Modeling of High-Speed Maglev Linear Synchronous Motors Considering Influence of Suspension System
-
摘要:
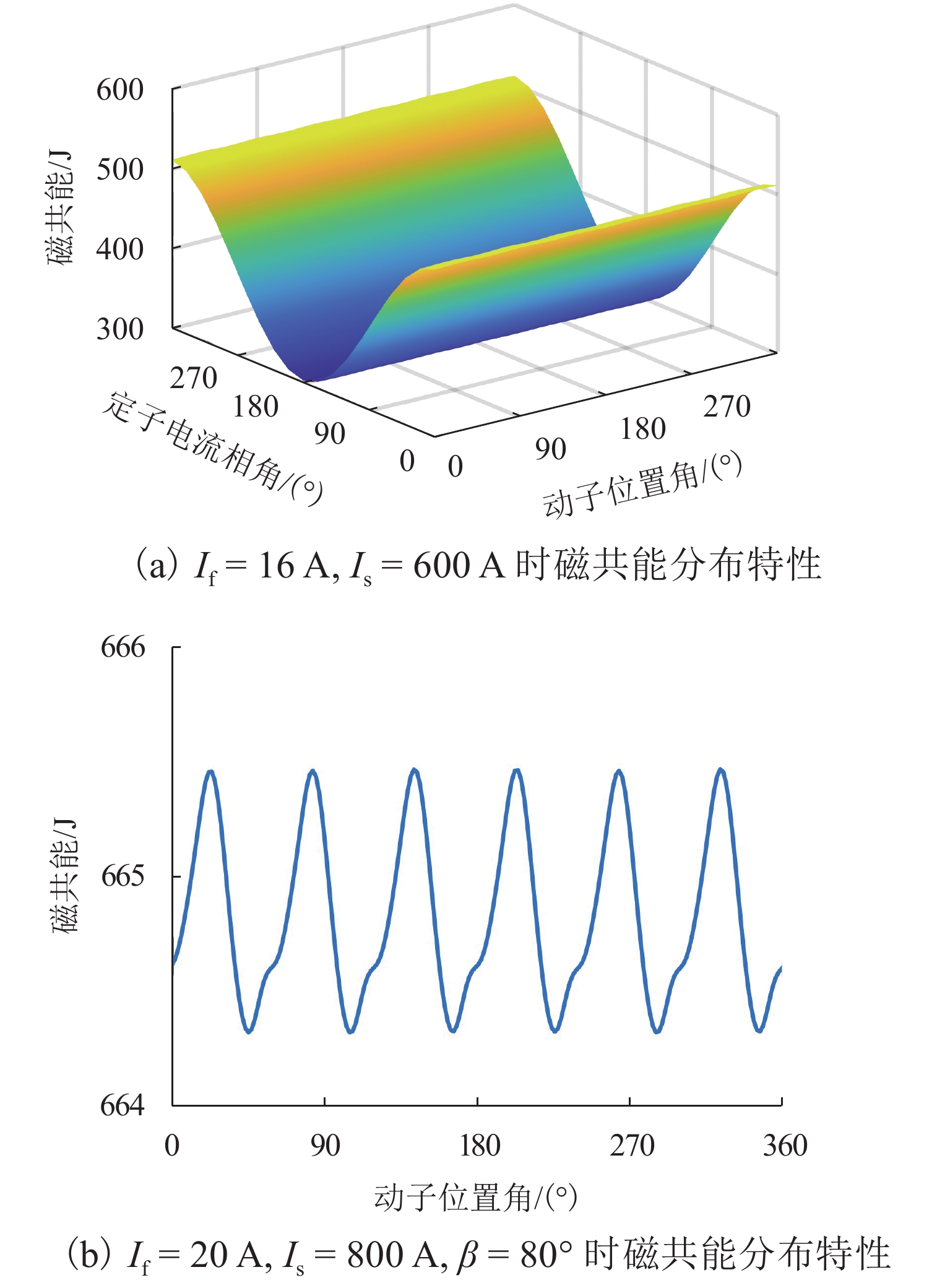
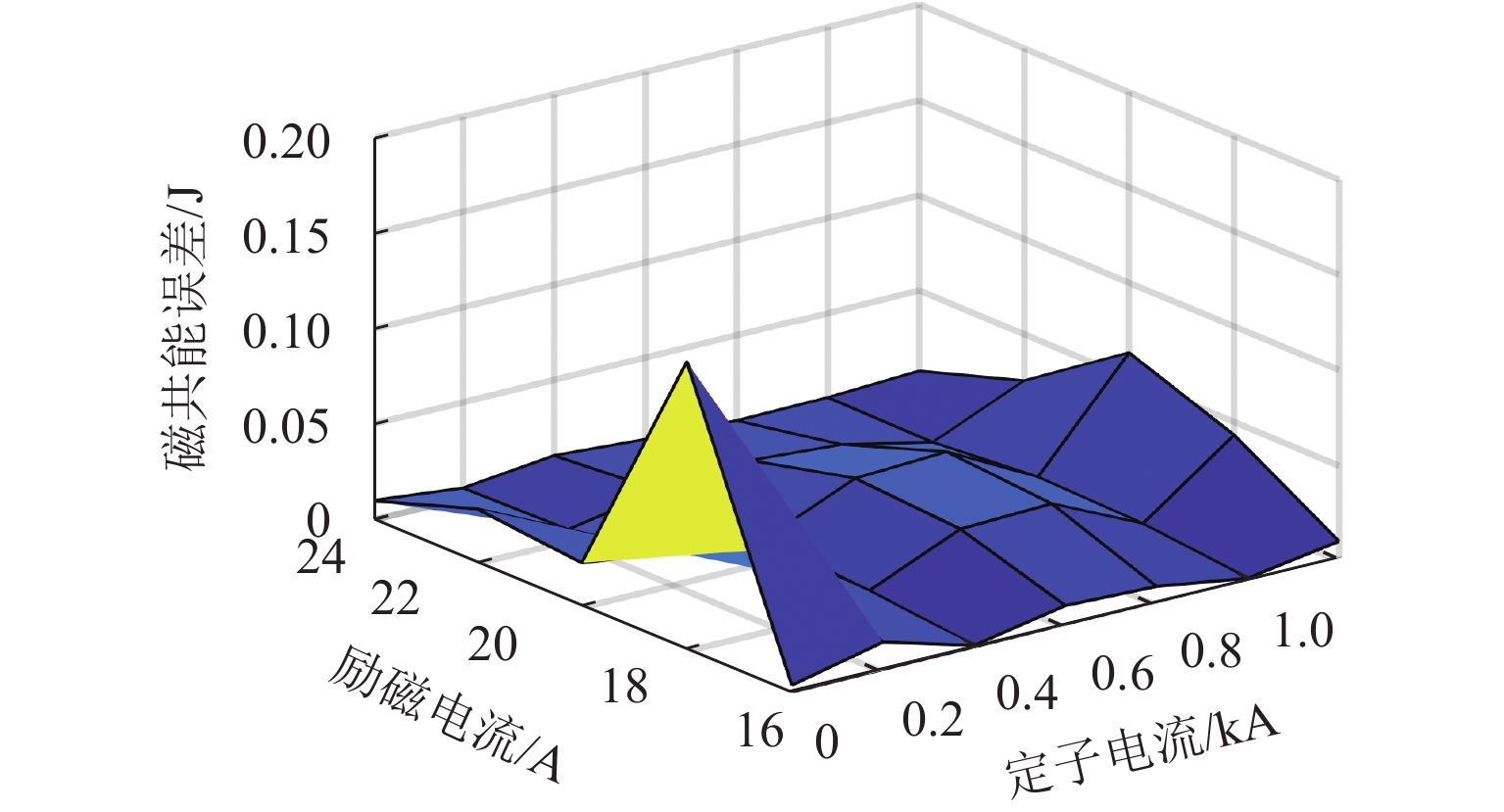
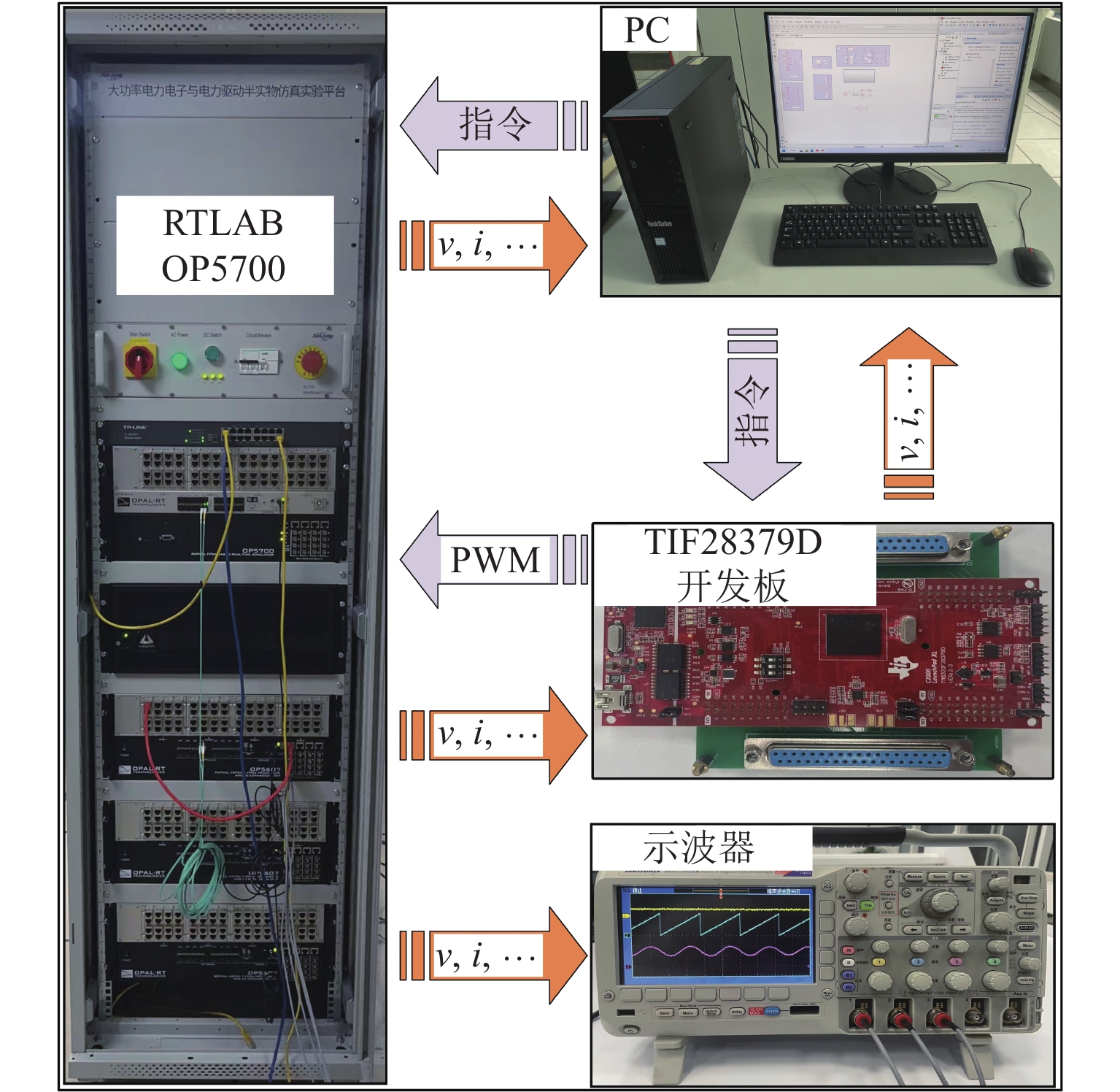
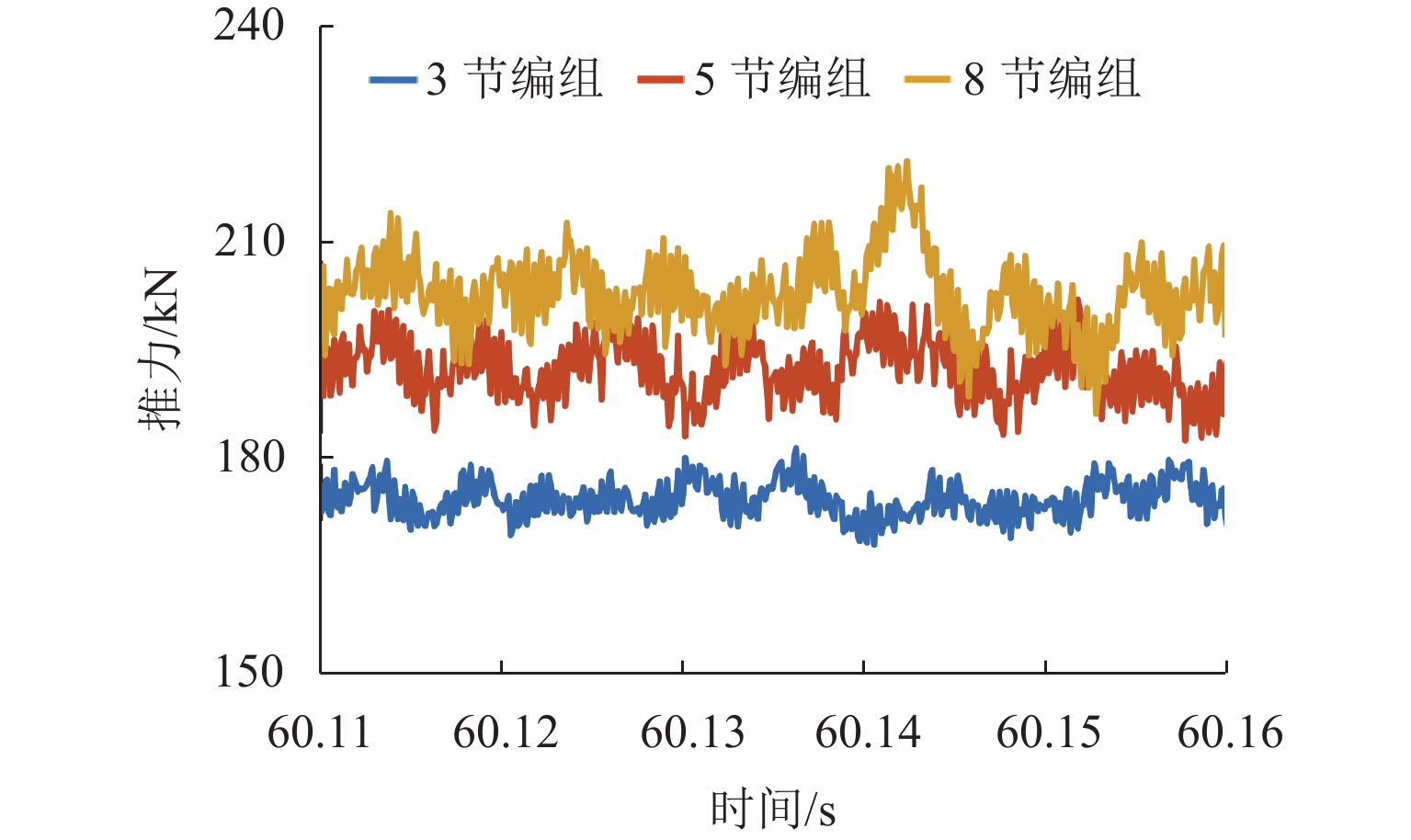
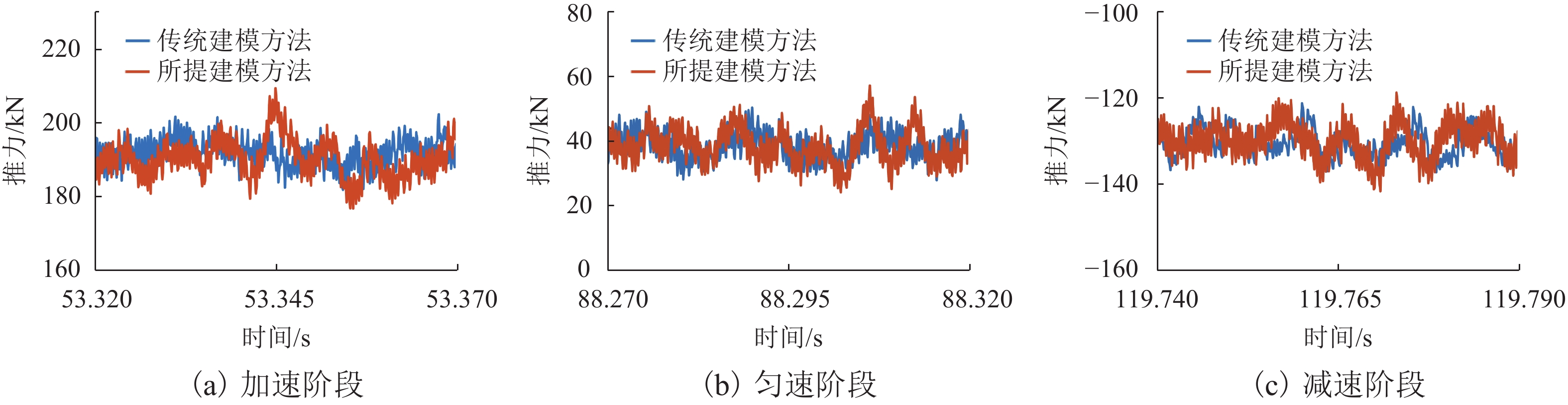
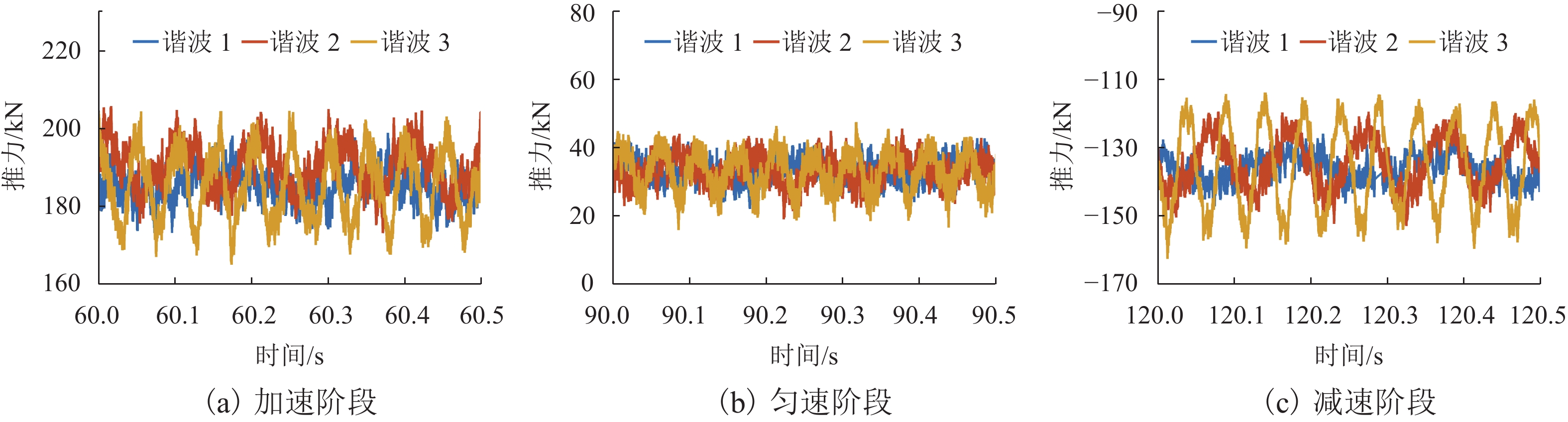
为提高高速磁浮直线同步电机模型精度,基于电磁铁模块磁共能重构,提出一种计及悬浮系统影响的分布参数建模方法. 首先,建立高速磁浮列车电磁铁模块的有限元模型,利用有限元数值分析获取电磁铁模块在不同工况下的磁共能数据,通过对磁共能进行傅里叶级数展开及多项式拟合构建磁共能的解析模型;其次,根据磁共能解析模型推导电磁铁模块的磁链、电压和推力方程;然后,根据列车编组数量和电磁铁模块数量分别建立左右两侧直线同步电机的数学模型,并通过运动学方程计算高速磁浮列车位置和速度;最后,通过硬件在环仿真系统进行实验验证. 试验结果表明:本文所提建模方法与传统建模方法相比,推力波动幅值增加超过6.8%;并且所提方法可以准确表征悬浮系统对牵引控制的影响,当励磁电流谐波幅值增加0.5、1.0、2.0 A时,推力波动幅值分别最大增加54.3%、26.2%、83.7%;当励磁电流谐波频率为5、10、20 Hz时,推力的谐波频率最大达到5.14%,21.75%和14.17%.
Abstract:To enhance the modeling accuracy of high-speed maglev linear synchronous motors, a distributed parameter modeling method considering the influence of the suspension system was proposed based on the magnetic co-energy reconstruction of the electromagnetic module. Firstly, a finite element model of the electromagnetic module of a high-speed maglev train was established. Finite element numerical analysis was conducted to obtain magnetic co-energy data of the electromagnet module under different operating conditions. The magnetic co-energy was then subjected to Fourier series expansion and polynomial fitting to construct an analytical model of the magnetic co-energy. Subsequently, based on the analytical model of the magnetic co-energy, equations for the flux linkage, voltage, and thrust force of the electromagnetic module were derived. Then, mathematical models for the left and right linear synchronous motors based on the number of train formations and the number of electromagnetic modules were established, and the position and velocity of the high-speed maglev train were calculated through kinematic equations. Finally, the proposed modeling method was validated through experiments using a hardware-in-the-loop simulation system. The experimental results indicate that compared to traditional modeling methods, the proposed modeling method increases the amplitude of thrust fluctuations by more than 6.8%. Moreover, the proposed method can accurately characterize the influence of the suspension system on traction control. When the harmonic amplitude of the excitation current increases by 0.5 A, 1.0 A, and 2.0 A, the maximum increase in the amplitude of thrust fluctuations is 54.3%, 26.2%, and 83.7%, respectively. Furthermore, when the harmonic frequency of the excitation current is at 5 Hz, 10 Hz, and 20 Hz, the harmonic frequency of the thrust reaches up to 5.14%, 21.75%, and 14.17%, respectively.
-
Key words:
- magnetic levitation /
- linear motors /
- traction control /
- suspension system /
- modeling method
-
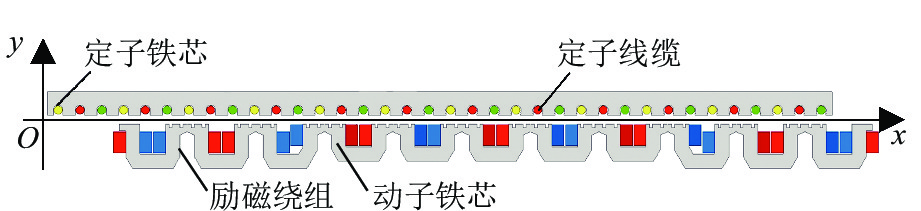
表 1 电磁铁模块主要参数
Table 1. Main parameters of electromagnet module
参数名称 数值 参数名称 数值 额定励磁电流/A 20 动子极距/mm 266.5 定子绕组匝数/匝 1 铁芯厚度/mm 185 励磁绕组匝数/匝 270 定子槽距/mm 86 定子极距/mm 258 额定气隙/mm 10 表 2 不同励磁电流时的推力谐波含量和波动对比
Table 2. Comparison of thrust harmonics and fluctuations at different excitation currents
阶段 类型 推力谐波占比/% 推力波动/kN f =5 Hz f =10 Hz f =20 Hz 加速 谐波 1 1.43 0.21 0.10 25.60 谐波 2 0.54 2.48 0.30 32.40 谐波 3 0.29 0.16 5.14 39.30 匀速 谐波 1 4.48 2.04 1.27 20.69 谐波 2 1.84 9.66 1.43 26.45 谐波 3 2.10 0.63 21.75 31.46 减速 谐波 1 3.86 0.10 1.01 22.00 谐波 2 0.59 7.98 0.37 33.40 谐波 3 0.48 0.63 14.17 48.50 -
[1] 丁叁叁. 时速600 公里高速磁浮交通系统[M]. 上海:上海科学技术出版社,2022. [2] 梁建英. 中国高速磁浮交通系统发展现状与展望[J]. 科学,2022,74(5): 31-36.LIANG Jianying. Development status and future prospects of the high-speed maglev transportation system in China[J]. Science, 2022, 74(5): 31-36. [3] 翟明达,龙志强,李晓龙,等. 考虑涡流效应的端部悬浮系统建模与控制器优化设计[J]. 同济大学学报(自然科学版),2021,49(12): 1652-1659.ZHAI Mingda, LONG Zhiqiang, LI Xiaolong, et al. Modeling of front magnetic levitation system and optimization design of controller considering eddy current effect[J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science), 2021, 49(12): 1652-1659. [4] JIANG S H, SHEN D, ZHANG T B, et al. Nonlinear robust composite levitation control for high-speed EMS trains with input saturation and track irregularities[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2022, 23(11): 20323-20336. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2022.3178122 [5] 徐飞,罗世辉,邓自刚. 磁悬浮轨道交通关键技术及全速度域应用研究[J]. 铁道学报,2019,41(3): 40-49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2019.03.006XU Fei, LUO Shihui, DENG Zigang. Study on key technologies and whole speed range application of maglev rail transport[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2019, 41(3): 40-49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2019.03.006 [6] 梁鑫,罗世辉,马卫华. 常导磁浮列车动态磁轨关系研究[J]. 铁道学报,2013,35(9): 39-45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2013.09.007LIANG Xin, LUO Shihui, MA Weihua. Study on dynamic magnet-track relationship of maglev vehicles[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2013, 35(9): 39-45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2013.09.007 [7] WANG B Y, WANG K. A novel propulsion control scheme of long stator linear synchronous motor for maglev vehicle considering the influence of suspension system[C]//2018 21st International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS). Jeju: IEEE, 2018: 1481-1485. [8] 朱进权,葛琼璇,张波,等. 考虑悬浮系统影响的高速磁悬浮列车牵引控制策略[J]. 电工技术学报,2022,37(12): 3087-3096.ZHU Jinquan, GE Qiongxuan, ZHANG Bo, et al. Traction control strategy of high-speed maglev considering the influence of suspension system[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2022, 37(12): 3087-3096. [9] 朱进权,葛琼璇,孙鹏琨,等. 基于自抗扰的高速磁浮列车牵引控制策略[J]. 电工技术学报,2020,35(5): 1065-1074.ZHU Jinquan, GE Qiongxuan, SUN Pengkun, et al. Traction-system research of high-speed maglev based on active disturbance rejection control[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2020, 35(5): 1065-1074. [10] 孙鹏琨,葛琼璇,王晓新,等. 磁悬浮列车在双端供电模式下的无速度传感器控制[J]. 电工技术学报,2018,33(18): 4249-4256.SUN Pengkun, GE Qiongxuan, WANG Xiaoxin, et al. Speed sensorless control of maglev train with double-end power supply[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2018, 33(18): 4249-4256. [11] 章九鼎,卢琴芬. 长定子直线同步电机齿槽效应的计算与影响[J]. 电工技术学报,2021,36(5): 964-972,1026.ZHANG Jiuding, LU Qinfen. Calculation and influences of cogging effects in long-stator linear synchronous motor[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2021, 36(5): 964-972,1026. [12] 彭兵,张囡,夏加宽,等. 永磁直线电机端部效应力的解析计算[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2016,36(2):547-553.PENG Bing, ZHANG Nan, XIA Jiakuan, et al. Analytical calculation for end effect forces in permanent magnet linear motors[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE,2016,36(2):547-553. [13] 施晓红,龙志强. 磁悬浮车轨耦合控制系统的非线性振动特性分析[J]. 铁道学报,2009,31(4): 38-42.SHI Xiaohong, LONG Zhiqiang. Nonlinear vibration analysis of the maglev guideway-vehicle coupling control system[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2009, 31(4): 38-42. [14] WANG X X, LIU H C, ZHANG S T. High performance propulsion control of magnetic levitation vehicle long stator linear synchronous motor[C]//2011 International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems. Beijing: IEEE, 2011: 1-6. [15] JEONG I, GU B G, KIM J, et al. Inductance estimation of electrically excited synchronous motor via polynomial approximations by least square method[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 2015, 51(2): 1526-1537. doi: 10.1109/TIA.2014.2339634 [16] AJILY E, ABBASZADEH K, ARDEBILI M. Three-dimensional field reconstruction method for modeling axial flux permanent magnet machines[J]. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, 2015, 30(1): 199-207. doi: 10.1109/TEC.2014.2353299 [17] JEONG I, NAM K. Analytic expressions of torque and inductances via polynomial approximations of flux linkages[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2015, 51(7): 1-9. [18] EBADI F, MARDANEH M, RAHIDEH A, et al. Analytical energy-based approaches for cogging torque calculation in surface-mounted PM motors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2019, 55(5): 1-10. [19] MONGELLAZ R, SELLIER F, CHISHKO S D, et al. Co-energy-based lookup table model for DC-excited flux-switching motor: study at vehicle level[C]//2015 IEEE Vehicle Power and Propulsion Conference (VPPC). Montreal: IEEE, 2015: 1-8. [20] CHISHKO S D, TANG Y, PAULIDES J J H, et al. CoEnergy-based model for DC excited flux-switching motor[C]//2015 Tenth International Conference on Ecological Vehicles and Renewable Energies (EVER). Monte Carlo: IEEE, 2015: 1-7. [21] ZHONG Z M, JIANG S, ZHOU Y K, et al. Active torque ripple reduction based on an analytical model of torque[J]. IET Electric Power Applications, 2017, 11(3): 331-341. doi: 10.1049/iet-epa.2016.0475 [22] KANG J S, MU S Y, NI F. Improved EL model of long stator linear synchronous motor via analytical magnetic coenergy reconstruction method[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2020, 56(8): 1-13. [23] LIU J X, GE Q X, WANG X X, et al. High performance controller on Real-Time simulation with Hardware-In-Loop for High-Speed Maglev[C]//2014 16th European Conference on Power Electronics and Applications. Lappeenranta: IEEE, 2014: 1-8.LIU J X,GE Q X,WANG X X,et al. High performance controller on Real-Time simulation with Hardware-In-Loop for High-Speed Maglev[C]//2014 16th European Conference on Power Electronics and Applications. Lappeenranta:IEEE,2014:1-8. -




 下载:
下载: