Analysis Method for Water-Rich and Fractured Risks in Tunnel Surrounding Rock Based on Fuzzy Bayesian Network
-
摘要:
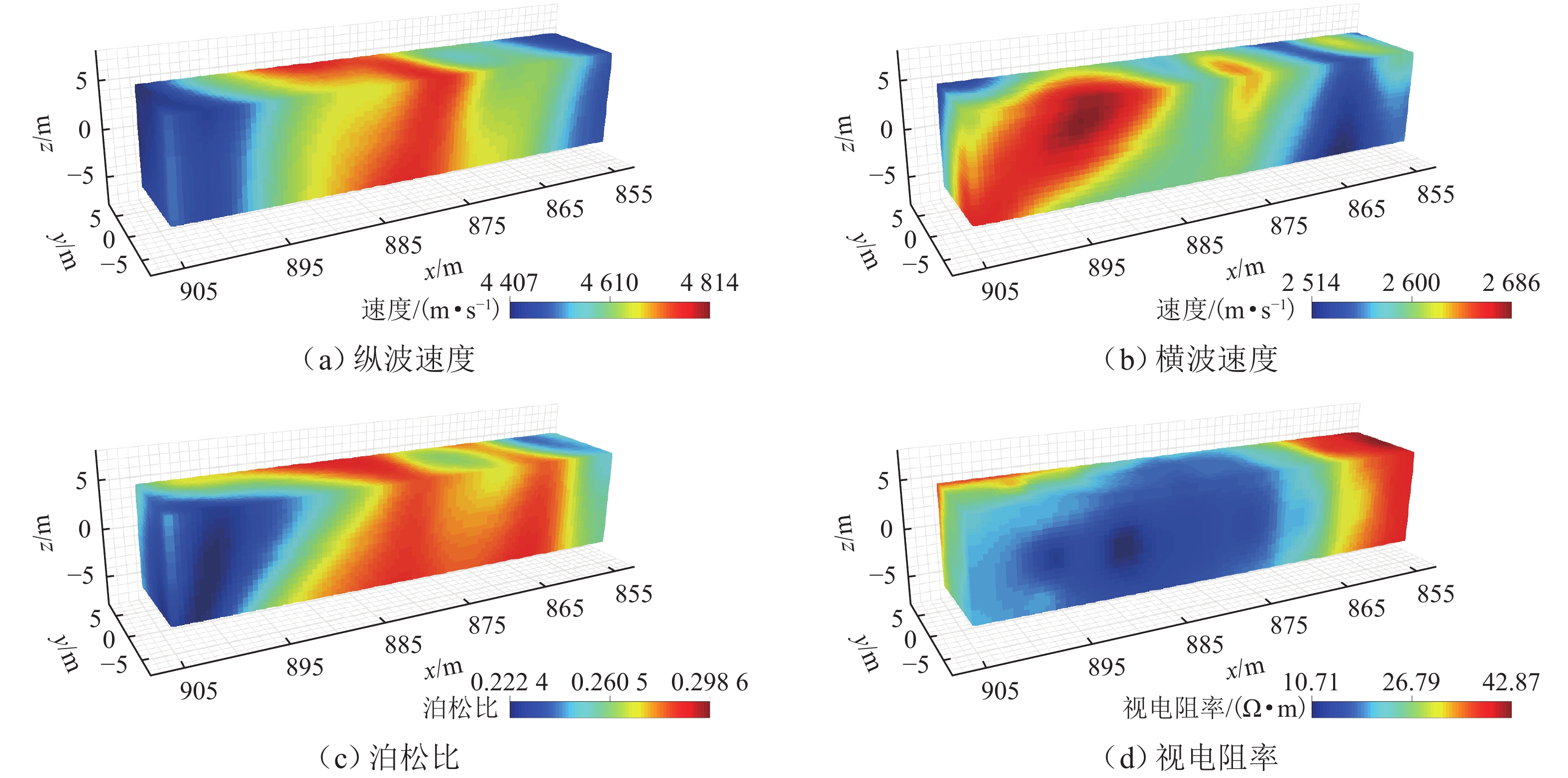
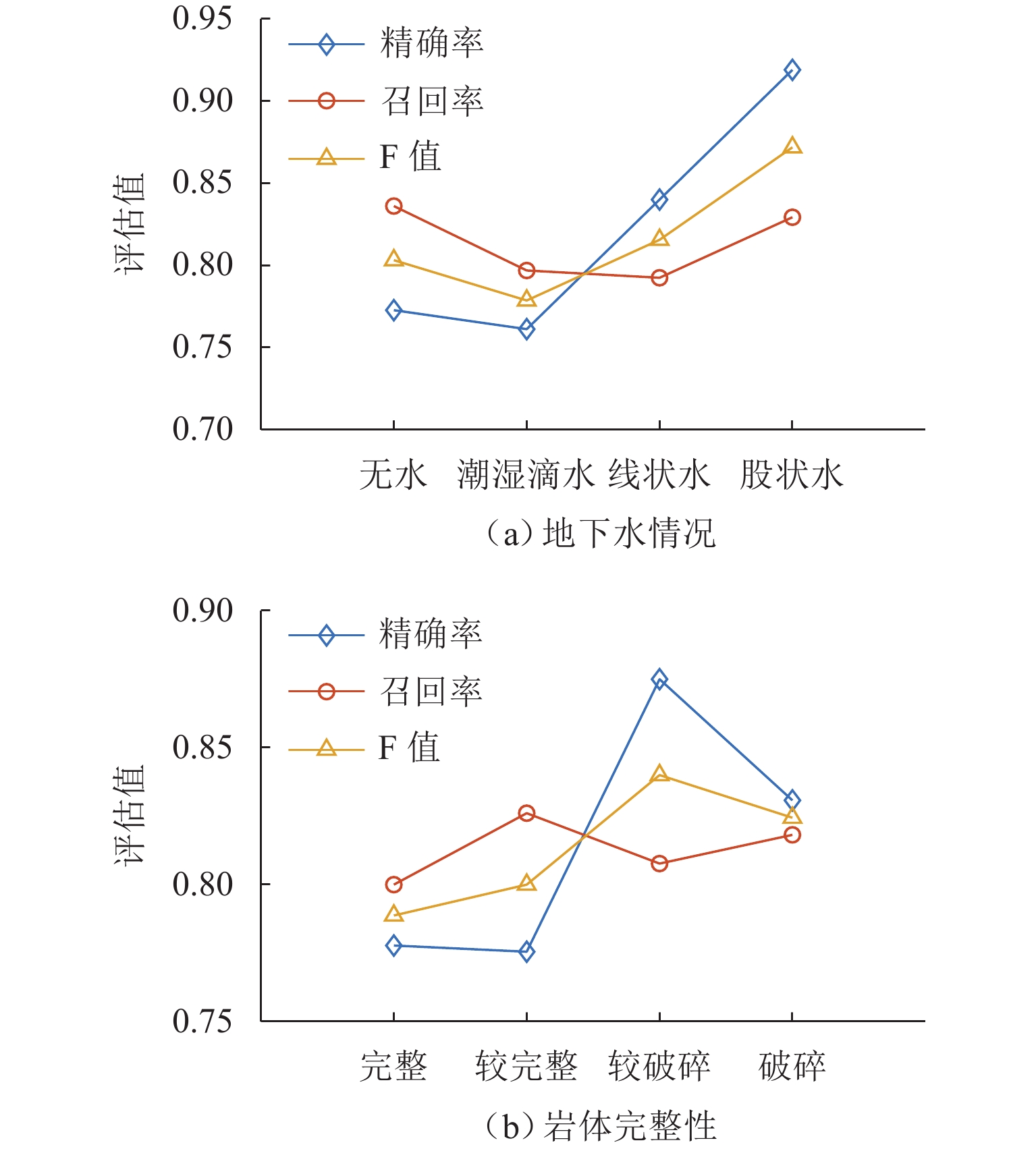
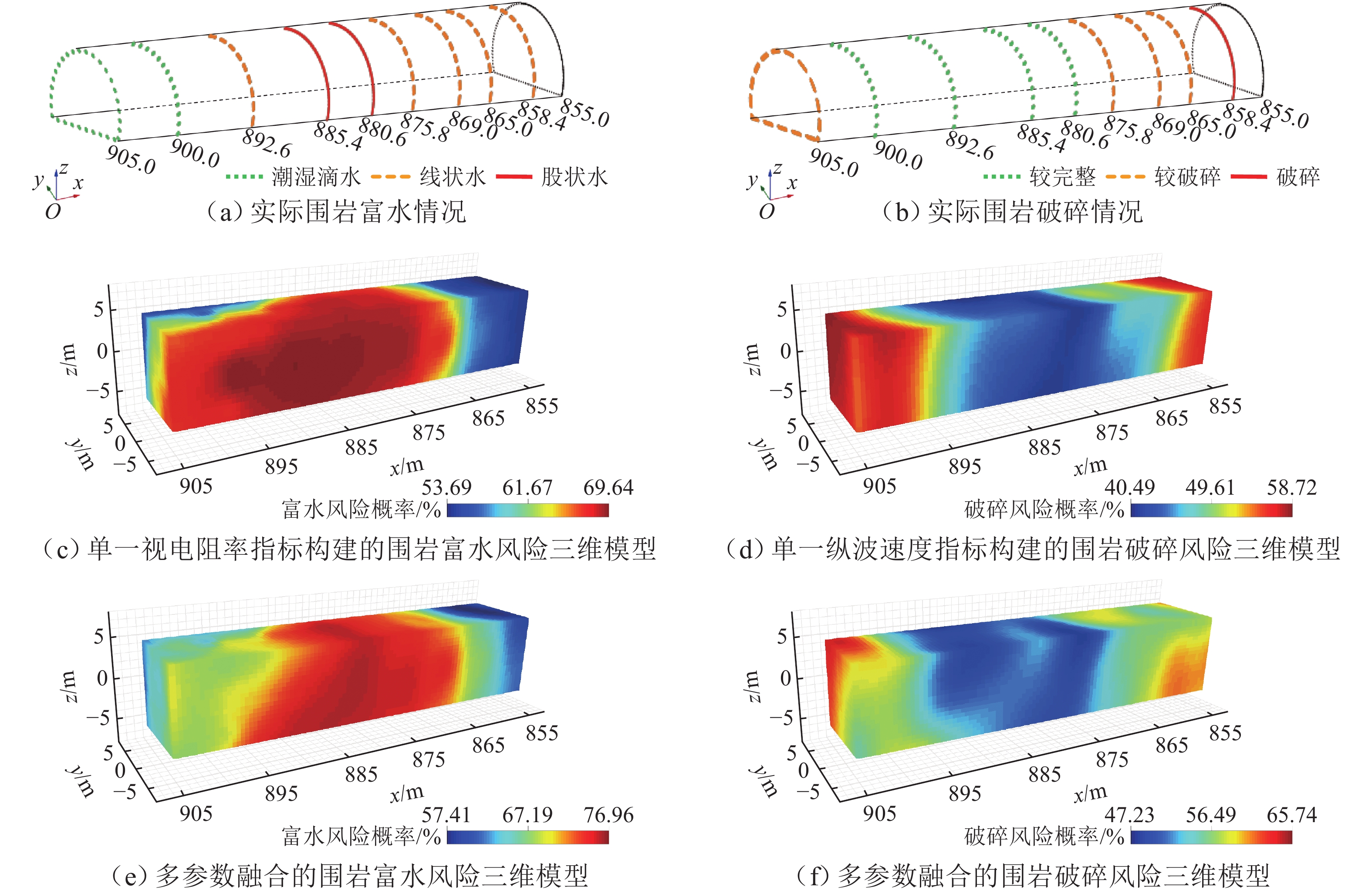
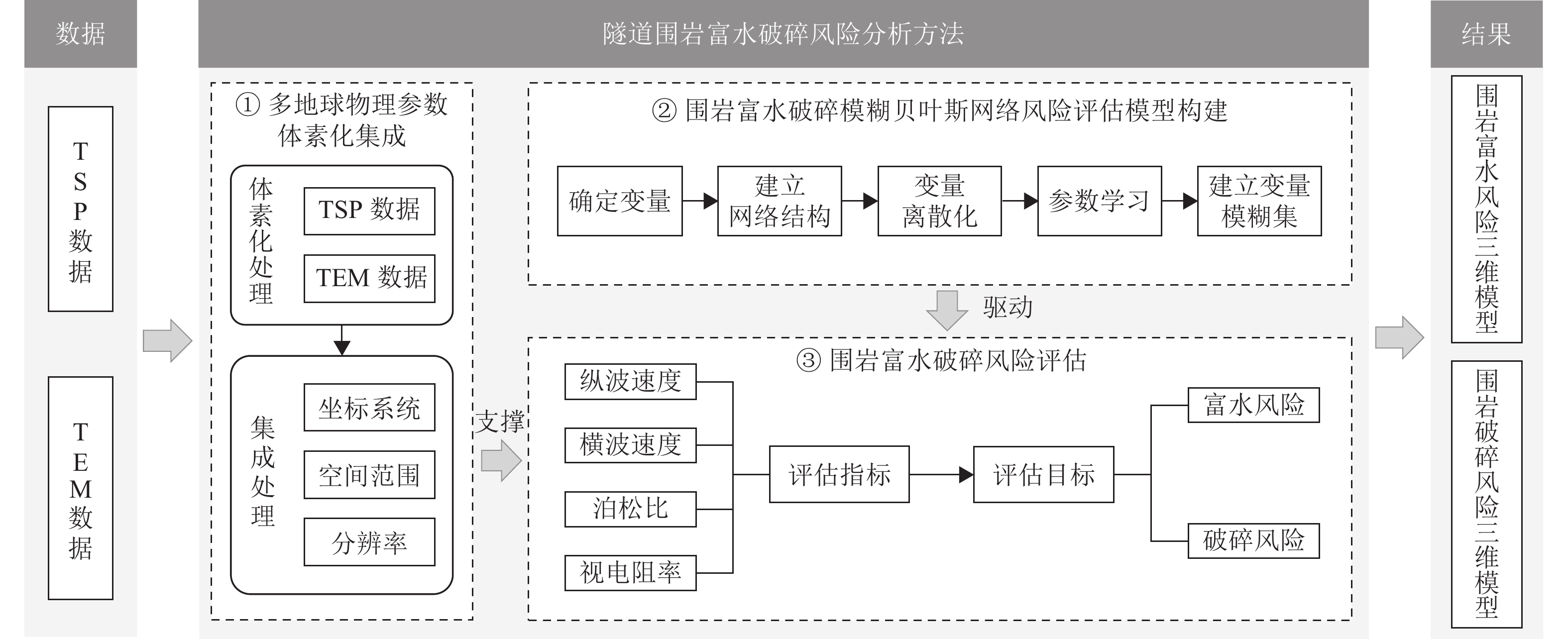
富水破碎不良地质区在隧道施工中容易诱发涌水灾害,为准确分析隧道围岩的富水破碎风险,且满足自动化、定量化风险分析需求,基于开挖数据构建模糊贝叶斯网络风险评估模型,通过隶属函数量化地质参数的不确定性,并结合贝叶斯概率推理,融合隧道地震预报法与瞬变电磁法的探测数据,得到围岩富水破碎风险概率;进一步利用三维体素模型将风险概率映射至三维坐标,可视化表达风险的空间分布特征. 选取典型长大深埋隧道进行实验分析,结果表明:评估模型对地下水情况与岩体完整性分类的准确率分别为80.91%和82.81%,且不受数据完备性限制,能够在单一或多源数据条件下完成定量分析;所建三维体素模型为风险防控提供了有效参考,其中,相较于单一数据,多源数据融合分析结果与现场揭露的富水区、破碎带位置吻合度更高.
Abstract:Unfavorable water-rich and fractured geological zones easily bring about water inrush disasters during tunnel construction. To accurately analyze water-rich and fractured risks in tunnel surrounding rock and address the need for automated and quantitative risk analysis, a fuzzy Bayesian network model for risk assessment was constructed by using tunnel excavation data. Geological parameter uncertainty was quantified via membership functions, and Bayesian probabilistic inference was employed to integrate data from tunnel seismic prediction and transient electromagnetic methods, yielding the probability of water-rich and fractured risks. A three-dimensional voxel model was used to map the risk probability to spatial coordinates, visualizing the spatial distribution of risks. A typical deep-buried long tunnel was selected for analysis. The results demonstrate that the assessment model achieves classification accuracies of 80.91% for groundwater conditions and 82.81% for rock mass integrity. Not affected by incomplete data, the model can conduct quantitative analysis under both single-source and multi-source data conditions. The constructed three-dimensional voxel model provides an effective reference for risk prevention and control. Analysis results of multi-source data fusion show higher spatial consistency with field-exposed water-rich and fractured zones than those of single-source data.
-
Key words:
- tunnel /
- risk analysis /
- three-dimensional geological modeling /
- fuzzy Bayesian network /
- data fusion
-
表 1 各指标变量富水破碎围岩响应特征
Table 1. Water-rich and fractured response features in surrounding rock of each indicator variable
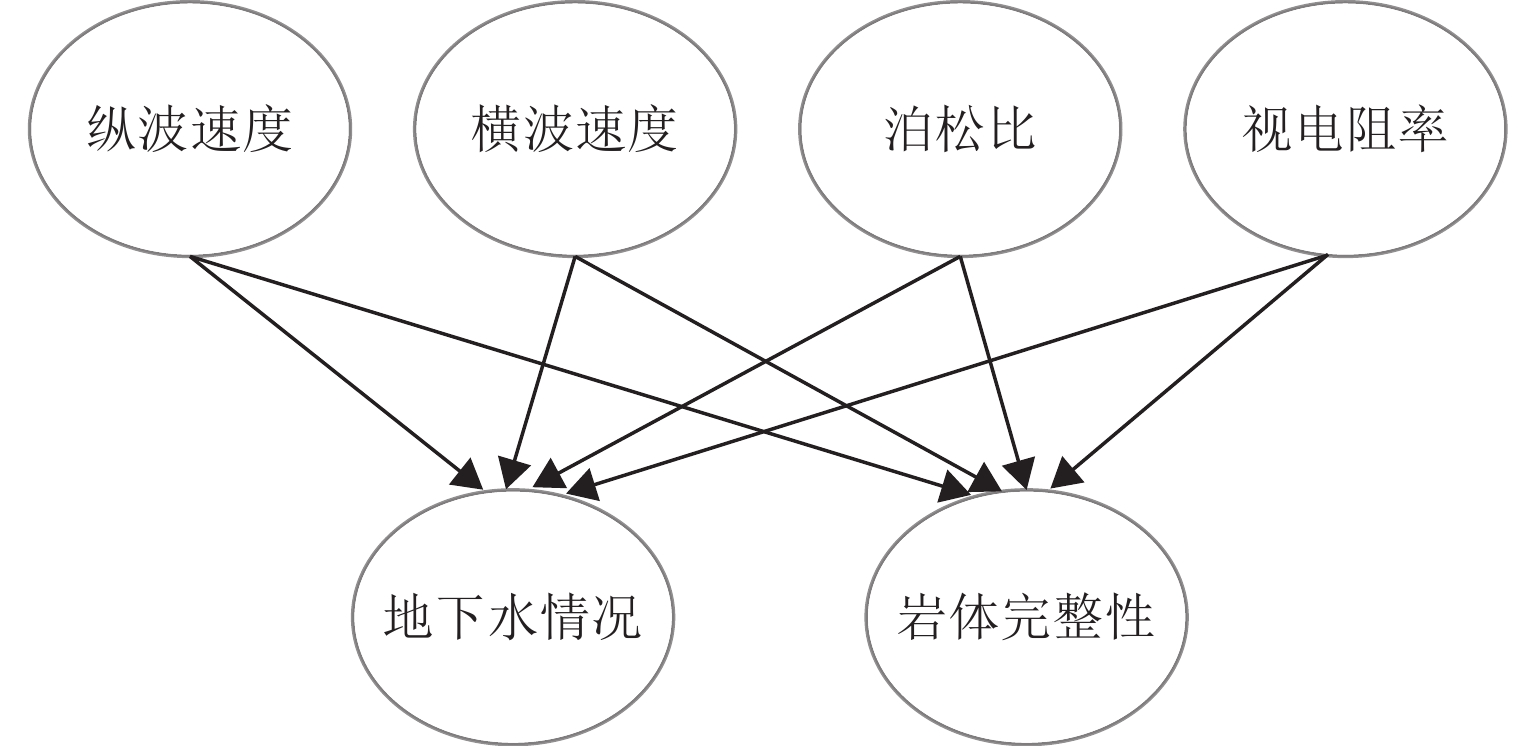
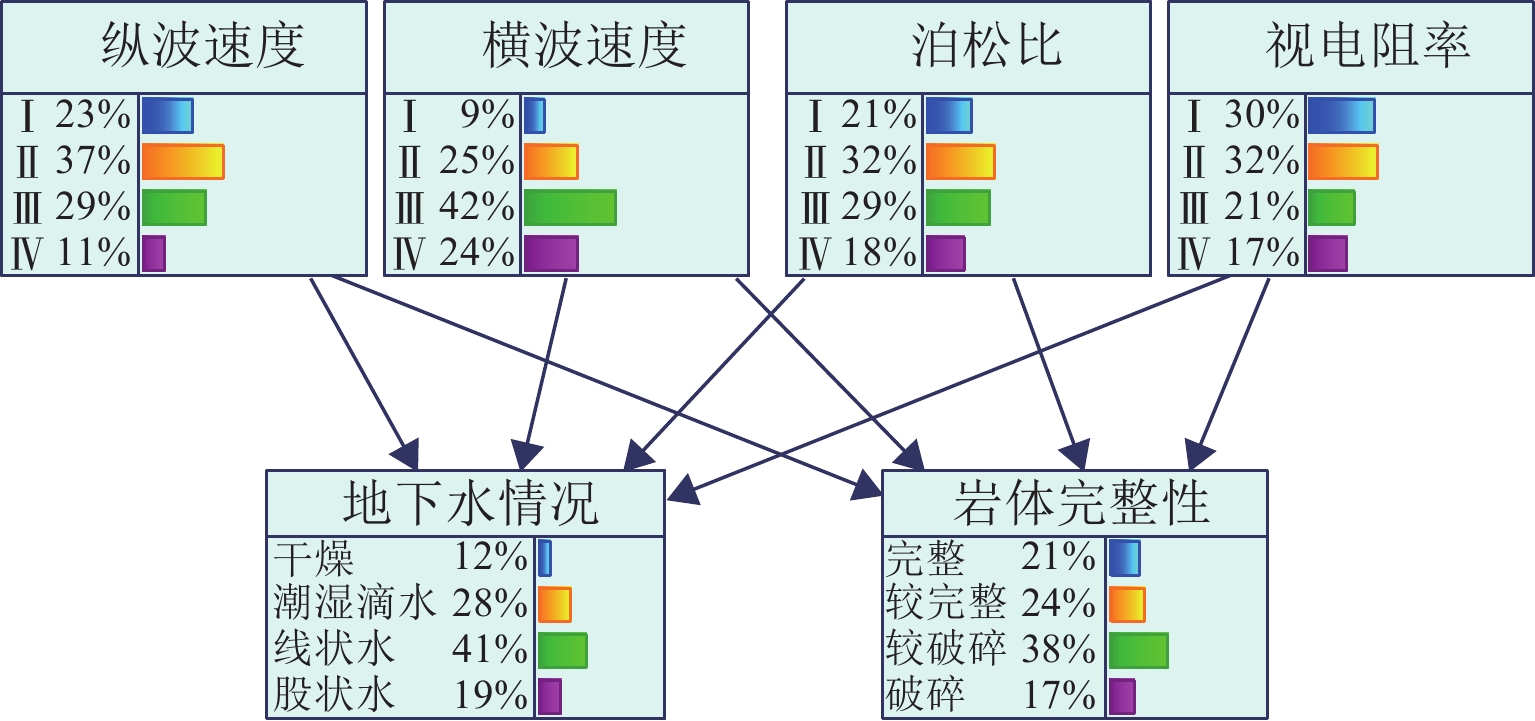
数据源 指标变量 富水围岩响应特征 破碎围岩响应特征 TSP 纵波速度 岩体含水影响纵波传递,含水量越高,波速越低[18] 岩体完整性显著影响纵波传递,岩体破碎导致传播路径不规律,表现出较低的波速[16-17] 横波速度 水体对横波传递抑制作用明显,横波从干燥岩体进入富水岩体,速度将显著降低[5, 18] 岩体完整性影响横波传递,岩体破碎导致传播路径不规律,表现出较低的波速[18] 泊松比 水分影响岩体的弹性性质,通常情况下,含水量较高的岩体表现出较高的泊松比[5] 岩体完整性影响岩体的弹性性质,通常情况下,高孔隙率的破碎岩体具有较高的泊松比[16] TEM 视电阻率 岩体中的水分作为导电体,对视电阻率有显著影响,含水量越高,视电阻率越低[5-6, 17] 岩体完整性影响视电阻率,破碎岩体更多的孔隙和裂隙,通常允许电流更容易通过,从而表现出较低的视电阻率[6] 表 2 各评价隶属函数类型
Table 2. Membership function types of each evaluation
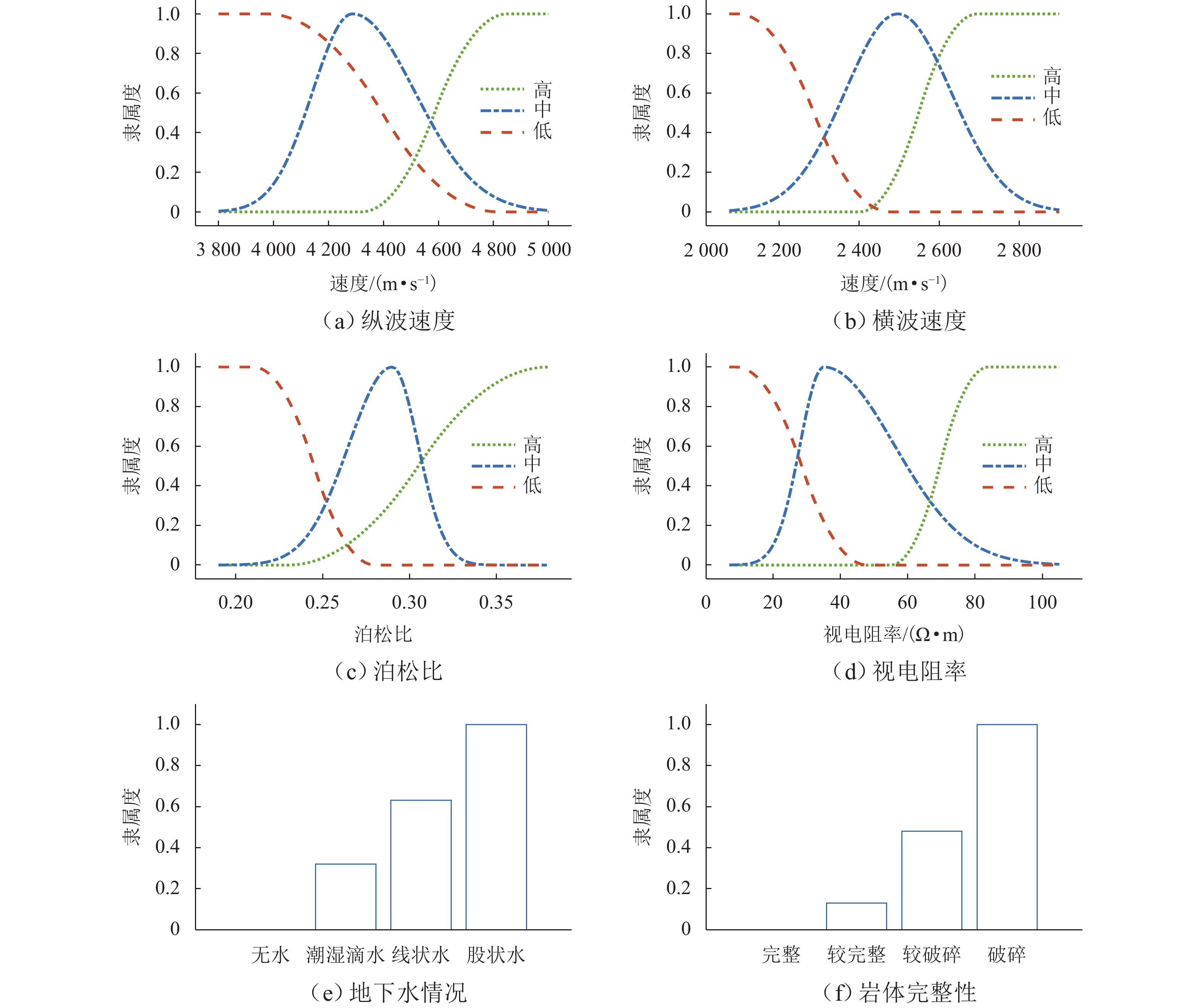
变量类型 评价 隶属函数类型 指标变量 高 S 形函数 中 双高斯函数 低 Z 形函数 目标变量 富水/破碎 阶梯形函数 表 3 岩体完整性与地下水情况变量敏感性分析结果
Table 3. Sensitivity analysis results of rock mass integrity and groundwater condition variables
影响程度排序 地下水情况 岩体完整性 评估指标 MI 评估指标 MI 1 视电阻率 0.40 纵波速度 0.67 2 横波速度 0.21 横波速度 0.50 3 泊松比 0.15 泊松比 0.27 4 纵波速度 0.12 视电阻率 0.17 -
[1] 薛翊国, 孔凡猛, 杨为民, 等. 川藏铁路沿线主要不良地质条件与工程地质问题[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2020, 39(3): 445-468.XUE Yiguo, KONG Fanmeng, YANG Weimin, et al. Main unfavorable geological conditions and engineering geological problems along Sichuan—Tibet railway[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2020, 39(3): 445-468. [2] 邵珠山, 张鹏举, 张喆, 等. 隧道施工超前地质预报研究进展[J]. 长江科学院院报, 2022, 39(1): 70-77, 85. doi: 10.11988/ckyyb.20200874SHAO Zhushan, ZHANG Pengju, ZHANG Zhe, et al. Research progress of advanced geological prediction in tunnel construction[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute, 2022, 39(1): 70-77, 85. doi: 10.11988/ckyyb.20200874 [3] 徐正宣, 张利国, 蒋良文, 等. 川藏铁路雅安至林芝段工程地质环境及主要工程地质问题[J]. 工程科学与技术, 2021(3): 29-42.XU Zhengxuan, ZHANG Liguo, JIANG Liangwen, et al. Engineering geological environment and main engineering geological problems of Ya’an: Linzhi section of the Sichuan—Tibet railway[J]. Advanced Engineering Sciences, 2021(3): 29-42. [4] LI S C, LIU B, XU X J, et al. An overview of ahead geological prospecting in tunneling[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2017, 63: 69-94. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2016.12.011 [5] DING Y L, YANG B R, XU G C, et al. Improved dempster–shafer evidence theory for tunnel water inrush risk analysis based on fuzzy identification factors of multi-source geophysical data[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(23): 6178.1-6178.19. [6] LIU B, FAN K R, NIE L C, et al. Mapping water-abundant zones using transient electromagnetic and seismic methods when tunneling through fractured granite in the Qinling Mountains, China[J]. Geophysics, 2020, 85(4): B147-B159. doi: 10.1190/geo2019-0067.1 [7] LU X L, HU X Q, XU Z Y, et al. Tunnel concealed Karst cave joint detection by tunnel seismic and transient electromagnetic[J]. Lithosphere, 2022, 2022(1): 2827582.1-2827582.13. [8] ZHANG Y, YAN X L, YANG L. Application of multiple geophysical prospecting methods and high precision survey in expressway construction[C]// International Conference on Geographic Information and Remote Sensing Technology (GIRST 2022). Kunming: SPIE, 2023: 445-452. [9] TSOKAS G N, TSOURLOS P I, KIM J H, et al. Assessing the condition of the rock mass over the tunnel of eupalinus in Samos (Greece) using both conventional geophysical methods and surface to tunnel electrical resistivity tomography[J]. Archaeological Prospection, 2014, 21(4): 277-291. doi: 10.1002/arp.1489 [10] CHEN L, ZHANG F K, REN Y X, et al. Tunnel prospecting based on integrated interpretation of geophysical data: Xiangyun tunnel, Yunnan Province, China[J]. Journal of Environmental and Engineering Geophysics, 2019, 24(1): 63-75. doi: 10.2113/JEEG24.1.63 [11] MA J J, LI T B, LI X, et al. A probability prediction method for the classification of surrounding rock quality of tunnels with incomplete data using Bayesian networks[J]. Scientific Reports, 2022, 12: 19846.1-19846.19. [12] WANG Y C, LIU Y, LI Z Y, et al. A new Bayesian network model for the risk assessment of water inrush in Karst tunnels[J]. Geofluids, 2022, 2022(1): 5697710.1-5697710.12. [13] BU L, LI S C, SHI S S, et al. Application of the comprehensive forecast system for water-bearing structures in a Karst tunnel: a case study[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 2019, 78(1): 357-373. doi: 10.1007/s10064-017-1114-4 [14] 晏雁. 瞬变电磁三维成像在煤矿含水体探测中的应用[J]. 工程地球物理学报, 2023, 20(1): 43-49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7940.2023.01.006YAN Yan. Application of TEM 3D imaging in water content detection of coal mine[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering Geophysics, 2023, 20(1): 43-49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7940.2023.01.006 [15] TANG H, LIU S. Basic theory of fuzzy Bayesian networks and its application in machinery fault diagnosis[C]//Fourth International Conference on Fuzzy Systems and Knowledge Discovery (FSKD 2007). Haikou: IEEE, 2007: 132-137. [16] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 工程岩体分级标准: GB/T 50218—2014[S]. 北京: 中国计划出版社, 2015. [17] 李天斌, 孟陆波, 朱劲, 等. 隧道超前地质预报综合分析方法[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2009, 28(12): 2429-2436. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2009.12.007LI Tianbin, MENG Lubo, ZHU Jin, et al. Comprehensive analysis method for advanced forecast of geology in tunnels[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2009, 28(12): 2429-2436. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2009.12.007 [18] 许振浩, 李术才, 张庆松, 等. TSP超前地质预报地震波反射特性研究[J]. 地下空间与工程学报, 2008, 4(4): 640-644, 716. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0836.2008.04.010XU Zhenhao, LI Shucai, ZHANG Qingsong, et al. Reflection characteristic of seismic wave in TSP advance geological prediction[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering, 2008, 4(4): 640-644, 716. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0836.2008.04.010 [19] FAYYAD U M, IRANI K B. Multi-interval discretization of continuous-valued attributes for classification learning[C]//International Joint Conferences on Artificial Intelligence. San Francisco: Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc., 1993: 1022-1029. [20] REED E, MENGSHOEL O J, REED E, et al. Bayesian network parameter learning using EM with parameter sharing[C]//Proceedings of the Eleventh UAI Conference on Bayesian Modeling Applications Workshop. Quebec: ACM, 2014: 48-59. [21] ZIMMERMANN H J. Fuzzy set theory[J]. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Computational Statistics, 2010, 2(3): 317-332. doi: 10.1002/wics.82 [22] 熊艳艳, 吴先球. 粗大误差四种判别准则的比较和应用[J]. 大学物理实验, 2010, 23(1): 66-68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2934.2010.01.022XIONG Yanyan, WU Xianqiu. The generalizing application of four judging criterions for gross errors[J]. Physical Experiment of College, 2010, 23(1): 66-68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2934.2010.01.022 [23] BOSCH D, LEDO J, QUERALT P. Fuzzy logic determination of lithologies from well log data: application to the KTB project data set (Germany)[J]. Surveys in Geophysics, 2013, 34(4): 413-439. doi: 10.1007/s10712-013-9242-2 [24] 冷彪, 张毅, 杨辉, 等. 隧道掌子面岩体裂隙快速识别方法[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2021, 56(2): 246-252, 322.LENG Biao, ZHANG Yi, YANG Hui, et al. Rapid recognition of rock mass fractures in tunnel faces[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2021, 56(2): 246-252, 322. [25] DAS M, GHOSH S K. Advanced Bayesian network models with fuzzy extension[M]//Enhanced Bayesian network models for spatial time series prediction. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2019: 101-113. [26] DAS M, GHOSH S K. Data-driven approaches for meteorological time series prediction: a comparative study of the state-of-the-art computational intelligence techniques[J]. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2018, 105: 155-164. doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2017.08.009 -




 下载:
下载: