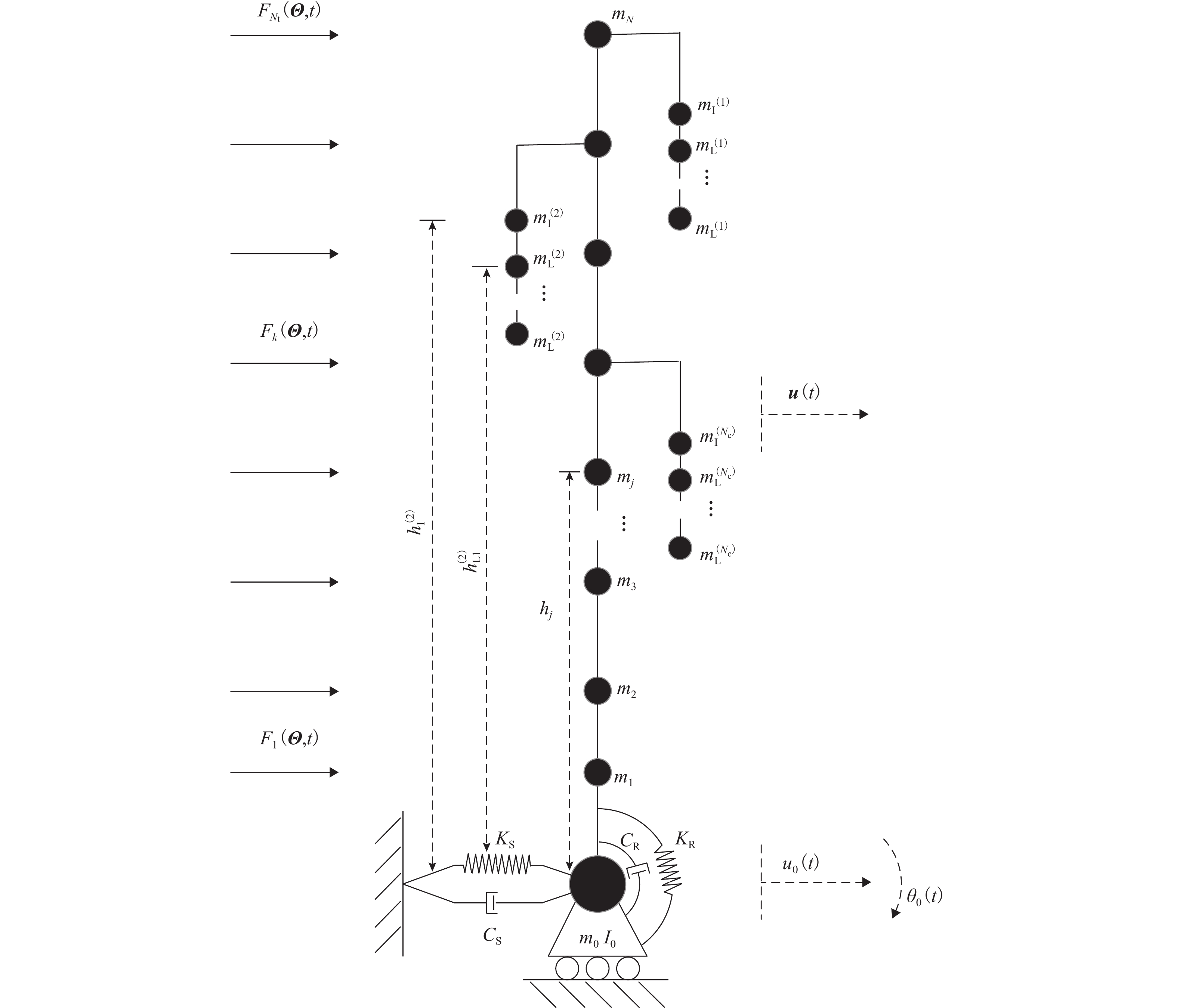
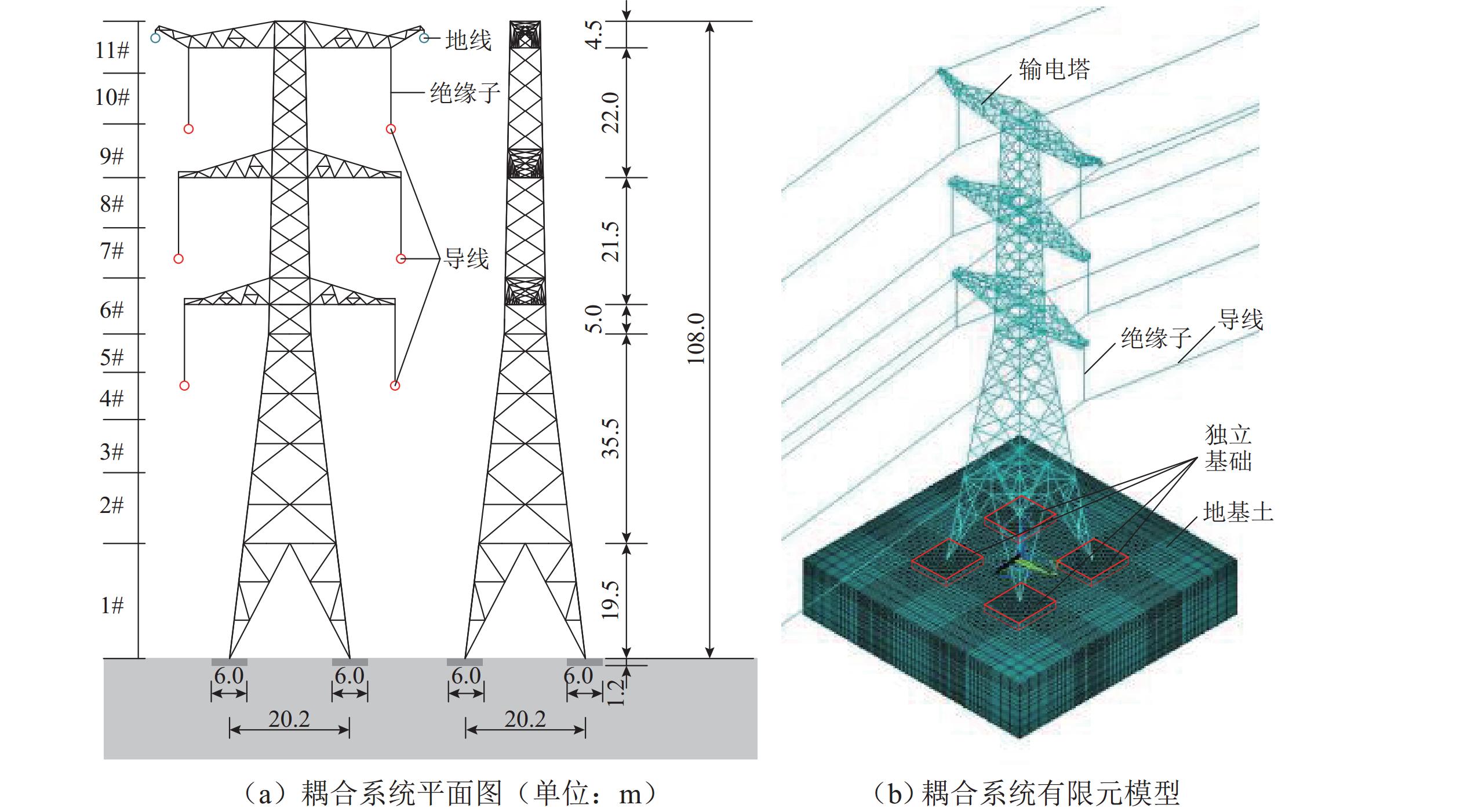
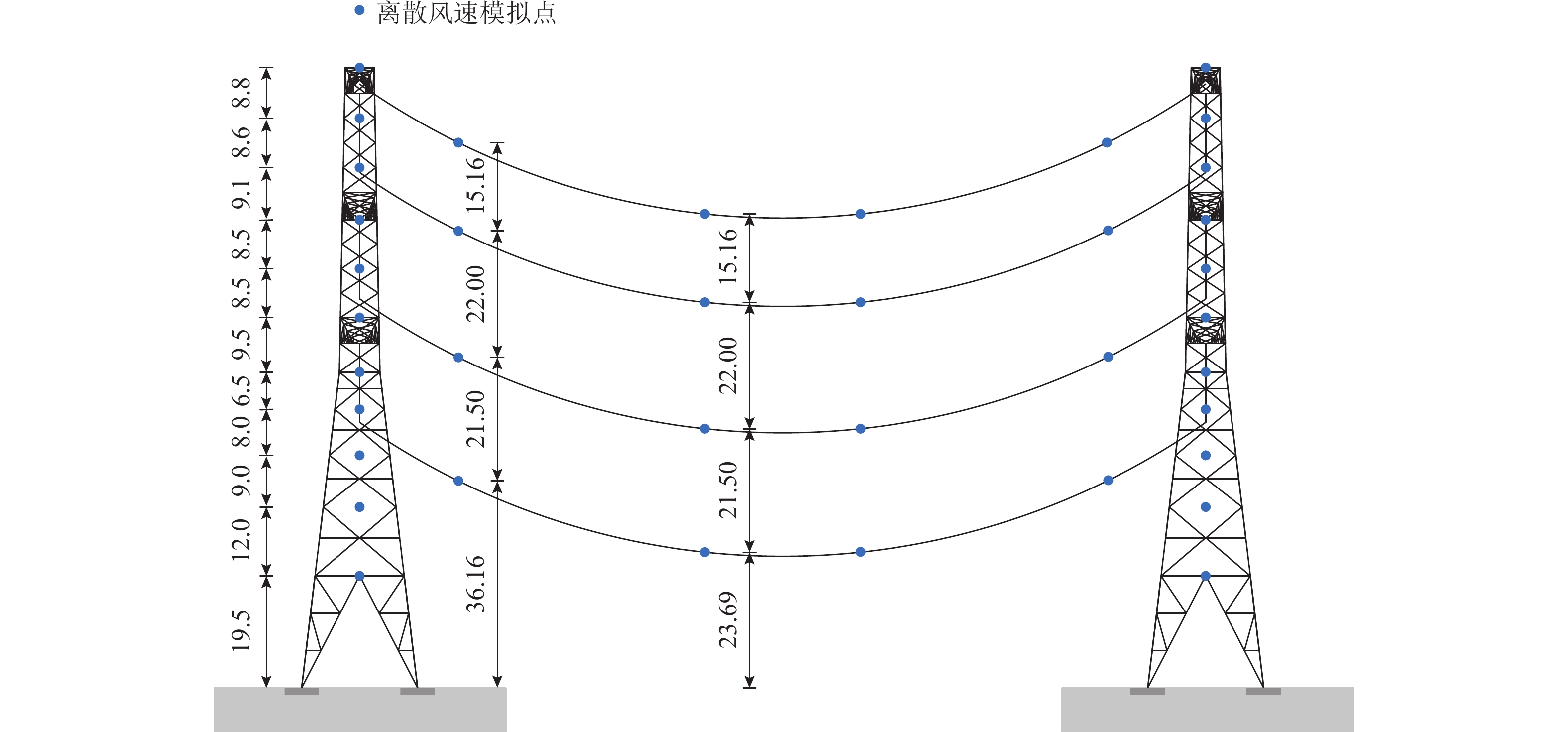
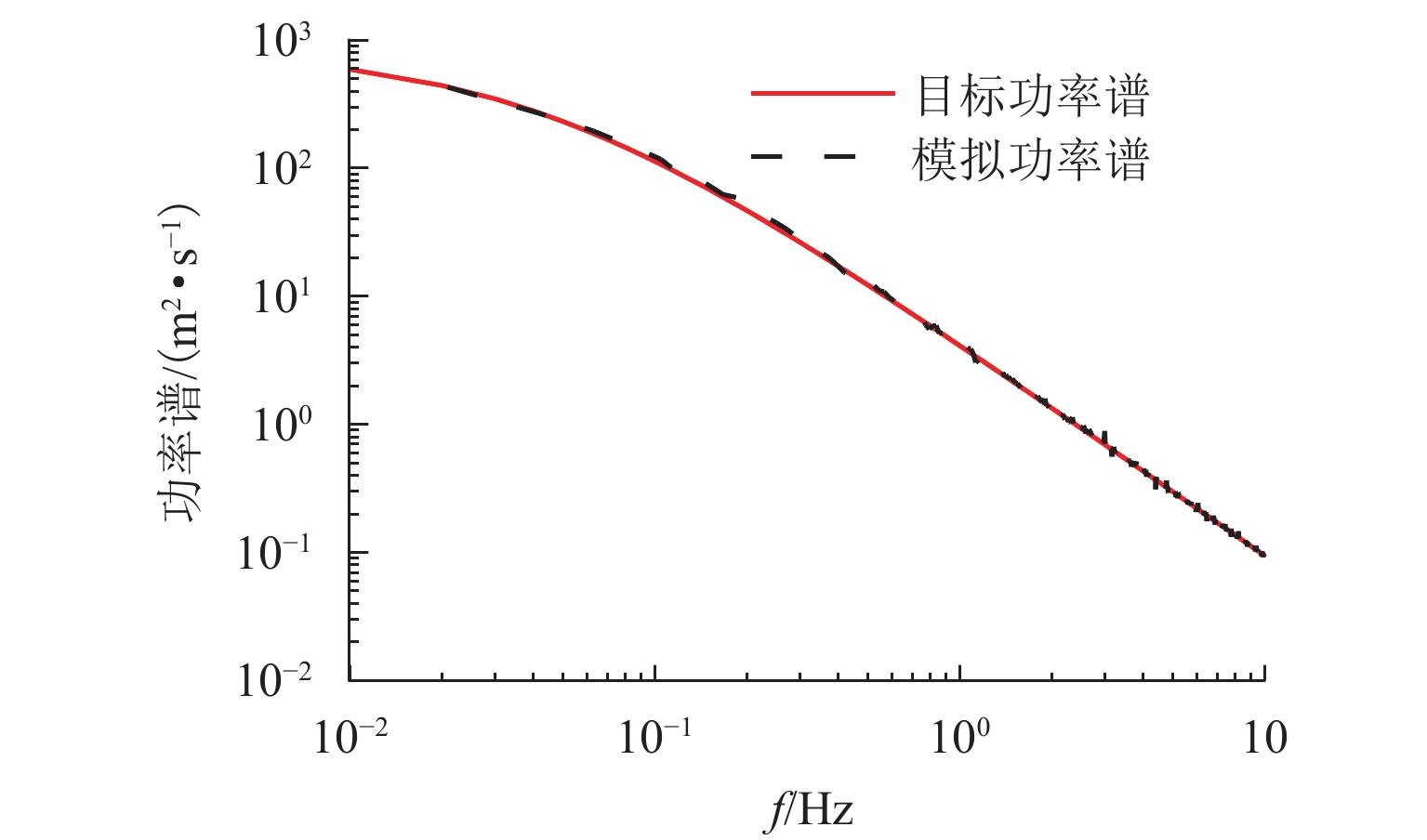
Global Reliability Analysis of Transmission Tower–Line Coupling System Considering Soil-Structure Interaction
-
摘要:
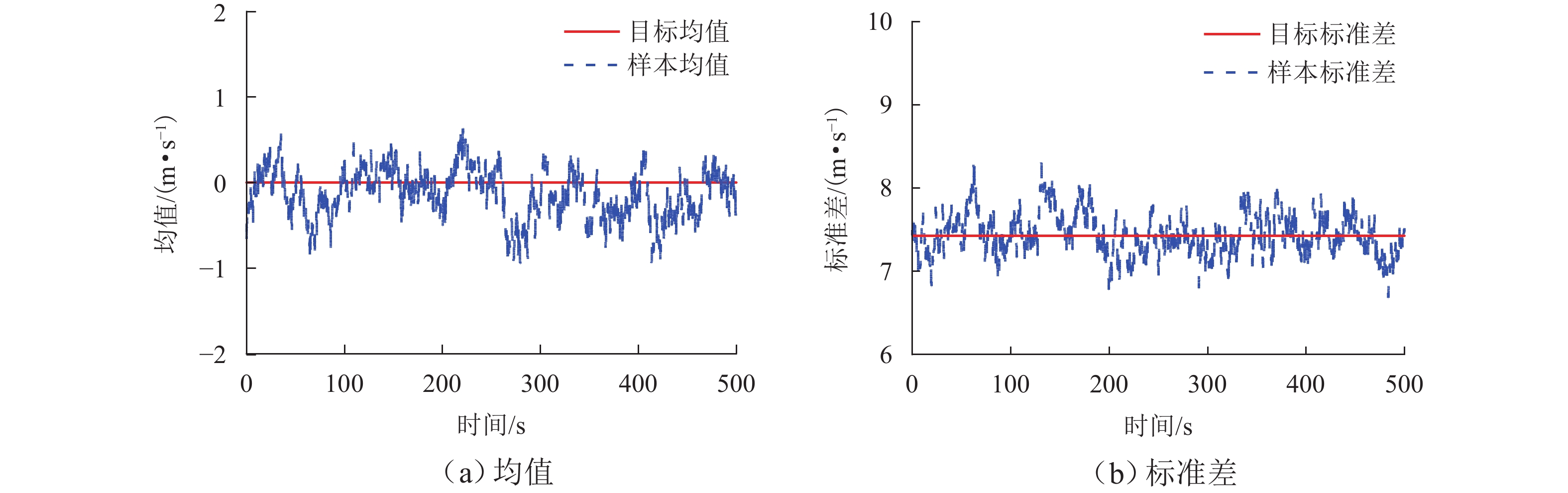
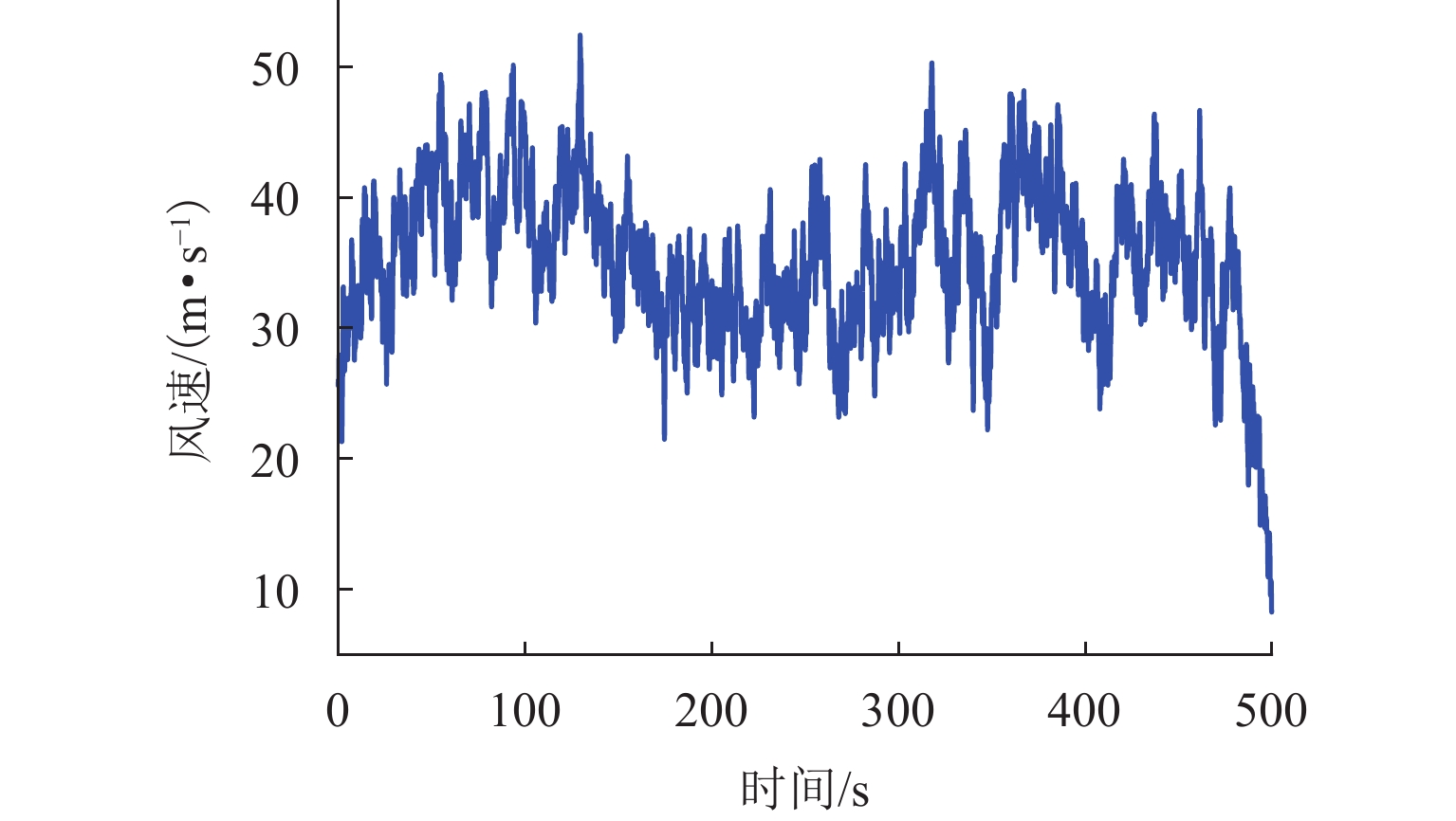
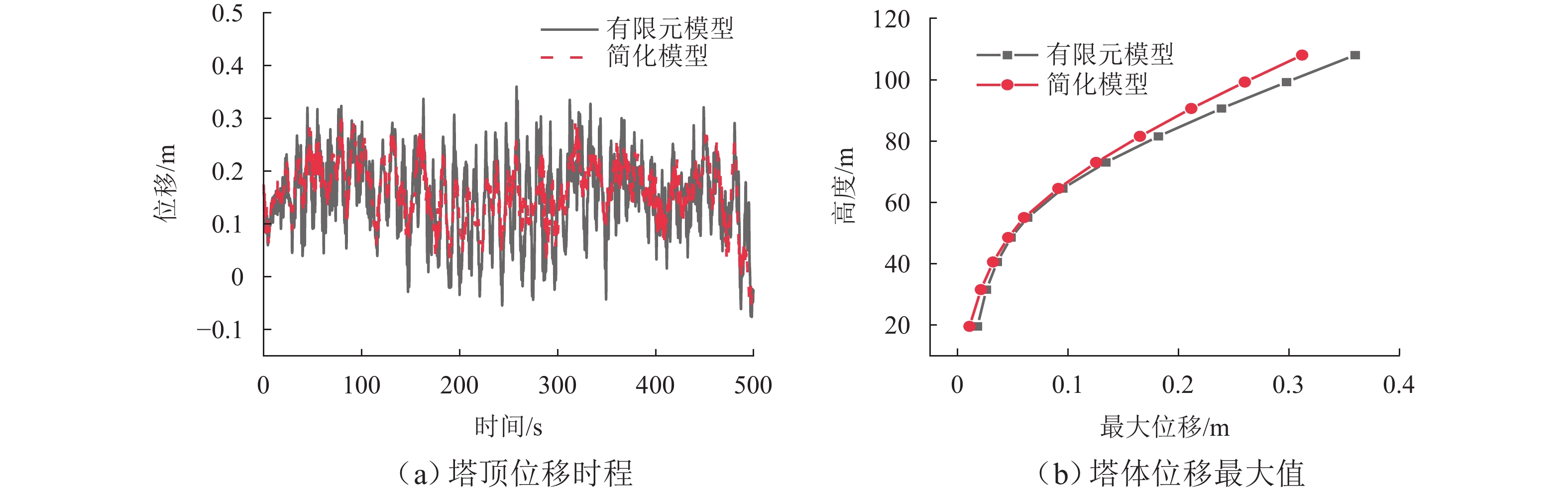
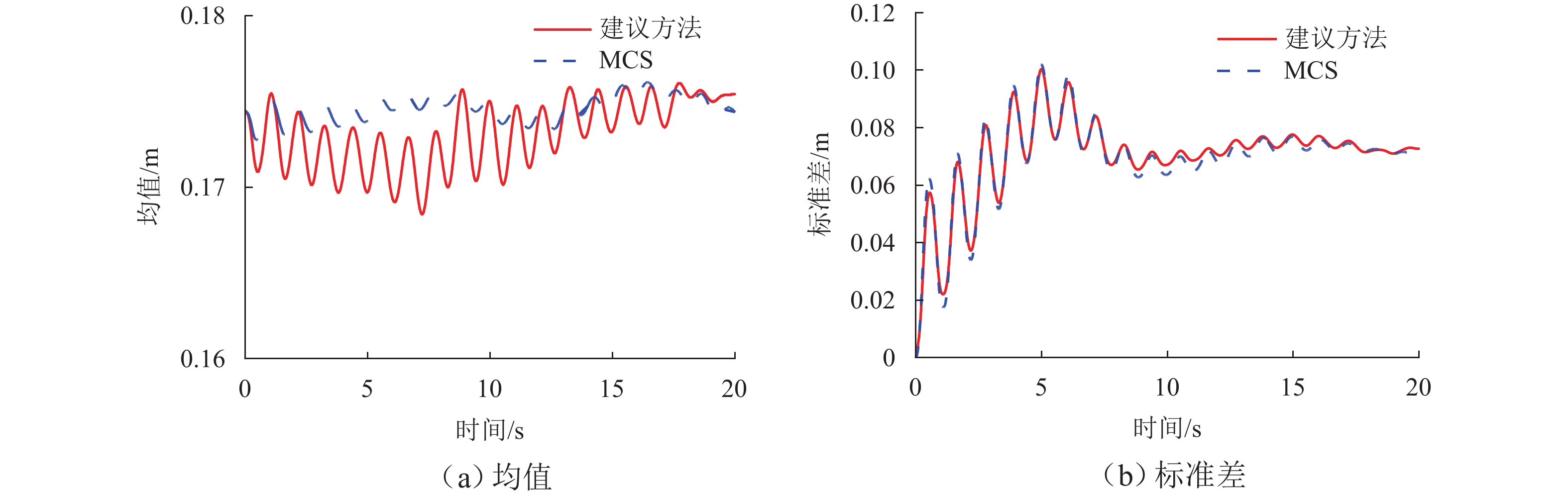
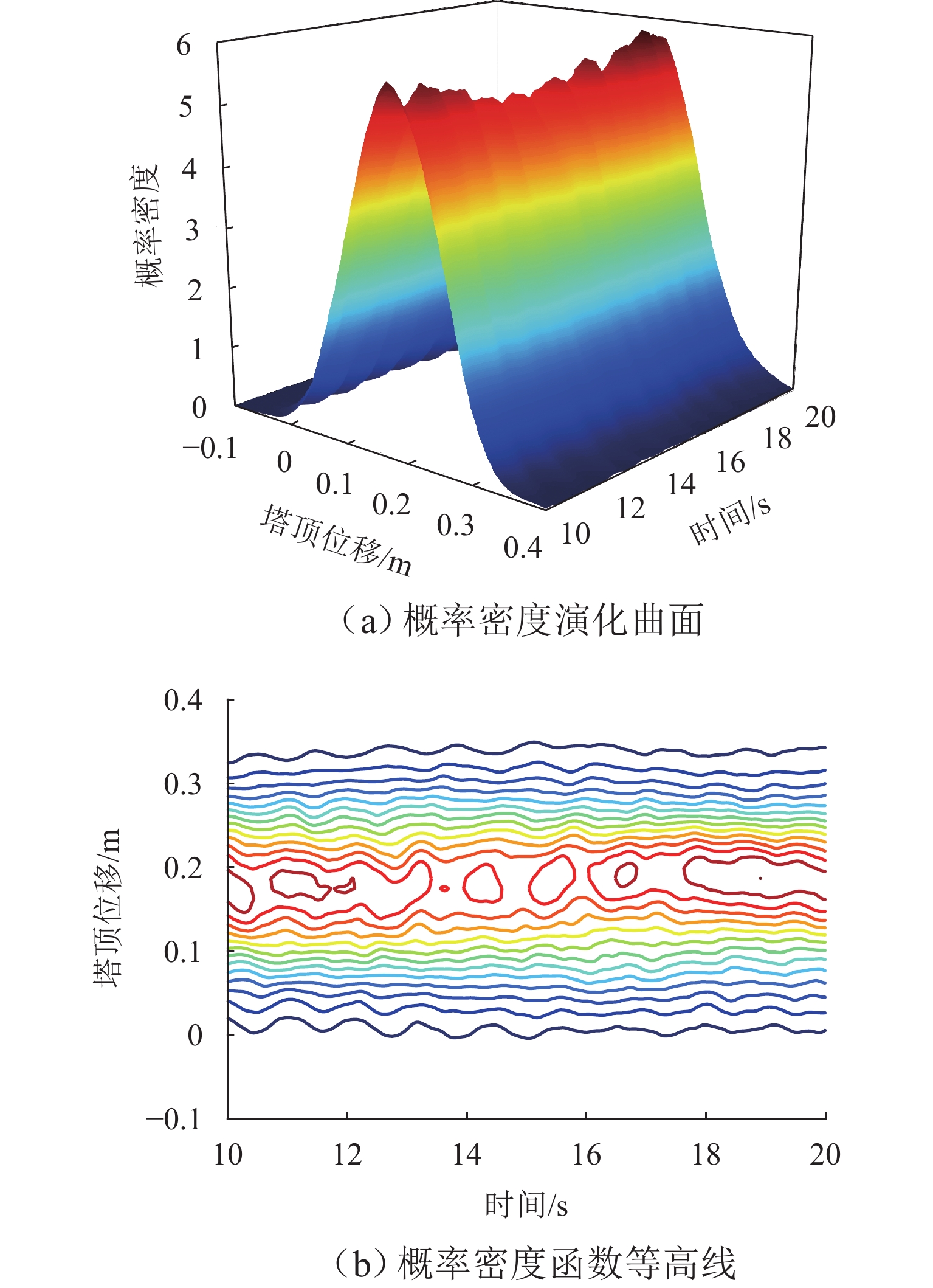
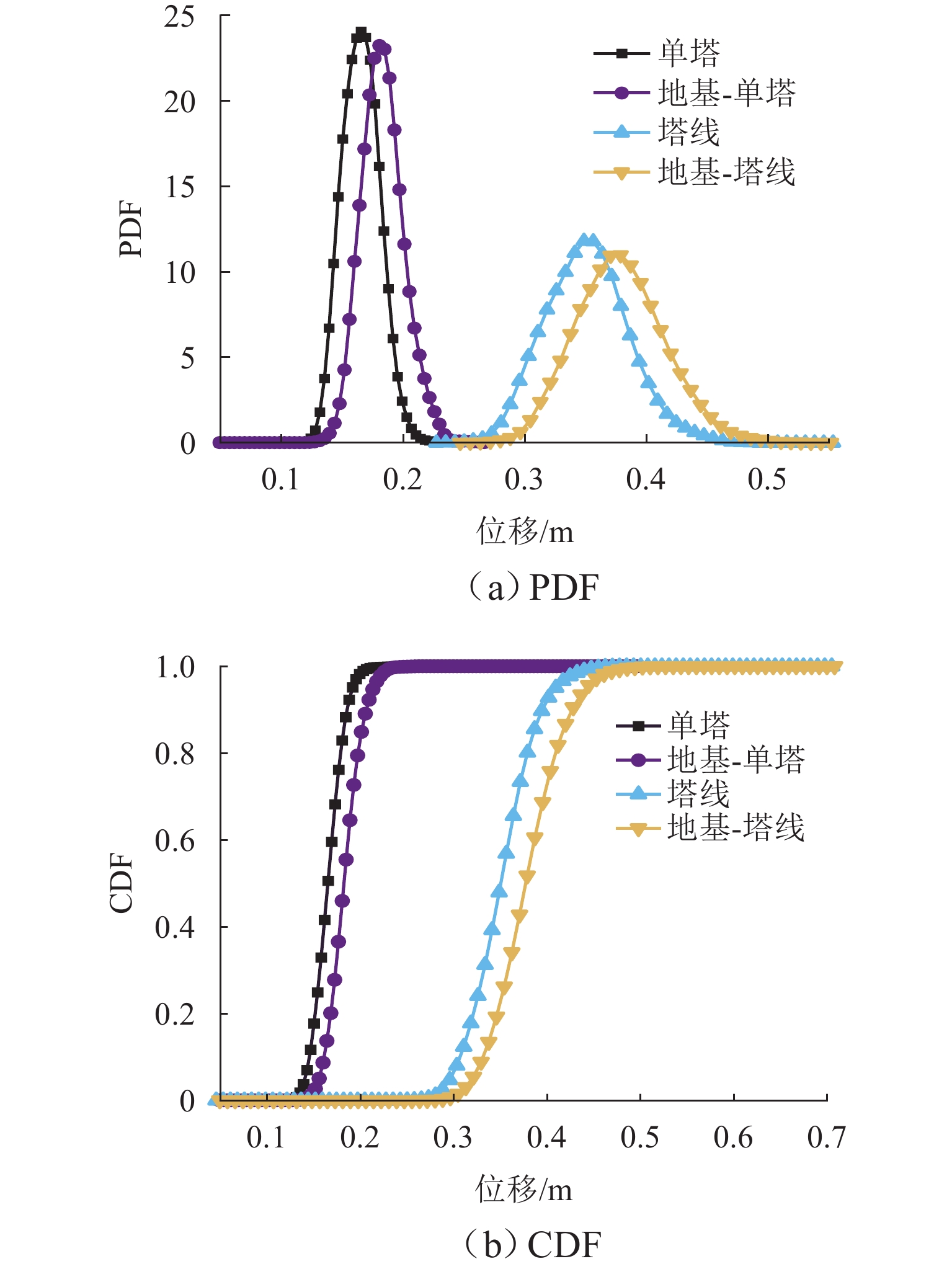
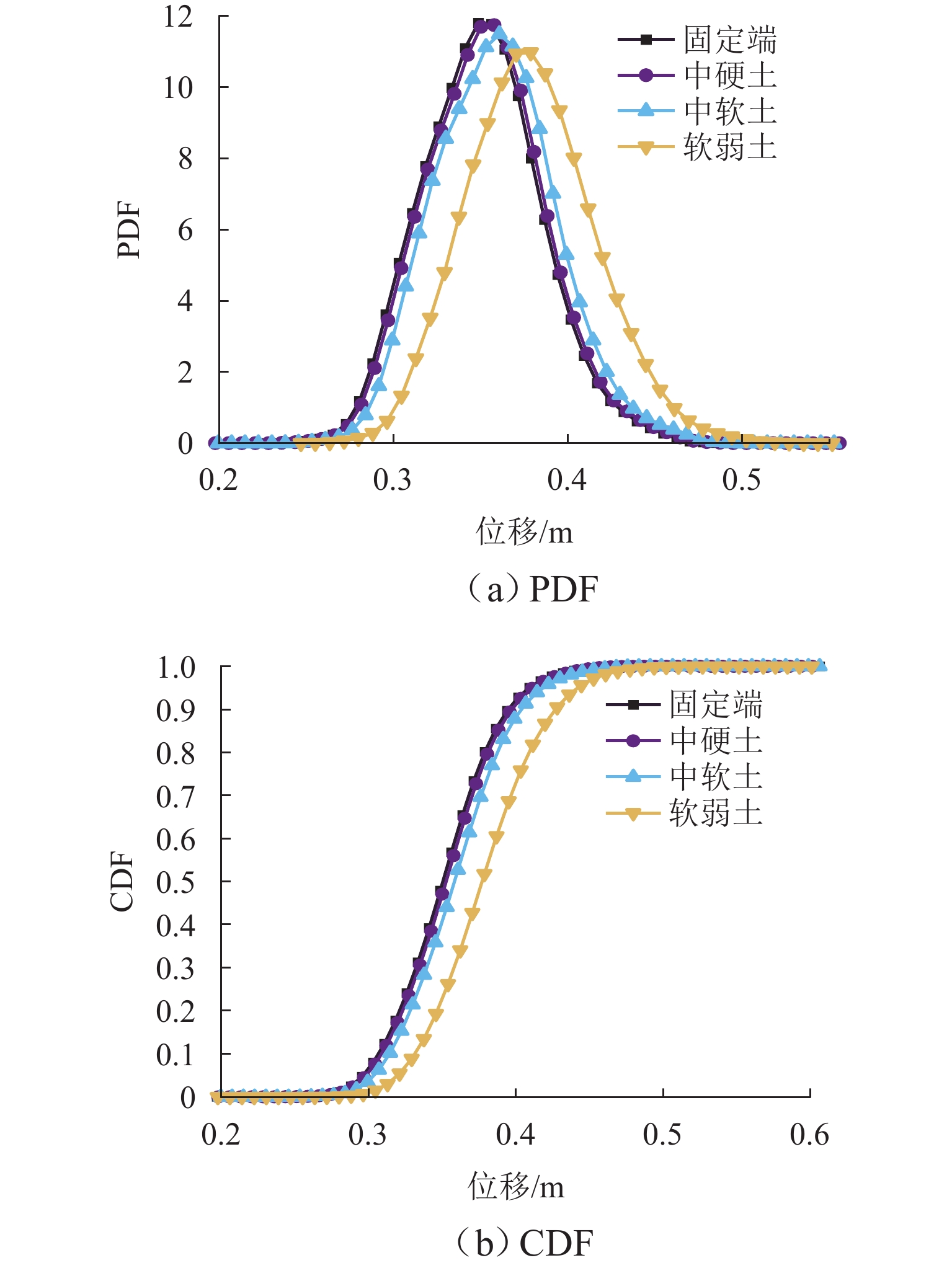
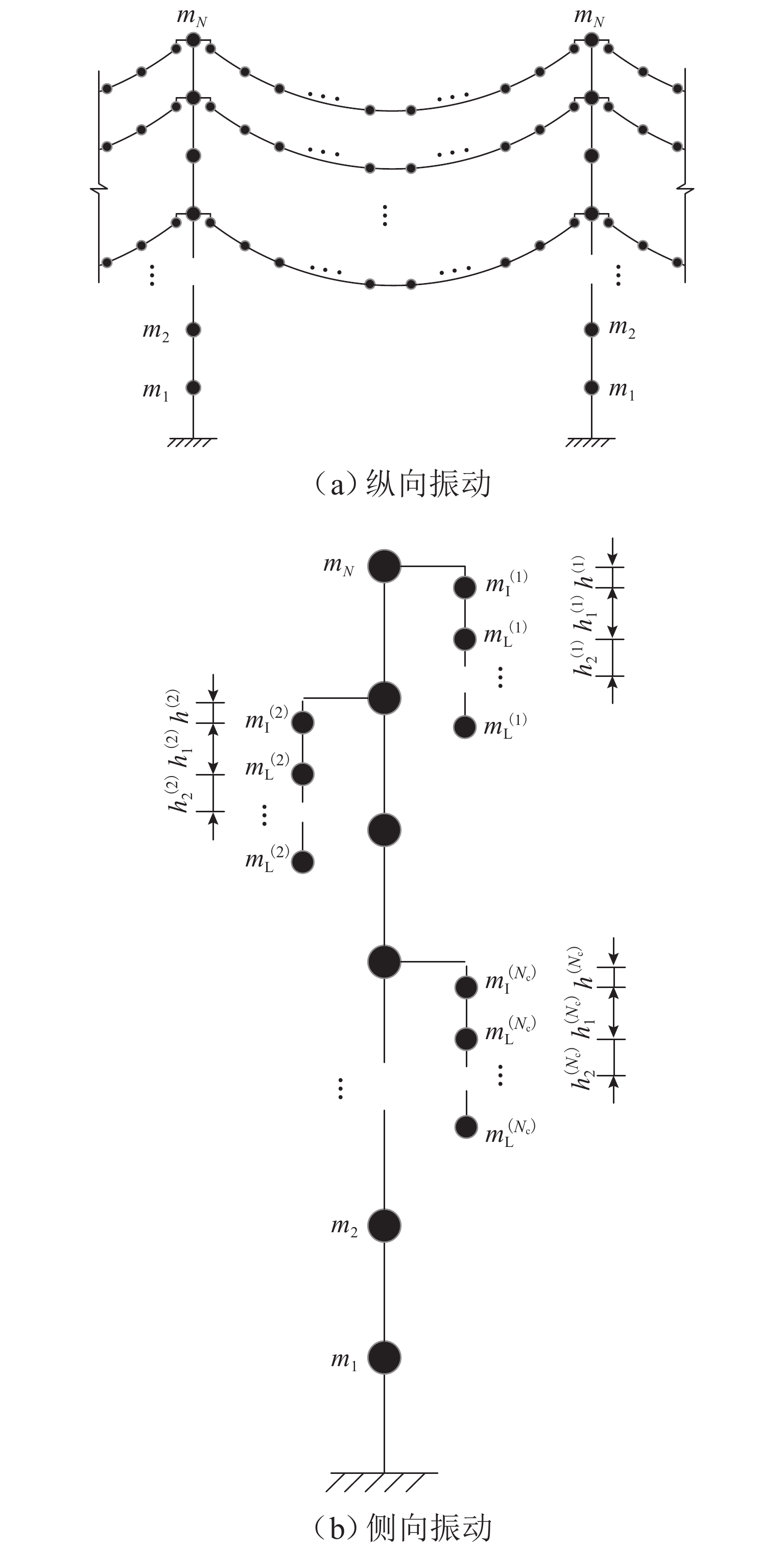
为研究土-结构相互作用和塔线耦合作用对输电塔整体可靠度的影响,建立随机风荷载作用下考虑土-结构相互作用的输电塔-线耦合系统简化力学模型,其中,输电塔、绝缘子、导线和基础4个结构采用多质点力学模型进行模拟,地基土对耦合系统动力响应的影响采用S-R (swing-rocking)模型进行模拟,耦合系统所处随机风场则采用谱表示-降维方法进行模拟;其次,基于耦合系统简化力学模型和概率密度演化方法(PDEM),提出适用于考虑土-结构相互作用的输电塔-线耦合系统整体可靠度分析方法;最后,以某特高压交流输变电线路的直线塔为例,分别计算塔顶位移的概率密度函数、均值和标准差,并以塔顶位移极值为控制变量求解耦合系统的整体可靠度. 分析结果表明:考虑塔线耦合作用后,塔顶位移响应极值的分布函数明显右移,结构失效概率由1.605 × 10−38增加至0.932;考虑土-结构相互作用后,塔顶位移响应极值的分布函数轻微右移,结构失效概率有所增加,与固定端工况相比,中硬土、中软土和软弱土工况下的结构失效概率增幅分别为4.44%、5.22%和11.76%;与蒙特卡洛方法相比,所提方法可高效获得塔顶位移的概率信息,其计算时间仅为蒙特卡洛方法的1/33,而均值与标准差的二范数相对误差在3%以内.
Abstract:To investigate the influence of soil-structure interaction and tower-line coupling effect on global reliability of transmission towers, a simplified mechanical model of a transmission tower–line coupling system considering soil-structure interaction under stochastic wind excitation was established. A multi-mass mechanical model was adopted to simulate the transmission tower, insulator, conductor, and foundation. The effect of the subsoil on the dynamic response of the coupling system was modeled using the swing-rocking (S-R) model, and the stochastic wind field was generated using the spectrum representation–dimension reduction method. The simplified mechanical model and the probability density evolution method (PDEM) were employed to develop a global reliability analysis method for transmission tower–line coupling systems considering soil-structure interaction. Finally, a suspension-type tower from an ultra-high voltage alternating current transmission line was used as an example. The probability density function (PDF), mean, and standard deviation of the tower-top displacement were calculated, and the global reliability was evaluated with the tower-top displacement extremum as the control variable. The results show that after considering tower-line coupling effect, the cumulative distribution function (CDF) of tower-top displacement extremum shifts noticeably to the right, and the failure probability increases from 1.605 × 10−38 to 0.932. After soil-structure interaction is taken into account, the CDF of tower-top displacement extremum shows a slight rightward shift, and the failure probability increases. Compared with the fixed-base condition, the increase ratios of failure probability under medium-hard soil, medium-soft soil, and weak soil conditions are 4.44%, 5.22%, and 11.76%, respectively. Compared with the Monte Carlo method, the proposed method efficiently obtains the probabilistic information of the tower-top displacement. The computational time is only 1/33 of that of the Monte Carlo method, while the two-norm relative errors of the mean and standard deviation are within 3%.
-
表 1 不同地基土参数
Table 1. Parameters of different subsoil types
土体类型 ρ/( kg·m−3) v VS/(m·s−1) G/(×108 N·m−2) 中硬土 2000 0.30 400 3.20 中软土 1900 0.40 200 0.76 软弱土 1800 0.49 100 0.18 表 2 不同结构体系的失效概率
Table 2. Failure probabilities of different structure systems
结构体系 失效概率 单塔 1.1974 × 10−59地基-单塔 1.6052 × 10−38塔线 0.7589 地基-塔线 0.9321 表 3 不同工况下耦合系统的失效概率
Table 3. Failure probabilities of coupling system under different conditions
工况 失效概率 变化率/% 固定端 0.7589 中硬土 0.7926 4.44 中软土 0.8340 5.22 软弱土 0.9320 11.76 -
[1] 李正良, 张智航, 王涛. 考虑多重性能水准的特高压双柱悬索拉线塔风灾易损性分析[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2024, 44(20): 8305-8317.LI Zhengliang, ZHANG Zhihang, WANG Tao. Wind fragility analysis of UHV double column suspended guyed tower considering multiple performance levels[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2024, 44(20): 8305-8317. [2] 李悦, 谢强, 张欣, 等. 强风作用下输电塔线体系连续性倒塌分析[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2024, 59(2): 423-430.LI Yue, XIE Qiang, ZHANG Xin, et al. Cascading failure analysis of transmission tower–line system under strong wind[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2024, 59(2): 423-430. [3] SKUODIS Š, DIRGĖLIE NĖ N, TAMOSIU NAS T, et al. Case study of pullout piles connected with cap[J]. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 2021, 727(1): 012015. [4] 汪之松, 刘兴龙, 武彦君, 等. 考虑SSI效应的输电塔-线体系风振响应简化分析[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2019, 54(2): 319-327.WANG Zhisong, LIU Xinglong, WU Yanjun, et al. Simplified analysis of wind-induced response of transmission tower-line system considering SSI effect[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2019, 54(2): 319-327. [5] WANG T, LI Z L, FAN W L, et al. Structural reliability assessment based on enhanced conjugate unscented transformation and improved maximum entropy method[J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 2021, 147(12): 04021213. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)ST.1943-541X.0003194 [6] NATARAJAN K, SANTHAKUMAR A R. Reliability-based optimization of transmission line towers[J]. Computers & Structures, 1995, 55(3): 387-403. [7] ZHANG L L, LI J. Probability density evolution analysis on dynamic response and reliability estimation of wind-excited transmission towers[J]. Wind and Structures, 2007, 10(1): 45-60. doi: 10.12989/was.2007.10.1.045 [8] 汪大海, 李杰. 强风下高压输电塔线系统非线性随机动力响应[J]. 振动与冲击, 2010, 29(6): 62-65, 235.WANG Dahai, LI Jie. Nonlinear stochastic response of transmission tower-line system under strong wind[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2010, 29(6): 62-65, 235. [9] 俞登科, 李正良, 李茂华, 等. 基于矩方法的特高压输电塔抗风可靠度分析[J]. 工程力学, 2013, 30(5): 311-316.YU Dengke, LI Zhengliang, LI Maohua, et al. Wind-resistant reliability analysis of UHV transmission tower based on moment methods[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2013, 30(5): 311-316. [10] 王成, 王涛, 黄兴, 等. 基于样本矩-最大熵法的长短腿输电塔整体可靠度分析[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2025, 60(5): 1315-1324.WANG Cheng, WANG Tao, HUANG Xing, et al. Overall reliability analysis of transmission towers with asymmetrical legs based on sample moment and maximum entropy method[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2025, 60(5): 1315-1324. [11] TANG Z Q, LI Z L, WANG T, et al. PDEM-based multi-component and global reliability evaluation framework for steel tubular transmission towers with semi-rigid connections[J]. Engineering Structures, 2023, 295: 116838. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2023.116838 [12] TANG Z Q, WANG T, LI Z L, et al. Stochastic stress response and dynamic reliability evaluation for transmission towers with semi-rigid behaviors[J]. Disaster Prevention and Resilience, 2023, 2(4): 22-30. [13] WANG L, WANG T, LI Z L, et al. Stochastic seismic dynamic response analysis for coupled transmission tower-insulator-line systems considering soil-structure interaction[J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 2024, 181: 108662. doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2024.108662 [14] 王磊, 李正良, 王涛. 考虑SSI效应的输电塔-线耦合系统抗震可靠度分析[J]. 湖南大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 50(11): 192-203.WANG Lei, LI Zhengliang, WANG Tao. Seismic reliability analysis of transmission tower-line coupling system considering SSI effect[J]. Journal of Hunan University (Natural Sciences), 2023, 50(11): 192-203. [15] 田利, 李兴建, 易思银, 等. 地震下考虑桩-土-结构相互作用的输电塔-线体系响应分析[J]. 世界地震工程, 2018, 34(3): 1-11.TIAN Li, LI Xingjian, YI Siyin, et al. Response analysis of transmission tower-line system considering pile-soil-structure interaction under earthquake loading[J]. World Earthquake Engineering, 2018, 34(3): 1-11. [16] 李宏男, 石文龙, 贾连光. 考虑导线影响的输电塔侧向简化抗震计算方法[J]. 振动工程学报, 2003, 16(2): 233-237.LI Hongnan, SHI Wenlong, JIA Lianguang. Simplified aseicmic calculation method considering effects of lines on transmission tower[J]. Journal of Vibration Engineering, 2003, 16(2): 233-237. [17] 刘章军, 刘增辉. 随机脉动风场的谱表示降维模拟[J]. 振动工程学报, 2018, 31(1): 49-56.LIU Zhangjun, LIU Zenghui. Dimension reduction based spectral representation of stochastic fluctuation wind field simulation[J]. Journal of Vibration Engineering, 2018, 31(1): 49-56. [18] 瓦尔夫. 土-结构动力相互作用[M]. 吴世明, 唐有职, 陈龙珠, 等译. 北京: 地震出版社, 1989. [19] NOVAK M, EL HIF NAWY L. Structural response to wind with soil-structure interaction[J]. Advances in Wind Engineering, 1988, 28(1-3): 329-338. [20] LI J, CHEN J B. Stochastic dy Namics of structures[M]. Clementi: John Wiley & Sons, 2009. [21] CHE N J B, YA NG J Y, LI J. A GF-discrepancy for point selection in stochastic seismic response analysis of structures with uncertain parameters[J]. Structural Safety, 2016, 59: 20-31. doi: 10.1016/j.strusafe.2015.11.001 [22] WANG T, Dong Y, WANG L, et al. Global reliability assessment of coupled transmission tower-insulator-line systems considering soil-structure interaction subjected to multi-hazard of wind and ice[J]. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 2024, 223: 109004. doi: 10.1016/j.jcsr.2024.109004 [23] KAIMAL J C, WY NGAARD J C J, IZUMI Y, et al. Spectral characteristics of surface-layer turbulence[J]. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 1972, 98(417): 563-589. [24] PICCARDO G, SOLARI G. Generalized equivalent spectrum technique[J]. Wind and Structures, 1998, 1(2): 161-174. doi: 10.12989/was.1998.1.2.161 [25] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 110 kV~750 kV架空输电线路设计规范( GB 50545—2010)[S]. 北京: 中国计划出版社, 2010. [26] WANG T, WANG Z Y, LU D G, et al. Galloping-induced global reliability assessment for ice-covered three-phase bundled conductors considering both mechanical and electrical functional failure modes[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2025, 262: 111240. [27] 鄢秀庆, 何松洋, 李正良, 等. 输电塔斜材不同节点型式下的受压承载力[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2024, 59(3): 712-719.YAN Xiuqing, HE Songyang, LI Zhengliang, et al. Compression bearing capacity of inclined members of transmission tower with different joint types[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2024, 59(3): 712-719. [28] SONG P, WANG T, LU D. Structural global reliability assessment considering nonlinear correlation effects by enhanced high-order moment method[J]. Acta Mechanica Sinica, 2023, 39(4): 722356. doi: 10.1007/s10409-022-22356-x -




 下载:
下载: