Influence of Vertical Stiffness of Continuous Girder on Dynamic Responses of High-Speed Electromagnetic Suspension Train and Bridge
-
摘要:
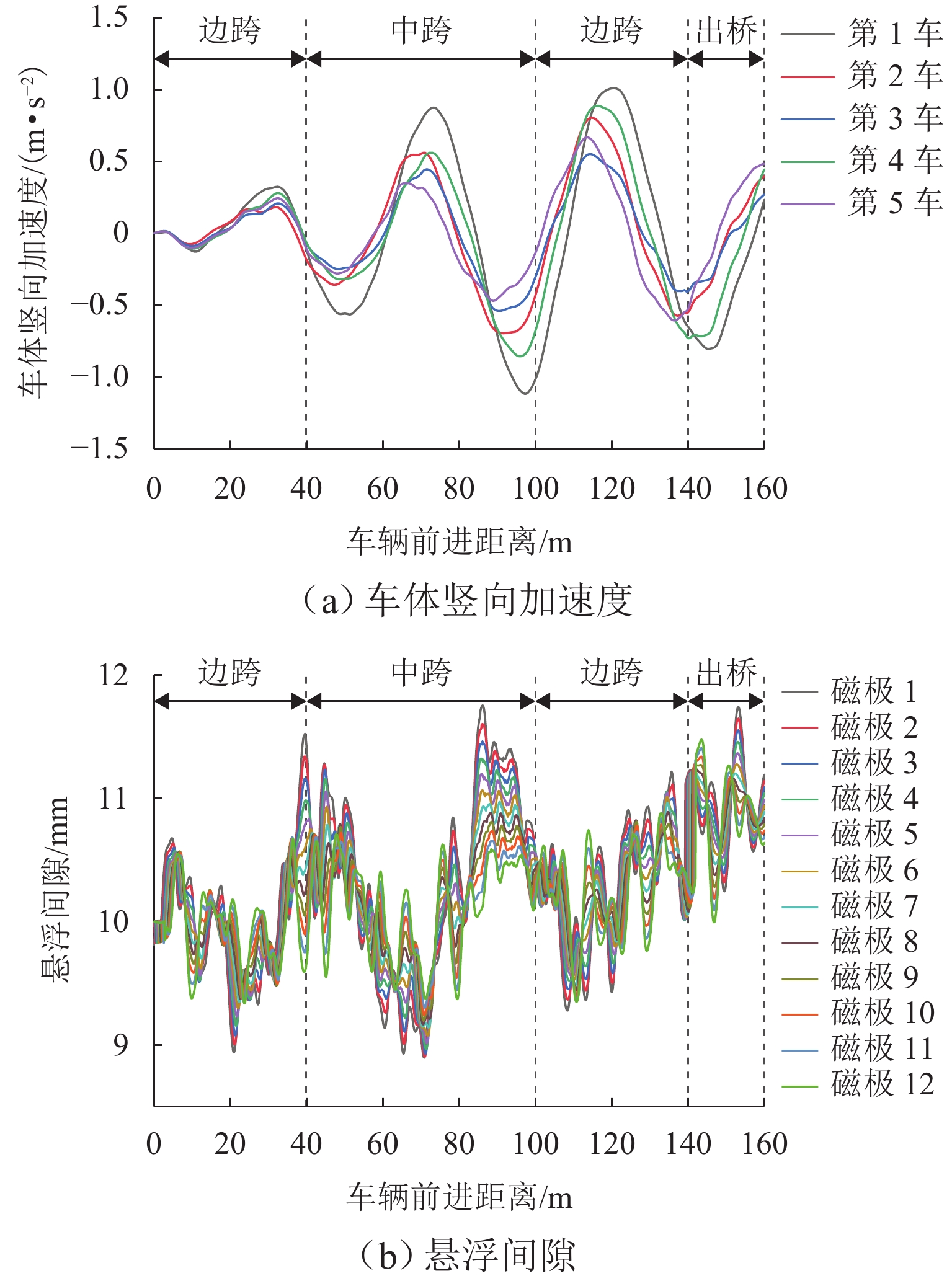
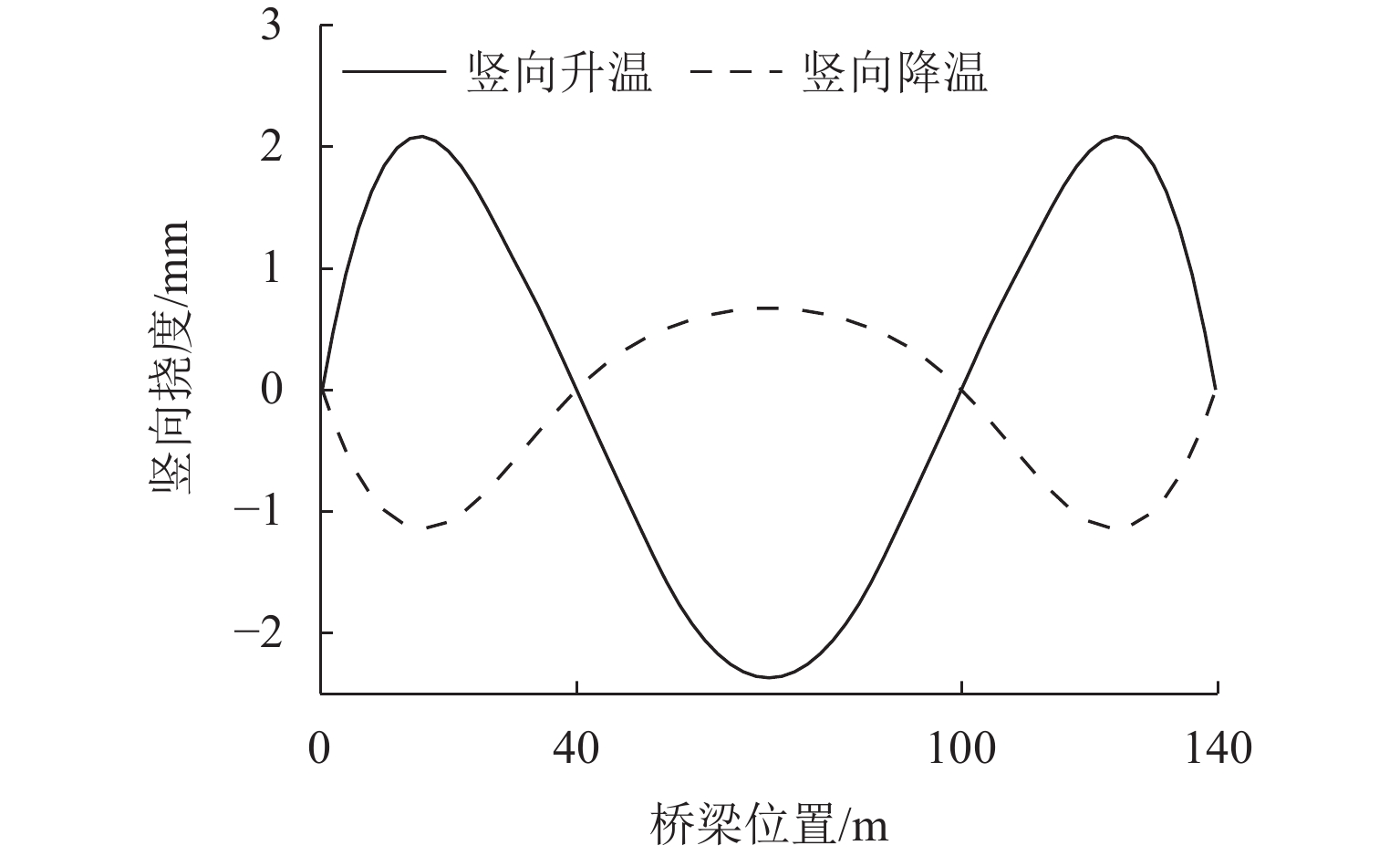
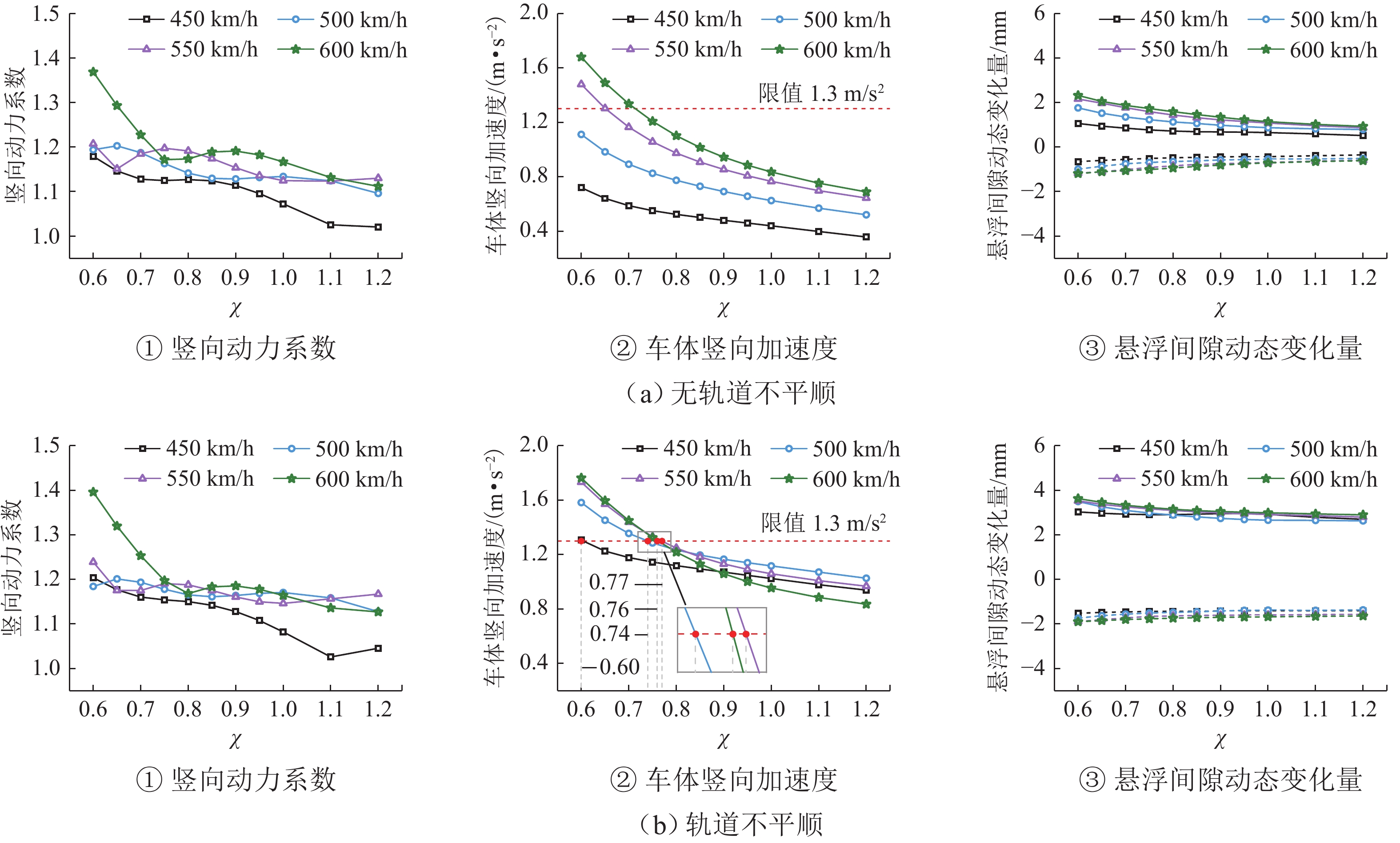
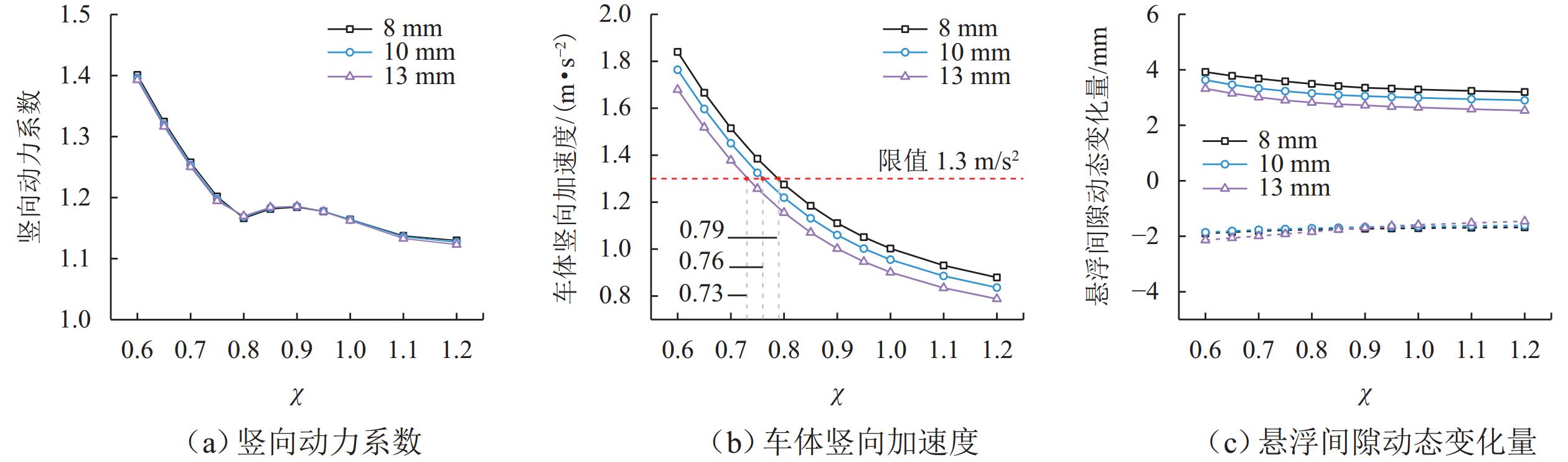
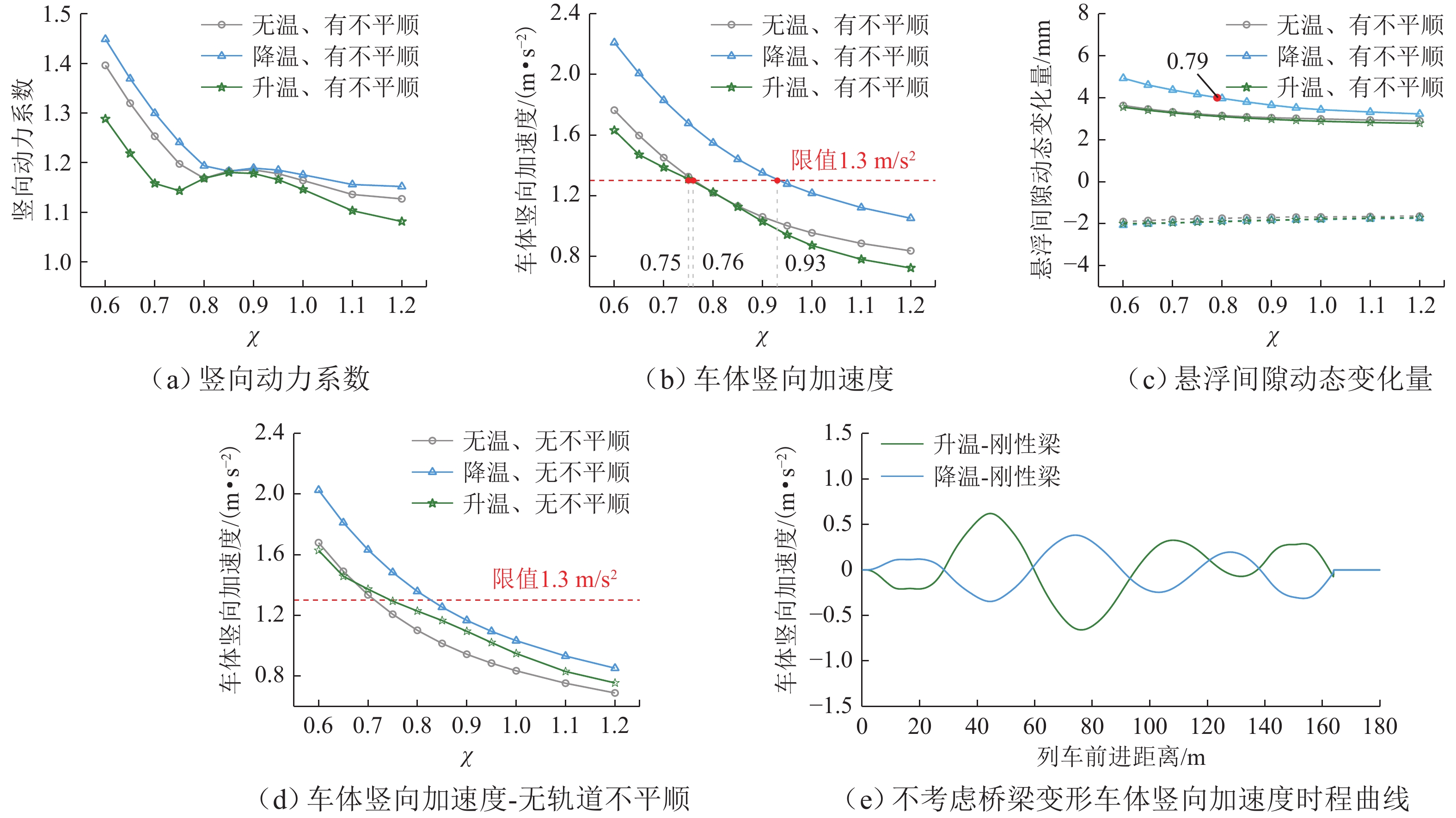
竖向刚度对保证高速磁浮列车在桥上行车安全和乘坐舒适性具有重要意义,是桥梁的重要设计指标之一. 以某3跨连续梁为研究对象,调整截面惯性矩改变桥梁竖向刚度,在不同车速、额定悬浮间隙及温度作用下进行磁浮列车-桥耦合振动分析,讨论桥梁动力系数、车体加速度和悬浮间隙动态变化量随桥梁竖向刚度调整系数的变化规律. 结果表明:刚度调整系数下降至0.75,桥梁动力系数迅速增加,车体竖向加速度相较于悬浮间隙动态变化量对桥梁竖向刚度变化更敏感;车速越大、考虑降温变形时,桥梁竖向动力响应越大,轨道不平顺和额定悬浮间隙对动力系数影响不明显;车速越大、额定悬浮间隙越小,考虑轨道不平顺和降温变形影响时,相同车辆动力响应大小对应的桥梁竖向刚度调整系数越大.
Abstract:Vertical stiffness is critically significant for the operational safety and ride comfort of high-speed electromagnetic suspension (EMS) trains on bridges, constituting one of the essential design parameters in bridge engineering. By using a three-span continuous girder as the study object, the vertical stiffness was modified by adjusting the cross-sectional moment of inertia. A coupled vibration analysis of the EMS train-bridge system was conducted under varying train speeds, rated suspension clearances, and temperatures. The variation rules of the dynamic coefficient of the bridge, acceleration of the train, and suspension clearance change with the adjustment coefficient of vertical stiffness of the bridge were discussed. The results show that when the adjustment coefficient of stiffness decreases to about 0.75, the dynamic coefficient of the bridge increases rapidly, and the vertical acceleration of the train is more sensitive to the vertical stiffness variation of the bridge than the suspension clearance change. When the cooling deformation is considered, higher train speed indicates greater vertical dynamic response of the bridge, and the track irregularity and rated suspension clearance have no obvious influence on the dynamic coefficient of the bridge. Higher train speed indicates smaller rated suspension clearance. When the effects of track irregularity and cooling deformation are considered, the adjustment coefficient of vertical stiffness of the bridge corresponding to the same vehicle dynamic response is larger.
-
-
[1] 马卫华, 胡俊雄, 李铁, 等. EMS型中低速磁浮列车悬浮架技术研究综述[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2023, 58(4): 720-733.MA Weihua, HU Junxiong, LI Tie, et al. Technologies research review of electro-magnetic suspension medium-low-speed maglev train levitation frame[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2023, 58(4): 720-733. [2] 邓自刚, 刘宗鑫, 李海涛, 等. 磁悬浮列车发展现状与展望[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2022, 57(3): 455-474, 530.DENG Zigang, LIU Zongxin, LI Haitao, et al. Development status and prospect of maglev train[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2022, 57(3): 455-474, 530. [3] 李小珍, 王党雄, 耿杰, 等. F轨对中低速磁浮列车-桥梁系统竖向耦合振动的影响研究[J]. 土木工程学报, 2017, 50(4): 97-106.LI Xiaozhen, WANG Dangxiong, GENG Jie, et al. Study on the influence of F-rail in vertical coupling vibration of low-medium speed maglev train-bridge system[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2017, 50(4): 97-106. [4] WANG D X, LI X Z, LIANG L, et al. Dynamic interaction analysis of bridges induced by a low-to-medium–speed maglev train[J]. Journal of Vibration and Control, 2020, 26(21/22): 2013-2025. [5] WANG D X, LI X Z, LIANG L, et al. Influence of the track structure on the vertical dynamic interaction analysis of the low-to-medium-speed maglev train-bridge system[J]. Advances in Structural Engineering, 2019, 22(14): 2937-2950. doi: 10.1177/1369433219854550 [6] 郑晓龙, 陈星宇, 徐昕宇, 等. 某磁浮大跨斜拉桥竖向刚度限值研究[J]. 中国铁道科学, 2021, 42(1): 43-48.ZHENG Xiaolong, CHEN Xingyu, XU Xinyu, et al. Investigation on limit value of vertical stiffness for a long-span cable-stayed maglev bridge[J]. China Railway Science, 2021, 42(1): 43-48. [7] 姜卫利, 高芒芒. 轨道梁参数对磁浮车—高架桥垂向耦合动力响应的影响研究[J]. 中国铁道科学, 2004, 25(3): 71-75. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-4632.2004.03.015JIANG Weili, GAO Mangmang. Study of the effect of track beam parameters on vertical coupled dynamic response of maglev vehicle-viaduct[J]. China Railway Science, 2004, 25(3): 71-75. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-4632.2004.03.015 [8] 徐昕宇, 杨国静, 陈星宇, 等. 高速磁浮简支箱梁桥车致动力响应分析[J]. 铁道标准设计, 2020, 64(10): 57-61.XU Xinyu, YANG Guojing, CHEN Xingyu, et al. Dynamic response analysis of high-speed maglev simply-supported box girder bridge under vehicle loads[J]. Railway Standard Design, 2020, 64(10): 57-61. [9] 向活跃, 刘科宏, 李永乐. 列车荷载作用下的磁浮轨道梁响应极值条件[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2024, 60(1): 27-34, 136.XIANG Huoyue , LIU Kehong , LI Yongle. Extremum conditions of response of maglev guideway under train loads[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2024, 60(1): 27-34, 136. [10] 滕延锋, 滕念管, 寇新建. 承受移动均布二系悬挂模型的磁浮三跨连续梁振动分析[J]. 振动与冲击, 2008, 27(3): 120-123. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3835.2008.03.029TENG Yanfeng, TENG Nianguan, KOU Xinjian. Vibration analysis of continuous maglev guideway traversed by distributed moving two-stages suspension model[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2008, 27(3): 120-123. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3835.2008.03.029 [11] 国家铁路局. 磁浮铁路技术标准(试行): TB 10630—2019[S]. 北京: 中国铁道出版社, 2019. [12] 秦世强, 黄春雷, 龚俊虎, 等. 中低速磁浮梁轨一体轨道梁钢混接头试验研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2024, 59(4): 867-876.QIN Shiqiang, HUANG Chunlei, GONG Junhu, et al. Experimental study on steel-concrete joint of integrated track beam for medium and low speed maglev[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2024, 59(4): 867-876. [13] YAGHOUBI H, ZIARI H. Development of a maglev vehicle/guideway system interaction model and comparison of the guideway structural analysis with railway bridge structures[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering, 2011, 137(2): 140-154. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)TE.1943-5436.0000197 [14] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 高速磁浮交通设计标准: CJJ/T 310—2021[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2021. [15] XIANG H Y, TIAN X F, LI Y L, et al. Dynamic interaction analysis of high-speed maglev train and guideway with a control loop failure[J]. International Journal of Structural Stability and Dynamics, 2022, 22(10): 1-28. [16] TIAN X F, XIANG H Y, ZHU J, et al. Effect of long-wave deviation of stator plane on high-speed maglev train and guideway system[J]. Journal of Vibration and Control, 2023, 29(9/10): 2348-2362. [17] WANG Z L, XU Y L, LI G Q, et al. Modelling and validation of coupled high-speed maglev train-and-viaduct systems considering support flexibility[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2019, 57(2): 161-191. doi: 10.1080/00423114.2018.1450517 [18] 陈绪黎, 向活跃, 田祥富, 等. 常导高速磁浮桥梁预拱度形式研究[J]. 振动工程学报, 2023, 36(3): 652-661.CHEN Xuli, XIANG Huoyue, TIAN Xiangfu, et al. Analysis on pre-camber forms of high-speed EMS maglev bridge[J]. Journal of Vibration Engineering, 2023, 36(3): 652-661. [19] SHI J, FANG W S, WANG Y J, et al. Measurements and analysis of track irregularities on high speed maglev lines[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University SCIENCE A, 2014, 15(6): 385-394. doi: 10.1631/jzus.A1300163 [20] CHEN N, LI Y L, XIANG H Y. A new simulation algorithm of multivariate short-term stochastic wind velocity field based on inverse fast Fourier transform[J]. Engineering Structures, 2014, 80: 251-259. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2014.09.012 [21] 翟婉明, 赵春发. 磁浮车辆/轨道系统动力学(Ⅰ)——磁/轨相互作用及稳定性[J]. 机械工程学报, 2005, 41(7): 1-10. doi: 10.3901/JME.2005.07.001ZHAI Wanming, ZHAO Chunfa. Dynamics of maglev vehicle/guideway systems (Ⅰ) magnet/rail interaction and system stability[J]. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2005, 41(7): 1-10. doi: 10.3901/JME.2005.07.001 [22] 邓亚士. 高速磁浮交通迭合式轨道梁变形及力学特性研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2010. [23] 国家铁路局. 铁路桥涵设计规范: TB 10002—2017[S]. 北京: 中国铁道出版社 2017. [24] 高捷. 温差对磁浮双跨轨道梁变形及振动的影响[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2015. [25] 张庆福. 磁浮连续轨道梁温度变形及对振动的影响[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2008. [26] 国家铁路局. 铁路桥涵混凝土结构设计规范: TB 10092—2017[S]. 北京: 中国铁道出版社, 2017. [27] 邓建良, 吴定俊, 李奇. 移动均布荷载作用下简支梁桥动力系数分析[J]. 工程力学, 2013, 30(5): 56-62.DENG Jianliang, WU Dingjun, LI Qi. Impact factor analysis of simply-supported girder bridges traversed by uniformly-distributed moving loads[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2013, 30(5): 56-62. -




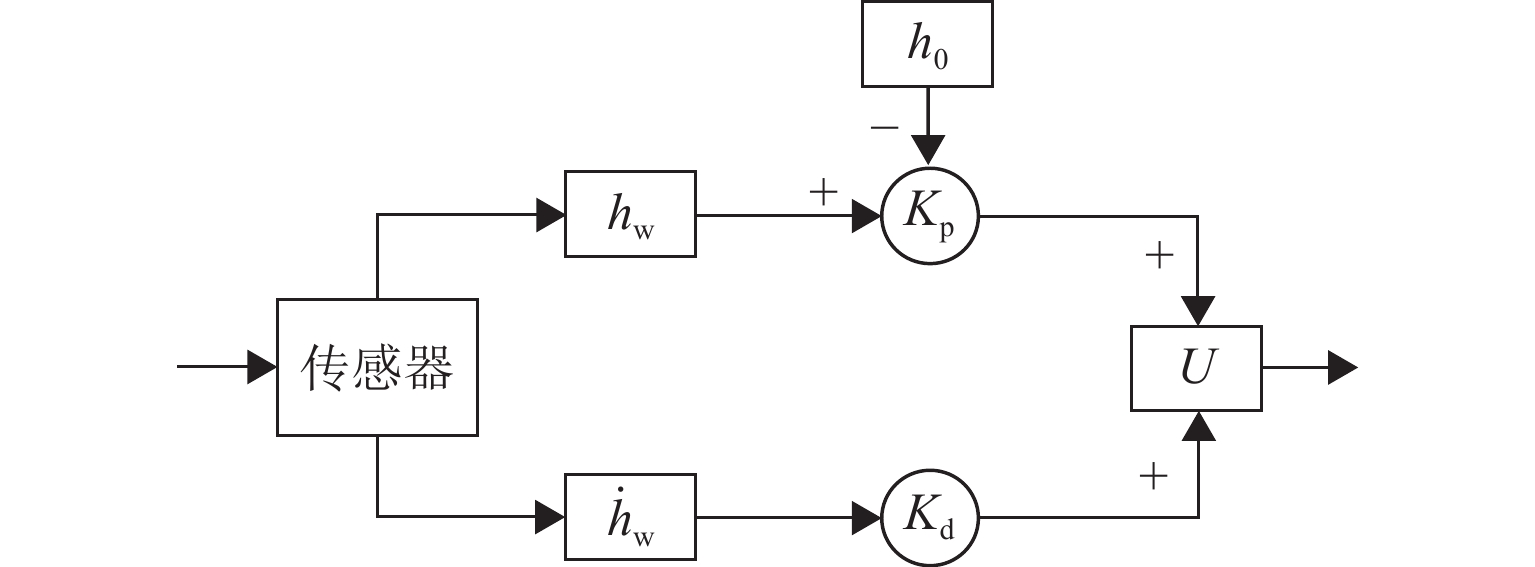
 下载:
下载: