Safety Risk Analysis of Connected and Automated Vehicle Platoons Considering Sensor Noise
-
摘要:
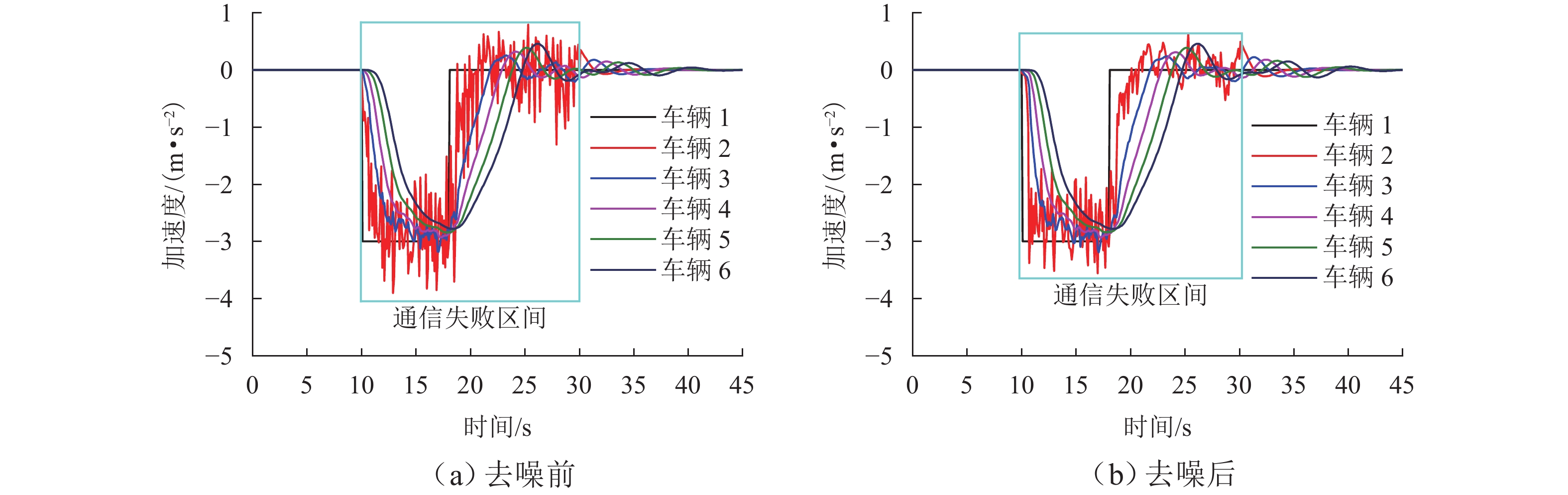
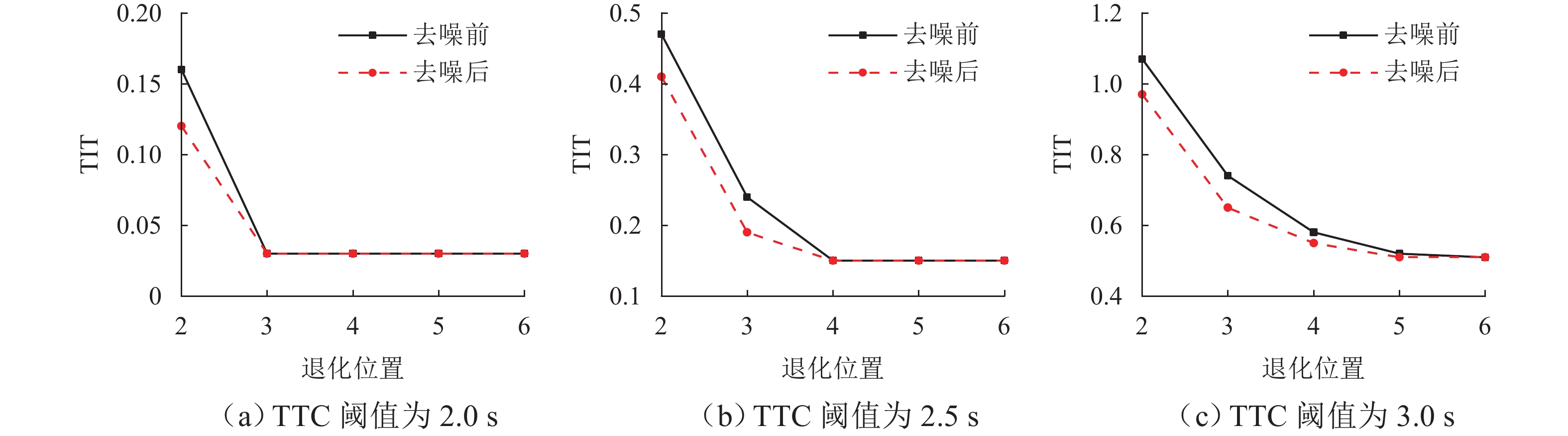
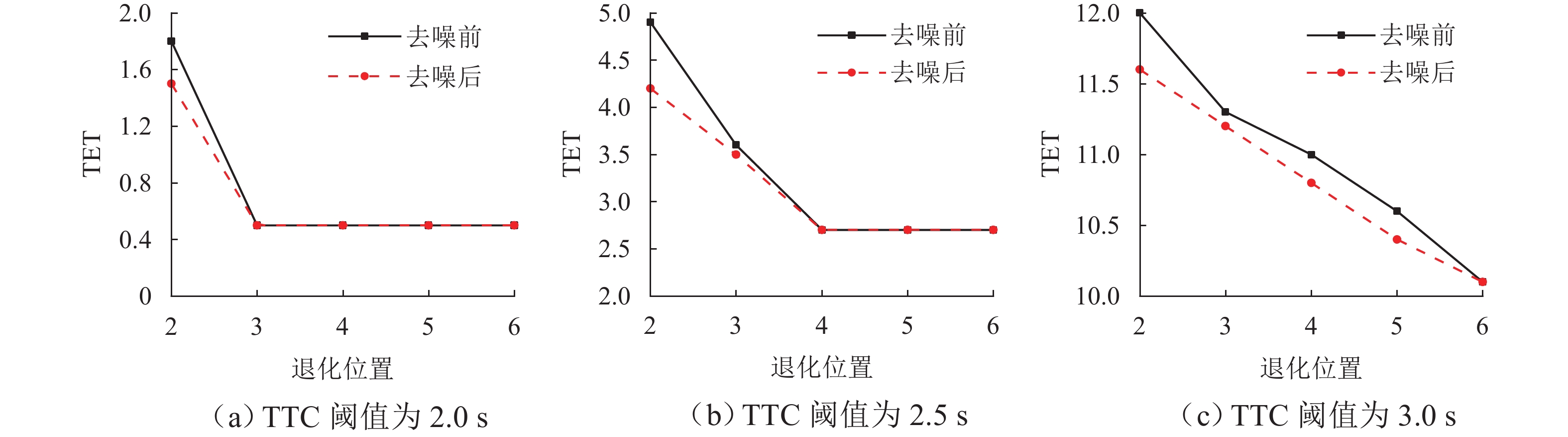
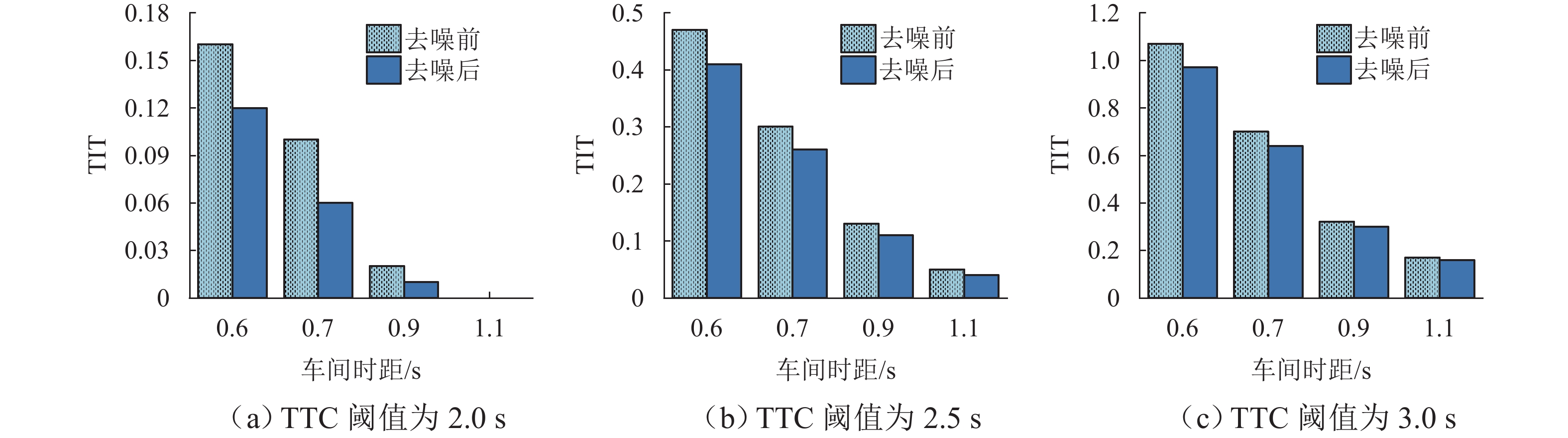
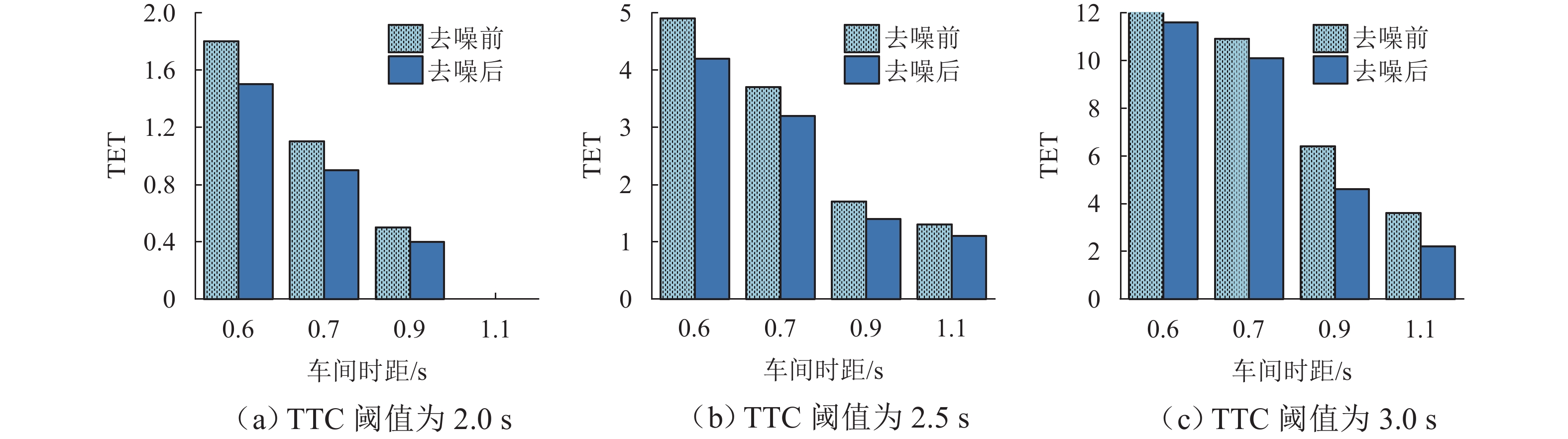
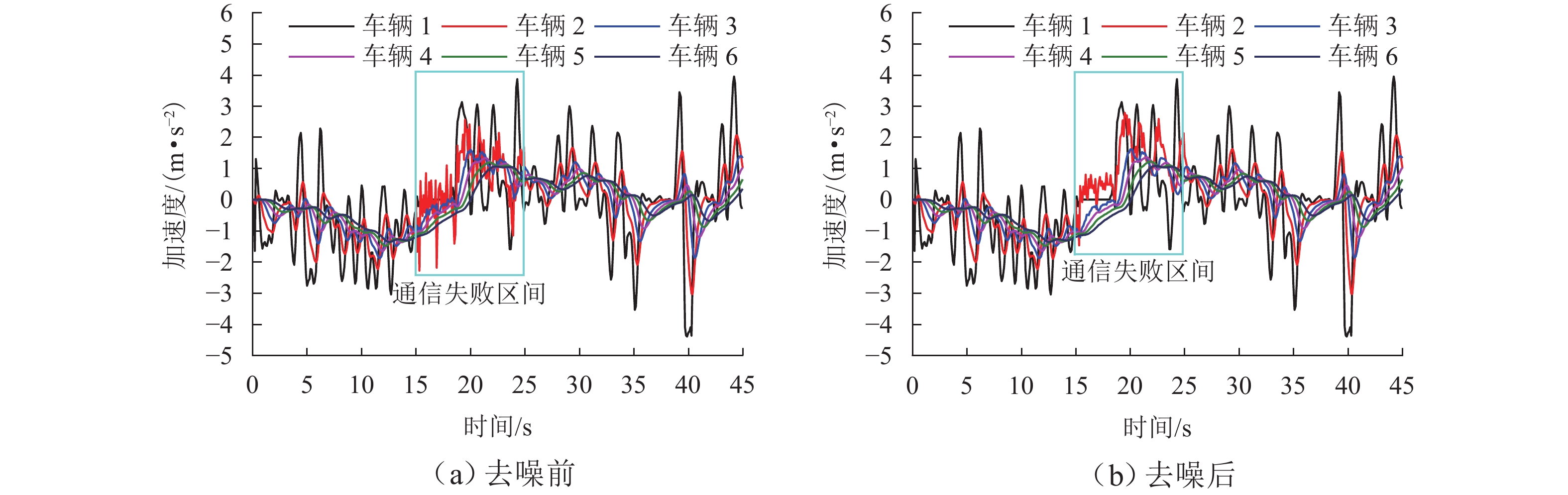
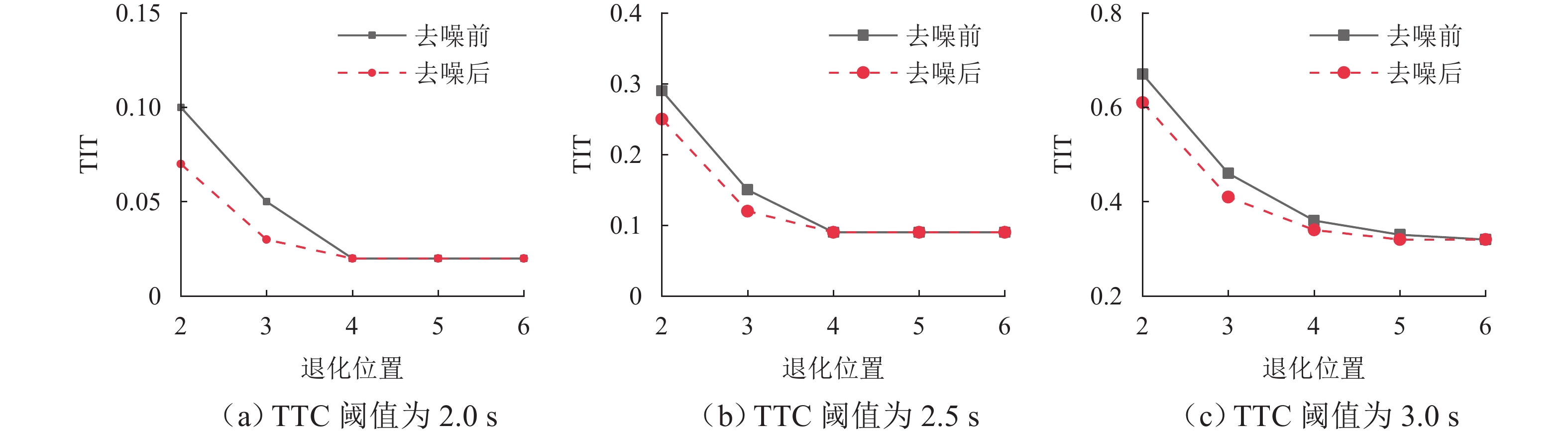
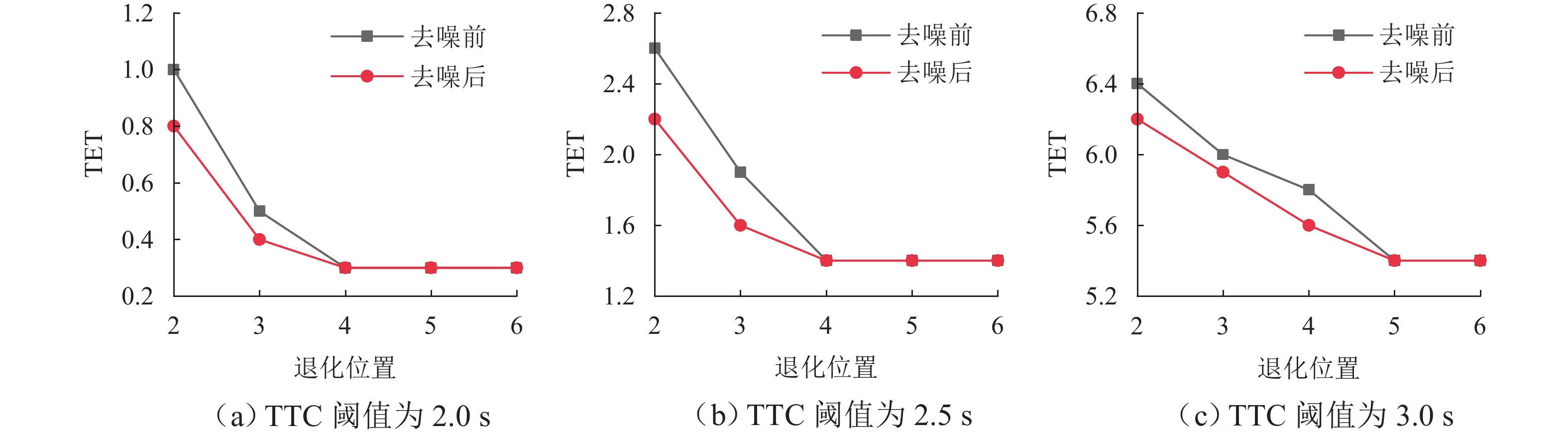
针对智能网联车辆(connected and automated vehicles, CAV)之间车车(vehicle-to-vehicle, V2V)通信失败情况下采用车载传感设备感知前车运动状态的场景,分析传感噪声对智能网联车队安全风险的影响. 首先,基于智能驾驶员模型(intelligent driver model, IDM)构建CAV车辆动力学模型,提出CAV车辆感知前车运动状态的2种模式;随后,分析出现噪声的原因,并采用自适应卡尔曼滤波算法(adaptive Kalman filter, AKF)对噪声进行处理;最后,开展智能网联车队头车突然减速(极端场景)和基于NGSIM (next generation simulation)的实车数据集(常规场景)仿真实验,采用替代安全评价指标TIT (time integrated time-to-collision)与TET (time exposed time-to-collision)分析不同位置车辆退化和不同车间时距下的车队某一时间段内整体安全风险以及噪声影响. 实验结果表明:去噪声后的TIT和TET均出现显著下降,车队安全风险随车辆退化位置靠后和车间时距增大逐渐降低;当车辆2退化、车间时距为0.6 s时,车队安全风险最大,车辆4及之后的车辆退化时,车队严重和中度安全风险达到最低,此时传感噪声影响不明显,车队安全风险只与车间时距有关.
Abstract:The scenario in which vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) communication between connected and automated vehicles (CAVs) fails was studied, and the onboard sensors were used to perceive the motion state of the preceding vehicle. The impact of sensor noise on the safety risk of the CAV platoon was analyzed. First, a CAV dynamics model was established based on the intelligent driver model (IDM), and two sensing modes for perceiving the predecessor’s motion state were proposed. The sources of sensor noise were analyzed, and an adaptive Kalman filter (AKF) was applied for noise processing. Finally, two simulation experiments were conducted under extreme (sudden deceleration of the lead vehicle) and normal (trajectory data based on the NGSIM dataset) scenarios. Surrogate safety metrics, including time integrated time-to-collision (TIT), were used to evaluate the overall platoon safety risk and the effect of noise under different vehicle degradation positions and time headways. The results indicate that after denoising, both TIT and TET significantly decrease. The safety risk of the platoon decreases as the degraded vehicle position moves rearward, and the time headway increases. The highest risk occurs when the second vehicle degrades with a time headway of 0.6 s. When degradation occurs from the fourth vehicle onward, the severe and moderate safety risks are minimized, and the influence of sensor noise becomes negligible. In this case, the safety risk is mainly determined by the time headway.
-
Key words:
- traffic control /
- vehicle safety /
- adaptive Kalman filter /
- sensor noise /
- surrogate safety metric
-
表 1 仿真实验参数
Table 1. Simulation experiment parameters
参数 取值 参数描述 $ T $/s 45 仿真时长 $ \Delta t $/s 0.1 仿真步长 $ {a_{\max }} $/(m·s−2) 4 车辆最大加速度 $ {d_{\max }} $/(m·s−2) −5 车辆最大减速度 $ d $/(m·s−2) 1.5 最大舒适加速度 $ {v_0} $/(m·s−1) 33.3 自由流速度 $ {s_0} $/m 2 最小安全车距 $ l $/m 5 车身长度 $ {q_1},{\text{ }}{q_2} $ 0.01,0.01 随机过程噪声 $ {\sigma _1} $/m 0.2 传感噪声车距 ${\sigma _2} $/(m·s−1) 0.2 传感噪声车速 $ N $ 3 移动时间窗口大小 表 2 头车减速场景下不同车间时距以及不同退化位置的TIT和TET值
Table 2. TIT and TET values under different time headways and degradation positions under lead vehicle deceleration scenario
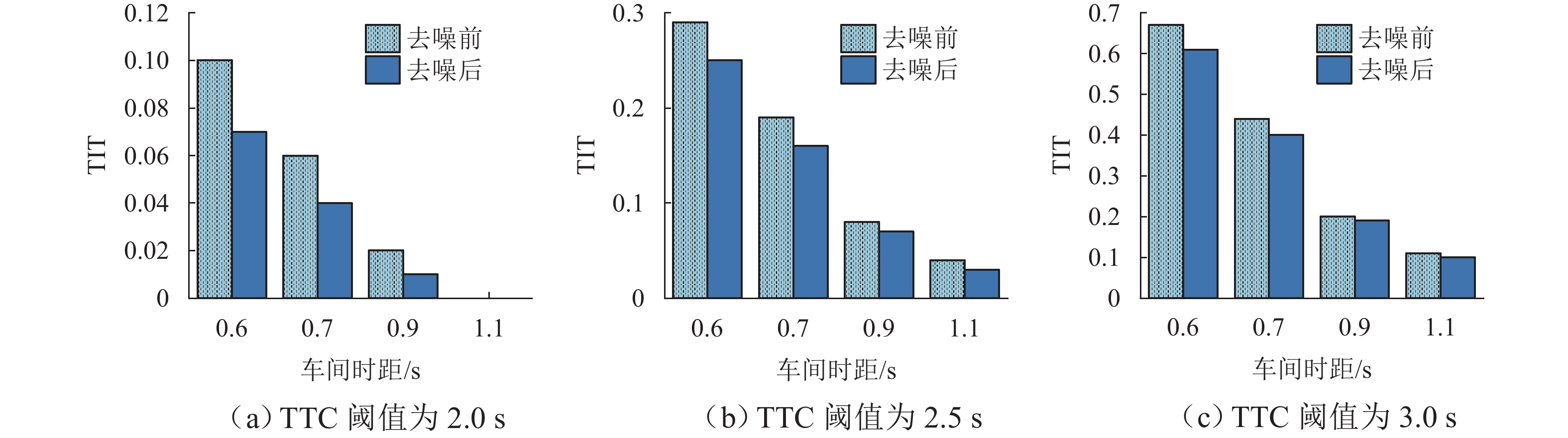
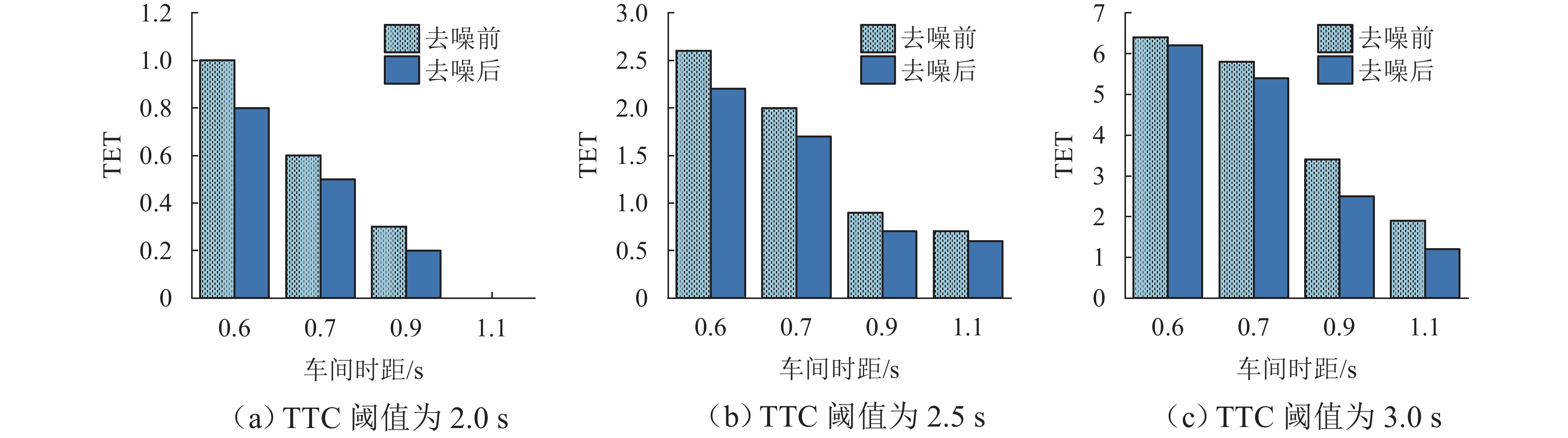
车间时距/s 噪声处理 TTC阈值/s 退化位置 2 3 4 5 6 TIT TET TIT TET TIT TET TIT TET TIT TET 0.6 去噪前 2.0 0.16 1.8 0.03 0.5 0.03 0.5 0.03 0.5 0.03 0.5 2.5 0.47 4.9 0.24 3.6 0.15 2.7 0.15 2.7 0.15 2.7 3.0 1.07 12.0 0.74 11.3 0.58 11.0 0.52 10.6 0.51 10.1 去噪后 2.0 0.12 1.5 0.03 0.5 0.03 0.5 0.03 0.5 0.03 0.5 2.5 0.41 4.2 0.19 3.5 0.15 2.7 0.15 2.7 0.15 2.7 3.0 0.97 11.6 0.65 11.2 0.55 10.8 0.51 10.4 0.51 10.1 0.7 去噪前 2.0 0.10 1.1 0.02 0.5 0.02 0.5 0.02 0.5 0.02 0.5 2.5 0.30 3.7 0.14 1.9 0.12 1.9 0.12 1.9 0.12 1.9 3.0 0.70 10.9 0.47 9.7 0.40 9.0 0.40 8.5 0.40 8.5 去噪后 2.0 0.06 0.9 0.02 0.5 0.02 0.5 0.02 0.5 0.02 0.5 2.5 0.26 3.2 0.13 1.9 0.12 1.8 0.12 1.8 0.12 1.8 3.0 0.64 10.1 0.42 9.2 0.40 8.3 0.40 7.9 0.40 7.7 0.9 去噪前 2.0 0.02 0.5 0 0.2 0 0.2 0 0.2 0 0.2 2.5 0.13 1.7 0.09 1.5 0.09 1.5 0.09 1.5 0.09 1.5 3.0 0.32 6.4 0.25 5.9 0.25 5.0 0.25 5.0 0.25 5.0 去噪后 2.0 0.01 0.4 0 0.2 0 0.2 0 0.2 0 0.2 2.5 0.11 1.4 0.09 1.4 0.09 1.4 0.09 1.4 0.09 1.4 3.0 0.30 4.6 0.24 4.6 0.25 4.6 0.25 4.6 0.25 4.6 1.1 去噪前 2.0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2.5 0.05 1.3 0.04 1.2 0.04 1.2 0.04 1.2 0.04 1.2 3.0 0.17 3.6 0.16 2.5 0.16 2.5 0.16 2.5 0.16 2.5 去噪后 2.0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2.5 0.04 1.1 0.04 1.1 0.04 1.1 0.04 1.1 0.04 1.1 3.0 0.16 2.2 0.16 2.2 0.16 2.2 0.16 2.2 0.16 2.2 表 3 NGSIM数据集场景下不同车间时距以及不同退化位置的TIT和TET值
Table 3. TIT and TET values under different time headways and degradation positions under NGSIM dataset scenario
车间时距/s 噪声处理 TTC阈值/s 退化位置 2 3 4 5 6 TIT TET TIT TET TIT TET TIT TET TIT TET 0.6 去噪前 2.0 0.10 1.0 0.05 0.5 0.02 0.3 0.02 0.3 0.02 0.3 2.5 0.29 2.6 0.15 1.9 0.09 1.4 0.09 1.4 0.09 1.4 3.0 0.67 6.4 0.46 6.0 0.36 5.8 0.33 5.4 0.32 5.4 去噪后 2.0 0.07 0.8 0.03 0.4 0.02 0.3 0.02 0.3 0.02 0.3 2.5 0.25 2.2 0.12 1.6 0.09 1.4 0.09 1.4 0.09 1.4 3.0 0.61 6.2 0.41 5.9 0.34 5.6 0.32 5.4 0.32 5.4 0.7 去噪前 2.0 0.06 0.6 0.01 0.3 0.01 0.3 0.01 0.3 0.01 0.3 2.5 0.19 2.0 0.09 1.0 0.07 1.0 0.07 1.0 0.07 1.0 3.0 0.44 5.8 0.29 5.2 0.25 4.8 0.25 4.5 0.25 4.5 去噪后 2.0 0.04 0.5 0.01 0.3 0.01 0.3 0.01 0.3 0.01 0.3 2.5 0.16 1.7 0.08 1.0 0.07 1.0 0.07 1.0 0.07 1.0 3.0 0.40 5.4 0.26 4.9 0.25 4.4 0.25 4.2 0.25 4.1 0.9 去噪前 2.0 0.02 0.3 0 0.1 0 0.1 0 0.1 0 0.1 2.5 0.08 0.9 0.05 0.8 0.05 0.8 0.05 0.8 0.05 0.8 3.0 0.20 3.4 0.15 3.1 0.15 2.7 0.15 2.7 0.15 2.7 去噪后 2.0 0.01 0.2 0 0.1 0 0.1 0 0.1 0 0.1 2.5 0.07 0.7 0.05 0.7 0.05 0.7 0.05 0.7 0.05 0.7 3.0 0.19 2.5 0.15 2.5 0.15 2.5 0.15 2.5 0.15 2.5 1.1 去噪前 2.0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2.5 0.04 0.7 0.03 0.6 0.03 0.6 0.03 0.6 0.03 0.6 3.0 0.11 1.9 0.10 1.3 0.10 1.3 0.10 1.3 0.10 1.3 去噪后 2.0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2.5 0.03 0.6 0.03 0.6 0.03 0.6 0.03 0.6 0.03 0.6 3.0 0.10 1.2 0.10 1.2 0.10 1.2 0.10 1.2 0.10 1.2 -
[1] XIAO L, WANG M, SCHAKEL W, et al. Unravelling effects of cooperative adaptive cruise control deactivation on traffic flow characteristics at merging bottlenecks[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2018, 96: 380-397. doi: 10.1016/j.trc.2018.10.008 [2] QIN Y Y, WANG H. Stabilizing mixed cooperative adaptive cruise control traffic flow to balance capacity using car-following model[J]. Journal of Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2023, 27(1): 57-79. doi: 10.1080/15472450.2021.1985490 [3] LIU R K, REN Y L, YU H Y, et al. Connected and automated vehicle platoon maintenance under communication failures[J]. Vehicular Communications, 2022, 35: 100467.1-100467.14. [4] TU Y, WANG W, LI Y, et al. Longitudinal safety impacts of cooperative adaptive cruise control vehicle’s degradation[J]. Journal of Safety Research, 2019, 69: 177-192. doi: 10.1016/j.jsr.2019.03.002 [5] WANG X, XU C, ZHAO X Y, et al. Stability and safety analysis of connected and automated vehicle platoon considering dynamic communication topology[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2024, 25(10): 13442-13452. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2024.3398111 [6] YAO Z H, DENG H W, CHEN Z K, et al. Linear internal stability for mixed traffic flow of CAVs with different automation levels[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and Its Applications, 2024, 642: 129759.1-129759.37. [7] WANG X, JIANG X G, LI H B, et al. Traffic safety assessment with integrated communication system of connected and automated vehicles at signalized intersections[J]. Transportation Research Record: Journal of the Transportation Research Board, 2024, 2678(6): 956-971. doi: 10.1177/03611981231201107 [8] 秦严严, 王昊, 王炜. 网联辅助驾驶混合交通流稳定性及安全性分析[J]. 东南大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 48(1): 188-194.QIN Yanyan, WANG Hao, WANG Wei. Analysis on stability and safety for mixed traffic flow with connected auxiliary driving[J]. Journal of Southeast University (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 48(1): 188-194. [9] 郝威, 俞海杰, 高志波, 等. 自动驾驶专用车道影响下的CACC车流管理策略[J]. 中国公路学报, 2022, 35(4): 230-242. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2022.04.019HAO Wei, YU Haijie, GAO Zhibo, et al. Management methods for cooperative adaptive cruise control vehicles flow considering dedicated lanes[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2022, 35(4): 230-242. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2022.04.019 [10] QIN Y Y, LUO Q Z, WANG H. Stability analysis and connected vehicles management for mixed traffic flow with platoons of connected automated vehicles[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2023, 157: 104370.1-104370.28. [11] QIN Y Y, LIU M X, HAO W. Energy-optimal car-following model for connected automated vehicles considering traffic flow stability[J]. Energy, 2024, 298: 131333.1-131333.13. [12] ZHENG Y, ZHANG Y, QU X, et al. Developing platooning systems of connected and automated vehicles with guaranteed stability and robustness against degradation due to communication disruption[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2024, 168: 104768.1-104768.20. [13] FENG W, WANG B. Stability analysis and delayed feedback control for platoon of connected automated vehicles with V2X and V2V infrastructure[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2025, 658: 130258.1-130258.24. [14] ZENG J W, QIAN Y S, WANG W H, et al. The impact of connected automated vehicles and platoons on the traffic safety and stability in complex heterogeneous traffic systems[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and Its Applications, 2023, 629: 129195.1-129195.11. [15] TREIBER M, HENNECKE A, HELBING D. Congested traffic states in empirical observations and microscopic simulations[J]. Physical Review E, 2000, 62(2): 1805-1824. [16] RAHMAN M H, ABDEL-ATY M, WU Y N. A multi-vehicle communication system to assess the safety and mobility of connected and automated vehicles[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2021, 124: 102887.1-102887.21. [17] DAI Y L, WANG C, XIE Y C. Explicitly incorporating surrogate safety measures into connected and automated vehicle longitudinal control objectives for enhancing platoon safety[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2023, 183: 106975.1-106975.21. [18] 杨涛, 马玉琴, 刘梦, 等. 智能网联环境下信号交叉口车辆轨迹重构模型[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2024, 59(5): 1148-1157.YANG Tao, MA Yuqin, LIU Meng, et al. Vehicle trajectory reconstruction model of signalized intersection in connected automated environments[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2024, 59(5): 1148-1157. [19] 梁军, 耿浩然, 陈龙, 等. 融入公交车与自动驾驶车队的异质交通流模型[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2023, 58(5): 1090-1099.LIANG Jun, GENG Haoran, CHEN Long, et al. Integrated heterogeneous traffic flow model of bus and autonomous vehicle platoon[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2023, 58(5): 1090-1099. [20] ZHANG Y, TIAN B, XU Z, et al. A local traffic characteristic based dynamic gains tuning algorithm for cooperative adaptive cruise control considering wireless communication delay[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2022, 142: 103766.1-103766.17. [21] WERRIES A, DOLAN J. Adaptive Kalman filtering methods for low-cost GPS/INS localization for autonomous vehicles[R]. Pittsburgh: Carnegie-Mellon University, 2016. [22] XIONG R, HE H W, SUN F C, et al. Evaluation on state of charge estimation of batteries with adaptive extended Kalman filter by experiment approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 62(1): 108-117. [23] ESSA M, SAYED T. Self-learning adaptive traffic signal control for real-time safety optimization[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2020, 146: 105713.1-105713.16. [24] WANG C, XIE Y C, HUANG H L, et al. A review of surrogate safety measures and their applications in connected and automated vehicles safety modeling[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2021, 157: 106157.1-106157.15. [25] 秦严严, 王昊. 智能网联车辆交通流优化对交通安全的改善[J]. 中国公路学报, 2018, 31(4): 202-210.QIN Yanyan, WANG Hao. Improving traffic safety via traffic flow optimization of connected and automated vehicles[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2018, 31(4): 202-210. [26] WANG P C, HE X Z, WEI Y, et al. Damping behavior analysis for connected automated vehicles with linear car following control[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2022, 138: 103617.1-103617.19. -





 下载:
下载: