Optimization Method for Train Formation Plan with Fuzzy Chance-Constrained Programming
-
摘要:
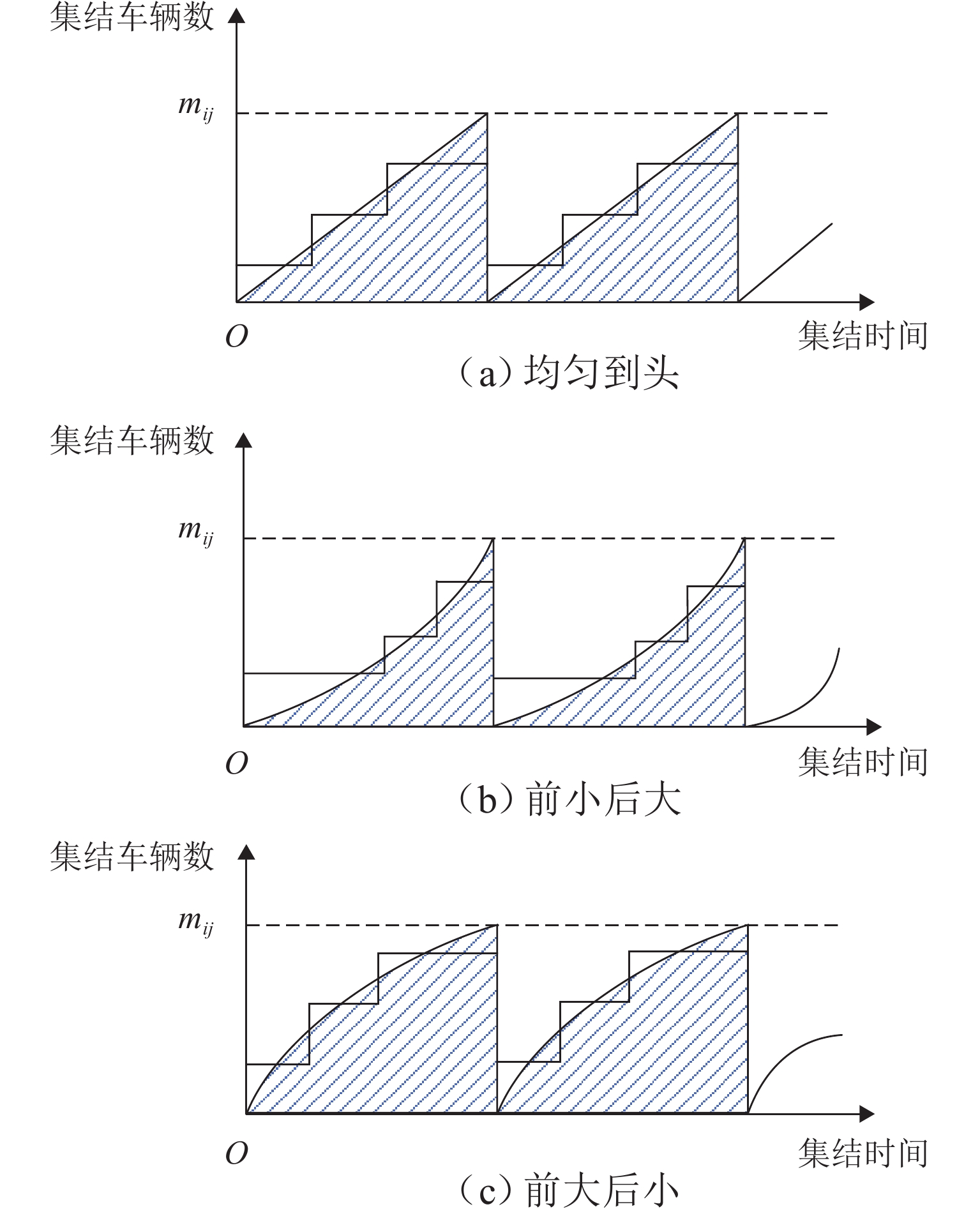
为提高铁路网的利用能力和运输效率,提出一种高适用性的列车编组计划优化方法. 首先,在车流径路未知的情况下综合考虑车辆集结与改编时间的随机性,采用模糊机会约束规划方法,将集结时间成本与改编时间成本限制在一定的波动区间,构建不确定性的0-1整数规划模型;以货车集结时间成本、货车改编时间成本和货车运输成本最小为目标函数,通过三角模糊数处理时间不确定性,引入车辆集结与改编时间的波动性约束,并采用粒子群算法进行寻优,获取列车编组计划,构造算例以验证所提方法的有效性. 研究结果表明:列车编组计划经优化后,货车在车站总停留时间为
3914 车·h,占货物运输总成本的54%,相较于铁路网实际货车在站平均停留时间降低13%左右,列车编组计划得到了较好的优化.Abstract:To improve the utilization capacity and transportation efficiency of the railway network, a highly applicable method for optimizing freight train formation plans was proposed. First, under the condition of unknown car flow routing, the stochastic nature of both accumulation time and shunting time was considered. A fuzzy chance-constrained programming method was adopted to limit the cost of accumulation time and shunting time within a certain fluctuation range, leading to the construction of a 0-1 integer programming model under uncertainty. By taking the minimum freight car accumulation time cost, shunting time cost, and transportation cost as the objective function, time uncertainty was addressed using triangular fuzzy numbers. The volatility constraints for accumulation time and shunting time were introduced. The particle swarm optimization algorithm was adopted to obtain the train formation plan. A numerical example was then constructed to validate the effectiveness of the proposed method. The results show that the optimized train formation plan reduces the total detention time of freight cars at stations to 3 914 car-hours, accounting for 54% of the total freight transportation cost. This represents a reduction of about 13% compared to the actual average station detention time of freight cars in the railway network, indicating a significant improvement in the freight train formation plan.
-
表 1 货流输送方案表
Table 1. Freight transportation schemes
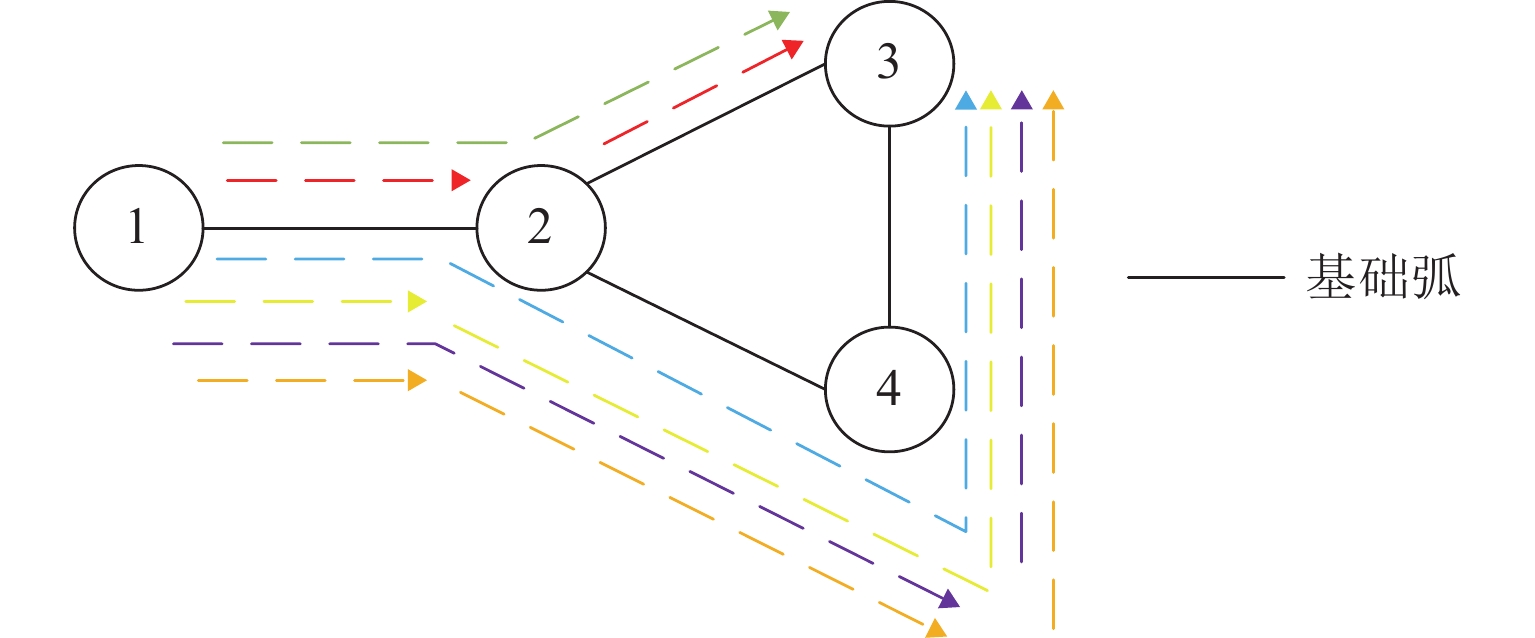
方案 路径 方案弧 改编节点 1 1→2→3 $ \left\{ {{l_{12}},{l_{23}}} \right\} $ 不改编 2 1→2→3 $ \left\{ {{l_{12}}} \right\} $,$ \left\{ {{l_{23}}} \right\} $ 2 3 1→2→4→3 $ \left\{ {{l_{12}},{l_{24}},{l_{43}}} \right\} $ 不改编 4 1→2→4→3 $ \left\{ {{l_{12}}} \right\} $,$ \left\{ {{l_{24}},{l_{43}}} \right\} $ 2 5 1→2→4→3 $ \left\{ {{l_{12}},{l_{24}}} \right\} $,$ \left\{ {{l_{43}}} \right\} $ 4 6 1→2→4→3 $ \left\{ {{l_{12}}} \right\} $,$ \left\{ {{l_{24}}} \right\} $,$ \left\{ {{l_{43}}} \right\} $ 2,4 表 2 参数说明
Table 2. Parameter description
符号 含义 $ P $ 运输需求 $ p $ 的集合,$ {p_{ij}} $ 为节点 $ i $ 去向节点 $ j $ 的运输需求 $ L_r $ 路径 $ r $ 的基础弧集合 $ R_p $ 运输需求$ p $的可选径路集合;$ R_{pl} = \left\{{r \in R_p \left| {l \in L_r } \right.} \right\} $,为需求 p 的基础弧集合 $ {w}_i^+ $ 以节点 $ i $ 为起点的方案弧集合 $ {w}_i^{-} $ 以节点 $ i $ 为终点的方案弧集合 $ {c_{pr}} $ 运输需求 $ p $通过路径 $ r $ 运输时在始发站的集结参数,为随机变量 $ {m_r} $ 路径 $ r $ 的列车平均编成辆数 $ {m_p} $ 运输需求 $ p $ 内的车辆数 $ {t_r} $ 货车在路径 $ r $ 上的走行时间 $ {t_{{\mathrm{run}}i}} $ 货车无改编通过节点 $ i $ 的车小时节省,为随机变量 $ {c_1} $ 货车单位时间集结成本 $ {c_2} $ 货车单位时间改编成本 $ {c_3} $ 货车单位时间运输成本 $ V_i$ 节点 $ i $ 的改编能力 $ U_l$ 区间 $ l $ 的通过能力 $ w_{l^*l} $ 0-1 变量,当 $ l^* $包含 $ l $时,其值为 1;否则,为 0 $ o_p $ 运输需求 $ p $ 的起点 $ d_p $ 运输需求 $ p $ 的终点 表 3 成都局各技术站相关参数
Table 3. Parameters related to technical stations of Chengdu Railway Bureau
车站 无改编通过节省小时/h 改编能力/列 1 (2.8,3.0,3.2) 149 2 (2.4,2.6,2.8) 55 3 (2.5,2.7,2.9) 44 4 (3.3,3.5,3.7) 39 5 (2.0,2.2,2.4) 50 6 (1.6,1.8,2.0) 68 7 (2.7,2.9,3.1) 53 8 (2.9,3.1,3.3) 168 9 (1.8,2.0,2.2) 109 表 4 部分集结参数
Table 4. Accumulation parameters
方向 集结参数 方向 集结参数 1—2 (7.2,7.8,8.2) 4—7 (7.9,8.3,8.7) 1—4 (7.4,7.8,8.2) 5—6 (8.1,8.5,8.9) 1—5 (7.7,8.1,8.5) 5—7 (9.7,10.1,10.5) 1—6 (7.5,7.9,8.3) 5—8 (9.0,9.4,9.8) 2—3 (8.7,9.1,9.5) 5—9 (8.1,8.5,8.9) 2—6 (8.9,9.3,9.7) 6—8 (7.5,7.9,8.3) 3—6 (10.1,10.5,10.9) 7—9 (7.6,8.0,8.4) 4—5 (9.3,9.7,10.1) 8—9 (9.2,9.6,10.0) 表 5 粒子群算法参数取值
Table 5. Parameter values for particle swarm optimization algorithm
符号 数值 $ N_{\mathrm{in}} $/次 $ \left| L \right| $ $ N_{\mathrm{out}} $/次 $ \left|N\right|^2 $ $ {N_{{\mathrm{in,stop}}}} $/次 $ N_{\mathrm{in}}/3 $ $ {N_{{\mathrm{out,stop}}}} $/次 $ N_{\mathrm{out}}/3 $ $ n $ $ 3\left|N\right| $ $ v_{\max} $ 6 $ {w_{\max }} $ 0.9 $ {w_{\min }} $ 0.1 $ {\alpha _1} $、$ {\alpha _2} $ 2 $ f_{\mathrm{best}} $ 10000000 $ k $ 0.4 $ \alpha_{\mathrm{con}} $ 1 $ s $ 0.5 $ A $ 10000 $ B $ 5000 $ \varOmega $ 2 表 6 部分求解结果
Table 6. Solution results
发站 途径站 到站 编组内容 车数/辆 1 2 1—2,4—2,5—2,7—2,9—2 146 1 2 3 1—3,4—3 78 1 4 1—4,2—4,3—4 49 1 5 1—5,2—5 74 1 6 1—6 57 1 4 7 1—7,2—7,4—7 103 1 5 8 1—8,5—8,7—8 54 1 5 9 1—9,2—9,5—9 89 2 1 2—1,3—1 146 表 7 运输成本
Table 7. Transport costs
运输成本 费用值/(车·h) 运输总成本 7165.8 列车集结时间成本 2035.0 货车改编时间成本 1879.0 货物途中运输时间成本 3251.8 表 8 各技术站的负荷情况
Table 8. Load conditions of technical stations
车站 改编车数/辆 改编能力/辆 改编能力利用率/% 1 67 149 44.90 2 5 55 9.09 3 0 44 0 4 9 39 23.07 5 4 50 8.00 6 7 68 10.20 7 0 53 0 8 41 168 24.40 9 16 109 14.60 表 9 部分线路区间的负荷情况
Table 9. Load conditions of railway line sections
区间 区间通过
能力/列列车平均编成
辆数/辆通过车
数/辆区间占
用率/%1—2 30 65 1569 80.46 1—4 34 65 1530 69.23 1—5 26 60 1435 91.99 1—6 23 65 1381 92.37 2—3 25 55 1042 75.78 2—6 21 60 641 50.87 3—6 33 55 589 32.45 4—5 28 60 483 28.75 4—7 30 65 754 38.67 5—6 24 65 681 43.65 5—7 24 60 948 65.83 5—8 22 60 354 26.82 5—9 26 65 1280 75.74 6—8 24 50 681 56.75 7—9 33 55 1637 90.19 -
[1] 马佳骥. 摘挂列车编组计划优化研究[J]. 物流技术与应用, 2022, 27(9): 162-165. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1059.2022.09.022MA Jiaji. Study on optimization of train formation plan for pick-up and drop-off train[J]. Logistics & Material Handling, 2022, 27(9): 162-165. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1059.2022.09.022 [2] 马博文, 魏玉光, 于宗泽, 等. 铁路装车地直达列车组织研究[J]. 铁道运输与经济, 2020, 42(1): 19-23.MA Bowen, WEI Yuguang, YU Zongze, et al. A study on the organization of direct train from loading station[J]. Railway Transport and Economy, 2020, 42(1): 19-23. [3] 陈崇双, 赵军, 薛锋, 等. 基于点-弧结构的路网单组列车编组计划优化线性0-1规划模型[J]. 铁道学报, 2021, 43(2): 9-20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2021.02.002CHEN Chongshuang, ZHAO Jun, XUE Feng, et al. A node-arc structure based linear 0-1 programming model for optimization of one block train formation plan in railway networks[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2021, 43(2): 9-20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2021.02.002 [4] 严余松, 户佐安, 李宵寅. 基于车流量波动的列车编组计划与车流径路综合优化[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2017, 17(4): 24-131.YAN Yusong, HU Zuoan, LI Xiaoyin. Comprehensive optimization of train formation plan and wagon-flow path based on fluctuating wagon-flow[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2017, 17(4): 24-131. [5] 林柏梁. 机车长交路条件下的技术站列车编组计划无调作业参数模型[J]. 铁道学报, 1999(6): 6-9. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8360.1999.06.002LIN Boliang. Non resort operating parameter model for technical station’s train formation plan with locomotive extended routing[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 1999(6): 6-9. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8360.1999.06.002 [6] BADETSKII A, MEDVED O. Improving the stability of the train formation plan to uneven operational work[J]. Transportation Research Procedia, 2021, 54: 559-567. doi: 10.1016/j.trpro.2021.02.108 [7] AHUJA R K, JHA K C, LIU J. Solving real-life railroad blocking problems[J]. Interfaces, 2007, 37(5): 404-419. doi: 10.1287/inte.1070.0295 [8] ZHAO Y Q, LI D W, YIN Y H, et al. Integrated optimization of demand-driven timetable, train formation plan and rolling stock circulation with variable running times and dwell times[J]. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review, 2023, 171: 103035. doi: 10.1016/j.tre.2023.103035 [9] ZHAO Y N, LIN B L. The multi-shipment train formation optimization problem along the ordered rail stations based on collection delay[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 75935-75948. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2921619 [10] XIAO J, LIN B L. Comprehensive optimization of the one-block and two-block train formation plan[J]. Journal of Rail Transport Planning & Management, 2016, 6(3): 218-236. [11] LIN B L, ZHAO Y N, LIN R X, et al. Integrating traffic routing optimization and train formation plan using simulated annealing algorithm[J]. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 2021, 93: 811-830. doi: 10.1016/j.apm.2020.12.031 [12] WEI X Q, LIANG D Y, YANG W H. Research on optimization method of multi-block train formation plan on railway corridor[J]. Advances in Applied Mathematics, 2020, 9(12): 2188-2198. doi: 10.12677/AAM.2020.912255 [13] 申永生, 何世伟, 黎浩东, 等. 自适应粒子群算法求解编组站车流推算问题的研究[J]. 铁道货运, 2010, 28(12): 5-10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2024.2010.12.002SHEN Yongshen, HE Shiwei, LI Haodong, et al. Study on solution of train flow calculation of marshalling station by using ADPSO[J]. Railway Freight Transport, 2010, 28(12): 5-10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2024.2010.12.002 [14] YAGHINI M, MOMENI M, SARMADI M. Solving train formation problem using simulated annealing algorithm in a simplex framework[J]. Journal of Advanced Transportation, 2014, 48(5): 402-416. doi: 10.1002/atr.1183 [15] 李宵寅. 基于不确定参数的列车编组计划与车流径路综合优化研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2011. [16] 李静. 市场竞争条件下铁路货物列车编成辆数优化问题研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2020. [17] 黎浩东. 铁路编组站鲁棒性阶段计划编制研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2008. [18] 景云. 不确定条件下编组站调度系统配流模型及算法研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2010. [19] 马亮, 胡宸瀚, 金福才, 等. 铁水运输调度双层多目标约束优化模型[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2023, 58(2): 357-366, 397.MA Liang, HU Chenhan, JIN Fucai, et al. Double-layer and multi-objective constraint optimization model for transportation scheduling of molten iron[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2023, 58(2): 357-366, 397. [20] 杜牧青, 鞠姿彦, 李大韦. 一种基于交叉口信号延误的超路径规划方法[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2024, 59(6): 1378-1388. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20220387DU Muqing, JU Ziyan, LI Dawei. Hyperpath searching algorithm method based on signal delay at intersections[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2024, 59(6): 1378-1388. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20220387 [21] 刘霞, 刘金凤, 赵文彬, 等. 抑制局部最优的粒子群算法[J]. 大庆石油学院学报, 2007, 31(6): 101-104.LIU Xia, LIU Jinfeng, ZHAO Wenbin, et al. The particle swarm optimization algorithm restraining local optimum[J]. Journal of Northeast Petroleum University, 2007, 31(6): 101-104. [22] 张学良, 温淑花, 李海楠, 等. 基于Tent映射的混沌粒子群优化算法及其应用[J]. 中国机械工程, 2008, 19(17): 2108-2112. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1004-132X.2008.17.021ZHANG Xueliang, WEN Shuhua, LI Hainan, et al. Chaotic particle swarm optimization algorithm based on tent mapping[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2008, 19(17): 2108-2112. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1004-132X.2008.17.021 -




 下载:
下载: