Coupling Optimization and Regulation of Roadbed and Environment in Mountainous Railways
-
摘要:
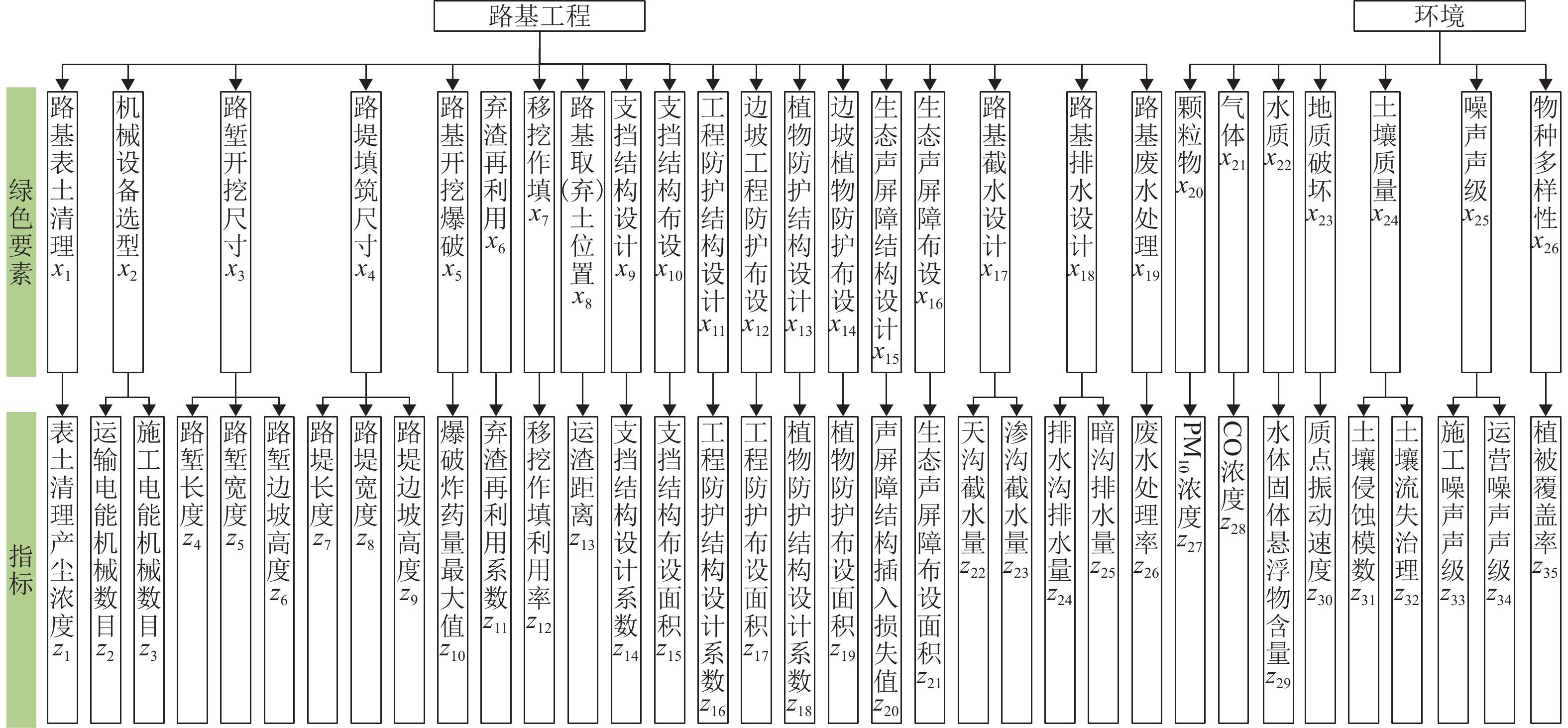
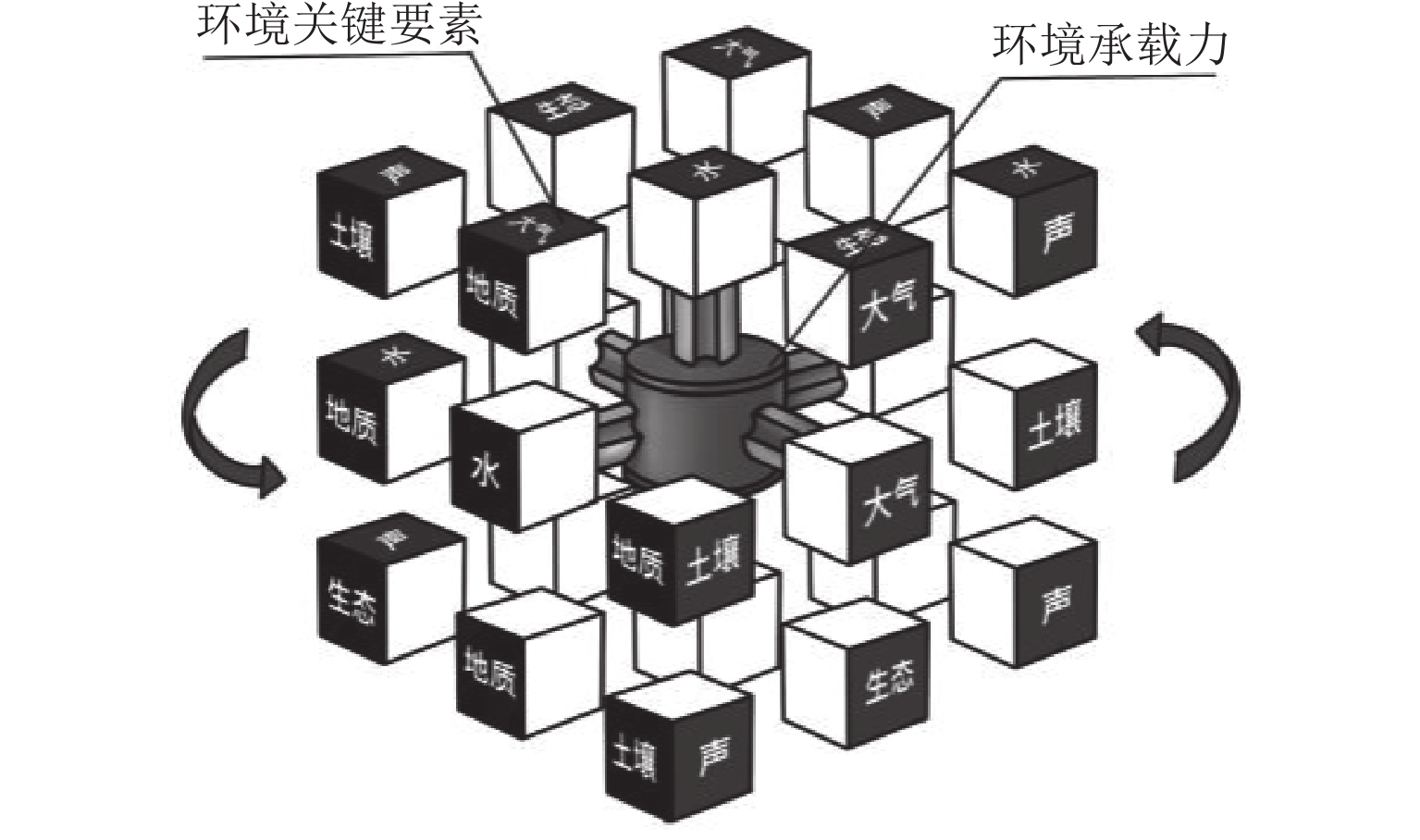
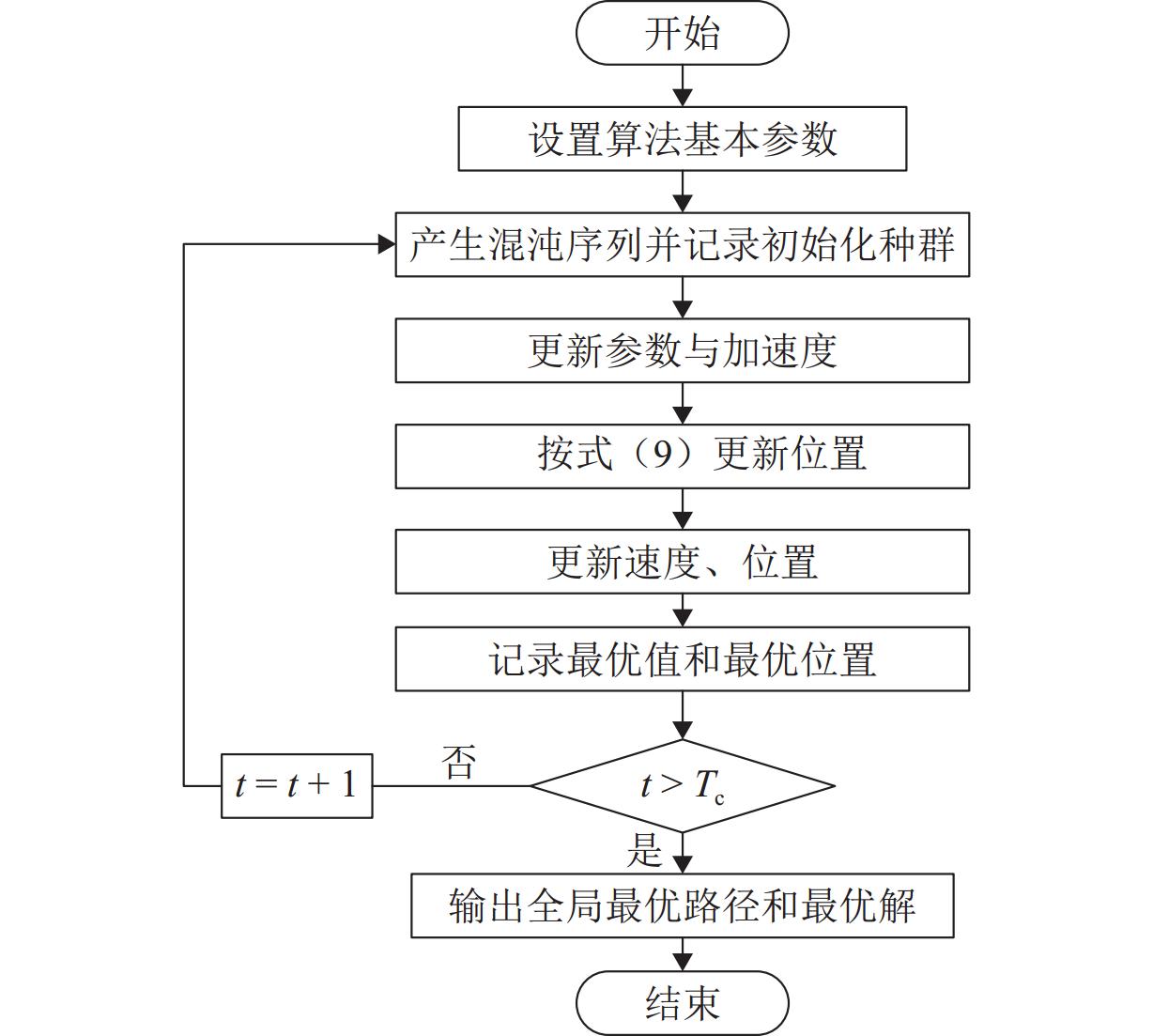
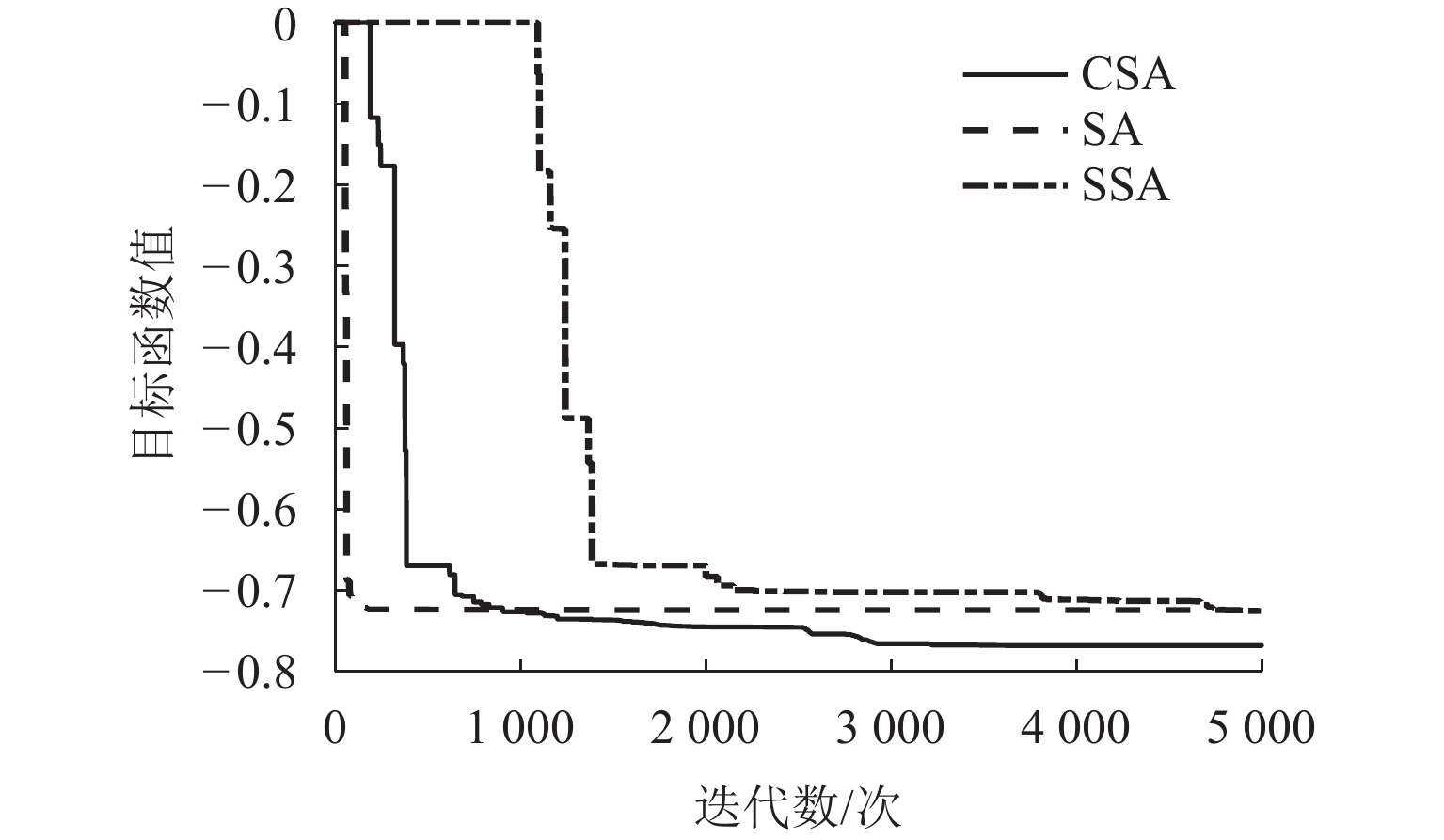
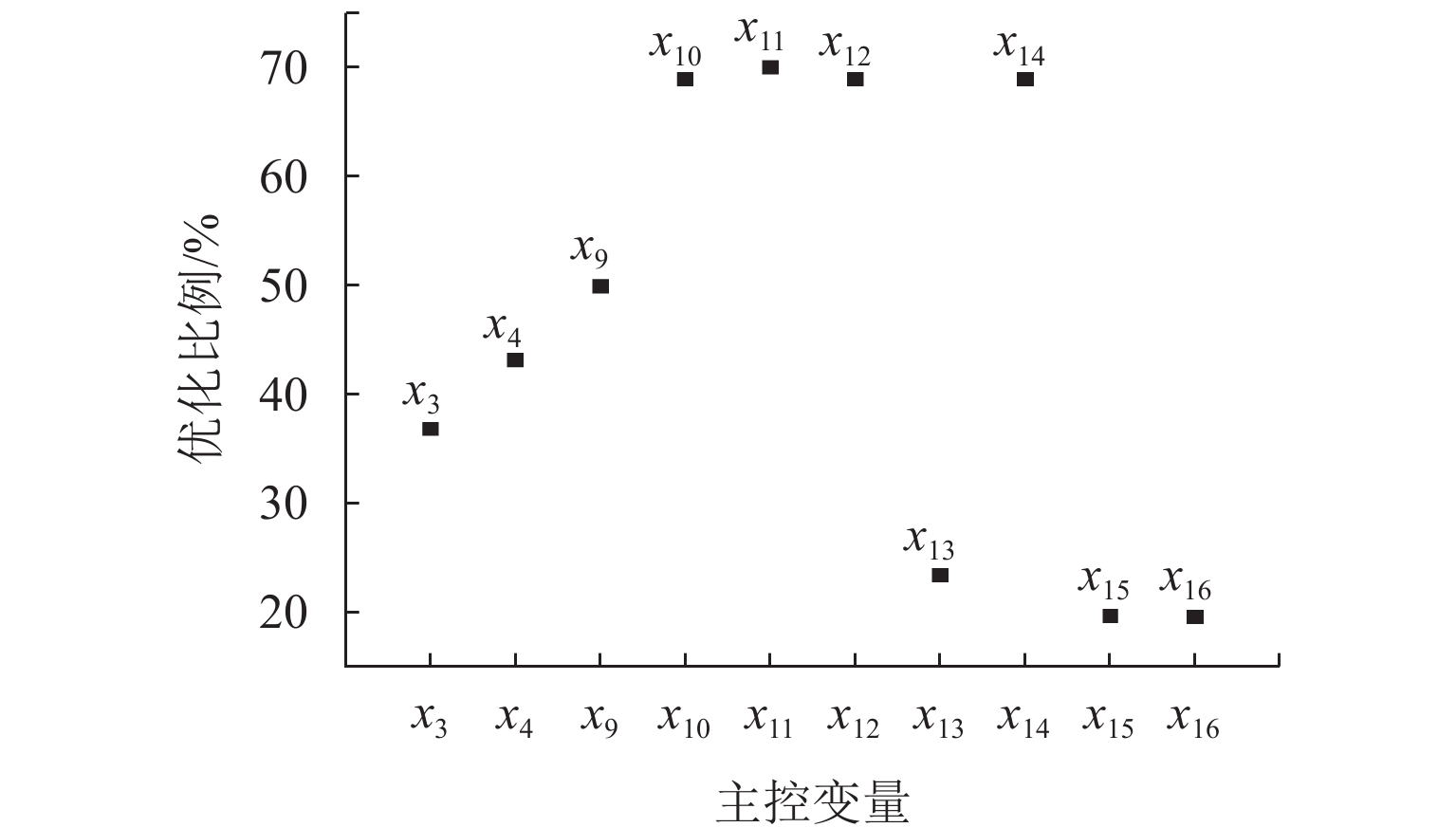
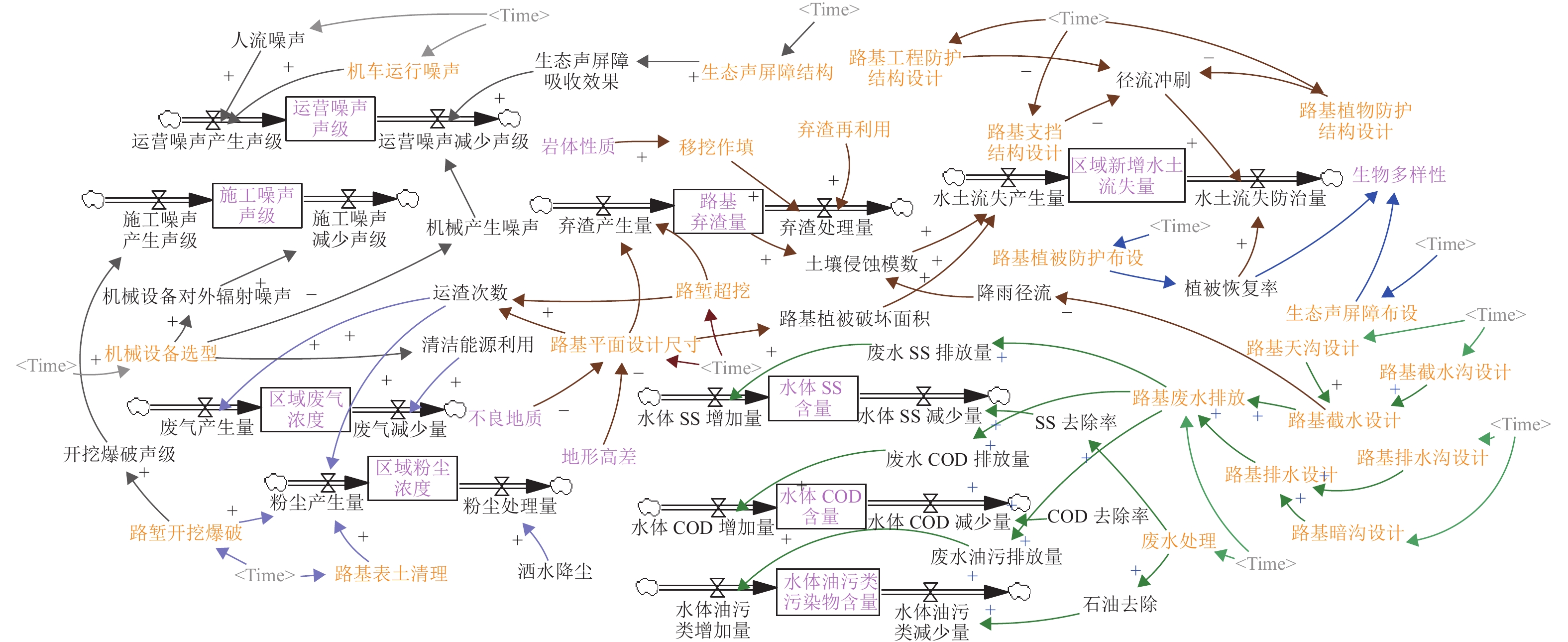
为实现山区铁路“路基-环境”高质量协调发展,提出一种“路基-环境”耦合优化调控方法. 首先,对于铁路“路基-环境”相容共生进行定义,构建绿色要素指标体系,并结合耦合魔方游戏模型明晰耦合调控框架;其次,利用耦合协调度模型、施压承载模型及各关键要素间的函数关系共同构建“路基-环境”调控优化目标函数及约束条件,将路基工程绿色关键要素作为主控变量,采取变色龙群优化算法(CSA)进行求解,得到相容共生状态下的各主控变量最优解;最后,以某山区铁路路基为例进行实证分析. 结果表明:当各主控变量路堑开挖尺寸、路堤填筑尺寸、支挡结构设计、支挡结构布设、工程防护结构设计、边坡工程防护布设、植物防护结构设计、边坡植物防护布设、生态声屏障结构设计、生态声屏障布设依次分别优化36.83%、43.14%、49.93%、68.91%、69.98%、68.91%、23.42%、68.91%、19.64%、19.60%比例时,可以实现铁路“路基-环境”从初级协调状态向中级协调状态的演化. 研究结果验证了构建的“路基-环境”调控优化模型的合理性以及CSA算法求最优解的有效性,为实现山区铁路路基工程绿色化建设提供了科学参考.
Abstract:To achieve high-quality coordinated development of roadbed and environment in mountainous railways, a coupling optimization and regulation method of roadbed and environment was proposed. Firstly, the compatibility and symbiosis between the railway roadbed and the environment were defined, and a green element indicator system was constructed. The coupling regulation framework was clarified by combining the coupled Rubik’s cube game model. Secondly, the coupling coordination degree model, pressure bearing model, and functional relationships between key elements were used to jointly construct the objective function and constraint conditions for roadbed and environment regulation and optimization. The green key elements of roadbed engineering were taken as the main control variables, and an intelligent optimization algorithm, namely the chameleon swarm algorithm (CSA) was adopted to solve them, obtaining the optimal solutions of each main control variable in a compatible and symbiotic state. Finally, an empirical analysis was conducted by using the railway roadbed in a certain mountainous area as an example. The results show that when the main control variables of road cut excavation size, embankment filling size, support structure design, support structure layout, engineering protection structure design, slope engineering protection layout, plant protection structure design, slope plant protection layout, ecological sound barrier structure design, and ecological sound barrier layout are optimized by 36.83%, 43.14%, 49.93%, 68.91%, 69.98%, 68.91%, 23.42%, 68.91%, 19.64%, and 19.60%, respectively, the evolution of railway roadbed and environment from primary coordination state to intermediate coordination state can be achieved. The research results verify the rationality of the constructed roadbed and environment regulation and optimization model and the effectiveness of CSA in finding the optimal solution, providing a scientific basis for achieving green construction of railway roadbed engineering in mountainous areas.
-
表 1 耦合协调度划分标准
Table 1. Classification criteria for coupling coordination degree
第 1 分类 划分标准 第 2 分类及划分标准 协调发展类 0.9<D≤1.0 优质协调 0.8<D≤0.9 良好协调 0.7<D≤0.8 中级协调 0.6<D≤0.7 初级协调 过渡发展类 0.5<D≤0.6 勉强发展 0.4<D≤0.5 濒临失调 0.3<D≤0.4 轻度失调 失调衰退类 0.2<D≤0.3 中度失调 0.1<D≤0.2 严重失调 0<D≤0.1 极度失调 -
[1] 李艳鸽, 姜楠, 韩征, 等. “绿色铁路设计” 核心理念的界定及应用探讨——以某西部铁路工程为例[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报, 2022, 19(11): 3439-3446.LI Yange, JIANG Nan, HAN Zheng, et al. Discussion on definition and application of the core concept of Green Railway Design―a case study of a Tibet railway project[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2022, 19(11): 3439-3446. [2] SU L J, HU B L, XIE Q J, et al. Experimental and theoretical study of mechanical properties of root-soil interface for slope protection[J]. Journal of Mountain Science, 2020, 17(11): 2784-2795. doi: 10.1007/s11629-020-6077-4 [3] SUKMAK P, SUKMAK G, HORPIBULSUK S, et al. Improved mechanical properties of cement-stabilized soft clay using garnet residues and tire-derived aggregates for subgrade applications[J]. Sustainability, 2021, 13(21): 11692.1-11692.22. [4] 郑雨茜, 鲍学英. 绿色施工下的铁路路基爆破效益分析[J]. 爆破, 2019, 36(1): 147-154. doi: 10.3963/j.issn.1001-487X.2019.01.022ZHENG Yuxi, BAO Xueying. Blasting benefits analysis of railway subgrade under green construction[J]. Blasting, 2019, 36(1): 147-154. doi: 10.3963/j.issn.1001-487X.2019.01.022 [5] 李雨浓, 鲍学英. 川藏铁路绿色施工节材措施综合效果评价研究[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报, 2021, 18(6): 1613-1621.LI Yunong, BAO Xueying. Study on comprehensive effect evaluation of material-saving measures for green construction of Sichuan-Tibet railway[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2021, 18(6): 1613-1621. [6] 鲍学英, 李亚娟, 胡所亭, 等. 铁路桥隧工程技术接口的关键要素均衡优化[J]. 浙江大学学报(工学版), 2022, 56(3): 558-568.BAO Xueying, LI Yajuan, HU Suoting, et al. Tradeoff optimization of key elements of technical interface of railway bridge-tunnel engineering[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science), 2022, 56(3): 558-568. [7] 李伟, 蒲浩, 赵海峰, 等. 基于分步编码改进遗传算法的铁路智能选线[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2013, 48(5): 831-838. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2013.05.008LI Wei, PU Hao, ZHAO Haifeng, et al. Intelligent railway aignment optimization based on stepwise encoding genetic algorithm[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2013, 48(5): 831-838. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2013.05.008 [8] 段晓晨, 喇海霞, 胡天明, 等. 桥梁工程运维成本三维非线性智能控制研究[J]. 铁道工程学报, 2020, 37(9): 102-107. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2020.09.018DUAN Xiaochen, LA Haixia, HU Tianming, et al. Research on the 3D nonlinear intelligent control for bridge engineering operation and maintenance cost[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society, 2020, 37(9): 102-107. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2020.09.018 [9] 薛新功, 李伟, 蒲浩. 铁路线路智能优化方法研究综述[J]. 铁道学报, 2018, 40(3): 6-15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2018.03.002XUE Xingong, LI Wei, PU Hao. Review on intelligent optimization methods for railway alignment[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2018, 40(3): 6-15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2018.03.002 [10] 肖建庄, 夏冰, 肖绪文. 工程结构可持续性设计理论架构[J]. 土木工程学报, 2020, 53(6): 1-12.XIAO Jianzhuang, XIA Bing, XIAO Xuwen. Theoretical framework for sustainability design of engineering structures[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2020, 53(6): 1-12. [11] 王思源, 赵敏敏, 闫晶, 等. 川藏铁路西藏昌都段生态保护重要性评价[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(1): 234-243.WANG Siyuan, ZHAO Minmin, YAN Jing, et al. Evaluation on the importance of ecological protection in Changdu section of the Sichuan-Tibet railway[J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(1): 234-243. [12] 彭建兵, 崔鹏, 庄建琦. 川藏铁路对工程地质提出的挑战[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2020, 39(12): 2377-2389.PENG Jianbing, CUI Peng, ZHUANG Jianqi. Challenges to engineering geology of Sichuan: Tibet railway[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2020, 39(12): 2377-2389. [13] 蔡迪文, 张克存, 安志山, 等. 青藏铁路格拉段风动力环境及其对铁路沙害的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2017, 37(1): 40-47. doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2015.00272CAI Diwen, ZHANG Kecun, AN Zhishan, et al. Wind energy environments and its impacts on railway sand hazards along gerlha section of the Qinghai–Tibet railway[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2017, 37(1): 40-47. doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2015.00272 [14] 国家铁路局. 铁路路基设计规范: TB 10001—2016[S]. 北京: 中国铁道出版社, 2017. [15] 国家铁路局. 铁路工程环境保护设计规范: TB 10501—2016[S]. 北京: 中国铁道出版社, 2016. [16] 刘海猛, 方创琳, 李咏红. 城镇化与生态环境“耦合魔方” 的基本概念及框架[J]. 地理学报, 2019, 74(8): 1489-1507. doi: 10.11821/dlxb201908001LIU Haimeng, FANG Chuanglin, LI Yonghong. The coupled human and natural cube: a conceptual framework for analyzing urbanization and eco-environment interactions[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2019, 74(8): 1489-1507. doi: 10.11821/dlxb201908001 [17] 鲍学英, 沈杜华, 郭海东, 等. 山区铁路工程 “路基-环境” 绿色关键要素识别研究[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2024, 24(2): 787-795.BAO Xueying, SHEN Duhua, GUO Haidong, et al. Study on the identification of “subgrade-environment” green key elements in mountain railway engineering[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2024, 24(2): 787-795. [18] 莫俊文, 滕仓国, 李甲, 等. 基于熵权—二维云模型的高铁建设工程系统韧性评价[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报, 2022, 19(1): 26-33.MO Junwen, TENG Cangguo, LI Jia, et al. Resilience evaluation of high-speed railway construction engineering system based on entropy weight-two dimensional cloud model[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2022, 19(1): 26-33. [19] 鲍学英, 肖岚月, 万炳彤, 等. 节材视角下山区铁路与材料资源协调发展研究[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报, 2023, 20(11): 4367-4376.BAO Xueying, XIAO Lanyue, WAN Bingtong, et al. Coordinated development of mountain railways and material resources from perspective of material saving[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2023, 20(11): 4367-4376. [20] 任慧君. 黄河流域9省区能源产业链与资源环境耦合关系研究[D]. 北京: 中国矿业大学(北京), 2020. [21] 王恒, 方兰. 中国水-能源-粮食纽带系统安全水平与全要素生产率时空耦合协调关系分析[J]. 水资源保护, 2023, 39(1): 150-157.WANG Heng, FANG Lan. Spatial-temporal coupling coordination relationship between the security level of water-energy-food nexus system and total factor productivity in China[J]. Water Resources Protection, 2023, 39(1): 150-157. [22] 贺振霞, 鲍学英, 胡所亭, 等. 铁路工程多系统技术接口复合网络信息质量耦合协调分析[J]. 土木工程学报, 2022, 55(11): 118-130.HE Zhenxia, BAO Xueying, HU Suoting, et al. Coupling and coordination analysis of information quality of railway engineering multi-system technical interface composite network[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2022, 55(11): 118-130. [23] 国家铁路局. 铁路声屏障工程设计规范: TB 10505—2019[S]. 北京: 中国铁道出版社, 2019. [24] 中华人民共和国水利部. 土壤侵蚀分类分级标准: SL 190—2007[S]. 北京: 中国水利水电出版社, 2008. [25] 国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 环境空气质量标准: GB 3095—2012[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2016. [26] 环境保护部. 声环境质量标准: GB 3096—2008[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2008. [27] 国家环境保护总局, 国家质量监督检验检疫总局. 地表水环境质量标准: GB 3838—2002[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2002. [28] 国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 爆破安全规程: GB 6722—2014[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2015. [29] 刘坚, 李泽华, 白和强, 等. 露天矿爆破粉尘排放量影响因素分析及试验研究[J]. 爆破, 2017, 34(4): 169-174. doi: 10.3963/j.issn.1001-487X.2017.04.030LIU Jian, LI Zehua, BAI Heqiang, et al. Research on influence factors of blasting dust emission of open-pit mine[J]. Blasting, 2017, 34(4): 169-174. doi: 10.3963/j.issn.1001-487X.2017.04.030 [30] 鲍学英, 郑雨茜, 王起才. 绿色施工下的深路堑施工群综合承载度分析[J]. 浙江大学学报(工学版), 2019, 53(3): 482-491.BAO Xueying, ZHENG Yuxi, WANG Qicai. Construction group comprehensive bearing capacity analysis of deep cutting under green construction[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science), 2019, 53(3): 482-491. [31] BRAIK M S. Chameleon Swarm Algorithm: a bio-inspired optimizer for solving engineering design problems[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2021, 174: 114685.1-114685.25. [32] KARYPIS G, HAN E H, KUMAR V. Chameleon: hierarchical clustering using dynamic modeling[J]. Computer, 1999, 32(8): 68-75. doi: 10.1109/2.781637 -




 下载:
下载: