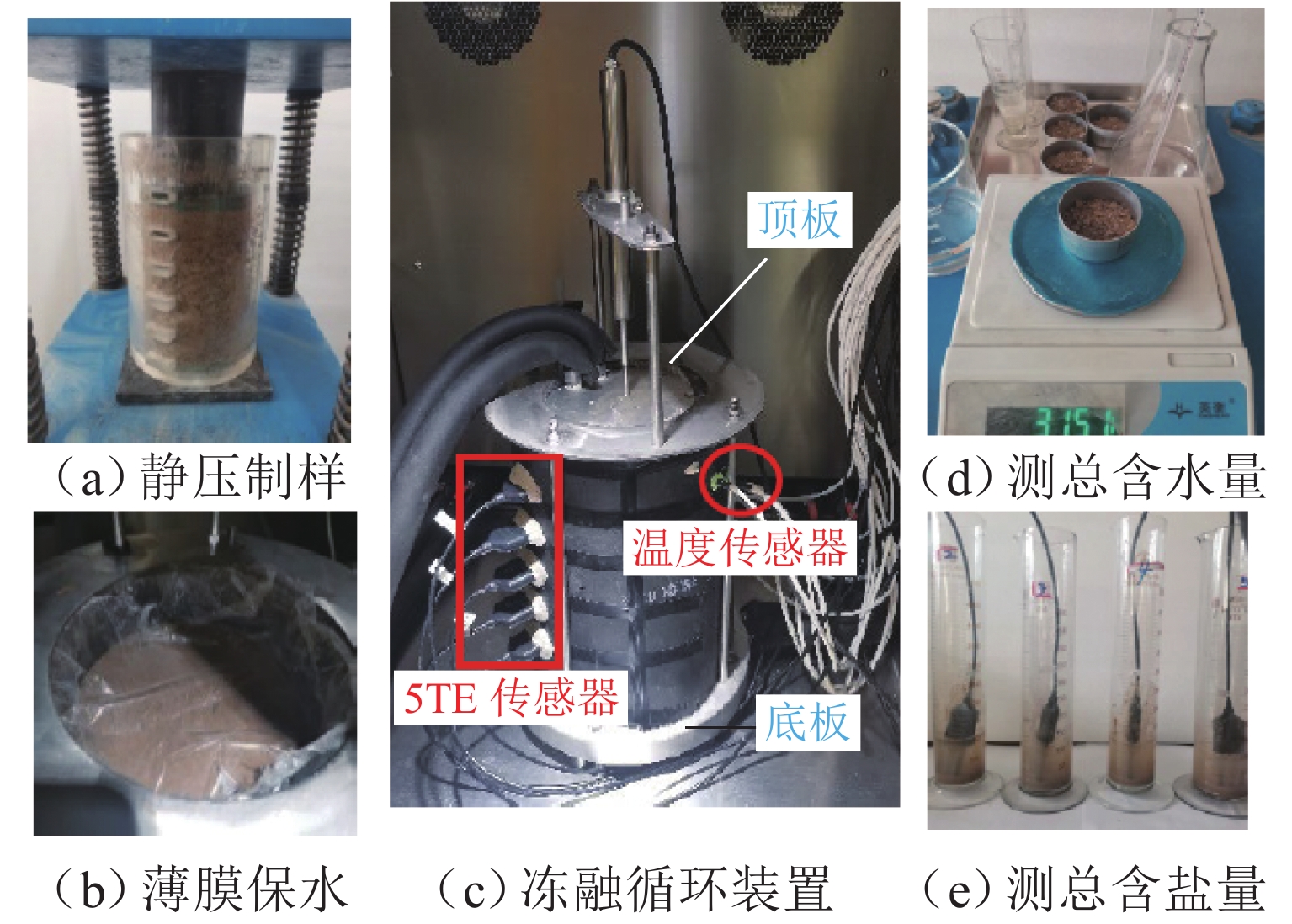
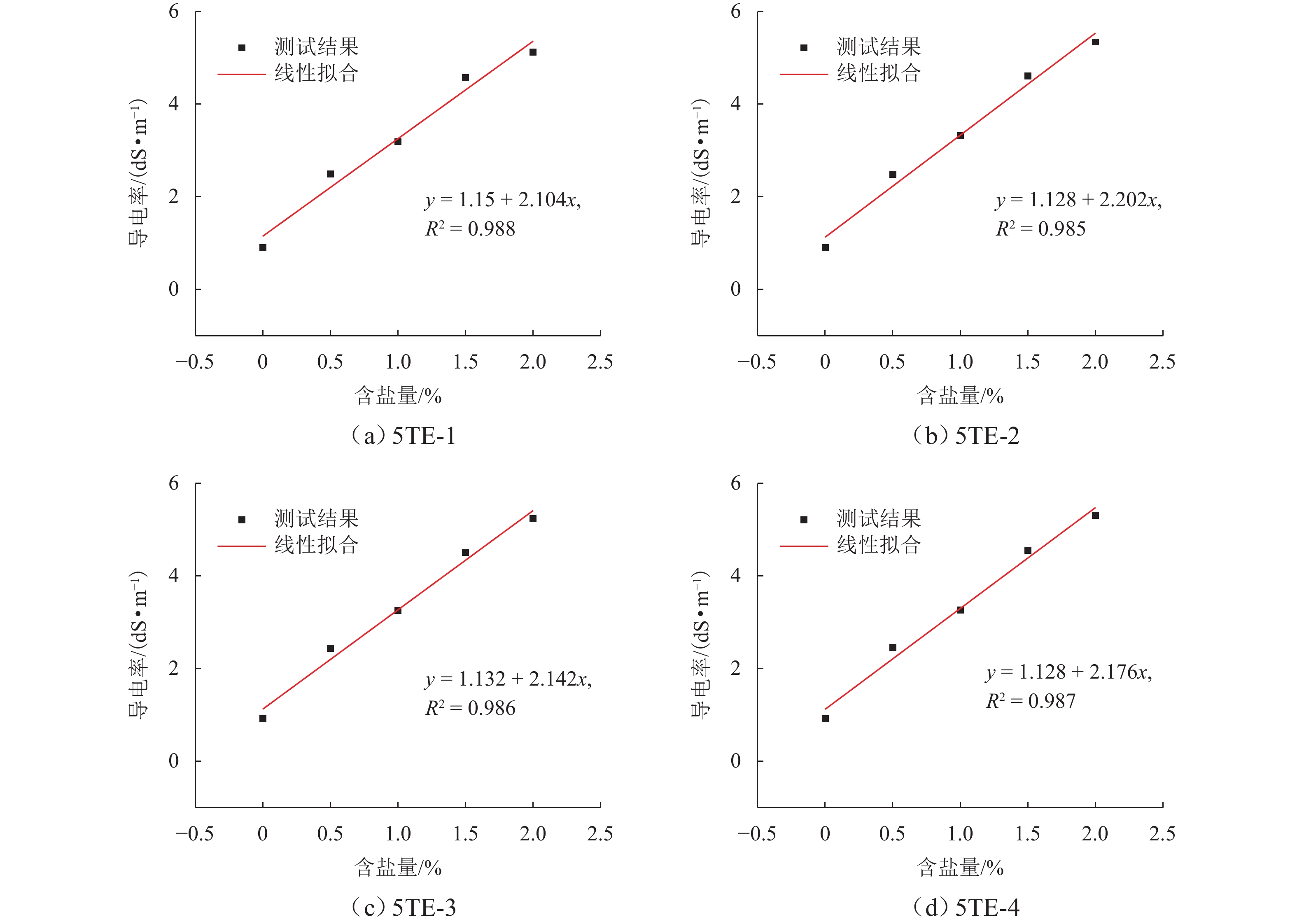
Heat–Mass Transfer and Salt-Frost Heave Mechanism of Saline Soil under Freeze–Thaw Cycle
-
摘要:
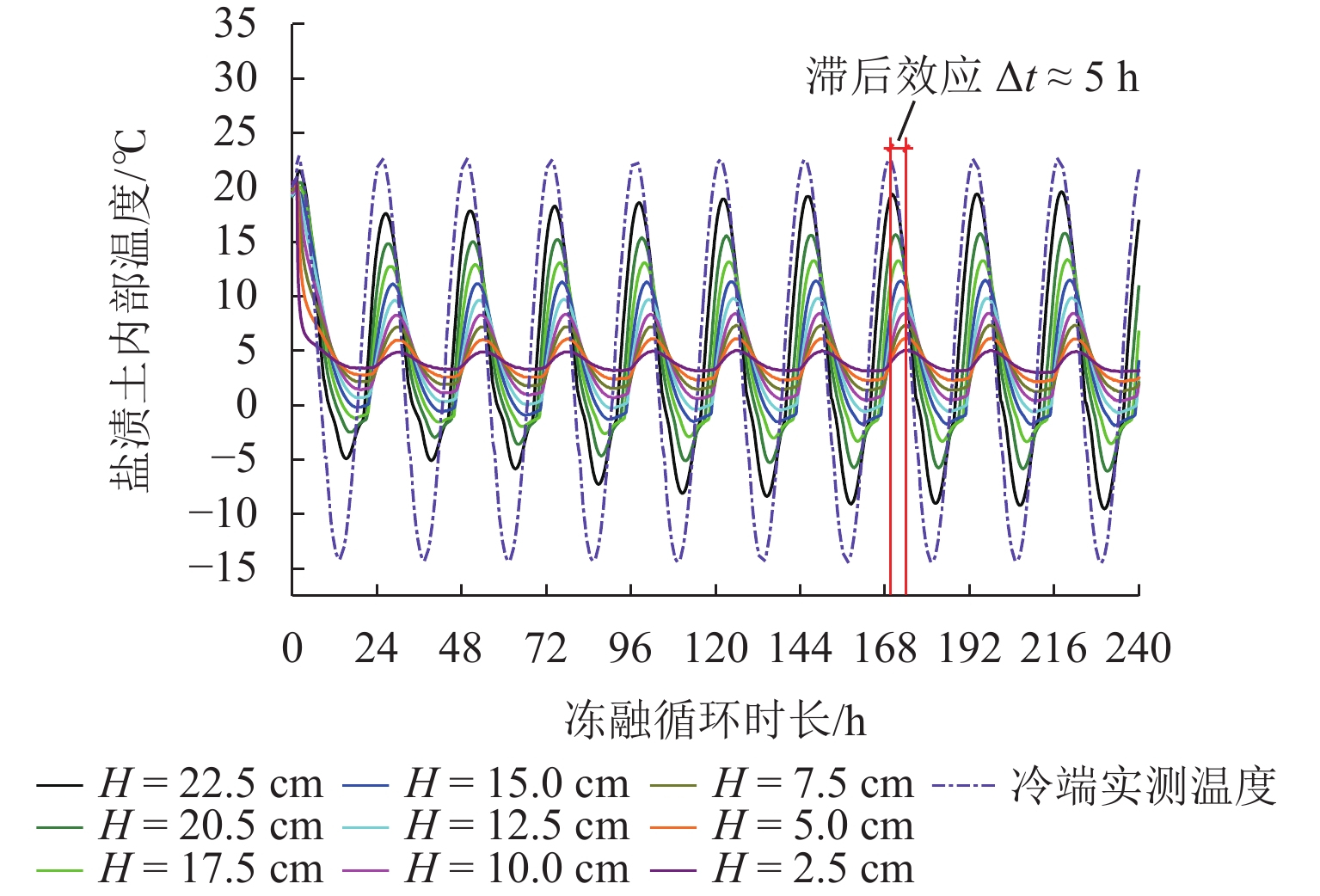
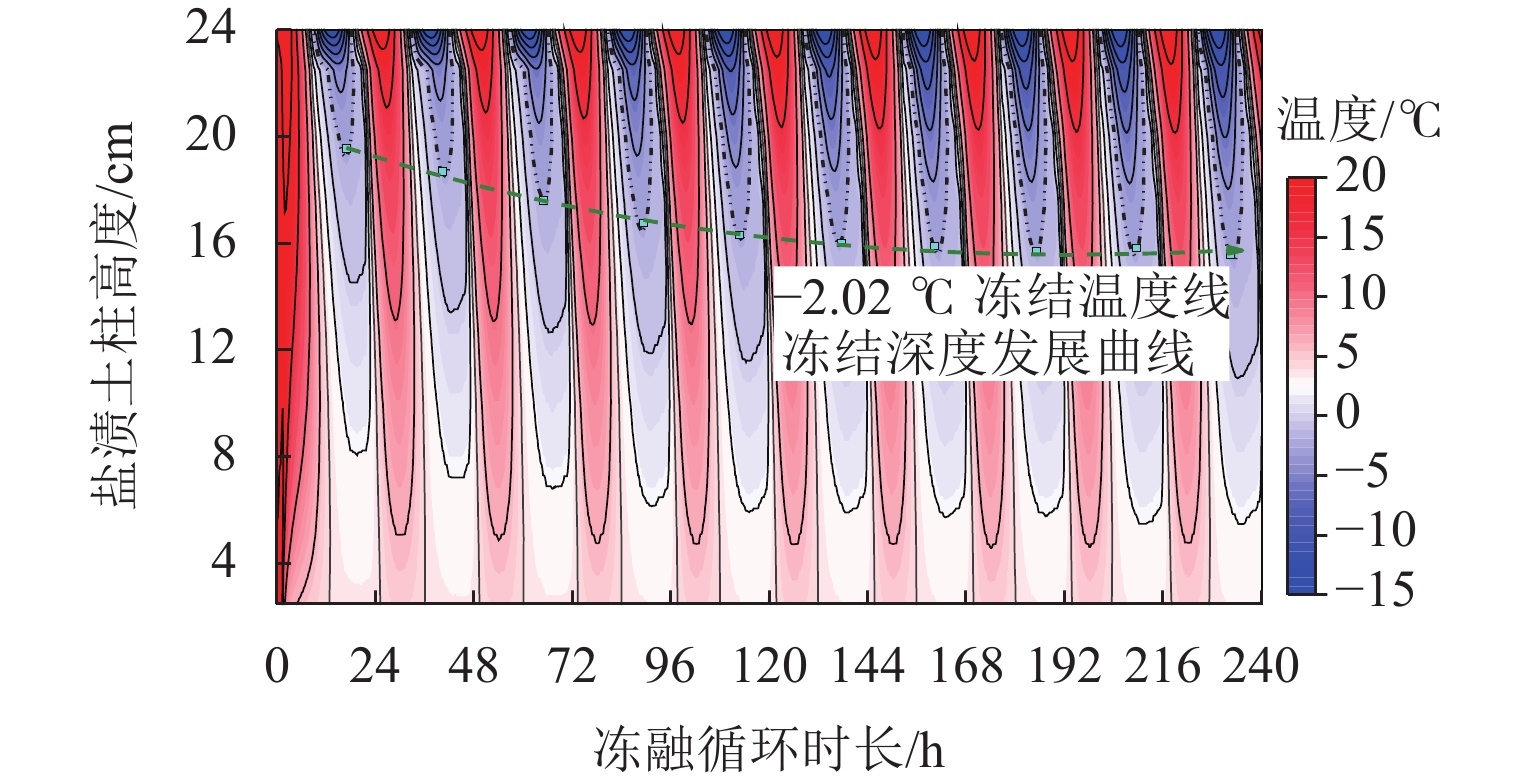
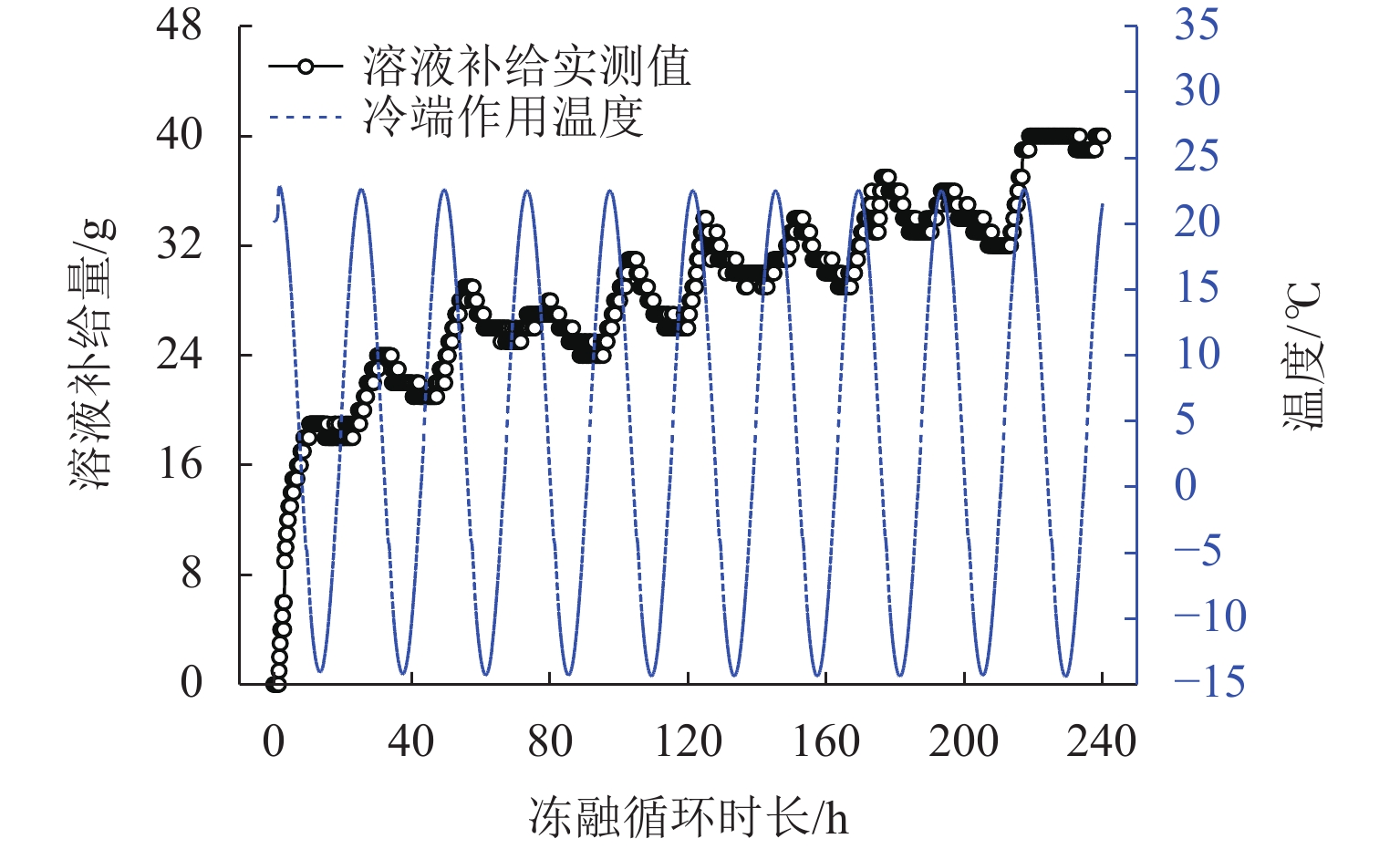
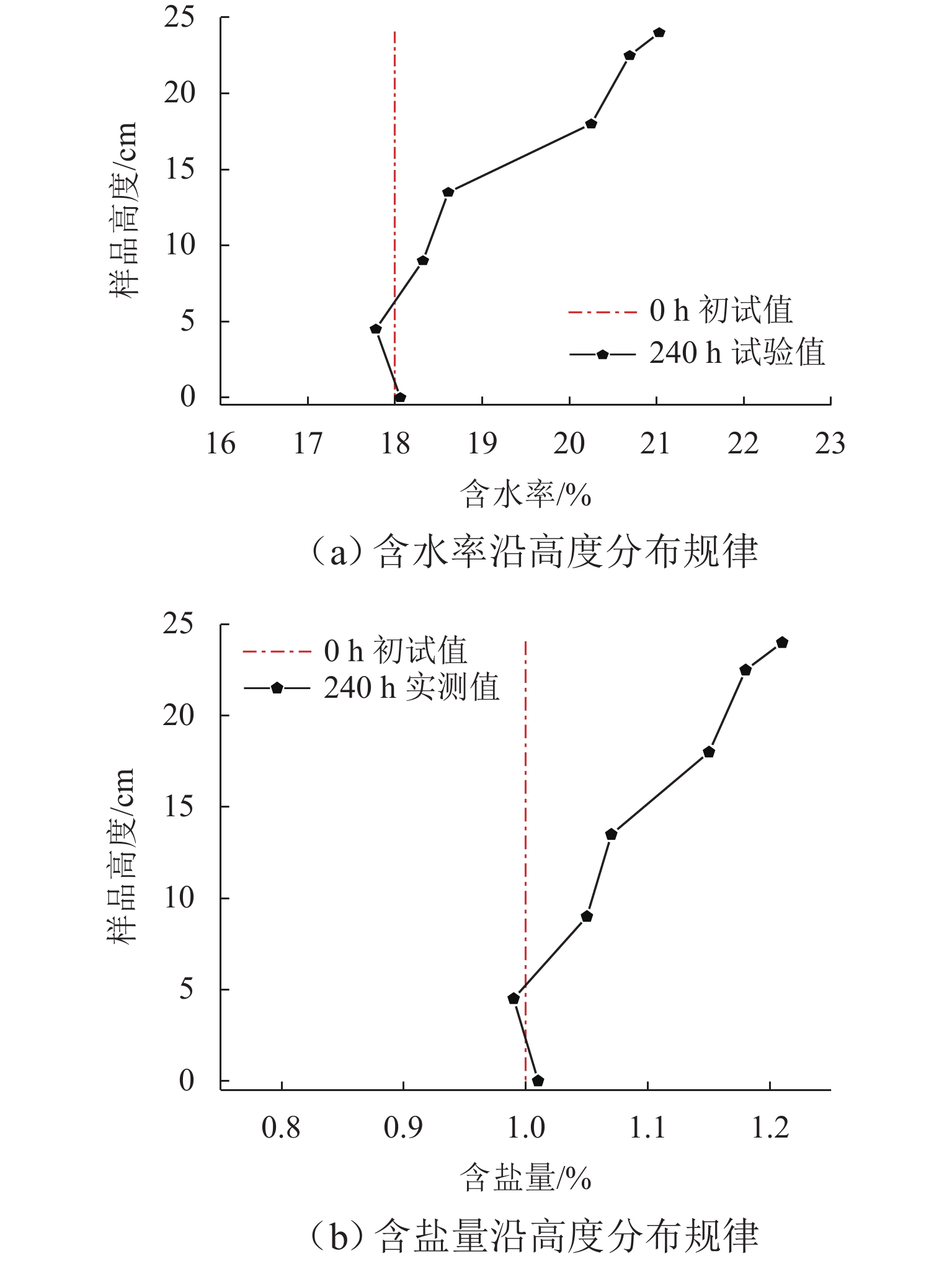
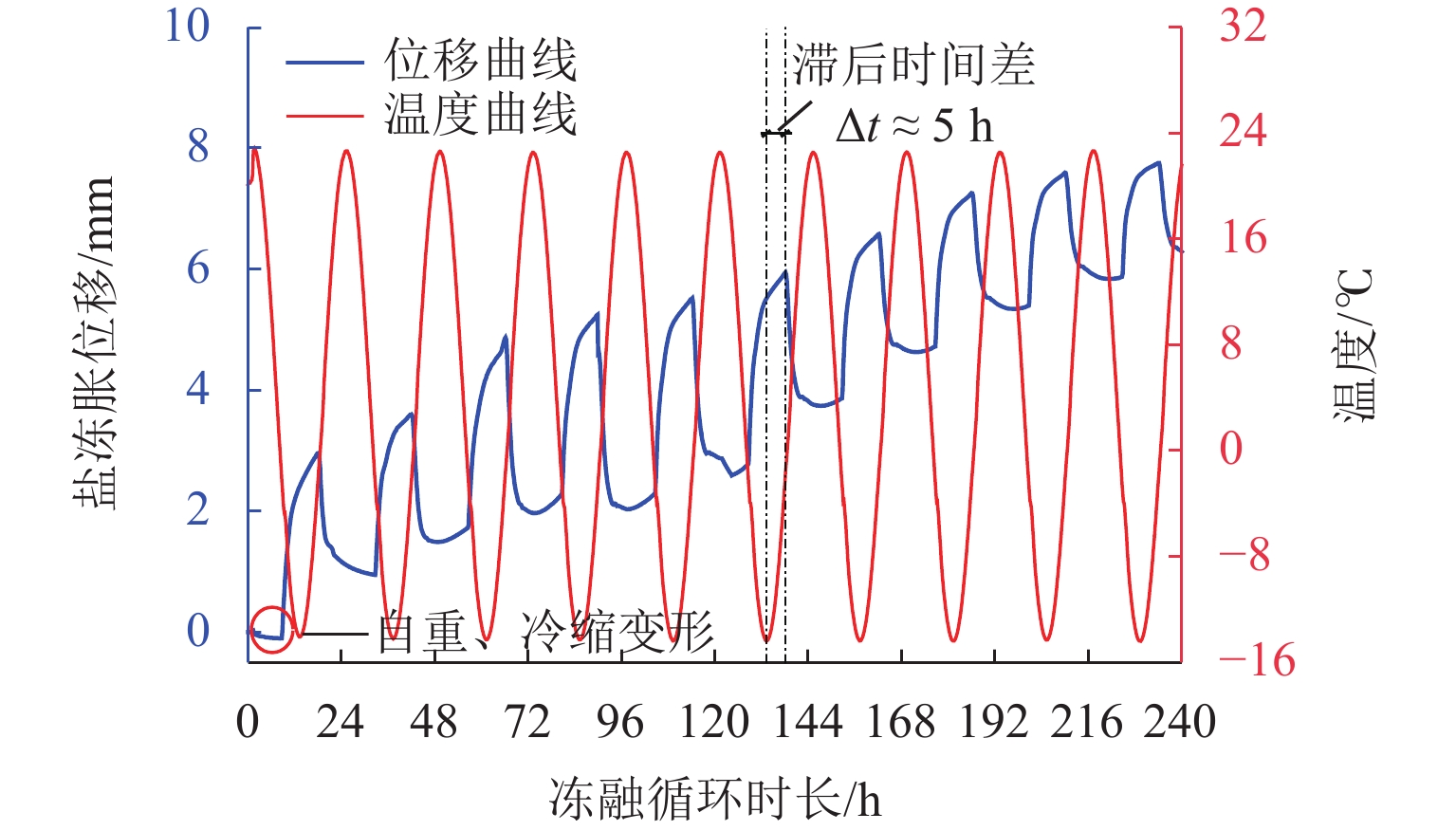
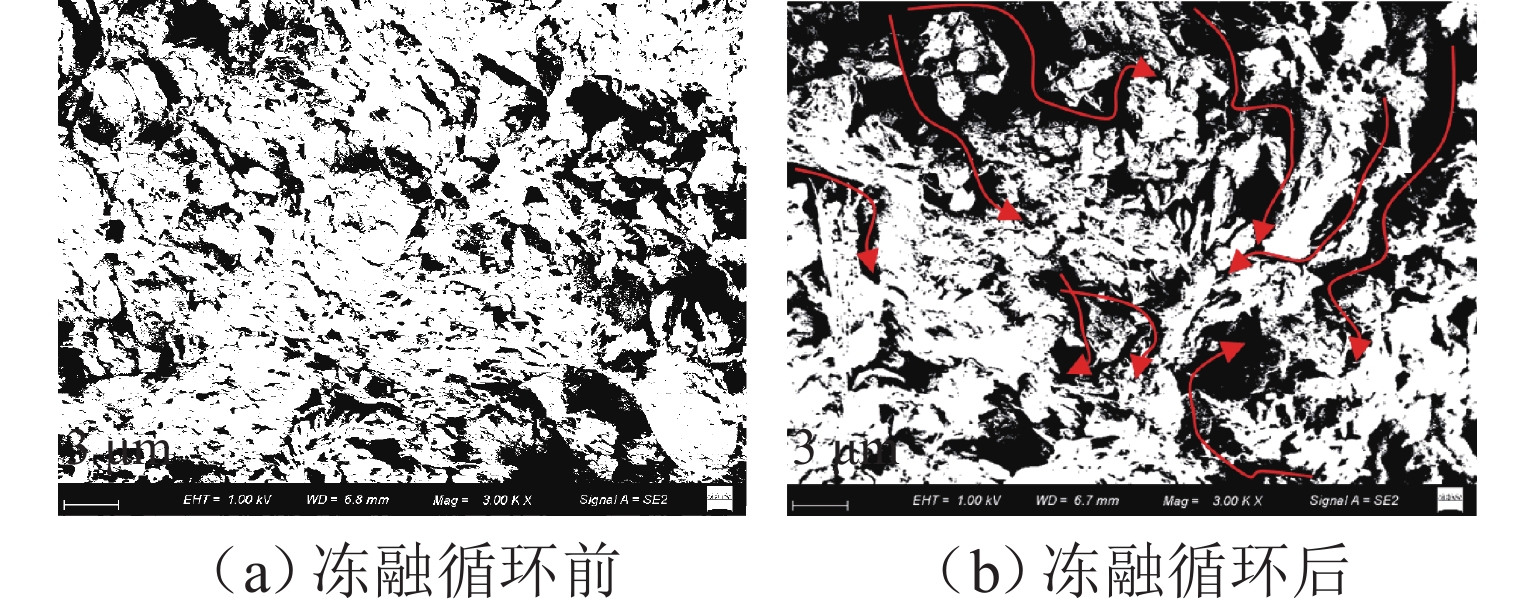
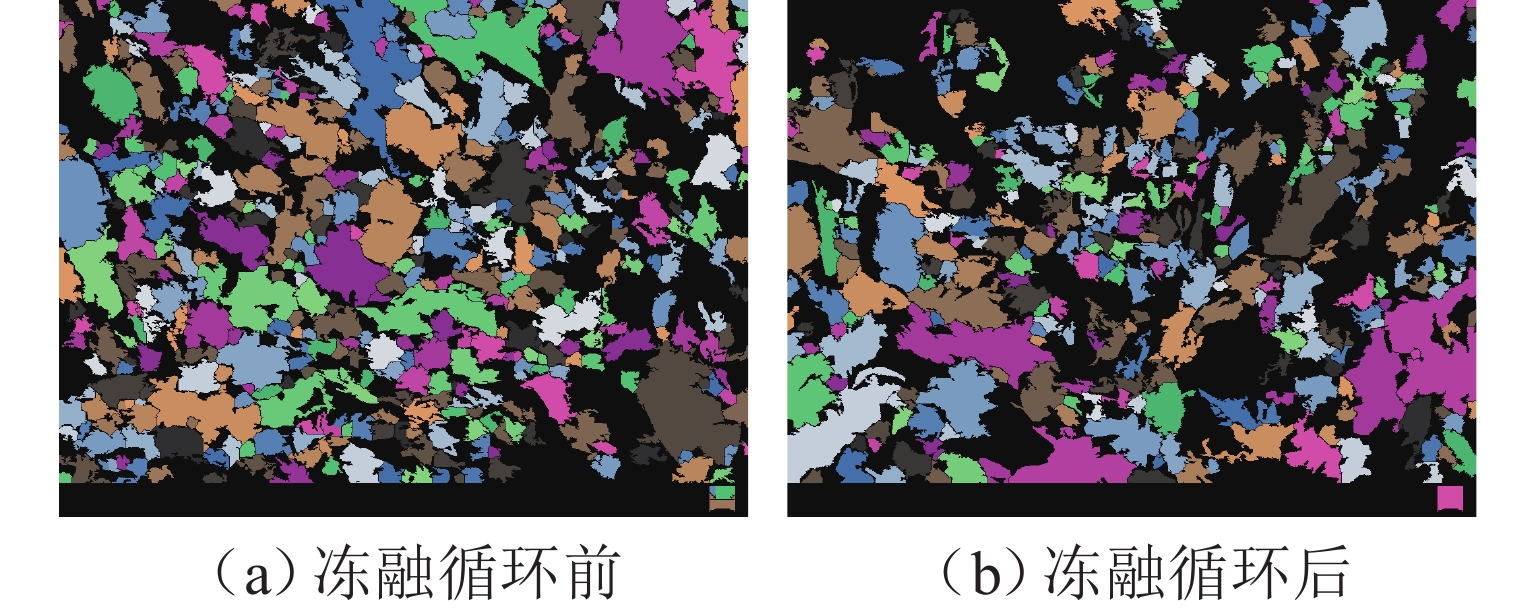
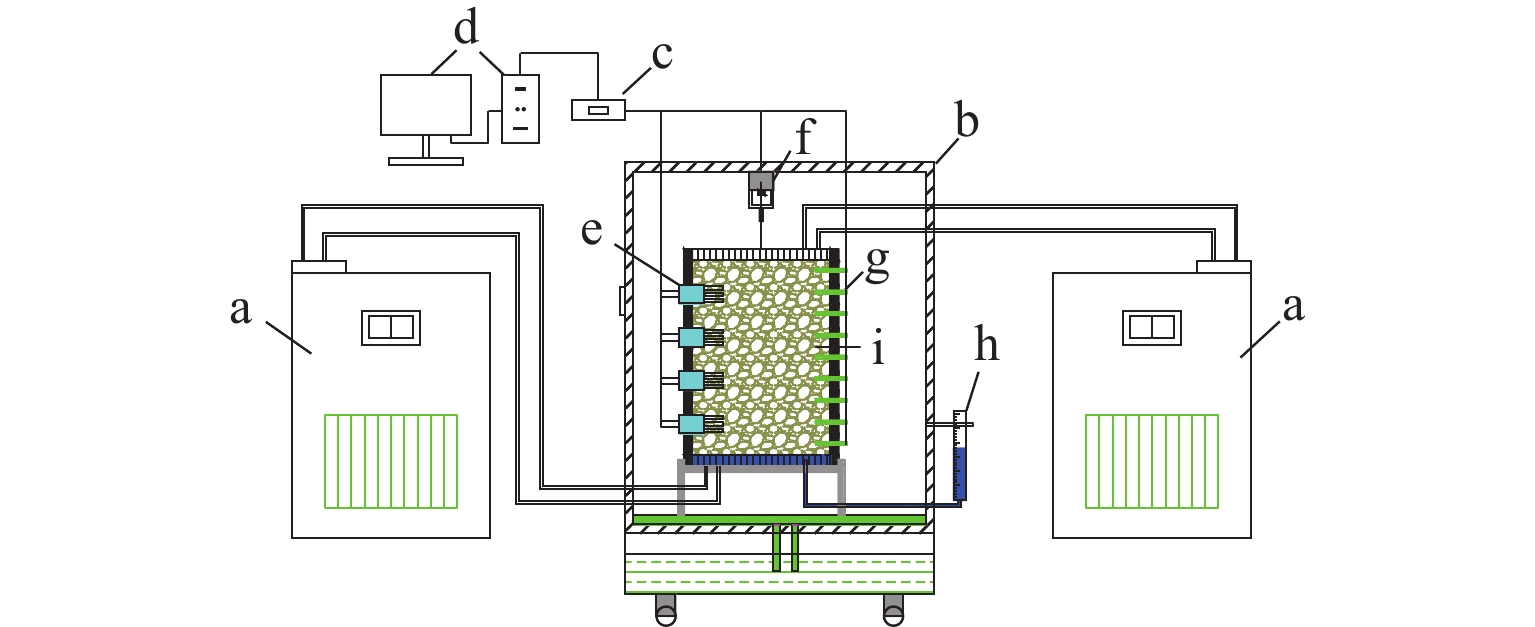
为研究冻融循环作用下硫酸盐渍土热-质迁移规律及结构损伤机理,以河西走廊盐渍土为研究对象,在无压补给条件下进行冻融循环试验,并借助核磁共振和SEM (scanning electron microscope)试验分析冻融循环前、后硫酸盐渍土的孔隙结构损伤机理. 研究表明:冻融循环作用下硫酸盐渍土内温度传递存在“深度效应”和“时间滞后效应”,时差约为5 h;冻结深度前期不断向下发展,后期逐渐趋于平稳,最大冻深为8.54 cm;溶液补给量随温度降低而增大,升高而减小;冻融循环240 h后水、盐含量在冻结区增大,非冻结区基本不变;盐渍土盐冻胀变形随温度变化呈周期性盐冻胀-融溶沉规律发展,且存在位移滞后温度效应;盐渍土经历一系列反复“冻结—冷凝—结晶—融化—溶解”过程后,中孔隙和大孔隙明显增多,并形成贯通的裂隙,土体结构由冻融前的片层状结构转变为絮状结构.
Abstract:To study the heat–mass transfer patterns and structural damage mechanisms of sulfate saline soil under freeze–thaw cycles, a freeze–thaw cycle test was carried out under non-pressurized supply condition with saline soil from Hexi Corridor as the research object. The pore structure damage mechanism of sulfate saline soil before and after freeze–thaw cycles was analyzed using nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and scanning electron microscope (SEM). The study shows that temperature transfer in the sulfate saline soil under freeze–thaw cycles exhibits the “depth effect” and “time-lag effect”, with a time lag of about five hours. The freezing depth initially develops downward before stabilizing, reaching a maximum depth of 8.54 cm. The solution supply amount increases as temperature decreases and decreases as temperature rises. Water and salt content increase in the frozen zone after a 240-hour freeze–thaw cycle while remaining basically unchanged in the unfrozen zone. The deformation of saline soil due to salt-frost heave follows a cyclic pattern of “heave and thaw”, with a time lag in response to temperature changes. Repeated cycles of “freezing–condensation–crystallization–thawing–dissolving” cause significant increases in medium and large pores of saline soil, leading to interconnected cracks. The soil structure transitions from a laminar structure before freeze–thaw cycle to a flocculent structure afterwards.
-
表 1 脱盐后土壤物理参数测试结果
Table 1. Test results of physical parameters of soil after desalination
参数 Gs ρmax/
(g•cm−3)ωopt/% wL/% wP/% Cu Cc 取值 2.70 1.78 13.7 25.35 12.62 5.29 0.59 -
[1] 黄佑芬, 吴道勇, 吴诗雨. 冻融循环条件下重塑硫酸盐渍土变形试验研究[J]. 冰川冻土, 2022, 44(2): 602-611.HUANG Youfen, WU Daoyong, WU Shiyu. Experimental study on deformation of remolded sulfate saline soil under freeze-thaw cycles[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 2022, 44(2): 602-611. [2] LUO C L, YU Y Y, ZHANG J, et al. Thermal-water-salt coupling process of unsaturated saline soil under unidirectional freezing[J]. Journal of Mountain Science, 2023, 20(2): 557-569. doi: 10.1007/s11629-022-7652-7 [3] 路建国, 万旭升, 刘力, 等. 降温过程硫酸钠盐渍土水-热-盐相互作用过程[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2022, 54(2): 126-134. doi: 10.11918/202102029LU Jianguo, WAN Xusheng, LIU Li, et al. Water-heat-salt interaction of sodium sulfate saline soil during a cooling process[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2022, 54(2): 126-134. doi: 10.11918/202102029 [4] LUO C L, YU Y Y, ZHANG J, et al. Study of heat–mass transfer and salt–frost expansion mechanism of sulfate saline soil during the unidirectional freezing process[J]. International Journal of Geomechanics, 2024, 24(10): 04024227. 1-04024227.13. [5] WEISBROD N, NIEMET M R, ROCKHOLD M L, et al. Migration of saline solutions in variably saturated porous media[J]. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 2004, 72(1/2/3/4): 109-133. [6] LAI Y M, ZHANG X F, XIAO J Z, et al. Nonlinear analysis for frost-heaving force of land bridges on Qing—Tibet railway in cold regions[J]. Journal of Thermal Stresses, 2005, 28(3): 317-331. [7] 张文, 罗艳珍, 刘昕, 等. 青海盐湖区路基结构层级配及其阻盐效果[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2020, 55(6): 1264-1271, 1296. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20190056ZHANG Wen, LUO Yanzhen, LIU Xin, et al. Gradation of subgrade soil and its salt-resistance effect in salt lake area in Qinghai[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2020, 55(6): 1264-1271, 1296. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20190056 [8] 冯博, 刘青, 钱永久. 高性能混凝土在氯盐侵蚀和冻融循环作用下的耐久性分析[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2023, 58(5): 1083-1089. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20220035FENG Bo, LIU Qing, QIAN Yongjiu. Durability analysis of high-performance concrete under chloride salt erosion and freeze-thaw cycles[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2023, 58(5): 1083-1089. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20220035 [9] 张树明, 蒋关鲁, 杜登峰, 等. 新型桩板结构路基在季节冻土区的适用性[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2021, 56(3): 541-549.ZHANG Shuming, JIANG Guanlu, DU Dengfeng, et al. Applicability of novel pile-plank embankment in seasonally frozen regions[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2021, 56(3): 541-549. [10] ZHANG Y, TIAN R Z, WANG T L. Study on salt expansion mechanism of subgrade-culvert transition section in saline soils and cold regions[J]. Cold Regions Science and Technology, 2023, 205: 103701.1-103701.12. [11] ZHANG D F, WANG S J. Mechanism of freeze–thaw action in the process of soil salinization in northeast China[J]. Environmental Geology, 2001, 41(1): 96-100. [12] 张殿发, 郑琦宏. 冻融条件下土壤中水盐运移规律模拟研究[J]. 地理科学进展, 2005, 24(4): 46-55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6301.2005.04.006ZHANG Dianfa, ZHENG Qihong. Simulation of water-salt movement law under the freeze-thawing condition[J]. Progress in Geography, 2005, 24(4): 46-55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6301.2005.04.006 [13] 张磊. 粗粒盐渍土冻融作用下水盐迁移及力学性能研究[J]. 当代化工, 2018, 47(6): 1162-1165. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0460.2018.06.017ZHANG Lei. Study on water and salt migration and mechanical properties of coarse saline soil under freeze-thaw conditions[J]. Contemporary Chemical Industry, 2018, 47(6): 1162-1165. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0460.2018.06.017 [14] 肖泽岸, 赖远明. 冻融和干湿循环下盐渍土水盐迁移规律研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2018, 37(增1): 3738-3746.XIAO Zean, LAI Yuanming. Study on water and salt transfer mechanism in saline soil under freezing-thawing and dry-wet conditions[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2018, 37(S1): 3738-3746. [15] 吴道勇, 赖远明, 马勤国, 等. 季节冻土区水盐迁移及土体变形特性模型试验研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2016, 37(2): 465-476.WU Daoyong, LAI Yuanming, MA Qinguo, et al. Model test study of water and salt migration and deformation characteristics in seasonally frozen soil[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2016, 37(2): 465-476. [16] 包卫星, 张莎莎. 路用砂类盐渍土盐胀及融陷特性试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2016, 38(4): 734-739. doi: 10.11779/CJGE201604019BAO Weixing, ZHANG Shasha. Experimental study on salt expansion and thawing subsidence properties of sandy saline soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2016, 38(4): 734-739. doi: 10.11779/CJGE201604019 [17] 张莎莎, 谢永利, 杨晓华, 等. 典型天然粗粒盐渍土盐胀微观机制分析[J]. 岩土力学, 2010, 31(1): 123-127. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2010.01.023ZHANG Shasha, XIE Yongli, YANG Xiaohua, et al. Research on microstructure of crude coarse grain saline soil under freezing and thawing cycles[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2010, 31(1): 123-127. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2010.01.023 [18] 罗崇亮, 余云燕, 张璟, 等. 硫酸盐渍土热-质迁移试验与耦合模型[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2023, 58(2): 470-478.LUO Chongliang, YU Yunyan, ZHANG Jing, et al. Heat-mass transfer test and coupling model of sulfate saline soil[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2023, 58(2): 470-478. [19] 周凤玺, 巨文涛, 张留俊. 单向冻结条件下硫酸盐渍土热质迁移及变形特性研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2023, 44(3): 708-716.ZHOU Fengxi, JU Wentao, ZHANG Liujun. Thermal mass transfer and deformation characteristics of sulphate saline soil under unidirectional freezing[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2023, 44(3): 708-716. [20] 中华人民共和国交通运输部. 公路土工试验规程: JTG 3430—2020[S]. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 2020. [21] 张彧, 房建宏, 刘建坤, 等. 察尔汗地区盐渍土水热状态变化特征与水盐迁移规律研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2012, 34(7): 1344-1348.ZHANG Yu, FANG Jianhong, LIU Jiankun, et al. Variation characteristics of hydrothermal state and migration laws of water and salt in Qarhan Salt Lake region[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2012, 34(7): 1344-1348. [22] 张沛然, 黄雪峰, 杨校辉, 等. 盐渍土水-热场耦合效应与盐胀变形试验[J]. 岩土力学, 2018, 39(5): 1619-1624.ZHANG Peiran, HUANG Xuefeng, YANG Xiaohui, et al. Experiment on coupling effect of water and thermal field and salt-expansion deformation of salty soil[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2018, 39(5): 1619-1624. [23] 张莎莎, 杨晓华, 戴志仁. 天然粗颗粒盐渍土多次冻融循环盐胀试验[J]. 中国公路学报, 2009, 22(4): 28-32. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7372.2009.04.005ZHANG Shasha, YANG Xiaohua, DAI Zhiren. Freezing-thawing cycles and salt expansion test of crude coarse grain clay salty soil[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2009, 22(4): 28-32. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7372.2009.04.005 [24] 张莎莎, 叶素纤, 张林, 等. 粗粒盐渍土路基水热盐力耦合方程修正及试验验证[J]. 公路交通科技, 2020, 37(3): 31-40.ZHANG Shasha, YE Suqian, ZHANG Lin, et al. Correction of hydrothermal salt force coupled equations for coarse-grained sulphate saline soil roadbed and its experimental verification[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2020, 37(3): 31-40. [25] ZHOU L Z, ZHOU F X, YING S, et al. Study on water and salt migration and deformation properties of unsaturated saline soil under a temperature gradient considering salt adsorption: numerical simulation and experimental verification[J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2021, 134: 104094.1-104094.22. [26] 廖亦涵, 张延杰, 李建东, 等. F1离子固化剂加固泥岩物理力学特性试验[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2022, 22(25): 11155-11162. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2022.25.042LIAO Yihan, ZHANG Yanjie, LI Jiandong, et al. Physical and mechanical properties experiment of solidified mudstone by F1 ionic soil stabilizer[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2022, 22(25): 11155-11162. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2022.25.042 -




 下载:
下载: