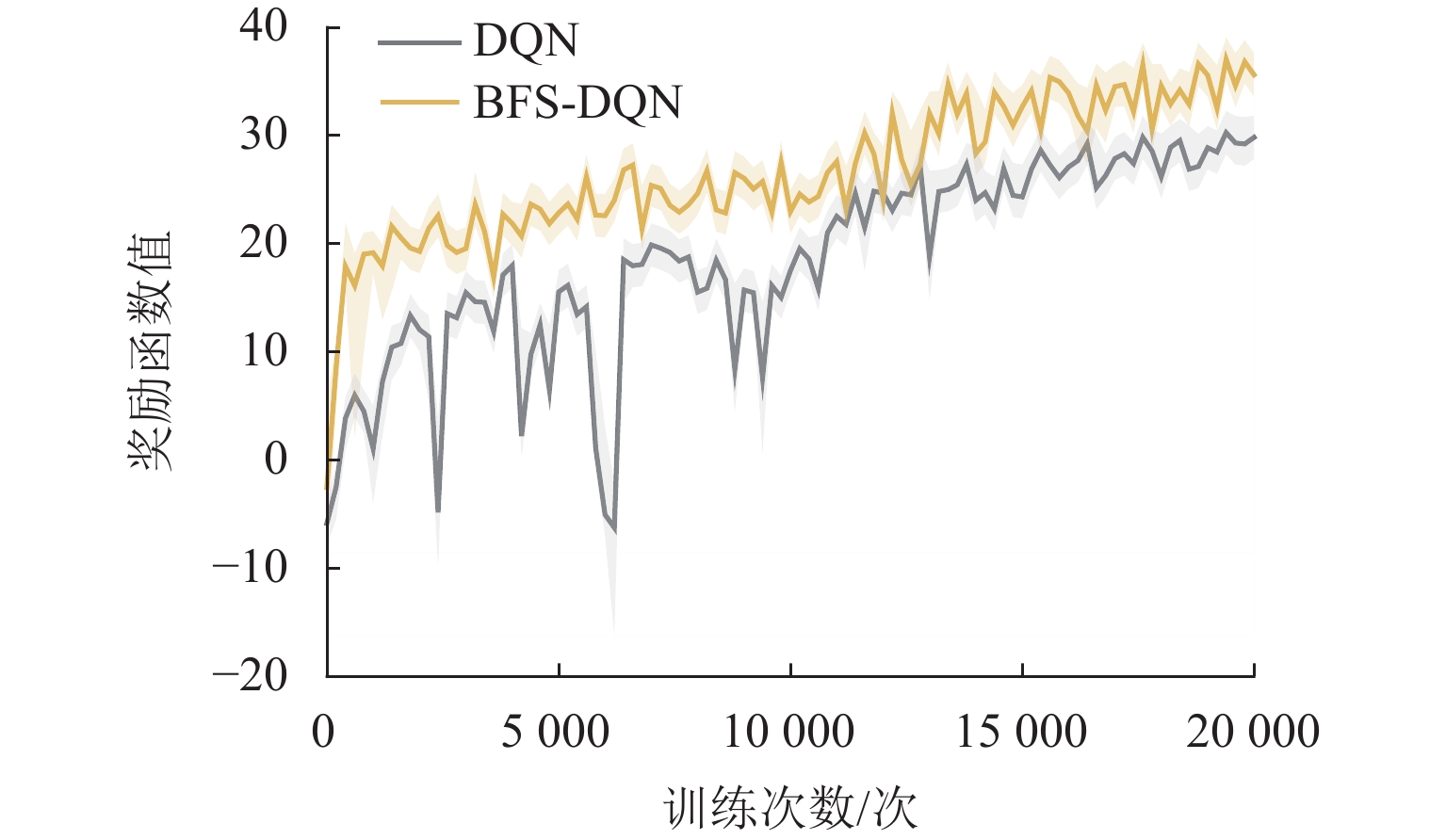
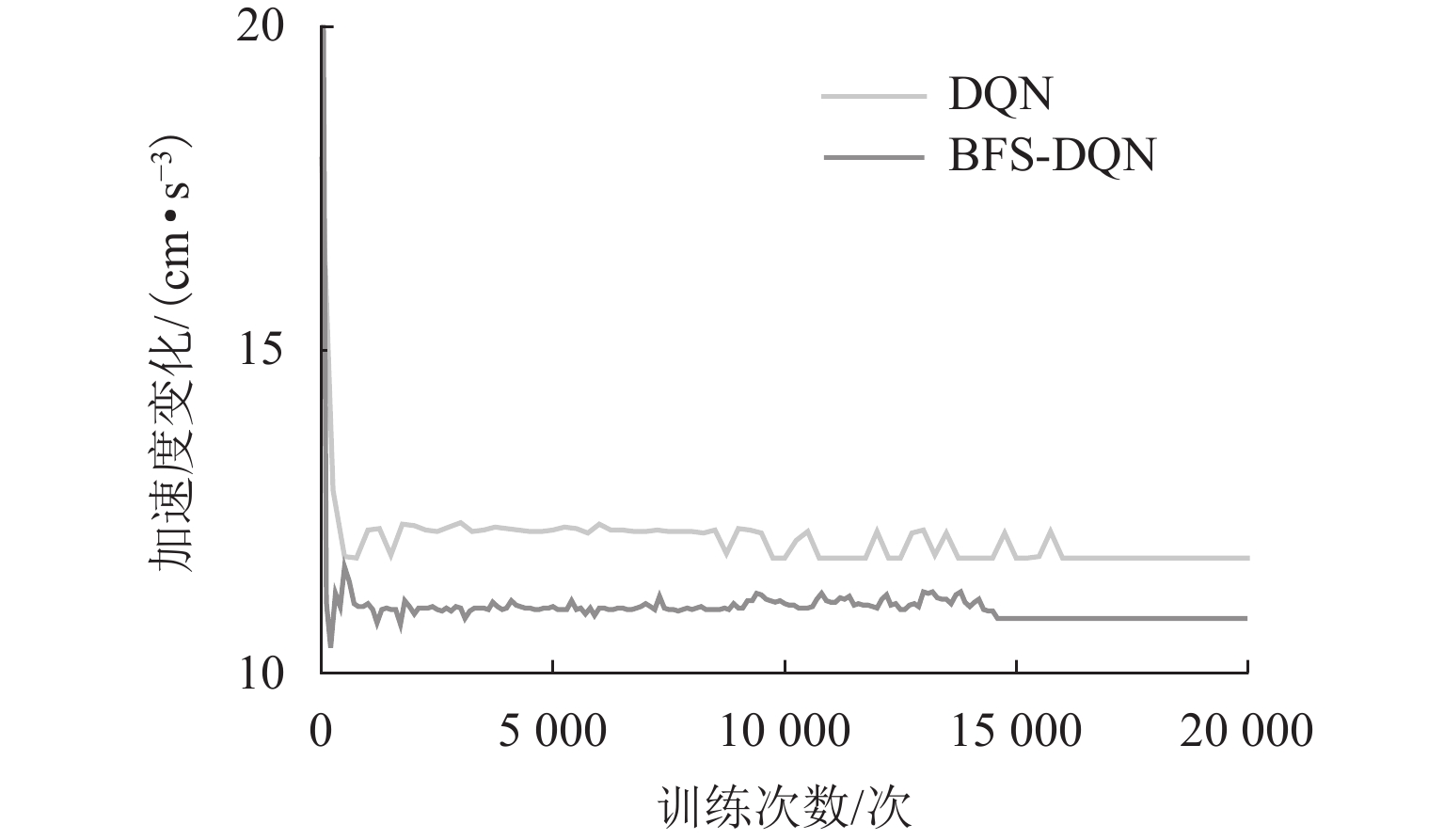
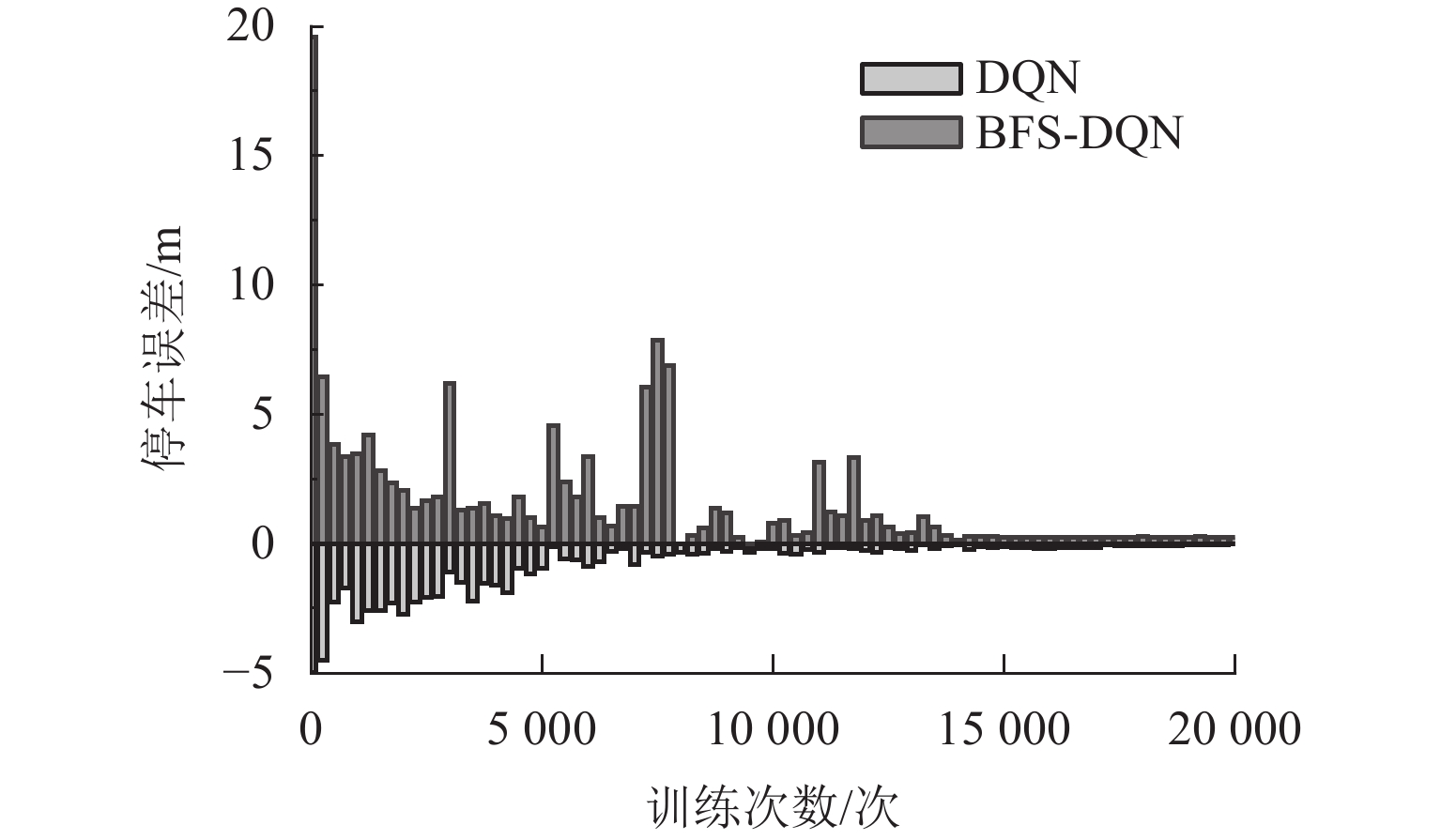
训练结果 BFS-DQN DQN 平均奖励值 33.5 27.8 平均状态转移次数/次 70 72 平均停车误差/m 0.10 0.15 平均加速度变化/(cm·s−3) 10.84 11.78 平均制动时间/s 14.0 14.4 表 4 算法性能
Table 4. Algorithm performance
制动控制策略 RMSE SD BFS-DQN 0.099048 0.070652 DQN 0.142815 0.110446 传统 ATO 0.276103 0.140018 表 5 停车误差分布情况
Table 5. Distribution of parking errors
次 停车误差/m BFS-DQN DQN ATO $ x \lt - 0.5 $ 0 0 3 $ - 0.5 \leqslant x \leqslant - 0.3 $ 0 2 3 $ - 0.3 \lt x \leqslant 0 $ 18 19 16 $0 \lt x \leqslant 0.3$ 32 29 20 $ 0.3 \lt x \leqslant 0.5 $ 0 0 6 $ x \gt 0.5 $ 0 0 2 -
[1] 邓自刚,刘宗鑫,李海涛,等. 磁悬浮列车发展现状与展望[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2022,57(3): 455-474,530.DENG Zigang, LIU Zongxin, LI Haitao, et al. Development status and prospect of maglev train[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2022, 57(3): 455-474,530. [2] 吴萌岭,马天和,田春,等. 列车制动技术发展趋势探讨[J]. 中国铁道科学,2019,40(1): 134-144.WU Mengling, MA Tianhe, TIAN Chun, et al. Discussion on development trend of train braking technology[J]. China Railway Science, 2019, 40(1): 134-144. [3] 李中奇,邢月霜. 动车组进站过程精准停车控制方法研究[J]. 系统仿真学报,2021,33(1): 149-158.LI Zhongqi, XING Yueshuang. Research on precision parking control method for EMU inbound process[J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2021, 33(1): 149-158. [4] 周嘉俊,吴萌岭,刘宇康,等. 基于改进史密斯预估器的列车制动减速度控制研究[J]. 同济大学学报(自然科学版),2020,48(11): 1657-1667.ZHOU Jiajun, WU Mengling, LIU Yukang, et al. Train braking deceleration control based on improved Smith estimator[J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science), 2020, 48(11): 1657-1667. [5] 马天和,吴萌岭,田春. 城轨列车减速度反馈制动力闭环控制方法[J]. 仪器仪表学报,2021,42(4): 197-205.MA Tianhe, WU Mengling, TIAN Chun. Deceleration-feedback braking force closed-loop control method for urban rail train[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2021, 42(4): 197-205. [6] 崔俊锋,王长远,王琦,等. 中低速磁浮列车制动过程的时滞补偿预测控制[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报,2024,21(2):735-747.CUI Junfeng, WANG Changyuan, WANG QI, et al. Time-delay compensation predictive control for braking process of medium-low speed maglev train[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering,2024,21(2):735-747. [7] YIN J T, SU S, XUN J, et al. Data-driven approaches for modeling train control models: comparison and case studies[J]. ISA Transactions, 2020, 98: 349-363. doi: 10.1016/j.isatra.2019.08.024 [8] LI Z, TANG T, GAO C H. Long short-term memory neural network applied to train dynamic model and speed prediction[J]. Algorithms, 2019, 12(8): 173.1-173.21. [9] YIN J T, NING C H, TANG T. Data-driven models for train control dynamics in high-speed railways[J]. Information Sciences:an International Journal, 2022, 600: 377-400. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2022.04.004 [10] LIU H E, YANG L J, YANG H. Cooperative optimal control of the following operation of high-speed trains[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2022, 23(10): 17744-17755. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2022.3163971 [11] LIU H E, YANG H, WANG D H. Robust speed prediction of high-speed trains based on improved echo state networks[J]. Neural Computing and Applications, 2021, 33(7): 2351-2367. doi: 10.1007/s00521-020-05096-y [12] JIANG S Y, GAO H J, WANG X H, et al. Deep reinforcement learning based multi-level dynamic reconfiguration for urban distribution network: a cloud-edge collaboration architecture[J]. Global Energy Interconnection, 2023, 6(1): 1-14. doi: 10.1016/j.gloei.2023.02.001 [13] QI X W, LUO Y D, WU G Y, et al. Deep reinforcement learning enabled self-learning control for energy efficient driving[J]. Transportation Research Part C:Emerging Technologies, 2019, 99: 67-81. doi: 10.1016/j.trc.2018.12.018 [14] YANG Y, LI J T, PENG L L. Multi-robot path planning based on a deep reinforcement learning DQN algorithm[J]. CAAI Transactions on Intelligence Technology, 2020, 5(3): 177-183. doi: 10.1049/trit.2020.0024 [15] 张淼,张琦,刘文韬,等. 一种基于策略梯度强化学习的列车智能控制方法[J]. 铁道学报,2020,42(1): 69-75.ZHANG Miao, ZHANG Qi, LIU Wentao, et al. A policy-based reinforcement learning algorithm for intelligent train control[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2020, 42(1): 69-75. [16] 高豪,张亚东,郭进,等. 基于动态规划的列车节能运行两阶段优化方法[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2020,55(5): 946-954.GAO Hao, ZHANG Yadong, GUO Jin, et al. Two-stage optimization method of train energy-efficient operation based on dynamic programming[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2020, 55(5): 946-954. [17] 蒋灵明,倪少权. 基于多智体强化学习的高效率货物列车运行动态调整方法[J]. 铁道学报,2023,45(8): 27-35.JIANG Lingming, NI Shaoquan. High-efficiency freight train rescheduling enabled by multi-agent reinforcement learning[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2023, 45(8): 27-35. [18] SHANG M Y, ZHOU Y H, FUJITA H. Deep reinforcement learning with reference system to handle constraints for energy-efficient train control[J]. Information Sciences, 2021, 570: 708-721. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2021.04.088 [19] LIU W T, SU S, TANG T, et al. A DQN-based intelligent control method for heavy haul trains on long steep downhill section[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2021, 129(10): 103249.1-103249.21 . [20] WANG H N, LIU N, ZHANG Y Y, et al. Deep reinforcement learning: a survey[J]. Frontiers of Information Technology & Electronic Engineering, 2020, 21(12): 1726-1744. [21] Wang Y, Chardonnet J R, Merienne F. Speed profile optimization for enhanced passenger comfort: An optimal control approach[C]//2018 21st International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC). [S.l.]: IEEE, 2018: 723-728. [22] 万里鹏,兰旭光,张翰博,等. 深度强化学习理论及其应用综述[J]. 模式识别与人工智能,2019,32(1): 67-81.WAN Lipeng, LAN Xuguang, ZHANG Hanbo, et al. A review of deep reinforcement learning theory and application[J]. Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence, 2019, 32(1): 67-81. -




 下载:
下载: