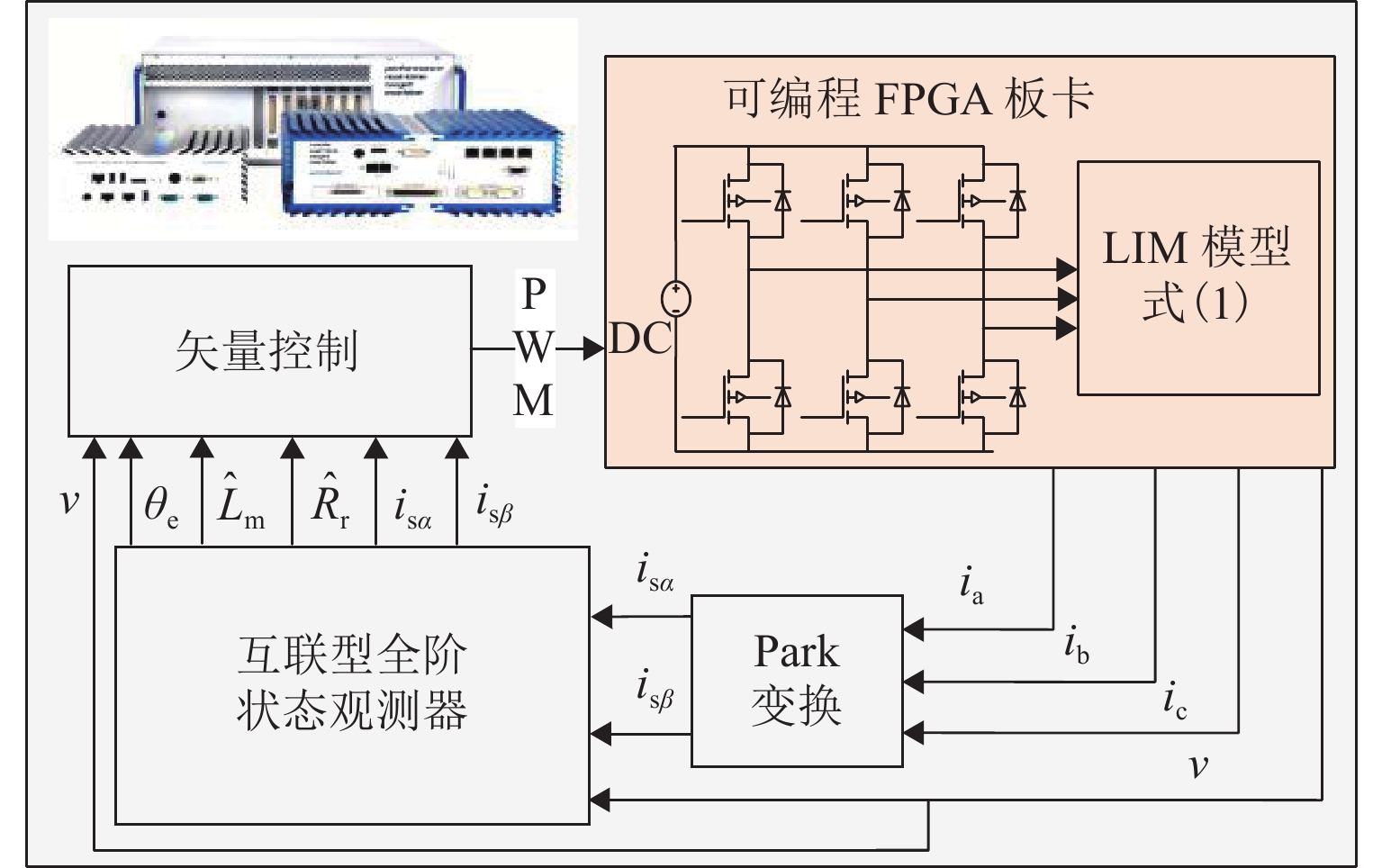
Online Parameter Identification of Linear Induction Motors Based on Improved Interconnected Full-Order Observer
-
摘要:
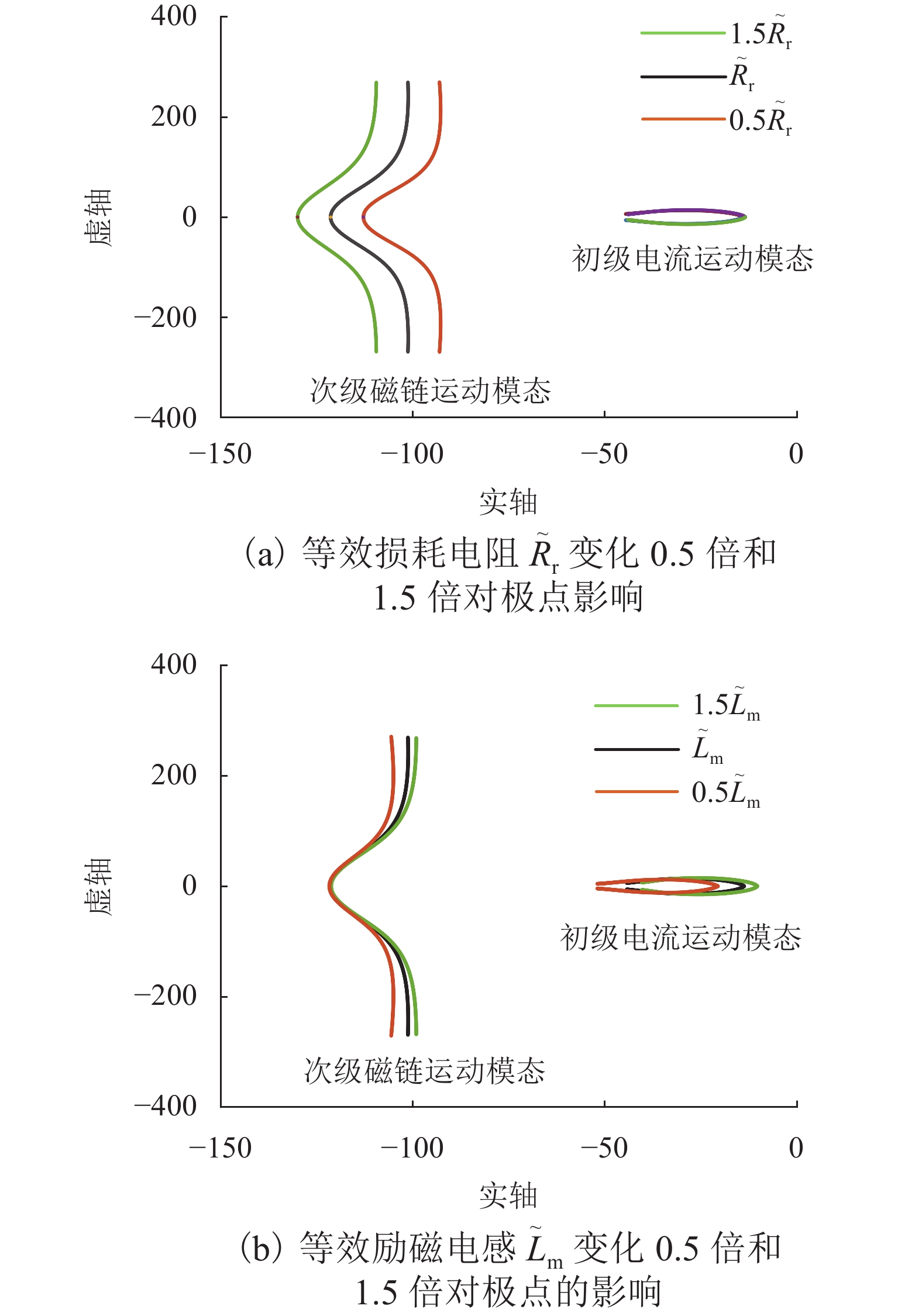
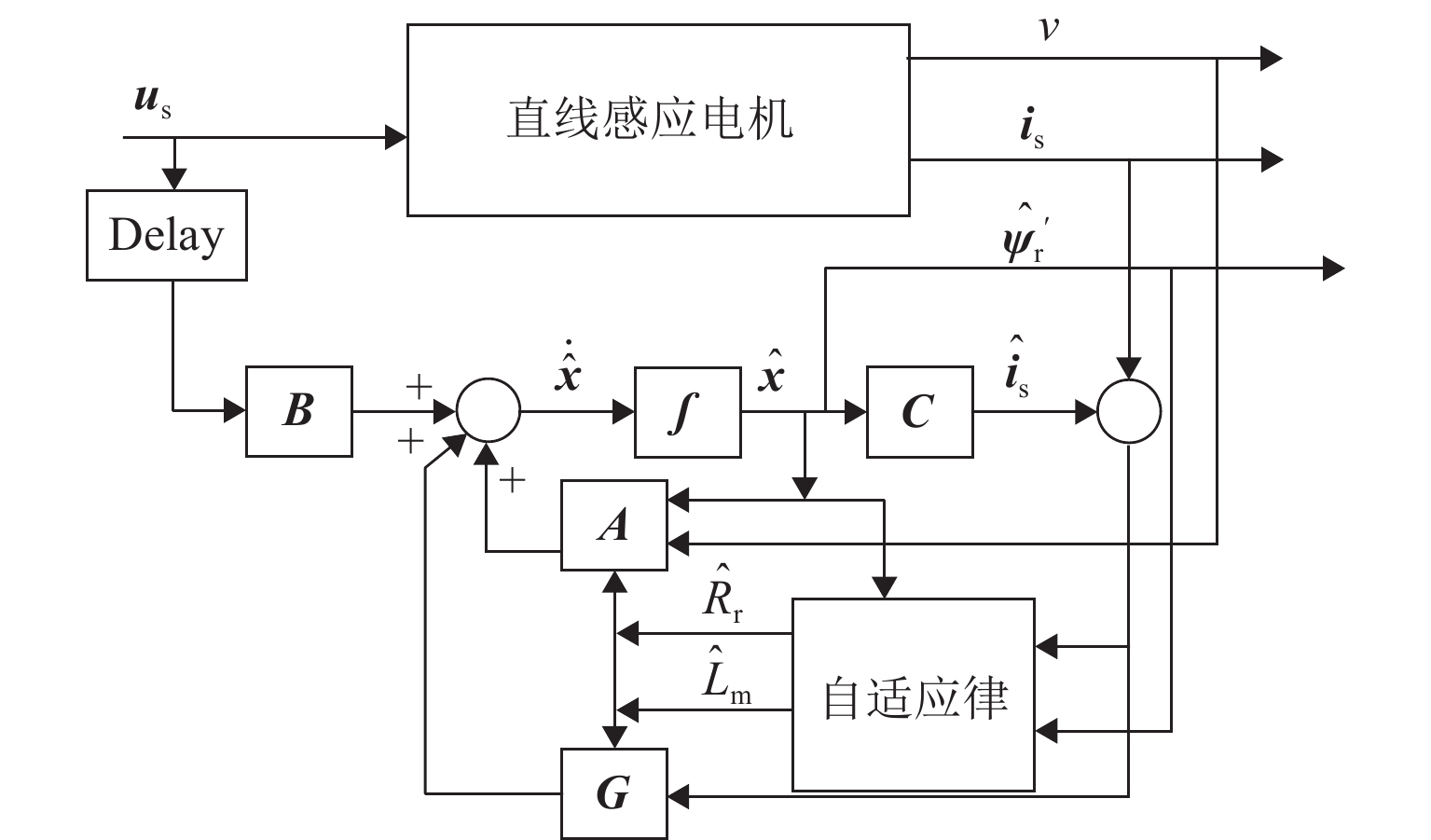
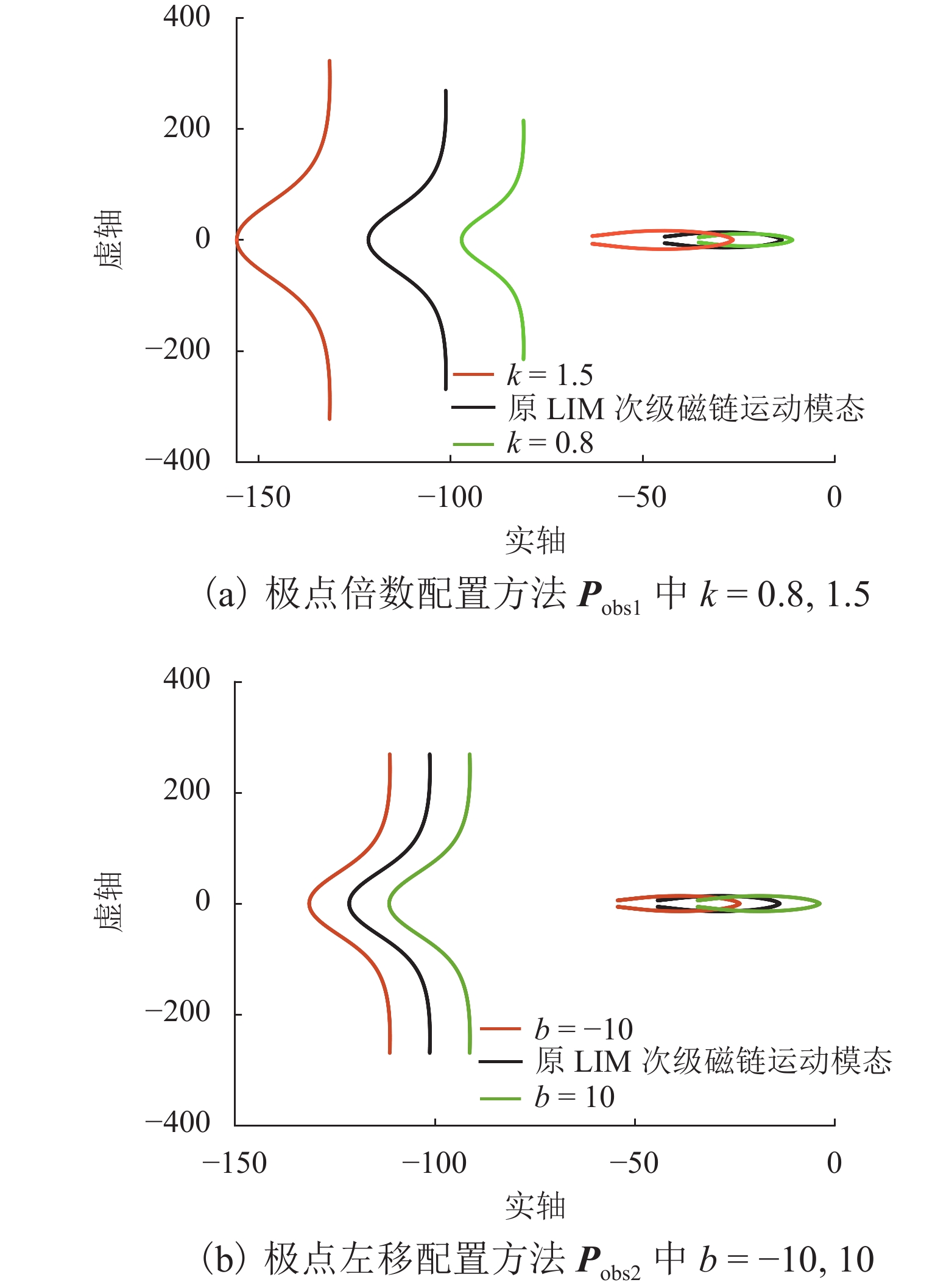
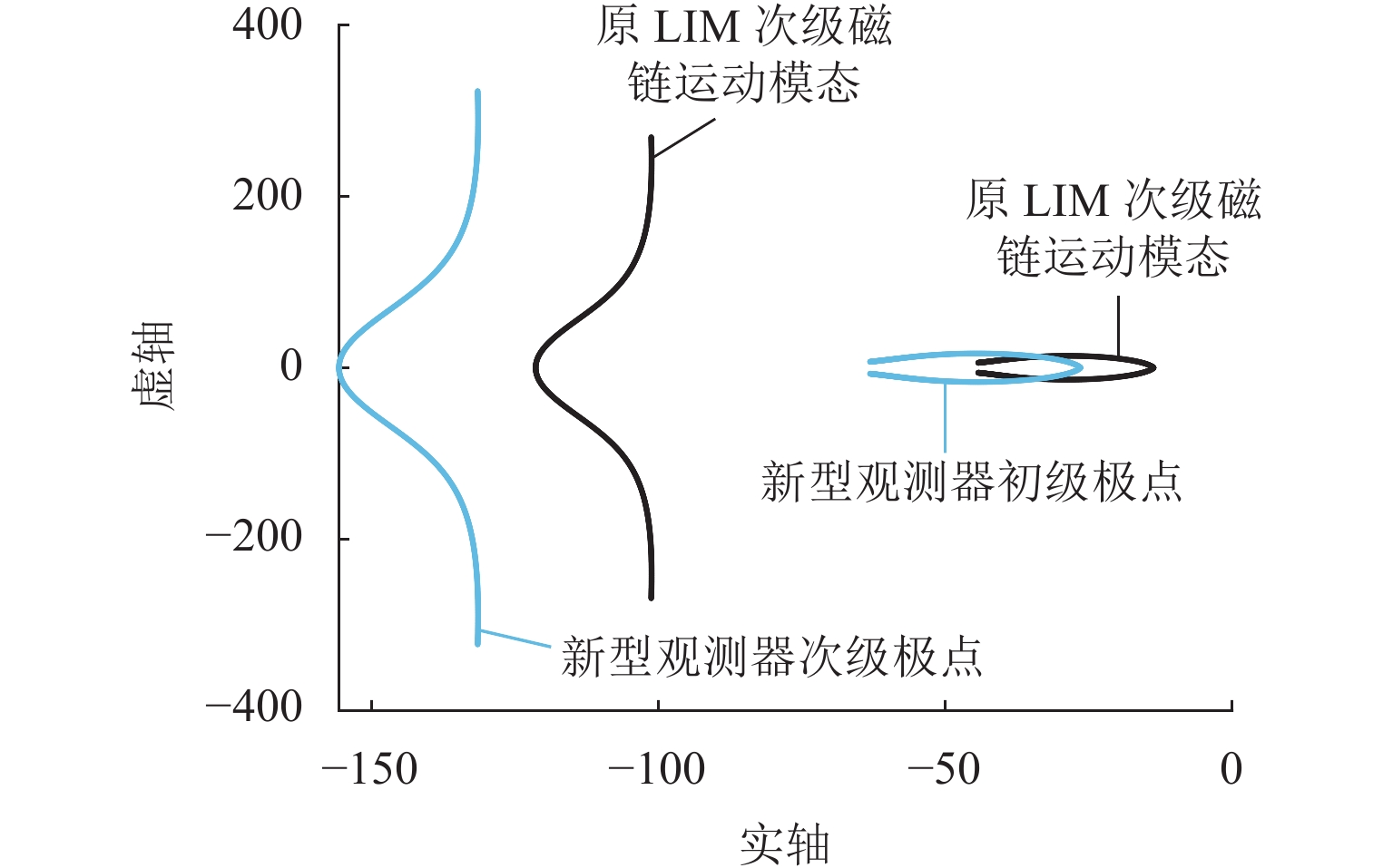
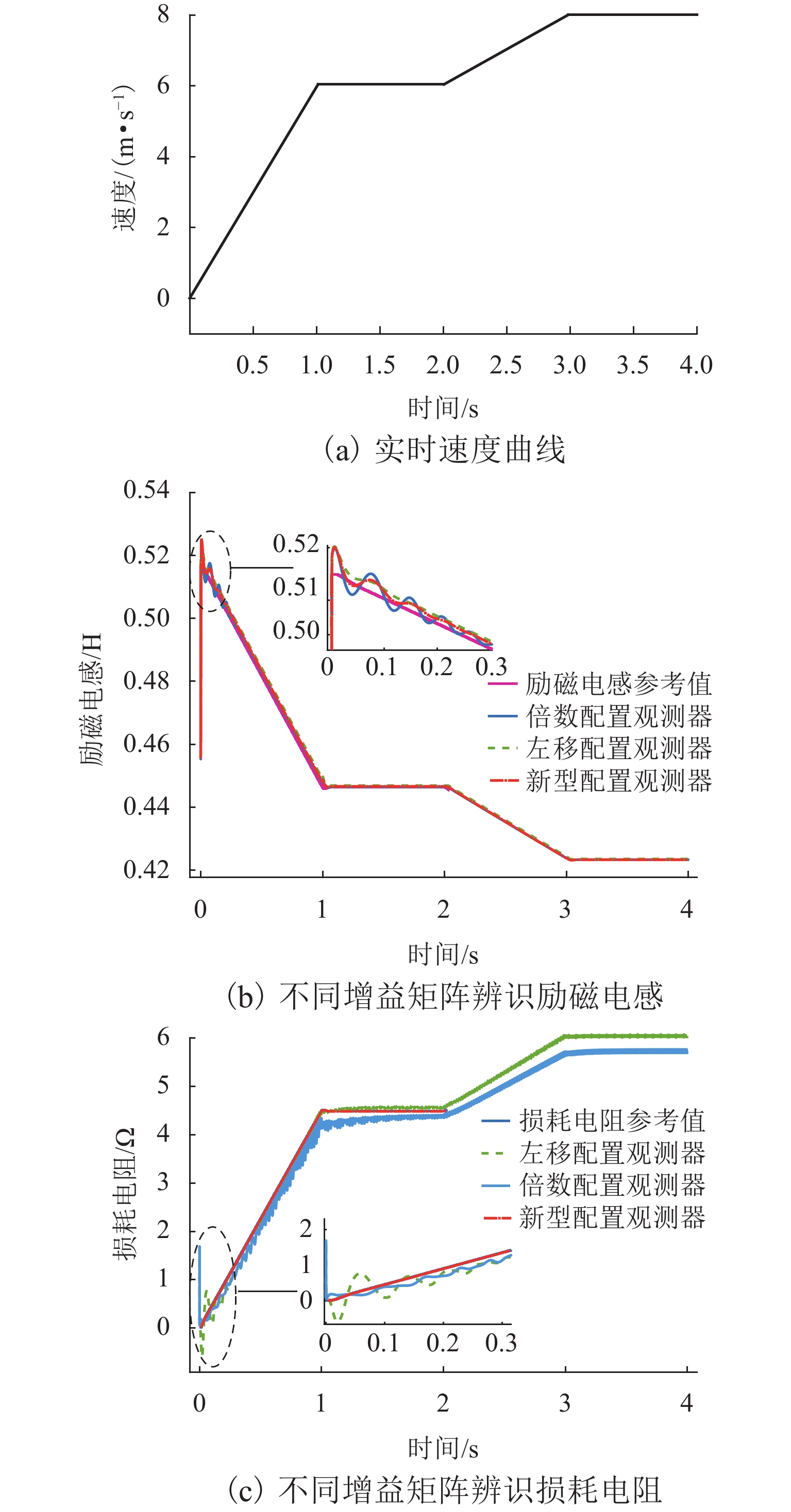
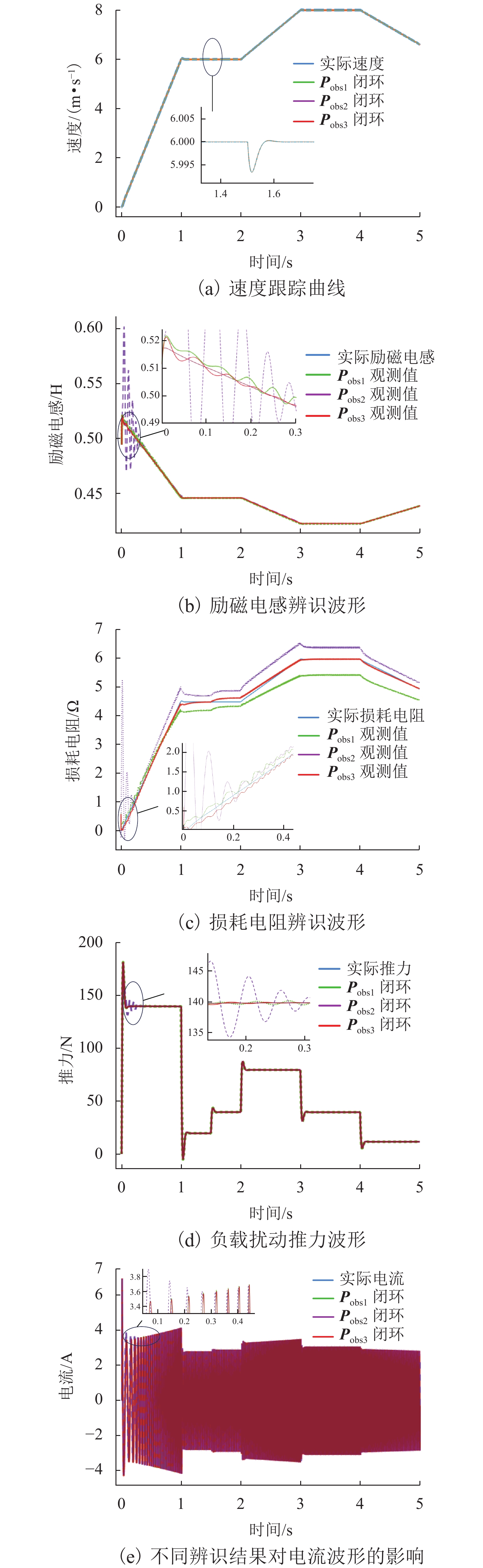
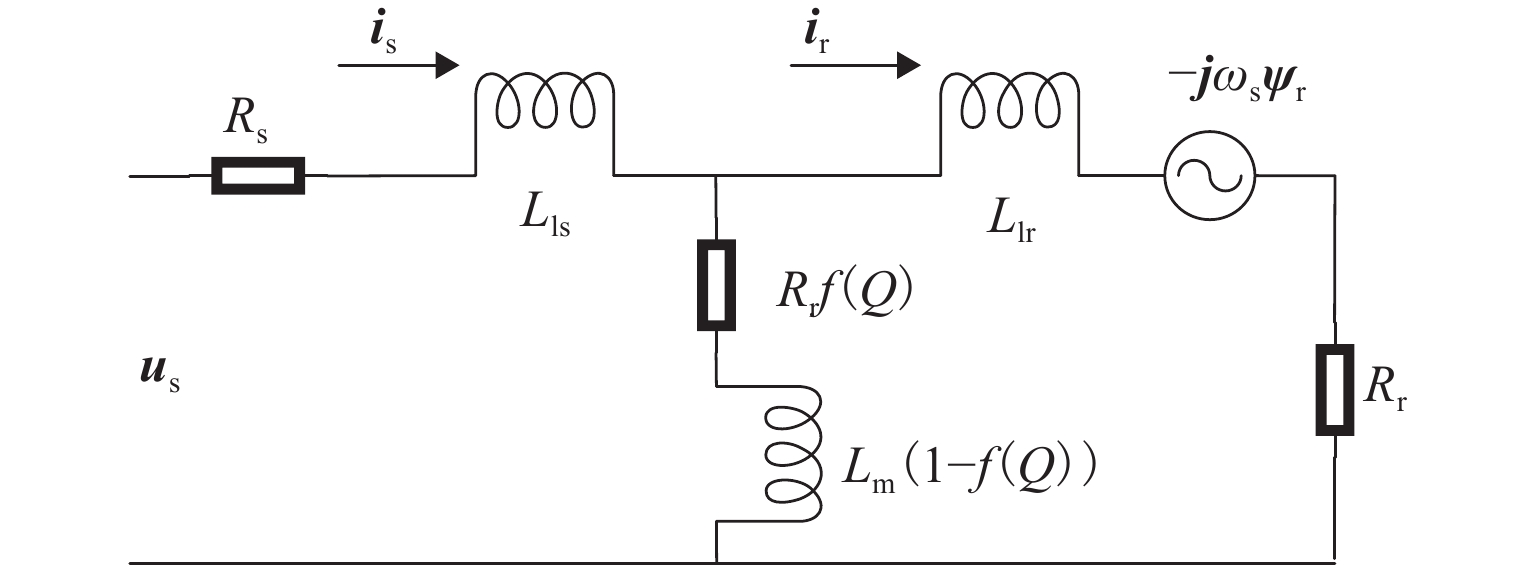
由于直线感应电机特殊结构和动态边端效应等影响,其励磁电感和次级损耗电阻的变化机理和规律复杂,为提高观测器对励磁电感和次级损耗电阻的辨识精度和性能,提出一种基于改进互联型全阶观测器的直线感应电机双参数在线辨识方法. 首先,根据考虑动态边端效应的直线感应电机T型等效电路,建立双参数变化的电机状态空间方程,并分析参数变化及耦合特性对电机极点影响;其次,为减小参数耦合对辨识精度的影响,建立双参数互联的低耦合辨识模型,完成互联型全阶自适应观测器设计,采用Popov超稳定性理论推导励磁电感和次级电阻在线辨识的自适应律,实现双参数在线辨识;然后,为提高观测器的稳定性和收敛速度,结合新型极点配置法完成反馈增益矩阵的推导与设计;最后,搭建仿真模型和硬件在环辨识模型进行实验验证. 结果表明:新型全阶自适应观测器在启动加速阶段时励磁电感和损耗电阻辨识误差在0.01%左右;在负载动态时损耗电阻辨识误差在0.03%左右.
Abstract:Due to the special structure and dynamic end effect of linear induction motors, the change mechanism and law of their excitation inductance and secondary loss resistance are complicated. In order to improve the identification accuracy and performance of the observer for excitation inductance and secondary loss resistance, an online dual-parameter identification method of linear induction motors based on an improved interconnected full-order observer was proposed. Firstly, based on the T-type equivalent circuit of the linear induction motor considering dynamic end effects, the state space equations with dual-parameter changes were established, and the influence of parameter changes and coupling characteristics on motor poles was analyzed. Secondly, to reduce the impact of parameter coupling on identification accuracy, a low-coupling identification model with dual-parameter interconnection was established, and an interconnected full-order adaptive observer was designed. The adaptive laws for online identification of excitation inductance and secondary resistance were derived using Popov hyperstability theory, realizing online dual-parameter identification. Then, to improve the stability and convergence speed of the observer, a feedback gain matrix was derived and designed by using a novel pole configuration method. Finally, a simulation model and hardware-in-the-loop identification model were built for experimental verification. The results show that the new full-order adaptive observer achieves excitation inductance and loss resistance identification errors of around 0.01% during the startup acceleration phase and around 0.03% during dynamic loading.
-
表 1 直线感应电机参数
Table 1. Parameters of linear induction motor
参数 取值 参数 取值 额定功率/W 424 互感/H 0.517 额定速度/(m·s−1) 8 初级电感/H 0.637 初级长度/m 1.014 初级电阻/Ω 11 极距/mm 0.205 次级电感/H 0.757 极对数 3 次级电阻/Ω 32.571 -
[1] 邓自刚,刘宗鑫,李海涛,等. 磁悬浮列车发展现状与展望[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2022,57(3): 455-474,530. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20220001DENG Zigang, LIU Zongxin, LI Haitao, et al. Development status and prospect of maglev train[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2022, 57(3): 455-474,530. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20220001 [2] 吕刚. 直线电机在轨道交通中的应用与关键技术综述[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2020,40(17): 5665-5675.LYU Gang. Review of the application and key technology in the linear motor for the rail transit[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2020, 40(17): 5665-5675. [3] 尚敬,杨大成,廖长鑫,等. 磁悬浮列车直线感应电机恒转差频率磁场定向控制[J]. 大功率变流技术,2010(1): 54-58.SHANG Jing, YANG Dacheng, LIAO Changxin, et al. Field oriented control with constant slip frequency of linear induction motor on maglev train[J]. High Power Converter Technology, 2010(1): 54-58. [4] ACCETTA A, CIRRINCIONE M, PUCCI M, et al. State space-vector model of linear induction motors including end-effects and iron losses part I: theoretical analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 2019, 56(1): 235-244. [5] XU W, ALI M M, ELMORSHEDY M F, et al. One improved sliding mode DTC for linear induction machines based on linear metro[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2020, 36(4): 4560-4571. [6] 徐伟,肖新宇,董定昊,等. 直线感应电机效率优化控制技术综述[J]. 电工技术学报,2021,36(5): 902-915,934.XU Wei, XIAO Xinyu, DONG Dinghao, et al. Review on efficiency optimization control strategies of linear induction machines[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2021, 36(5):902-915,934. [7] MOUSAEI A, BANNAE SHARIFIAN M B, ROSTAMI N. An improved predictive current control strategy of linear induction motor based on ultra-local model and extended state observer[C]//2022 13th Power Electronics, Drive Systems, and Technologies Conference (PEDSTC). Tehran:IEEE,2022:12-18. [8] 韩正清,许金,芮万智,等. 高速短初级直线感应电动机等效电路模型及时变参数辨识[J]. 电机与控制学报,2021,25(11): 8-15.HAN Zhengqing, XU Jin, RUI Wanzhi, et al. Equivalent circuit model and time-varying parameter identification of high speed short primary linear induction motors[J]. Electric Machines and Control, 2021, 25(11): 8-15. [9] 徐伟,孙广生. 单边直线感应电机等效电路参数研究[J]. 中国工程科学,2008,10(8): 76-80.XU Wei, SUN Guangsheng. Research on the equivalent circuit parameter of single linear induction motor[J]. Engineering Sciences, 2008, 10(8): 76-80. [10] RAPTIS D S, KLADAS A G, TEGOPOULOS J A. Accurate induction motor estimator based on magnetic field analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2008, 44(6): 1574-1577. doi: 10.1109/TMAG.2007.915848 [11] 邸珺,范瑜,刘亚静. 基于等效次级的直线感应电机的电磁分析与参数辨识[J]. 电工技术学报,2017,32(11): 145-154.DI Jun, FAN Yu, LIU Yajing. Electromagnetic analysis and parameter estimation for the linear induction motor based on equivalent secondary[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2017, 32(11): 145-154. [12] 吕刚,杨琛. 直线感应电机离线参数辨识及关键辨识参量研究[J]. 电机与控制学报,2020,24(2): 55-62.LÜ Gang, YANG Chen. Off-line parameter estimation of a linear induction motor and the study for key parameters[J]. Electric Machines and Control, 2020, 24(2): 55-62. [13] WANG H M, GE X L, LIU Y C. Second-order sliding-mode MRAS observer-based sensorless vector control of linear induction motor drives for medium-low speed maglev applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2018, 65(12): 9938-9952. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2018.2818664 [14] 刘可安,田红旗,刘勇. 直线感应电机过无次级感应板区检测[J]. 浙江大学学报(工学版),2016,50(12): 2409-2417.LIU Kean, TIAN Hongqi, LIU Yong. Detection of passing area of no secondary reaction plate for linear induction motor[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science), 2016, 50(12): 2409-2417. [15] 王惠民,张颖,葛兴来. 基于全阶状态观测器的直线牵引电机励磁电感在线参数辨识[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2017,37(20): 6101-6108.WANG Huimin, ZHANG Ying, GE Xinglai. On-line parameter identification of linear induction motor magnetizing inductance based on full-order observer[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2017, 37(20): 6101-6108. [16] DONG D H, XU W, XIAO X Y, et al. Online identification strategy of secondary time constant and magnetizing inductance for linear induction motors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2022, 37(10): 12450-12462. doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2022.3171412 [17] WANG B, ZHAO Y Z, YU Y, et al. Speed-sensorless induction machine control in the field-weakening region using discrete speed-adaptive full-order observer[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2015, 31(8): 5759-5773. [18] 张钦培,李健,卢阳,等. 低载波比牵引系统的感应电机特征根离散化模型研究[J]. 电工技术学报,2024,39(2): 434-444,454.ZHANG Qinpei, LI Jian, LU Yang, et al. Research on discretization model of induction motor for low switching-to-fundamental frequency ratio traction system[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2024, 39(2): 434-444,454. [19] ZHANG Y C, BAI Y N, YANG H T, et al. Low switching frequency model predictive control of three-level inverter-fed IM drives with speed-sensorless and field-weakening operations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2018, 66(6): 4262-4272. [20] 尹忠刚,张延庆,杜超,等. 基于双辨识参数全阶自适应观测器的感应电机低速性能[J]. 电工技术学报,2016,31(20): 111-121.YIN Zhonggang, ZHANG Yanqing, DU Chao, et al. Low-speed performance of sensorless vector control for induction motor based on two-parameter identified adaptive full-order observer[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2016, 31(20): 111-121. [21] NGUYEN N D, NAM N N, YOON C, et al. Speed sensorless model predictive torque control of induction motors using a modified adaptive full-order observer[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2021, 69(6): 6162-6172. [22] DUNCAN J. Linear induction motor-equivalent-circuit model[J]. IEEE Proceedings B:Electric Power Applications, 1983, 130(1): 51-57. doi: 10.1049/ip-b.1983.0008 [23] PUCCI M. State space-vector model of linear induction motors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 2014, 50(1): 195-207. doi: 10.1109/TIA.2013.2266351 [24] 张永昌. 感应电机模型预测控制[M]. 北京:机械工业出版社,2020. -




 下载:
下载: